LRSAR-Net Semantic Segmentation Model for Computer Aided Diagnosis for Covid-19 CT Image
-
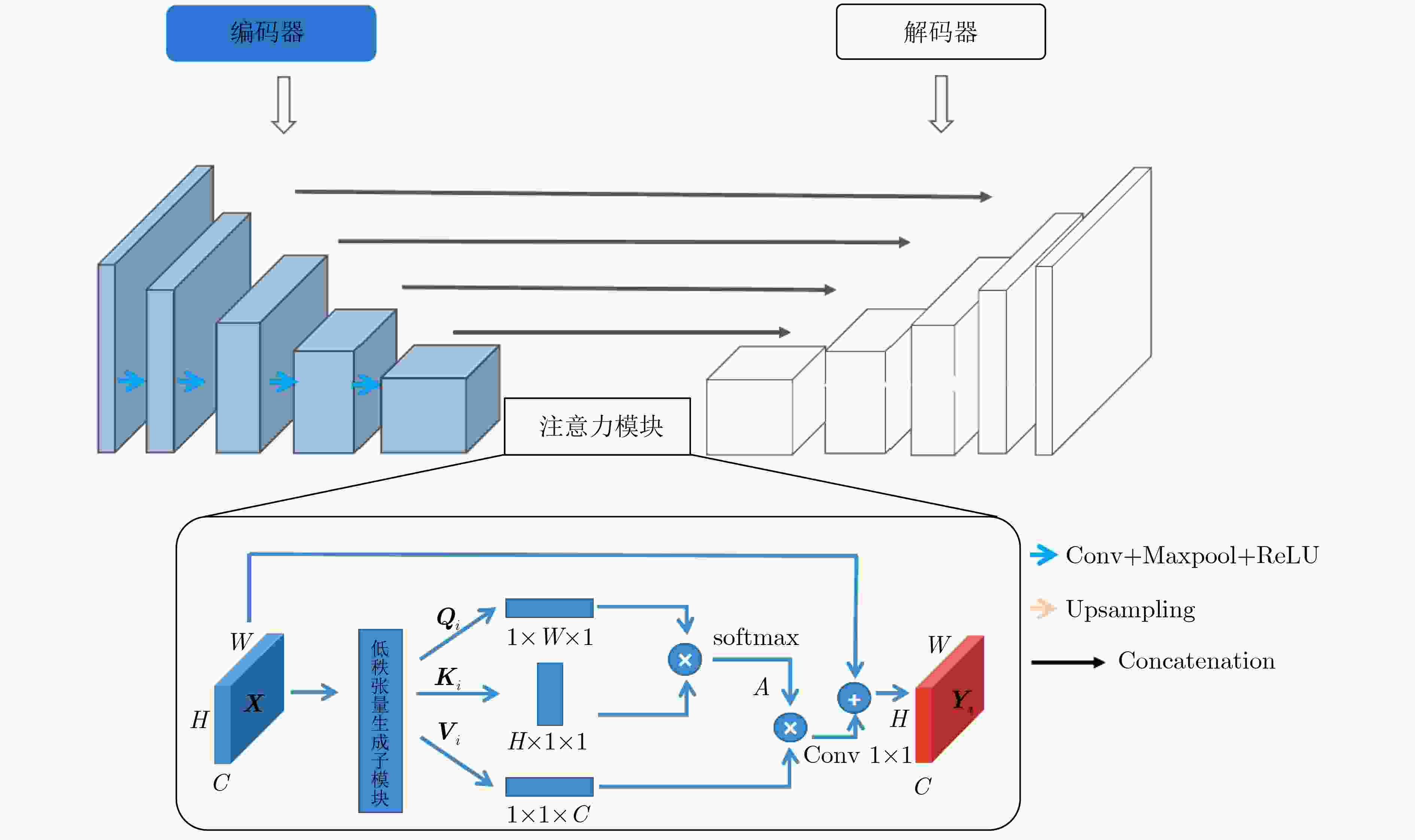
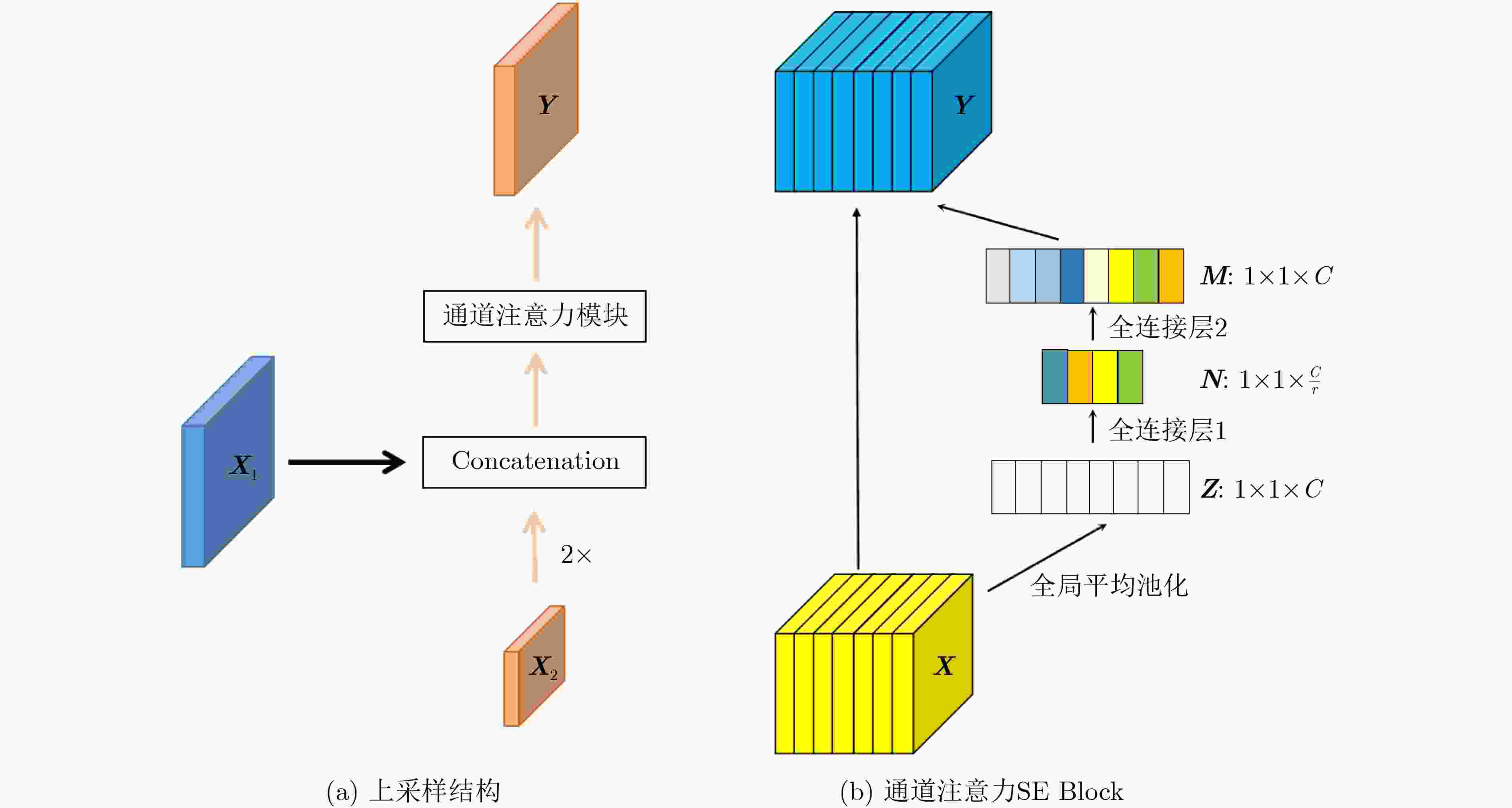
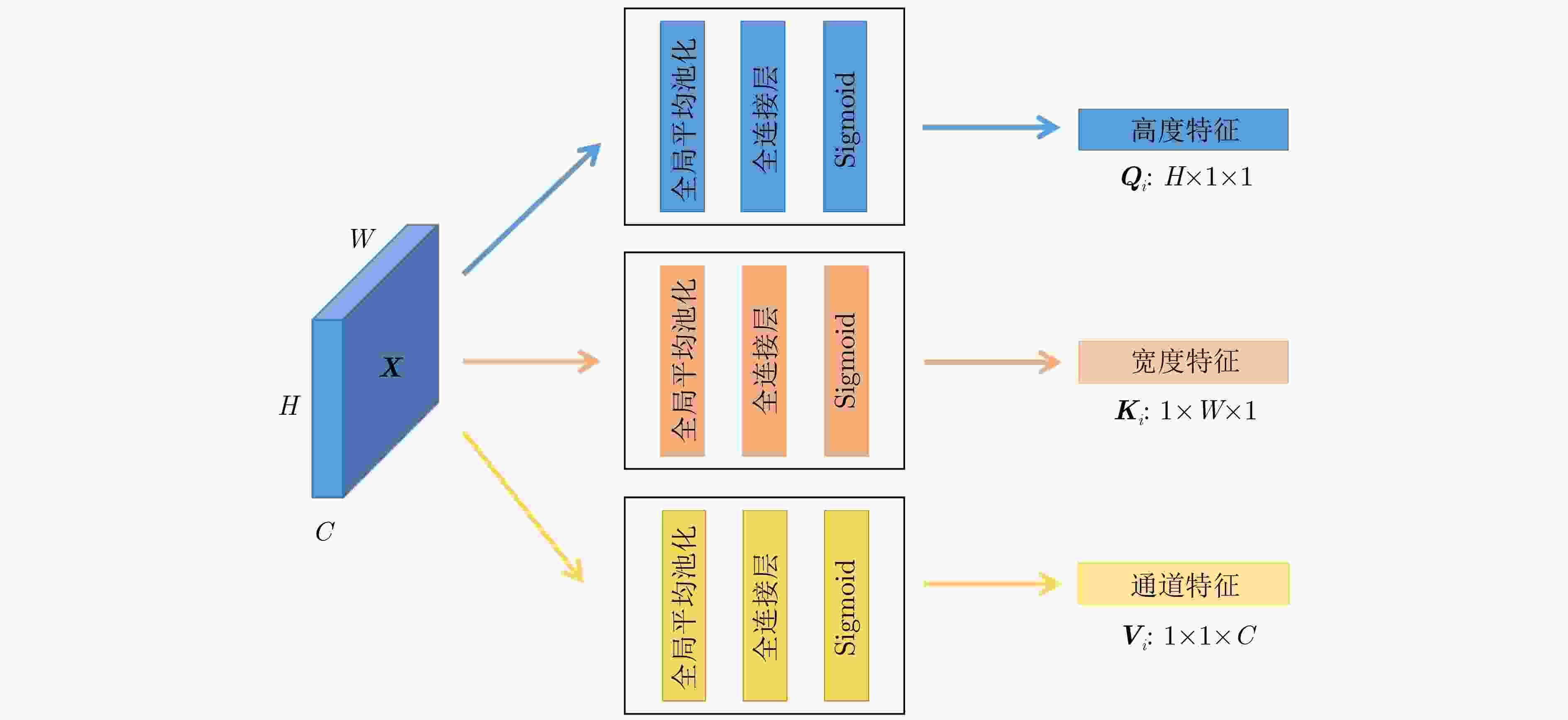
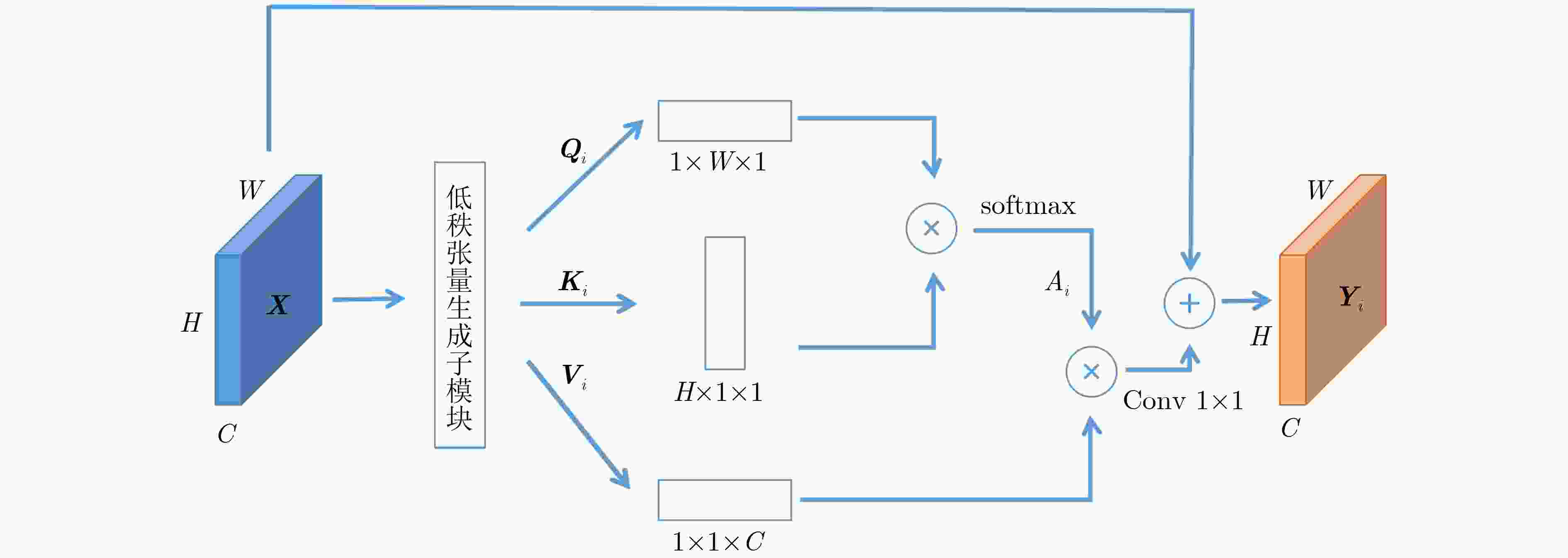
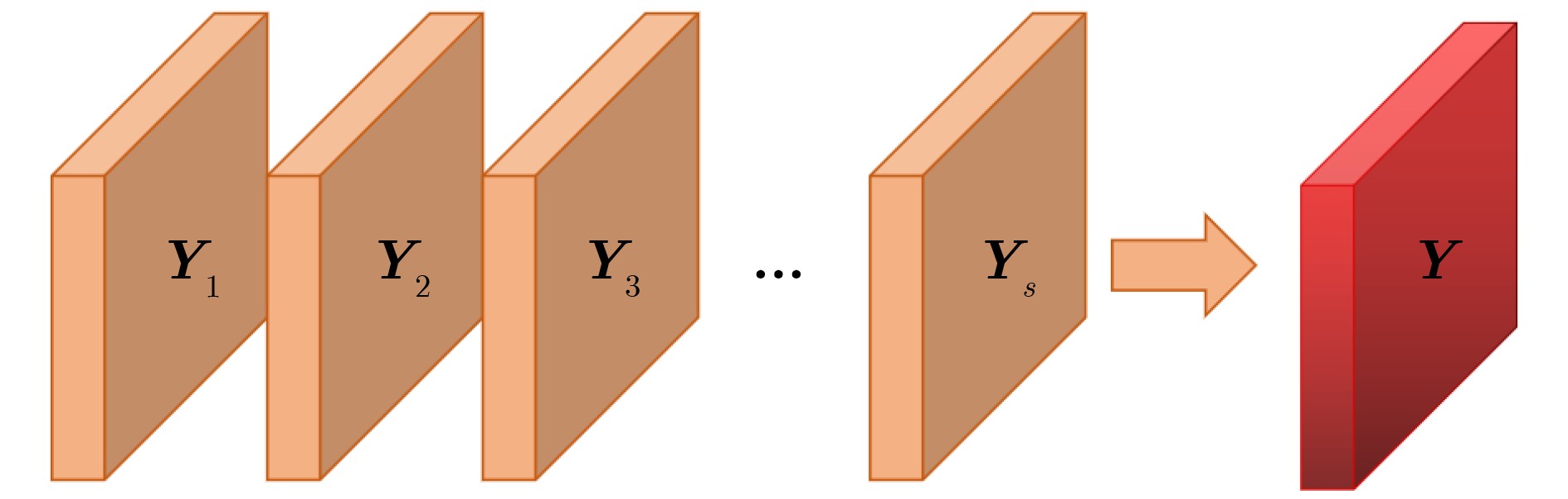
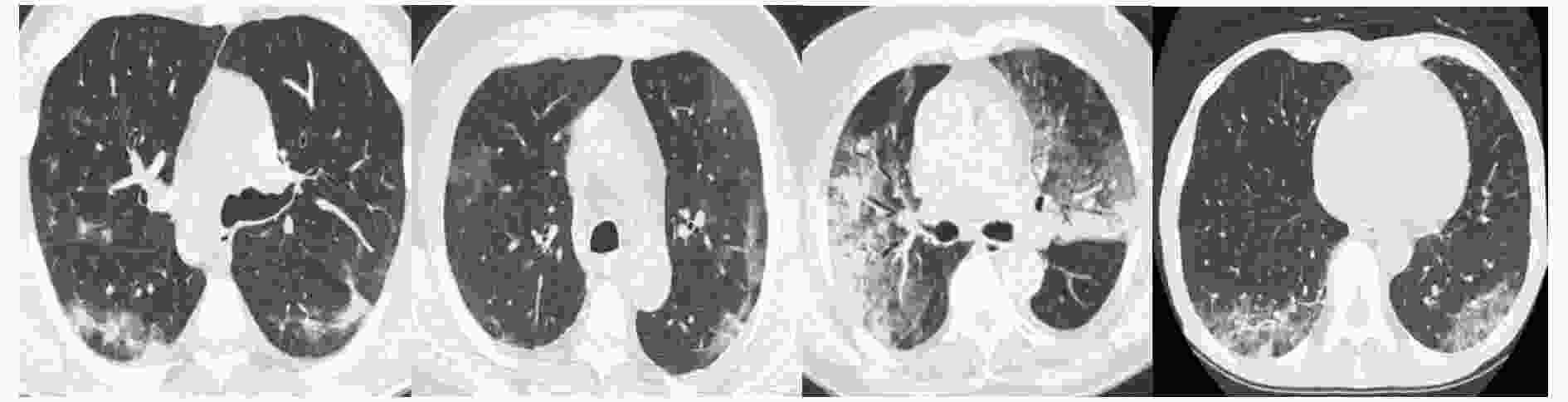
摘要: 自2019年末新型冠状病毒(Covid-19)疫情在全球爆发以来,世界各国都处于疫情的危害之下。新冠病毒通过入侵人体的呼吸系统,造成肺部感染,甚至死亡。CT(Computed Tomography)图是医生对肺炎患者进行诊断的常规方法。为了提高医生对新冠感染者进行诊断的效率,该文提出一种基于低秩张量自注意力重构的语义分割网络LRSAR-Net,其中低秩张量自注意力重构模块用来获取长范围的信息。低秩张量自注意力重构模块主要包括:低秩张量生成子模块、低秩自注意力子模块、高秩张量重构子模块3个部分。低秩张量自注意力模块先生成多个低秩张量,构建低秩自注意力特征图,然后将多个低秩张量注意力特征图重构成高秩注意力特征图。自注意力模块通过计算相似度矩阵来获取长范围的语义信息。与传统的自注意力模块Non-Local相比,低秩张量自注意力重构模块计算复杂度更低,计算速度更快。最后,该文与其他优秀的语义分割模型进行了对比,体现了模型的有效性。Abstract: Since the outbreak of the Covid-19 epidemic in the world in late 2019, all countries in the world are under the threat of epidemic. Covid-19 invades the body's respiratory system, causing lung infection or even death. Computed Tomography (CT) is a routine method for doctors to diagnose patients with pneumonia. In order to improve the efficiency of doctors in diagnosing patients with new crown infection, this paper proposes a semantic segmentation network LRSAR-Net based on low rank tensor self-attention reconstruction, in which the low rank tensor self-attention reconstruction module is used to obtain long-range information. The low rank tensor self-attention reconstruction module mainly includes three parts: low rank tensor generation sub module, low rank self-attention sub module and high rank tensor reconstruction module. The low rank tensor self-attention module is divided into multiple low rank tensors, the low rank self-attention feature map is constructed, and then the multiple low rank tensor attention feature maps are reconstructed into a high rank attention feature map. The self-attention module obtains long-range semantic information by calculating the similarity matrix. Compared with the traditional self-attention module Non Local, the low rank tensor self-attention reconstruction module has lower computational complexity and faster computing speed. Finally, this paper compares with other excellent semantic segmentation models to reflect the effectiveness of the model.
-
表 1 不同的特征提取网络的模型对比DataSet
数据集 图片数量 Covid-19 数量 Covid-19 CT100 100 100 Covid-19 P9 829 373 表 2 注意力模块的影响
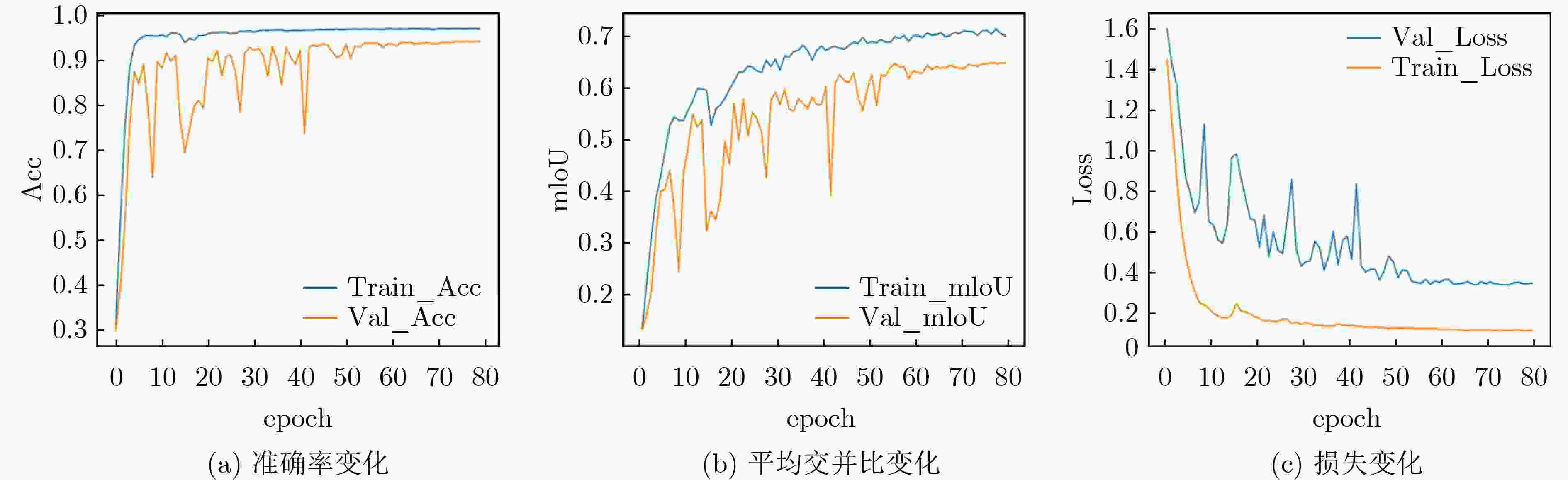
模型 Train_mIoU(%) Train_Acc(%) Test_mIoU(%) Test_Acc(%) 参数量(M) FLOPs(G) ED Net 73.7 96.9 65.4 94.7 32.51 10.59 +Non-Local 72.4 96.9 67.0 94.6 +34.27 +2.56 +LRSAR 74.0 97.0 69.0 95.0 +17.13 +1.28 +SE 74.9 97.0 69.1 95.3 +1.3 +0.02 Reco Net[18] 73.4 96.9 67.5 94.5 113.85 16.35 LRSAR-Net 73.7 97.1 70.0 95.1 50.94 11.88 表 3 不同的特征提取网络的模型对比
表 4 不同的语义分割网络之间的对比
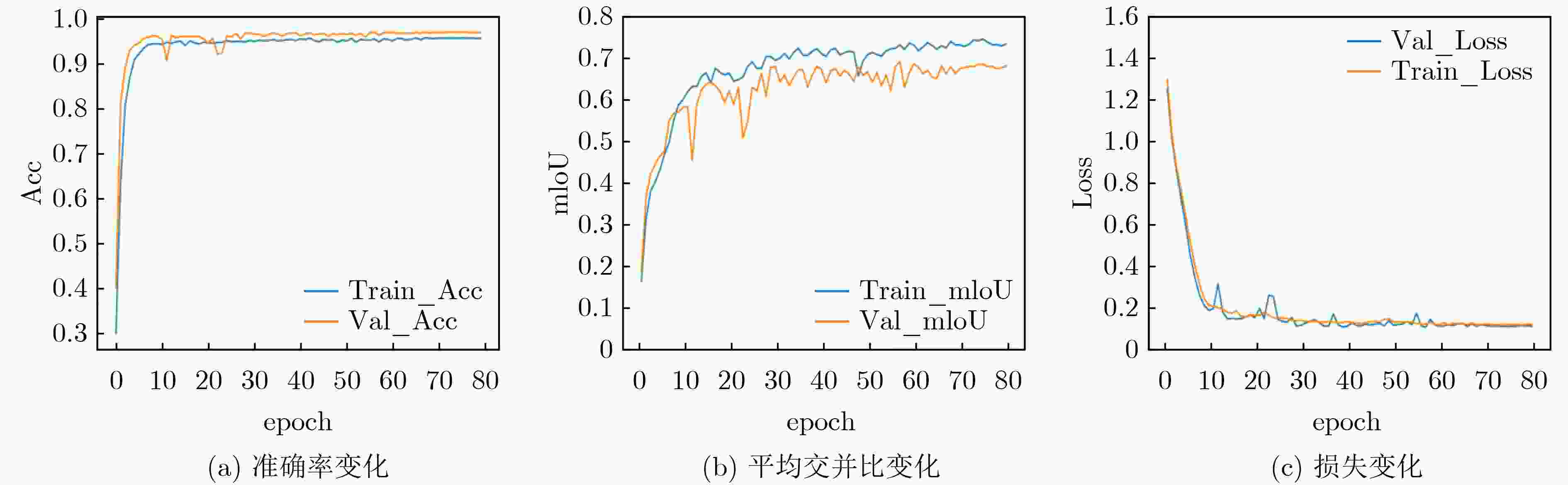
模型 Train_mIoU(%) Train_Acc(%) Test_mIoU(%) Test_Acc(%) 参数量(M) FLOPs(G) U-Net[30] 73.7 96.9 65.4 94.7 32.5 10.6 U-Net++[31] 73.7 96.7 66.1 94.9 48.9 57.4 DeepLabV3[32] 71.6 96.5 66.0 94.1 39.6 40.8 DeepLabV3+[33] 73.3 97.1 65.7 94.6 26 9.1 PSPNet[34] 71.6 96.7 67.3 94.3 2.2 2.8 Reco-Net[18] 73.4 96.9 67.5 94.5 113.85 16.35 LRSAR-Net 73.7 96.8 70.0 95.1 34.2 10.8 -
[1] MUNUSAMY H, MUTHUKUMAR K J, GNANAPRAKASAM S, et al. FractalCovNet architecture for COVID-19 Chest X-ray image classification and CT-scan image Segmentation[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 41(3): 1025–1038. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2021.06.011 [2] ILESANMI A E, CHAUMRATTANAKUL U, and MAKHANOV S S. A method for segmentation of tumors in breast ultrasound images using the variant enhanced deep learning[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 41(2): 802–818. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2021.05.007 [3] HAMBARDE P, TALBAR S, MAHAJAN A, et al. Prostate lesion segmentation in MR images using radiomics based deeply supervised U-Net[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 40(4): 1421–1435. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2020.07.011 [4] KHANNA A, LONDHE N D, GUPTA S, et al. A deep Residual U-Net convolutional neural network for automated lung segmentation in computed tomography images[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 40(3): 1314–1327. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2020.07.007 [5] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017. [6] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. [7] LI Chen, TAN Yusong, CHEN Wei, et al. ANU-Net: Attention-based nested U-Net to exploit full resolution features for medical image segmentation[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2020, 90: 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2020.05.003 [8] FAN Dengping, ZHOU Tao, JI Gepeng, et al. Inf-Net: Automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(8): 2626–2637. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2996645 [9] LIU Zhihua, TONG Lei, CHEN Long, et al. CANet: Context aware network for brain glioma segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(7): 1763–1777. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3065918 [10] DOU Haoran, KARIMI D, ROLLINS C K, et al. A deep attentive convolutional neural network for automatic cortical plate segmentation in fetal MRI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(4): 1123–1133. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3046579 [11] JIANG Yi, CHEN Weixun, LIU Min, et al. 3D neuron microscopy image segmentation via the ray-shooting model and a DC-BLSTM network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 40(1): 26–37. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3021493 [12] ZHANG Yuqiang, LIU Min, YU Fuhao, et al. An O-shape neural network with attention modules to detect junctions in biomedical images without segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, To be published. [13] CHEN Jieneng, LU Yongyi, YU Qihang, et al. TransUNet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2102.04306, 2021. [14] KOLDA T G and BADER B W. Tensor decompositions and applications[J]. SIAM Review, 2009, 51(3): 455–500. doi: 10.1137/07070111X [15] LEBEDEV V, GANIN Y, RAKHUBA M, et al. Speeding-up convolutional neural networks using fine-tuned CP-decomposition[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [16] WU Jia’nan. Compression of fully-connected layer in neural network by Kronecker product[C]. Proceedings of 2016 Eighth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2016: 173–179. [17] SUN Weize, CHEN Shaowu, HUANG Lei, et al. Deep convolutional neural network compression via coupled tensor decomposition[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(3): 603–616. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2020.3038227 [18] CHEN Wanli, ZHU Xinge, SUN Ruoqi, et al. Tensor low-rank reconstruction for semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 52–69. [19] ZHANG Yanbo, MOU Xuanqin, WANG Ge, et al. Tensor-based dictionary learning for spectral CT reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(1): 142–154. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2600249 [20] WU Weiwen, LIU Fenglin, ZHANG Yanbo, et al. Non-local low-rank cube-based tensor factorization for spectral CT reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(4): 1079–1093. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2878226 [21] HATVANIY J, MICHETTI J, BASARAB A, et al. Single image super-resolution of noisy 3d dental Ct images using tucker decomposition[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 2021: 1673–1676. [22] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [23] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [24] JENSSEN H B. COVID-19 CT segmentation dataset[EB/OL]. http://medicalsegmentation.com/ covid19/, 2020. [25] MedSeg[EB/OL].https://www.medseg.ai/. [26] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [27] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510–4520. [28] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278–4284. [29] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1800–1807. [30] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015. [31] ZHOU Zongwei, SIDDIQUEE M M R, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. UNet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(6): 1856–1867. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2959609 [32] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. arXiv: 1706.05587, 2017. [33] CHEN L C, ZHU Yukun, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018. [34] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. -





 下载:
下载:
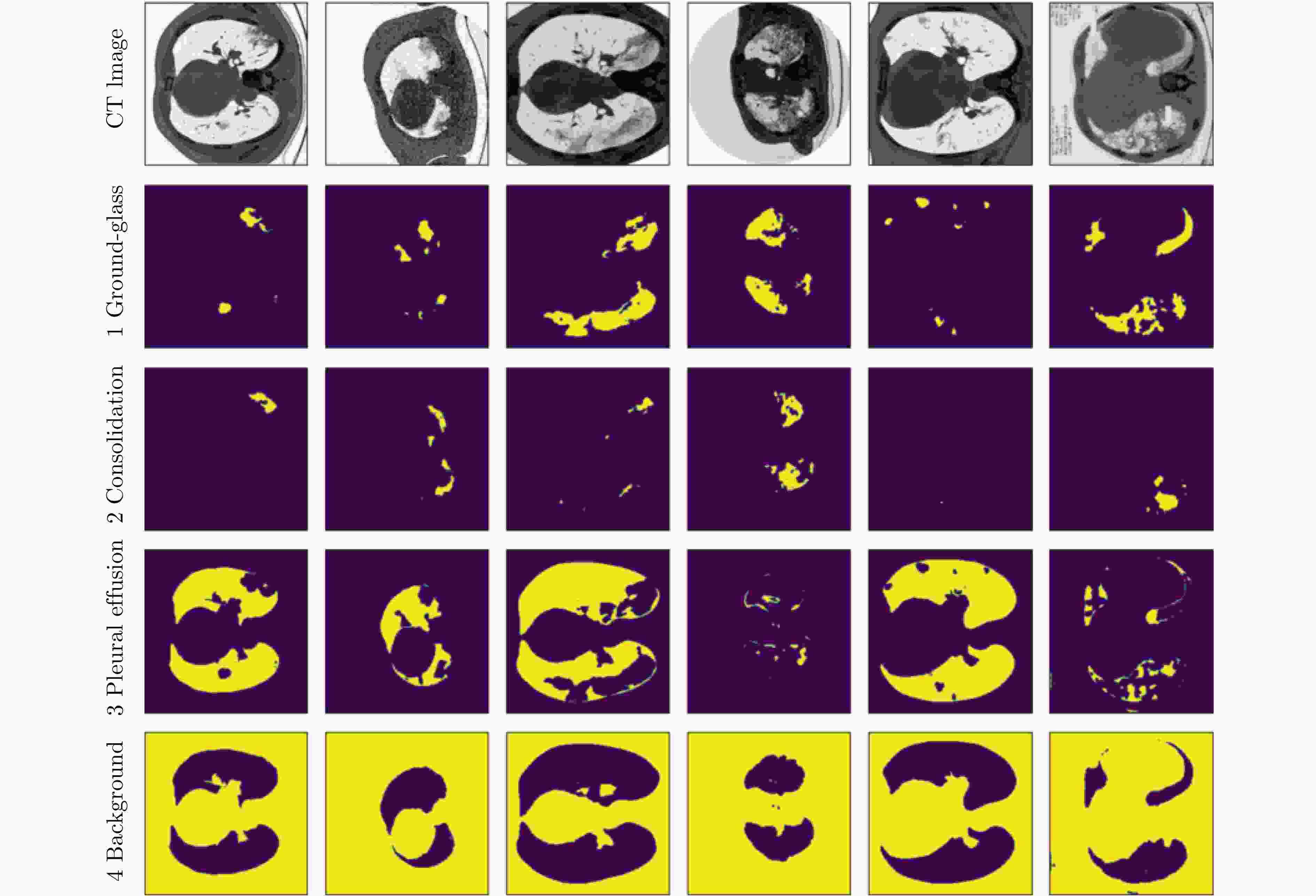


 下载:
下载:
