Robot Localization Based on Planned Path Constraints
-
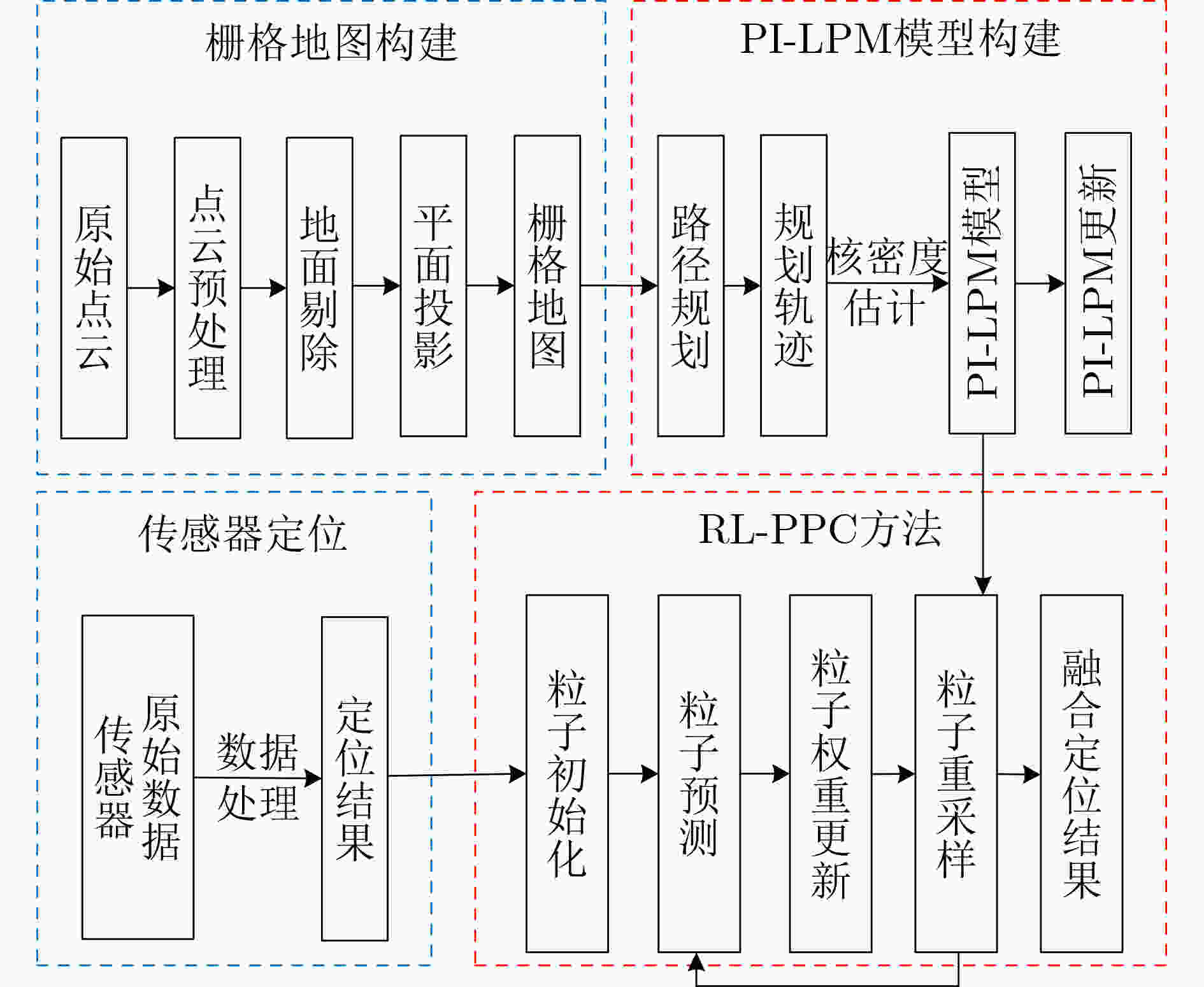
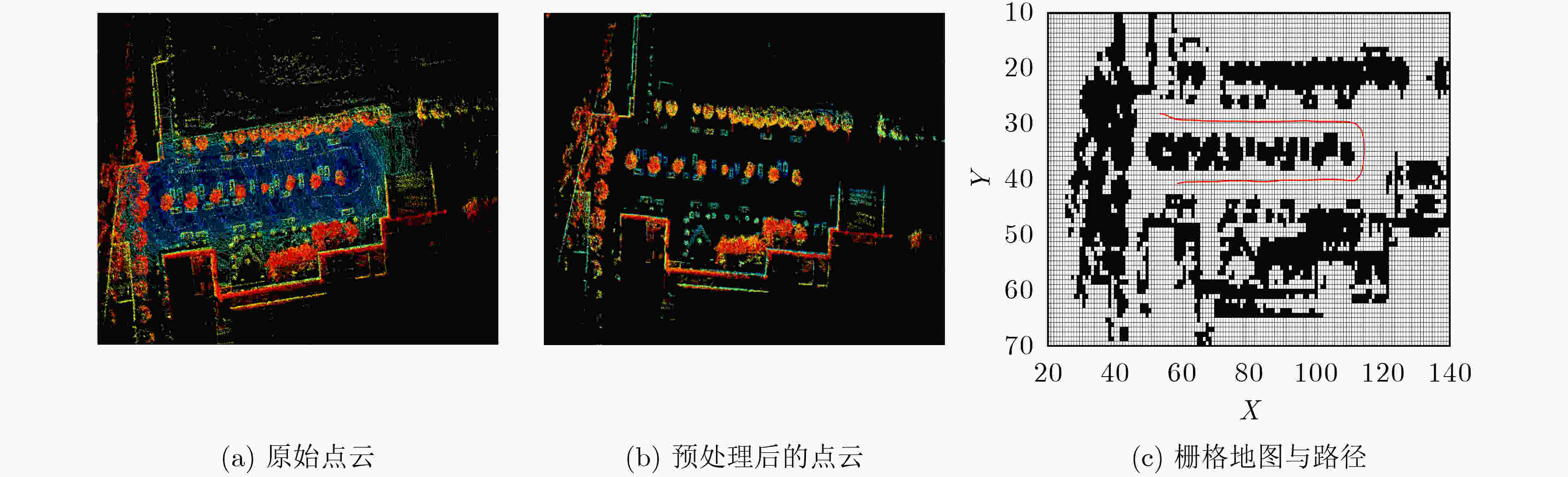
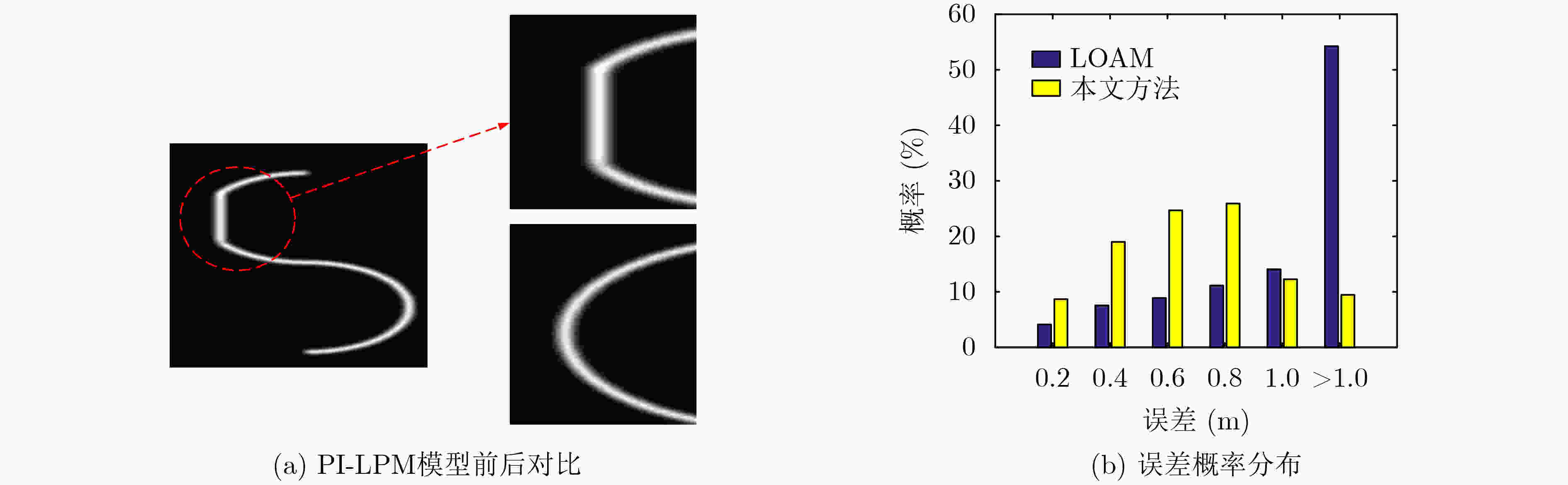
摘要: 路径规划是为机器人生成可行驶路径以实现循迹的过程。因此,机器人的位置应该位于或靠近规划的行驶路径。从而,路径规划可为机器人定位产生重要的约束。该文提出一种规划路径约束的位置概率图 (PI-LPM)模型,该模型通过概率来表征机器人在整个地图范围内所处的位置的可能性。其中,模型中概率密度函数是通过核密度估计 (KDE)方法从表征规划路径的所有数据点生成。在所提出的PI-LPM模型基础上,提出一种规划路径约束的机器人定位新算法 (RL-PPC)来提高机器人定位精度。在该方法中,应用粒子滤波算法来融合所提出的PI-LPM模型和已有的传感器定位方法。融合过程中,从PI-LPM模型中计算得到的概率是分配粒子权重的一个重要因素。实验中分别利用仿真数据和真实数据对所提出的模型与算法进行验证。实验结果表明,所提RL-PPC算法可有效融合PI-LPM模型与主流的定位系统(如GPS和LiDAR定位系统),并显著提高机器人定位的整体性能。Abstract: Path planning is a step to generate a feasible path for a robot to track along. Locations of the robot are supposed to lie on or at least nearby the planned path, which can thus generate important constraints for robot localization. In this paper, a model, called Path-Induced Location Probability Map (PI-LPM), to exploit such constraint on robot localization is proposed. The proposed PI-LPM model is a Probability Density Function (PDF) over the entire map with the probability to describe the likelihood that the robot is located. The PDF is generated from all the points representing the path by applying the Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) method with each point as a sampling point. Based on the PI-LPM model, a Robot Localization from Planned Path Constraints (RL-PPC) method to enhance robot localization is proposed. In this method, particle filter is applied to fuse the develop PI-LPM model and existing localization methods, where the probability from PI-LPM is an important factor to assign weights to the particles. The proposed method is validated with both simulation and real data. In the experiment, the proposed PI-LPM model is integrated into both GPS and LiDAR based localization systems. Experimental results demonstrate that the RL-PPC method can effectively improve the over-all performance of robot localization.
-
表 1 不同轨迹下RL-PPC方法定位误差对比
轨迹 最大误差(m) 平均误差(m) 误差1 m内概率(%) GPS RL-PPC GPS RL-PPC GPS RL-PPC 半椭圆 3.6545 2.0103 1.1822 0.5681 45.19 86.16 圆 3.6837 1.6219 1.1595 0.5316 44.78 88.57 “S”形 3.4489 1.9076 1.1742 0.6107 48.14 86.08 表 2 “S”形轨迹二次规划前后RL-PPC定位误差对比
轨迹 最大误差(m) 平均误差(m) 误差1 m内概率(%) 一次规划“S”形 1.9076 0.6107 86.08 二次规划“S”形 1.9044 0.6889 90.54 -
[1] 宿晨庚, 郭树人, 刘旭楠, 等. 北斗三号基本系统空间信号质量评估[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2689–2697. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190683SU Chengeng, GUO Shuren, LIU Xunan, et al. Signal quality assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2689–2697. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190683 [2] LEE B H, SONG J H, IM J H, et al. GPS/DR error estimation for autonomous vehicle localization[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(8): 20779–20798. doi: 10.3390/s150820779 [3] DU Xinxin and TAN K K. Vision-based approach towards lane line detection and vehicle localization[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2016, 27(2): 175–191. doi: 10.1007/s00138-015-0735-5 [4] VALIENTE D, GIL A, PAYÁ L, et al. Robust visual localization with dynamic uncertainty management in omnidirectional SLAM[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(12): 1294. doi: 10.3390/app7121294 [5] 胡钊政, 刘佳蕙, 黄刚, 等. 融合WiFi、激光雷达与地图的机器人室内定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2308–2316. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200671HU Zhaozheng, LIU Jiahui, HUANG Gang, et al. Integration of WiFi, laser, and map for robot indoor localization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2308–2316. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200671 [6] WON P, BIGLARBEGIAN M, and MELEK W. Development of an effective docking system for modular mobile self-reconfigurable robots using extended Kalman filter and particle filter[J]. Robotics, 2015, 4(1): 25–49. doi: 10.3390/robotics4010025 [7] WANG Fasheng, LIN Baowei, ZHANG Junxing, et al. Object tracking using langevin monte Carlo particle filter and locality sensitive histogram based likelihood model[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2018, 70: 214–223. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2017.07.023 [8] CAI Hao, HU Zhaozheng, HUANG Gang, et al. Integration of GPS, monocular vision, and high definition (HD) map for accurate vehicle localization[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3270. doi: 10.3390/s18103270 [9] 曹祥红, 李欣妍, 魏晓鸽, 等. 基于Dijkstra-ACO混合算法的应急疏散路径动态规划[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1502–1509. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190854CAO Xianghong, LI Xinyan, WEI Xiaoge, et al. Dynamic programming of emergency evacuation path based on Dijkstra-ACO hybrid algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1502–1509. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190854 [10] YANG Hui, QI Jie, MIAO Yongchun, et al. A new robot navigation algorithm based on a Double-Layer ant algorithm and trajectory optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(11): 8557–8566. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2886798 [11] 李东方, 李科伟, 邓宏彬, 等. 基于人工势场与IB-LBM的机器蛇水中2D避障控制算法[J]. 机器人, 2018, 40(3): 346–359. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.170421LI Dongfang, LI Kewei, DENG Hongbin, et al. The 2D aquatic obstacle avoidance control algorithm of the Snake-Like Robot based on artificial potential field and IB-LBM[J]. Robot, 2018, 40(3): 346–359. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.170421 [12] SHAN Tixiao and ENGLOT B. LeGO-LOAM: Lightweight and ground-optimized Lidar Odometry and mapping on variable terrain[C]. 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018: 4758–4765. [13] 叶珏磊, 周志峰, 王立端, 等. 一种多线激光雷达与GNSS/INS系统标定方法[J]. 激光与红外, 2020, 50(1): 30–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.01.006YE Juelei, ZHOU Zhifeng, WANG Liduan, et al. A calibration method of Lidar and GNSS/INS system[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2020, 50(1): 30–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.01.006 [14] 王任栋, 李华, 赵凯, 等. 基于核密度估计的城市动态密集场景激光雷达定位[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(5): 0528003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0528003WANG Rendong, LI Hua, ZHAO Kai, et al. Robust localization based on kernel density estimation in dynamic diverse city scenes using Lidar[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 0528003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0528003 [15] BI Haiyun, MA Jianwen, and WANG Fangjian. An improved particle filter algorithm based on ensemble Kalman filter and Markov chain monte Carlo method[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(2): 447–459. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2322096 [16] 刘海涛, 林艳明, 陈永华, 等. 基于遗传算法的智能粒子滤波重采样策略研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3459–3466. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200561LIU Haitao, LIN Yanming, CHEN Yonghua, et al. A study on resampling strategy of intelligent particle filter based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3459–3466. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200561 [17] 徐公国, 单甘霖, 段修生, 等. 基于马尔科夫决策过程的多传感器协同检测与跟踪调度方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2201–2208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181129XU Gongguo, SHAN Ganlin, DUAN Xiusheng, et al. Scheduling method based on Markov decision process for multi-sensor cooperative detection and tracking[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2201–2208. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181129 [18] ZHANG Ji and SINGH S. LOAM: Lidar Odometry and mapping in real-time[C]. Robotics: Science and Systems, Berkeley, USA, 2014: 1–10. -





 下载:
下载:



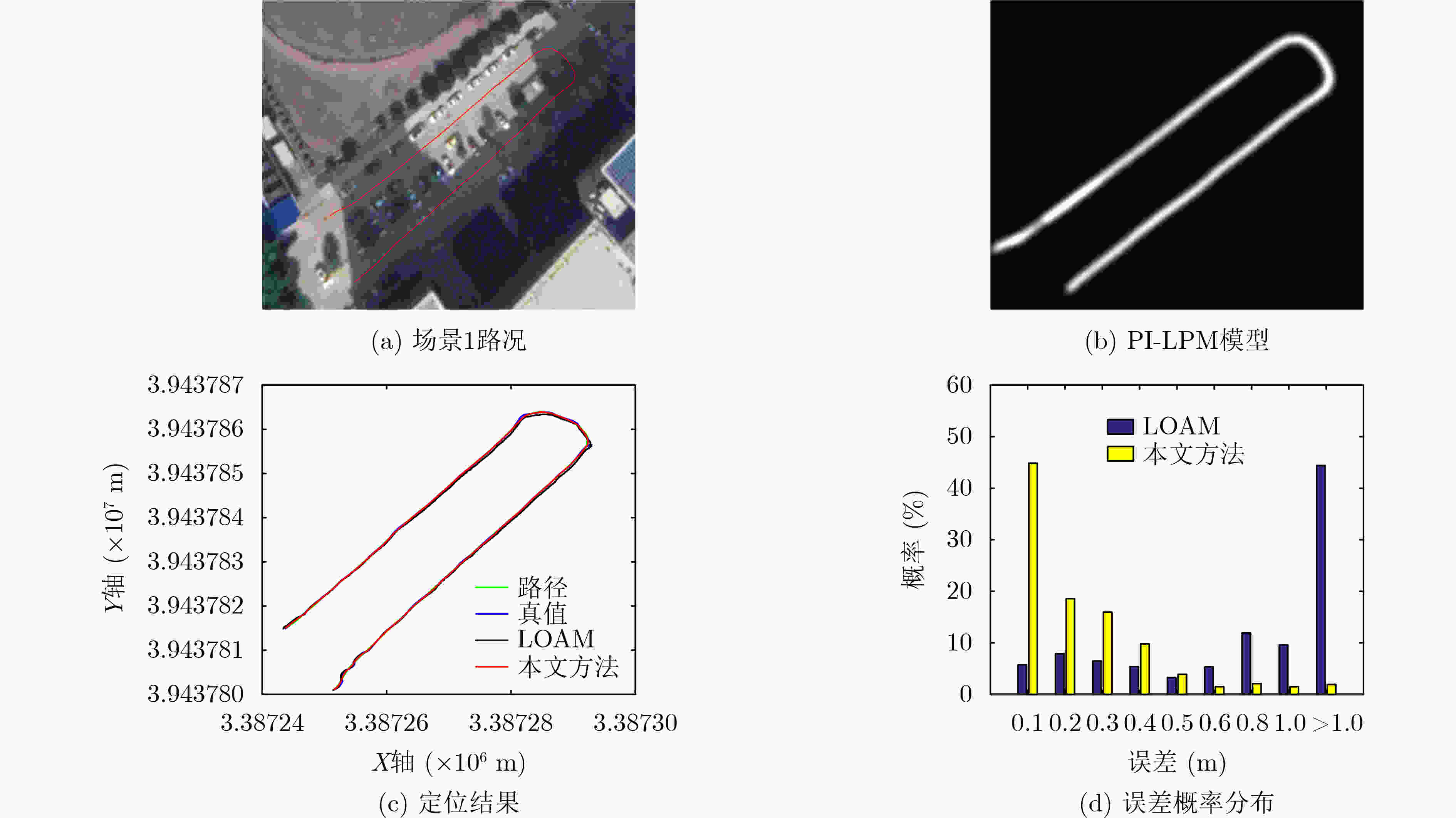
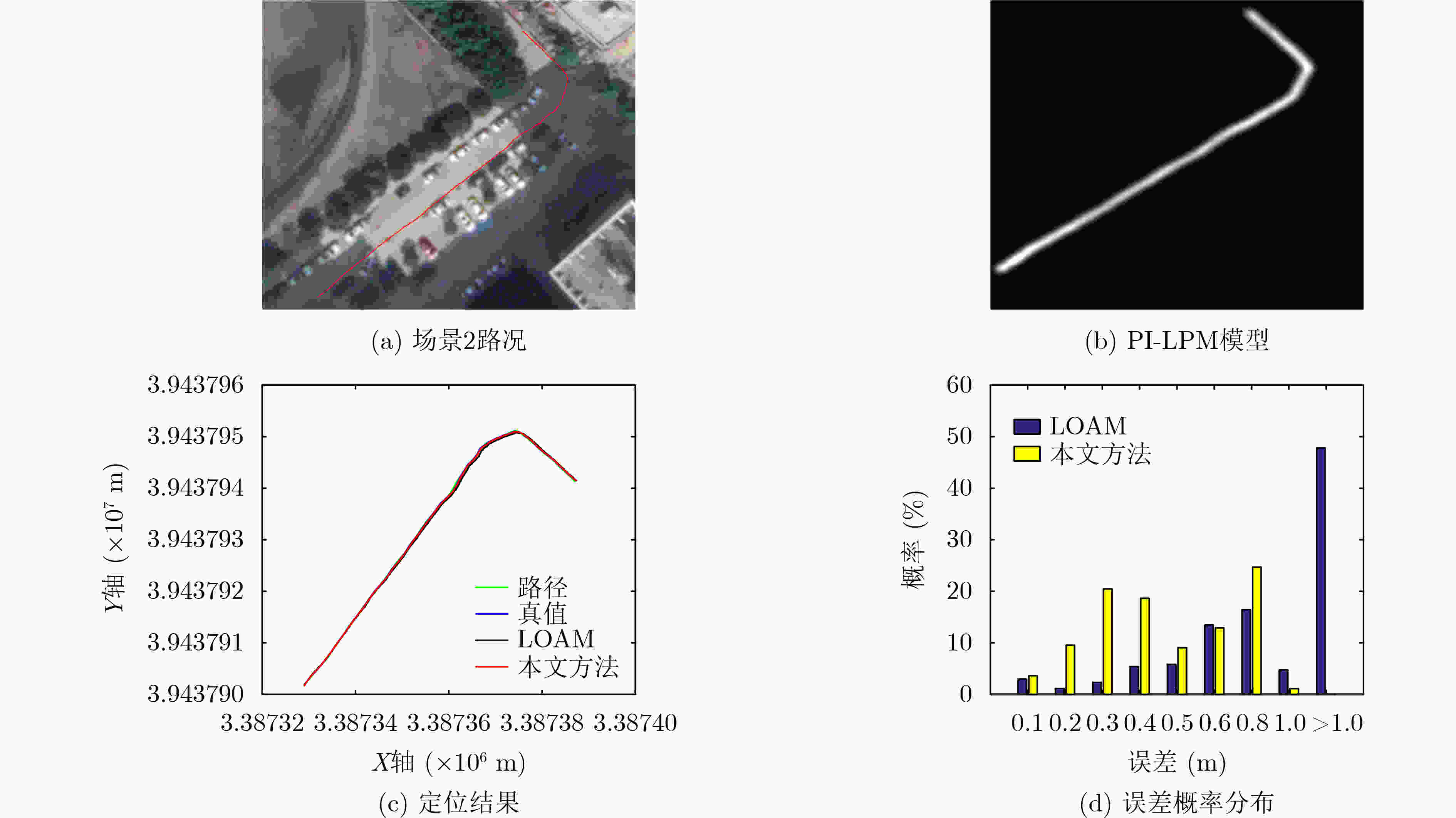
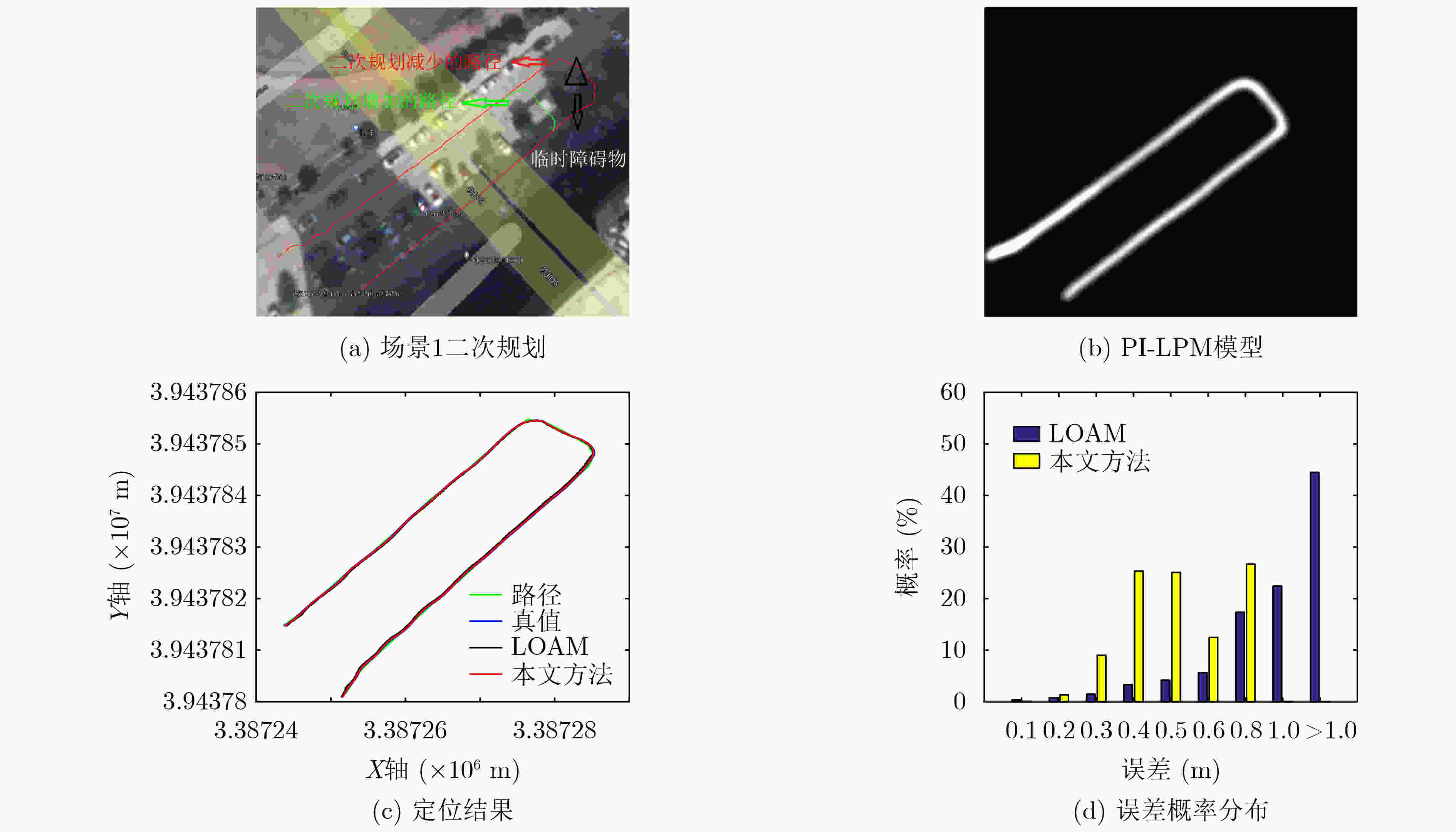


 下载:
下载:
