Multi-stage Multi-scale Color Guided Depth Image Completion for Road Scenes
-
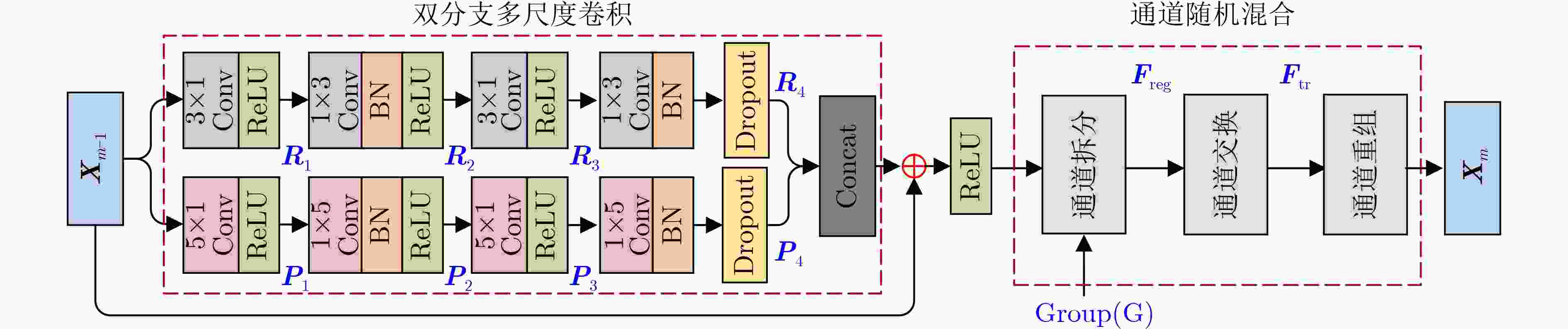
摘要: 道路场景深度图像对于道路目标检测、智能驾驶汽车、场景3维重建等研究和应用都是至关重要的,但是由于硬件条件的限制,激光雷达获取的场景深度图像非常稀疏,道路场景深度补全旨在利用稠密的场景彩色图像指导稀疏雷达深度图像的补全重建,是目前的研究热点。该文设计了一种新型的多阶段多尺度引导的轻量化编解码网络来实现道路深度图像的高质量补全。该文网络由“彩色引导”和“精细化补全”两个阶段构成。在两个阶段的编码端,提出带有通道随机混合的轻量化多尺度卷积模块,更好地提取图像特征的同时控制网络的参数量。在两个阶段的解码端,采用通道感知机制来实现对重要特征的聚焦。同时将“彩色引导”阶段解码端的多尺度特征融合到“精细化补全”阶段的编码端中,实现多阶段多尺度的特征引导。在训练过程中,该文设计了多损失函数策略来完成由粗到细的深度图像补全。实验表明所提算法能实现高质量的深度图像补全并且具有轻量化的网络结构。Abstract: Depth completion is a task of estimating dense depth maps from sparse measurements under the guidance of dense RGB images. Dense depth map is critical for object detection, autonomous driving and scene reconstruction. Hence, depth completion of road scenes is a hot research topic at present. In this paper, a novel multi-stage multi-scale lightweight encoder-decoder network for depth completion is proposed. Specifically, the network consists of two sub-encoder-decoder branches named color-guided branch and fine-completion branch. At the encoders, a lightweight multiscale convolution module with channel random mixing is proposed to extract better image features while controlling the parameter amount. At the decoders, a channel-aware mechanism is devised to focus on the important features. Moreover, multi-scale features from the decoder of color-guided branch are fused into the encoder of fine-completion branch to achieve multi-stage multi-scale guidance. Furthermore, an efficient multi-loss strategy is developed for depth completion from coarse to fine in the training process. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed model is relatively lightweight and can achieve superior performance compared with other state-of-the-art methods.
-
Key words:
- Road scene /
- Depth image completion /
- Color guided /
- Attention mechanism
-
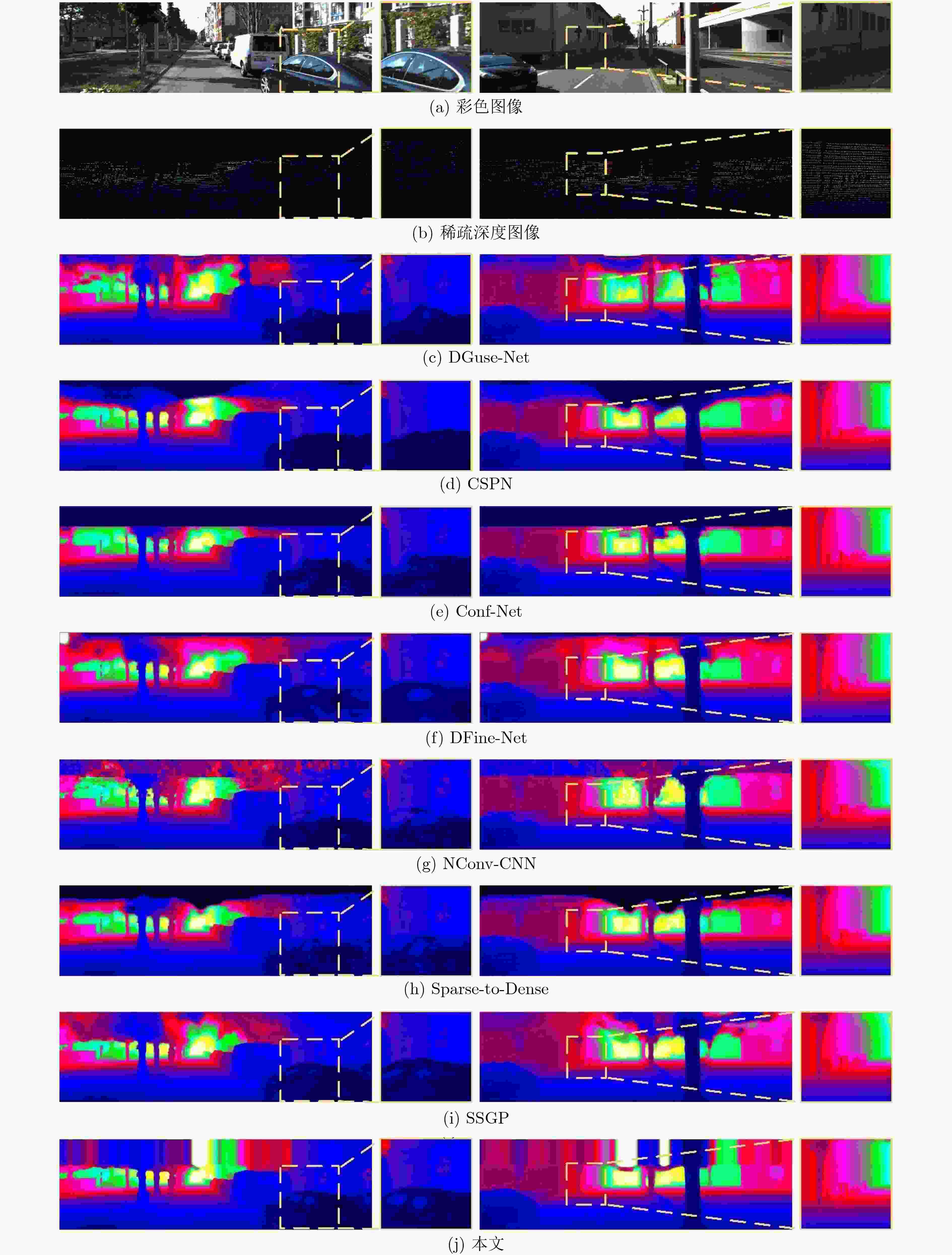
表 1 基于KITTI 测试集的实验结果比较
方法 RMSE MAE iRMSE iMAE Params(M) DFuse-Net 1206.66 429.93 3.62 1.79 4.66 CSPN 1019.64 279.46 2.93 1.15 256.08 Conf-Net 962.28 257.54 3.10 1.09 / DFine-Net 943.89 304.17 3.21 1.39 / Sparse-to-Dense(gd) 814.73 249.95 2.80 1.21 26.1 NConv-CNN-L2 829.98 233.26 2.60 1.03 / SSGP 838.22 244.70 2.51 1.09 / CrossGuide 807.42 253.98 2.73 1.33 30 PwP 777.05 235.17 2.23 1.13 / DeepLiDAR 758.38 226.50 2.56 1.15 144 本文 767.29 225.94 2.18 1.00 4.05 表 2 基于KITTI验证集的消融实验结果比较
Case 彩色引导分支 精细补全分支 单损失函数 双损失函数 通道感知模块 多尺度卷积模块 RMSE MAE 1 √ √ 836.10 247.90 2 √ √ 845.20 255.70 3 √ √ √ 830.50 243.40 4 √ √ √ 809.90 231.50 5 √ √ √ √ 816.20 240.20 6 √ √ √ √ 783.37 217.60 7 √ √ √ √ √ 775.43 209.80 表 3 不同算法运行时间比较(s)
CSPN SSGP CrossGuidence PwP 本文 时间 1.0 0.14 0.2 0.1 0.09 -
[1] 周武杰, 潘婷, 顾鹏笠, 等. 基于金字塔池化网络的道路场景深度估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2509–2515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180957ZHOU Wujie, PAN Ting, GU Pengli, et al. Depth estimation of monocular road images based on pyramid scene analysis network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2509–2515. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180957 [2] 王灿, 孔斌, 杨静, 等. 基于三维激光雷达的道路边界提取和障碍物检测算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2020, 33(4): 353–362. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003–6059.202004008WANG Can, KONG Bin, YANG Jing, et al. An algorithm for road boundary extraction and obstacle detection based on 3D lidar[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 33(4): 353–362. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003–6059.202004008 [3] PANG Su, MORRIS D, and RADHA H. CLOCs: Camera-LiDAR object candidates fusion for 3D object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 10386–10393. [4] YANG Zetong, SUN Yanan, LIU Shu, et al. 3DSSD: Point-based 3D single stage object detector[C/OL]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11037–11045. [5] 马浩杰. 基于卷积神经网络的单目深度估计和深度补全研究[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江大学, 2019.MA Haojie. Monocular depth estimation and depth completion based on convolutional neural network[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2019. [6] 邱佳雄. 基于深度学习的稀疏深度图补全[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.QIU Jiaxiong. Sparse depth completion based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. [7] HUANG Zixuan, FAN Junming, CHENG Shenggan, et al. Hms-net: Hierarchical multi-scale sparsity-invariant network for sparse depth completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3429–3441. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2960589 [8] MA Fangchang, CAVALHEIRO G V, and KARAMAN S. Self-supervised sparse-to-dense: Self-supervised depth completion from LiDAR and monocular camera[C]. 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 2019: 3288–3295. [9] SHIVAKUMAR S S, NGUYEN T, MILLER I D, et al. Dfusenet: Deep fusion of RGB and sparse depth information for image guided dense depth completion[C]. 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 2019: 13–20. [10] LEE S, LEE J, KIM D, et al. Deep architecture with cross guidance between single image and sparse LiDAR data for depth completion[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 79801–79810. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990212 [11] QIU Jiaxiong, CUI Zhaopeng, ZHANG Yinda, et al. DeepLiDAR: Deep surface normal guided depth prediction for outdoor scene from sparse LiDAR data and single color image[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3313–3322. [12] 徐从安, 吕亚飞, 张筱晗, 等. 基于双重注意力机制的遥感图像场景分类特征表示方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 683–691. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200568XU Cong’an, LÜ Yafei, ZHANG Xiaohan, et al. A discriminative feature representation method based on dual attention mechanism for remote sensing image scene classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 683–691. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200568 [13] 周勇, 王瀚正, 赵佳琦, 等. 基于可解释注意力部件模型的行人重识别方法[J/OL]. 自动化学报, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.c200493, 2020.ZHOU Yong, WANG Hanzheng, ZHAO Jiaqi, et al. Interpretable attention part model for person Re-identification[J/OL]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.c200493, 2020. [14] MA Benteng, ZHANG Jing, XIA Yong, et al. Auto learning attention[C/OL]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33, online, 2020. [15] ZHANG Yulun, LI Kunpeng, LI Kai, et al. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 294–310. [16] 张帅勇, 刘美琴, 姚超, 等. 分级特征反馈融合的深度图像超分辨率重建[J/OL]. 自动化学报, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.c200542, 2020.ZHANG Shuaiyong, LIU Meiqin, YAO Chao, et al. Hierarchical feature feedback network for depth super-resolution reconstruction[J/OL]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.c200542, 2020. [17] UHRIG J, SCHNEIDER N, SCHNEIDER L, et al. Sparsity invariant CNNs[C]. 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 2017: 11–20. [18] XU Yan, ZHU Xinge, SHI Jianping, et al. Depth completion from sparse LiDAR data with depth-normal constraints[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 2811–2820. [19] ELDESOKEY A, FELSBERG M, and KHAN F S. Confidence propagation through CNNs for guided sparse depth regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2423–2436. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2929170 [20] HEKMATIAN H, JIN Jingfu, and AL-STOUHI S. Conf-net: Toward high-confidence dense 3D point-cloud with error-map prediction[J]. arXiv: 1907.10148, 2019. [21] CHENG Xinjing, WANG Peng, and YANG Ruigang. Learning depth with convolutional spatial propagation network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2361–2379. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2947374 [22] ZHANG Yilun, NGUYEN T, MILLER I D, et al. DFineNet: Ego-motion estimation and depth refinement from sparse, noisy depth input with RGB guidance[J]. arXiv: 1903.06397, 2019. [23] SCHUSTER R, WASENMÜLlER O, UNGER C, et al. SSGP: Sparse spatial guided propagation for robust and generic interpolation[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 197–206. -





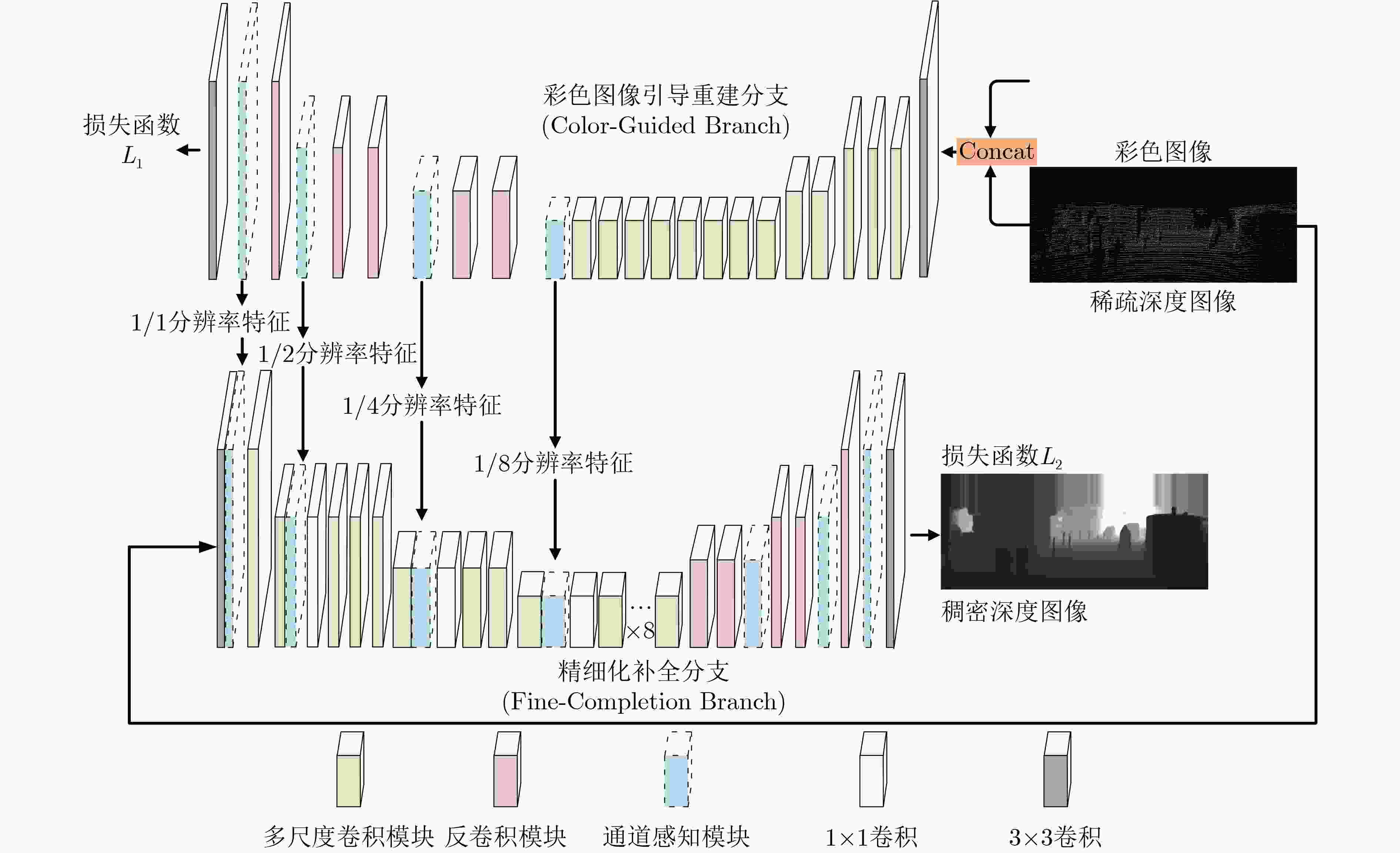
 下载:
下载:
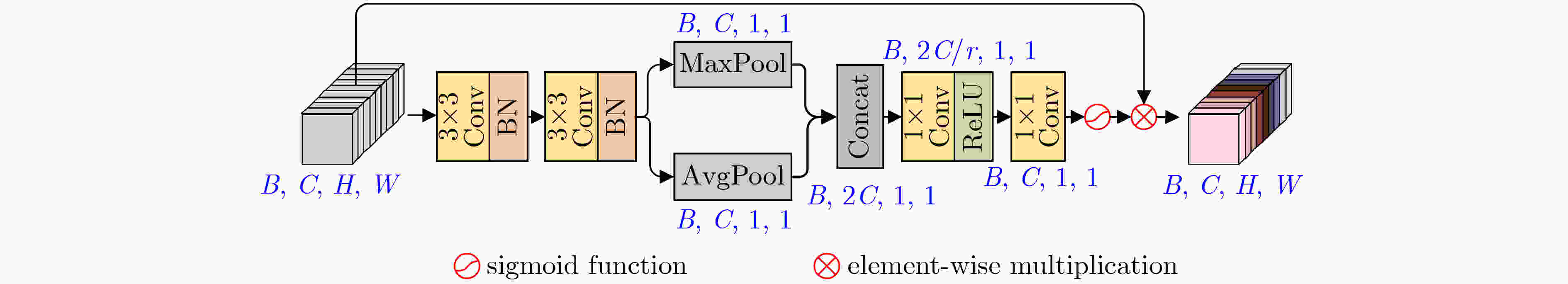


 下载:
下载:
