Research Progress Analysis of Point Cloud Segmentation Based on Deep Learning
-
摘要: 深度传感器及激光扫描技术的快速发展使人们可以轻易地采集到大量的点云数据。点云数据可以提供丰富的场景及对象信息,现已成为自动驾驶、虚拟现实、机器人导航等应用的首选研究对象。作为点云处理的有效手段,点云分割技术受到了各界的广泛关注。尤其是在深度学习的推动下,点云分割的精度和鲁棒性有了很大的提升。该文首先介绍了点云分割存在的问题与挑战,接着从间接、直接处理点云的角度对点云分割近年来的工作进行了对比分析,其中,间接的方法有基于多视图、基于体素的方法两类,对于直接的方法,该文将其归纳为5类,分别为基于点处理、基于优化卷积神经网络、基于图卷积、基于时序和基于无监督学习的方法。然后介绍了每个类别中具有代表性的方法的基本思想,并阐述了每个方法的优缺点。此外,该文还介绍了点云分割的常用数据集以及评价指标。最后对点云分类、分割技术的未来进行了展望。Abstract: The rapid development of depth sensor and laser scanning technology allows people to collect easily a large amount of point cloud data. Point cloud data can provide rich scene and object information, and has become the preferred research object for applications such as autonomous driving, virtual reality, and robot navigation. As an important research method, point cloud segmentation has received extensive attention from industry and academia. Especially driven by deep learning, the effect of point cloud segmentation has been significantly improved. In order to stimulate future research, the latest progress in point cloud segmentation are comprehensively reviewed , and comparative studies are conducted from the perspective of indirect and direct processing of point clouds. Among them, the method based on indirect processing can be divided into the multi-view and voxel-based method. The method based on direct processing can be divided into point processing, optimized convolutional neural networks , graph convolution, timing and unsupervised learning. Then the basic ideas and characteristics of the representative methods are introduced in each category. In addition, the common data sets and evaluation indexes of point cloud segmentation are sorted out. Finally, the future of point cloud classification and segmentation technology is prospected.
-
Key words:
- Deep learning /
- Point cloud /
- Point cloud segmentation /
- Progress analysis
-
图 3 SpiderCNN的网络结构[42]
图 4 无监督域适应点云分类网络模型[61]
表 1 基于视图的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 MVCNN[25] 2017 对同一个3维形状的每一个视角通过独立的卷积网络提取特征,通过池化聚合特征 利用传统的2维图像卷积网络训练模型,于3维点云学习具有启发性意义 SnapNet[26] 2017 针对RGB图像使用全卷积网络进行像素标记,同时将3D点云数据对空间中的点进行标记 跨模态结合RGB图像与点云数据 PVRNet[27] 2018 直接处理点云数据得到点云特征,同时利用卷积提取点云多视图特征,将两个特征融合进行点云学习 融合点云和视图数据来进行3D形状识别 MVD[28] 2021 从数据分布的角度,基于立面对象的特征构建了一个新的分层网格多视图数据域,实现深度学习模型和先验知识的融合 将不同的信息应用于网络中 文献[29] 2021 利用场景视点偏移预测模块从多视图中过滤冗余视图 点云变换引起的信息丢失和遮挡问题 VMF[30] 2020 选择不同虚拟视图的3D网格和渲染多个2D通道训练模型 将虚拟视图与真实视图融合 SVPC[17] 2020 将语义注释从合成模型转移到单视点云,用指导模型与点云建立匹配关系,最终将注释从指导模型转移至输入点云 代替多视图,使用单视图实现点云的局部分割 表 2 基于体素的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 3D ShapeNet[31] 2015 将几何3D形状表示为3D体素网格上2元变量的概率分布,通过视图规划进行目标激活 支持联合目标识别,同时构建了大型CAD数据集 3DCNN[32] 2017 使用随机体素填充网格,并利用3D卷积进行点云标记 提供了在3D网络的体素化,有效处理大数据 3DMV[33] 2018 从RGB图像中提取特征,使用可微后向投影层将这些特征映射到体素特征网格中 将RGB数据与几何数据组合在端到端的联合网络架构中 Pointgrid[34] 2019 设计了一种包含恒定数量点的网格,可以用于3D卷积 更好地表达尺度变化,减少了信息丢失 LP-3DCNN[35] 2019 设计了局部相量模块代替3D卷积在3D局部邻域内提取输入特征图每个位置的相,获取特征图 大幅度缩小了体素卷积的计算量,同时提高了点云分类的性能 GV-CNN[18] 2020 结合了基于点的图和体素表示以增强空间上下文和局部的特征提取能力 将基于点的图和体素相结合进行卷积 文献[36] 2020 提出了轻量级的稀疏点体素卷积,利用神经架构搜索在搜索空间中自动快速筛选出最优的网络结构 将神经架构搜索与体素卷积相结合 文献[15] 2021 提出了一种统一的、分层的方法构建点云特征,设计多尺度的自下而上的体素特征聚合 自上而下的方式提取多尺度体素信息,将空间金字塔池化应用到点云中 表 3 基于点处理的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 PointNet[10] 2017 对称函数解决了点云无序性问题 点云数据直接处理的先驱 PointNet++[16] 2017 使用分层的思想处理点云数据,利用空间距离对点集局部区域进行特征迭代提取,自适应密度特征提取 分区域提取点云的特征,考虑点云数据的局部特征 SCNet[37] 2018 利用多个子区间填充点云形状,构建区间之间的关联矩阵,之后聚合相关点的特征,完成特征提取 保证性能的同时减少了空间开销 文献[38] 2021 采用共享权重的多层感知器获取自适应注意力权重 有效解决点云特征获取和无序性问题 GCA-Conv[39] 2020 分解局部点集来生成表示全局形状特征的锚点,并转换为最终的旋转不变特征 将输入点云的全局上下文信息集成到卷积来增强特征区分 PAConv[40] 2021 提出了位置自适应卷积,通过动态组装基本权重矩阵来构建卷积核,从点位置自适应学习特征 通过位置信息,应用自适应卷积 SGAS[41] 2019 以顺序贪婪的方式选择和删除候选操作 将神经架构搜索技术和点云学习结合 表 4 基于卷积的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 SpiderCNN[42] 2018 参数化一系列基于泰勒多项式的卷积滤波器,将卷积运算从规则的栅格扩展到可嵌入的不规则点集 利用可解释的泰勒多项式和简单阶跃函数设计卷积单元 Pointwise[43] 2018 针对不规则点云使用固定大小的卷积核,对卷积核内的点都和权重相乘得出卷积核的平均值 逐点进行卷积,所以卷积核会将每一个点都作为中心 A-CNN[44] 2019 在计算中指定环形结构和方向,并针对点云特征学习设计了一种环卷积 环卷积避免了重叠,更好地捕捉每个点的局部邻域几何 文献[45] 2021 提出局部关系卷积来自适应产生卷积核 提高了网络对局部形状变化感知的鲁棒性 RS-CNN[46] 2019 使用点云的形状关系数据,利用多层感知机网络,学习出携带着点云形状关系信息的卷积核参数 从几何关系中推理学习 3D 形状 DensePoint[47] 2019 将CNN扩展到不规则点配置卷积算子,将密集的不同层的不同感受野处理得到的信息进行聚合增强卷积效果 引入上下文信息更好地完成点云形状识别 PointConv[48] 2019 将卷积核看作由权函数和密度函数组成的3维点的局部坐标的非线性函数 在3维空间中任意点集上,学习的卷积核可用于计算平移不变卷积和置换不变卷积 3D-GCN[49] 2020 定义了具有图最大池化机制的可学习内核;在从跨尺度的点云中提取局部 3D 特征 保持平移和尺度不变性属性 PatchCNN[50] 2021 每个点上的卷积权重被视为由多层感知器和局部区域中的集成特征近似的 Lipschitz 连续函数 集成的特征编码了几何关系和周围点的影响,带来了足够的形状意识和鲁棒性 表 5 基于图卷积的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 KCNet[51] 2018 将点集内核定义为一组可学习的3D点,在最近邻图上聚合重复特征,充分利用局部高维特征结构 能够有效地捕获局部信息,算法更加稳健,性能得到提升 GACNet[52] 2018 将每个点与其周围点构建一个图结构,在计算中心点与其周围点的边缘权重时,引入注意力机制,差异化点与点之间的联系性 将图卷积注意力与点云任务结合,利用注意力学习边权重来代替固定权重 HGNN[53] 2019 利用超图结构表征非欧几何数据中的信息传播,超边关注多个点之间的联系性 提高了超图用于点云分割的精度 DHGNN[54] 2019 设计了超图卷积,利用动态图构造和超图卷积动态地编码信息 更为灵活的动态超图模型 Grid-GCN[55] 2020 使用覆盖感知网格查询,提高空间覆盖率并减少了运行时间 借助网格上下文聚合模块实现特征融合 表 6 基于时序点云分割的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 Spacial-Context[56] 2017 利用多尺度的点块和网格块来获取输入级上下文,并逐块提取特征输入到综合单位或循环综合单位来获取输出级上下文 首次利用点云的上下文信息 RS-Net[14] 2018 轻量级的局部依赖性建模模块,并利用分片池化层将无序的点特征集变成一个有序的特征向量序列 有效建模局部点云的局部结构并减少了计算量 文献[57] 2018 逐点级金字塔池化模块捕获不同尺度的局部上下文信息 结合了RNN的时序信息与局部上下文 DARNet[58] 2019 自适应的感受域,提供可变的半局部感受野和权重,连接局部卷积特征提取器和全局循环特征聚合器的桥梁 既考虑了场景的复杂结构也结合了局部几何特征 文献[59] 2019 融合了3D卷积神经网络、深层Q网络和残差递归神经网络,可以有效地定位和分割对象类别的点 提高了大规模点云语义解析效率 表 7 基于无监督点云分割的主要工作
方法名称 年份 关键思想 特点 PointDAN[60] 2019 多层次联合全局和局部特征,设计了自适应节点模块,用于对齐域的判别性局部结构,利用对抗策略实现全局特征对齐 利用现有的经典数据集设计了点云域适应数据集,为后续的工作做了铺垫 MAP-VAE[61] 2019 从每个角度将一个点云分割成前半部分和后半部分,使网络能从相应的前半部分序列中预测后半部序列 启用全局和局部几何的学习共同利用全局与本地的监督,增强了学习特征的可辨识性 文献[62] 2020 将输入点云编码为一组局部特征。然后将局部特征通过一种新颖的点集成模块生成一组3D结构点。采用倒角距离作为重构损失,保证结构点靠近输入点云 该方法生成的3D结构点对形状结构进行了内在编码,并在所有结构相似的形状实例中表现出语义一致性 3DAAE[63] 2020 扩展了一个深度对抗式自动编码器模型来接受3D输入和输出,对潜在空间的对抗训练学习有意义的紧凑二值描述符 允许学习一个潜在的表示空间,并从中生成3D形状 GLBR[64] 2020 从单个部分推断整个对象,网络能够表示应该建模的属性之间共享的部分和整个对象,并区别于其他对象 在不需要人工监督的情况下双向推理来习点云的表示 -
[1] 王肖锋, 张明路, 刘军. 基于增量式双向主成分分析的机器人感知学习方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(3): 618–625. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170561WANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Minglu, and Liu Jun. Robot perceptual learning method based on incremental bidirectional principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(3): 618–625. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170561 [2] 周汉飞, 李禹, 粟毅. 利用多角度SAR数据实现三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(10): 2467–2474. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01534ZHOU Hanfei, LI Yu, and SU Yi. Three-dimensional imaging with multi-aspect SAR data[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(10): 2467–2474. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01534 [3] QI C R, LIU Wei, WU Chenxia, et al. Frustum pointnets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 918–927. [4] 陈境焕, 李海艳, 林景亮. 基于深度学习的零件点云分割算法研究[J]. 机电工程, 2020, 37(3): 326–331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2020.03.020CHEN Jinghuan, LI Haiyan, and LIN Jingliang. Part point cloud segmentation algorithm based on deep learning[J]. Mechanical &Electrical Engineering, 2020, 37(3): 326–331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2020.03.020 [5] KLOKOV R and LEMPITSKY V. Escape from cells: Deep kd-networks for the recognition of 3D point cloud models[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 863–872. [6] CHEN Xuzhan, CHEN Youping, and NAJJARAN H. 3D object classification with point convolution network[C]. 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 783–788. [7] HU Qingyong, YANG Bo, XIE Linhai, et al. RandLA-Net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11105–11114. [8] CHEN Xiaozhi, MA Huimin, WAN Ji, et al. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6526–6534. [9] ZHOU Dingfu, FANG Jin, SONG Xibin, et al. Joint 3D instance segmentation and object detection for autonomous driving[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1836–1846. [10] QI C R, SU Hao, MO Kaichun, et al. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77–85. [11] LI Ruihui, LI Xianzhi, HENG P A, et al. PointAugment: An auto-augmentation framework for point cloud classification[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6377–6386. [12] GADELHA M, WANG Rui, and MAJI S. Multiresolution tree networks for 3D point cloud processing[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 105–122. [13] GRAHAM B, ENGELCKE M, and VAN DER MAATEN L. 3D semantic segmentation with submanifold sparse convolutional networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9224–9232. [14] HUANG Qiangui, WANG Weiyue, and NEUMANN U. Recurrent slice networks for 3D segmentation of point clouds[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2626–2635. [15] KUMAR K S C and AL-STOUHI S. Multi-scale voxel class balanced ASPP for LIDAR pointcloud semantic segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Waikola, USA, 2021: 117–124. [16] QI C R, YI Li, SU Hao, et al. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105–5114. [17] PENG Haotian, ZHOU Bin, YIN Liyuan, et al. Semantic part segmentation of single-view point cloud[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(12): 224101. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9689-9 [18] ZHANG Jinming, HU Xiangyun, and DAI Hengming. A graph-voxel joint convolution neural network for ALS point cloud segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 139781–139791. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013293 [19] SU Hang, JAMPANI V, SUN Deqing, et al. SPLATNet: Sparse lattice networks for point cloud processing[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2530–2539. [20] 秦彩杰, 管强. 三维点云数据分割研究现状[J]. 宜宾学院学报, 2017, 17(6): 30–35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5365.2017.06.007QIN Caijie and GUAN Qiang. Research status of 3D point cloud data segmentation[J]. Journal of Yibin University, 2017, 17(6): 30–35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5365.2017.06.007 [21] CUI Yaodong, CHEN Ren, CHU Wenbo, et al. Deep learning for image and point cloud fusion in autonomous driving: A review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(2): 722–739. [22] ZHANG Jiaying, ZHAO Xiaoli, CHEN Zheng, et al. A review of deep learning-based semantic segmentation for point cloud[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 179118–179133. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2958671 [23] 俞斌, 董晨, 刘延华, 等. 基于深度学习的点云分割方法综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(1): 38–45. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1910-0157YU Bin, DONG Chen, LIU Yanhua, et al. Deep learning based point cloud segmentation: A survey[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(1): 38–45. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1910-0157 [24] LIU Kui and KANG Guixia. Multiview convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2017, 27(1): 12–22. doi: 10.1002/ima.22206 [25] SU Hang, MAJI S, KALOGERAKIS E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 945–953. [26] BOULCH A, GUERRY J, LE SAUX B, et al. SnapNet: 3D point cloud semantic labeling with 2D deep segmentation networks[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2018, 71: 189–198. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2017.11.010 [27] YOU Haoxuan, FENG Yifan, ZHAO Xibin, et al. PVRNet: Point-view relation neural network for 3D shape recognition[C]. The 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 9119–9126. [28] WANG Wei, XU Yuan, REN Yingchao, et al. Parsing of urban facades from 3D point clouds based on a novel multi-view domain[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2021, 87(4): 283–293. doi: 10.14358/PERS.87.4.283 [29] 郑阳, 林春雨, 廖康, 等. 场景视点偏移的激光雷达点云分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(10): 2514–2523. doi: 10.11834/jig.200424ZHENG Yang, LIN Chunyu, LIAO Kang, et al. LiDAR point cloud segmentation through scene viewpoint offset[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(10): 2514–2523. doi: 10.11834/jig.200424 [30] KUNDU A, YIN Xiaoqi, FATHI A, et al. Virtual multi-view fusion for 3D semantic segmentation[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 518–535. [31] WU Zhirong, SONG Shuran, KHOSLA A, et al. 3D shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1912–1920. [32] HUANG Jing and YOU Suya. Point cloud labeling using 3D convolutional neural network[C]. The 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 2670–2675. [33] DAI A and NIEßNER M. 3DMV: Joint 3D-multi-view prediction for 3D semantic scene segmentation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 458–474. [34] LE T and DUAN Ye. PointGrid: A deep network for 3D shape understanding[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9204–9214. [35] KUMAWAT S and RAMAN S. LP-3DCNN: Unveiling local phase in 3D convolutional neural networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4898–4907. [36] TANG Haotian, LIU Zhijian, ZHAO Shengyu, et al. Searching efficient 3D architectures with sparse point-voxel convolution[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 685–702. [37] 孙一珺, 胡辉, 李子钥, 等. 适用于点云数据的注意力机制研究[J/OL]. 计算机工程与应用. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=JSGG20211011003&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=3Qinehu7XHJEb8HcZQOml03a3GuI8TbdofNxjvnLvZ_l8jGtSqM5aNjUQVMqm-LC, 2021.SUN Yijun, HU Hui, LI Ziyue, et al. Research on attention mechanism for point cloud data[J/OL]. Computer Engineering and Applications. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=JSGG20211011003&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=3Qinehu7XHJEb8HcZQOml03a3GuI8TbdofNxjvnLvZ_l8jGtSqM5aNjUQVMqm-LC, 2021. [38] XIE Saining, LIU Sainan, CHEN Zeyu, et al. Attentional ShapeContextNet for point cloud recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4606–4615. [39] ZHANG Zhiyuan, HUA B S, CHEN Wei, et al. Global context aware convolutions for 3D point cloud understanding[C]. 2020 International Conference on 3D Vision, Fukuoka, Japan, 2020: 210–219. [40] XU Mutian, DING Runyu, ZHAO Hengshuang, et al. PAConv: Position adaptive convolution with dynamic kernel assembling on point clouds[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 3172–3181. [41] LI Guohao, QIAN Guocheng, DELGADILLO I C, et al. SGAS: Sequential greedy architecture search[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1617–1627. [42] XU Yifan, FAN Tianqi, XU Mingye, et al. SpiderCNN: Deep learning on point sets with parameterized convolutional filters[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 95–105. [43] HUA B S, TRAN M K, and YEUNG S K. Pointwise convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 984–993. [44] KOMARICHEV A, ZHONG Zichun, and HUA Jing. A-CNN: Annularly convolutional neural networks on point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7413–7422. [45] 高金金, 李潞洋. 基于局部关系卷积的点云分类与分割模型[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(19): 276–283.GAO Jinjin and LI Luyang. Local relation convolution network for 3D point cloud classification and segmentation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(19): 276–283. [46] LIU Yongcheng, FAN Bin, XIANG Shiming, et al. Relation-shape convolutional neural network for point cloud analysis[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 8887–8896. [47] LIU Yongcheng, FAN Bin, MENG Gaofeng, et al. Densepoint: Learning densely contextual representation for efficient point cloud processing[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 5238–5247. [48] WU Wenxuan, QI Zhongang, and LI Fuxin. PointConv: Deep convolutional networks on 3D point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9613–9622, [49] LIN Zhihao, YU Shengyu, WANG Y C F. Convolution in the cloud: Learning deformable kernels in 3D graph convolution networks for point cloud analysis[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1797–1806. [50] WANG Fei, ZHANG Xing, JIANG Yong, et al. PatchCNN: An explicit convolution operator for point clouds perception[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(4): 726–730. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2981507 [51] SHEN Yiru, FENG Chen, YANG Yaoqing, et al. Mining point cloud local structures by kernel correlation and graph pooling[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4548–4557. [52] WANG Lei, HUANG Yuchun, HOU Yaolin, et al. Graph attention convolution for point cloud semantic segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 10288–10297. [53] FENG Yifan, YOU Haoxuan, ZHANG Zizhao, et al. Hypergraph neural networks[C]. The 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hawaii, USA, 2019: 3558–3565. [54] JIANG Jianwen, WEI Yuxuan, FENG Yifan, et al. Dynamic hypergraph neural networks[C]. The 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 2019: 2635–2641. [55] XU Qiangeng, SUN Xudong, WU C Y, et al. Grid-GCN for fast and scalable point cloud learning[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 5660–5669. [56] ENGELMANN F, KONTOGIANNI T, HERMANS A, et al. Exploring spatial context for 3D semantic segmentation of point clouds[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 2017: 716–724. [57] YE Xiaoqing, LI Jiamao, HUANG Hexiao, et al. 3D recurrent neural networks with context fusion for point cloud semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 415–430. [58] ZHAO Zongyue, LIU Min, and RAMANI K. DAR-Net: Dynamic aggregation network for semantic scene segmentation[J]. arXiv: 1907.12022. [59] LIU Fangyu, LI Shuaipeng, ZHANG Liqiang, et al. 3DCNN-DQN-RNN: A deep reinforcement learning framework for semantic parsing of large-scale 3D point clouds[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5679–5688. [60] QIN Can, YOU Haoxuan, WANG Lichen, et al. PointDAN: A multi-scale 3D domain adaption network for point cloud representation[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 7192–7203. [61] HAN Zhizhong, WANG Xiyang, LIU Yushen, et al. Multi-angle point cloud-VAE: Unsupervised feature learning for 3D point clouds from multiple angles by joint self-reconstruction and half-to-half prediction[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 10441–10450. [62] CHEN Nenglun, LIU Lingjie, CUI Zhiming, et al. Unsupervised learning of intrinsic structural representation points[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9118–9127. [63] ZAMORSKI M, ZIEBA M, KLUKOWSKI P, et al. Adversarial autoencoders for compact representations of 3D point clouds[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2020, 193: 102921. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2020.102921 [64] RAO Yongming, LU Jiwen, and ZHOU Jie. Global-local bidirectional reasoning for unsupervised representation learning of 3D point clouds[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 5375–5384. [65] CHANG A X, FUNKHOUSER T, GUIBAS L, et al. ShapeNet: An information-rich 3D model repository[J]. arXiv: 1512.03012, 2015. [66] DAI A, CHANG A X, SAVVA M, et al. ScanNet: Richly-annotated 3D reconstructions of indoor scenes[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2432–2443. [67] HACKEL T, SAVINOV N, LADICKY L, et al. Semantic3D. net: A new large-scale point cloud classification benchmark[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2017, IV-1/W1: 91–98. doi: 10.5194/isprs-annals-IV-1-W1-91-2017 -





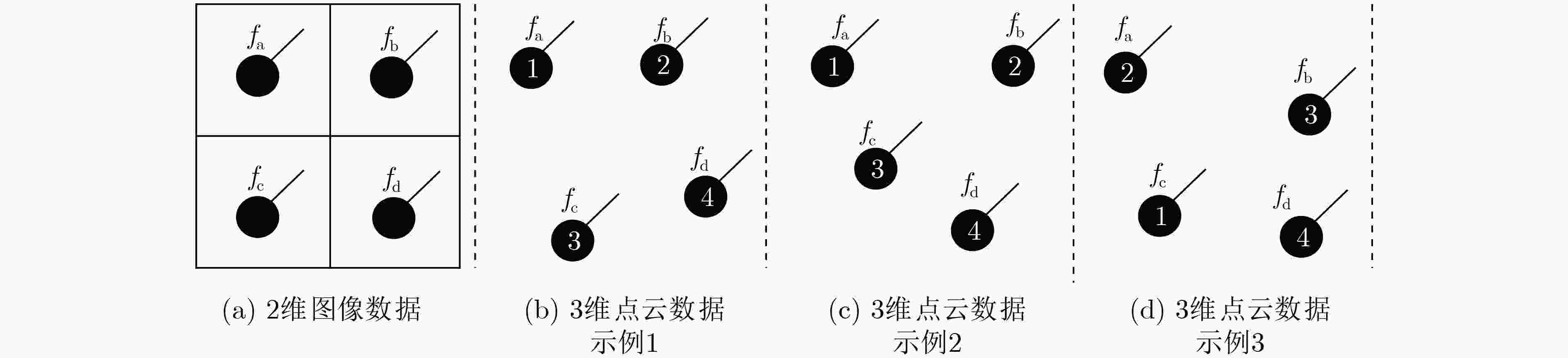
 下载:
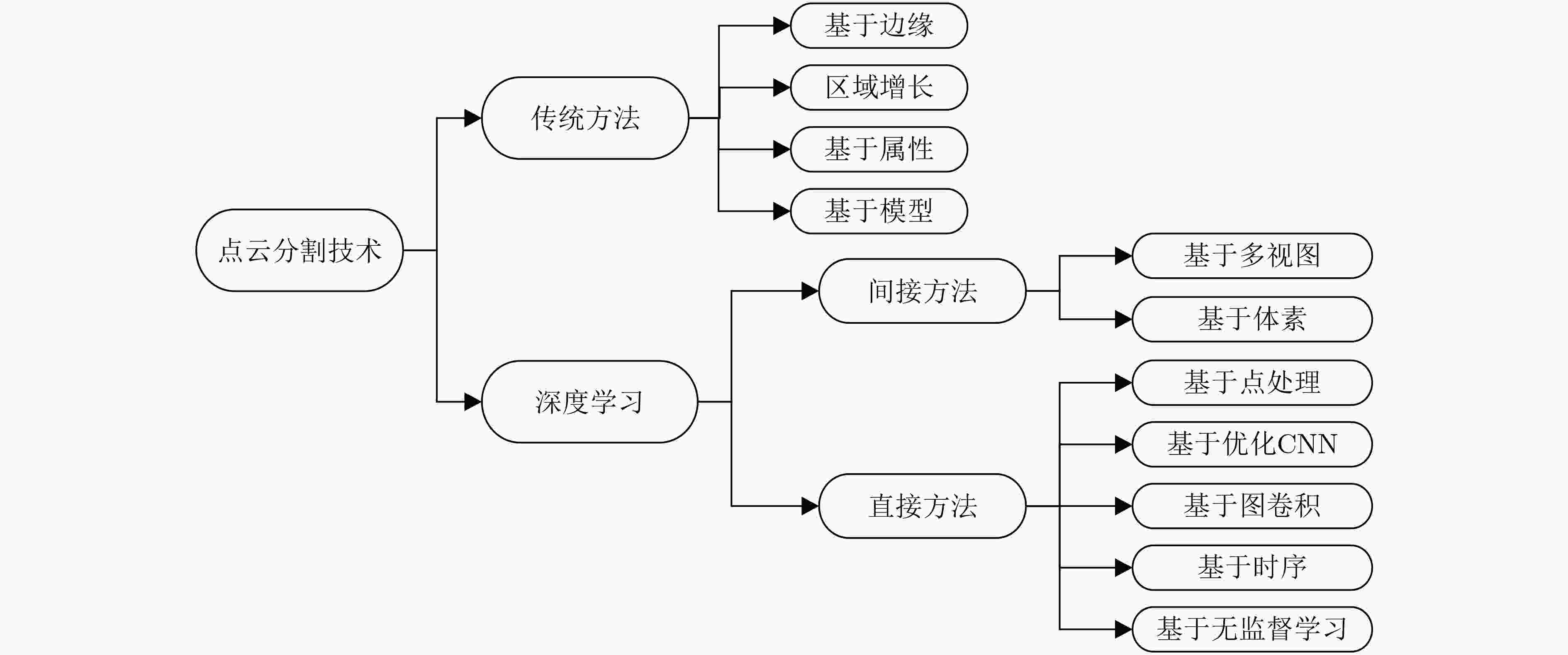
下载:
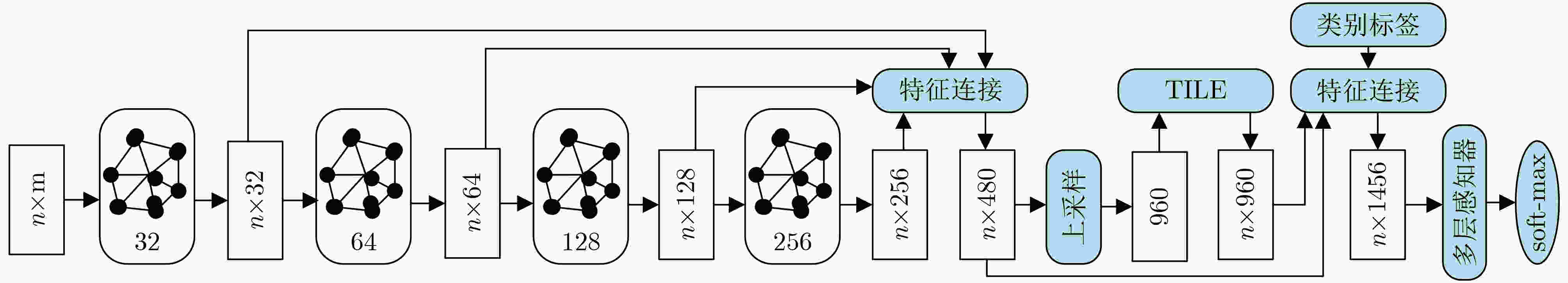
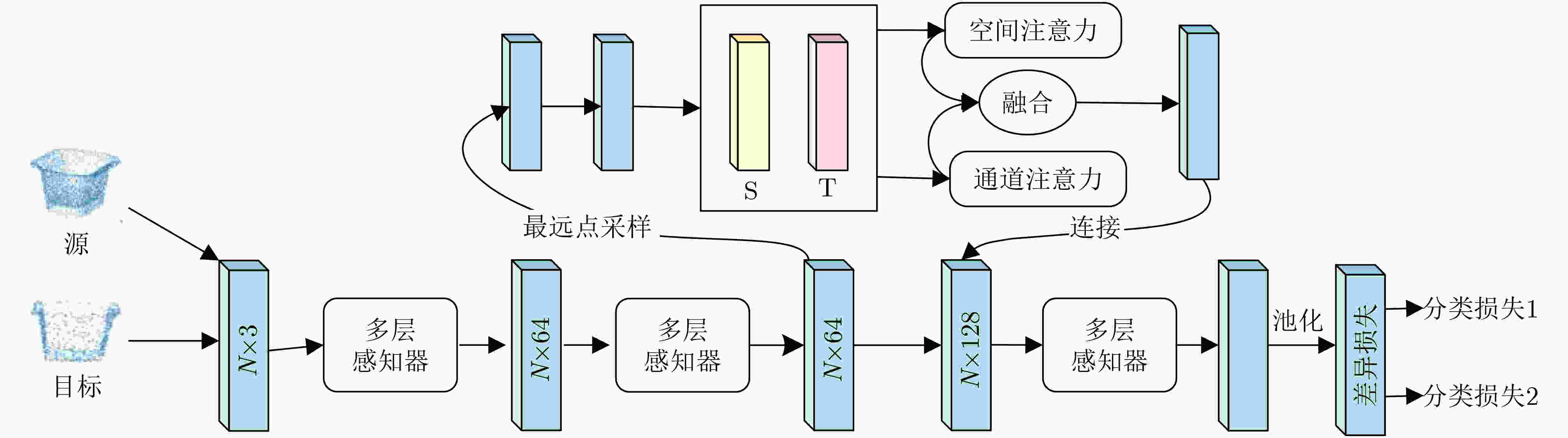
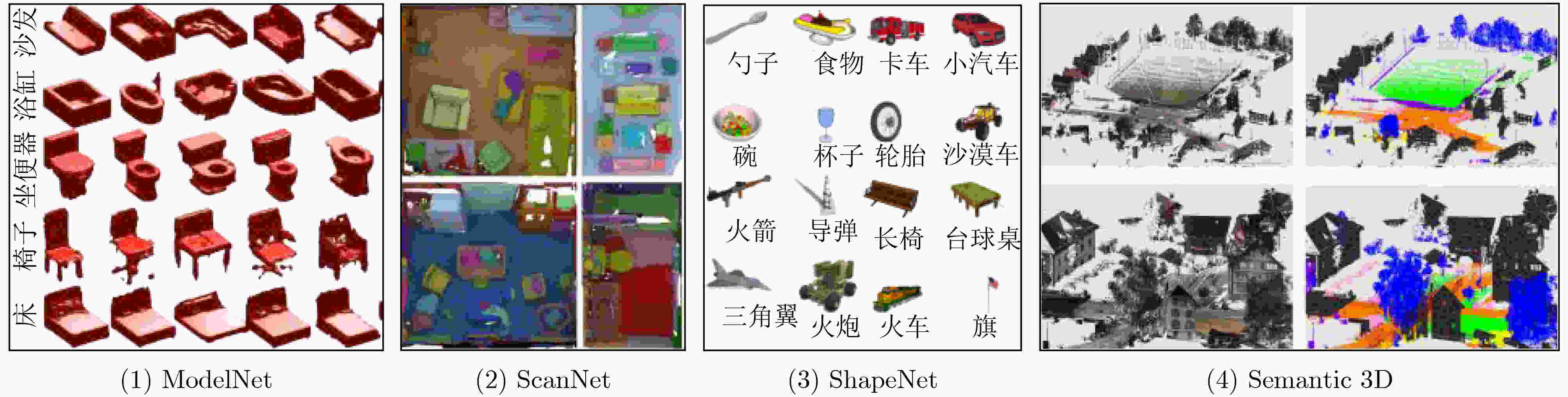


 下载:
下载:
