Reversible Data Hiding in Encrypted Images Based on Polynomial Secret Sharing
-
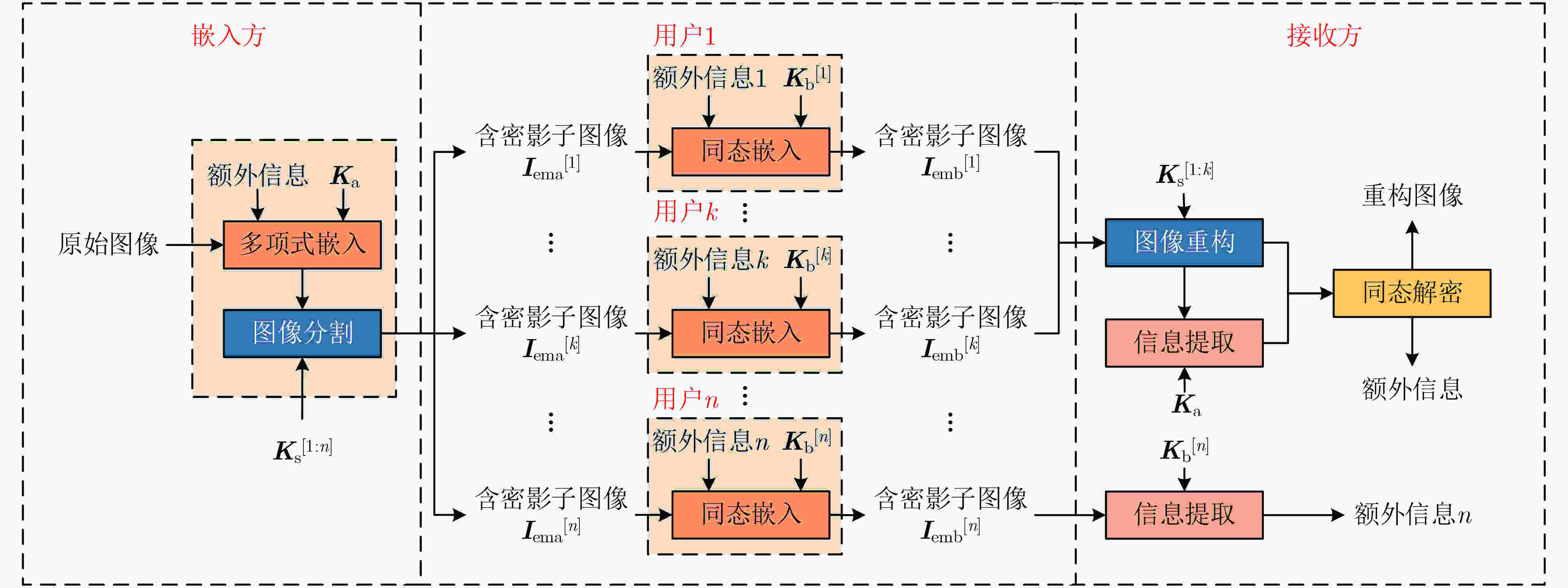
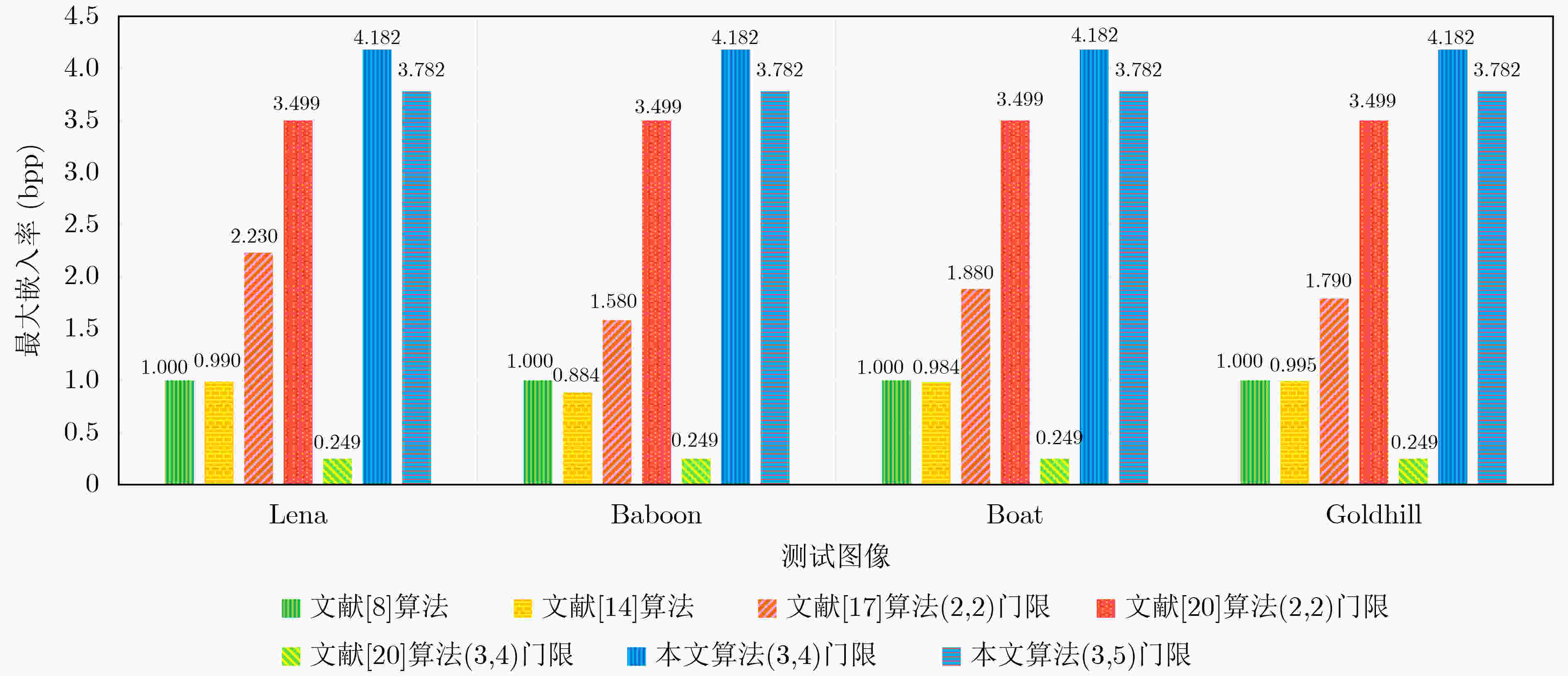
摘要: 针对密文域可逆信息隐藏在多用户场景下算法嵌入率低、载体图像容灾性能较弱等问题,该文提出一种基于多项式秘密共享的图像密文域可逆信息隐藏方案。通过将图像分割成多幅影子图像并存储在不同的用户端,可以增强图像的容灾性,为了实现额外信息在图像重构前后提取的可分离性,该方案包括两种嵌入算法:算法1在图像分割的过程中,将额外信息嵌入多项式的冗余系数中得到含有额外信息的影子图像,该算法支持在图像重构之后提取额外信息;算法2针对图像分割后的任一影子图像,利用秘密共享的加法同态特性实施嵌入,该算法支持直接从影子图像中提取额外信息。实验在不同门限方案和影子图像压缩率的条件下进行测试,当压缩率为50%时,(3, 4)门限方案的嵌入率达4.18 bpp(bit per pixel),(3, 5)门限方案的嵌入率达3.78 bpp。结果表明,两种嵌入算法分别支持从影子图像与重构图像中提取额外信息,实现了方案的可分离性;与现有方案相比,所提算法嵌入率较高、计算复杂度较低,具有较强的实用性。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of low embedding rate of reversible data hiding in encrypted domain with multi-users and weak disaster tolerance of cover image, a reversible data hiding in encrypted images based on polynomial secret sharing scheme is proposed. The cover image is divided into multiple shadow images and stored to multiple users, so that the image disaster tolerance can be enhanced. Separability is achieved by combining two embedding algorithms, where Algorithm 1 embeds additional data into the redundancy coefficients of the polynomial during the process of image sharing to generate shadow images containing additional data, which can extract data after image reconstruction; Algorithm 2, for any shadow image, embeds additional data by using the additive homomorphism of secret sharing, which supports extracting additional data directly from the shadow image. Experiments are performed in different threshold and shadow image compression rates. When the compression rate is 50%, the embedding rate reaches 4.18 bit per pixel (bpp) for the (3, 4) threshold scheme and 3.78 bpp for the (3, 5) threshold scheme. The results show that the algorithms support extracting additional data from the shadow images and the reconstructed images respectively, which achieves the separability of the scheme. The proposed scheme has a higher embedding rate and lower computational complexity than the existing schemes, and is more practical.
-
表 1 相关变量说明
变量 变量说明 变量 变量说明 ${\boldsymbol{I}}$ 原始图像 $ {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\text{s}}^{[i]},i = 1,2, \cdots ,n $ 用户共享密钥 ${ {\boldsymbol{I} }_{\rm{e}}}$ 置乱图像 ${{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ 多项式嵌入时,额外信息隐藏密钥 ${ {\boldsymbol{m} }_{{a} } }$ 多项式嵌入的额外信息 ${\boldsymbol{K} }_{{b} }^{[i]},i = 1,2, \cdots ,n$ 同态嵌入时,额外信息隐藏密钥 ${ {\boldsymbol{m} }_{{b} } }$ 同态嵌入的额外信息 ${\boldsymbol{I}}_{{\text{ema}}}^{[i]},i = 1,2, \cdots ,n$ 包含额外信息的影子图像 ${{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\text{e}}}$ 图像置乱密钥 ${\boldsymbol{I}}_{{\text{emb}}}^{[i]},i = 1,2, \cdots ,n$ 包含额外信息和标记信息的影子图像 表 2 译码表
生成多项式 ${\boldsymbol{E}}$ 0000000 0000001 0000010 0000100 0001000 0010000 0100000 1000000 ${q_1}(x) = {x^3} + x + 1$ ${{\boldsymbol{S}}_1}$ 000 001 010 100 011 110 111 101 $ {q_2}(x) = {x^3} + {x^2} + 1 $ ${{\boldsymbol{S}}_2}$ 000 001 010 100 101 111 011 110 表 3 实际最大嵌入率
最大嵌入率
(bpp)n = 4 n = 5 n = 6 n = 7 w = 2 w = 2 w = 3 w = 2 w = 3 w = 4 w = 2 w = 3 w = 4 w = 5 k = 3 4.1818 3.7818 \ 3.5152 \ \ 3.3247 \ \ \ k = 4 \ 5.3818 3.7818 4.8485 3.5152 \ 4.4675 3.3247 \ \ k = 5 \ \ \ 6.1818 4.8485 3.5152 5.6104 4.4675 3.3247 \ k = 6 \ \ \ \ \ \ 6.7532 5.6104 4.4675 3.3247 表 4 同态解密前后重构图像质量
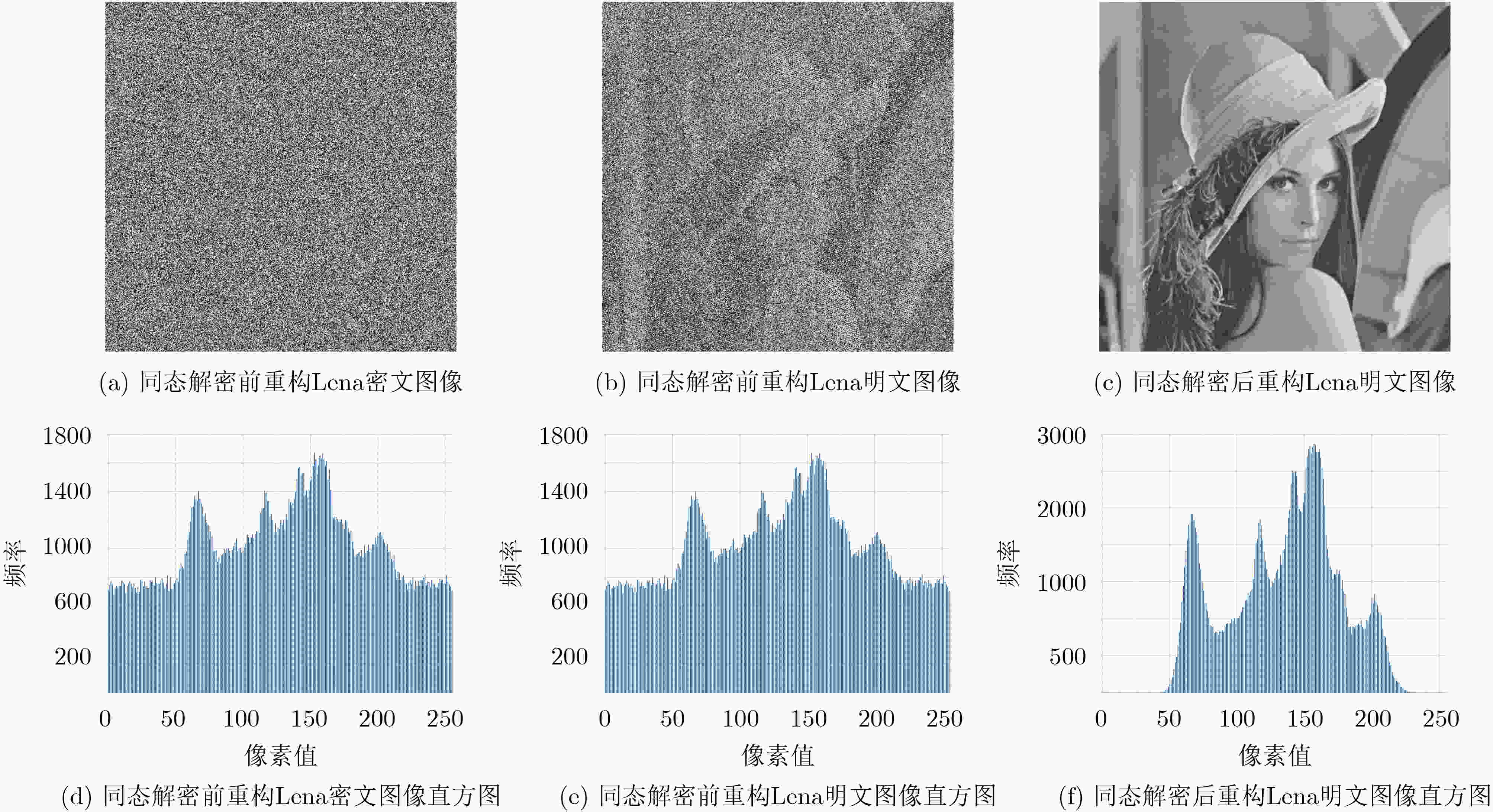
测试图像 同态解密前重构密文图像 同态解密前重构明文图像 同态解密后重构明文图像 PSNR(dB) 信息熵 PSNR(dB) 信息熵 PSNR(dB) 信息熵 Lena 10.166119 7.955290 10.870086 7.955290 $ + \infty $ 7.218498 Baboon 10.571863 7.951466 11.136816 7.951466 $ + \infty $ 7.139099 Boat 9.628571 7.928695 10.478454 7.928695 $ + \infty $ 7.046737 Goldhill 9.688918 7.967631 10.387593 7.967631 $ + \infty $ 7.472315 表 5 信息嵌入前后含密影子图像安全性分析
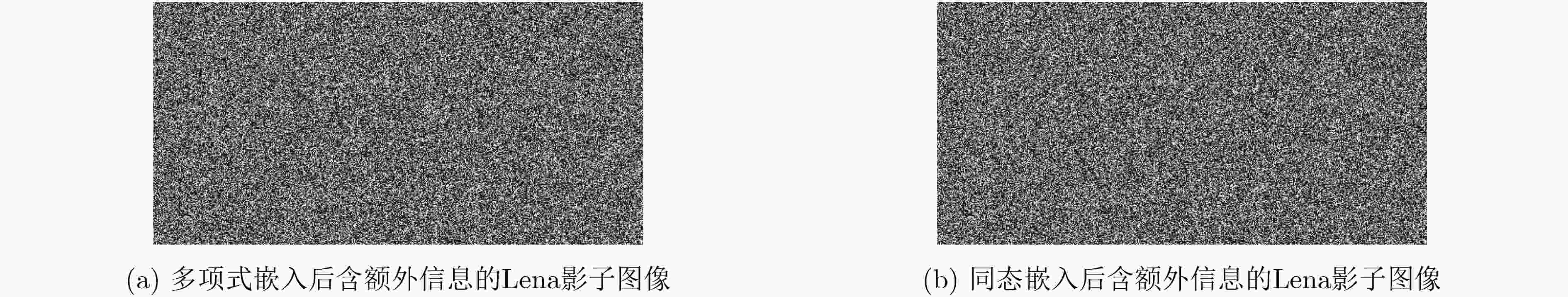
测试图像 未嵌入信息的影子图像 多项式嵌入后的影子图像 同态嵌入后的影子图像 信息熵 NPCR(%) UACI(%) 信息熵 NPCR(%) UACI(%) 信息熵 Lena 7.998589 99.617195 33.423751 7.998618 99.611473 33.433949 7.998648 Baboon 7.998515 99.599838 33.412525 7.998594 99.601936 33.402735 7.998660 Boat 7.998591 99.606895 33.435428 7.998544 99.605942 33.412868 7.998607 Goldhill 7.998551 99.619293 33.476432 7.998505 99.608231 33.459180 7.998645 表 6 不同算法特性对比
算法 算法框架 加密方式 时间复杂度 密文扩展 可分离性 信息隐藏者 文献[8] VRBE 流密码 $O(N)$ 1 否 单用户 文献[18] VRBE 多秘密共享 $O(N)$ 1 否 单用户 文献[25] VRBE Paillier $O({N^3})$ 128 是 单用户 文献[3] VRAE 流密码 $O(N)$ 1 否 单用户 文献[15] VRAE Paillier $O({N^3})$ 128 否 单用户 文献[17] VRAE 秘密共享 $O(N)$ n 否 单用户 文献[20] VRAE 秘密共享 $O(N)$ n 是 多用户 文献[13] VRIE LWE $O({N^2})$ 16 否 单用户 文献[14] VRIE 流密码 $O(N)$ 1 否 单用户 本文算法 VRIE 秘密共享 ${\mathbf{O(N)}}$ n/w 是 多用户 -
[1] SHI Yunqing, LI Xiaolong, ZHANG Xinpeng, et al. Reversible data hiding: Advances in the past two decades[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 3210–3237. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2573308 [2] PUECH W, CHAUMONT M, and STRAUSS O. A reversible data hiding method for encrypted images[C]. SPIE 6819, Security, Forensics, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents X, San Jose, United States, 2008: 68191E. [3] ZHANG Xinpeng. Reversible data hiding in encrypted image[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2011, 18(4): 255–258. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2011.2114651 [4] ZHANG Xinpeng. Separable reversible data hiding in encrypted image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2012, 7(2): 826–832. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2011.2176120 [5] CELIK M U, SHARMA G, TEKALP A M, et al. Lossless generalized-LSB data embedding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(2): 253–266. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.840686 [6] CHEN C C, CHANG C C, and CHEN Kaimeng. High-capacity reversible data hiding in encrypted image based on huffman coding and differences of high nibbles of pixels[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2021, 76: 103060. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2021.103060 [7] THODI D M and RODRIGUEZ J J. Prediction-error based reversible watermarking[C]. 2004 International Conference on Image Processing, Singapore, 2004: 1549–1552. [8] PUTEAUX P and PUECH W. An efficient MSB prediction-based method for high-capacity reversible data hiding in encrypted images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(7): 1670–1681. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2799381 [9] WU Haotian, YANG Zhiyuan, CHEUNG Y M, et al. High-capacity reversible data hiding in encrypted images by bit plane partition and MSB prediction[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 62361–62371. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916355 [10] WESTFELD A. F5—a steganographic algorithm: High capacity despite better steganalysis[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Information Hiding, Pittsburgh, USA, 2001: 289–302. [11] WU Haotian, CHEUNG Y M, YANG Zhiyuan, et al. A high-capacity reversible data hiding method for homomorphic encrypted images[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2019, 62: 87–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2019.04.015 [12] 张敏情, 柯彦, 苏婷婷. 基于LWE的密文域可逆信息隐藏[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 354–360. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150702ZHANG Minqing, KE Yan, and SU Tingting. Reversible steganography in encrypted domain based on LWE[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 354–360. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150702 [13] KE Yan, ZHANG Minqing, LIU Jia, et al. A multilevel reversible data hiding scheme in encrypted domain based on LWE[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2018, 54: 133–144. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.05.002 [14] HUANG Delu and WANG Jianjun. High-capacity reversible data hiding in encrypted image based on specific encryption process[J]. Signal Processing Image Communication, 2020, 80: 115632. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2019.115632 [15] CHEN Y C, SHIU C W, and HORNG G. Encrypted signal-based reversible data hiding with public key cryptosystem[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2014, 25(5): 1164–1170. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.04.003 [16] WU Xiaotian, CHEN Bing, and WENG Jian. Reversible data hiding for encrypted signals by homomorphic encryption and signal energy transfer[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2016, 41: 58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2016.09.005 [17] WU Xiaotian, WENG Jian, and YAN Weiqi. Adopting secret sharing for reversible data hiding in encrypted images[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 143: 269–281. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.09.017 [18] CHEN Yuchi, HUNG T H, HSIEH S H, et al. A new reversible data hiding in encrypted image based on multi-secret sharing and lightweight cryptographic algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(12): 3332–3343. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2914557 [19] KE Yan, ZHANG Minqing, ZHANG Xinpeng, et al. A reversible data hiding scheme in encrypted domain for secret image sharing based on Chinese remainder theorem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(4): 2469–2481. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3081575 [20] CHEN Bing, LU Wei, HUANG Jiwu, et al. Secret sharing based reversible data hiding in encrypted images with multiple data-hiders[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(2): 978–991. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2020.3011923 [21] SHAMIR A. How to share a secret[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(11): 612–613. doi: 10.1145/359168.359176 [22] THIEN C C and LIN J C. Secret image sharing[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2002, 26(5): 765–770. doi: 10.1016/S0097-8493(02)00131-0 [23] FRIDRICH J and SOUKAL D. Matrix embedding for large payloads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2006, 1(3): 390–395. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2006.879281 [24] 邓晓衡, 廖春龙, 朱从旭, 等. 像素位置与比特双重置乱的图像混沌加密算法[J]. 通信学报, 2014, 35(3): 216–223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.03.025DENG Xiaoheng, LIAO Chunlong, ZHU Congxu, et al. Image encryption algorithms based on chaos through dual scrambling of pixel position and bit[J]. Journal on Communications, 2014, 35(3): 216–223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.03.025 [25] ZHANG Xinpeng, LONG Jing, WANG Zichi, et al. Lossless and reversible data hiding in encrypted images with public-key cryptography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(9): 1622–1631. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2433194 -





 下载:
下载:

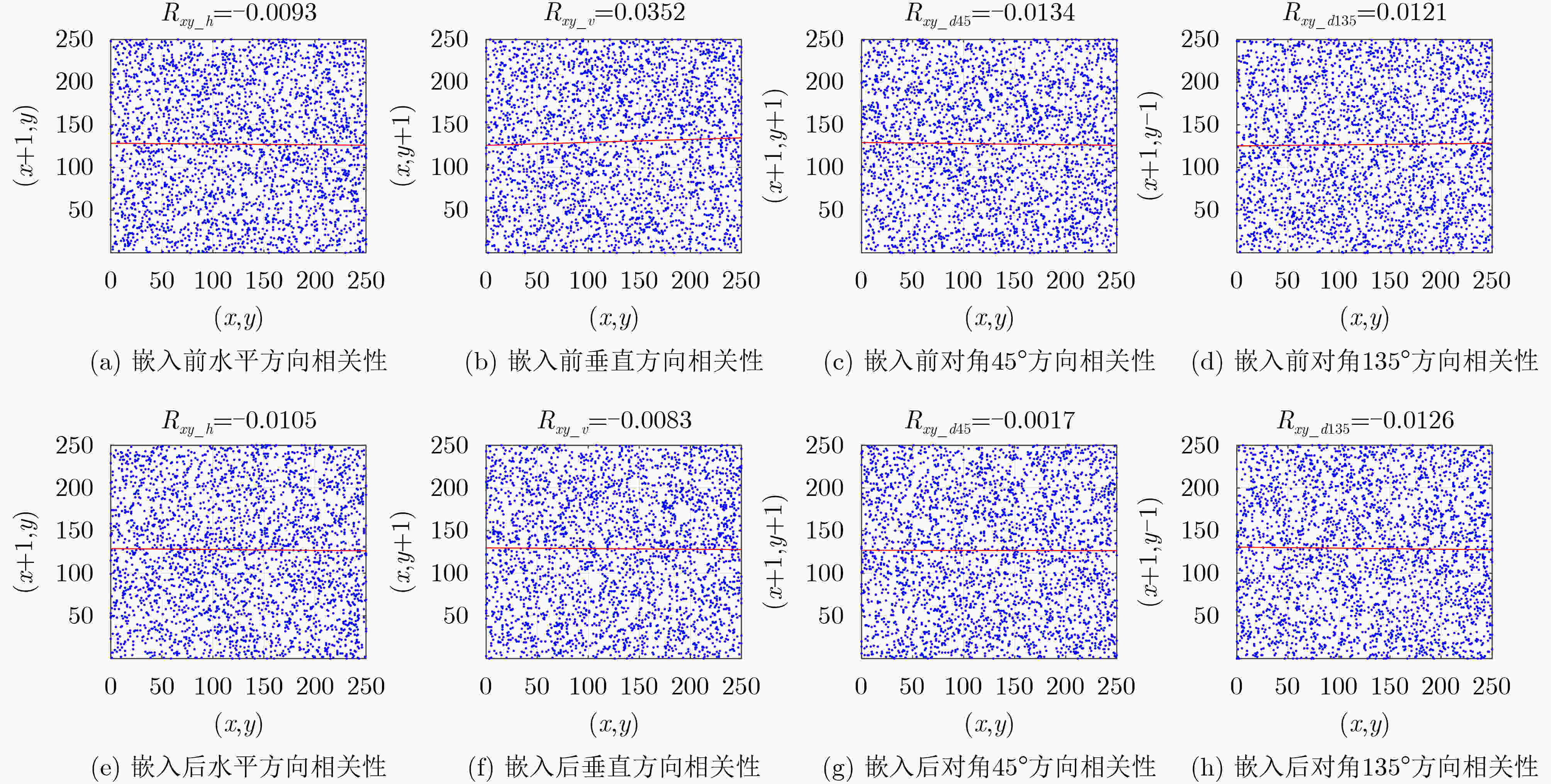


 下载:
下载:
