Fast Partition Algorithm in Depth Map Intra-frame Coding Unit Based on Multi-branch Network
-
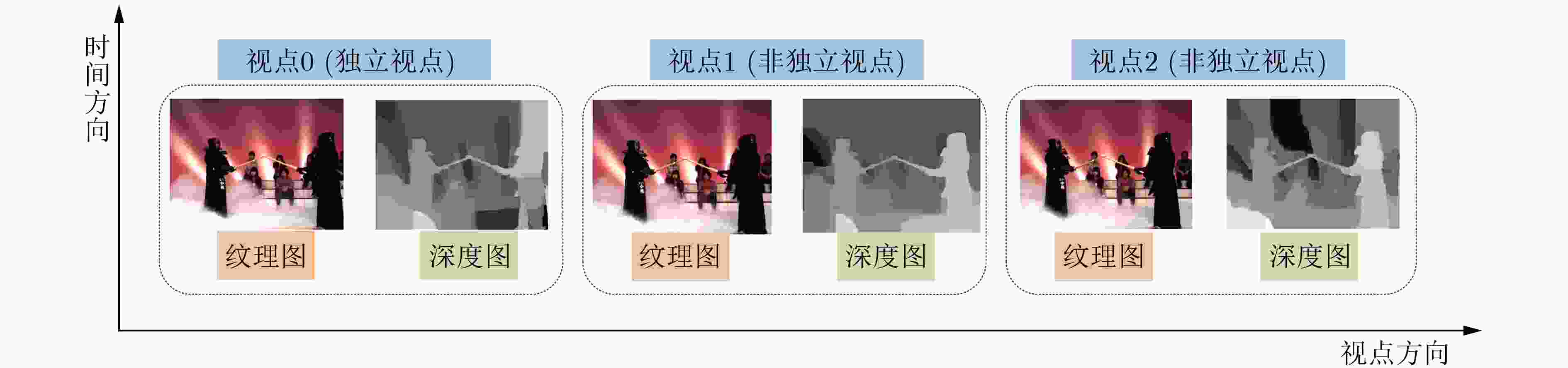
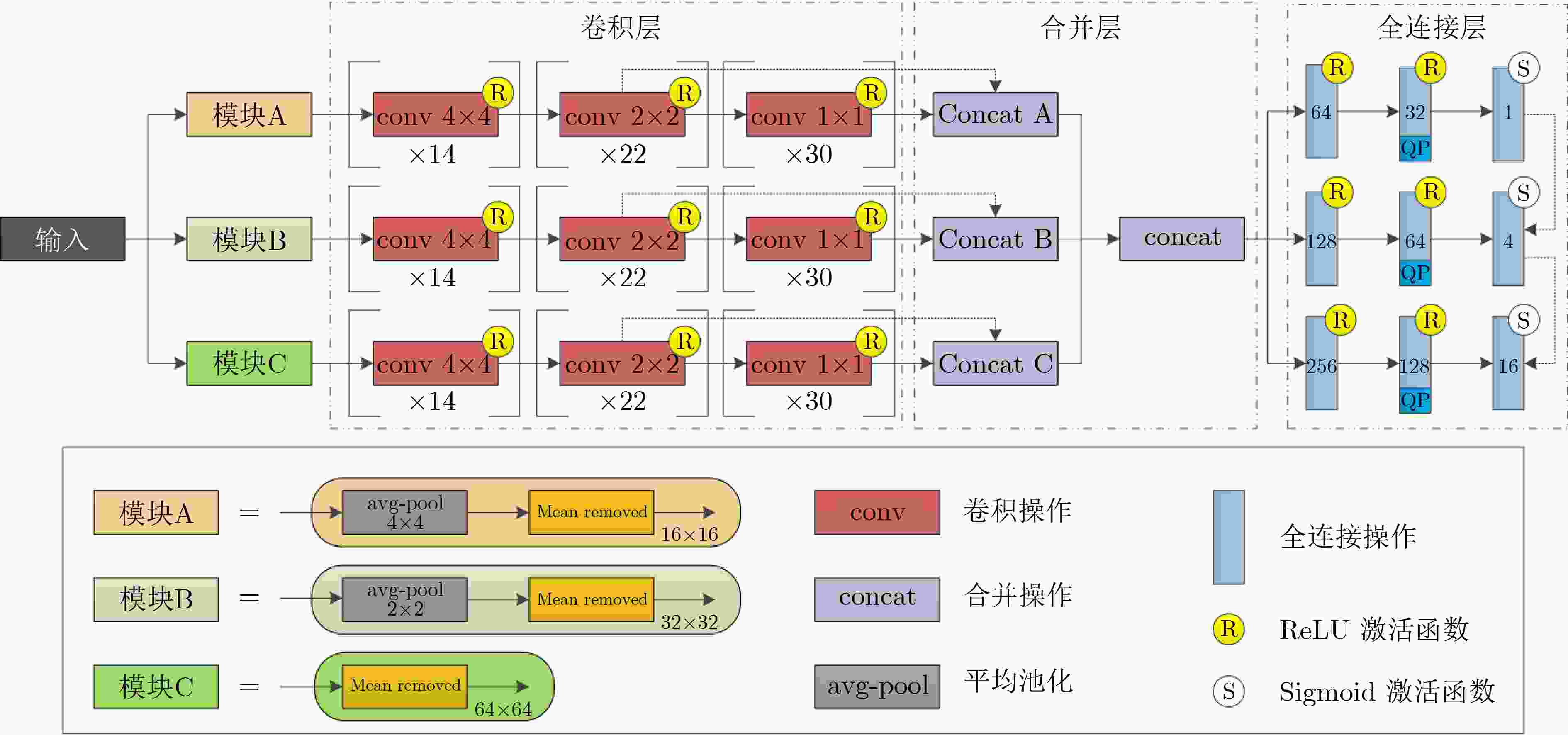
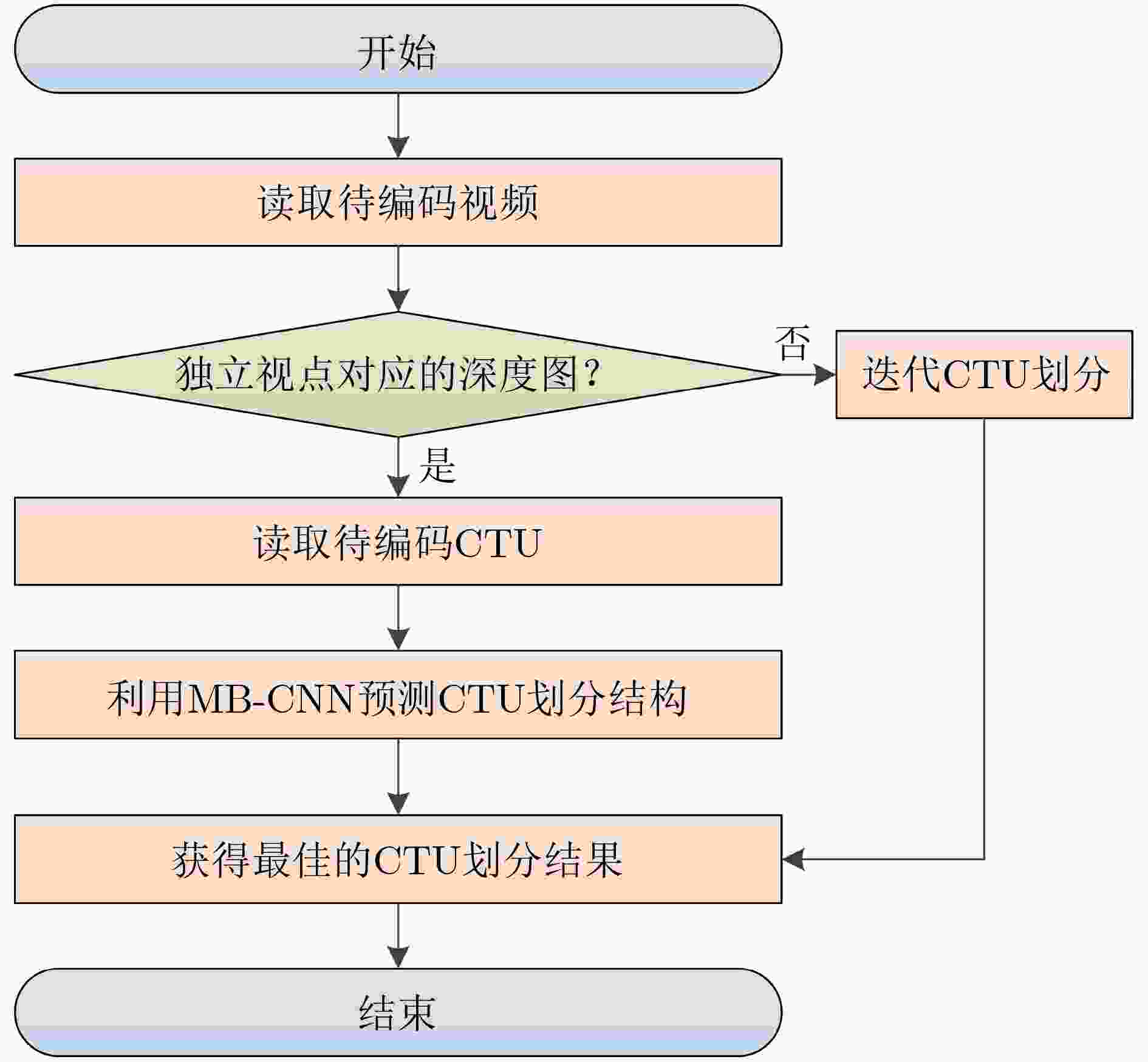
摘要: 3维高效视频编码(3D-HEVC)标准是最新的3维(3D)视频编码标准,但由于其引入深度图编码技术导致编码复杂度大幅增加。其中,深度图帧内编码单元(CU)的四叉树划分占3D-HEVC编码复杂度的90%以上。对此,在3D-HEVC深度图帧内编码模式下,针对CU四叉树划分复杂度高的问题,该文提出一种基于深度学习的CU划分结构快速预测方案。首先,构建学习深度图CU划分结构信息的数据集;其次,搭建预测CU划分结构的多分支卷积神经网络(MB-CNN)模型,并利用构建的数据集训练MB-CNN模型;最后,将MB-CNN模型嵌入3D-HEVC的测试平台,通过直接预测深度图帧内编码模式下CU的划分结构来降低CU划分复杂度。与标准算法相比,编码复杂度平均降低了37.4%。实验结果表明,在不影响合成视点质量的前提下,该文所提算法有效地降低了3D-HEVC的编码复杂度。Abstract: Three Dimensional-High Efficiency Video Coding (3D-HEVC) standard is the latest Three-Dimensional (3D) video coding standard, but the coding complexity increases greatly due to the introduction of depth map coding technology. Among them, the quad-tree partition of depth map intra-frame Coding Unit (CU) accounts for more than 90% of the coding complexity in 3D-HEVC. Therefore, for the intra-frame coding of depth map in 3D-HEVC, considering the high complexity of CU quad-tree partition, a fast prediction scheme of CU partition structure based on deep learning is proposed. Firstly, the dataset of CU partition structure information for learning depth map is constructed. Secondly, a Multi-Branch Convolutional Neural Network (MB-CNN) model for predicting the CU partition structure is built. Then, the MB-CNN model is trained by using the built dataset. Finally, the MB-CNN model is embedded into the 3D-HEVC test platform, which reduces greatly the complexity of CU partition by predicting the partition structure of CU in depth map intra-frame coding. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm reduces effectively the coding complexity of 3D-HEVC without significant synthesized view quality distortion. Specifically, compared to the standard method, the coding complexity on the standard test sequence is reduced by 37.4%.
-
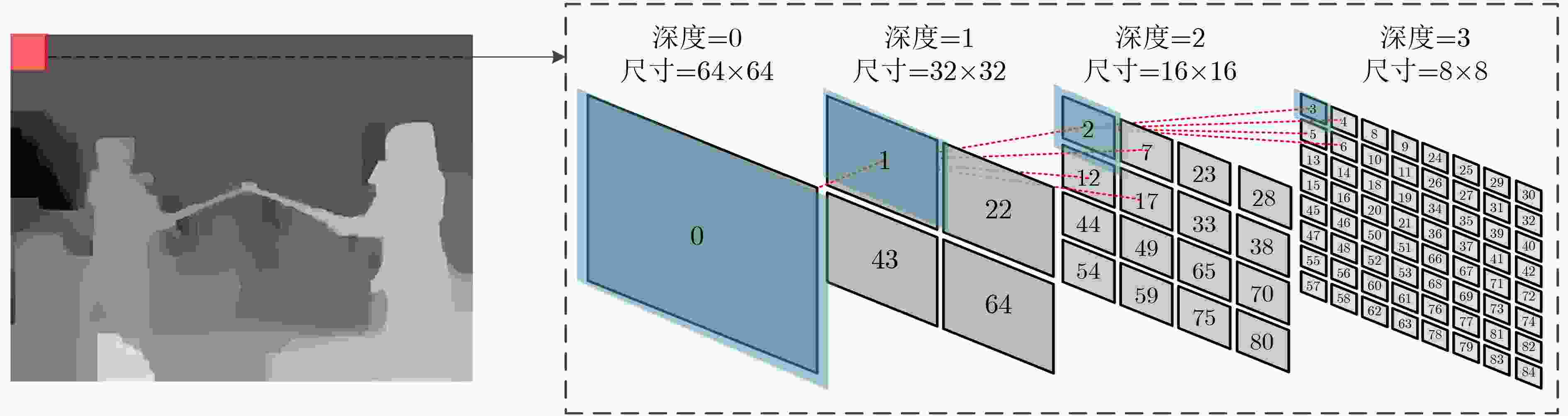
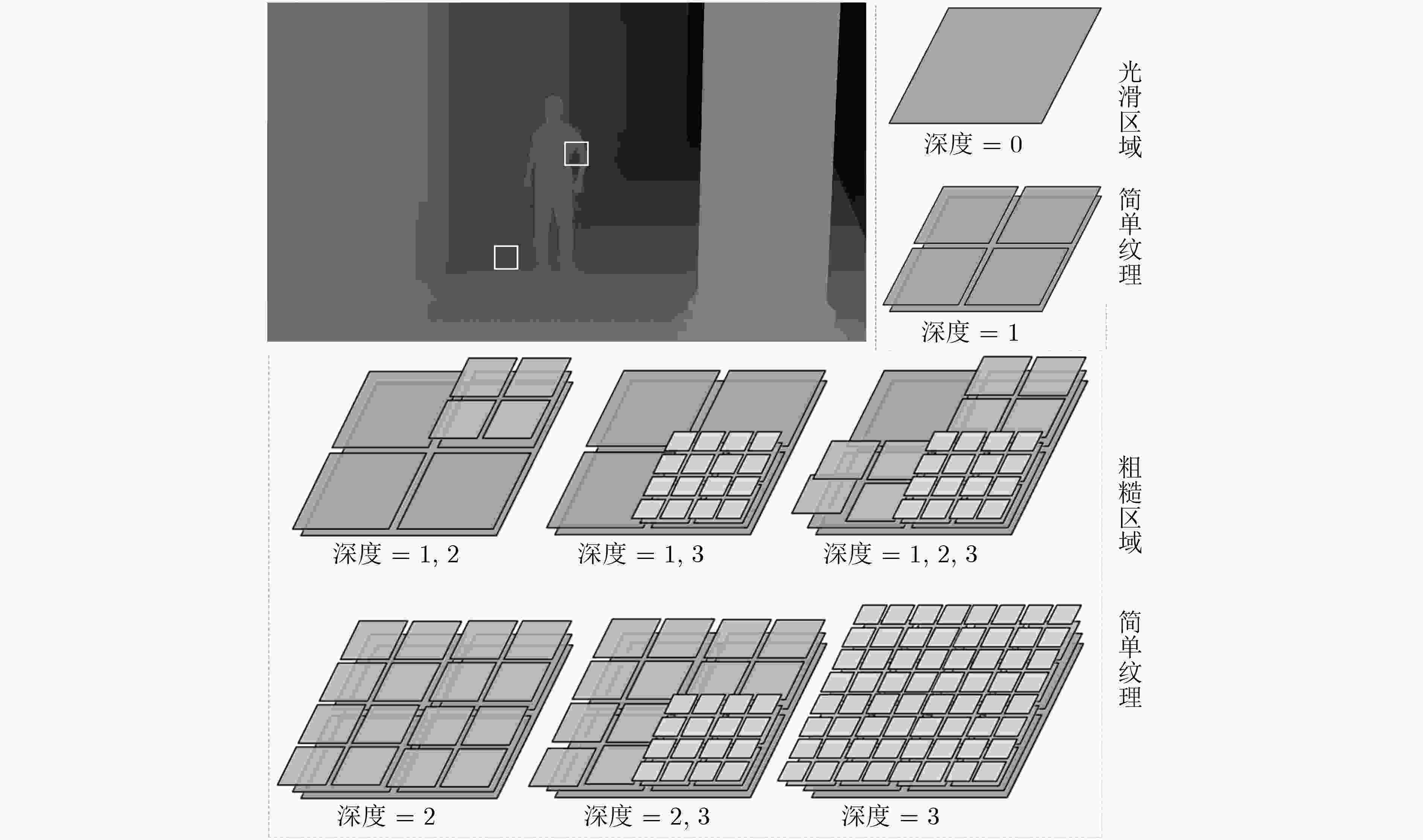
表 1 编码单元深度和QP的关系(%)
深度=0(尺寸=64×64) 深度=1(尺寸=32×32) 深度=2(尺寸=16×16) 深度=3(尺寸=8×8) QP=22,不同CU深度占比 29.29 3.43 10.75 56.10 QP=39,不同CU深度占比 70.72 10.25 8.87 10.17 平均占比 50.01 6.84 9.81 33.13 表 2 本文构建的数据集
数据集类型 序列 分辨率 帧范围 样本个数 训练集 Kendo 1024×768 0~299 57600 GT_Fly 1920×1088 0~249 127500 验证集 Balloons 1024×768 290~299 1920 Poznan_Hall2 1920×1088 210~219 5100 测试集 Newspaper 1024×768 280~299 3840 Undo_Dancer 1920×1088 230~249 10200 样本总和 206160 表 3 训练样本的组成形式
深度 划分:0,不划分:1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 3 最小编码单元为8×8,向下不再划分 组成形式 1, 1011, 0000, 0000, 1010, 0010 表 4 实验环境
硬件实验环境 名称 型号 处理器 Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E31230@ 3.20 GHz 运行内存 8.00 GB RAM 显卡适配器 NVIDIA Quadro K2000 软件实验环境 名称 型号 操作系统 Windows 10 Python 3.5 Tensorflow 1.4.0 CUDA 8.0 表 5 编码参数配置
编码配置参数 数量 Max CU Width 64 Max CU Height 64 Max Partition Depth 4 GOPSize 1 QP值 (纹理, 深度) {(25, 34), (30, 39), (35, 42), (40, 45)} 表 6 标准测试序列及其参数
序列 分辨率 帧率 视点 Balloons 1024×768 30 3 1 5 Newspaper 1024×768 30 4 2 6 Poznan_Hall2 1920×1088 25 6 7 5 Poznan_Street 1920×1088 25 4 5 3 表 7 本文算法、参考文献算法与HTM16.0的时间节省比较(%)
表 8 本文算法与HTM16.0的率失真性能比较(%)
序列 纹理视频 0 纹理视频 1 纹理视频 2 纹理视频 PSNR /
纹理视频比特率纹理视频 PSNR /
总比特率合成视点 PSNR /
总比特率Balloons 0 0 0 0 0.4 7.7 Newspaper 0 0 0 0 0.3 4.4 Poznan_Hall2 0 0 0 0 0 6.2 Poznan_Street 0 0 0 0 –0.1 5.4 1024×768 0 0 0 0 0.4 6.0 1920×1088 0 0 0 –0.4 –0.1 5.8 平均值 0 0 0 0 0.2 5.9 -
[1] LIU Shan, LIU Lu, YANG Hua, et al. Research on 5G technology based on Internet of things[C]. 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 2020: 1821–1823. [2] KUFA J and KRATOCHVIL T. Visual quality assessment considering ultra HD, Full HD resolution and viewing distance[C]. The 29th International Conference Radioelektronika, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 2019: 1–4. [3] LI Tiansong, YU Li, WANG Hongkui, et al. A bit allocation method based on inter-view dependency and spatio-temporal correlation for multi-view texture video coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2021, 67(1): 159–173. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2020.3028340 [4] 王莉, 曹一凡, 杜高明, 等. 一种低延迟的3维高效视频编码中深度建模模式编码器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1625–1632. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180798WANG Li, CAO Yifan, DU Gaoming, et al. A low-latency depth modelling mode-1 encoder in 3D-high efficiency video coding standard[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1625–1632. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180798 [5] CHEN Ying, HANNUKSELA M M, SUZUKI T, et al. Overview of the MVC + D 3D video coding standard[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2014, 25(4): 679–688. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2013.03.013 [6] TIAN Shishun, ZHANG Lu, ZOU Wenbin, et al. Quality assessment of DIBR-synthesized views: An overview[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 423: 158–178. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.09.062 [7] 齐美彬, 陈秀丽, 杨艳芳, 等. 高效率视频编码帧内预测编码单元划分快速算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(7): 1699–1705. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01148QI Meibin, CHEN Xiuli, YANG Yanfang, et al. Fast coding unit splitting algorithm for high efficiency video coding intra prediction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(7): 1699–1705. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01148 [8] ZUO Jiabao, CHEN Jing, ZENG Huanqiang, et al. Bi-layer texture discriminant fast depth intra coding for 3D-HEVC[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 34265–34274. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2897161 [9] LI Tiansong, WANG Hongkui, CHEN Yamei, et al. Fast depth intra coding based on spatial correlation and rate distortion cost in 3D-HEVC[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2020, 80: 115668. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2019.115668 [10] LI Tiansong, YU Li, WANG Shengwei, et al. Simplified depth intra coding based on texture feature and spatial correlation in 3D-HEVC[C]. 2018 Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, USA, 2018: 421. [11] SALDANHA M, SANCHEZ G, MARCON C, et al. Fast 3D-HEVC depth map encoding using machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(3): 850–861. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2898122 [12] FU Changhong, CHEN Hao, CHAN Y L, et al. Fast depth intra coding based on decision tree in 3D-HEVC[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 173138–173147. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956994 [13] SALDANHA M, SANCHEZ G, MARCON C, et al. Fast 3D-HEVC depth maps intra-frame prediction using data mining[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Canada, 2018: 1738–1742. [14] XU Mai, LI Tianyi, WANG Zulin, et al. Reducing complexity of HEVC: A deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(10): 5044–5059. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2847035 [15] TANG Genwei, JING Minge, ZENG Xiaoyang, et al. Adaptive CU split decision with pooling-variable CNN for VVC intra encoding[C]. 2019 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Sydney, Australia, 2019: 1–4. [16] 李雅婷, 杨静. 3D-HEVC深度图帧内预测快速编码算法[J]. 光电子·激光, 2020, 31(2): 222–228. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2020.02.0344LI Yating and YANG Jing. Fast intra coding algorithm for depth map in 3D-HEVC[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics Laser, 2020, 31(2): 222–228. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2020.02.0344 [17] XIE Saining and TU Zhuowen. Holistically-nested edge detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 125(1/3): 3–18. doi: 10.1007/s11263-017-1004-z [18] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–14. [19] Tanimoto Lab. Nagoya University multi-view sequences download list[EB/OL].https://www.fujii.nuee.nagoya-u.ac.jp/multiview-data/, 2017. [20] FENG Zeqi, LIU Pengyu, JIA Kebin, et al. Fast intra CTU depth decision for HEVC[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 45262–45269. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2864881 [21] JCT-3V. 3D-HEVC reference software[EB/OL]. https://mpeg.chiariglione.org/standards/mpeg-h/hevc-reference-software. [22] BJONTEGAARD G. Calculation of average PSNR differences between RD curves[C]. The 13th Video Coding Experts Group Meeting, Austin, USA, 2001: VCEG-M33. -





 下载:
下载:
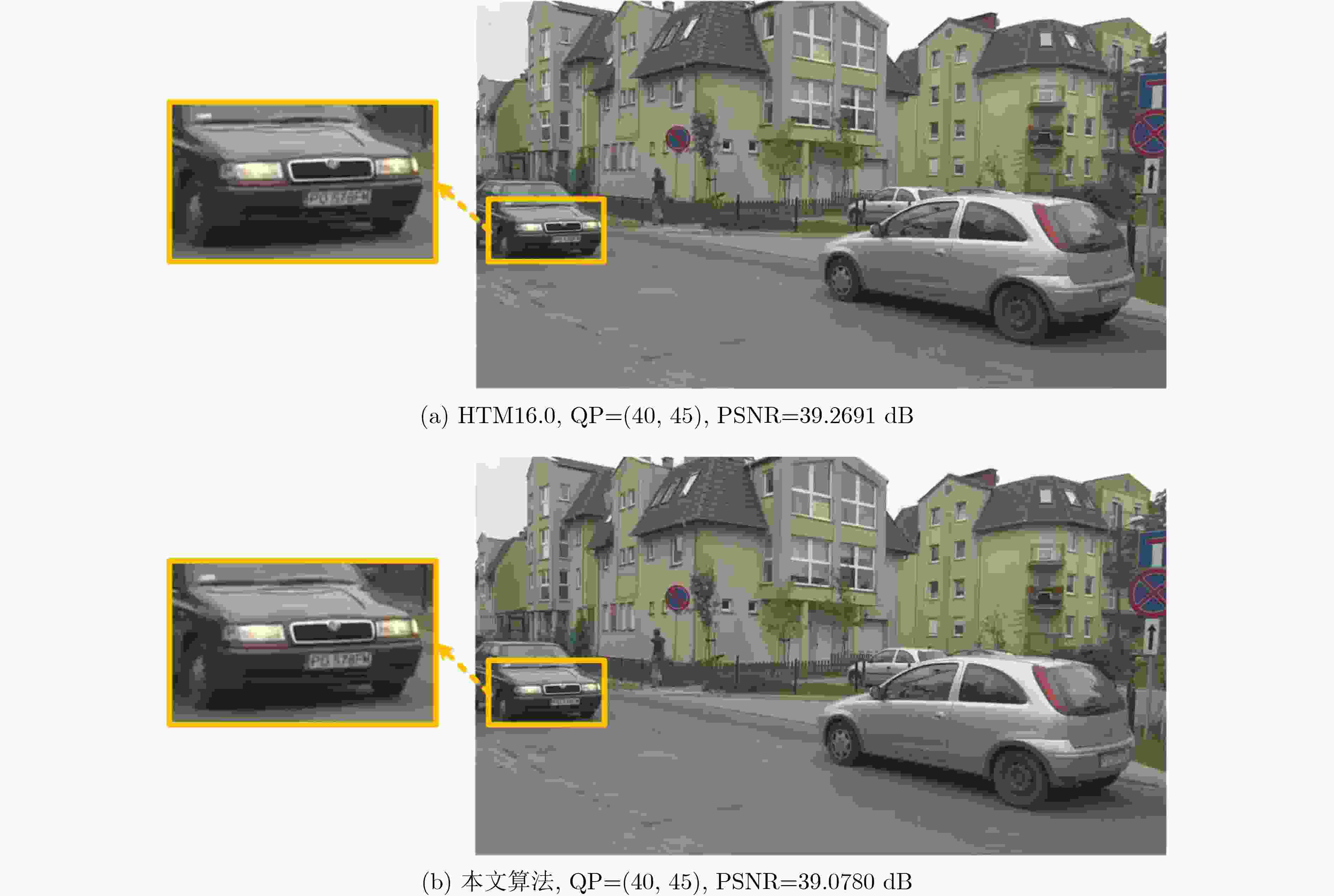

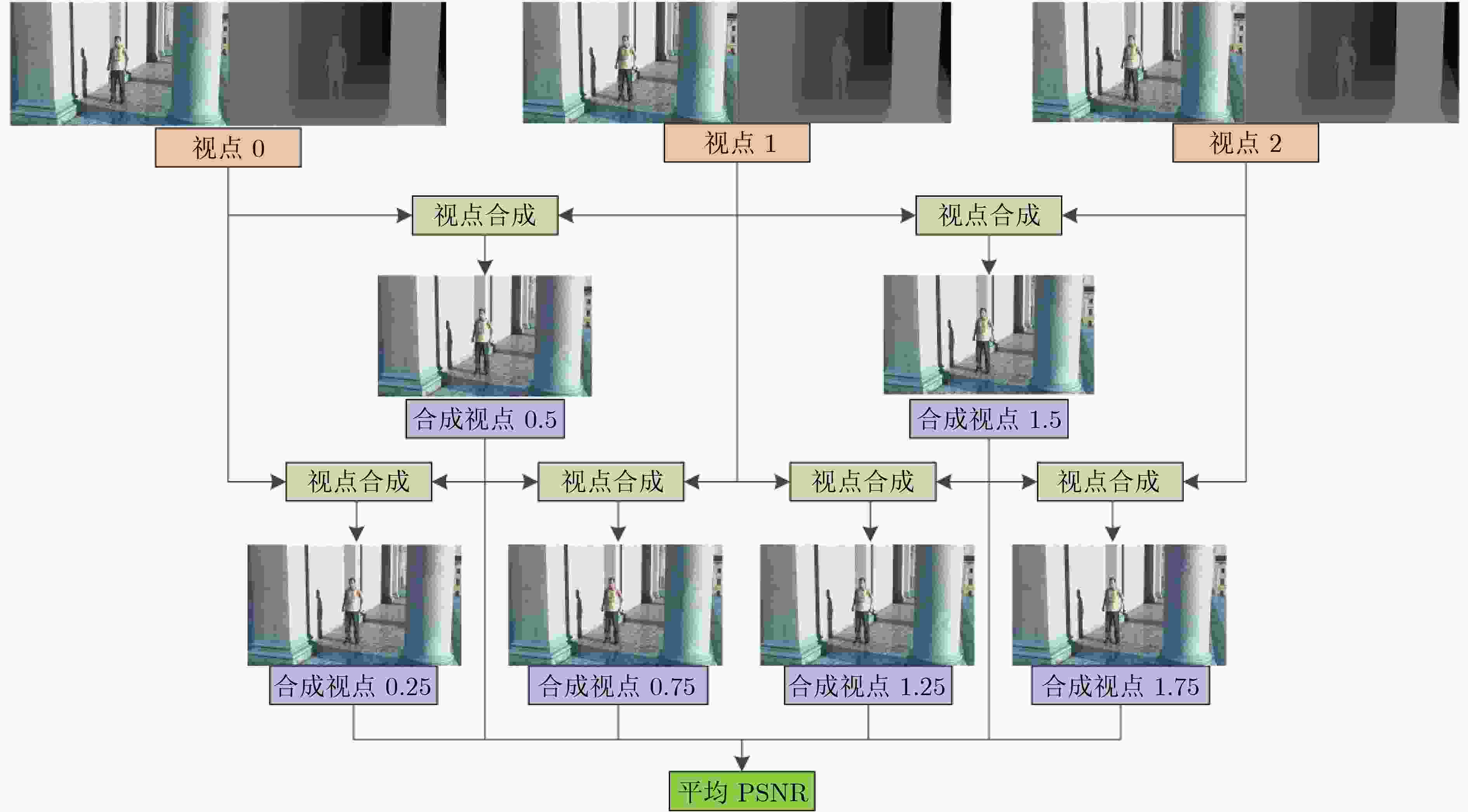
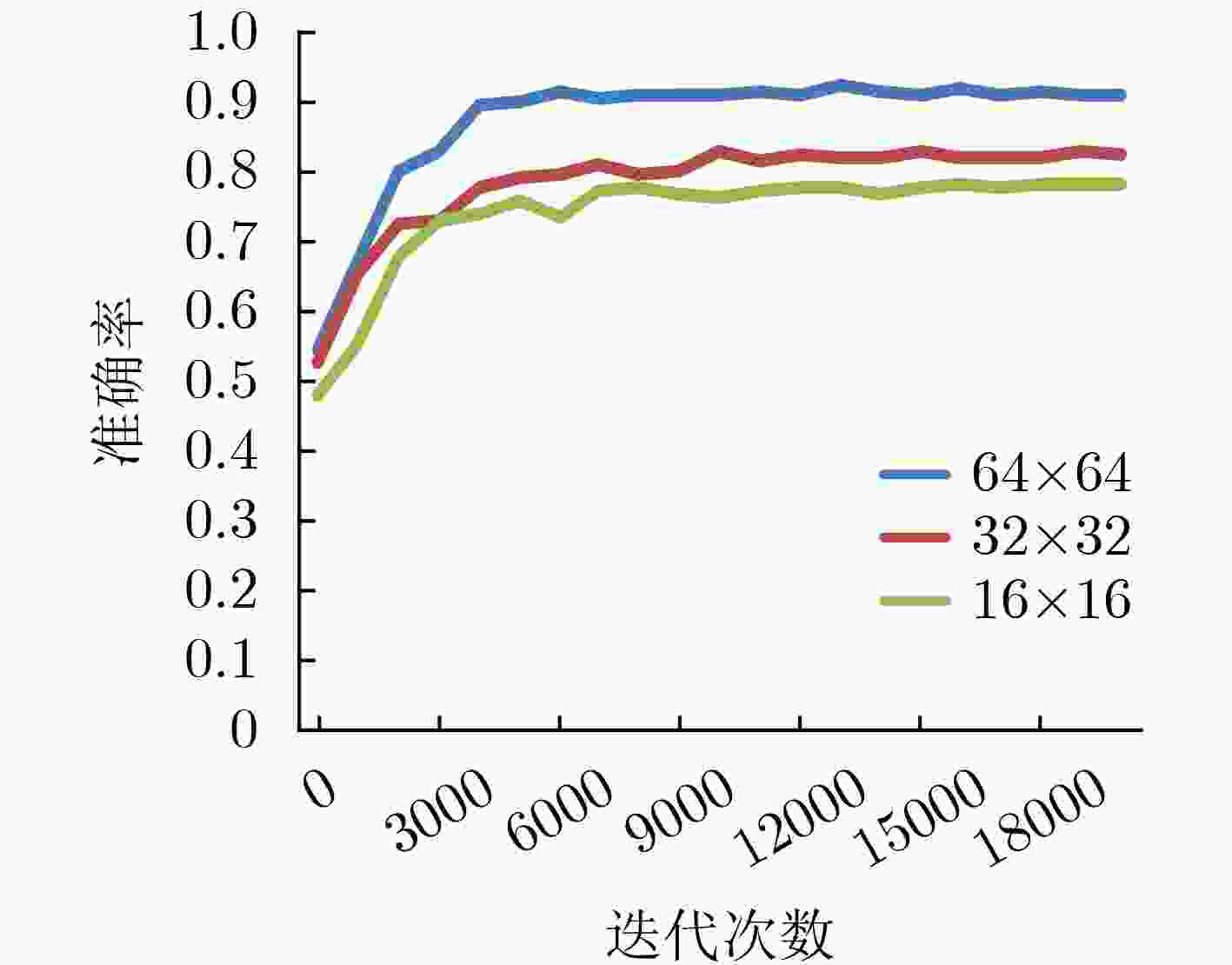



 下载:
下载:
