Moving Ship Detection Method Based on Multi-scale Dual-neighborhood Saliency for GF-4 Satellite Remote Sensing Images
-
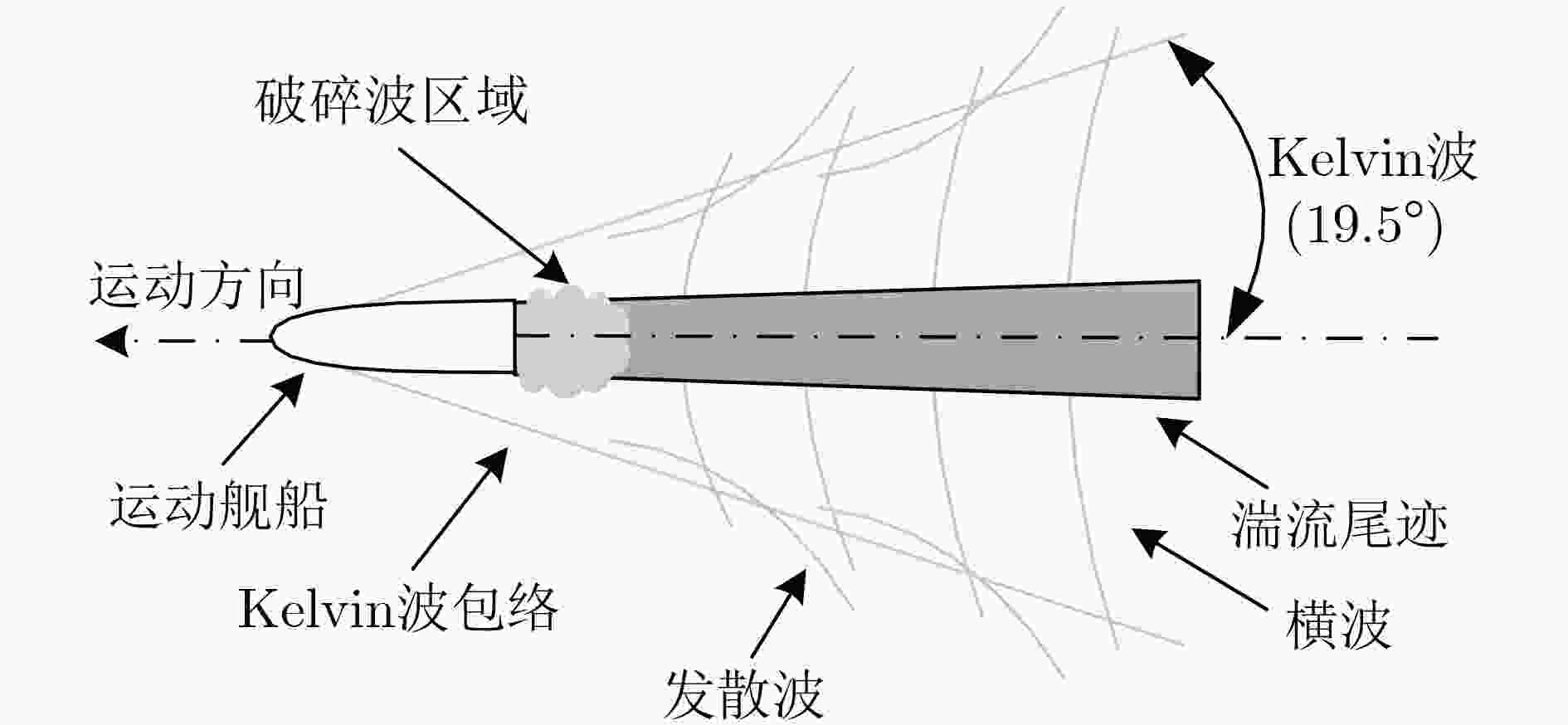
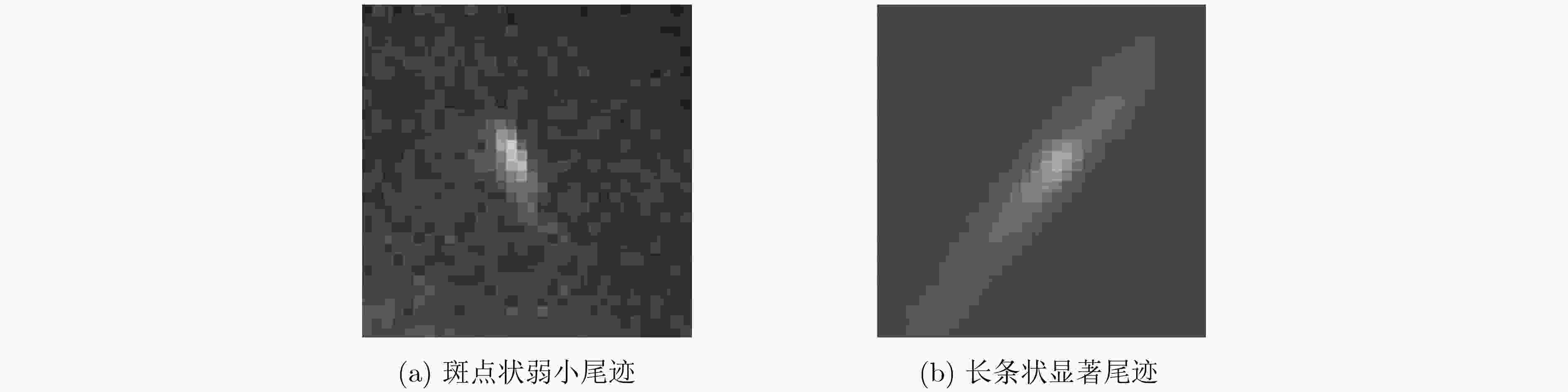
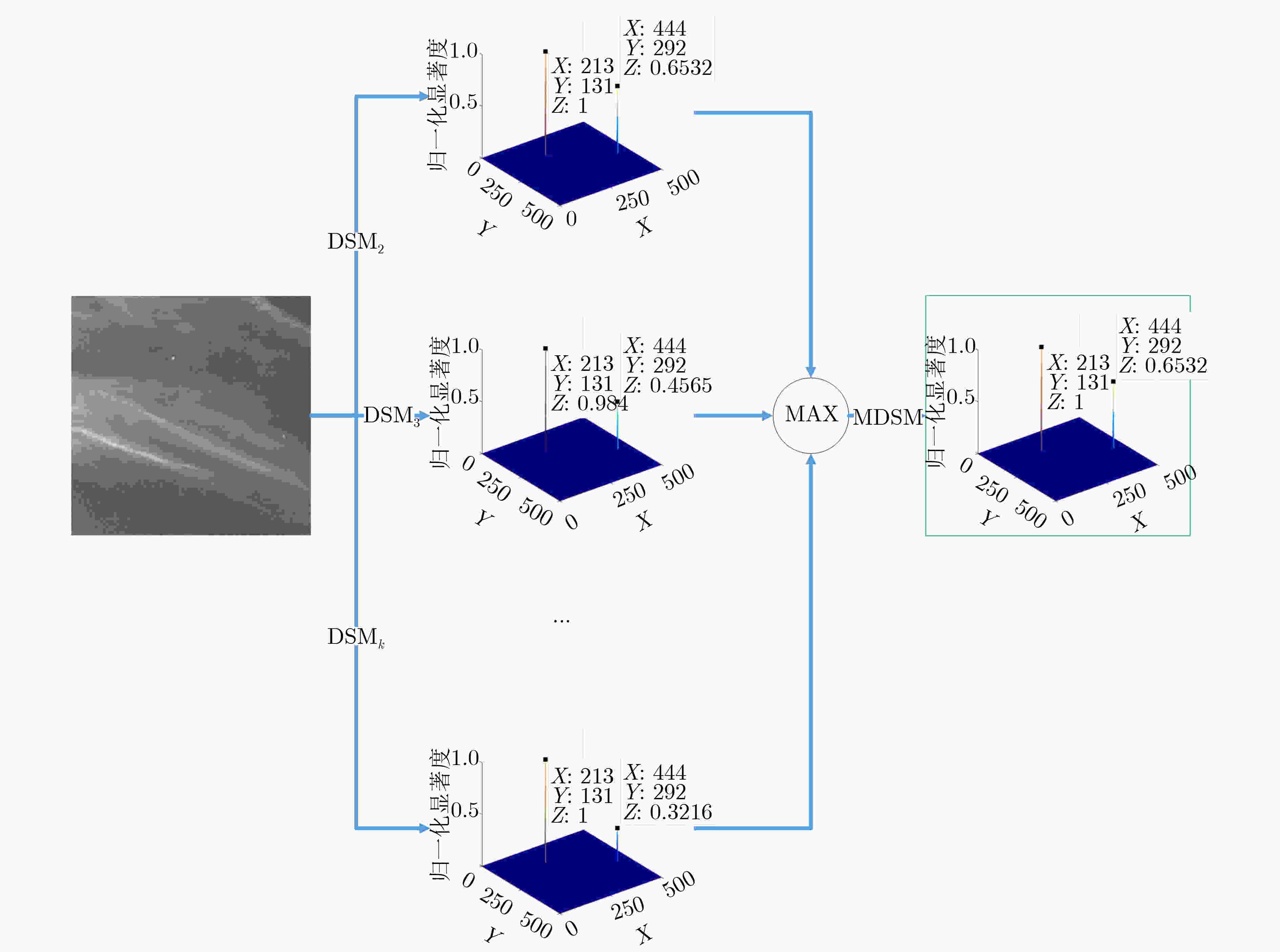
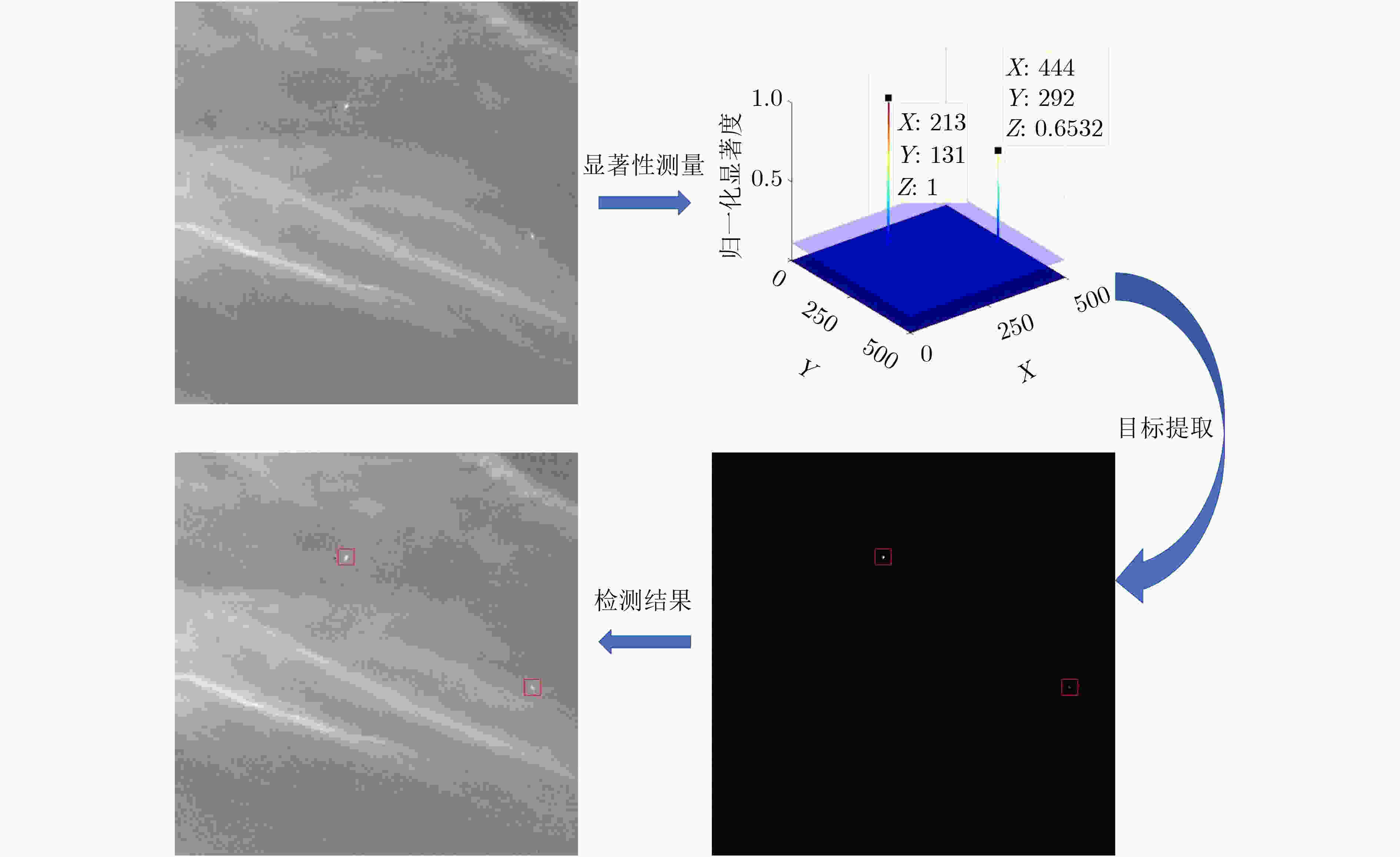
摘要: 静止轨道(GEO)的高分四号(GF-4)卫星具备对海上运动船舶进行连续观测的能力,由于轨道高,海面船舶在GF-4卫星遥感图像中比较弱小不易检测。该文分析海面运动船舶的尾迹特征,提出一种基于多尺度双邻域显著性(MDSM)的GF-4卫星遥感图像运动船舶检测方法。首先依据多尺度双邻域显著性模型计算显著度,生成显著图;然后使用自适应阈值分割提取运动船舶的位置;最后利用尾迹几何特征对候选目标的形状进行校验,进一步去除虚假目标。实验结果和分析表明,所提方法可以有效地检测GF-4卫星遥感图像中的多个运动船舶目标,相比目前主流的视觉显著性检测算法,该文所提算法具有更好的检测性能。Abstract: The GEostationary Orbit(GEO) GF-4 satellite has the ability to observe continuously moving ships at sea. Ship targets are often weak in the optical remote sensing images of GF-4 satellite, making it difficult to detect directly. By analyzing the wake characteristics of moving ships, a moving ship detection method based on Multi-scale Dual-neighborhood Saliency Model (MDSM) is proposed. First, the saliency of the image is calculated based on MDSM. Then, the position of the moving ship is extracted by adaptive segmentation threshold. Finally, the shape of the candidate target is verified to remove further the false target. Experimental results and analysis show that the proposed method can effectively detect multiple moving targets in GF-4 satellite images, and has better detection performance compared with the current mainstream visual saliency algorithms.
-
表 1 实验数据说明
序号 图像数目 图像大小 波段 图像场景 Group1 87 500×500 全色 密卷云 Group2 87 500×500 全色 薄云遮盖目标 Group3 24 500×500 全色 厚云+斑点云 Group4 12 500×500 全色 薄云 表 2 实验参数说明
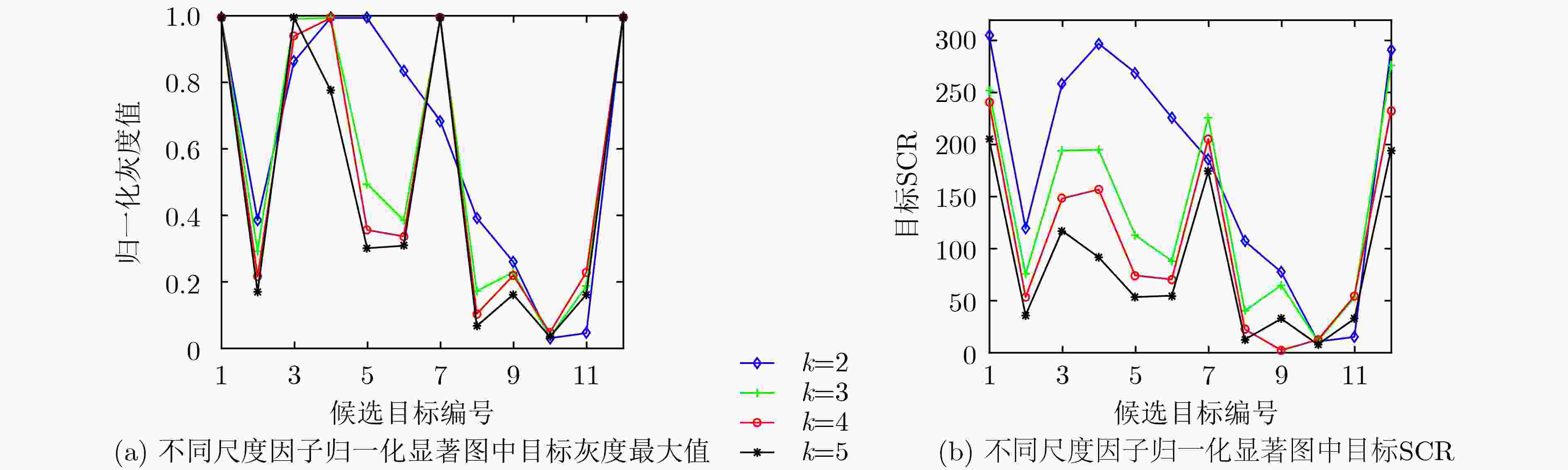
方法 参数符号 参数说明 参数取值 MPCM K 多尺度中心窗口大小 3, 5 SR n 卷积核大小 3 MDSM k 多尺度因子 2,3,4 表 3 实验结果统计
方法 PT NF PF TDR(%) FAR(%) MPCM 955 12 597 98.8 38.5 SR 641 326 104 66.3 14.0 MDSM 944 23 116 97.6 10.9 MDSM + 形态校验 920 47 37 95.1 3.9 表 4 不同分块策略用时统计
分块数 分块大小 重叠区大小 并发线程数 检测总用时(s) 1 10000×10000 − 1 903 4 5100×5100 100 4 308 9 3400×3400 100 9 317 16 2700×2700 100 16 335 -
[1] LI Bo, XIE Xiaoyang, WEI Xingxing, et al. Ship detection and classification from optical remote sensing images: A survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(3): 145–163. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.09.022 [2] 孟令杰, 郭丁, 唐梦辉, 等. 地球静止轨道高分辨率成像卫星的发展现状与展望[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2016, 37(4): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2016.04.001MENG Lingjie, GUO Ding, TANG Menghui, et al. Development status and prospect of high resolution imaging satellite in geostationary orbit[J]. Spacecraft Recovery &Remote Sensing, 2016, 37(4): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2016.04.001 [3] WANG Mi, CHENG Yufeng, CHANG Xueli, et al. On-orbit geometric calibration and geometric quality assessment for the high-resolution geostationary optical satellite GaoFen4[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 125: 63–77. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.01.004 [4] ZHANG Zhixin, SHAO Yun, TIAN Wei, et al. Application potential of GF-4 images for dynamic ship monitoring[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(6): 911–915. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2687700 [5] 王晓辉, 胡玉新, 吕鹏. 基于显著图融合的高分四号光学遥感图像多运动舰船检测方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2021, 38(5): 649–659. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2021.05.009WANG Xiaohui, HU Yuxin, and LÜ Peng. Multiple moving ships detection method based on saliency map fusion for GF-4 satellite remote sensing image[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 38(5): 649–659. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2021.05.009 [6] LIU Yong, YAO Libo, XIONG Wei, et al. GF-4 satellite and automatic identification system data fusion for ship tracking[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(2): 281–285. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2869561 [7] YAO Libao, LIU Yong, and HE You. A novel ship-tracking method for GF-4 satellite sequential images[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(7): 2007. doi: 10.3390/s18072007 [8] XIAO Fengqi, YUAN Fei, and CHENG En. Detection and tracking method of maritime moving targets based on geosynchronous orbit satellite optical images[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(7): 1092. doi: 10.3390/electronics9071092 [9] DIAO Wenhui, SUN Xian, ZHENG Xinwei, et al. Efficient saliency - based object detection in remote sensing images using deep belief networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 137–141. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2498644 [10] ZHU Hu, NI Haopeng, LIU Shiming, et al. TNLRS: Target-aware non-local low-rank modeling with saliency filtering regularization for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 9546–9558. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3028457 [11] CHEN C L P, LI Hong, WEI Yantao, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574–581. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 [12] WEI Yantao, YOU Xinge, and LI Hong. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 58: 216–226. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.04.002 [13] HOU Xiaodi and ZHANG Liqing. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1–8. -





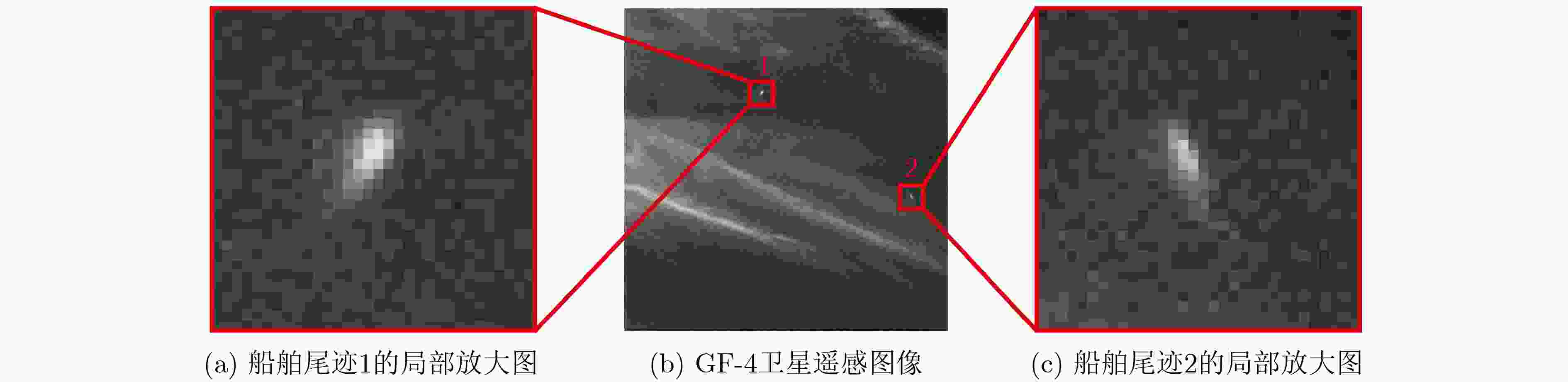
 下载:
下载:
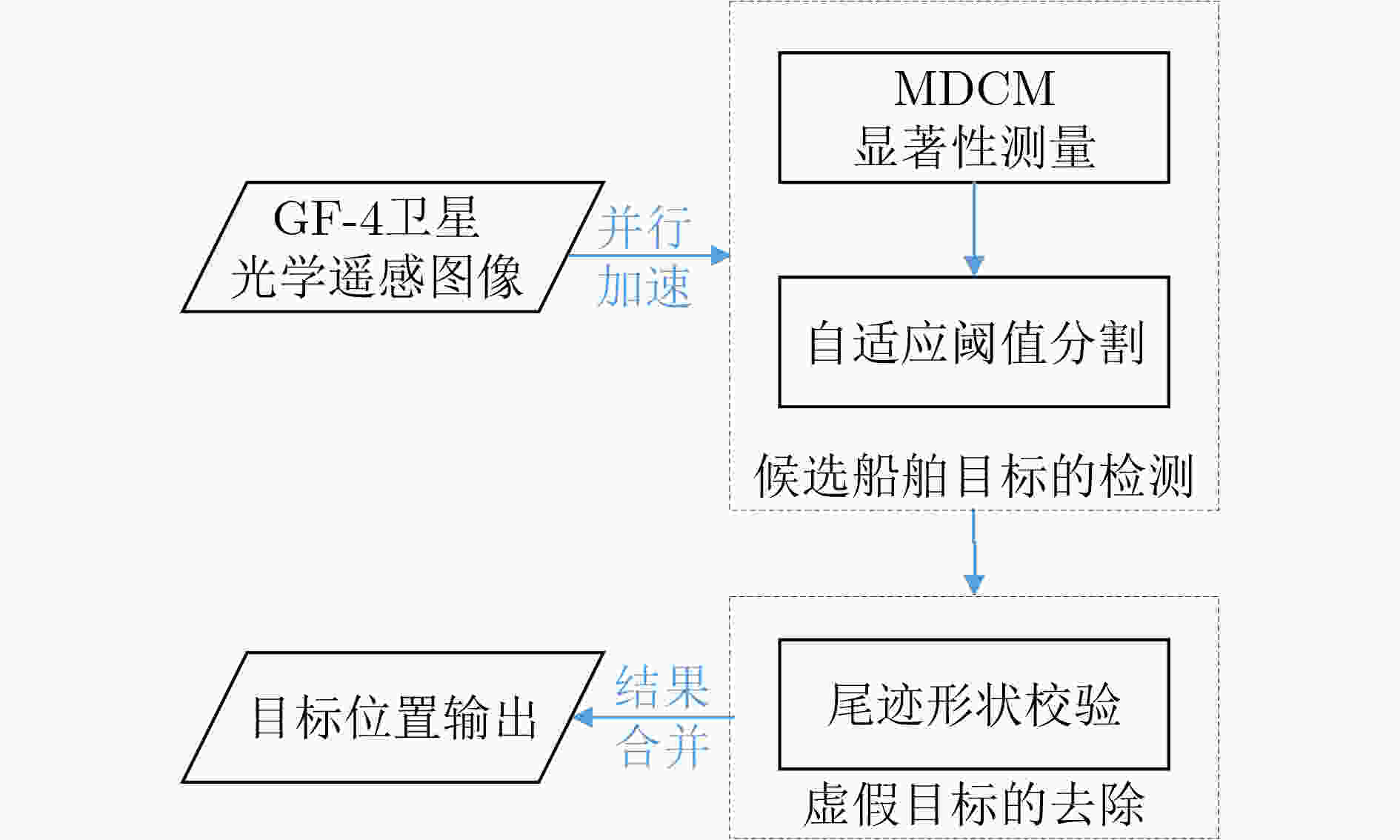
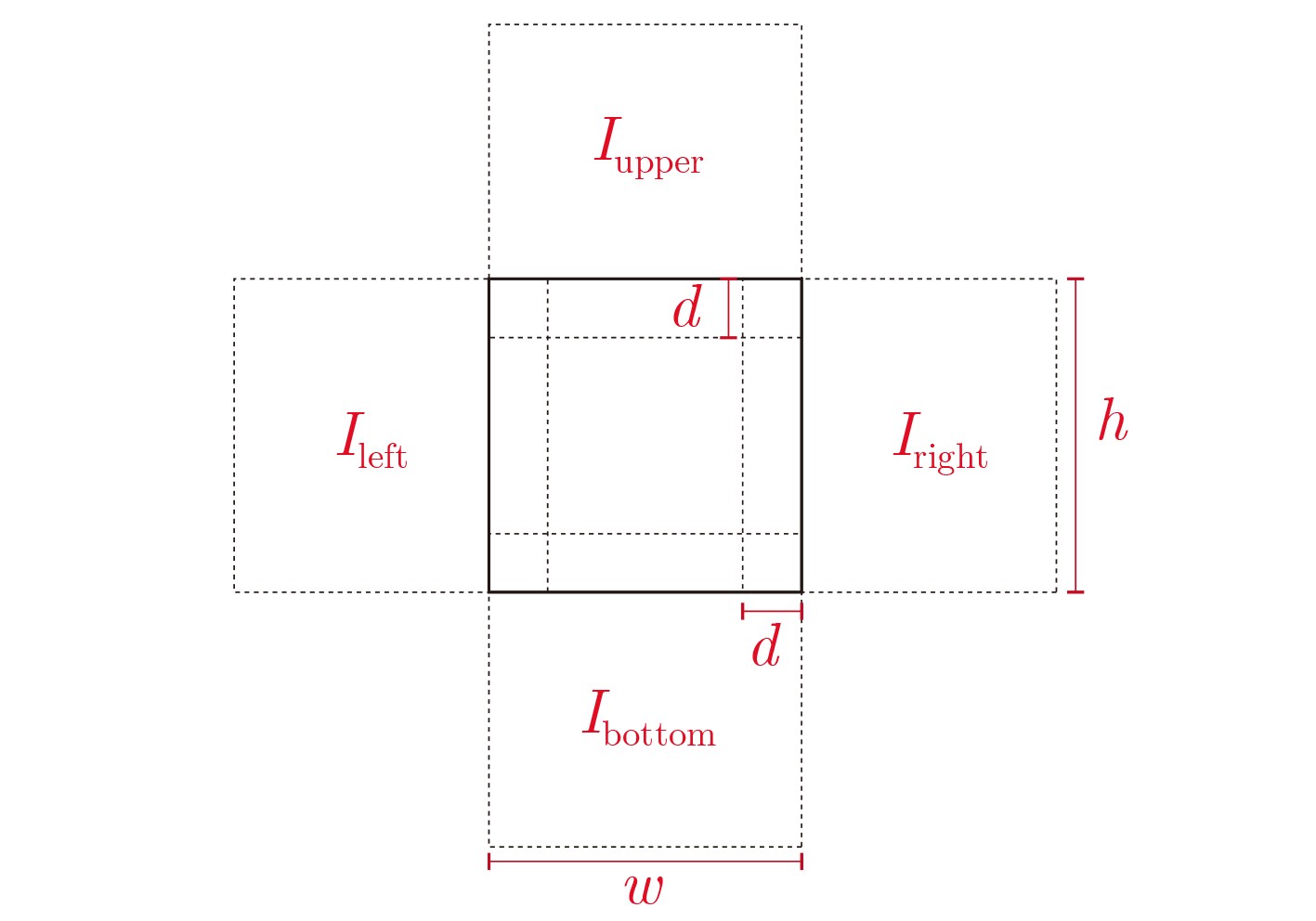
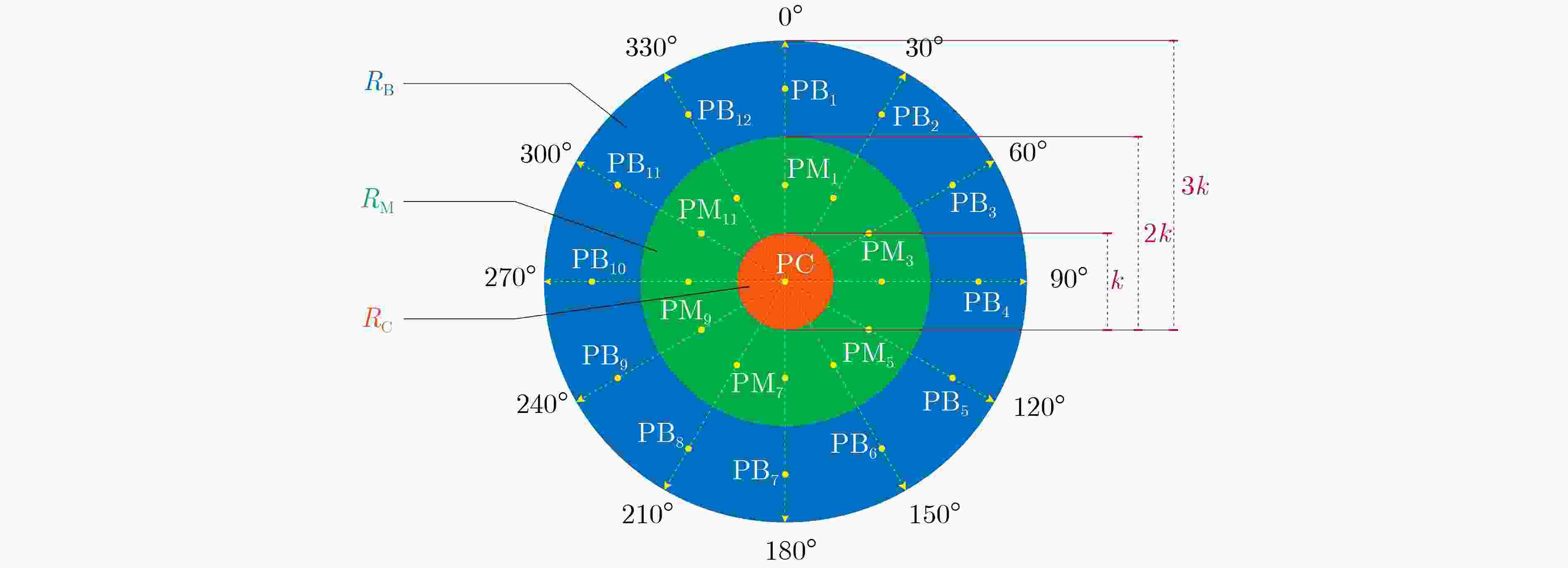



 下载:
下载:
