Underwater Target Tracking Algorithm Based on Improved Adaptive IMM-UKF
-
摘要: 针对现有自适应交互式多模型算法(AIMM)在水下目标跟踪过程中模型切换和跟踪精度上的不足,该文结合无迹卡尔曼滤波(UKF)算法,提出一种改进的AIMM-UKF算法。该算法在自适应修正马尔可夫转移概率矩阵的基础上,利用判定窗对其进行二次修正,实现匹配模型概率的快速增大和对非匹配模型的抑制。仿真结果表明,改进算法相比原有自适应算法,能更加充分地利用后验信息,拥有更好的模型切换速度,跟踪精度提升约24%。Abstract: To solve the lack of model switching and tracking accuracy of the existing Adaptive Interacting Multiple Model (AIMM) in the underwater target tracking, combined with the Unscented Kalman Filter, an improved AIMM-UKF algorithm is proposed. On the basis of adaptively modifying the Markov probability transition matrix, this algorithm uses the decision window to modify it twice to increase the probability of the matching model observably and reduce the effects of the mismatch model. Simulation results show that compared with the original adaptive algorithm, the improved algorithm can make fuller use of posterior information, has a better model switching speed, and improves tracking accuracy by about 24%.
-
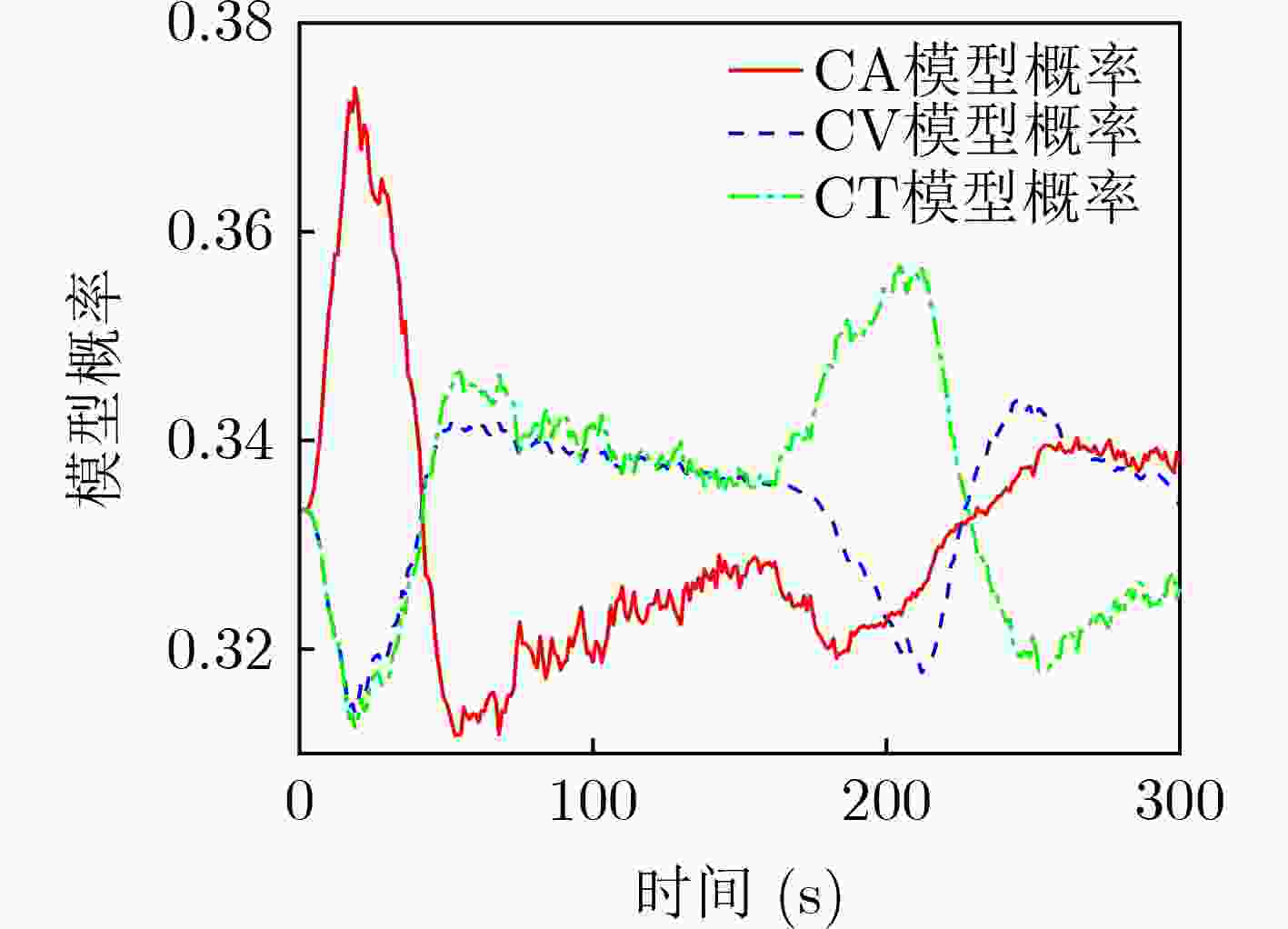
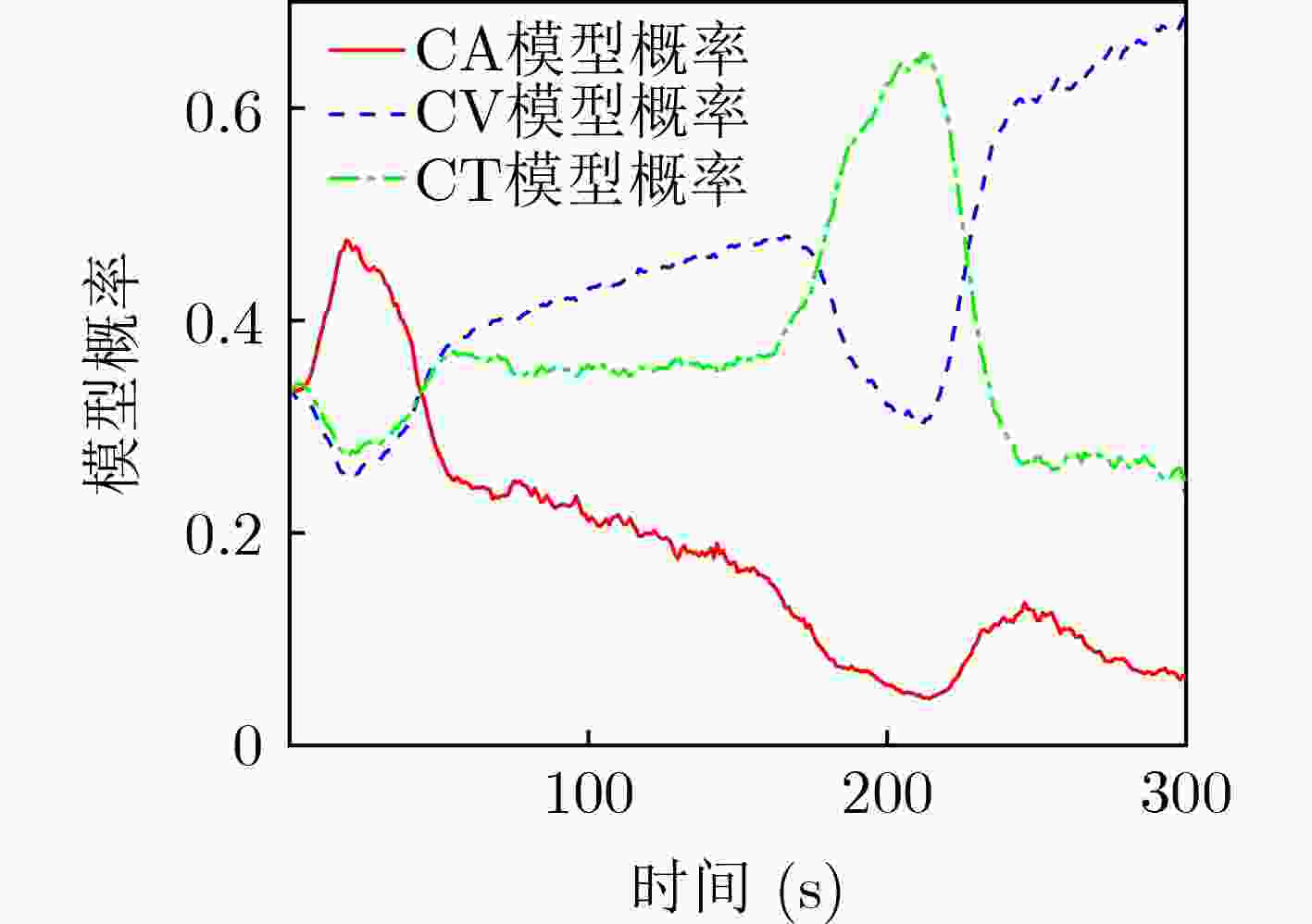
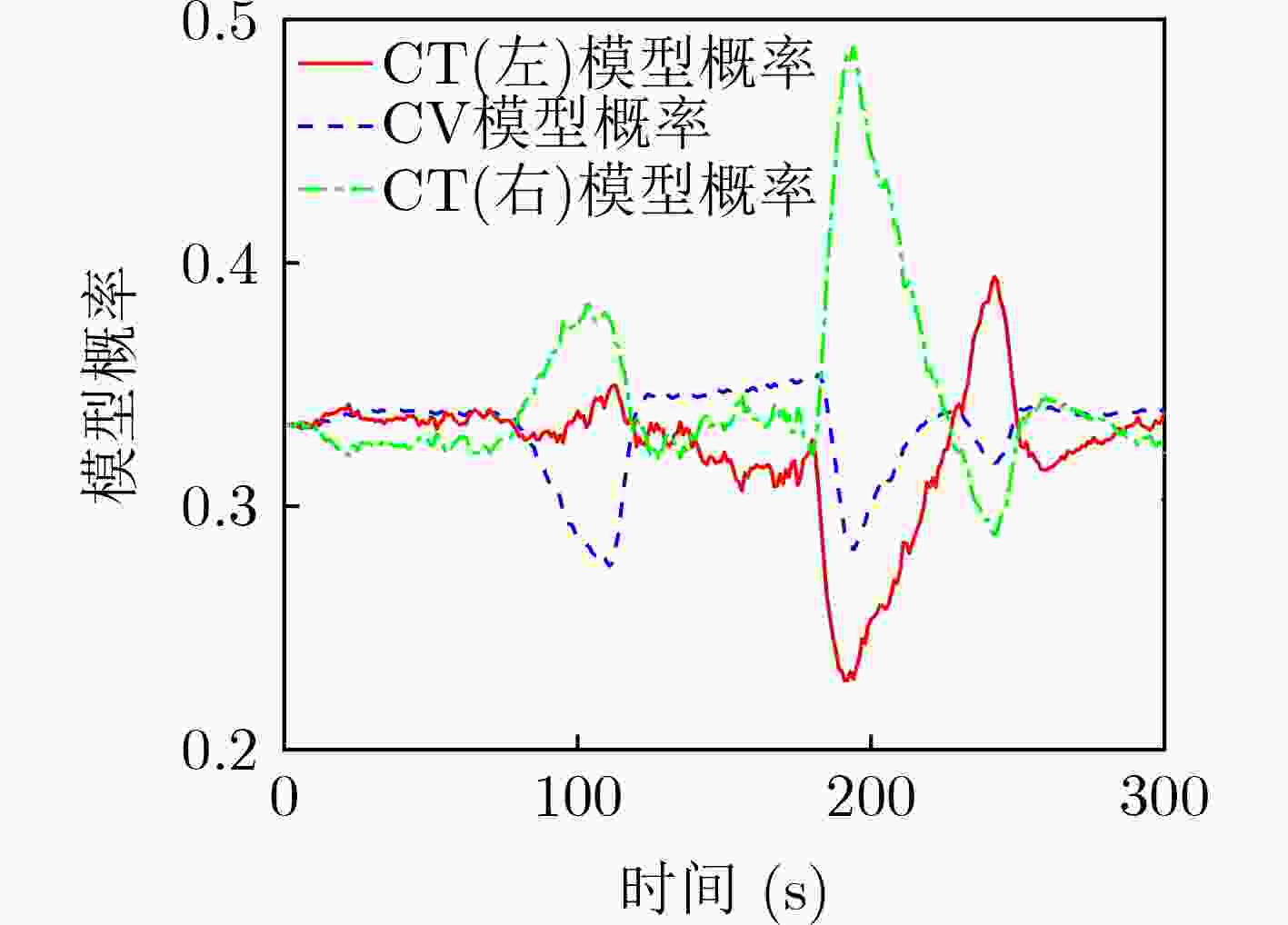
图 6 文献[12]模型概率变化曲线
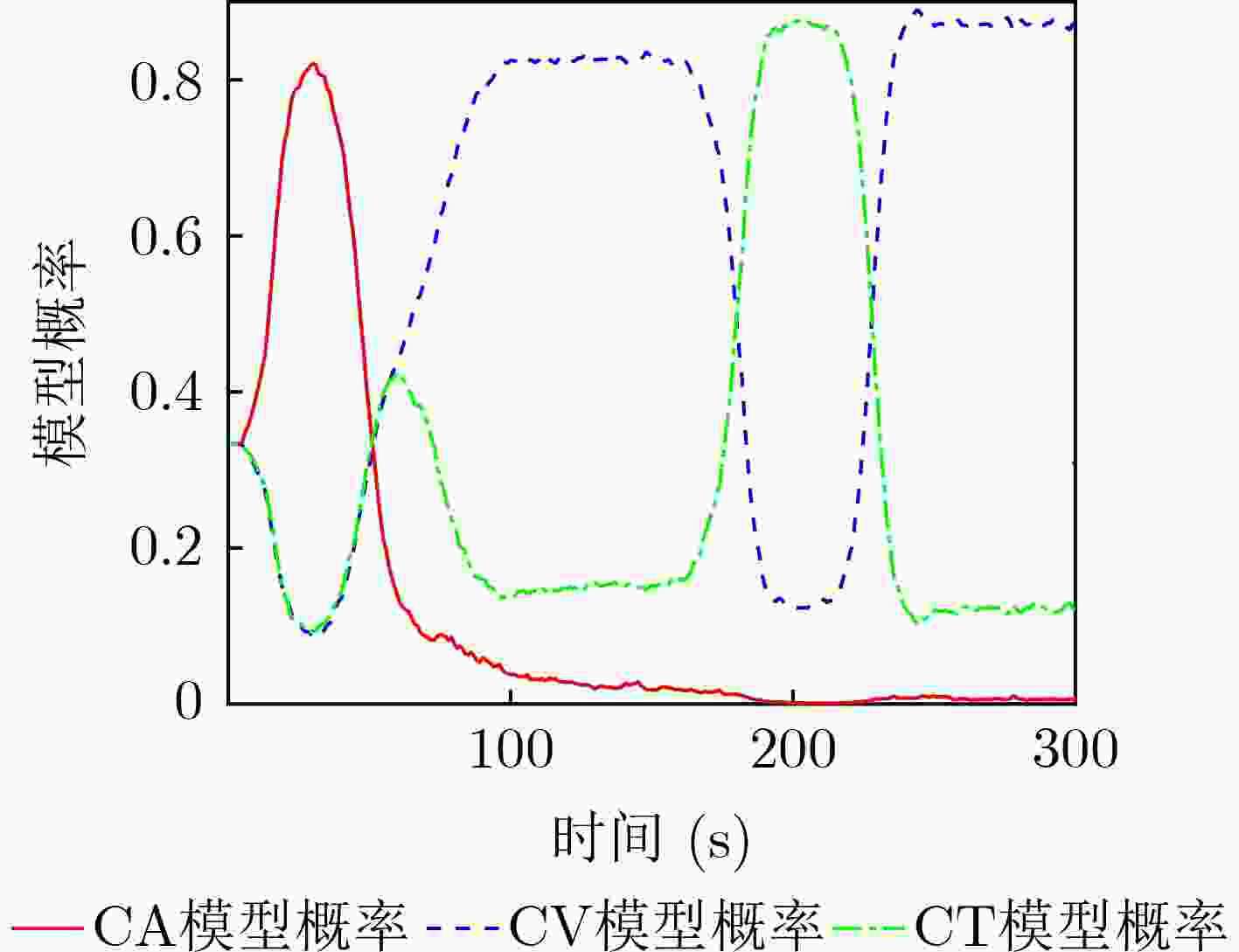
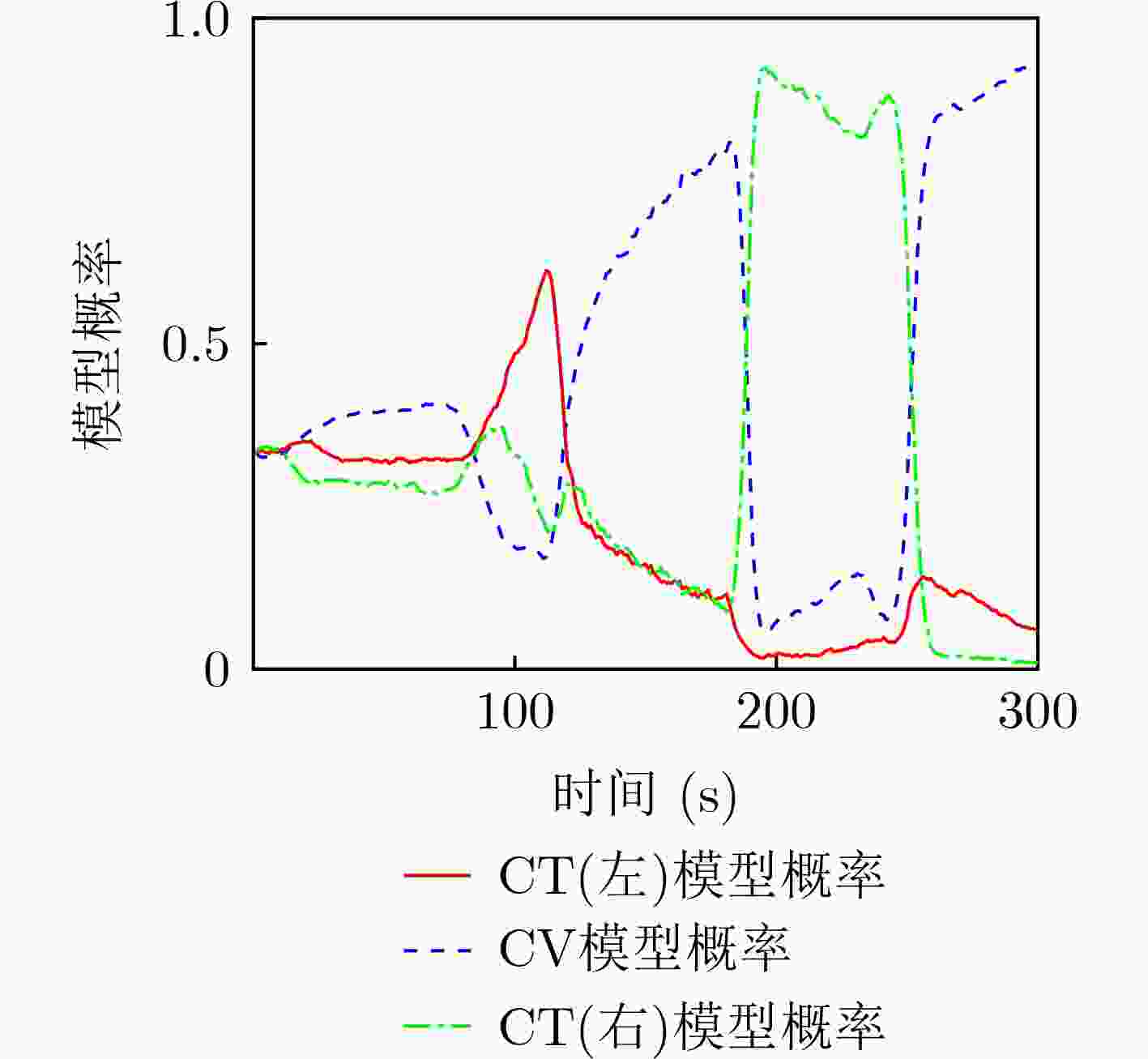
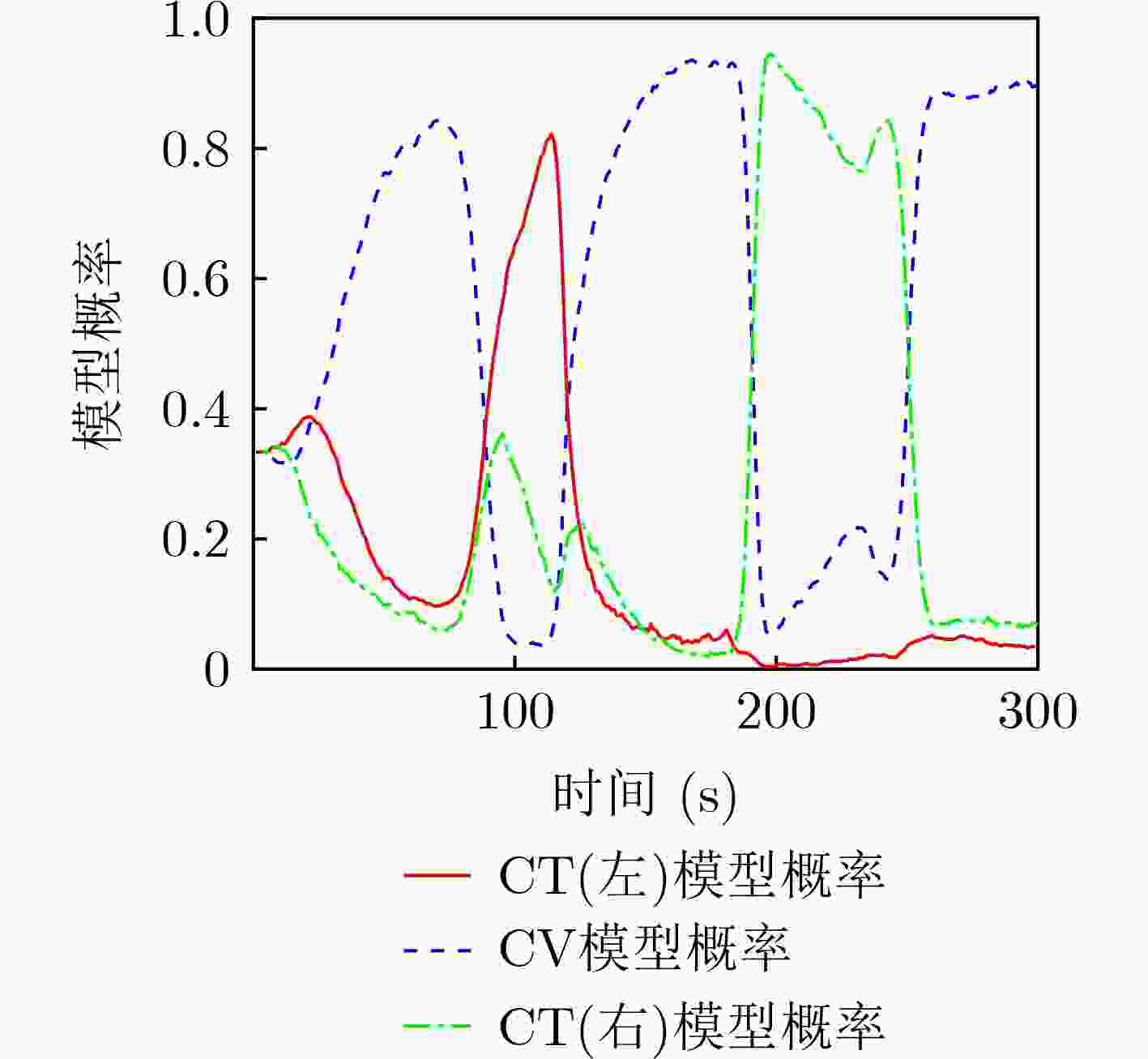
图 12 文献[12]算法模型概率变化曲线
表 1 仿真参数
参数 名称 数值 X0 目标初始状态向量 (3000,4000,0,0,0.5,0.5) S 声呐平台位置(m) (0,0) R 量测噪声协方差阵 diag(502 0.092) T 采样间隔(s) 1 Th 概率修正阈值 0.5 L 判定窗长度 5 $ \eta $ 模型概率切换门限值 4 $ \lambda $ 转移概率矩阵调节参数 0.99 表 2 各算法跟踪性能数据
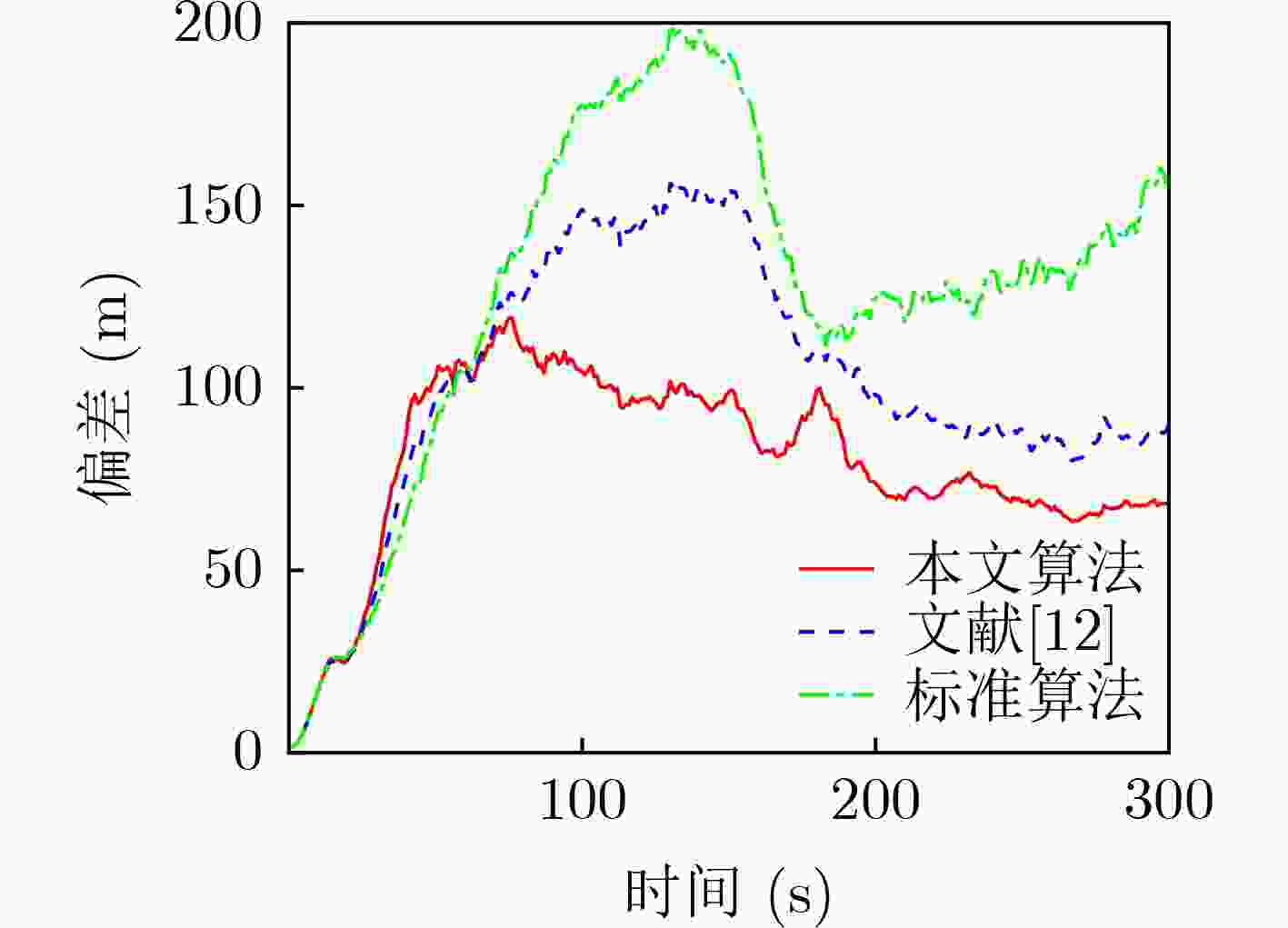
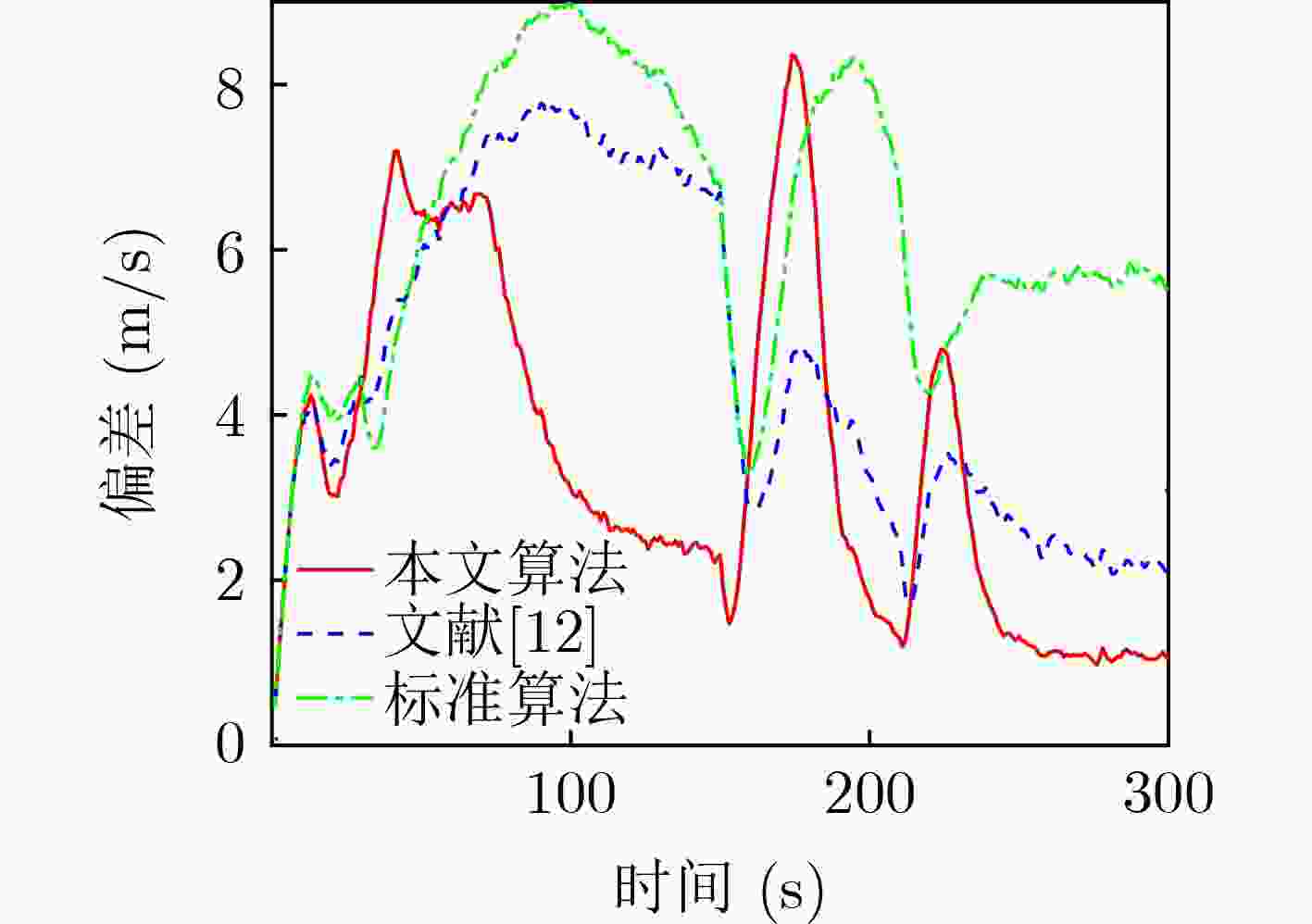
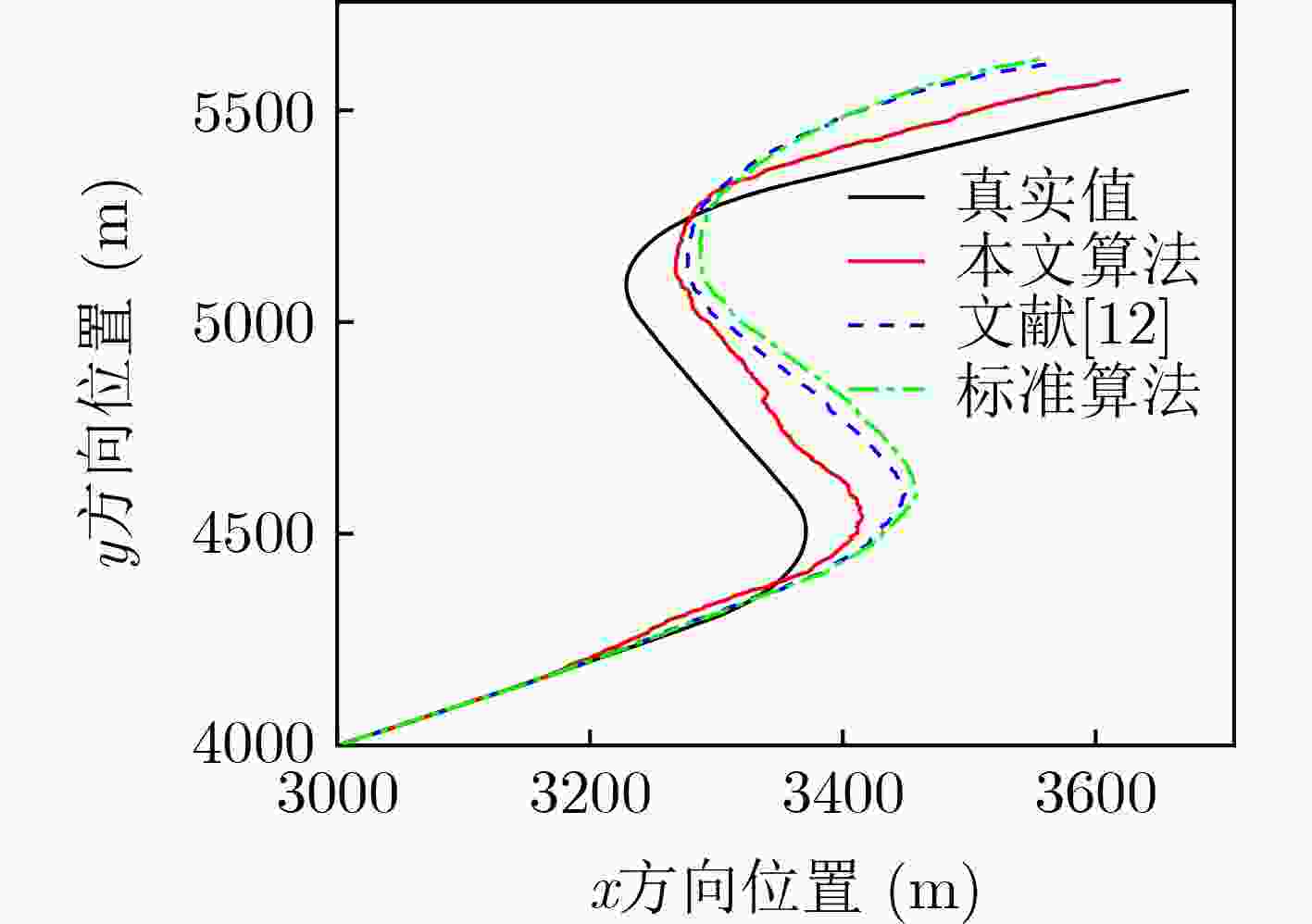
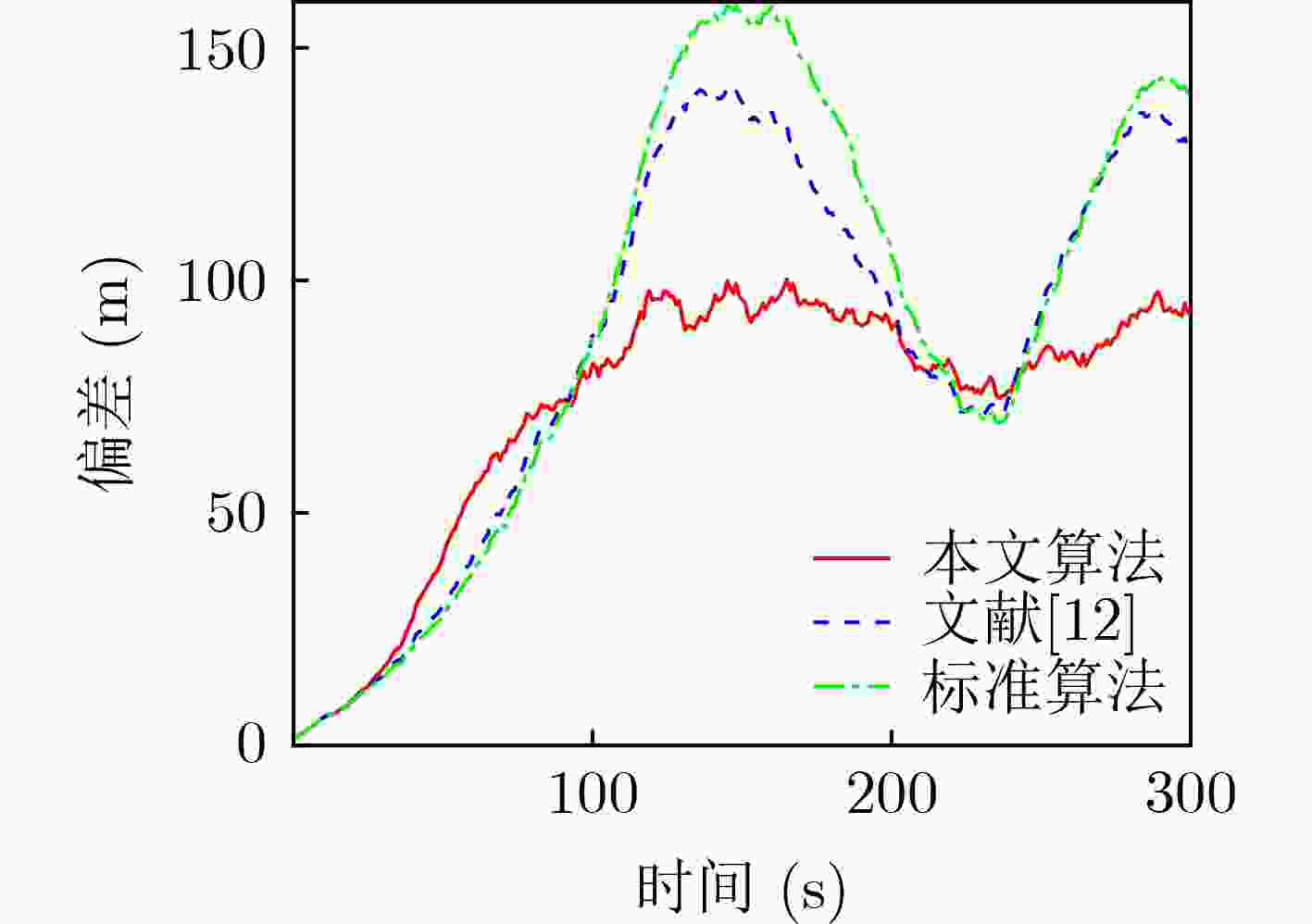
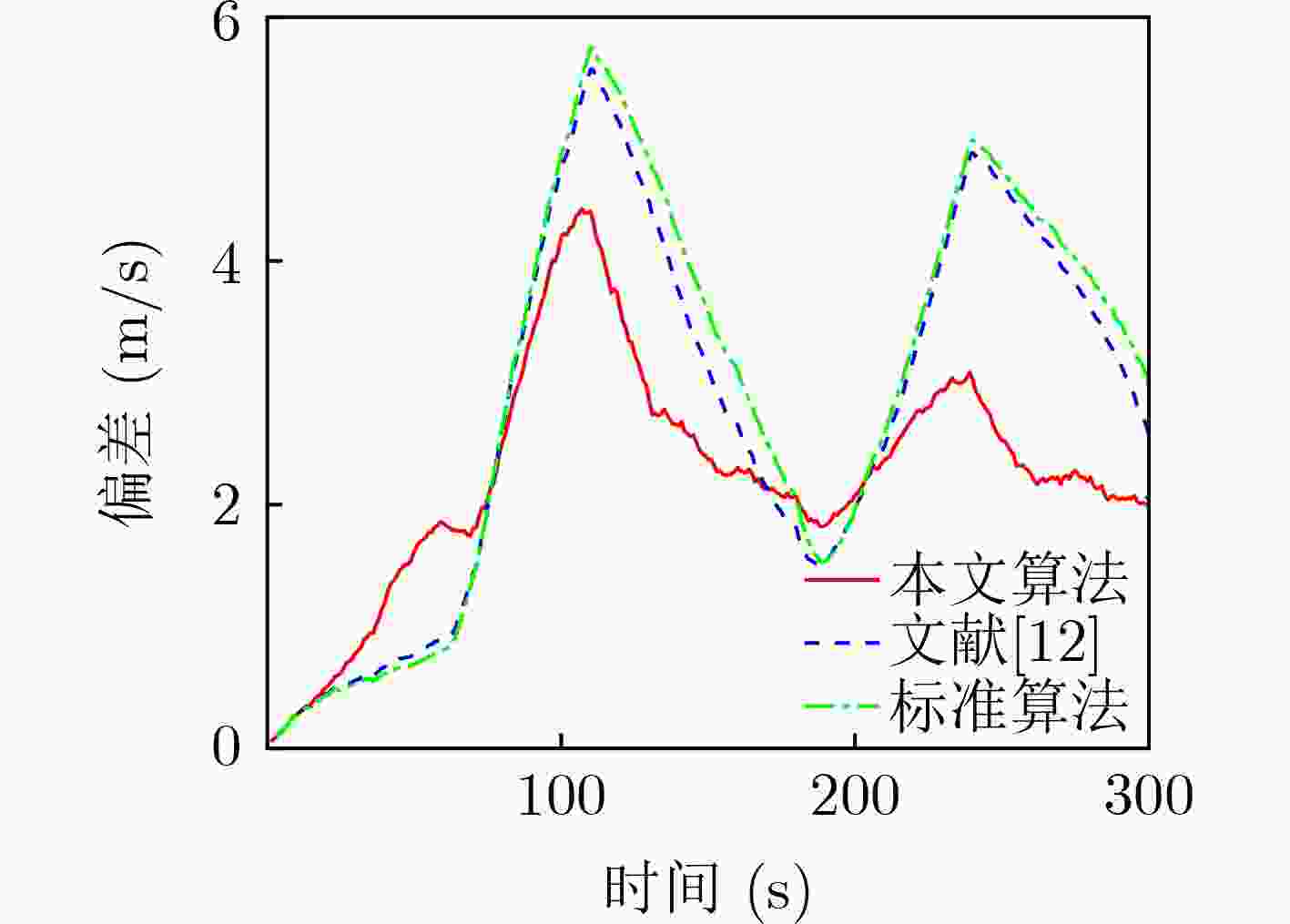
算法 平均均方根误差 均方根误差峰值 位置(m) 速度(m/s) 位置(m) 速度(m/s) 本文算法 80.33 3.44 101.85 8.05 文献[12] 106.74 4.80 173.44 8.21 标准IMM-UKF算法 130.36 6.42 201.42 8.97 表 3 各算法跟踪性能数据
算法 平均均方根误差 均方根误差峰值 位置(m) 速度(m/s) 位置(m) 速度(m/s) 本文算法 72.75 2.25 100.25 4.32 文献[12] 86.16 2.79 141.27 5.47 标准IMM-UKF算法 95.51 3.01 158.97 5.70 -
[1] MAZOR E, AVERBUCH A, BAR-SHALOM Y, et al. Interacting multiple model methods in target tracking: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(1): 103–123. doi: 10.1109/7.640267 [2] KALMAN R E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1960, 82(1): 35–45. doi: 10.1115/1.3662552 [3] 许红, 谢文冲, 袁华东, 等. 基于自适应的增广状态-交互式多模型的机动目标跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2749–2755. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190516XU Hong, XIE Wenchong, YUAN Huadong, et al. Maneuvering target tracking algorithm based on the adaptive augmented state interracting multiple model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2749–2755. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190516 [4] DAUM F. Nonlinear filters: Beyond the Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2005, 20(8): 57–69. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2005.1499276 [5] SONG T and SPEYER J. A stochastic analysis of a modified gain extended Kalman filter with applications to estimation with bearings only measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1985, 30(10): 940–949. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1985.1103821 [6] TIAN Mengchu, BO Yuming, CHEN Zhimin, et al. Multi-target tracking method based on improved firefly algorithm optimized particle filter[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 359: 438–448. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.003 [7] 马艳, 刘小东. 状态自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波算法及其在水下机动目标跟踪中的应用[J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(2): 361–368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.02.016MA Yan and LIU Xiaodong. State adaptive unscented Kaiman filter algorithm and its application in tracking of underwater maneuvering target[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(2): 361–368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.02.016 [8] 许登荣, 程水英, 包守亮. 自适应转移概率交互式多模型跟踪算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(9): 2113–2120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.009XU Dengrong, CHENG Shuiying, and BAO Shouliang. Interacting multiple model algorithm based on adaptive transition probability[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(9): 2113–2120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.009 [9] 周昆正. 基于IMM-RDCKF的机动目标跟踪算法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2018, 16(6): 656–660,666. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2018.06.013ZHOU Kunzheng. Maneuvering target tracking algorithm based on IMM-RDCKF[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2018, 16(6): 656–660,666. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2018.06.013 [10] 周非, 罗晓勇, 刘云萍. 基于概率模型的实时修正IMM目标跟踪算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(21): 85–92. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1909-0012ZHOU Fei, LUO Xiaoyong, and LIU Yunping. Real-time correction of IMM target tracking algorithm based on probability model[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(21): 85–92. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1909-0012 [11] 戴定成, 姚敏立, 蔡宗平, 等. 改进的马尔可夫参数自适应IMM算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(5): 1198–1205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.024DAI Dingcheng, YAO Minli, CAI Zongping, et al. Improved adaptive Markov IMM algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(5): 1198–1205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.024 [12] 叶瑾, 许枫, 杨娟, 等. 一种改进的时变转移概率AIMM跟踪算法[J]. 应用声学, 2020, 39(2): 246–252. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2020.02.011YE Jin, XU Feng, YANG Juan, et al. An improved AIMM tracking algorithm based on adaptivetransition probability[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2020, 39(2): 246–252. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2020.02.011 [13] 罗笑冰, 王宏强, 黎湘. 模型转移概率自适应的交互式多模型跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27(10): 1539–1541.LUO Xiaobing, WANG Hongqiang, and LI Xiang. Interacting multiple model algorithm with adaptive Markov transition probabilities[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2005, 27(10): 1539–1541. -





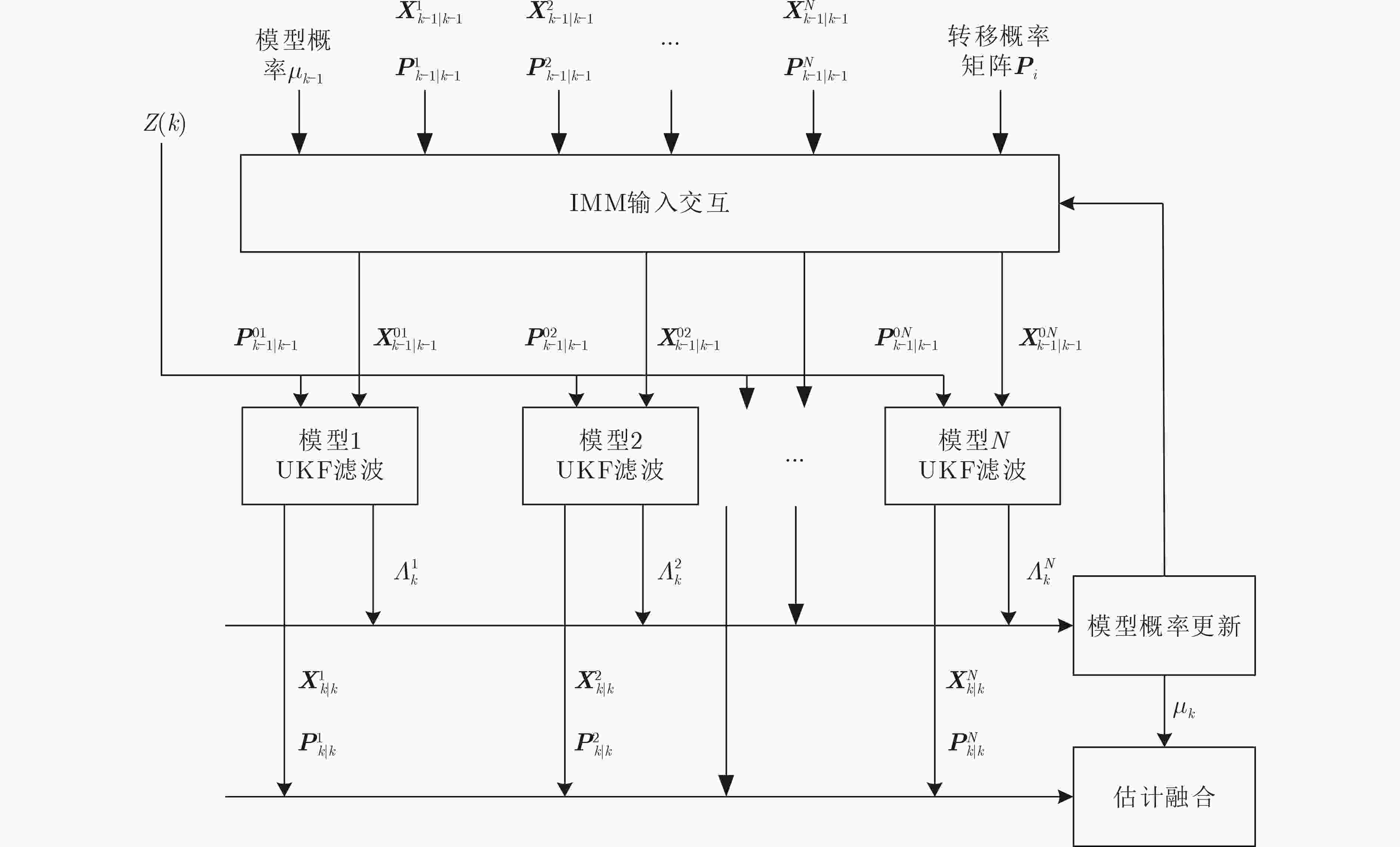
 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
