Research Status and Prospect of Human Movement Recognition Technique Using Through-Wall Radar
-
摘要: 在人体目标的动作识别应用中,穿墙雷达(TWR)具有隐蔽性高、探测能力强和不易受环境因素限制等优点,同时兼具良好的目标隐私信息保护能力,在武装反恐、安保监控和医疗看护等领域发挥出重要作用。为了梳理穿墙雷达对人体目标动作识别技术的发展脉络以及预测该技术的未来发展趋势,该文首先简要介绍穿墙探测的工作原理,并对不同体制穿墙雷达的特点进行比较和讨论;然后,围绕穿墙雷达人体动作识别应用中的雷达成像、特征参数提取和动作状态判决等关键技术,对国内外公开发表的相关文献进行了归纳分析;最后,对穿墙雷达的人体动作识别技术研究进行总结和展望,指出该技术在目前实际应用中所面临的潜在问题和挑战。Abstract: In applications of human action recognition, Through-Wall Radar (TWR) is a promising tool because of its outstanding advantages in aspects of concealment, detection ability and robustness against environmental restrictions. Besides, TWR can provide targets with satisfactory privacy protection. As a result, TWR is widely used in a series of areas including anti-terrorism, security monitoring and medical caring. To hackle and forecast the development process of the TWR-based human action recognition theory, the detection principle of different kinds of TWRs is first introduced in this article, and their properties are compared. Then aiming at the key technologies involved in human action recognition, such as radar imaging, feature information extraction, and action state judgement, the relevant literature published at home and abroad is classified and analyzed. Finally, the TWR-based human action recognition theory is summarized and prospected, and some potential problems and challenges in practical applications are pointed out.
-
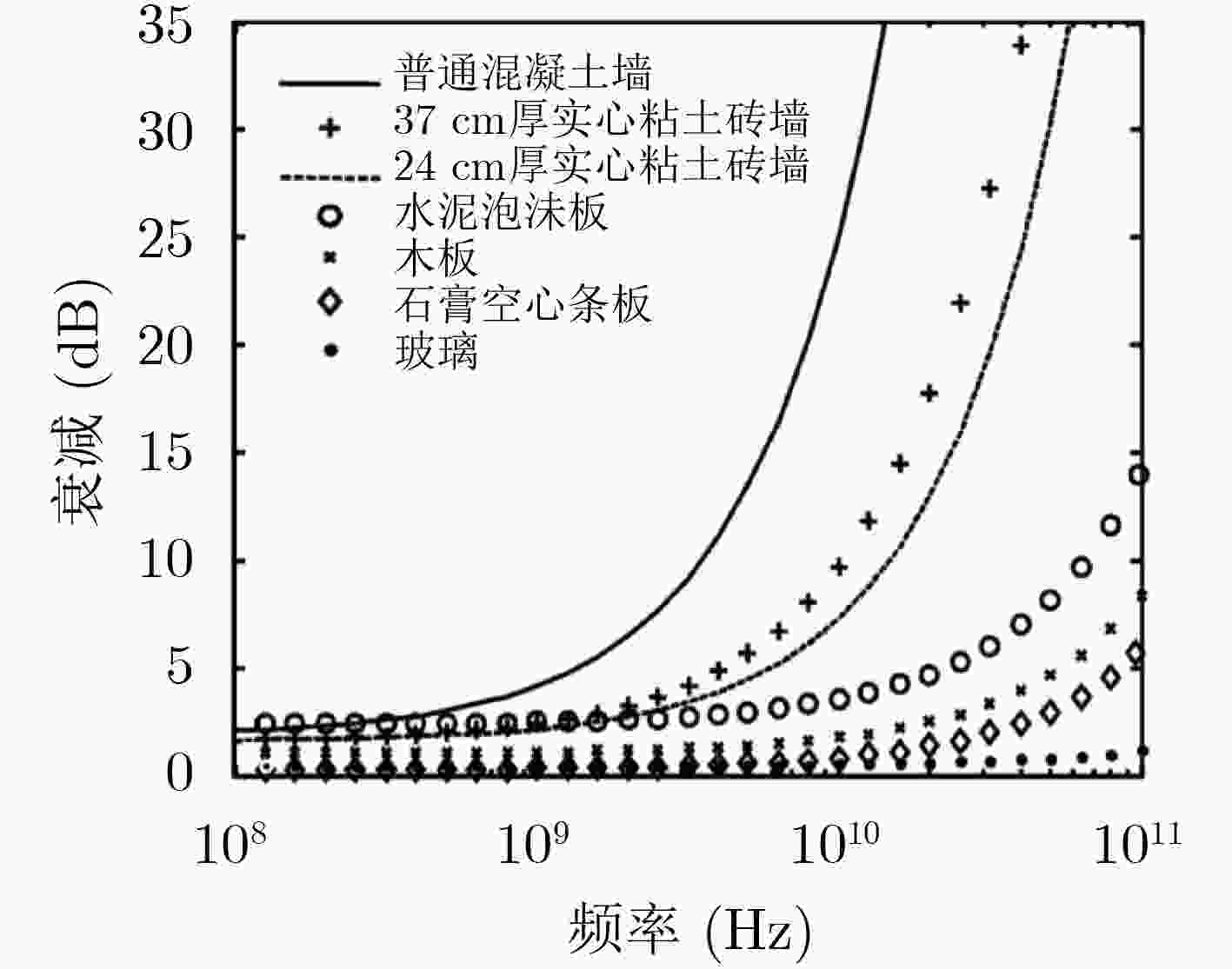
图 2 常见障碍物材料对不同频率电磁波信号的衰减效用对比图[13]
图 4 Soldovieri等人[38]的人体目标探测场景和成像结果示意
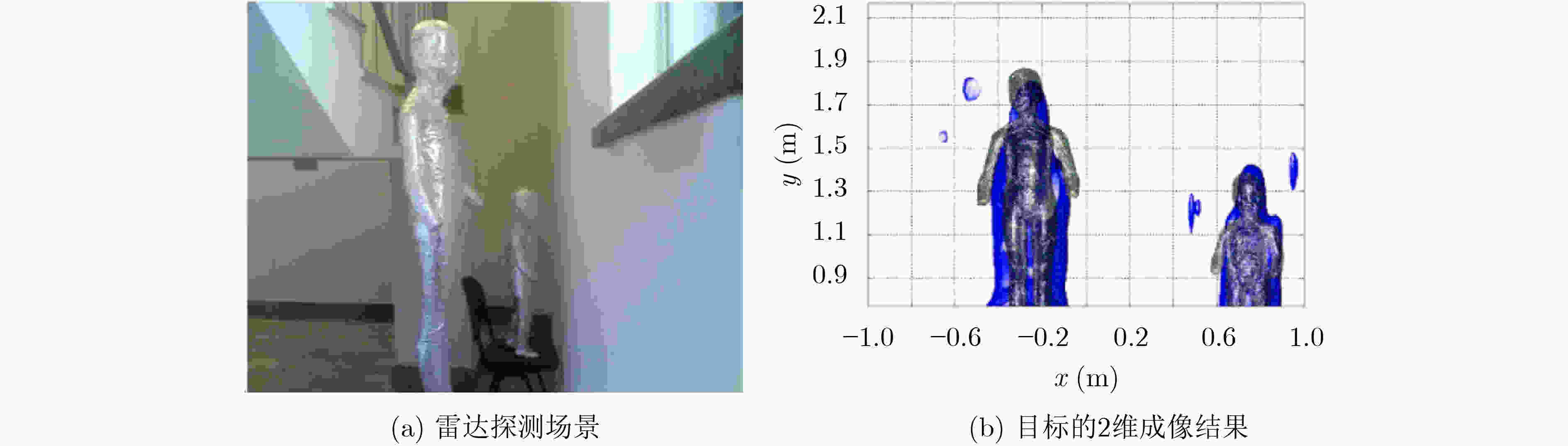
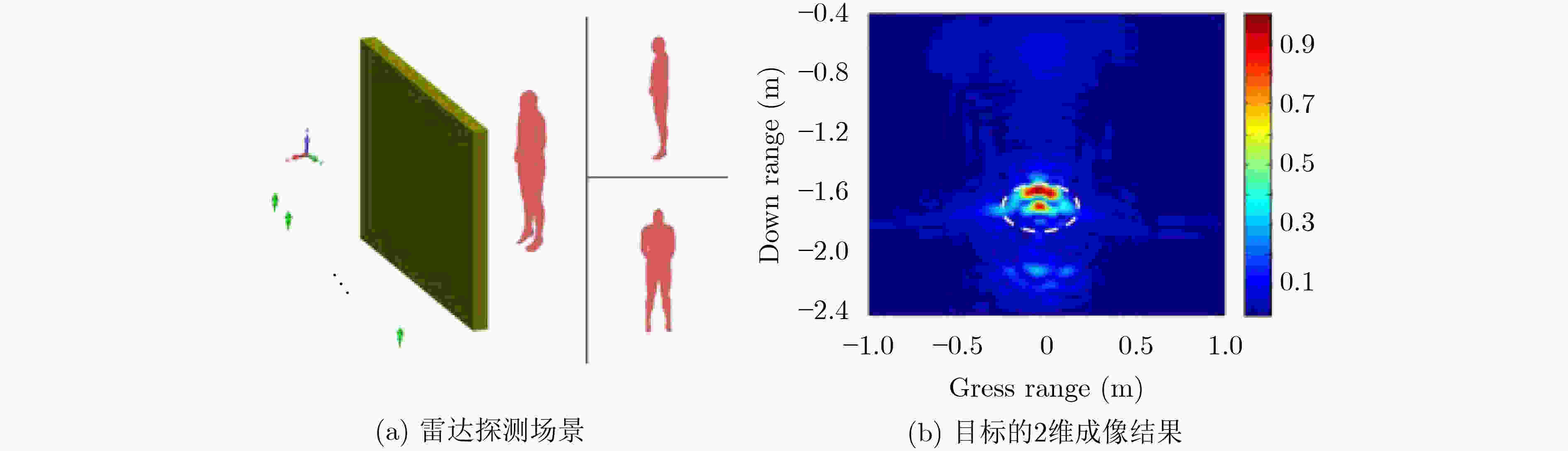
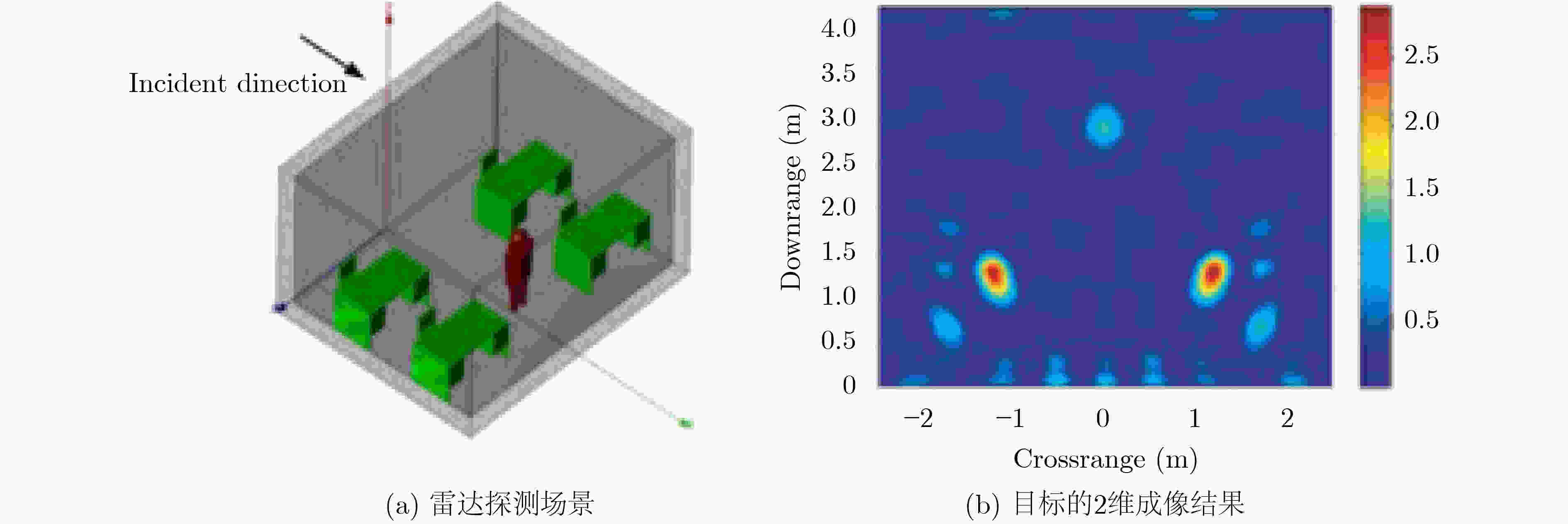
图 5 Zhang等人[39]的人体目标探测场景和2维成像结果示意
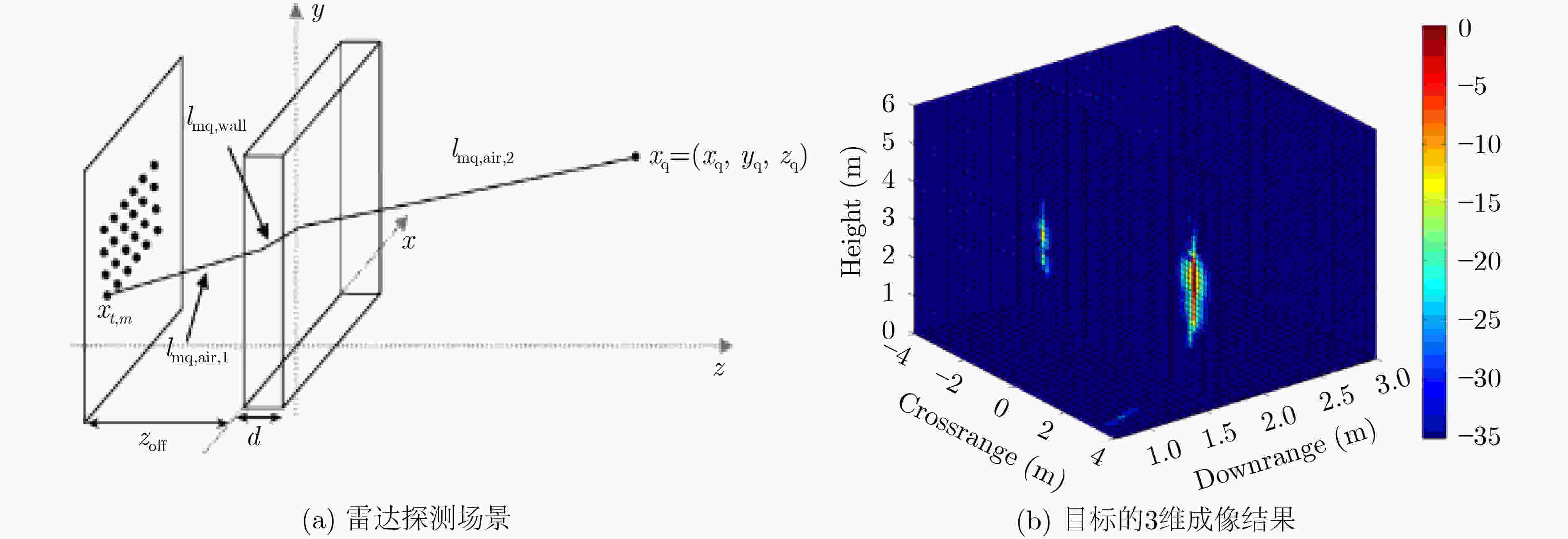
图 6 Zhang等人[40]的人体目标探测场景和3维成像结果示意
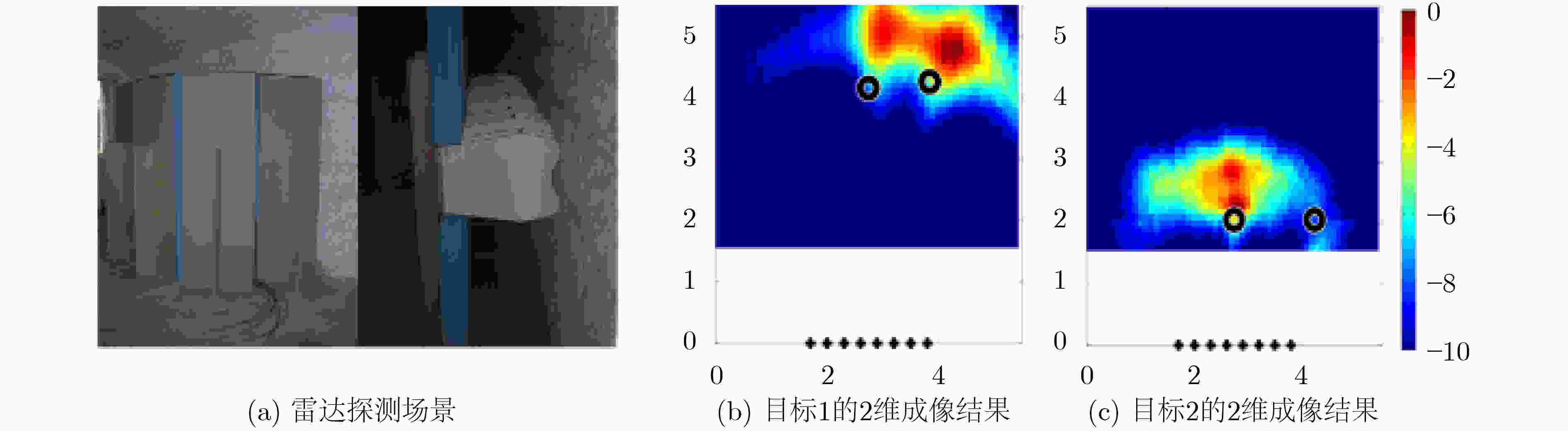
图 7 Dubroca等人[48]的人体目标探测场景和成像结果示意
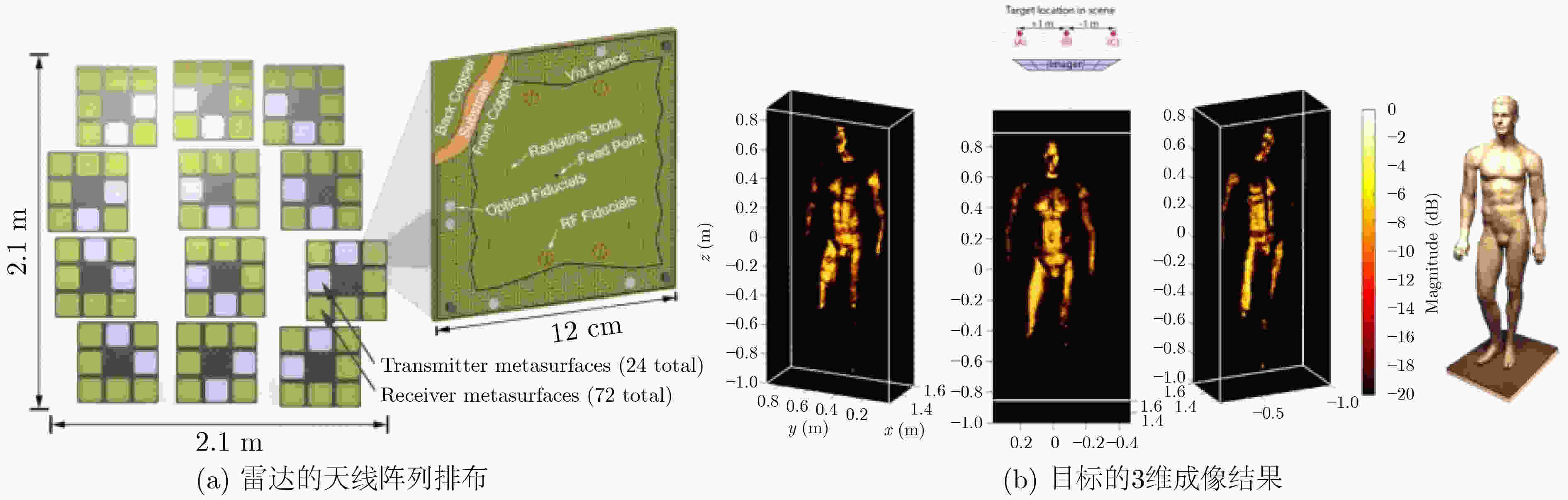
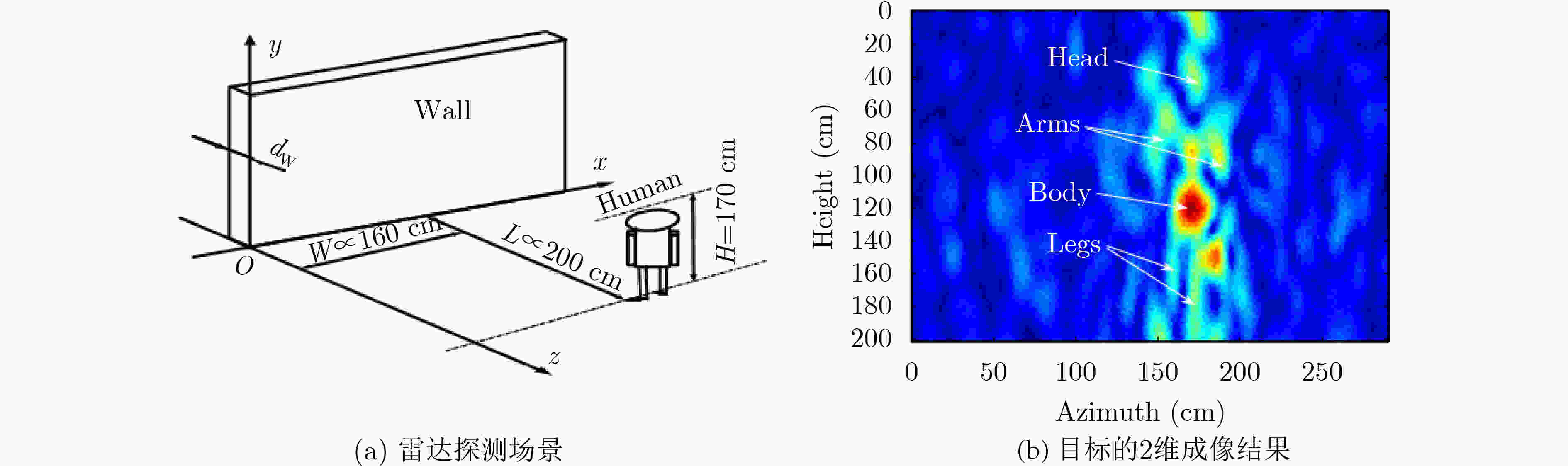
图 8 Gollub等人[49]的人体目标探测场景和成像结果示意
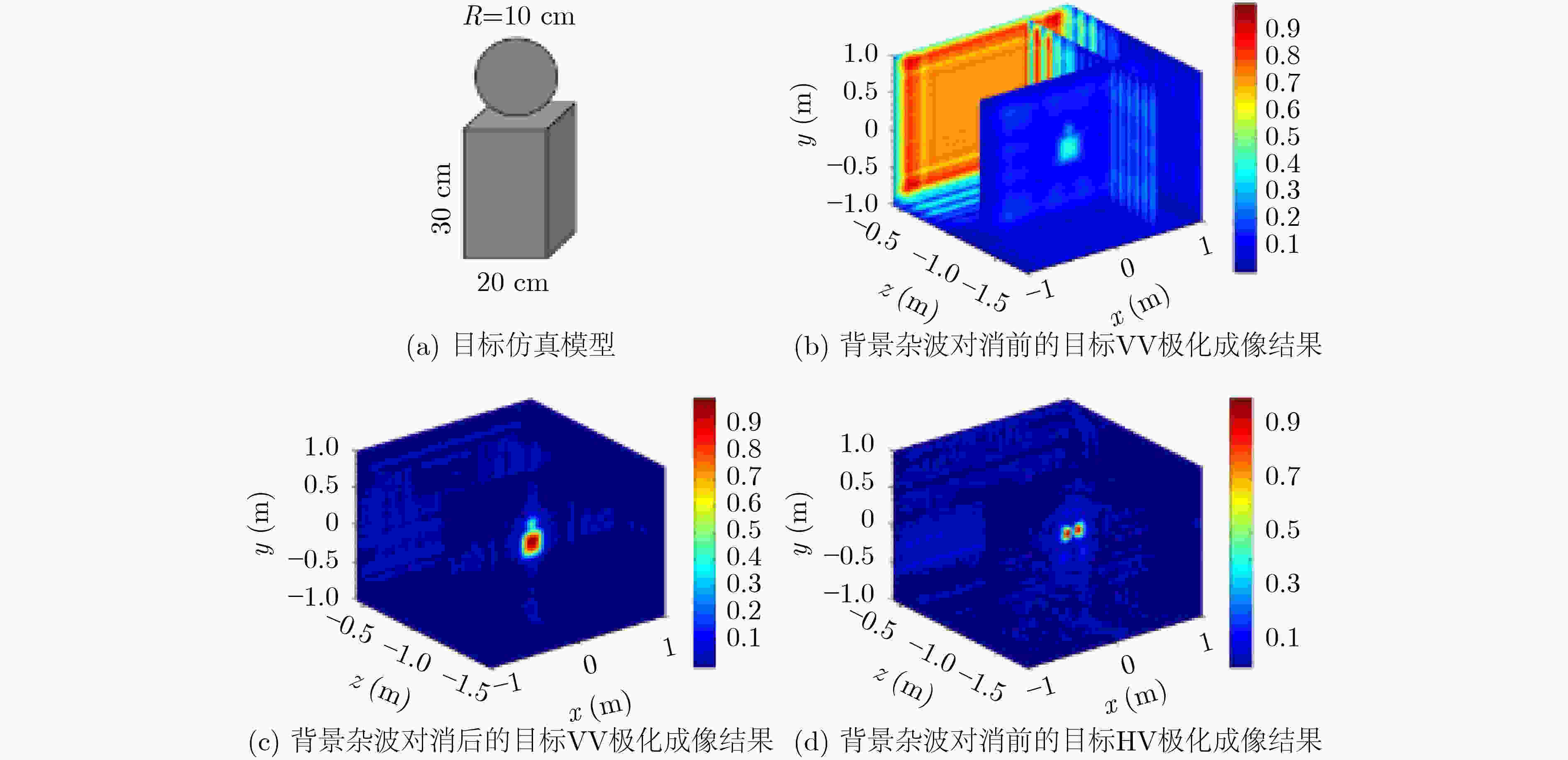
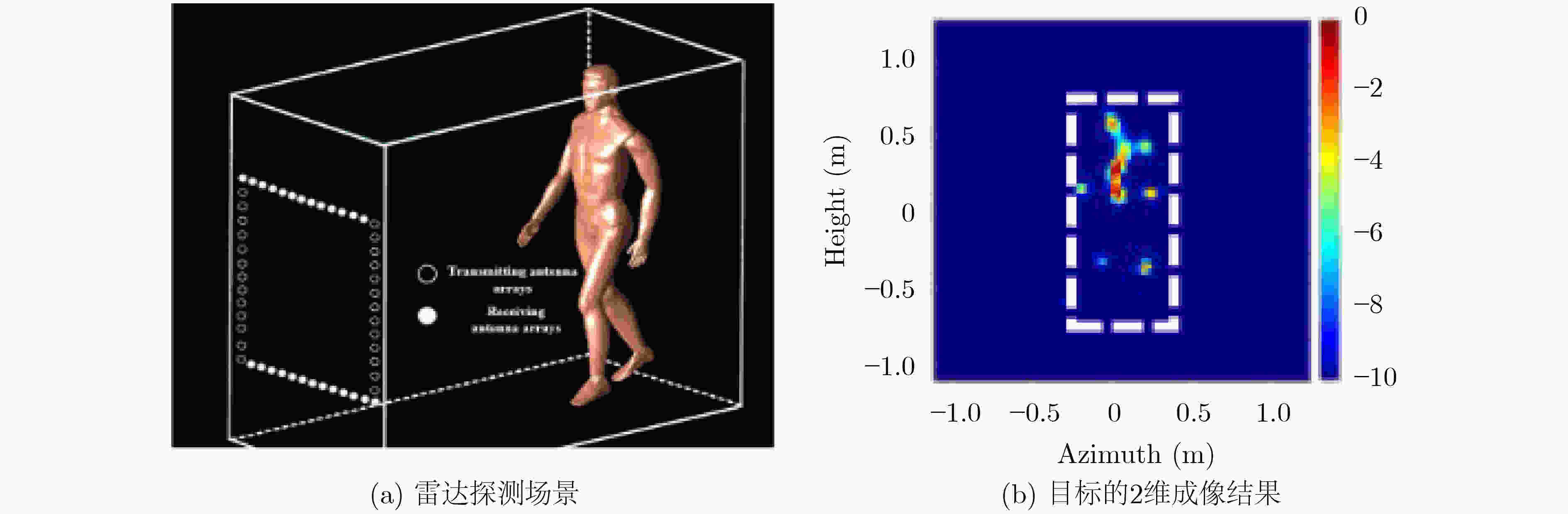
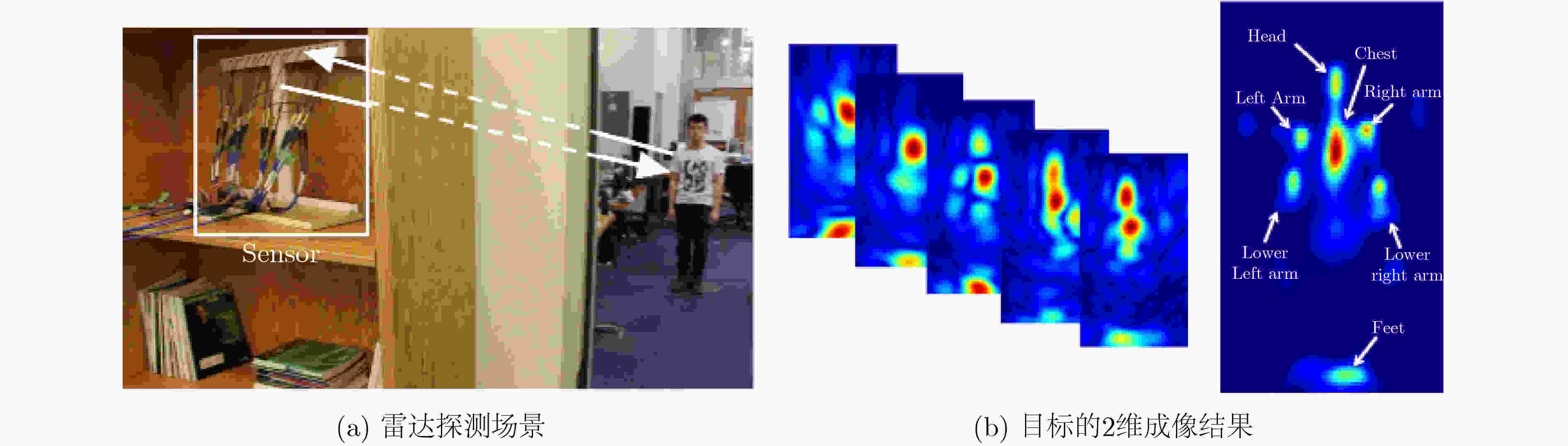
图 9 Wang等人[52]的人体目标探测场景和2维成像结果示意
图 10 Ahmad等人[53]的目标探测场景和3维成像结果示意
图 11 Kong等人[55]的人体目标探测场景和3维成像结果示意
图 12 Zhao等人[56]的人体目标探测场景和成像结果示意
图 13 Adib等人[57]的人体目标探测场景和成像结果示意
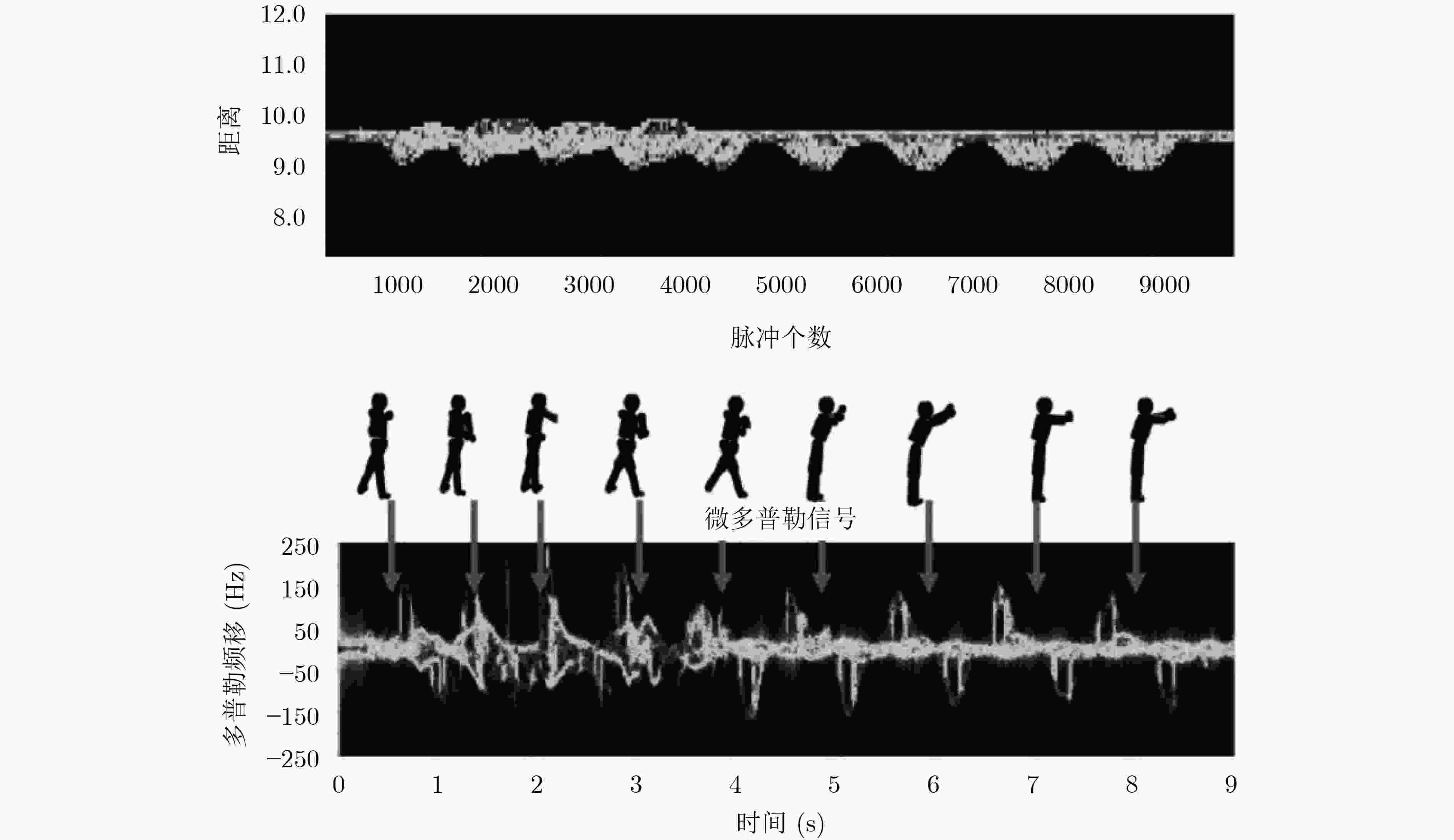
图 14 Chen等人[61]的目标特征参数提取结果示意
图 15 Kim等人[62]的目标探测场景与特征参数提取结果示意
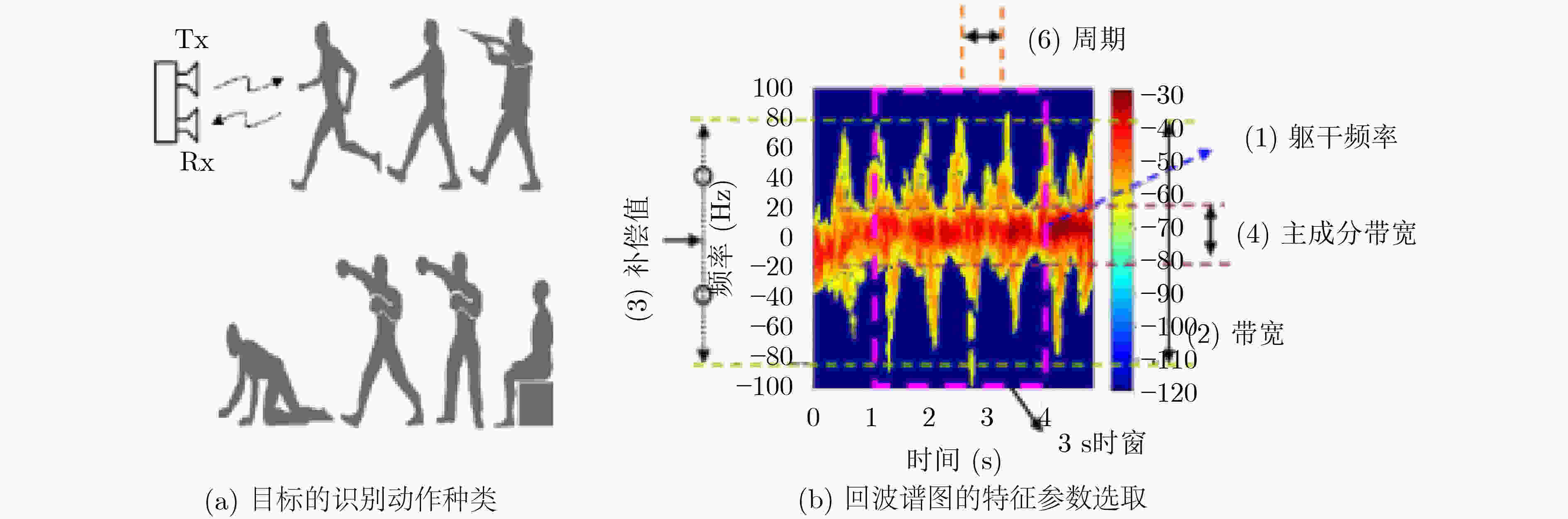
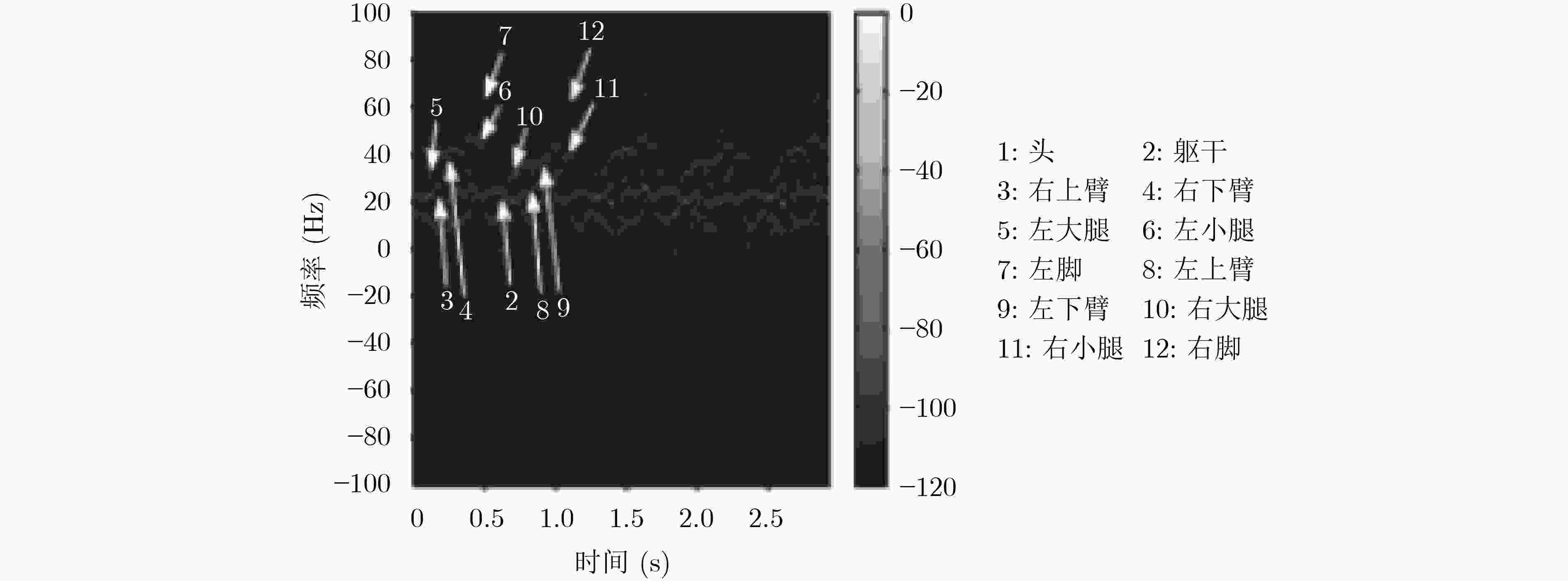
图 16 Zeng等人[63]的目标探测场景与特征参数提取结果示意
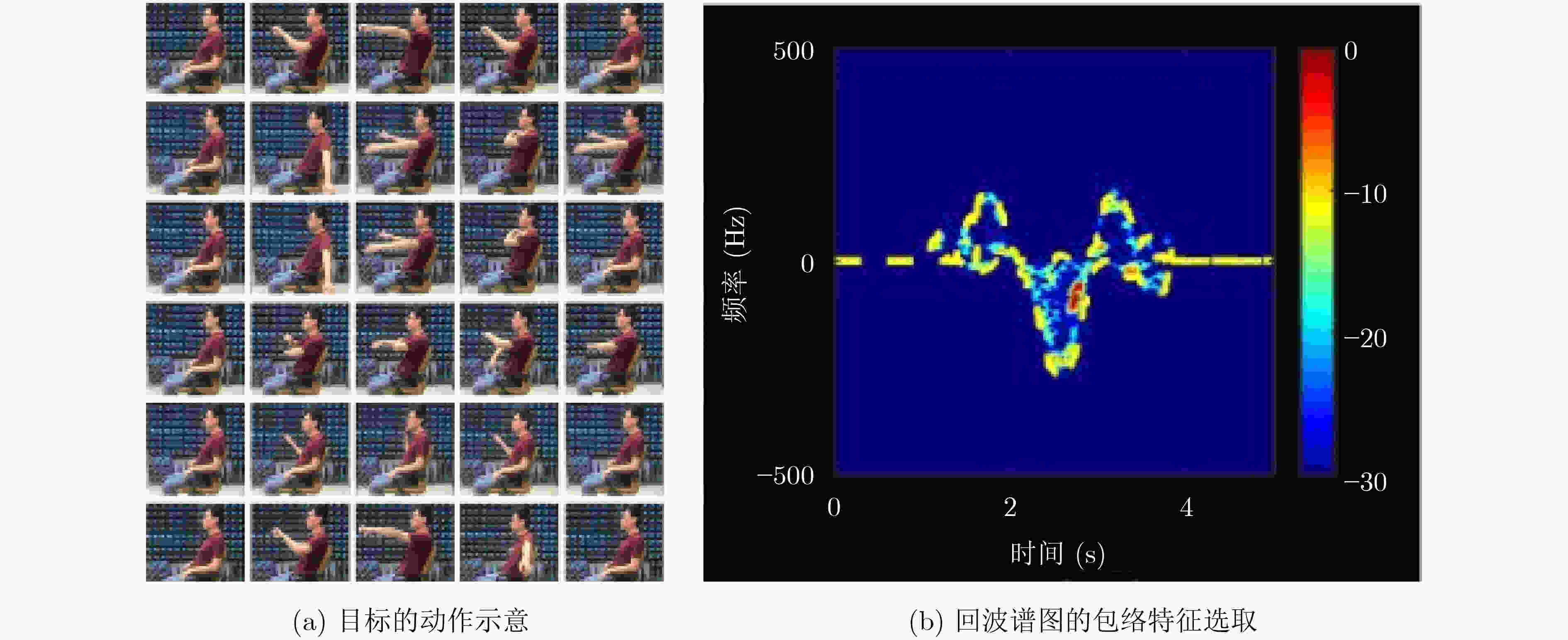
图 17 Du等人[65]的目标特征参数提取结果示意
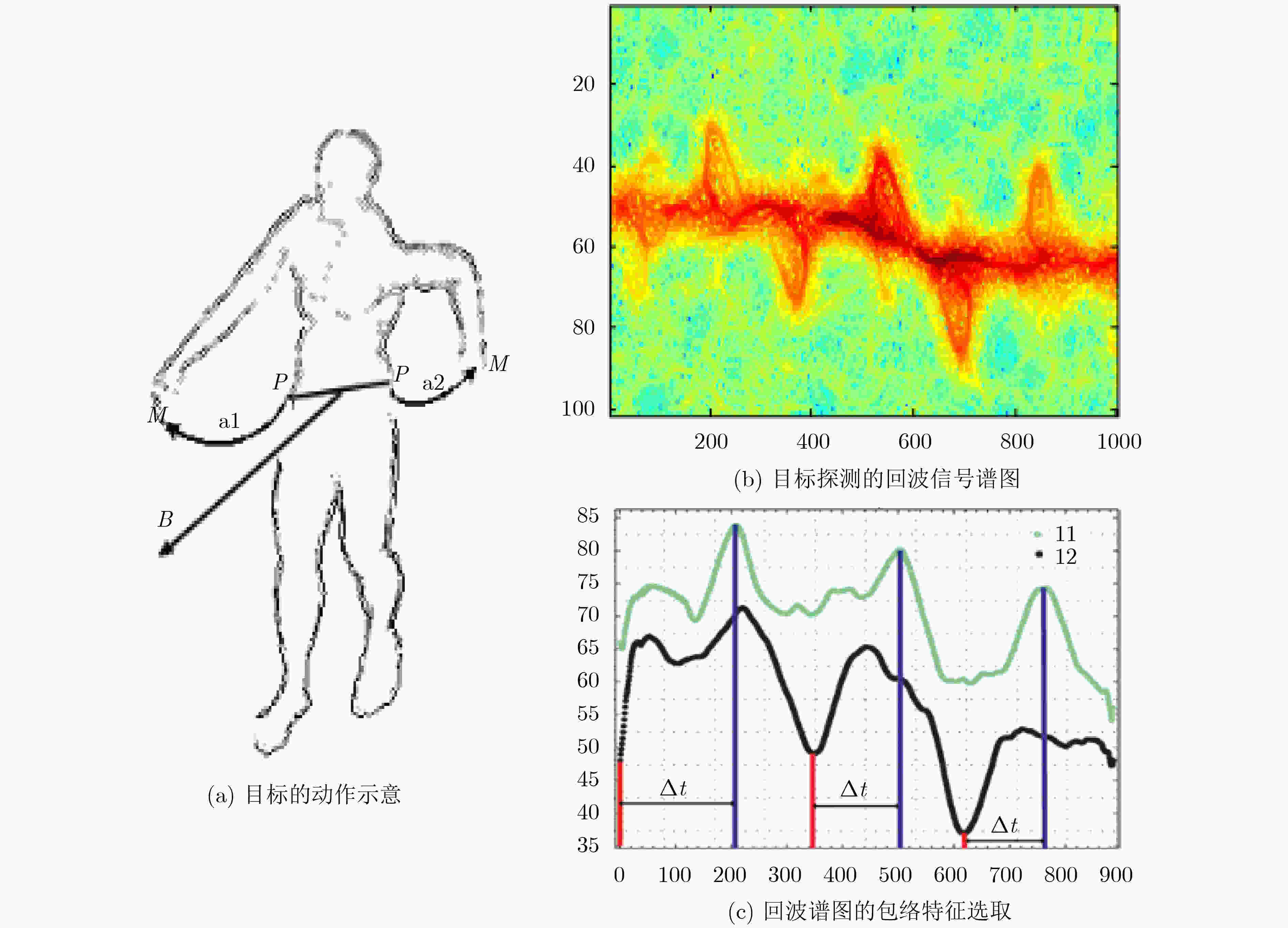
图 18 Orovic等人[68]的目标特征参数提取结果示意
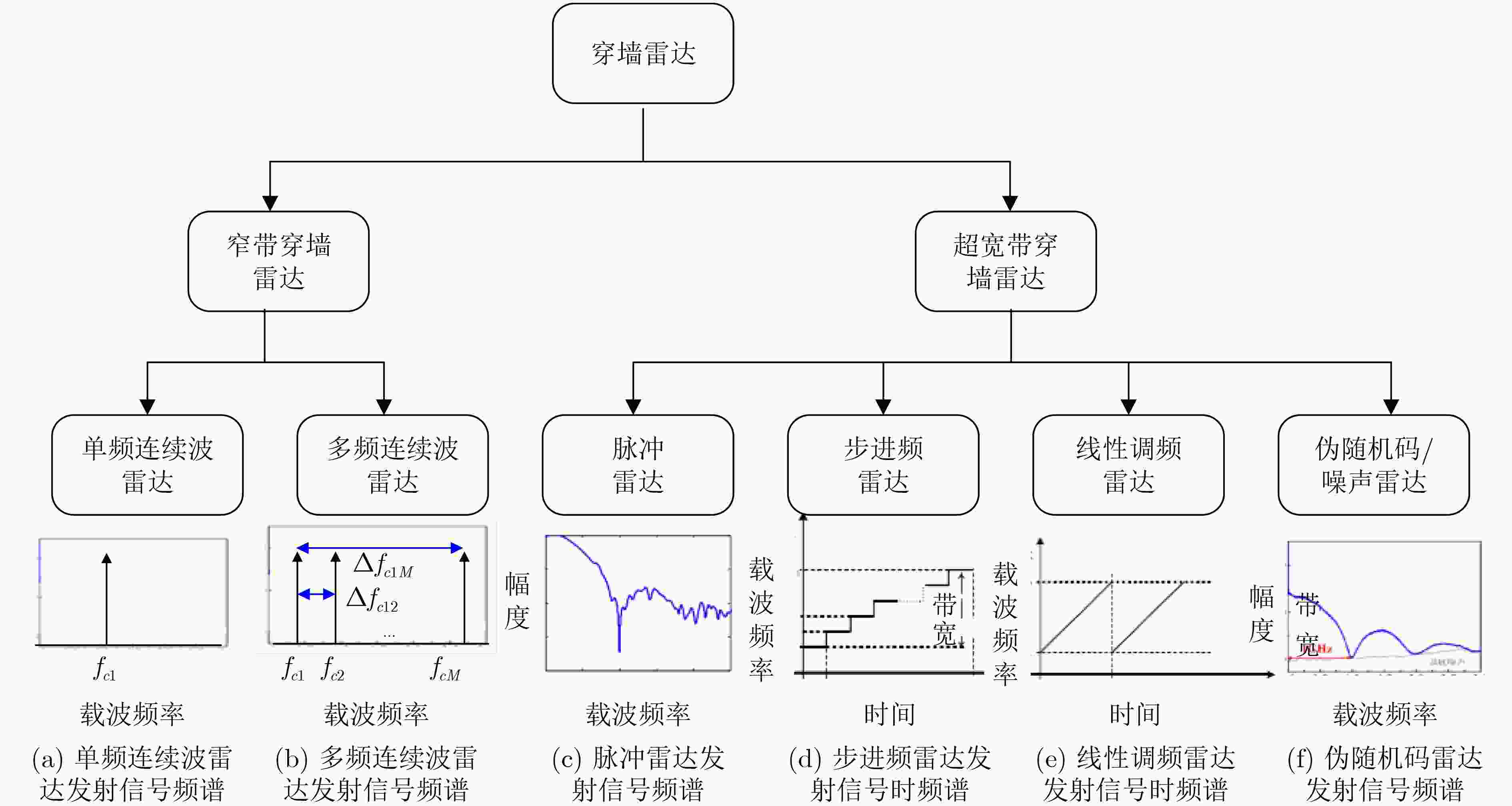
表 1 部分穿墙雷达产品的性能参数
研发机构 产品名称 中心频率(GHz) 带宽(GHz) 最大探测距离(m) 距离分辨率(cm) 主要功能 时域公司(美国) Radar Vision 3.85 3.5 10 5 2维定位 劳伦斯 ⋅利物摩亚实验室(美国) MIR-I 2.5 1 50 15 2维定位 卡梅罗公司(以色列) Xaver 800 4.8 3.4 20 20 2维定位/3维成像 剑桥咨询公司(英国) Prism 200 1.95 0.5 20 30 3维成像 华诺星空(中国) CE200 ? ? 30 30 2维定位 必肯科技(中国) 警视-2 0.50 ? 9 ? 2维定位 凌天世纪(中国) YSR-120 1.2 1.2 12 ? 2维定位 表 2 不同体制穿墙雷达的探测特点比较
雷达体制 发射波形 优点 缺点 窄带
穿墙雷达单频/多频连续波信号 系统简单,抗静态干扰能力强,
信号处理速度快获取的目标信息量少,对目标参数的估计精度低,
识别准确率较差,能耗大超宽带
穿墙雷达窄脉冲信号 穿透能力强,分辨率高 存在探测范围和距离分辨率间的取舍矛盾,
抗干扰能力弱,探测存在盲区步进频/线性调频信号 同时获得优秀的探测范围和距离分辨率 抗干扰能力弱,信号处理实时性差,难以对快速变化的目标信息做出及时反应 伪随机码/噪声信号 穿透能力强,分辨率高,抗干扰能力强,隐蔽性强 发射信号的产生困难,系统成本高,功率受限于特定器件限制。信号的伪随机特性容易导致误差累积效应,
在长时间工作条件下性能不稳定 -
[1] 刘云, 薛盼盼, 李辉, 等. 基于深度学习的关节点行为识别综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1789–1802. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200267LIU Yun, XUE Panpan, LI Hui, et al. A review of action recognition using joints based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1789–1802. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200267 [2] 罗会兰, 童康, 孔繁胜. 基于深度学习的视频中人体动作识别进展综述[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(5): 1162–1173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.05.025LUO Huilan, TONG Kang, and KONG Fansheng. The progress of human action recognition in videos based on deep learning: A review[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(5): 1162–1173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.05.025 [3] 黄华宾. 遮蔽人体目标行为识别方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019.HUANG Huabin. Research on method of hiden human targets behavior recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. [4] CICCHETTI R, PISA S, PIUZZI E, et al. Numerical and experimental comparison among a new hybrid FT-music technique and existing algorithms for through-the-wall radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(7): 3372–3387. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3061500 [5] 金添, 宋勇平. 穿墙雷达人体目标探测技术综述[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Review on human target detection using through-wall radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804 [6] 王宏. 超宽带穿墙雷达成像及多普勒特性研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2010.WANG Hong. Study of UWB through-wall imaging and Doppler characteristic[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010. [7] TAYLOR J D, 胡明春, 王建明, 孙俊, 等译. 超宽带雷达应用与设计[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017: 328–340.TAYLOR J D, HU Mingchun, WANG Jianming, SUN Jun, et al. translation. Ultrawideband Radar: Applications and Design[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry Press, 2017: 328–340. [8] GAUGUE A C and POLITANO J L. Overview of current technologies for through-the-wall surveillance[C]. SPIE 5989, Technologies for Optical Countermeasures II; Femtosecond Phenomena II; and Passive Millimetre-Wave and Terahertz Imaging II, Bruges, Belgium, 2005: 59891H. [9] BOREK S E. An overview of through the wall surveillance for homeland security[C]. 34th Applied Imagery and Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR'05), Washington, USA, 2006: 1–6. [10] 狄培. 便携式穿墙雷达成像技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.DI Pei. Research on portable through-wall radar imaging technology[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019. [11] 北京凌天智能装备集团股份有限公司. YSR-120 手持式穿墙雷达 [EB/OL]. https://www.bjltsj.com/ html/product/1004.html, 2015.BEIJING TOPSKY INTELLIGENT EQUIPMENT GROUP Co.,Ltd. YSR-120 Handheld, Through Wall Radar [EB/OL]. https://www.bjltsj.com/ html/product/1004.html, 2015. [12] 华诺星空股份有限公司. 军事反恐救援利器: 二维定位—CE系列穿墙雷达[EB/OL]. http://www.insight-safety.com/productinfo/243693.html, 2009. [13] 郭山红, 孙锦涛, 谢仁宏, 等. 电磁波穿透墙体的衰减特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2009, 21(1): 113–117.GUO Shanhong, SUN Jintao, XIE Renhong, et al. Attenuation characteristics of electromagnetic wave penetrating walls[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 21(1): 113–117. [14] DING Yipeng, YU Xiali, ZHANG Juan, et al. Application of linear predictive coding and data fusion process for target tracking by Doppler through-wall radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave theory and Techniques, 2019, 67(3): 1244–1254. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2018.2885973 [15] QI Fugui, LI Zhao, MA Yangyang, et al. Generalization of channel micro-Doppler capacity evaluation for improved finer-grained human activity classification using MIMO UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4748–4761. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3076055 [16] TROMMEL R P, HARMANNY R I A, CIFOLA L, et al. Multi-target human gait classification using deep convolutional neural networks on micro-Doppler spectrograms[C]. 2016 European Radar Conference (EuRAD), London, UK, 2016: 81–84. [17] CHUMA E L and IANO Y. A movement detection system using continuous-wave Doppler radar sensor and convolutional neural network to detect cough and other gestures[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(3): 2921–2928. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3028494 [18] ZHENG Chen, XI Xiaoli, SONG Zhongguo, et al. Multilevel delay lock loop approach for wall clutter mitigation in through-the-wall radar imaging[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2018, 12(12): 1986–1992. doi: 10.1049/iet-map.2018.5234 [19] SOLIMENE R and CUCCARO A. Front wall clutter rejection methods in TWI[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(6): 1158–1162. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2288491 [20] YOON Y S and AMIN M G. Spatial filtering for wall-clutter mitigation in through-the-wall radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(9): 3192–3208. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2019728 [21] DING Yipeng, TANG Jingtian, XU Xuemei, et al. Echo interference suppression approach for Doppler through-wall radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(6): 3395–3402. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2374419 [22] 郑晨, 席晓莉, 宋忠国, 等. 基于子空间技术中奇异向量分析的穿墙雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(4): 848–854. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.04.012ZHENG Chen, XI Xiaoli, SONG Zhongguo, et al. A singular vector stationarity method for clutter mitigation in through-the-wall radar based on subspace method[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(4): 848–854. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.04.012 [23] 李家强, 徐小敏, 卢宝宝, 等. 倾斜阵列下奇异值分解穿墙雷达杂波抑制[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2019, 17(5): 531–537. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2019.05.010LI Jiaqiang, XU Xiaomin, LU Baobao, et al. Clutter reduction of through-the-wall radar based on singular value decomposition under tilted array[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2019, 17(5): 531–537. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2019.05.010 [24] 赵中兴, 孔令讲, 贾勇, 等. 一种有效的穿墙雷达成像杂波抑制算法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2014, 12(1): 51–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2014.01.009ZHAO Zhongxing, KONG Lingjiang, JIA Yong, et al. An Efficient clutter reduction method in through-wall-radar imaging[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2014, 12(1): 51–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2014.01.009 [25] 韩银萍, 刘丽, 王冰洁, 等. 基于鲁棒主成分分析的混沌穿墙成像雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 电子器件, 2020, 43(1): 142–146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2020.01.029HAN Yinping, LIU Li, WANG Bingjie, et al. Clutter removal using robust principal component analysis for chaos through-wall imaging radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Electron Devices, 2020, 43(1): 142–146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2020.01.029 [26] 黄臣, 刘宏清, 罗臻, 等. 一种低秩联合稀疏模型下的杂波抑制方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(6): 60–66. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2019.06.009HUANG Chen, LIU Hongqing, LUO Zhen, et al. Method for suppressing clutters with the joint low rank and sparse model[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(6): 60–66. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2019.06.009 [27] WATERS A E, SANKARANARAYANAN A C, and BARANIUK R G. SpaRCS: Recovering low-rank and sparse matrices from compressive measurements[C]. The 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Granada, Spain, 2011: 1089–1097. [28] 宋勇平, 金添, 陆必应, 等. 一种新的MIMO线阵穿墙成像模型及其环境参数估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(12): 2980–2985. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2014.00018SONG Yongping, JIN Tian, LU Biying, et al. A novel linear MIMO array through-the-wall imaging model and its associated environmental parameters estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(12): 2980–2985. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2014.00018 [29] LEE D, FONG B, MORITA P, et al. Imaging of walking human behind the wall using impulse radar[C]. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting, Montreal, Canada, 2020: 1263–1264. [30] RENEAU J and ADHAMI R R. Phase-coded LFMCW waveform analysis for short range measurement applications[C]. 2014 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2014: 1–6. [31] SHRAVANKUMAR S M, LENKA M K, and BANERJEE G. Integrated wideband frequency-hopping radar system for see-through-wall sensor application[C]. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and RF Conference (IMARC), Mumbai, India, 2019: 1–7. [32] 夏正欢, 张群英, 叶盛波, 等. 一种便携式伪随机编码超宽带人体感知雷达设计[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027XIA Zhenghuan, ZHANG Qunying, YE Shengbo, et al. Design of a handheld pseudo random coded UWB radar for human sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027 [33] 王明阳. 穿墙雷达人体行为识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019.WANG Mingyang. Research on human action recognition exploiting through-wall radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. [34] 胡志鹏. 超宽带MIMO雷达系统设计与穿墙成像方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 吉林大学, 2020.HU Zhipeng. Design of UWB MIMO radar system and research on the method of through-wall imaging[D]. [Master dissertation], Jilin University, 2020. [35] ANDRE D, WATSON F, and FINNIS M. Multistatic dual-polarimetric through-wall 3D-SAR[C]. 13th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR 2021), 2021: 1–4. [36] GENNARELLI G and SOLDOVIERI F. A linear inverse scattering algorithm for radar imaging in multipath environments[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(5): 1085–1089. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2230314 [37] FEDELI A, PASTORINO M, PONTI C, et al. Forward and inverse scattering models applied to through-wall imaging[C]. 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020: 1–4. [38] SOLDOVIERI F, AHMAD F, and SOLIMENE R. Validation of microwave tomographic inverse scattering approach via through-the-wall experiments in semicontrolled conditions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(1): 123–127. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2051014 [39] ZHANG Wenji and HOORFAR A. Two-dimensional through-the-wall radar imaging with diffraction tomographic algorithm[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Microwave Technology & Computational Electromagnetics, Beijing, China, 2011: 96–99. [40] ZHANG Wenji and HOORFAR A. Three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging through multilayered walls[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(1): 459–462. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2287274 [41] 孟庆阳. 微波逆散射成像中的若干问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 浙江大学, 2017.MENG Qingyang. Several researches on microwave inverse scattering imaging[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2017. [42] 蔡继亮, 童创明, 姬伟杰. 超宽带穿墙雷达成像技术研究现状[J]. 电讯技术, 2012, 52(9): 1541–1546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2012.09.025CAI Jiliang, TONG Chuangming, and JI Weijie. Recent progress of ultra-wideband through-the-wall radar imaging[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2012, 52(9): 1541–1546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2012.09.025 [43] SU Yurou and LU Guizhen. An improved inversion model for two-dimensional microwave imaging[C]. 2019 Cross Strait Quad-Regional Radio Science and Wireless Technology Conference (CSQRWC), Taiyuan, China, 2019: 1–3. [44] BOGERT B. Demonstration of delay distortion correction by time-reversal techniques[J]. IRE Transactions on Communications Systems, 1957, 5(3): 2–7. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1957.1097511 [45] FINK M. Time reversal of ultrasonic fields. I. Basic principles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 1992, 39(5): 555–566. doi: 10.1109/58.156174 [46] 王凌, 郑文军. 时间反转技术在超宽带穿墙雷达中的应用[J]. 无线电工程, 2012, 42(5): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2012.05.014WANG Ling and ZHENG Wenjun. Application of time reversal technique in ultra-wideband through-the-wall radar[J]. Radio Engineering, 2012, 42(5): 42–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2012.05.014 [47] ODEDO V C, YAVUZ M E, COSTEN F, et al. Time reversal technique based on spatiotemporal windows for through the wall imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(6): 3065–3072. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2696421 [48] DUBROCA R, FORTINO N, DAUVIGNAC J Y, et al. Time reversal-based processing for human targets detection in realistic through-the-wall scenarios[C]. 2011 8th European Radar Conference, Manchester, UK, 2011: 1–4. [49] GOLLUB J N, YURDUSEVEN O, TROFATTER K P, et al. Large metasurface aperture for millimeter wave computational imaging at the human-scale[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42650. doi: 10.1038/srep42650 [50] KHORASHADI-ZADEH V and DEHMOLLAIAN M. Through a cinder block wall refocusing using SAR back projection method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(2): 1212–1222. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2882599 [51] 杨泽民, 孙光才, 吴玉峰, 等. 一种新的基于极坐标格式的快速后向投影算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(3): 537–544. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00613YANG Zemin, SUN Guangcai, WU Yufeng, et al. A new fast back projection algorithm based on polar format algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(3): 537–544. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00613 [52] WANG Hong, NARAYANAN R M, and ZHOU Zheng’ou. Through-wall imaging of moving targets using UWB random noise radar[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2009, 8: 802–805. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2009.2021586 [53] AHMAD F, ZHANG Yimin, and AMIN M G. Three-dimensional wideband beamforming for imaging through a single wall[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(2): 176–179. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.915742 [54] SONG Yongping, HU Jun, CHU Ning, et al. Building layout reconstruction in concealed human target sensing via UWB MIMO through-wall imaging radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(8): 1199–1203. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2834501 [55] KONG Lingjiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Xiaobo, et al. Three-dimensional human imaging for through-the-wall radar[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–4. [56] ZHAO Dizhi, DAI Yongpeng, SONG Yongping, et al. A three-dimensional enhanced imaging method based on deconvolution[C]. 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2017: 2076–2079. [57] ADIB F, HSU C Y, MAO Hongzhi, et al. Capturing the human figure through a wall[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(6): 219. doi: 10.1145/2816795.2818072 [58] WANG Mingyang, CUI Guolong, HUANG Huabin, et al. Through-wall human motion representation via autoencoder-self organized mapping network[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. [59] AN Qiang, WANG Shuoguang, YAO Lei, et al. RPCA-based high resolution through-the-wall human motion feature extraction and classification[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(17): 19058–19068. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3088122 [60] LAI C P and NARAYANAN R M. Through-wall imaging and characterization of human activity using ultrawideband (UWB) random noise radar[C]. SPIE 5778, Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C3I) Technologies for Homeland Security and Homeland Defense IV, Orlando, USA, 2005: 186–195. [61] CHEN V C. Doppler signatures of radar backscattering from objects with micro-motions[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 291–300. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070137 [62] KIM Y and LING Hao. Human. Human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using a support vector machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1328–1337. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2012849 [63] ZENG Zhengxin, AMIN M G, and SHAN Tao. Automatic arm motion recognition based on radar micro-Doppler signature envelopes[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13523–13532. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3004581 [64] RAM S S and LING Hao. Analysis of microDopplers from Human gait using reassigned joint time-frequency transform[J]. Electronic Letters, 2007, 43(23): 1309–1311. doi: 10.1049/el:20071515 [65] DU L, LI J, STOICA P P, et al. Doppler spectrogram analysis of human gait via iterative adaptive approach[J]. Electronics Letters, 2009, 45(3): 186–188. doi: 10.1049/el:20092769 [66] DING Yipeng, LIU Runjin, LI Zhengmin, et al. Human micro-Doppler frequency estimation using CESP-based Viterbi algorithm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 3506105. [67] AMIN M G, AHMAD F, ZHANG Y D, et al. Human gait recognition with cane assistive device using quadratic time–frequency distributions[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1224–1230. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0119 [68] OROVIĆ I, STANKOVIĆ S, and AMIN M. A new approach for classification of human gait based on time-frequency feature representations[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 91(6): 1448–1456. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.08.013 [69] LI Po, WANG Dechun, and WANG Lu. Separation of micro-Doppler signals based on time frequency filter and Viterbi algorithm[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2013, 7(3): 593–605. doi: 10.1007/s11760-011-0263-3 [70] JOKANOVIĆ B and AMIN M G. Suitability of data representation domains in expressing human motion radar signals[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2370–2374. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2765341 [71] GROOT S R, YAROVOY A G, HARMANNY R I A, et al. Model-based classification of human motion: Particle filtering applied to the micro-Doppler spectrum[C]. 2012 9th European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012: 198–201. [72] LE H T, PHUNG S L, and BOUZERDOUM A. Human gait recognition with micro-Doppler radar and deep autoencoder[C]. 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 2018: 3347–3352. [73] LIU Liang, POPESCU M, SKUBIC M, et al. Automatic fall detection based on Doppler radar motion signature[C]. The 5th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (PervasiveHealth) and Workshops, Dublin, Ireland, 2011: 222–225. [74] FAIRCHILD D P and NARAYANAN R M. Classification of human motions using empirical mode decomposition of human micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(5): 425–434. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0165 [75] 蒋留兵, 李骢, 车俐. 利用二维小波包分解实现超宽带雷达人体动作识别[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2018, 32(8): 69–75. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.2018.08.010JIANG Liubing, LI Cong, and CHE Li. Human motion recognition using ultra-wide band radar based on two-dimensional wavelet packet decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2018, 32(8): 69–75. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.2018.08.010 [76] DING Yipeng, LEI Chengxi, XU Xuemei, et al. Human micro-Doppler frequency estimation approach for Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 6149–6159. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2793277 [77] EROL B, AMIN M G, and BOASHASH B. Range-Doppler radar sensor fusion for fall detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 819–824. [78] KILIÇ A, BABAOĞLU I, BABALIK A, et al. Through-wall radar classification of human posture using convolutional neural networks[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 2019: 7541814. doi: 10.1155/2019/7541814 [79] ZHANG Yang, QI Fugui, LV Hao, et al. Bioradar technology: Recent research and advancements[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2019, 20(8): 58–73. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2019.2915491 [80] CORTES C and VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273–297. doi: 10.1023/A:1022627411411 [81] YANG Yinan, ZHANG Wenxue, and LU Chao. Classify human motions using micro-Doppler radar[C]. SPIE 6944, Biometric Technology for Human Identification V, Orlando, USA, 2008: 69440V. [82] LI Jingli, PHUNG S L, TIVIVE F H C, et al. Automatic classification of human motions using Doppler radar[C]. The 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Brisbane, Australia, 2012: 1–6. [83] LI Fangmin, YANG Chao, XIA Yuqing, et al. An Adaptive S-method to analyze micro-Doppler signals for human activity classification[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(12): 2769. doi: 10.3390/s17122769 [84] ALVEE B I, TISHA S N, and CHAKRABARTY A. Application of machine learning classifiers for predicting human activity[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence, and Communications Technology (IAICT), Bandung, Indonesia, 2021: 39–44. [85] SMITH G E, WOODBRIDGE K, and BAKER C J. Naive Bayesian radar micro-Doppler recognition[C]. 2008 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2008: 111–116. [86] RICCI R and BALLERI A. Recognition of humans based on radar micro-Doppler shape spectrum features[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1216–1223. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0551 [87] PADAR M O, ERTAN A E, and CANDAN Ç Ĝ. Classification of human motion using radar micro-Doppler signatures with hidden Markov models[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6. [88] LEI Peng, WANG Jun, GUO Peng, et al. Automatic classification of radar targets with micro-motions using entropy segmentation and time-frequency features[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2011, 65(10): 806–813. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2011.01.013 [89] 谢非, 徐贵力, 吕东岳, 等. 一种基于决策树的多种人体姿态识别方法[P]. 中国专利, 101533467B, 2013.XIE Fei, XU Guili, LV Dongyue, et al. Method for identifying a plurality of human postures based on decision tree[P]. China Patent, 101533467B, 2013. [90] KIM Y and MOON T. Human detection and activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 8–12. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2491329 [91] KIM Y and TOOMAJIAN B. Hand gesture recognition using micro-Doppler signatures with convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 7125–7130. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2617282 [92] PAPANASTASIOU V S, TROMMEL R P, HARMANNY R I A, et al. Deep Learning-based identification of human gait by radar micro-Doppler measurements[C]. 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 49–52. [93] ZHU Jianping, CHEN Haiquan, and YE Wenbin. A hybrid CNN–LSTM network for the classification of human activities based on micro-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24713–24720. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971064 [94] ZHANG Zhenyuan, TIAN Zengshan, and ZHOU Mu. Latern: Dynamic continuous hand gesture recognition using FMCW radar sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(8): 3278–3289. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2808688 [95] WANG Saiwen, SONG Jie, LIEN J, et al. Interacting with soli: Exploring fine-grained dynamic gesture recognition in the radio-frequency spectrum[C]. The 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 2016: 851–860. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
