Life Signal Extraction Based on Multi-channel Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave Radar
-
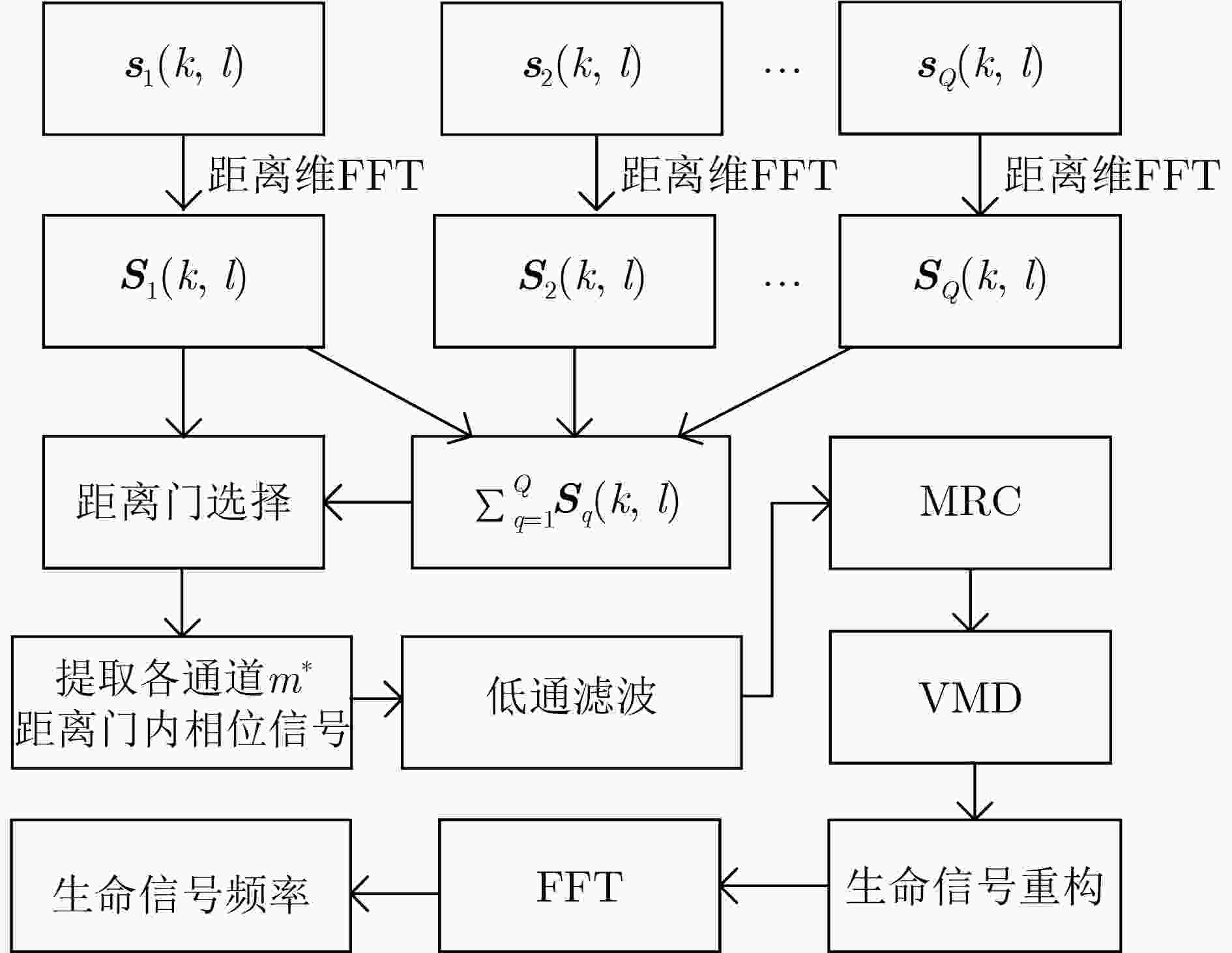
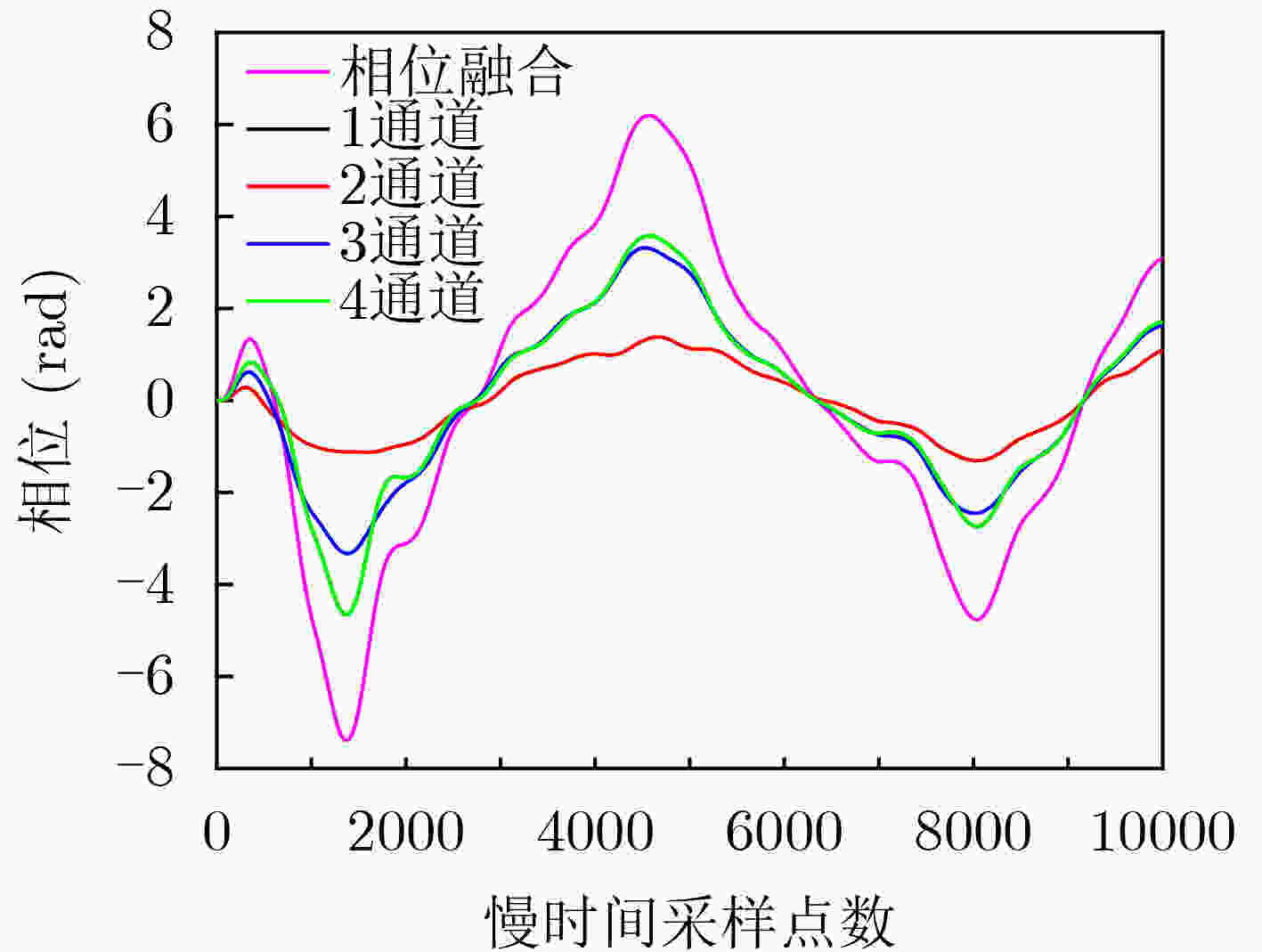
摘要: 针对单通道调频连续波(FMCW)雷达不能保证生命信号检测准确度的问题,该文提出一种基于多通道的FMCW雷达生命信号提取方法。所提方法对各等效接收通道进行距离像重构和相位信号提取后,首先采用最大比率融合(MRC)技术对各通道提取的相位信号进行融合,接着对融合后的相位信号进行变分模态分解(VMD)并对生命信号进行重构,最后对重构信号进行快速傅里叶变换(FFT)得到呼吸和心跳信号频率。实测数据处理结果表明相比于单通道FMCW雷达,所提多通道方法能够更加稳健准确地提取生命体征信号,且结合MRC技术与VMD的信号处理方法明显优于结合MRC技术与带通滤波(BPF)的信号处理方法。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that the Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar could not guarantee the detection accuracy of life signal, a life signal extraction method based on multichannel FMCW radar is proposed in this paper. After the proposed method achieves the reconstruction of the range profiles and the extraction of phase signal corresponding to each equivalent receiving channel, the Maximum Ratio Combining (MRC) technique is used to fuse the phase signals from the multiple receiving channels. Then the Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) is adopted to decompose the fused phase signal to reconstruct the life signal. Finally, the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is performed on the reconstructed the life signal to obtain the respiration rate and heartbeat rate. The experimental results show that the proposed life signal extraction method based on multichannel FMCW radar can extract the life signal more robustly and accurately compared to single channel FMCW radar. In addition, the combined MRC and VMD signal processing method outperforms the combined MRC and Band-Pass Filter (BPF) method.
-
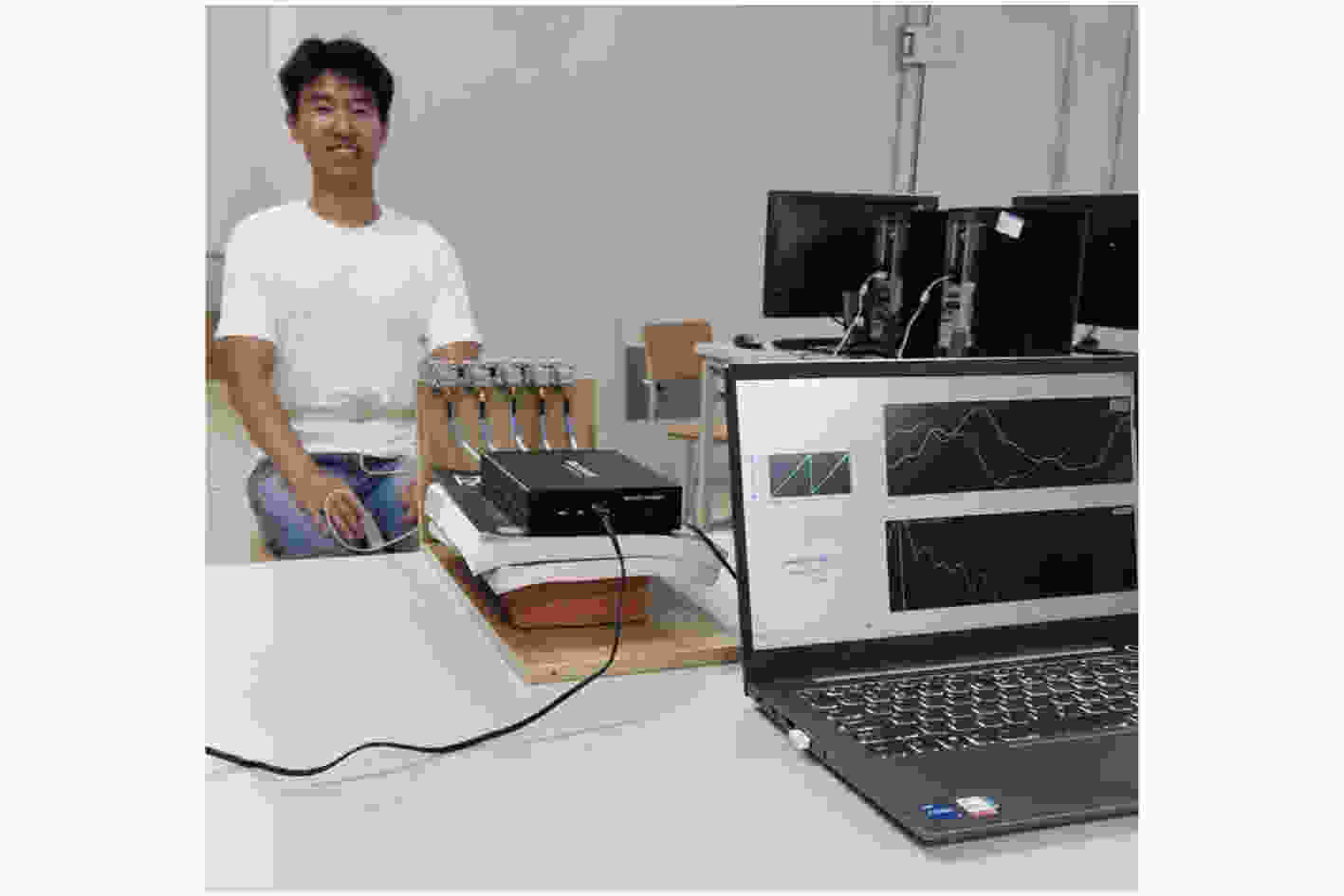
表 1 多通道FMCW雷达参数
起始频率${f_{\text{c}}}$ 带宽$B$ Chirp波形持续时间$T$ 慢时间维采样周期${T_{\text{s}}}$ 慢时间维采样数$L$ 快时间维采样数$K$ 参数值 24 GHz 2 GHz 1 ms 1 ms 10000 256 表 2 重构结果SNR(dB)
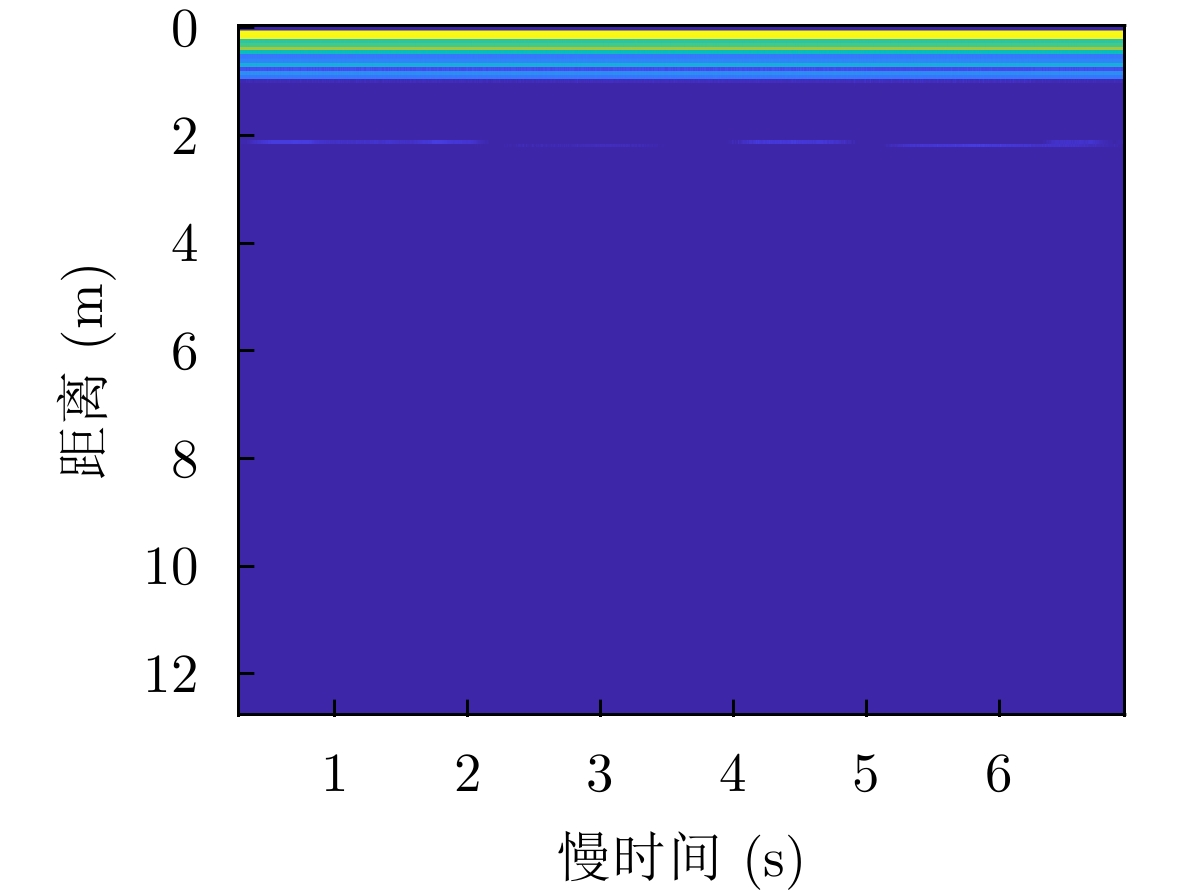
重构结果SNR 测量通道 目标距离
(1 m)目标距离
(2 m)1号志愿者呼吸重构结果SNR 相位融合 36.87 36.76 1通道 36.83 36.53 2通道 36.88 36.62 3通道 36.81 36.50 4通道 36.83 36.53 1号志愿者心跳重构结果SNR 相位融合 36.06 35.88 1通道 32.42 34.55 2通道 32.14 32.78 3通道 34.62 30.74 4通道 32.42 34.26 2号志愿者呼吸重构结果SNR 相位融合 37.29 36.35 1通道 37.24 35.26 2通道 37.41 34.43 3通道 37.24 34.28 4通道 37.24 34.93 2号志愿者心跳重构结果SNR 相位融合 33.12 33.70 1通道 32.61 30.99 2通道 32.95 32.73 3通道 32.42 31.69 4通道 32.61 30.98 -
[1] SACCO G and PISA S. A MIMO radar for vital signs recording[C]. 2019 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Spring, Rome, Italy, 2019: 387–393. [2] CARDILLO E and CADDEMI A. Radar range-breathing separation for the automatic detection of humans in cluttered environments[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(13): 14043–14050. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3024961 [3] WANG Wen, WANG Yong, ZHOU Mu, et al. A novel vital sign sensing algorithm for multiple people detection based on FMCW radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2020: 1104–1106. [4] WEISHAUPT F, WALTERSCHEID I, BIALLAWONS O, et al. Vital sign localization and measurement using an LFMCW MIMO radar[C]. The 2018 19th International Radar Symposium, Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–8. [5] SHANG Xiaolei, LIU Jian, and LI Jian. Multiple object localization and vital sign monitoring using IR-UWB MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4437–4450. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2990817 [6] SAKAMOTO T. Noncontact measurement of human vital signs during sleep using low-power millimeter-wave ultrawideband MIMO array radar[C]. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference, Nanjing, China, 2019: 1–4. [7] LIU Qiwei, GUO Hanqing, XU Junhong, et al. Non-contact non-invasive heart and respiration rates monitoring with MIMO radar sensing[C]. 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018: 1–6. [8] HUANG Qianlan, LU Dawei, HU Jiemin, et al. Simultaneous location and parameter estimation of human vital sign with MIMO-FMCW radar[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing, Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–4. [9] VO DAI T K, OLEKSAK K, KVELASHVILI T, et al. Enhancement of remote vital sign monitoring detection accuracy using multiple-input multiple-output 77 GHz FMCW radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology, 2022, 6(1): 111–122. doi: 10.1109/JERM.2021.3082807 [10] YAN Jiaming, HONG Hong, ZHAO Heng, et al. Through-wall multiple targets vital signs tracking based on VMD algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(8): 1293. doi: 10.3390/s16081293 [11] PARK B K, BORIC-LUBECKE O, and LUBECKE V M. Arctangent demodulation with DC offset compensation in quadrature Doppler radar receiver systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2007, 55(5): 1073–1079. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2007.895653 [12] SAKAMOTO T and YAMASHITA K. Noncontact measurement of autonomic nervous system activities based on heart rate variability using ultra-wideband array radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology, 2020, 4(3): 208–215. doi: 10.1109/JERM.2019.2948827 [13] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [14] SUN Li, HUANG Shuaiming, LI Yusheng, et al. Remote measurement of human vital signs based on joint-range adaptive EEMD[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 68514–68524. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985286 [15] WEI Jiaqi, ZHANG Lei, and LIU Hongwei. Non-contact life signal extraction and reconstruction technique based on MAE[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 110826–110834. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2934573 [16] 冯久超, 潘水洋. 基于经验模态分解的生命信号提取算法[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 38(10): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2010.10.001FENG Jiuchao and PAN Shuiyang. Extraction algorithm of vital signals based on empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2010, 38(10): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2010.10.001 [17] REN Lingyun, WANG Haofei, NAISHADHAM K, et al. Phase-based methods for heart rate detection using UWB impulse Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(10): 3319–3331. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2597824 -





 下载:
下载:
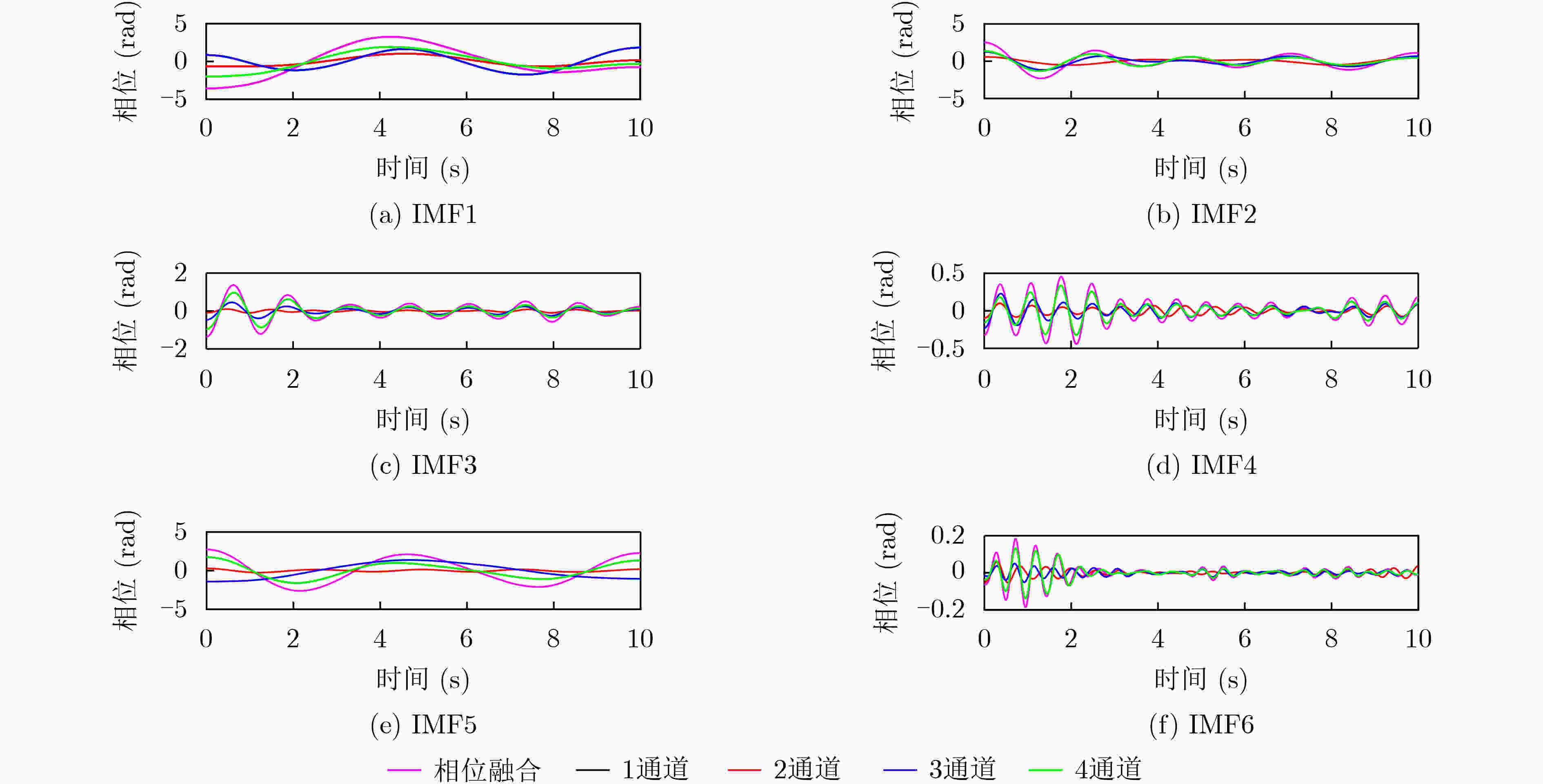
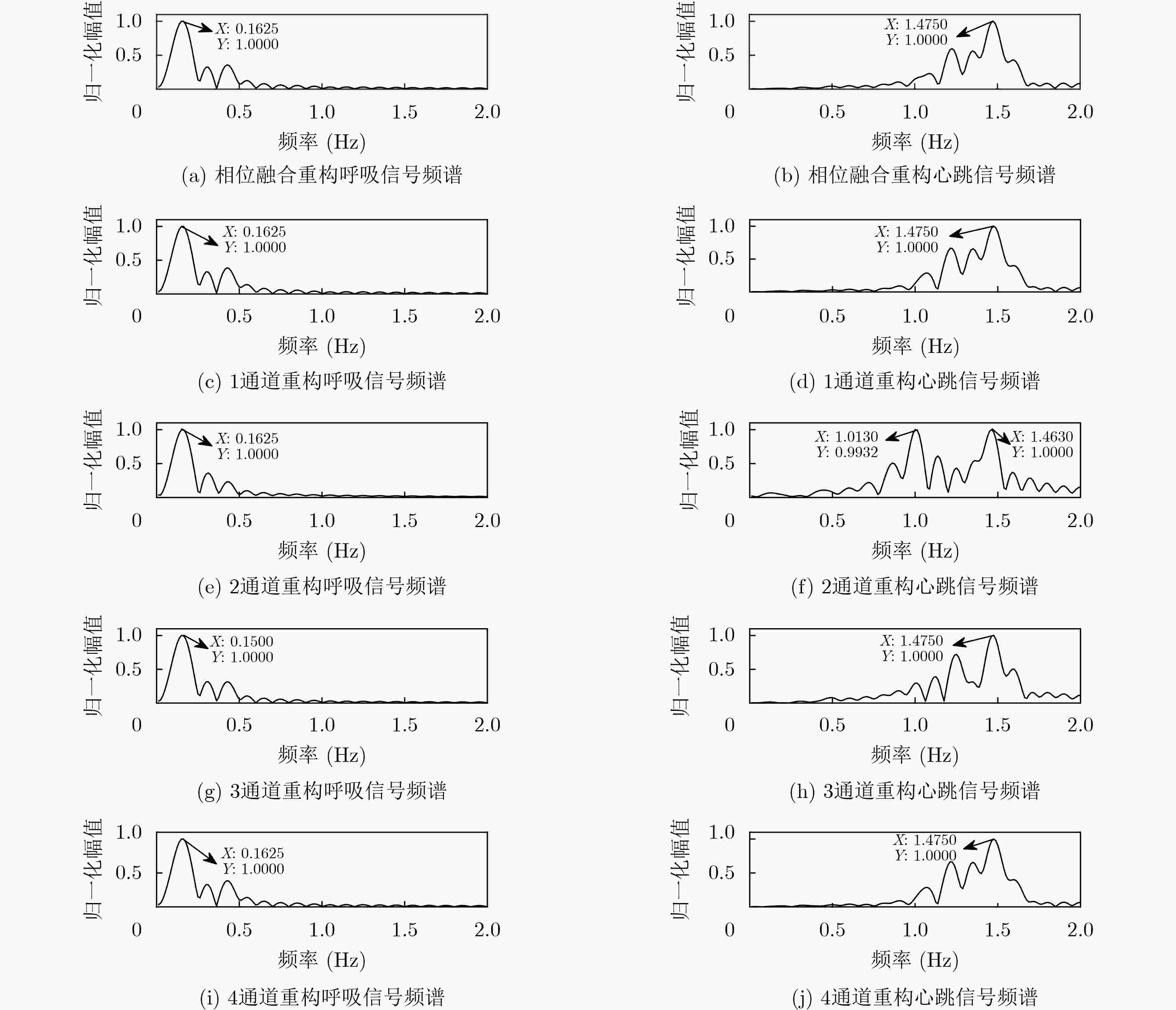
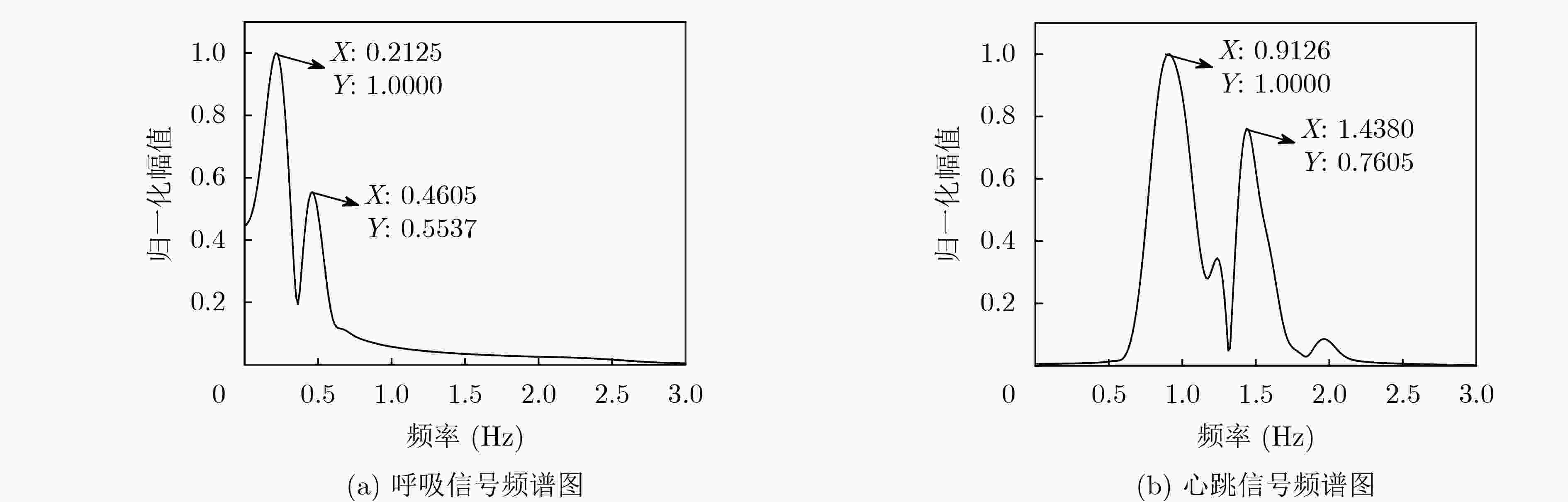
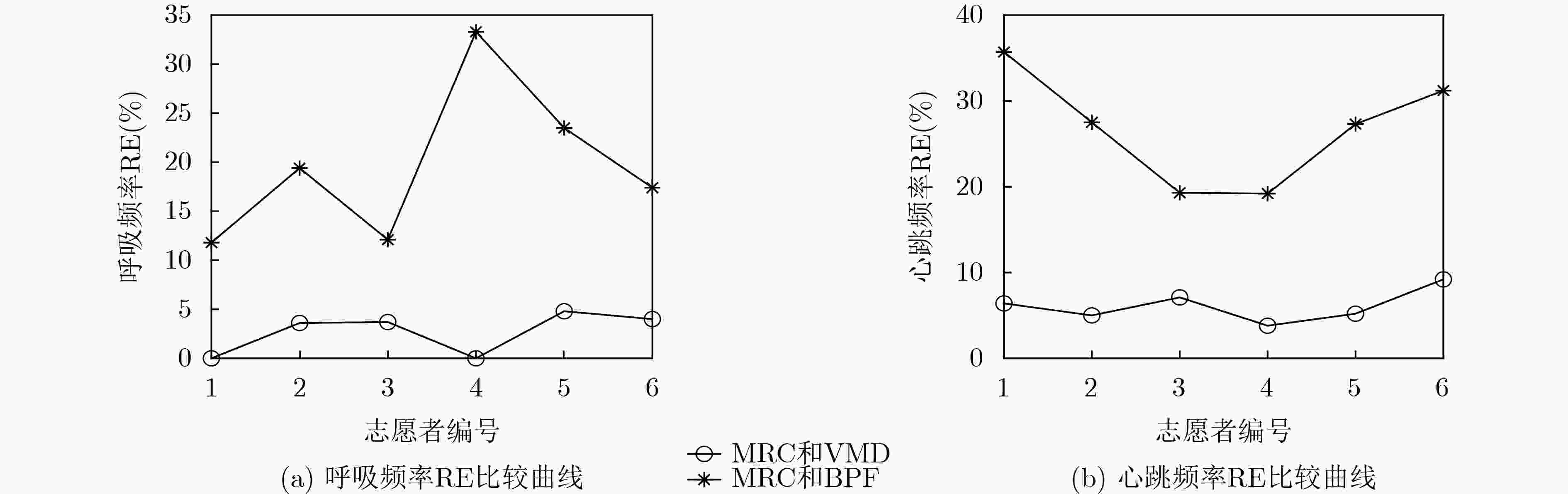


 下载:
下载:
