A Meta-learning Knowledge Reasoning Framework Combining Semantic Path and Language Model
-
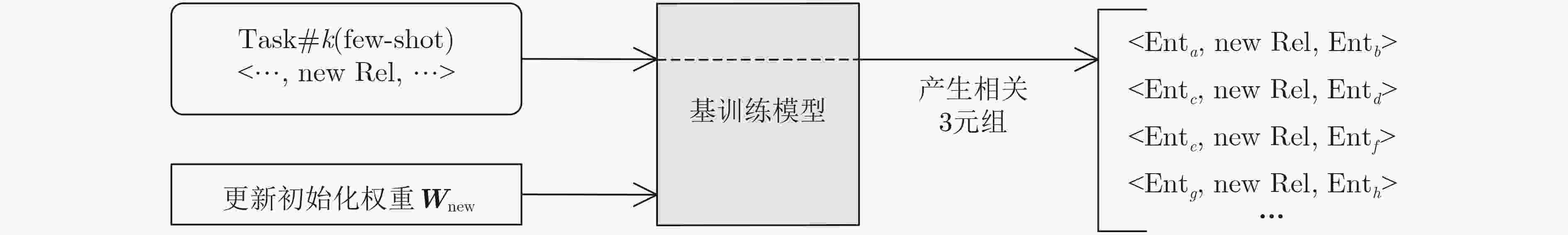
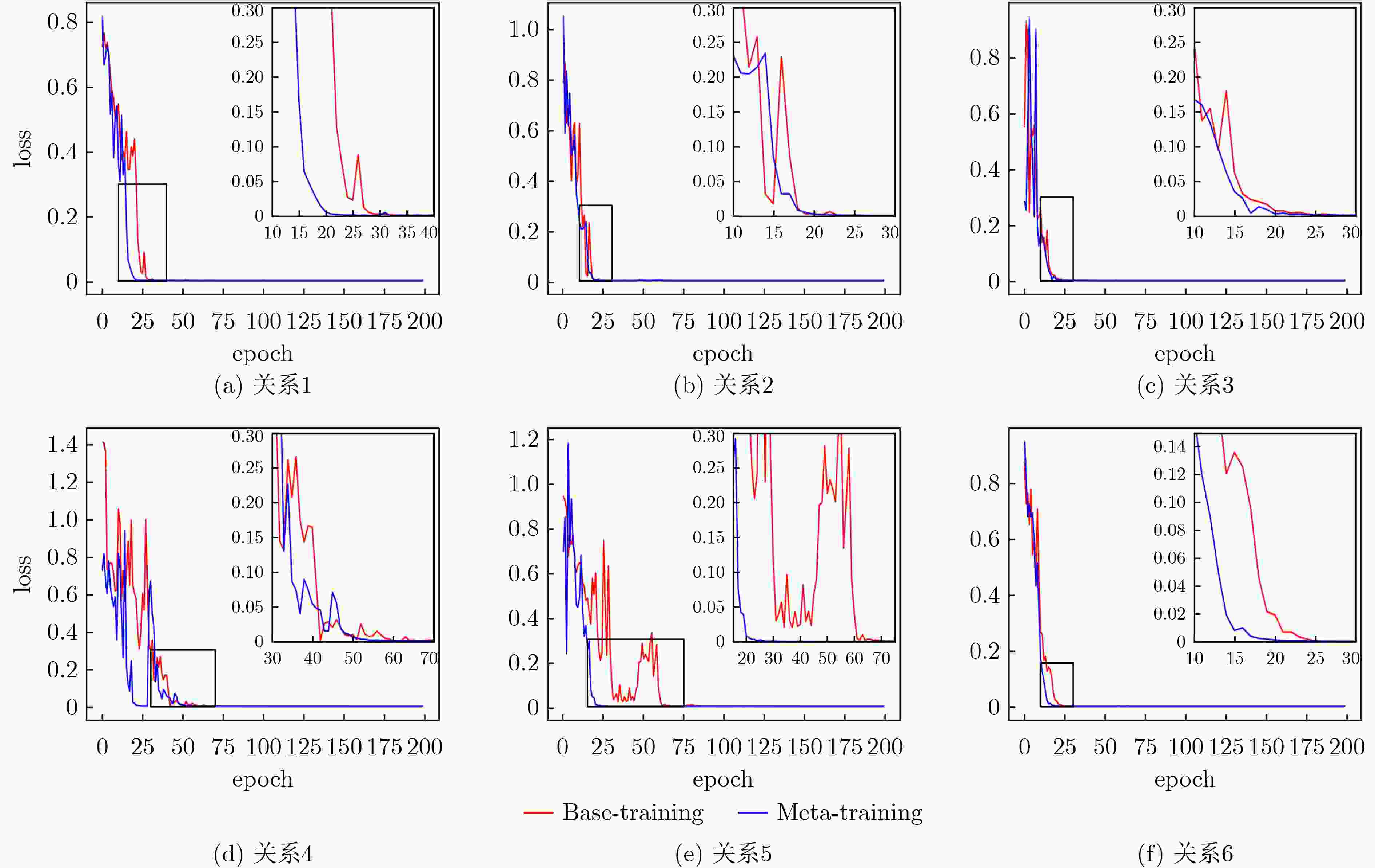
摘要: 针对传统推理方法无法兼顾计算能力与可解释性,同时在小样本场景下难以实现知识的快速学习等问题,该文设计一款融合语义路径与双向Transformer编码(BERT)的模型无关元学习(MAML)推理框架,该框架由基训练和元训练两个阶段构成。基训练阶段,将图谱推理实例用语义路径表示,并代入BERT模型微调计算链接概率,离线保存推理经验;元训练阶段,该框架基于多种关系的基训练过程获得梯度元信息,实现初始权值优化,完成小样本下知识的快速学习。实验表明,基训练推理框架在链接预测与事实预测任务中多项指标高于平均水平,同时元学习框架可以实现部分小样本推理问题的快速收敛。
-
关键词:
- 知识推理 /
- 语义路径 /
- 双向Transformer编码表示 /
- 模型无关元学习
Abstract: In order to solve the problems that traditional knowledge reasoning methods can not combine computing power and interpretability, and it is difficult to learn quickly in few-shot scenarios, a Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) reasoning framework is proposed in this paper, which combines semantic path and Bidirectional Encoder Representations for Transformers (BERT), and consists of two stages: base-training and meta-training. In base-training stage, the graph reasoning instances is represented by semantic path and BERT model, which is used to calculate the link probability and save reasoning experience offline by fine-tuning. In meta-training stage, the gradient meta-information based on the base-training process of multiple relations is obtained by this framework, which realizes the initial weight optimization, and completes the rapid learning of knowledge under few-shot. Experiments show that better performance in link prediction and fact prediction can be achieved by the base-training reasoning framework, and fast convergence of some few-shot reasoning problems can be achieved by the meta-learning framework. -
表 1 部分变量标识
变量种类 变量含义 表示方式 元素标识 实体i Enti 关系j Relj 方向标识 正向标识符 [FWD] 反向标识符 [RVS] 语义标识 语义路径起始符 [CLS] 语义路径分隔符 [SEP] 表 2 Task举例与表示
Task#1 (配偶) Support <[CLS]王健林[FWD]配偶林宁[SEP]王健林[RVS]父亲王思聪[FWD]母亲林宁[SEP]>··· Query <[CLS]约瑟夫·拜登[FWD]配偶吉尔·拜登[SEP]约瑟夫·拜登[RVS]父亲亨特·拜登[FWD]母亲吉尔·拜登[SEP]>··· Task#2 (所属地区) Support <[CLS]江汉路[FWD]所属地区武汉[SEP]江汉路 [FWD]所属地区汉口[FWD]所属地区武汉[SEP]>··· Query <[CLS]伊夫岛[FWD]所属地区普罗旺斯[SEP]伊夫岛 [FWD]所属地区马赛[FWD]所属地区普罗旺斯 [SEP]>··· Task#3 (前型级) Support <[CLS]f-35战斗机[FWD]前型级YF-22[SEP]f-35战斗机[RVS]衍生型f-22战斗机[FWD]前型级YF-22 [SEP]> ··· Query <[CLS]歼-16[FWD]前型级苏-27SK[SEP]歼-16 [FWD]前型级歼-11[FWD]前型级苏-27SK [SEP]>··· Task#m 表 3 基础参数设定
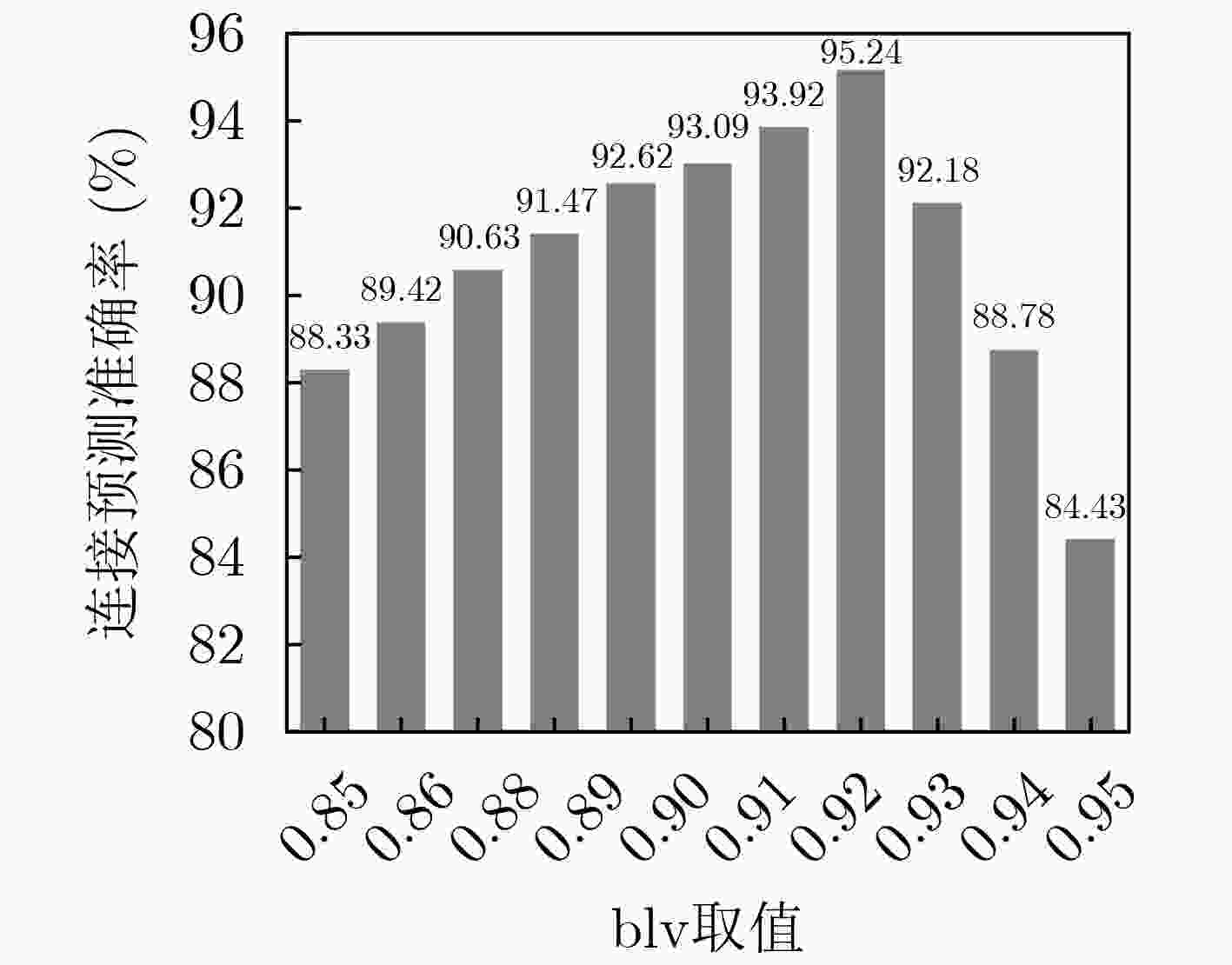
参数 值 (BERT) 最大句子长度 50(词) (BERT) 批处理数 64(条) (BERT) 学习率 5e-5 (MAML) α 0.01 (MAML) β 0.001 表 4 不同方案链接预测效果比较
方案 FB15K-237 WN18RR 人际关系图谱 CN-DBpedia子集 MRR MR Hits@10 MRR MR Hits@10 MRR MR Hits@10 MRR MR Hits@10 TransE 0.294 357 0.465 0.226 3384 0.501 0.428 38 0.523 0.269 163 0.482 ComplEx 0.247 339 0.428 0.440 5261 0.510 0.440 34 0.600 0.331 132 0.525 R-GCNs 0.248 – 0.417 – – – 0.452 32 0.623 0.308 134 0.495 KBGAN 0.278 – 0.458 0.214 – 0.472 0.476 32 0.556 0.299 120 0.536 ConvKB 0.243 311 0.421 0.249 3324 0.524 0.436 26 0.621 0.324 146 0.461 VR-GCN 0.248 – 0.432 – – – 0.468 31 0.566 0.292 143 0.531 本文 0.288 321 0.443 0.285 3201 0.532 0.452 31 0.513 0.315 117 0.513 表 5 不同方案事实预测效果对比
方案 FB15K-237 WN18RR 关系图谱 DB子图 TransE 0.277 0.243 0.310 0.203 ComplEx 0.309 0.210 0.413 0.231 R-GCNs 0.289 0.255 0.382 0.198 KBGAN 0.313 0.243 0.369 0.228 ConvKB 0.301 0.241 0.425 0.235 VR-GCN 0.324 0.236 0.401 0.242 本文 0.317 0.289 0.411 0.225 -
[1] 马忠贵, 倪润宇, 余开航. 知识图谱的最新进展、关键技术和挑战[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(10): 1254–1266. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.02.28.001MA Zhonggui, NI Runyu, and YU Kaihang. Recent advances, key techniques and future challenges of knowledge graph[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(10): 1254–1266. doi: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.02.28.001 [2] 官赛萍, 靳小龙, 贾岩涛, 等. 面向知识图谱的知识推理研究进展[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(10): 2966–2994. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005551GUAN Saiping, JIN Xiaolong, JIA Yantao, et al. Knowledge reasoning over knowledge graph: A survey[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(10): 2966–2994. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005551 [3] LAO Ni and COHEN W W. Relational retrieval using a combination of path-constrained random walks[J]. Machine Learning, 2010, 81(1): 53–67. doi: 10.1007/s10994-010-5205-8 [4] YANG Fan, YANG Zhilin, and COHEN W W. Differentiable learning of logical rules for knowledge base completion[J]. arXiv: 1702.08367, 2017. [5] 康世泽, 吉立新, 张建朋. 一种基于图注意力网络的异质信息网络表示学习框架[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 915–922. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200034KANG Shize, JI Lixin, and ZHANG Jianpeng. Heterogeneous information network representation learning framework based on graph attention network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 915–922. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200034 [6] 刘藤, 陈恒, 李冠宇. 联合FOL规则的知识图谱表示学习方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(4): 100–107. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1911-0436LIU Teng, CHEN Heng, and LI Guanyu. Knowledge graph representation learning method jointing FOL rules[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(4): 100–107. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1911-0436 [7] ZHANG Linli, LI Dewei, XI Yugeng, et al. Reinforcement learning with actor-critic for knowledge graph reasoning[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(6): 169101. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9820-3 [8] WANG Heng, LI Shuangyin, PAN Rong, et al. Incorporating graph attention mechanism into knowledge graph reasoning based on deep reinforcement learning[C]. The 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 2019: 2623–2631. [9] 陈海旭, 周强, 刘学军. 一种结合路径信息和嵌入模型的知识推理方法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2020, 41(6): 1147–1151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2020.06.005CHEN Haixu, ZHOU Qiang, and LIU Xuejun. Knowledge graph reasoning combining path information and embedding model[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2020, 41(6): 1147–1151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2020.06.005 [10] LÜ Xin, GU Yuxian, HAN Xu, et al. Adapting meta knowledge graph information for multi-hop reasoning over few-shot relations[C]. The 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 2019: 3376–3381. [11] CHEN Mingyang, ZHANG Wen, ZHANG Wei, et al. Meta relational learning for few-shot link prediction in knowledge graphs[C]. The 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 2019: 4217–4226. [12] DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, USA, 2019. [13] FINN C, ABBEEL P, and LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126–1135. [14] YANG Zhilin, DAI Zihang, YANG Yiming, et al. XLNet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding[C]. The 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019. [15] SUN Yu, WANG Shuohuan, LI Yukun, et al. ERNIE: Enhanced representation through knowledge integration[J]. arXiv: 1904.09223, 2019. [16] SUN Chi, QIU Xipeng, XU Yige, et al. How to fine-tune BERT for text classification?[C]. The 18th China National Conference on Chinese Computational Linguistics, Kunming, China, 2019: 194–206. [17] 任进军, 王宁. 人工神经网络中损失函数的研究[J]. 甘肃高师学报, 2018, 23(2): 61–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9020.2018.02.019REN Jinjun and WANG Ning. Research on cost function in artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Gansu Normal Colleges, 2018, 23(2): 61–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9020.2018.02.019 [18] BORDES A, USUNIER N, GARCIA-DURÁN A, et al. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data[C]. The 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2013: 2787–2795. [19] SCHLICHTKRULL M, KIPF T N, BLOEM P, et al. Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks[C]. The 15th International Conference on The Semantic Web, Heraklion, Greece, 2018: 593–607. -





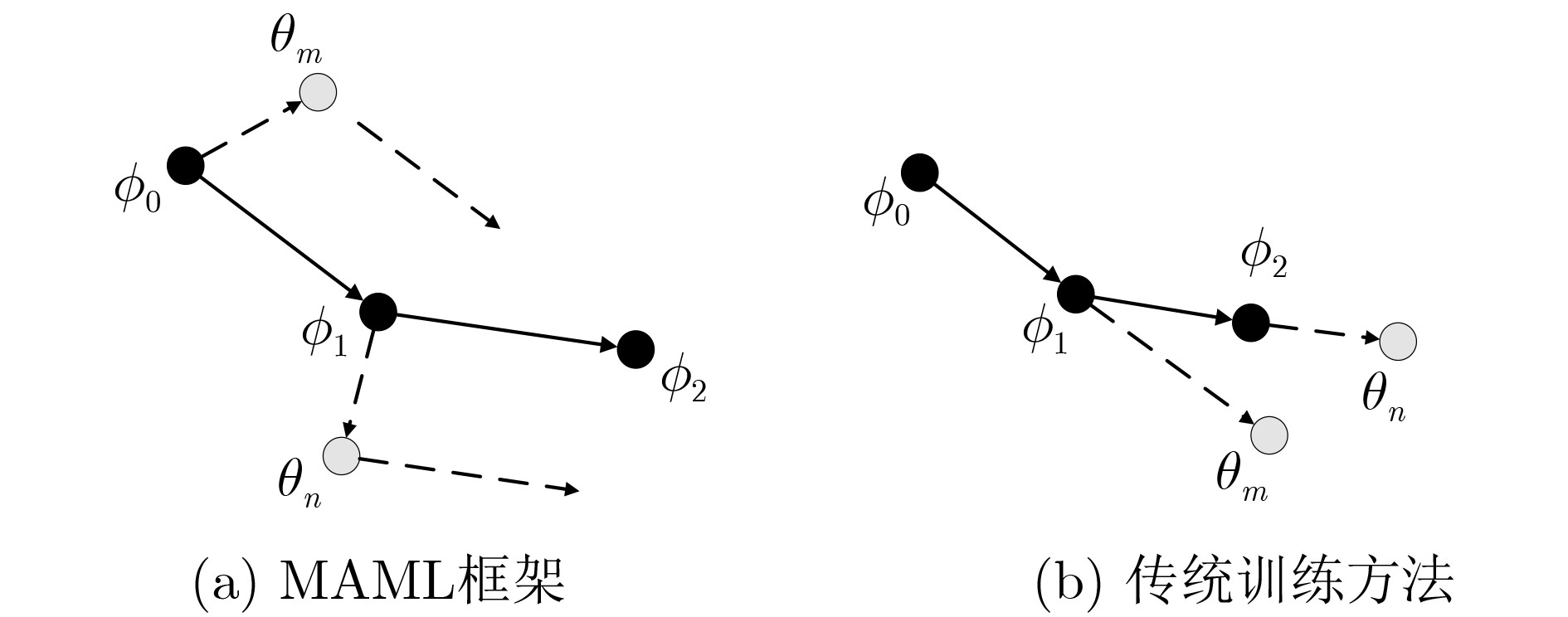
 下载:
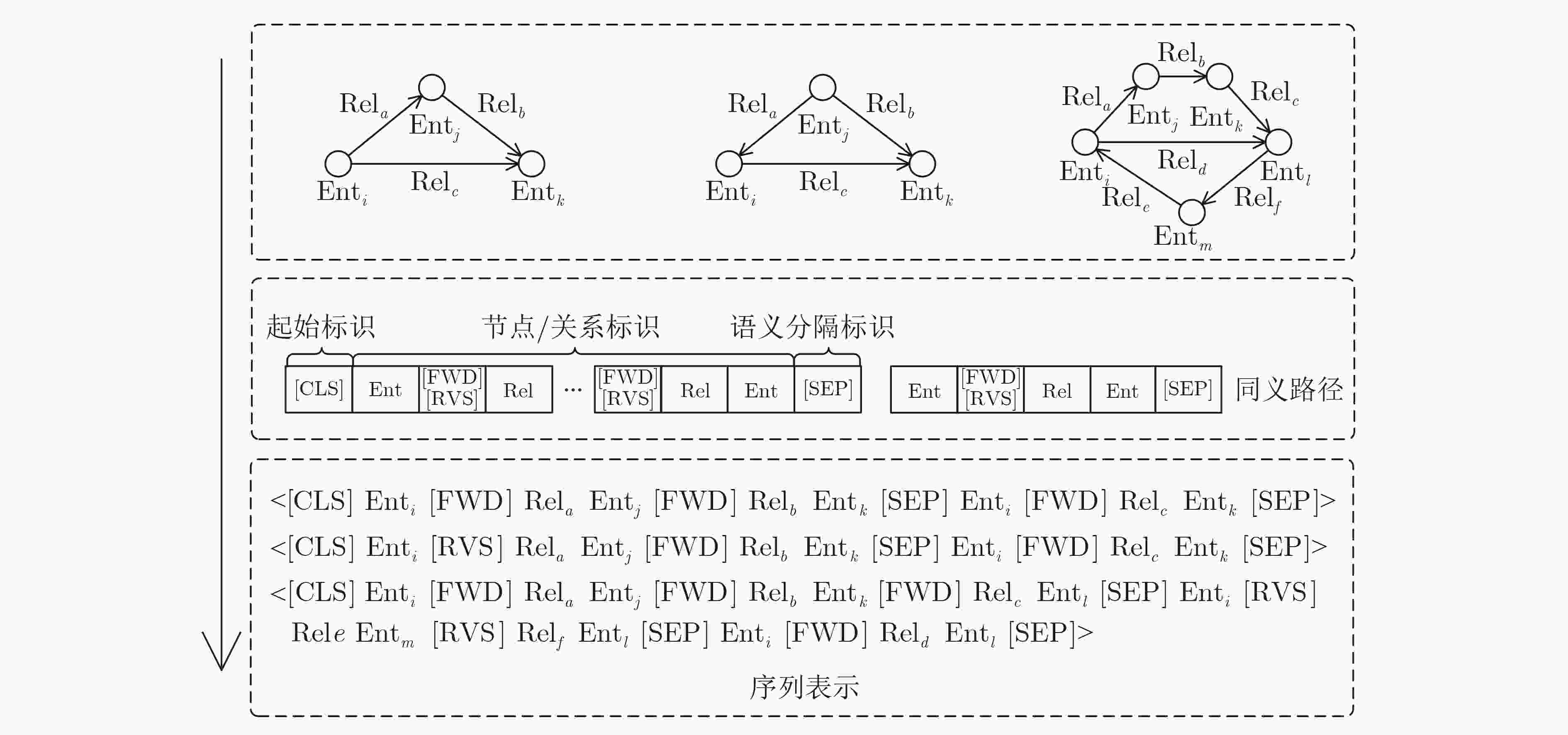
下载:
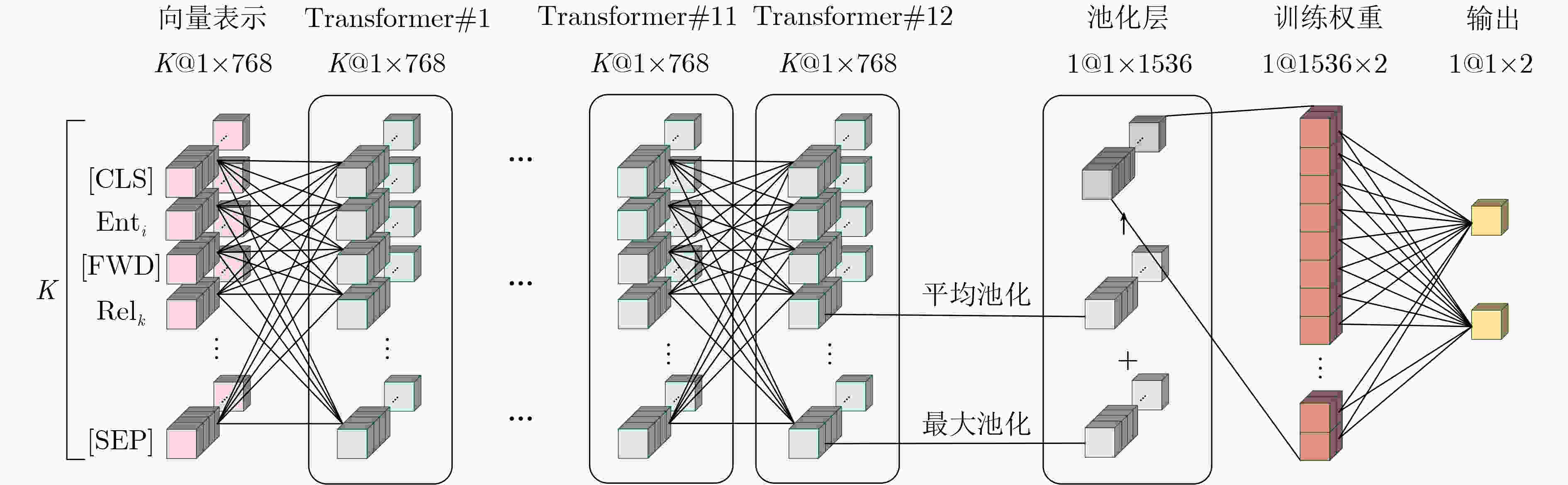


 下载:
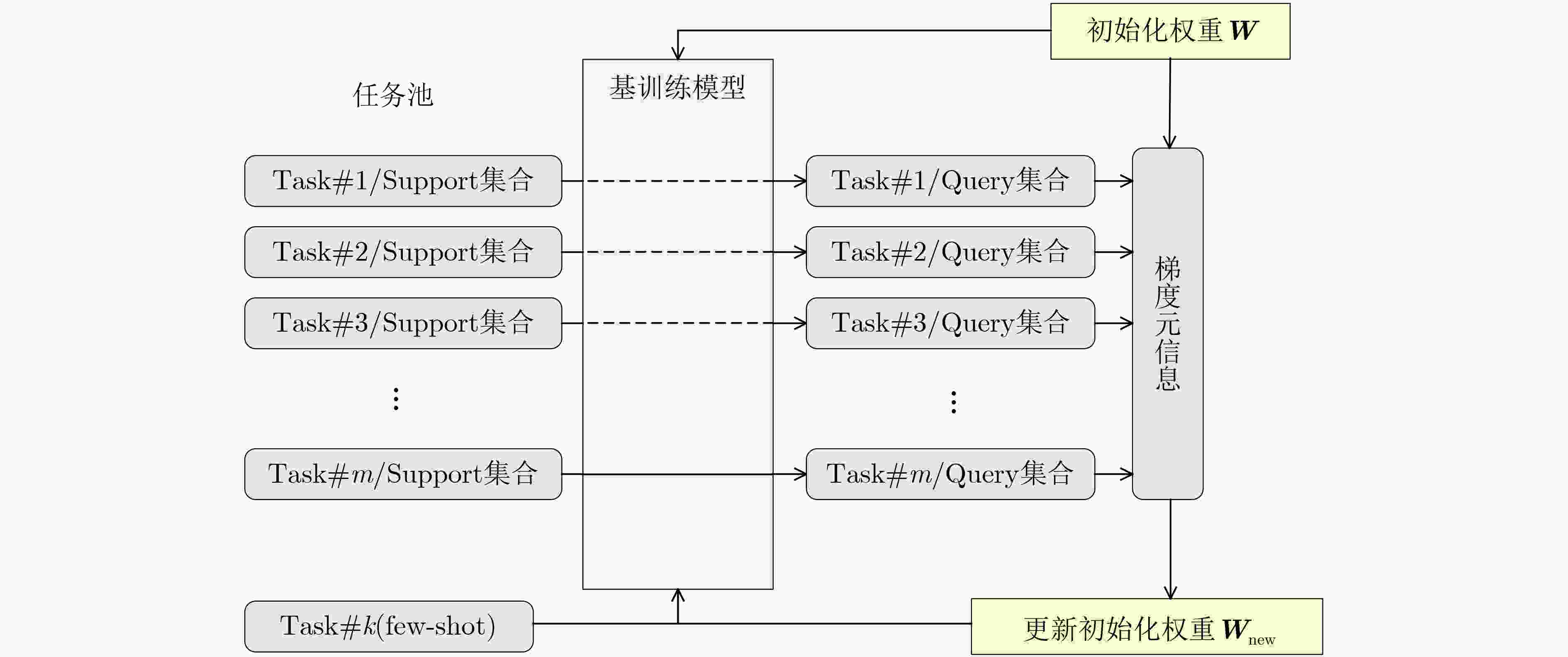
下载:
