Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Method Based on Degradation Model
-
摘要: 基于深度学习的红外与可见光图像融合算法依赖人工设计的相似度函数衡量输入与输出的相似度,这种无监督学习方式不能有效利用神经网络提取深层特征的能力,导致融合结果不理想。针对该问题,该文首先提出一种新的红外与可见光图像融合退化模型,把红外和可见光图像视为理想融合图像通过不同退化过程后产生的退化图像。其次,提出模拟图像退化的数据增强方案,采用高清数据集生成大量模拟退化图像供训练网络。最后,基于提出的退化模型设计了简单高效的端到端网络模型及其网络训练框架。实验结果表明,该文所提方法不仅拥有良好视觉效果和性能指标,还能有效地抑制光照、烟雾和噪声等干扰。Abstract: Infrared and visible image fusion algorithms based on deep learning rely on artificially designed similarity functions to measure the similarity between input and output. The unsupervised learning method can not effectively utilize the ability of neural networks to extract deep features, resulting in unsatisfactory fusion results. Considering this problem, a new fusion degradation model of infrared and visible image is proposed in this paper, which regards infrared and visible images as the degraded images produced by ideal fusion images through mixed degradation processes. Secondly, a data enhancement scheme for simulating image degradation is proposed, and a large number of simulated degradation images are generated by using high-definition datasets for training the network. Finally, a simple and efficient end-to-end network model and its network training framework are designed based on the proposed degradation model. The experimental results show that the method proposed in this paper not only has good visual effects and performance indicators, but also can effectively suppress interferences such as illumination, smoke and noise.
-
Key words:
- Image fusion /
- Deep learning /
- Degradation model /
- Data augmentation
-
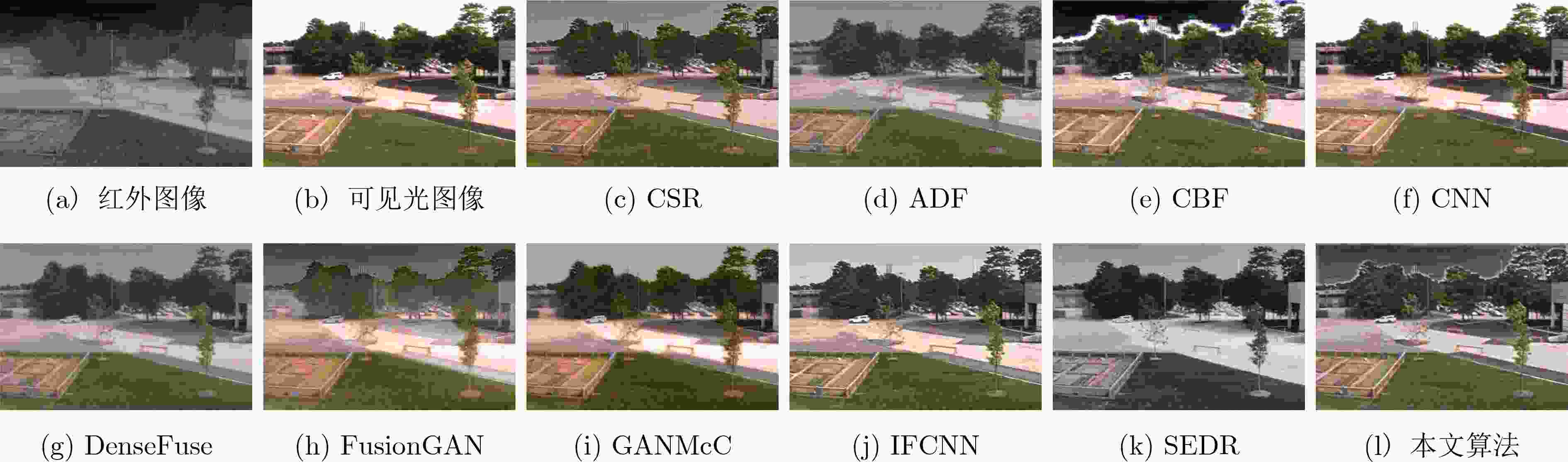
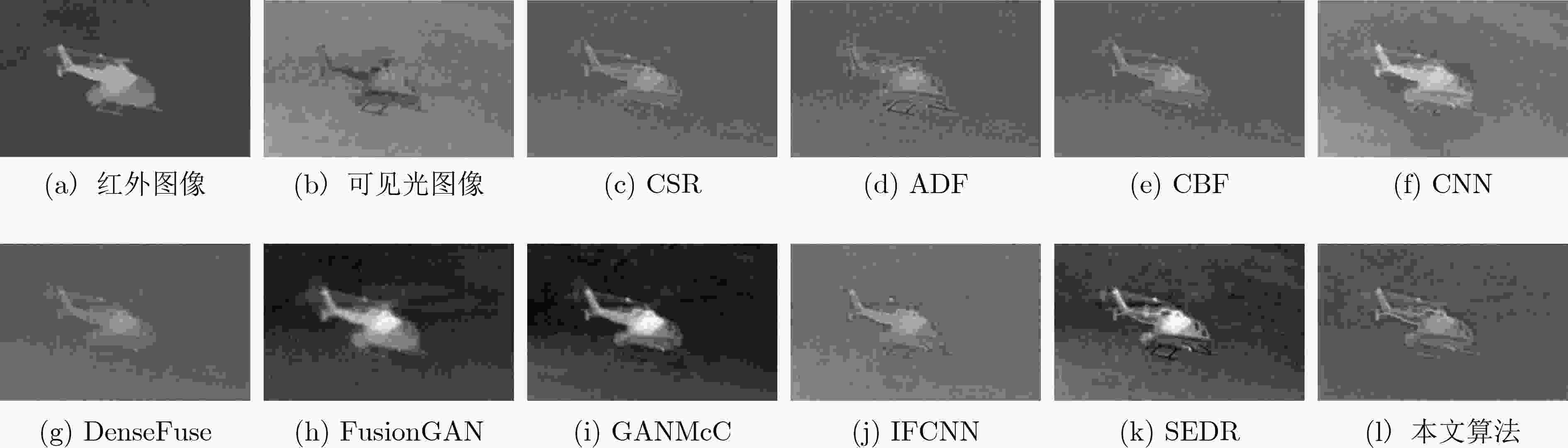
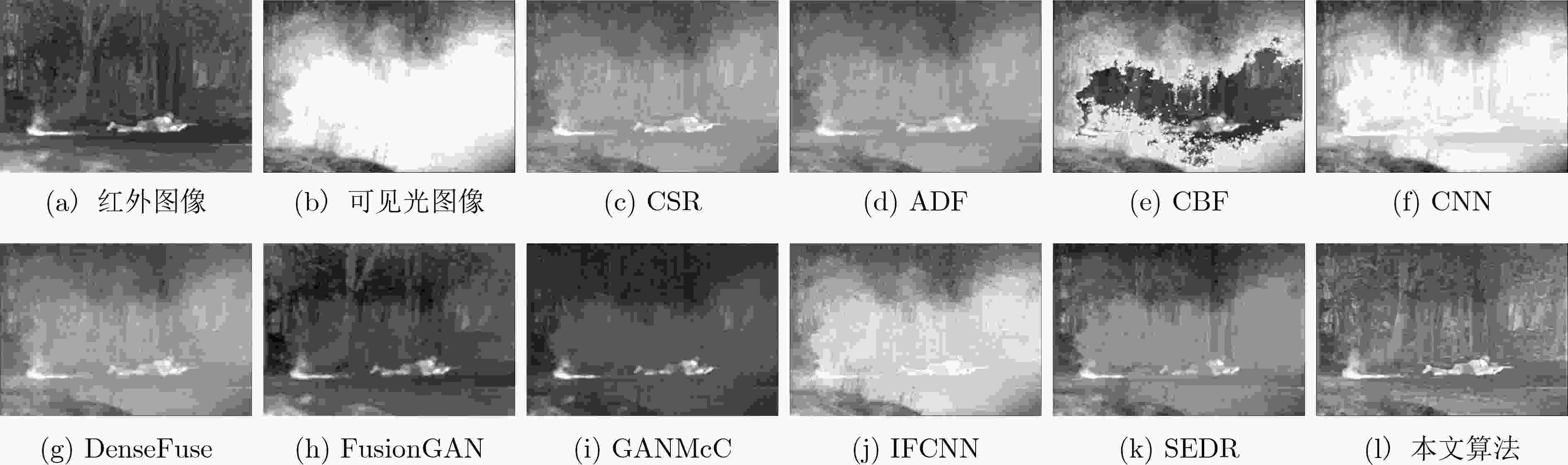
表 1 TNO数据集中各对比算法定性对比表
方法 PSNR SSIM RMSE QAB/F QCB QCV MI CE AG EI CSR 59.6039 1.5411 0.0749 0.5061 0.4184 1127.6 1.4239 2.3364 2.7586 28.1597 ADF 59.6072 1.4897 0.0748 0.4100 0.4294 1109.4 1.3295 2.2883 3.0174 30.0279 CBF 59.0803 1.1989 0.0901 0.4386 0.4149 1232.6 1.7015 1.7311 5.1555 53.3435 CNN 59.7454 1.4630 0.0856 0.5583 0.4273 1290.5 1.7308 1.5476 3.7210 37.6166 DenseFuse 59.6121 1.5503 0.0747 0.3274 0.3975 1132.5 1.5057 1.9123 2.0987 21.2670 FusionGAN 57.1494 1.2190 0.1319 0.2243 0.3338 2311.5 0.9305 2.7054 2.0468 21.0156 GANMcC 58.2399 1.3488 0.1077 0.2486 0.3656 1510.7 1.5257 2.3445 2.1575 22.3753 IFCNN 59.4001 1.4637 0.0833 0.4718 0.4239 878.5 1.7012 2.3640 3.8218 38.0881 SEDR 58.7989 1.4187 0.0947 0.4410 0.4148 1016.6 1.7085 2.0540 3.5073 35.5028 本文算法 60.2263 1.5615 0.0650 0.3997 0.4296 1169.2 1.7760 1.4619 3.2250 33.7834 表 2 VIFB数据集中各对比算法定性对比表
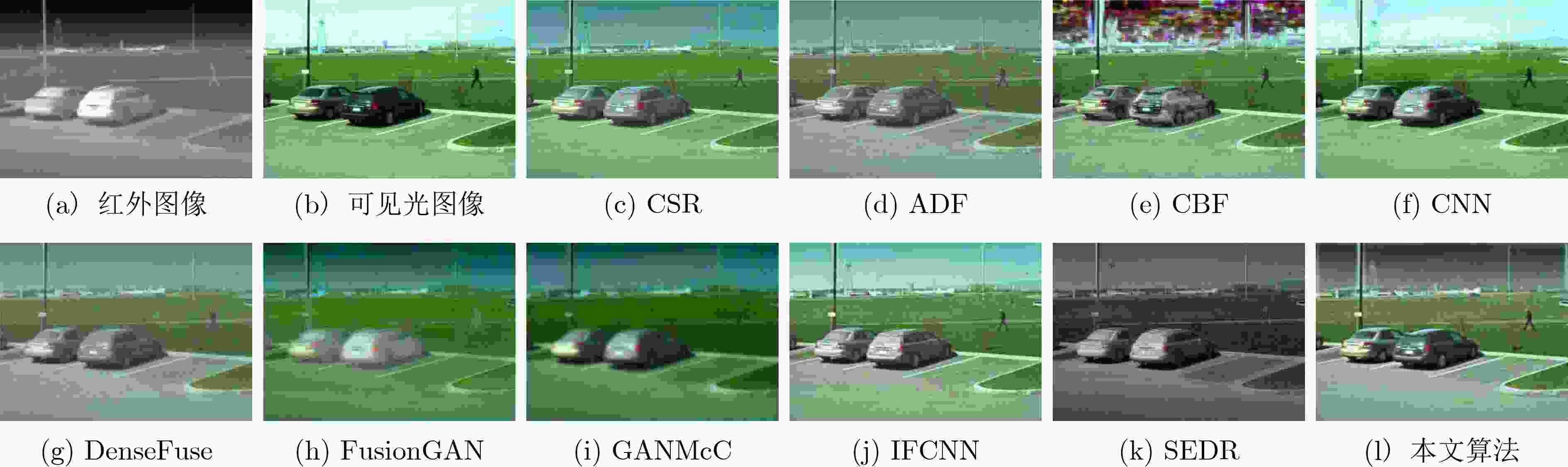
方法 PSNR SSIM RMSE QAB/F QCB QCV MI CE AG EI CSR 58.3143 1.4293 0.1178 0.5957 0.4909 748.8 1.9155 1.4851 5.1440 52.8505 ADF 58.4053 1.4001 0.1043 0.5202 0.4743 777.8 1.9211 1.4641 4.5821 46.5293 CBF 57.5951 1.1711 0.1257 0.5786 0.5263 1575.3 2.1612 0.9946 7.1541 74.5901 CNN 57.9323 1.3914 0.1178 0.6580 0.6221 512.6 2.6533 1.0301 5.8082 60.2415 DenseFuse 58.4449 1.4586 0.1035 0.3637 0.4386 763.2 2.0259 1.3293 3.5263 35.9694 FusionGAN 57.4476 1.3001 0.1295 0.2395 0.3641 1632.0 1.5988 2.2331 3.0546 31.7554 GANMcC 57.5574 1.3471 0.1258 0.3029 0.3986 1012.6 1.9665 1.9955 3.2732 34.5361 IFCNN 56.4970 1.1285 0.1535 0.3339 0.4507 1021.9 2.1392 2.5603 3.9612 40.5405 SEDR 57.7989 1.4187 0.0947 0.4410 0.4148 1016.6 1.7085 2.0540 3.5073 35.5028 本文算法 58.6251 1.4815 0.0850 0.5936 0.5149 669.2 2.7560 0.9544 3.2250 33.7834 表 3 各退化过程对融合结果的影响
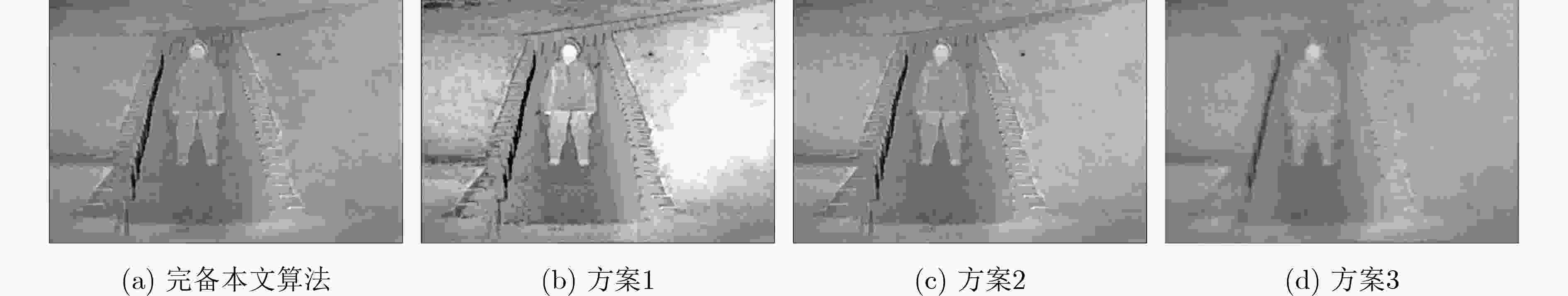
情况 PSNR SSIM RMSE QAB/F QCB QCV MI CE AG EI 方案1 59.7091 1.2766 0.0764 0.3588 0.4171 1761.7 1.5652 1.4759 4.8728 52.6447 方案2 59.7536 1.4893 0.0727 0.4059 0.4256 1537.8 1.4174 1.5975 3.5434 36.5904 方案3 59.4052 1.4518 0.0782 0.2327 0.3686 1665.1 1.2652 1.7959 1.8075 18.5773 完备本文算法 60.2263 1.5615 0.0650 0.3997 0.4296 1169.2 1.7760 1.4619 3.2250 33.7834 表 4 不同损失函数对融合结果的影响
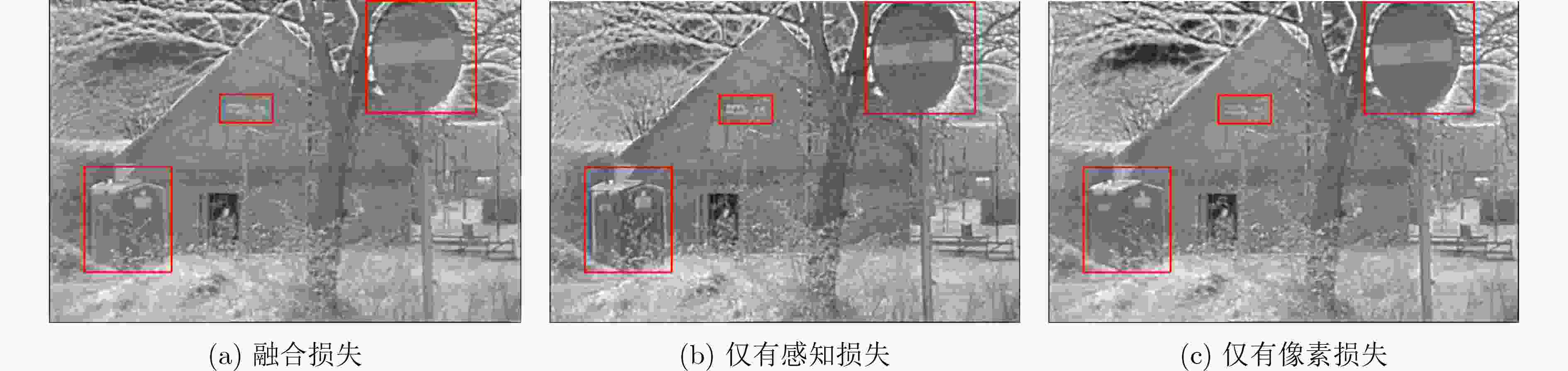
情况 PSNR SSIM RMSE QAB/F QCB QCV MI CE AG EI 仅有像素损失 60.0821 1.5826 0.0684 0.4045 0.4223 1682.4 2.0132 1.2808 2.9093 30.8049 仅有感知损失 60.2380 1.4970 0.0652 0.3676 0.4309 1342.6 1.7313 1.1493 3.4832 36.7749 混合损失 60.2263 1.5615 0.0650 0.3997 0.4296 1169.2 1.7760 1.4619 3.2250 33.7834 -
[1] LI Shutao, KANG Xudong, and HU Jianwen. Image fusion with guided filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(7): 2864–2875. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2244222 [2] LIU Chunhui and DING Wenrui. Variational model for infrared and visible light image fusion with saliency preservation[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2019, 28(2): 023023. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.28.2.023023 [3] ZHAO Jufeng, ZHOU Qiang, CHEN Yueting, et al. Fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency analysis and detail preserving based image decomposition[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2013, 56: 93–99. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2012.11.003 [4] HE Guiqing, XING Siyuan, HE Xingjian, et al. Image fusion method based on simultaneous sparse representation with non‐subsampled contourlet transform[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2019, 13(2): 240–248. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2018.5496 [5] YANG Bin and LI Shutao. Visual attention guided image fusion with sparse representation[J]. Optik, 2014, 125(17): 4881–4888. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2014.04.036 [6] WANG Jun, PENG Jinye, FENG Xiaoyi, et al. Fusion method for infrared and visible images by using non-negative sparse representation[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2014, 67: 477–489. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2014.09.019 [7] 雷大江, 杜加浩, 张莉萍, 等. 联合多流融合和多尺度学习的卷积神经网络遥感图像融合方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 237–244. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200792LEI Dajiang, DU Jiahao, ZHANG Liping, et al. Multi-stream architecture and multi-scale convolutional neural network for remote sensing image fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 237–244. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200792 [8] 陈书贞, 曹世鹏, 崔美玥, 等. 基于深度多级小波变换的图像盲去模糊算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 154–161. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190947CHEN Shuzhen, CAO Shipeng, CUI Meiyue, et al. Image blind deblurring algorithm based on deep multi-level wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 154–161. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190947 [9] 李明鸿, 常侃, 李恒鑫, 等. 双阶段信息蒸馏的轻量级图像超分辨率网络[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(5): 991–1005. doi: 10.11834/jig.200265LI Minghong, CHANG Kan, LI Hengxin, et al. Lightweight image super-resolution network via two-stage information distillation[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(5): 991–1005. doi: 10.11834/jig.200265 [10] PRABHAKAR K R, SRIKAR V S, and BABU R V. DeepFuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4714–4722. [11] LI Hui and WU Xiaojun. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614–2623. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342 [12] LIU Yu, CHEN Xun, PENG Hu, et al. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 36: 191–207. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.12.001 [13] XU Han, MA Jiayi, JIANG Junjun, et al. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 502–518. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548 [14] MA Jiayi, TANG Linfeng, XU Meilong, et al. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5009513. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3075747 [15] ZHU Depeng, ZHAN Weida, JIANG Yichun, et al. MIFFuse: A multi-level feature fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 130778–130792. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3111905 [16] JIANG Yichun, LIU Yunqing, ZHAN Weida, et al. Lightweight dual-stream residual network for single image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 129890–129901. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3112002 [17] JIANG Haijun, CHEN Fei, LIU Xining, et al. Thermal wave image deblurring based on depth residual network[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2021, 117: 103847. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2021.103847 [18] HAN J, LEE H, and KANG M G. Thermal image restoration based on LWIR sensor statistics[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(16): 5443. doi: 10.3390/s21165443 [19] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3262–3271. [20] IGNATOV A, TIMOFTE R, VAN VU T, et al. PIRM challenge on perceptual image enhancement on smartphones: Report[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 2018: 315–333. [21] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [22] ZHANG Xingchen, YE Ping, and XIAO Gang. VIFB: A visible and infrared image fusion benchmark[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 104–105. [23] LIU Yu, CHEN Xun, WARD R K, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1882–1886. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2618776 [24] BAVIRISETTI D P and DHULI R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and Karhunen-Loeve transform[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(1): 203–209. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2478655 [25] SHREYAMSHA KUMAR B K. Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2015, 9(5): 1193–1204. doi: 10.1007/s11760–013-0556–9 [26] MA Jiayi, YU Wei, LIANG Pengwei, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11–26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004 [27] MA Jiayi, ZHANG Hao, SHAO Zhenfeng, et al. GANMcC: A generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5005014. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3038013 [28] ZHANG Yu, LIU Yu, SUN Peng, et al. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 54: 99–118. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.07.011 [29] JIAN Lihua, YANG Xiaomin, LIU Zheng, et al. SEDRFuse: A symmetric encoder–decoder with residual block network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5002215. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3022438 -





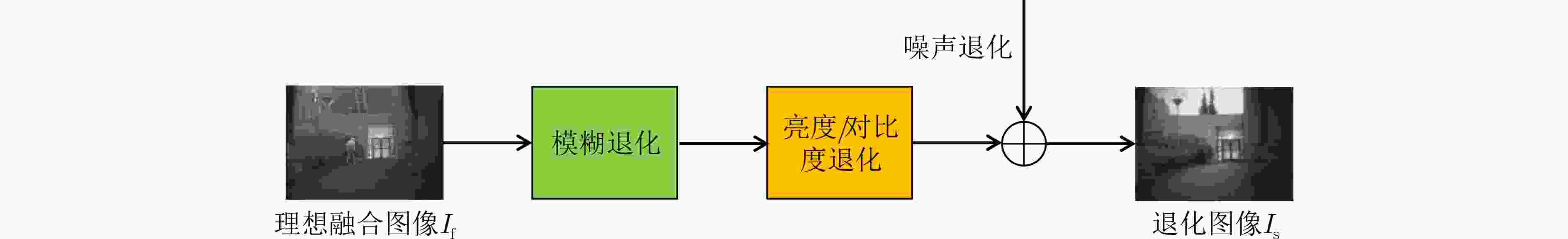
 下载:
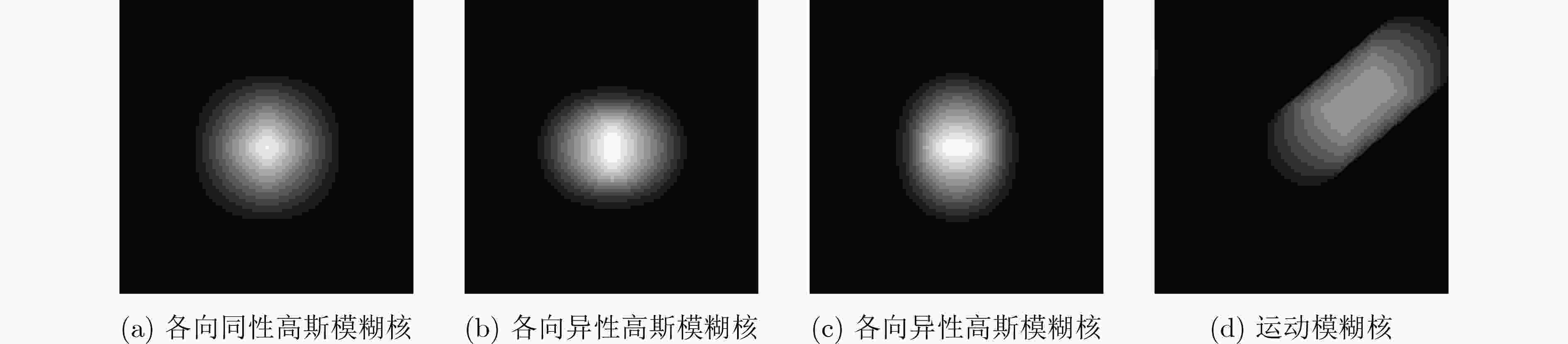
下载:
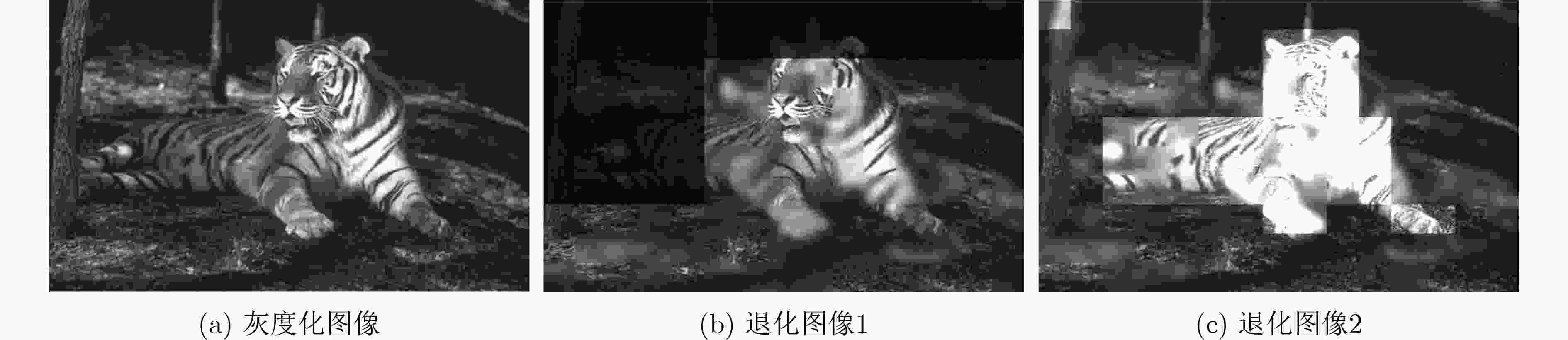

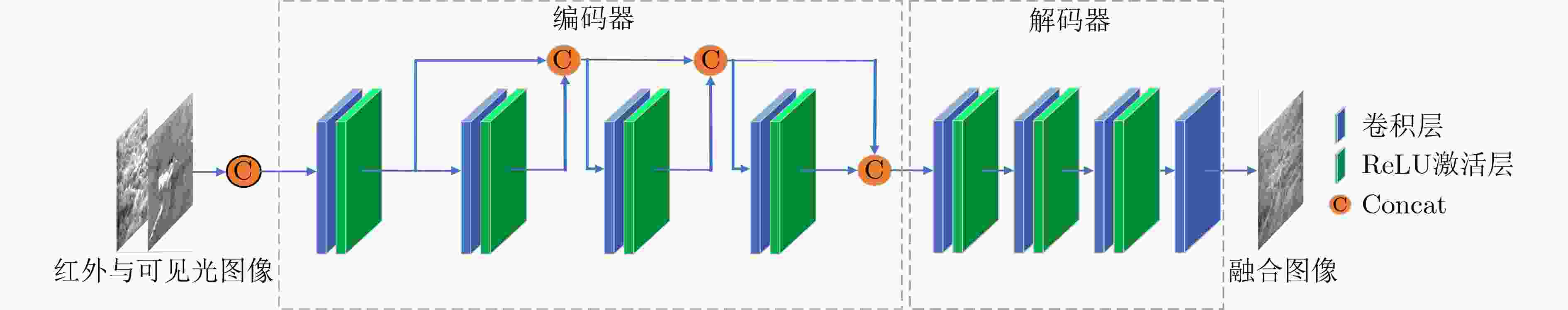





 下载:
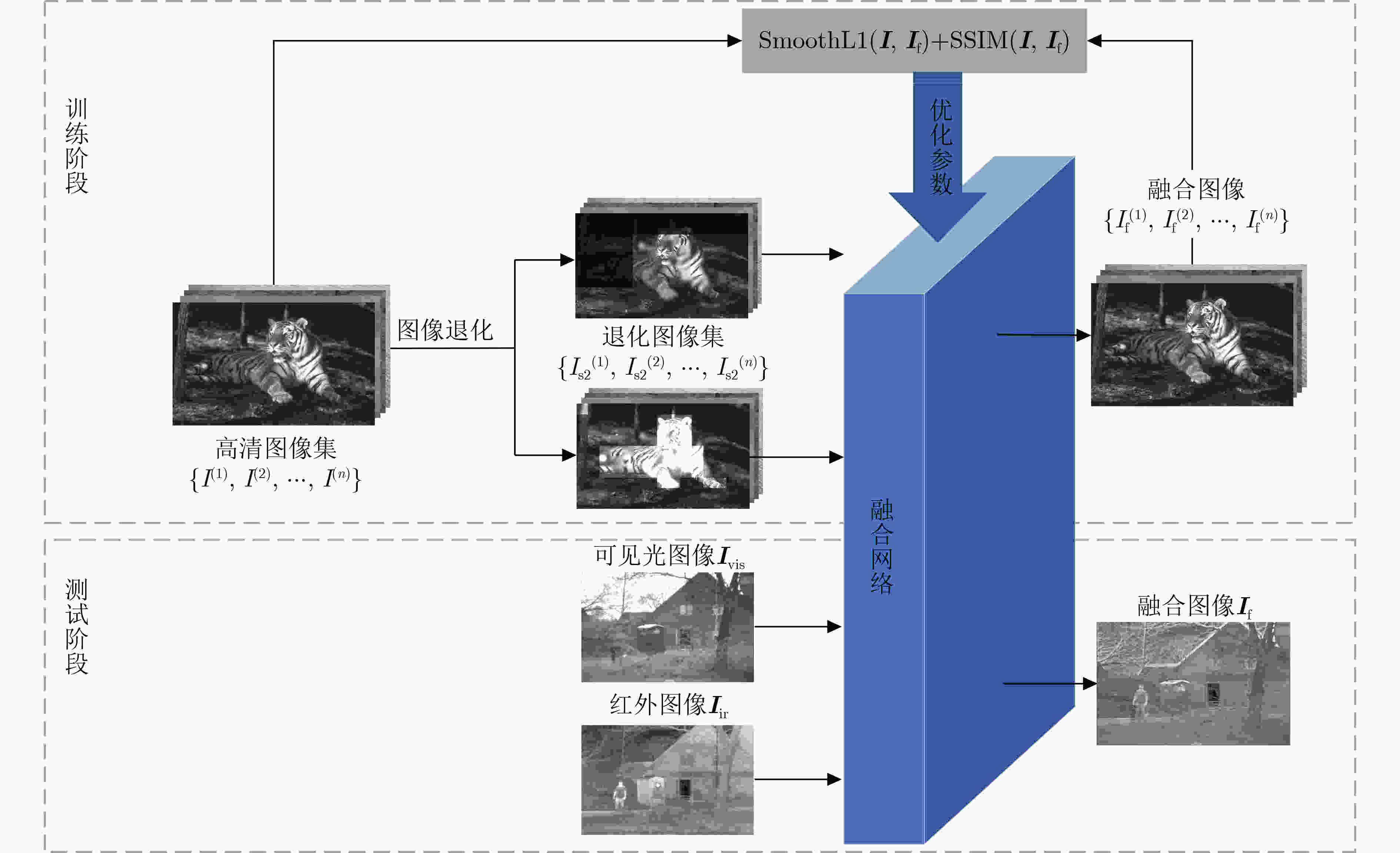
下载:
