Research on Maneuvering State Recognition Method of Hypersonic Glide Vehicle
-
摘要: 高超声速滑翔飞行器(HGV)的迅猛发展改变了传统的作战样式,开辟了军事斗争的新领域。对HGV的机动状态进行识别可以为威胁评估、轨迹预测和防御决策提供有力支撑。为提高HGV机动状态识别精度,该文提出一种基于注意力机制的卷积长短时记忆网络识别模型(AT-ConvLSTM)。在对HGV进行机动建模和特性分析基础上,将HGV在空间的机动状态分为8类,构造了对应的特征识别参数,建立了包含不同初始条件和控制模式下HGV机动轨迹的轨迹库。推导了从雷达跟踪信息到特征识别参数的转换步骤,使用提出的状态识别模型对HGV机动轨迹的时空特征进行提取,并通过SoftMax分类器输出机动状态分类。最后,通过仿真实验对模型性能进行验证。结果表明,所提状态识别模型能够有效在线识别HGV机动状态,具有较好的实时性和准确性。Abstract: The rapid development of Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV) has changed the traditional combat style and opened a new field of military struggle. Identifying the maneuvering state of HGV can provide a powerful support for threat assessment, trajectory prediction and defense decision. In order to improve the accuracy of HGV maneuver state recognition, an HGV maneuver state recognition model based on ATtention Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory network (AT-ConvLSTM) is proposed. First, on the basis of maneuvering modeling and characteristic analysis of HGV, the maneuvering state of HGV in space is divided into eight categories, and the corresponding feature recognition parameters are constructed. A trajectory library containing HGV maneuvering trajectories under different initial conditions and control modes is established. Then, the conversion steps from radar tracking information to feature recognition parameters are deduced. The proposed state recognition model is used to extract the spatial features of HGV motion trajectory, and the maneuvering state is classified by the SoftMax classifier. Finally, the algorithm is verified by simulation experiments. The results show that the proposed method can effectively identify HGV maneuvering state online, which has good real-time and accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Hypersonic /
- Vehicle /
- State recognition /
- Deep learning /
- Maneuver modeling
-
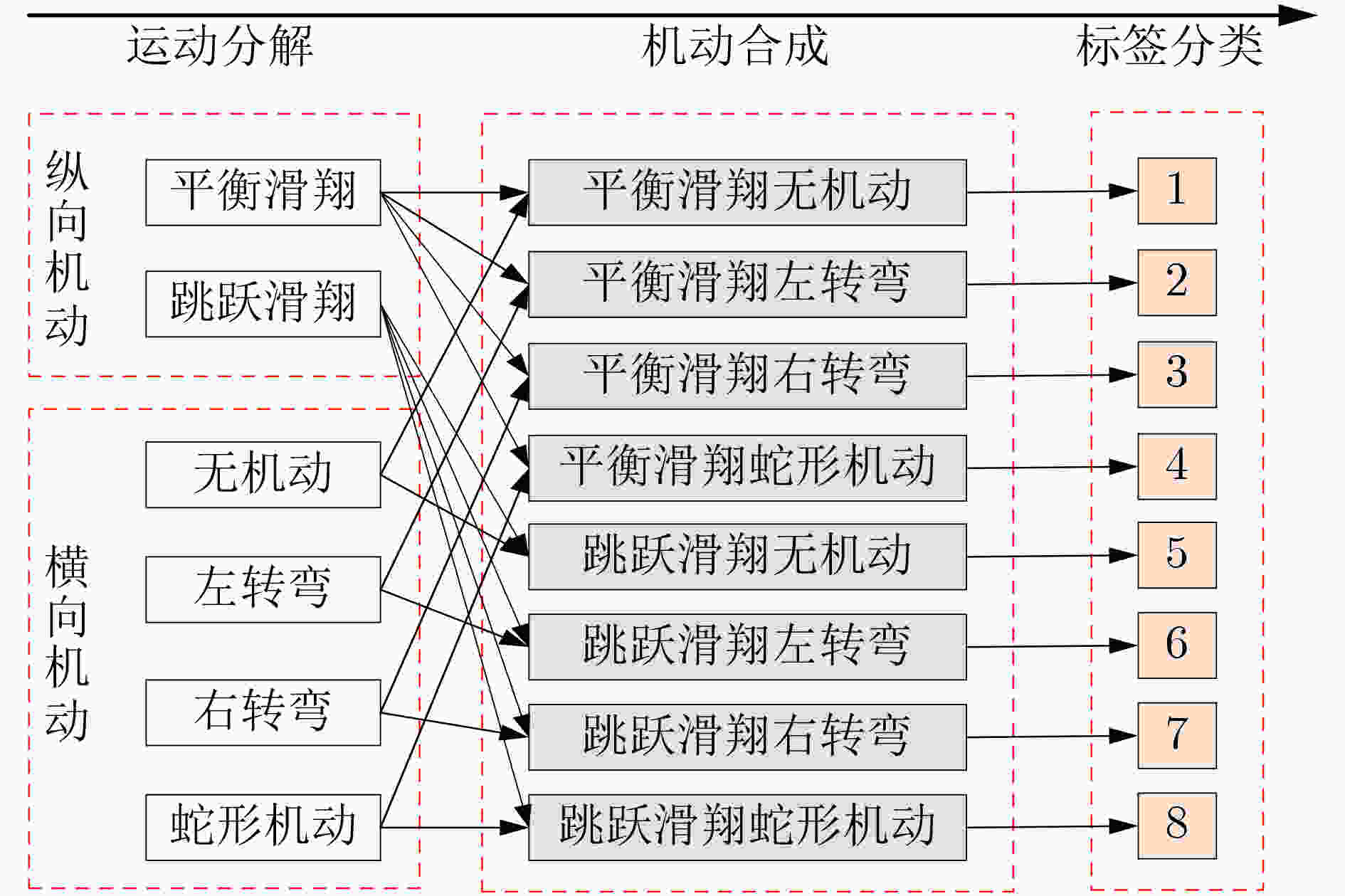
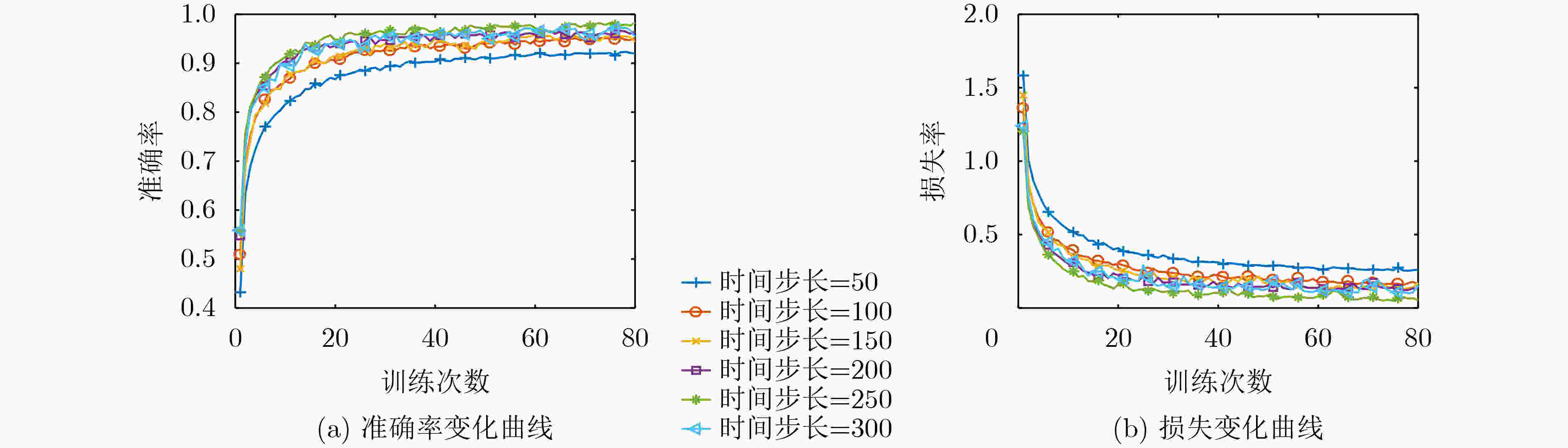
表 1 不同步长对应的模型训练结果
时间步长 精度(%) 训练集精度 验证集精度 50 92.36 91.25 100 95.97 94.68 150 96.13 95.54 200 97.41 96.32 250 98.59 97.75 300 97.98 97.04 表 2 模型精度对比
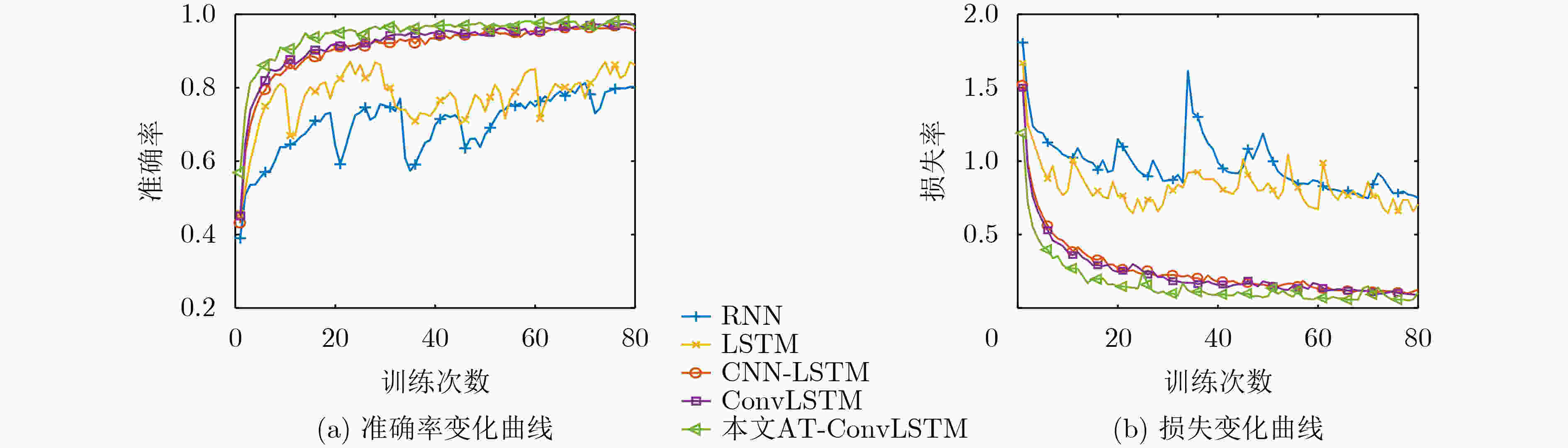
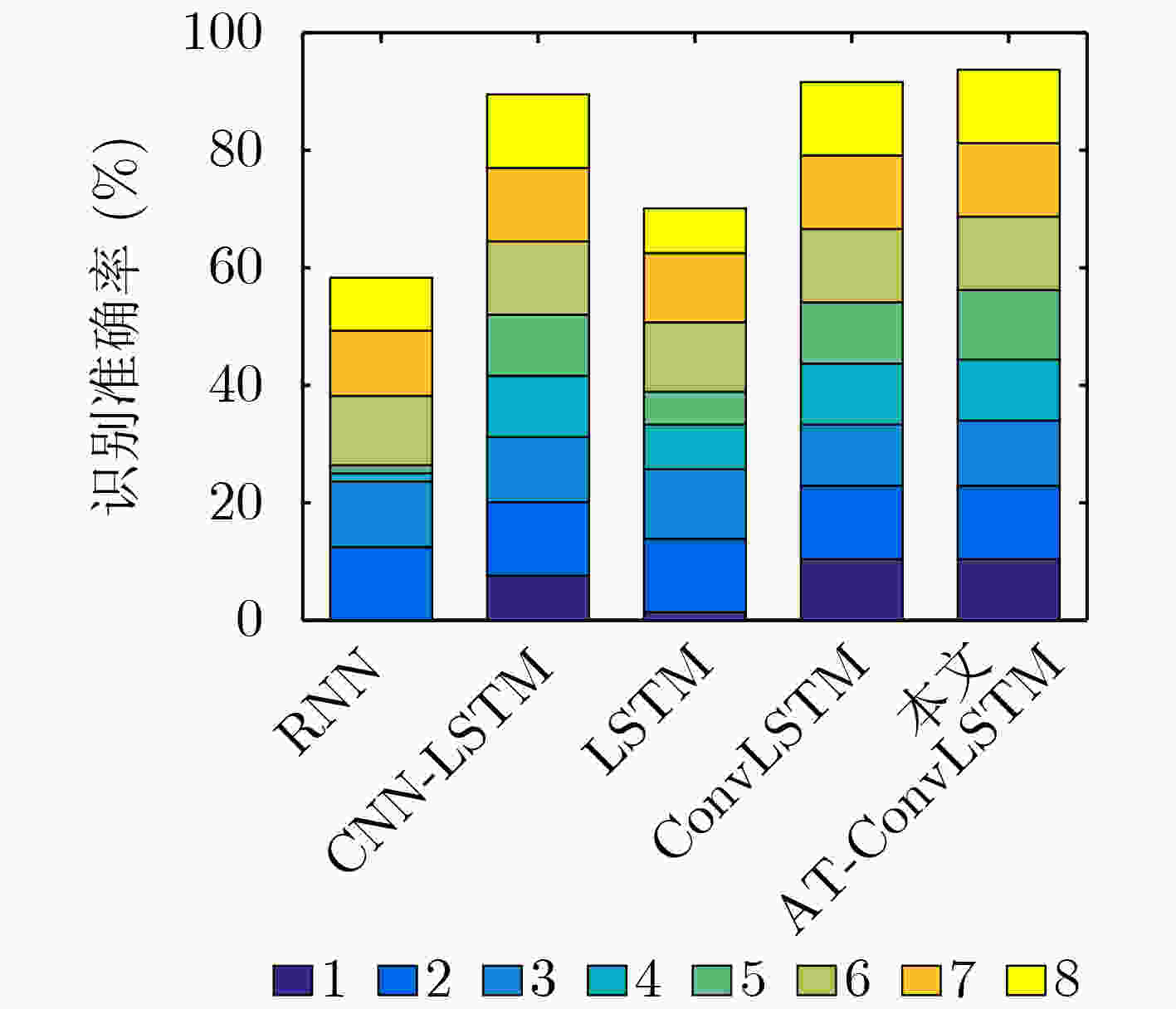
网络模型 精度(%) 训练集精度 验证集精度 RNN 80.51 77.51 LSTM 86.18 82.31 CNN-LSTM 97.33 96.79 ConvLSTM 98.06 97.41 本文AT-ConvLSTM 98.59 97.75 表 3 模型识别准确率(%)
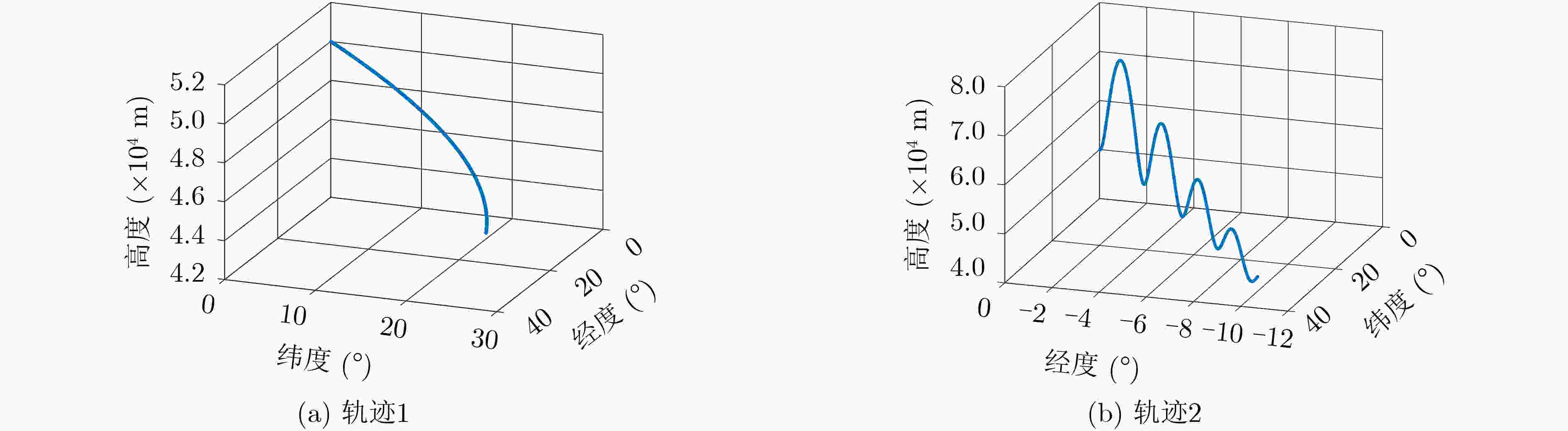
轨迹 CNN-LSTM ConvLSTM 本文AT-ConvLSTM LSTM RNN 轨迹1 89.44 90.00 91.67 88.89 87.22 轨迹2 90.00 91.11 92.78 73.33 66.67 表 4 模型识别准确率结果
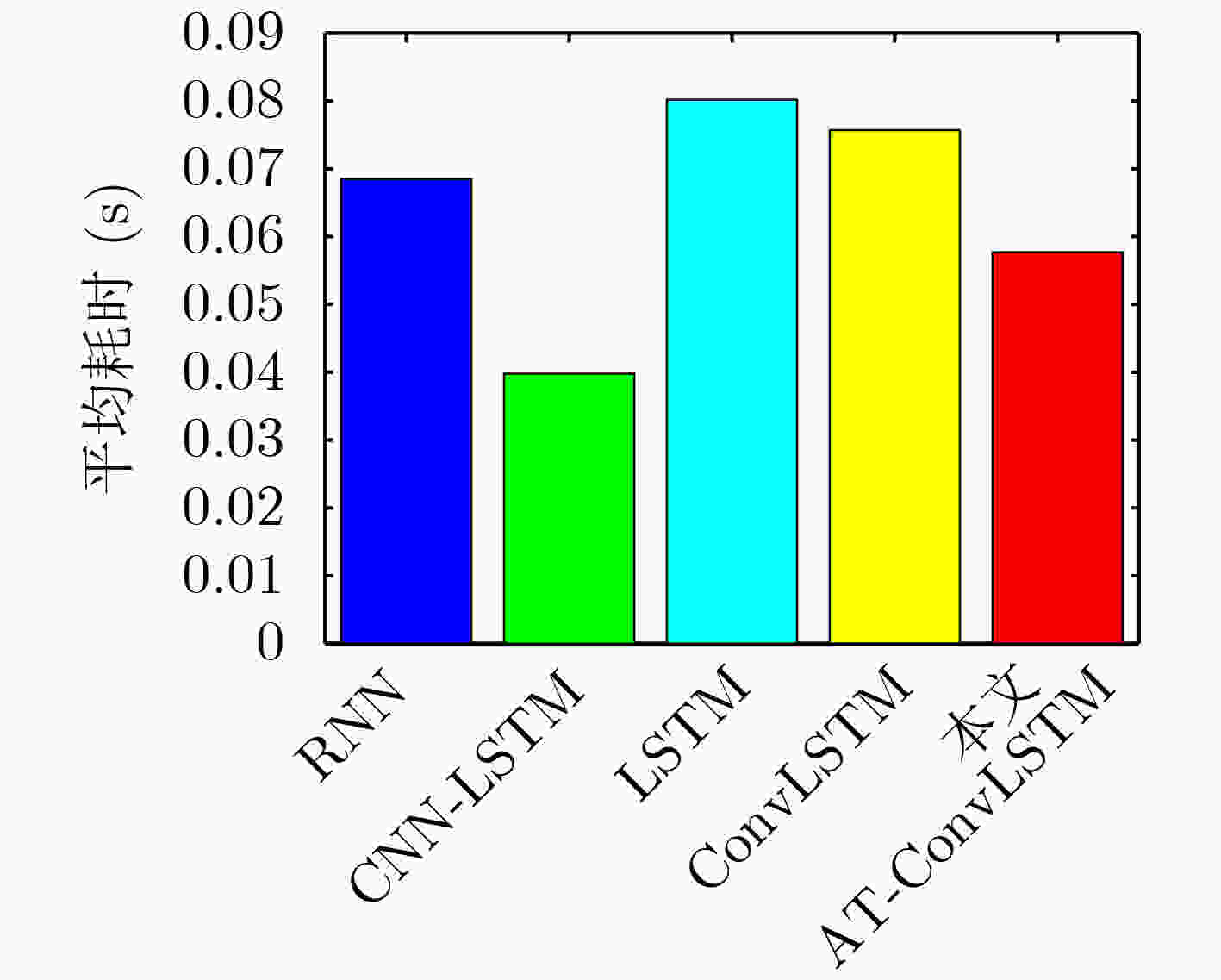
网络模型 错误点数/总点数 准确率(%) RNN 18000/43200 58.33 LSTM 12600/43200 71.53 CNN-LSTM 4500/43200 89.58 ConvLSTM 3600/43200 91.66 本文AT-ConvLSTM 3300/43200 92.36 -
[1] 王国宏, 李岳峰, 于洪波, 等. 三维空间中高超声速目标修正三级Hough变换-检测前跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 890–897. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170622WANG Guohong, LI Yuefeng, YU Hongbo, et al. Modified triple-stage Hough transform track-before-detect algorithm in three-dimensional space for hypersonic target[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 890–897. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170622 [2] 肖松, 谭贤四, 王红, 等. 地基雷达部署对探测临近空间高超声速目标影响研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(7): 1723–1728. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141024XIAO Song, TAN Xiansi, WANG Hong, et al. Detection performance assessment of near-space hypersonic target based on ground-based radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(7): 1723–1728. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141024 [3] WANG Yongjun, DONG Jiang, LIU Xiaodong, et al. Identification and standardization of maneuvers based upon operational flight data[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(1): 133–140. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2014.12.026 [4] MA Yanjun, ZHAO Shunyi, and HUANG Biao. Multiple-model state estimation based on Variational Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(4): 1679–1685. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2854897 [5] 孟光磊, 张慧敏, 朴海音, 等. 自动化飞行训练评估中的战机机动动作识别[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(7): 1267–1274. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0445MENG Guanglei, ZHANG Huimin, PIAO Haiyin, et al. Recognition of fighter maneuver in automatic flight training evaluation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(7): 1267–1274. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0445 [6] 徐西蒙, 杨任农, 于洋, 等. 基于运动分解和H-SVM的空战目标机动识别[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(5): 1265–1272. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.1210XU Ximeng, YANG Rennong, YU Yang, et al. Target maneuver recognition in air combat based on motion decomposition and H-SVM[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(5): 1265–1272. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.1210 [7] 熊邦书, 刘雨, 莫燕, 等. 基于SVM的直升机飞行状态识别[J]. 应用科学学报, 2016, 34(4): 469–474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0255-8297.2016.04.012XIONG Bangshu, LIU Yu, MO Yan, et al. Recognition of helicopter flight condition based on support vector machine[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2016, 34(4): 469–474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0255-8297.2016.04.012 [8] 张裕禄, 毕红葵, 叶泽浩, 等. 基于随机森林的HRGV滑翔段飞行状态识别[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2020(2): 1–8,21. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2020.9.142ZHANG Yulu, BI Hongkui, YE Zehao, et al. Flight state recognition of HRGV glide section based on random forest[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2020(2): 1–8,21. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.2020.9.142 [9] 周旺旺, 姚佩阳, 张杰勇, 等. 基于深度神经网络的空中目标作战意图识别[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(11): 322468–322476. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22468ZHOU Wangwang, YAO Peiyang, ZHANG Jieyong, et al. Combat intention recognition for aerial targets based on deep neural network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(11): 322468–322476. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22468 [10] 季学武, 费聪, 何祥坤, 等. 基于LSTM网络的驾驶意图识别及车辆轨迹预测[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6): 34–42. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.06.003JI Xuewu, FEI Cong, HE Xiangkun, et al. Intention recognition and trajectory prediction for vehicles using LSTM network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(6): 34–42. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.06.003 [11] 贾镇泽, 樊晓光, 薛明浩, 等. 基于机动动作元的敌机战术机动在线识别方法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(8): 820–827. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.08.009JIA Zhenze, FAN Xiaoguang, XUE Minghao, et al. Online identification method for tactical maneuver of target based on air combat maneuver element[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(8): 820–827. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.08.009 [12] ZHENG Tianyu, YAO Yu, HE Fenghua, et al. Active switching multiple model method for tracking a noncooperative gliding flight vehicle[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(9): 192202. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-1515-2 [13] FAUST O, SHENFIELD A, KAREEM M, et al. Automated detection of atrial fibrillation using long short-term memory network with RR interval signals[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2018, 102: 327–335. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.07.001 [14] 张君彪, 熊家军, 兰旭辉, 等. 基于自适应滤波的高超声速滑翔目标三维跟踪算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(2): 628–636. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.33ZHANG Junbiao, XIONG Jiajun, LAN Xuhui, et al. 3D tracking algorithm of hypersonic gliding target based on adaptive filtering[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 628–636. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.33 [15] LI Guanghua, ZHANG Hongbo, and TANG Gguojian. Maneuver characteristics analysis for hypersonic glide vehicles[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2015, 43: 321–328. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2015.03.016 [16] JOSHI A, SIVAN K, and AMMA S S. Predictor-corrector reentry guidance algorithm with path constraints for atmospheric entry vehicles[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2007, 30(5): 1307–1318. doi: 10.2514/1.26306 [17] 陈克俊, 刘鲁华, 孟云鹤. 远程火箭飞行动力学与制导[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014: 146–156.CHEN Kejun, LIU Luhua, MENG Yunhe. Launch Vehicle Flight Dynamics and Guidance[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2014: 146–156. [18] 王璐璐, 秦玉亮, 王宏强, 等. 飞行器升阻比估计误差分析方法研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2012, 10(2): 174–179,186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2012.02.011WANG Lulu, QIN Yuliang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Study on vehicle lift-to-drag ratio estimation error analysis method[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2012, 10(2): 174–179,186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2012.02.011 [19] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [20] SAJJAD M, KHAN S, HUSSAIN T, et al. CNN-based anti-spoofing two-tier multi-factor authentication system[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2019, 126: 123–131. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.02.015 [21] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [22] QING Xiangyun and NIU Yugang. Hourly day-ahead solar irradiance prediction using weather forecasts by LSTM[J]. Energy, 2018, 148: 461–468. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.177 [23] SHI Xingjian, CHEN Zhourong, WANG Hao, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation Nowcasting[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 802–810. [24] CHEN Zhenghua, WU Min, ZHAO Rui, et al. Machine remaining useful life prediction via an attention-based deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(3): 2521–2531. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2972443 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
