Partial Overlapped Channel Assignment for Wireless Mesh Networks Based on Improved Discrete Bat Algorithm
-
摘要: 针对应急通信背景下无线Mesh网络(WMN)中存在的信道干扰和频谱资源利用不充分的问题,该文提出一种改进的离散蝙蝠算法(IDBA)用于求解最优部分重叠信道(POCs)分配方案。该方法采用K-means聚类算法优化网络拓扑,引入樽海鞘群的链式行为提高局部搜索能力,建立以最小化链路加权干扰为目标的线性规划模型来解决流量汇聚情况可能造成的网络瓶颈链路问题。仿真结果表明,在不同网络规模下,相比于其他基于群智能优化算法的信道分配方法,该方法具有较快的收敛速度和较优的搜索能力。此外,该方法能够在节点密集时显著降低网络干扰并保持网络的稳定性。Abstract: To address the problems of channel interference and inadequate utilization of spectrum resources in Wireless Mesh Networks (WMN) in the context of emergency communications, an Improved Discrete Bat Algorithm (IDBA) is proposed for solving the optimal Partially Overlapped Channels (POCs) assignment scheme. K-means clustering algorithm is used to optimize the network topology, the chaining behavior of the sea squirt is introduced to improve the local search capability, and a linear programming model with the goal of minimizing link-weighted interference is established to solve the network bottleneck link problem that may be caused in the case of traffic convergence. Results show that the method has a faster convergence speed and better search capability than other group intelligence optimization algorithm-based channel assignment methods at different network sizes. In addition, the method can significantly reduce the global interference and maintain the network stability when the nodes are dense.
-
表 1 信道重叠度
信道间隔$\tau $ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7~10 重叠度${\text{od(}}x,y{\text{)}}$ 1.0000 0.7272 0.2714 0.0375 0.0054 0.0008 0.0002 0 表 2 蝙蝠位置编码示例
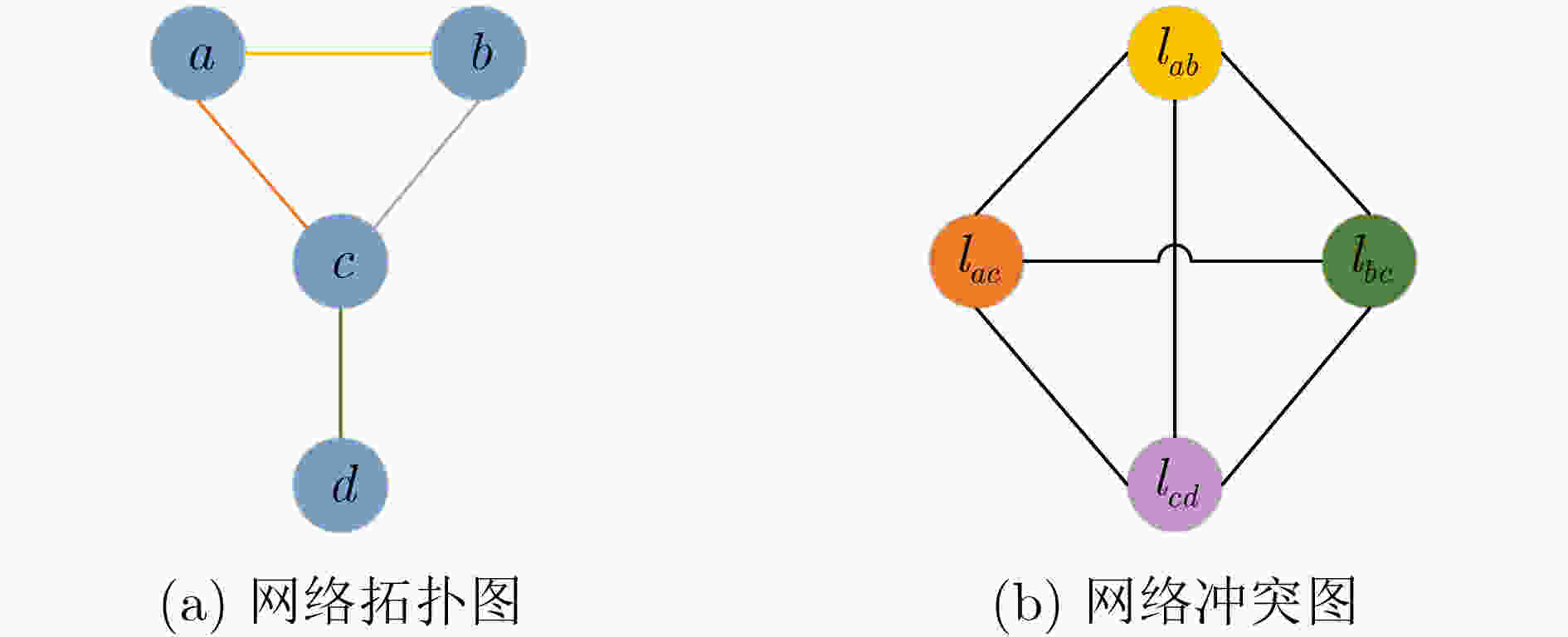
编号 1 2 3 4 链路 ${l_{ab}}$ ${l_{ac}}$ ${l_{bc}}$ ${l_{cd}}$ 信道 8 5 10 3 $x_i^t$ 8 5 10 3 表 3 信道分配过程
输入:可用信道集${\mathbf{C}}$、节点和接口数量、初始脉冲率和初始响度等参数 输出:最优信道分配方案、最小适应度值 (1)根据网络结构生成随机网络拓扑图;根据干扰模型生成网络冲突图。 (2)为蝙蝠种群随机分配公共信道并初始化速度,计算初始适应度并进行比较,最小者为当前全局最优解${ {{\rm{fitness}}} _{{\rm{bestz}}} }$。 (3)根据式(17)更新频率,根据式(20)—式(23)更新种群的速度和位置。 (4)产生一个(0,1)的随机数${\text{rand}}$,按照式(26)进行局部搜索产生新解,计算其适应度值${\text{fitnes}}{{\text{s}}_{{\text{new}}}}$。 (5)产生一个(0,1)的随机数${\text{rand}}$,若${\text{rand}}$$ < {A_i}$且${\text{fitnes}}{{\text{s}}_{{\text{new}}}}$<${ {{\rm{fitness}}} _{{\rm{bestz}}} }$,则接受新解同时根据式(24)—式(25)增加${r_i}$,减小${A_i}$,否则保持个
体不变。(6)按照适应度值排列种群中所有蝙蝠个体,适应度值最小者为当前最优解。 (7)判断是否达到最大迭代次数,达到则结束循环,输出最优方案;否则返回步骤(3)。 表 4 仿真参数设置表
仿真参数 参数值 传输范围 250 m 同信道干扰范围 550 m 路径损耗因子$k$ 2 部分重叠信道数目 11 接口数目 3 节点发射功率 15.6 dBm 背景噪声 –97 dBm 初始脉冲率 0.7 初始响度 1.6 $\alpha $和$\varepsilon $因子 0.8 表 5 不同算法总耗时对比(s)
算法 节点数量 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 DPSO 0.771 1.303 2.834 8.293 18.797 26.647 48.032 IDBA 0.775 1.979 4.984 9.764 19.460 29.318 56.893 CSA 5.865 21.628 57.789 226.368 438.633 1135.647 1954.663 BPIO 7.543 23.026 135.038 343.607 1014.142 1386.537 3395.169 -
[1] GHEISARI M, ALZUBI J, ZHANG Xioabo, et al. A new algorithm for optimization of quality of service in peer to peer wireless mesh networks[J]. Wireless Networks, 2020, 26(7): 4965–4973. doi: 10.1007/s11276-019-01982-z [2] KURT A, SAPUTRO N, AKKAY K, et al. Distributed connectivity maintenance in swarm of drones during post-disaster transportation applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(9): 6061–6073. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3066843 [3] HONG Xiaoyan, GU Bo, HOQUE M, et al. Exploring multiple radios and multiple channels in wireless mesh networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2010, 17(3): 76–85. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2010.5490982 [4] LUO Yizhou and CHIN K W. Learning to bond in dense WLANs with random traffic demands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11868–11879. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3006218 [5] MISHRA A, ROZNER E, BANERJEE S, et al. Exploiting partially overlapping channels in wireless networks: Turning a peril into an advantage[C]. The 5th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, Berkeley, USA, 2005: 29. [6] BOKHARI F S and ZÁRUBA G V. I-POCA: Interference-aware partially overlapping channel assignment in 802.11-based meshes[C]. 2013 IEEE 14th International Symposium on "A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks" (WoWMoM), Madrid, Spain, 2013: 1–6. [7] LIU Kaiming, LI Nan, and LIU Yuanan. Min-interference and connectivity-oriented partially overlapped channel assignment for multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks[C]. 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2017: 84–88. [8] 张海波, 李虎, 陈善学, 等. 超密集网络中基于移动边缘计算的任务卸载和资源优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592ZHANG Haibo, LI Hu, CHEN Shanxue, et al. Computing offloading and resource optimization in ultra-dense networks with mobile edge computation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592 [9] SELVAKUMAR K and REVATHY G. Escalating quality of services with channel assignment and traffic scheduling in wireless mesh networks[J]. Cluster Computing, 2019, 22(5): 11949–11955. doi: 10.1007/s10586-017-1528-6 [10] 刘炜, 李东坤, 徐畅, 等. 应急通信网络中基于粒子群优化的信道分配算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(5): 277–282. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200400042LIU Wei, LI Dongkun, XU Chang, et al. Channel assignment algorithm based on particle swarm optimization in emergency communication networks[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(5): 277–282. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200400042 [11] TIAN Yi and YOSHIHIRO T. Traffic-demand-aware collision-free channel assignment for multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120712–120723. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006275 [12] ZHAO Xiongwen, ZHANG Siyuan, LI Liang, et al. A multi-radio multi-channel assignment algorithm based on topology control and link interference weight for a power distribution wireless mesh network[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2018, 99(1): 555–566. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-5132-0 [13] BACKHAUS M, ROSSBERG M, and SCHAEFER G. Towards a realistic maximum flow model in hybrid multi-channel wireless mesh networks[C]. 2021 Wireless Days (WD), Paris, France, 2021: 1–8. [14] YAN Qingran, MA Linhua, and SUN Jin. Novel bat algorithms for scheduling independent tasks in collaborative Internet-of-Things[C]. 2020 IEEE 22nd International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 18th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 6th International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Yanuca Island, Fiji, 2020: 674–681. [15] CHAUDHRY A U, HAFEZ R H M, and CHINNECK J W. On the impact of interference models on channel assignment in multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2015, 27: 68–80. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2014.11.019 [16] WANG Jihong, SHI Wenxiao, CUI Keqiang, et al. Partially overlapped channel assignment for multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2015, 2015(1): 25. doi: 10.1186/s13638-015-0259-8 [17] 金凤. 无线Mesh网络部分重叠信道分配算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 吉林大学, 2015.JIN Feng. Research on partially overlapped channel assignment for wireless Mesh networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Jilin University, 2015. [18] SUBBAIAH K V and NAIDU M M. An efficient interference aware channel allocation algorithm for wireless mesh networks[C]. 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Engineering Systems, Guntur, India, 2015: 416–420. [19] MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, and YANG Xinshe. Binary bat algorithm[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2014, 25(3): 663–681. doi: 10.1007/s00521-013-1525-5 [20] YANG Xinshe. A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm[M]. GONZÁLEZ J R, PELTA D A, CRUZ C, et al. Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization (NICSO 2010). Berlin: Springer, 2010: 65–74. [21] MIRJALILI S, GANDOMI A H, MIRJALILI S Z, et al. Salp swarm algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2017, 114: 163–191. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.07.002 [22] ALAM S, AQDAS N, QURESHI I M, et al. Joint power and channel allocation scheme for IEEE 802.11af based smart grid communication network[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 95: 694–712. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.01.027 [23] 张达敏, 张绘娟, 闫威, 等. 异构网络中基于能效优化的D2D资源分配机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 480–487. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190042ZHANG Damin, ZHANG Huijuan, YAN Wei, et al. D2D resource allocation mechanism based on energy efficiency optimization in heterogeneous networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 480–487. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190042 -





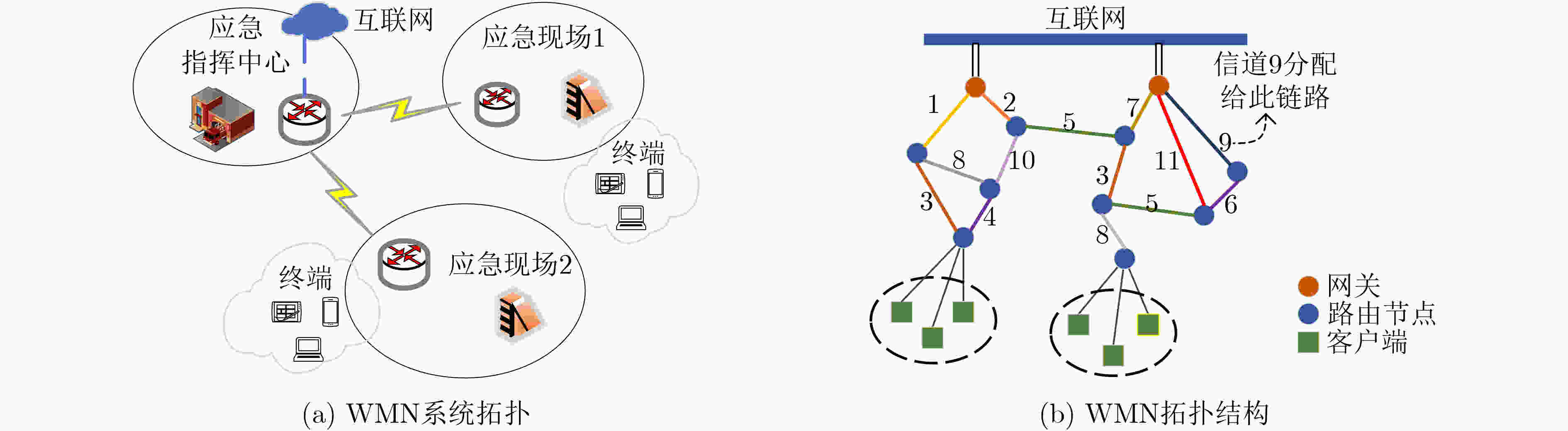
 下载:
下载:
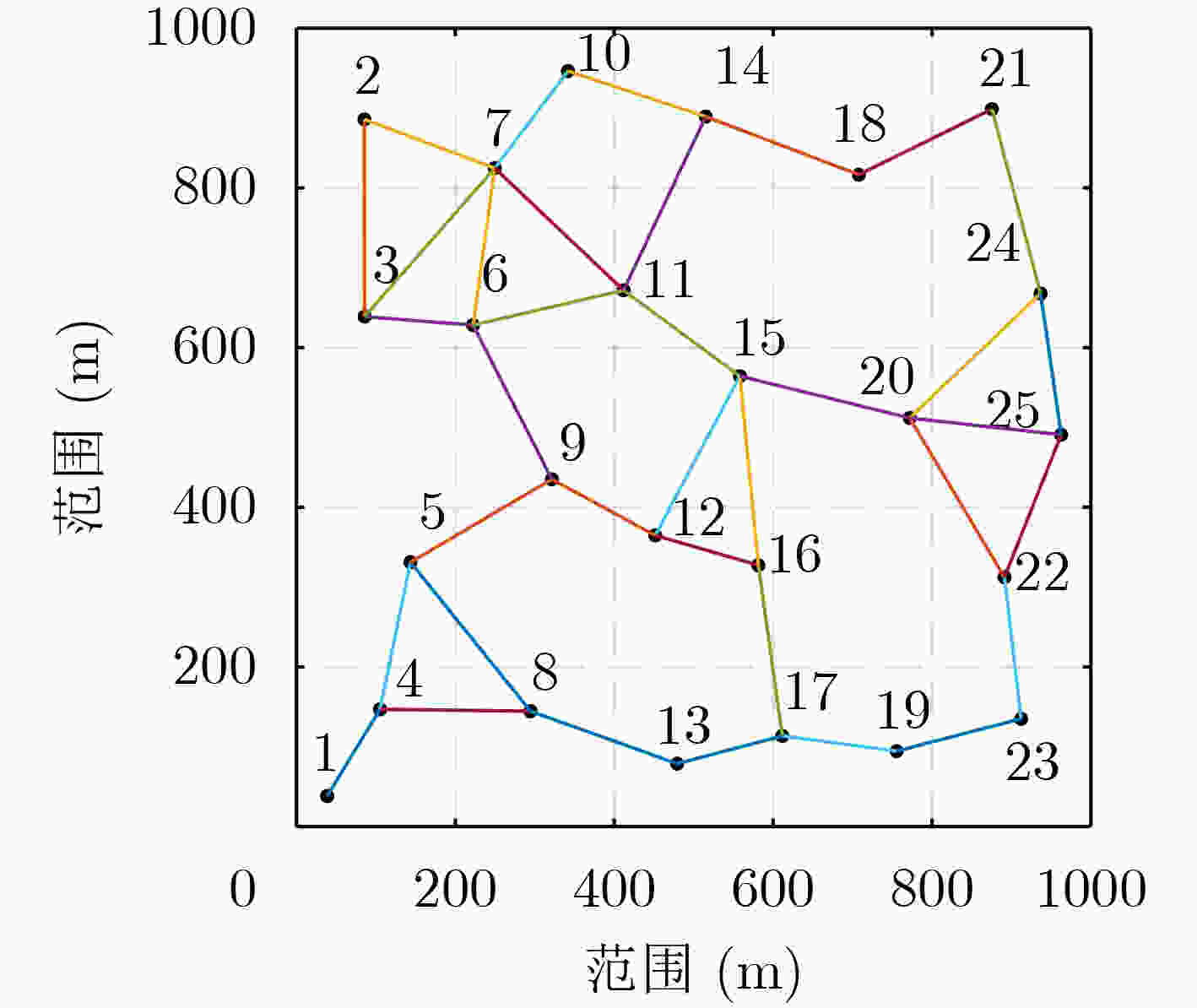
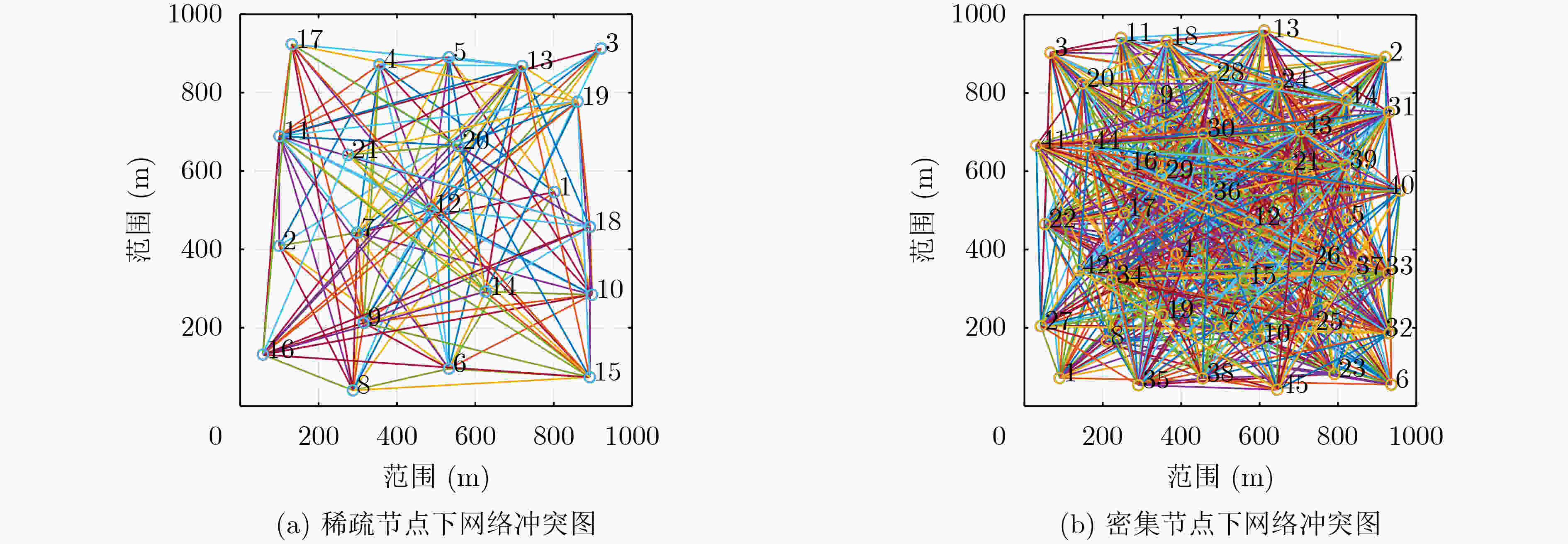
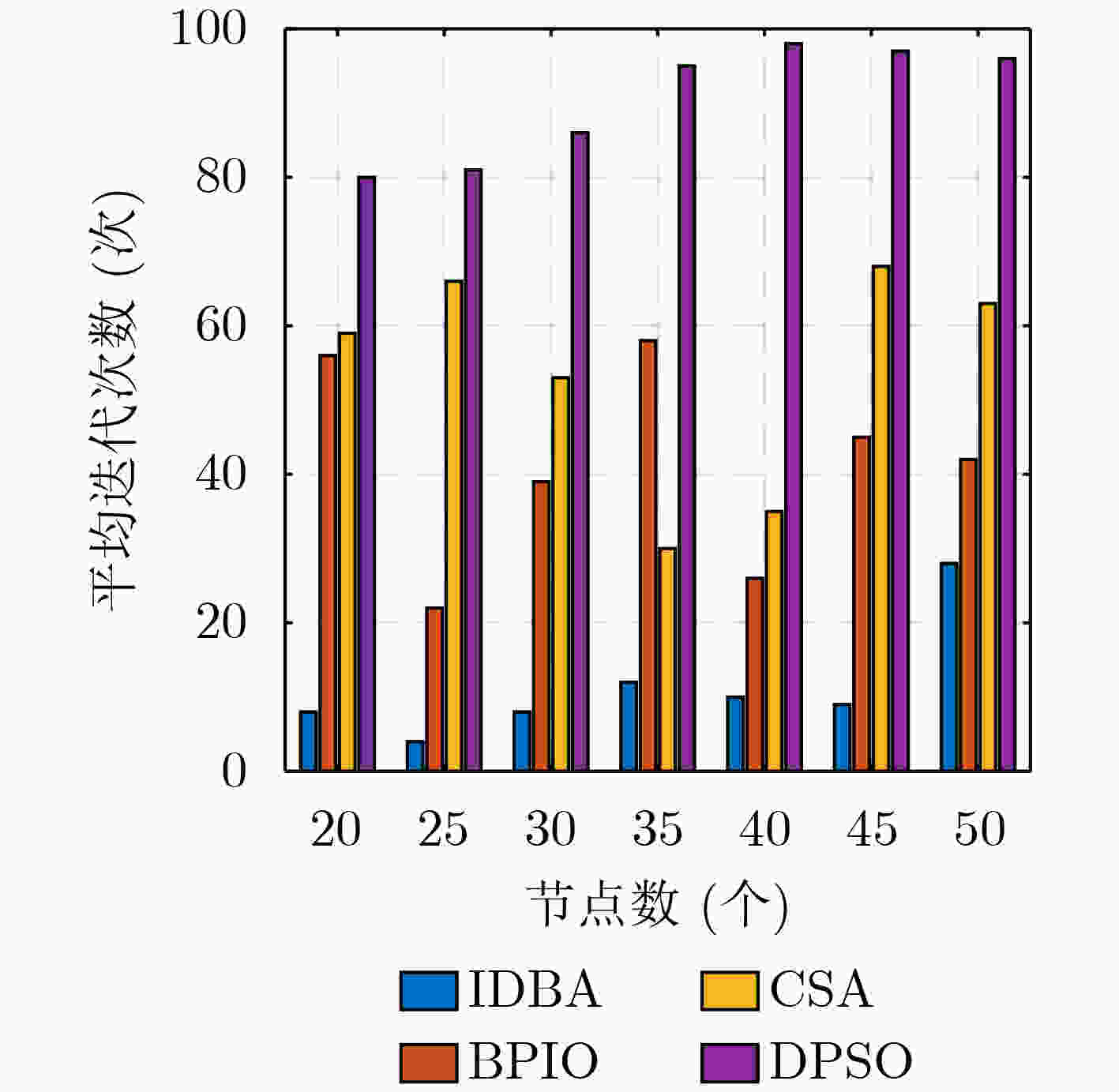
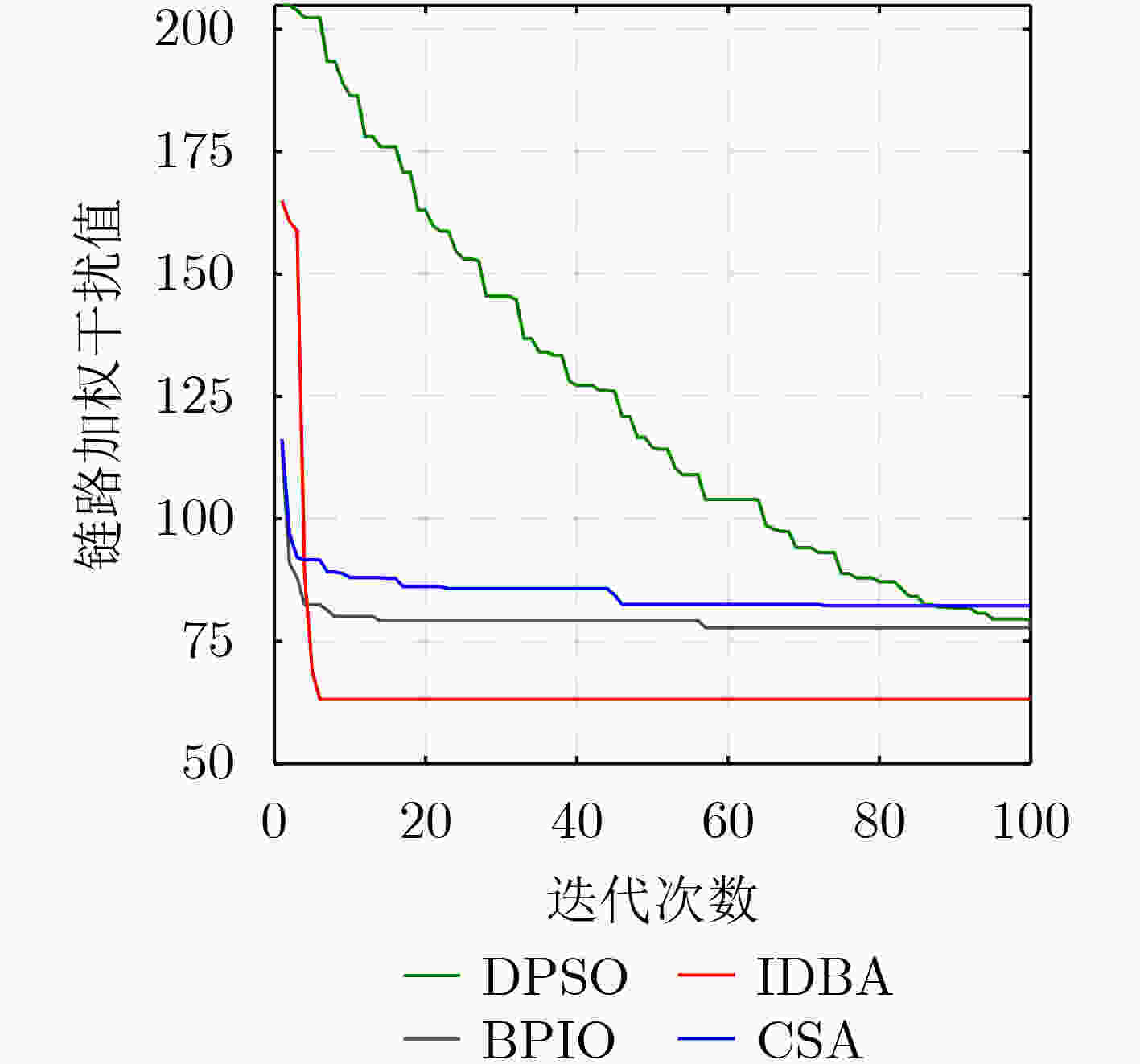
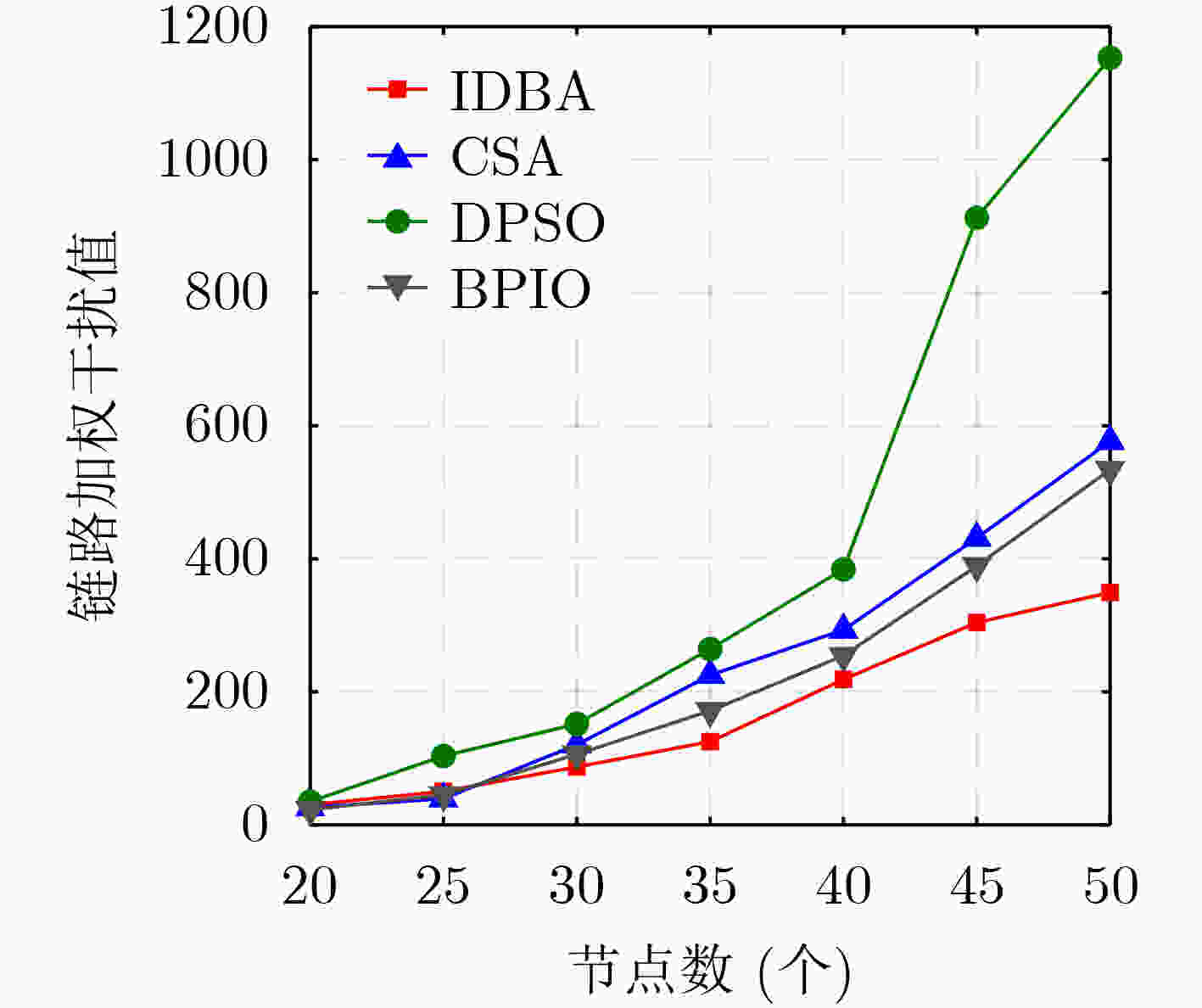
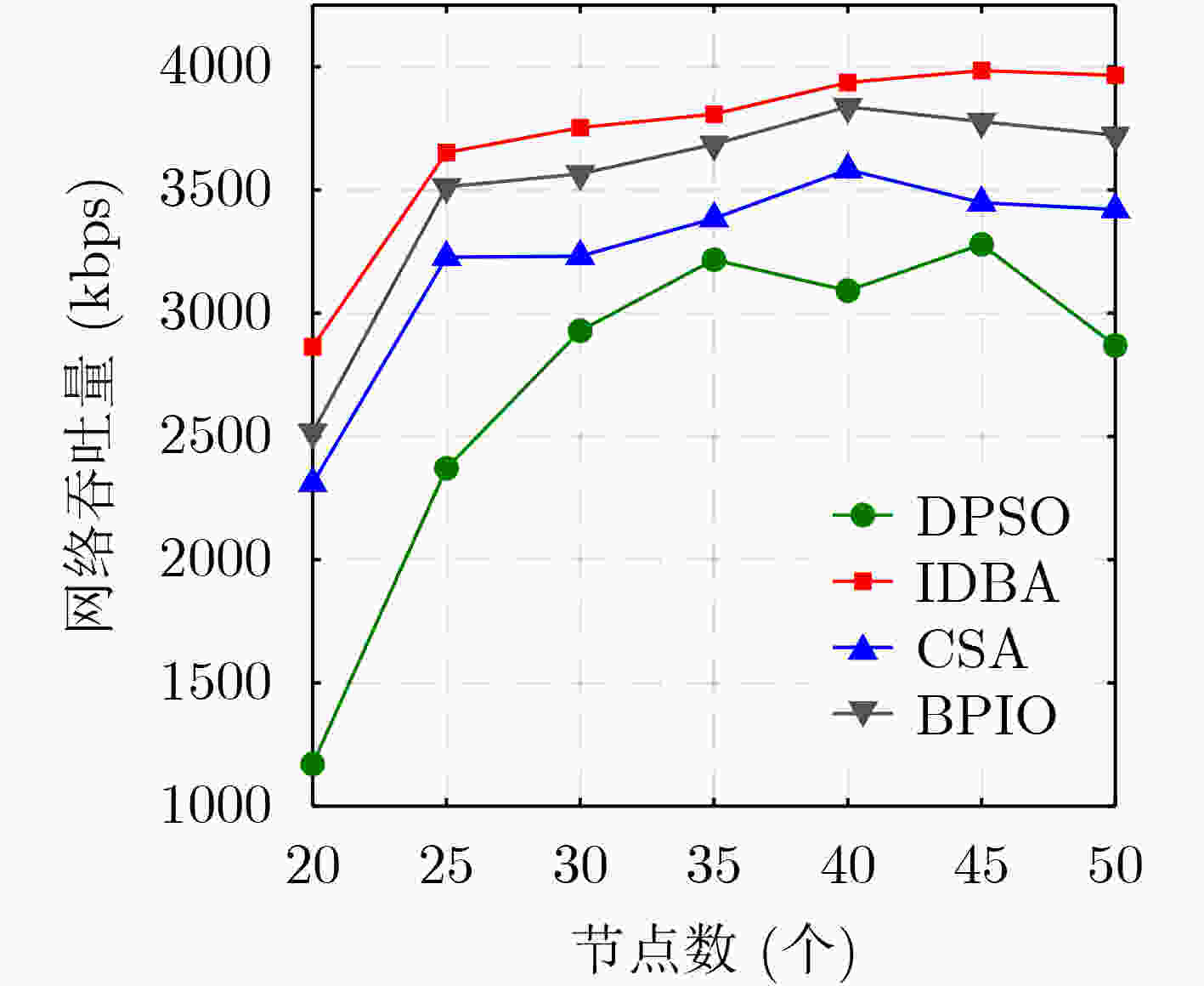


 下载:
下载:
