Advances in Human Activity Sensing Using Ultra-Wide Band Radar
-
摘要: 超宽带 (UWB) 雷达人体行为感知主要研究如何利用人体目标电磁散射回波对位置、行为、意图等进行判别,是光学感知手段的有益补充,应对无光照、地物遮挡、非视距等情况下的应用场合。该文将超宽带雷达人体行为感知研究方法分成基于空间位置和基于微动特征两类技术。在介绍这类技术基本原理的基础上,对比分析了国内外代表性工作的能力现状。最后对超宽带雷达人体行为感知领域的后续重点研究方向进行了展望。Abstract: Human target sensing technology with Ultra-WideBand (UWB) radar studies mainly how to recognize the position, behavior and intention of the human target according to the electromagnetic scattering echoes. It is an efficient complement to the optical-based target sensing, and can be applied to many scenarios such as the scenarios without light, the scenarios with occlusion, and the non-line-of-sight scenarios. Two key human sensing technologies are presented in this paper, i.e., the spatial location-based method and the micro-Doppler-based method, and the relevant literatures about the two technologies are summarized. Finally, The future research directions of the UWB radar-based human target sensing filed are discussed in the conclusion.
-
Key words:
- Ultra-WideBand (UWB) radar /
- Human target sensing /
- Micro-Doppler /
- Deep learning
-
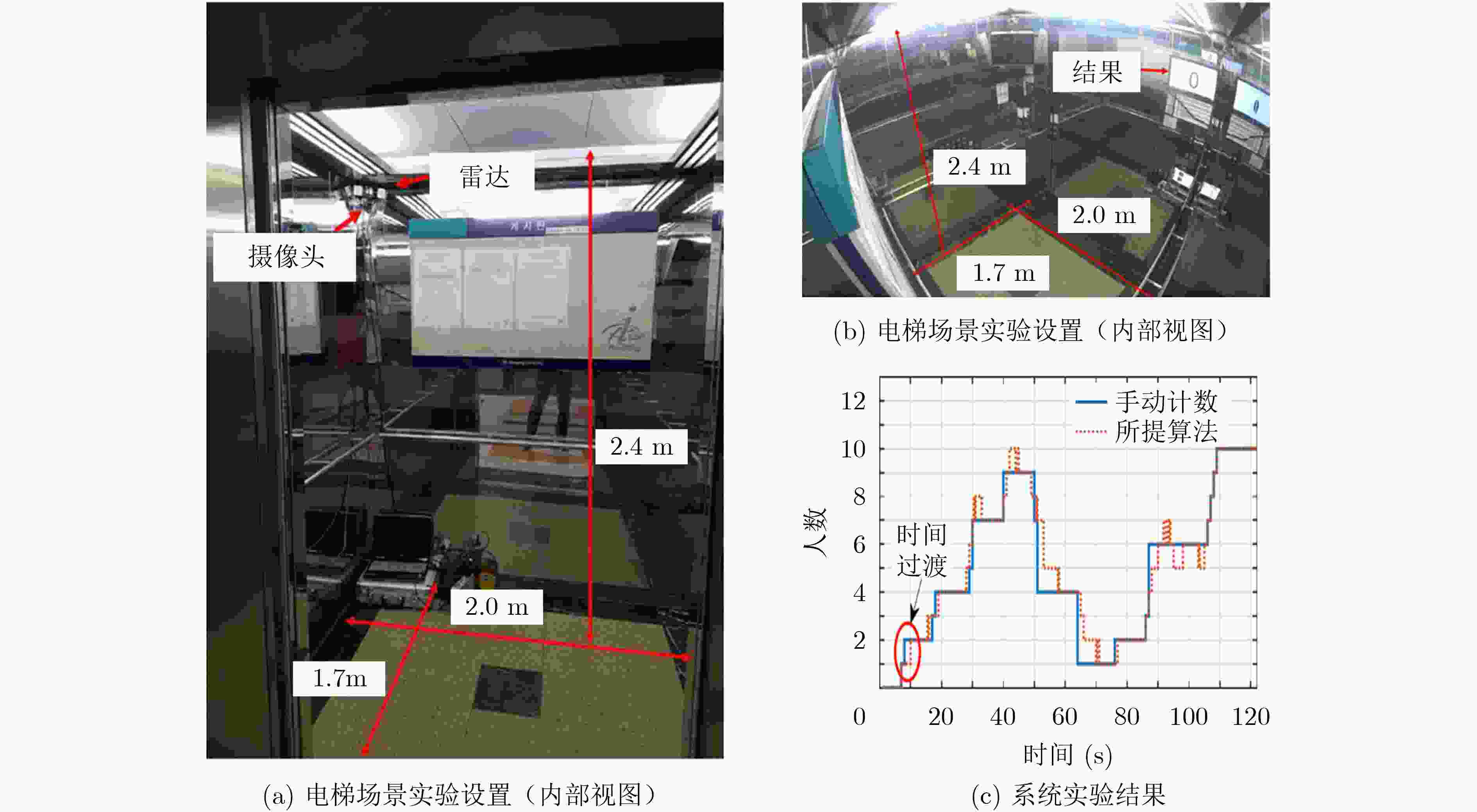
图 1 单通道雷达人群数量检测系统[2]
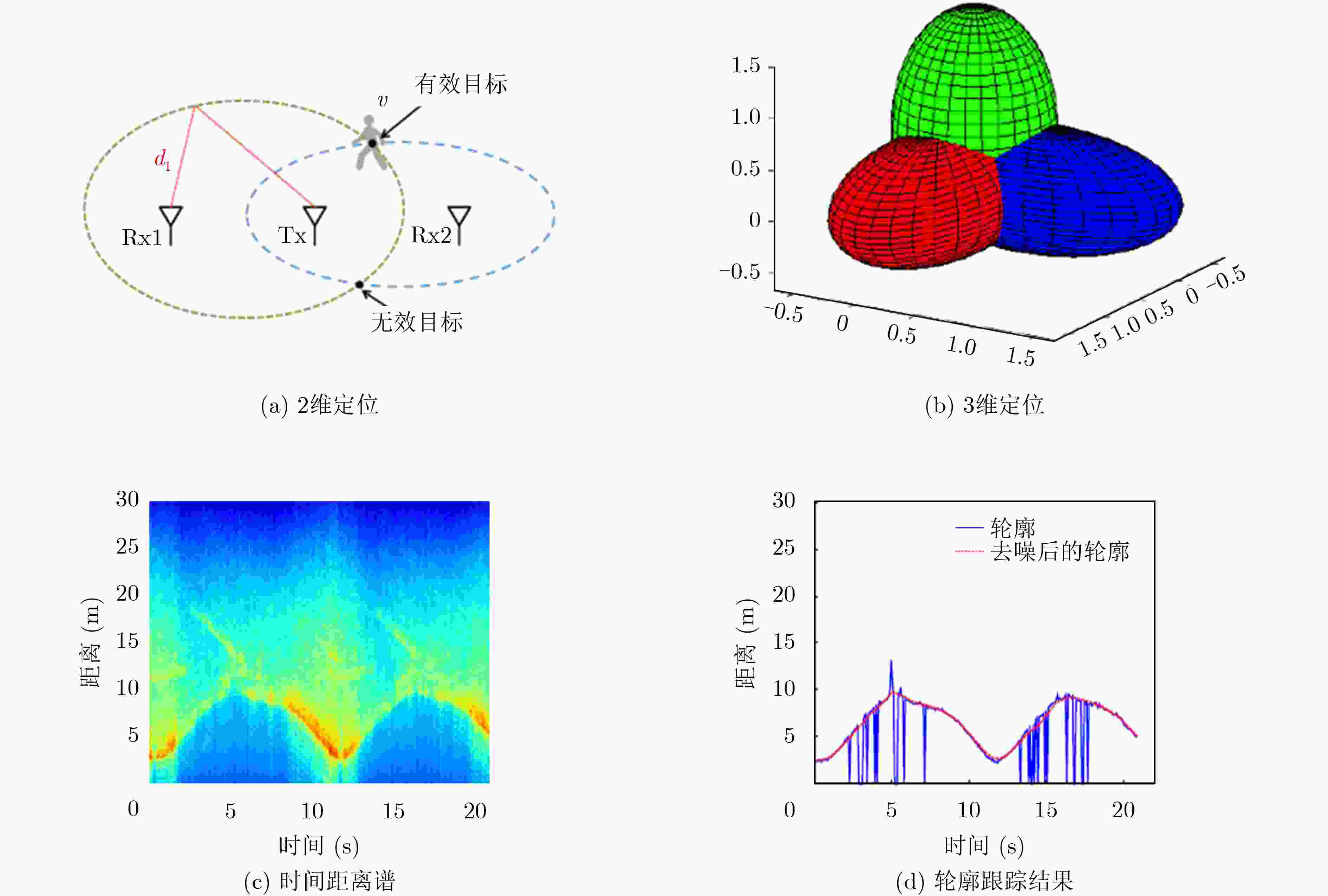
图 2 基于1发双收系统的人体目标探测[5]
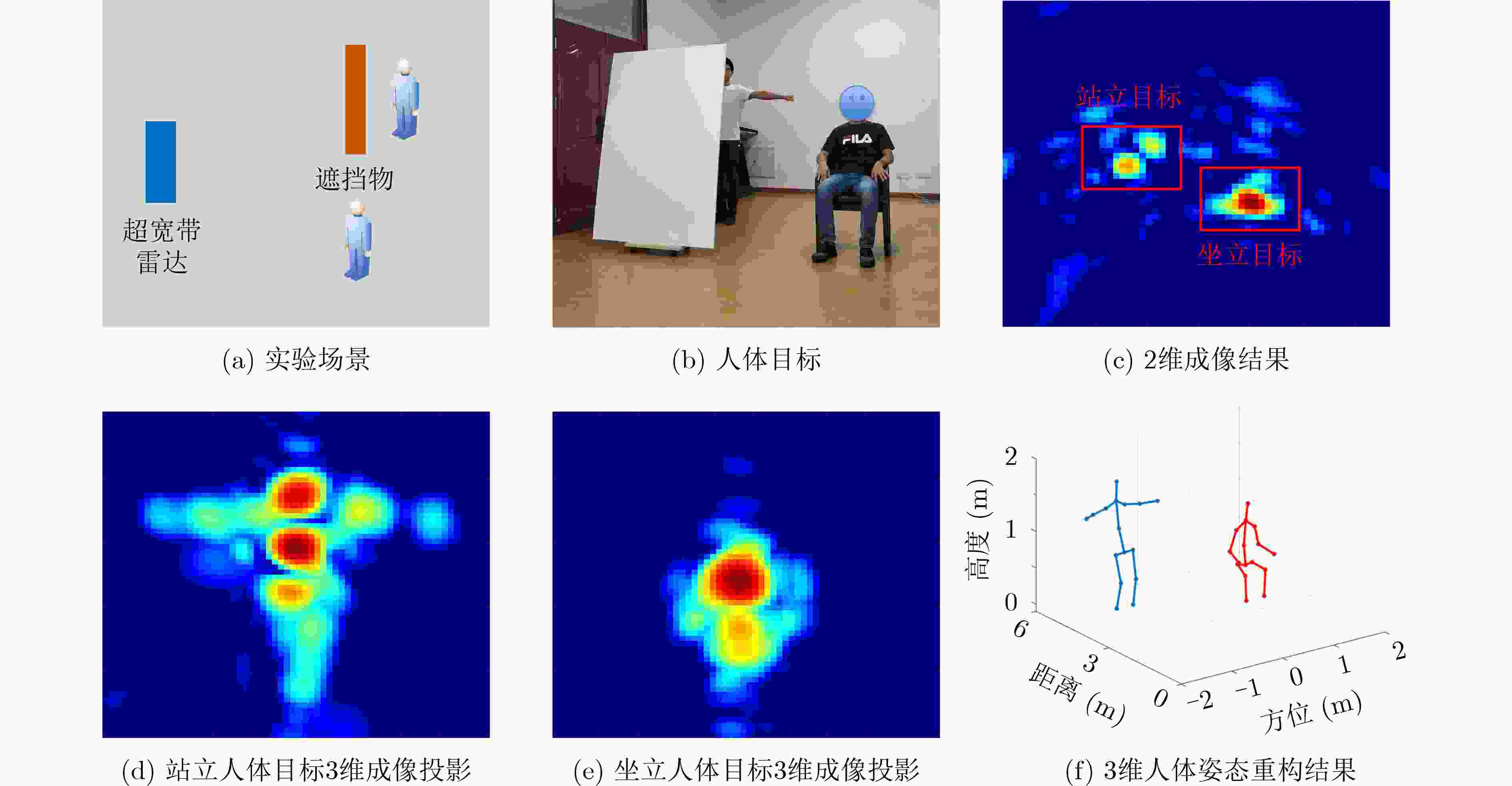
图 3 基于3维雷达图像的人体姿态重构[16]
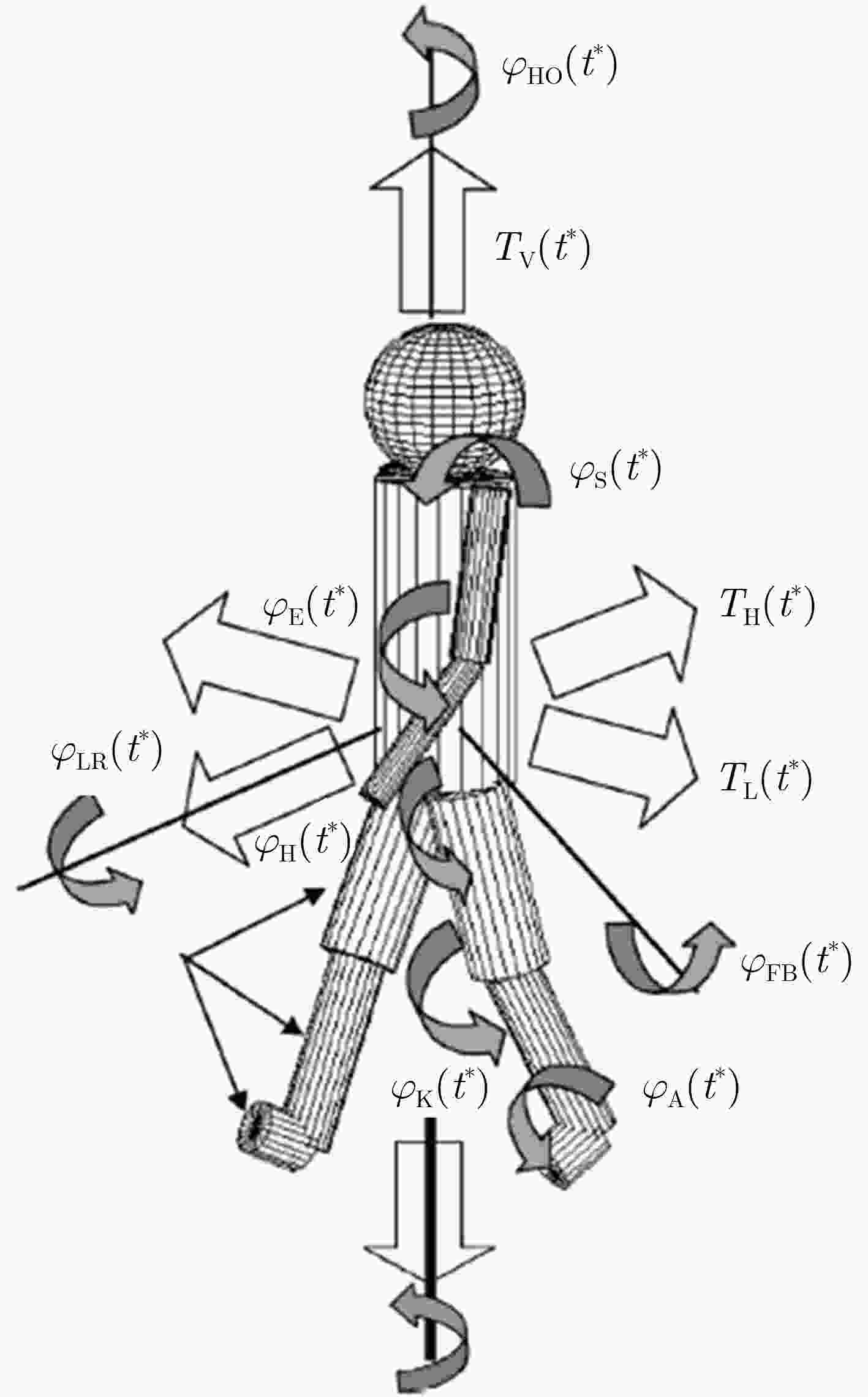
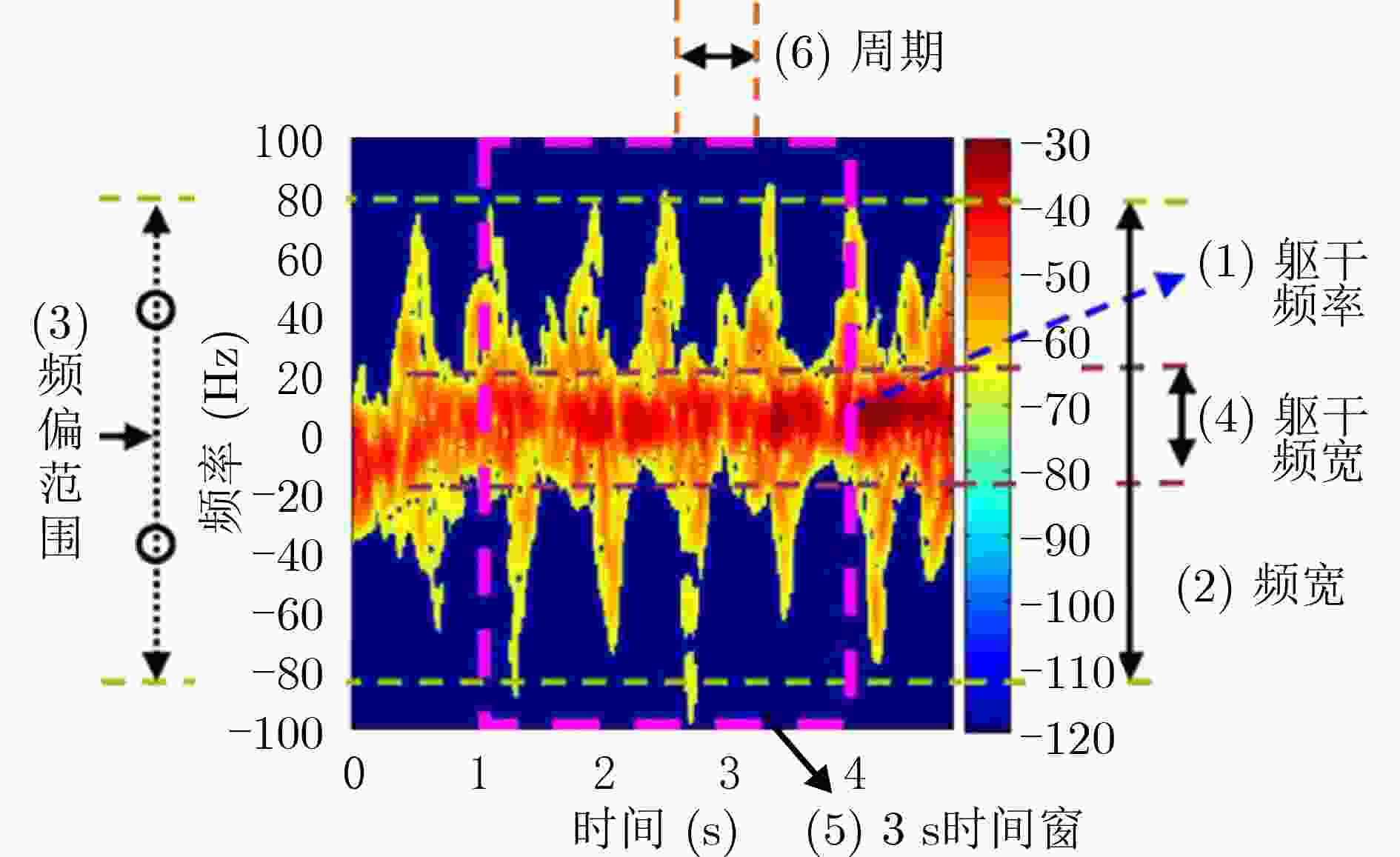
图 5 基于人体运动特性设计的6种微多普勒谱特征[23]
-
[1] LI Xinyu, HE Yuan, and JING Xiaojun. A survey of deep learning-based human activity recognition in radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1068. doi: 10.3390/rs11091068 [2] CHOI J W, YIM D H, and CHO S H. People counting based on an IR-UWB radar sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(17): 5717–5727. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2723766 [3] SETLUR P, SMITH G E, AHMAD F, et al. Target localization with a single sensor via multipath exploitation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(3): 1996–2014. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237575 [4] ADIB F and KATABI D. See through walls with WiFi![C]. The ACM SIGCOMM Conference on SIGCOMM, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 75–86. [5] ADIB F, KABELAC Z, KATABI D, et al. 3D tracking via body radio reflections[C]. The 11th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI’14), Seattle, USA, 2014: 317–329. [6] LIU Haiping, YANG Ruixia, YANG Yang, et al. Human–human interaction recognition based on ultra-wideband radar[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2020, 14(6): 1181–1188. doi: 10.1007/s11760-020-01658-8 [7] SAKAMOTO T, MATSUKI Y, and SATO T. A novel UWB radar 2-D imaging method with a small number of antennas for simple-shaped targets with arbitrary motion[C]. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Vancouver, Canada, 2009: 449–453. [8] QIAN Jiang, AHMAD F, and AMIN M G. Joint localization of stationary and moving targets behind walls using sparse scene recovery[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2013, 22(2): 021002. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.22.2.021002 [9] ZHUGE X, SAVELYEV T G, YAROVOY A G, et al. Human body imaging by microwave UWB radar[C]. 2008 European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, Holland, 2008: 148–151. [10] RAM S S and MAJUMDAR A. High-resolution radar imaging of moving humans using Doppler processing and compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1279–1287. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140481 [11] 李廉林, 周小阳, 崔铁军. 结构化信号处理理论和方法的研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 491–502.LI Lianlin, ZHOU Xiaoyang, and CUI Tiejun. Perspectives on theories and methods of structural signal processing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 491–502. [12] 崔国龙, 孔令讲, 杨建宇, 等. 穿墙雷达三维合成孔径成像算法研究[C]. 第十届全国雷达学术年会论文集, 北京, 2008: 535–538. [13] ZHAO Mingmin, LI Tianhong, ALSHEIKH M A, et al. Through-wall human pose estimation using radio signals[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7356–7365. [14] LI Tianhong, FAN Lijie, ZHAO Mingmin, et al. Making the invisible visible: Action recognition through walls and occlusions[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 872–881. [15] 赵帝植. 超宽带MIMO雷达三维增强成像技术[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科技大学, 2018.ZHAO Dizhi. Ultra-wideband MIMO radar three-dimensional enhanced imaging method[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2018. [16] SONG Yongkun, JIN Tian, DAI Yongpeng, et al. Through-wall human pose reconstruction via UWB MIMO radar and 3D CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(2): 241. doi: 10.3390/rs13020241 [17] BOULIC R, THALMANN N M, and THALMANN D. A global human walking model with real-time kinematic personification[J]. The Visual Computer, 1990, 6(6): 344–358. doi: 10.1007/BF01901021 [18] VAN DORP P and GROEN F C A. Human walking estimation with radar[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(5): 356–365. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030568 [19] RAM S S, CHRISTIANSON C, KIM Y, et al. Simulation and analysis of human micro-Dopplers in through-wall environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2015–2023. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037219 [20] Carnegie Mellon university motion capture database[EB/OL]. http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu/, 2020. [21] EROL B and GURBUZ S Z. A kinect-based human micro-Doppler simulator[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2015, 30(5): 6–17. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2015.7119820 [22] SHI Xiaoran, YAO Xin, BAI Xueru, et al. Radar echoes simulation of human movements based on MOCAP data and EM calculation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 859–863. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2887310 [23] KIM Y and LING Hao. Human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using a support vector machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1328–1337. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2012849 [24] SUN Zhongsheng, WANG Jun, SUN Jinping, et al. Parameter estimation method of walking human based on radar micro-Doppler[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 567–570. [25] 崔文. 多站低频雷达运动人体微多普勒特征提取与跟踪技术[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2017.CUI Wen. Technique of human micro-Doppler feature extraction and tracking with multi -station low frequency radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2017. [26] LEI Jiajin and LU Chao. Target classification based on micro-Doppler signatures[C]. The IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2005: 179–183. [27] FIORANELLI F, RITCHIE M, GÜRBÜZ S Z, et al. Feature diversity for optimized human micro-Doppler classification using multistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(2): 640–654. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2651678 [28] PADAR M O, ERTAN A E, and CANDAN Ç Ĝ. Classification of human motion using radar micro-Doppler signatures with hidden markov models[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6. [29] LANG Yue, WANG Qing, YANG Yang, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for micro-Doppler human motion classification via feature fusion[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(3): 392–396. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2873776 [30] KIM Y and MOON T. Human detection and activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 8–12. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2491329 [31] JOKANOVIĆ B and AMIN M. Fall detection using deep learning in range-Doppler radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 180–189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2740098 [32] SEYFIOĞLU M S and GÜRBÜZ S Z. Deep neural network initialization methods for micro-Doppler classification with low training sample support[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2462–2466. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2771405 [33] CRALEY J, MURRAY T S, MENDAT D R, et al. Action recognition using micro-Doppler signatures and a recurrent neural network[C]. The 51st Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–5. [34] MURRAY T S, MENDAT D R, SANNI K A, et al. Bio-inspired human action recognition with a micro-Doppler sonar system[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 6: 28388–28403. [35] WANG Mingyang, ZHANG Y D, and CUI Guolong. Human motion recognition exploiting radar with stacked recurrent neural network[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2019, 87: 125–131. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2019.01.013 [36] WANG Saiwen, SONG Jie, LIEN J, et al. Interacting with soli: Exploring fine-grained dynamic gesture recognition in the radio-frequency spectrum[C]. The 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 2016: 851–860. [37] DU Hao, JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, et al. A three-dimensional deep learning framework for human behavior analysis using range-Doppler time points[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(4): 611–615. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2930636 [38] SEYFIOGLU M S, EROL B, GURBUZ S Z, et al. DNN transfer learning from diversified micro-Doppler for motion classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(5): 2164–2180. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2883847 [39] LI Xinyu, HE Yuan, FIORANELLI F, et al. Human motion recognition with limited radar micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6586–6599. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3028223 [40] LI Xinyu, HE Yuan, FIORANELLI F, et al. Semisupervised human activity recognition with radar micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–12. [41] DU Hao, JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, et al. Unsupervised adversarial domain adaptation for micro-Doppler based human activity classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2917301 [42] LANG Yue, HOU Chunping, JI Haoran, et al. A dual generation adversarial network for human motion detection using micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(16): 17995–18003. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3084241 [43] FIORANELLI F, SHA S A, LI Haobo, et al. Radar sensing for healthcare[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(19): 1022–1024. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.2378 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
