ResNet and Its Application to Medical Image Processing: Research Progress and Challenges
-
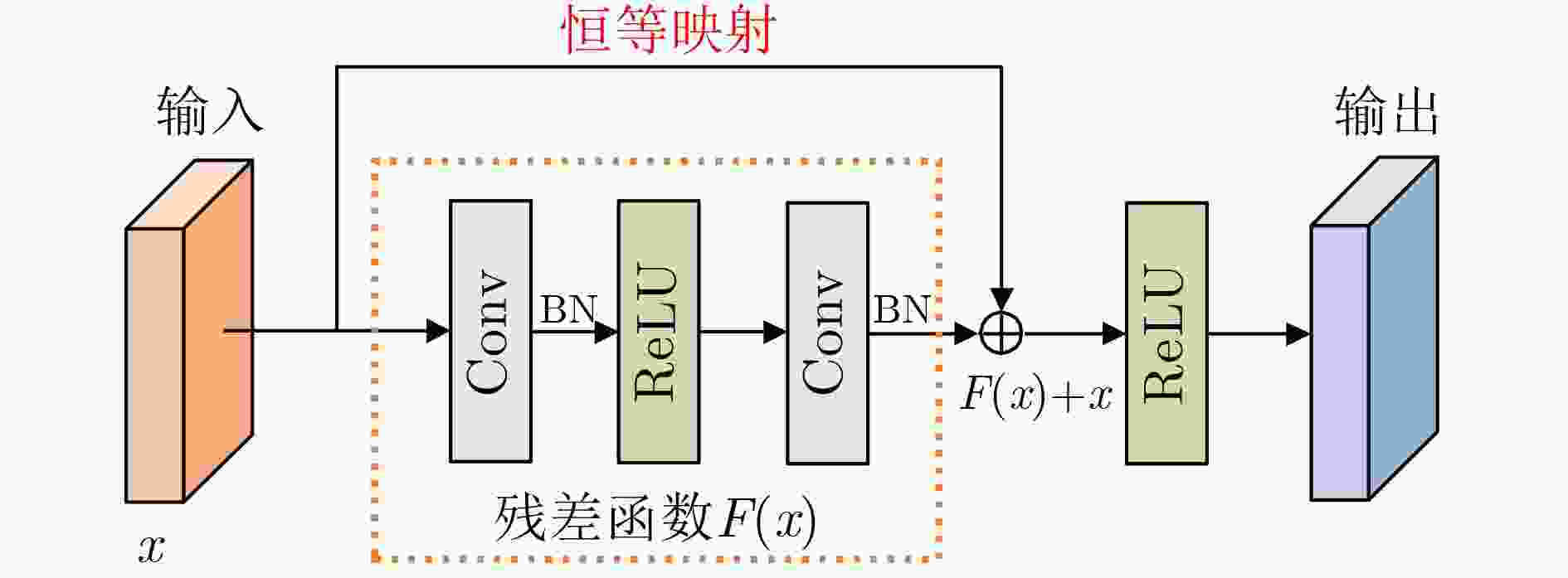
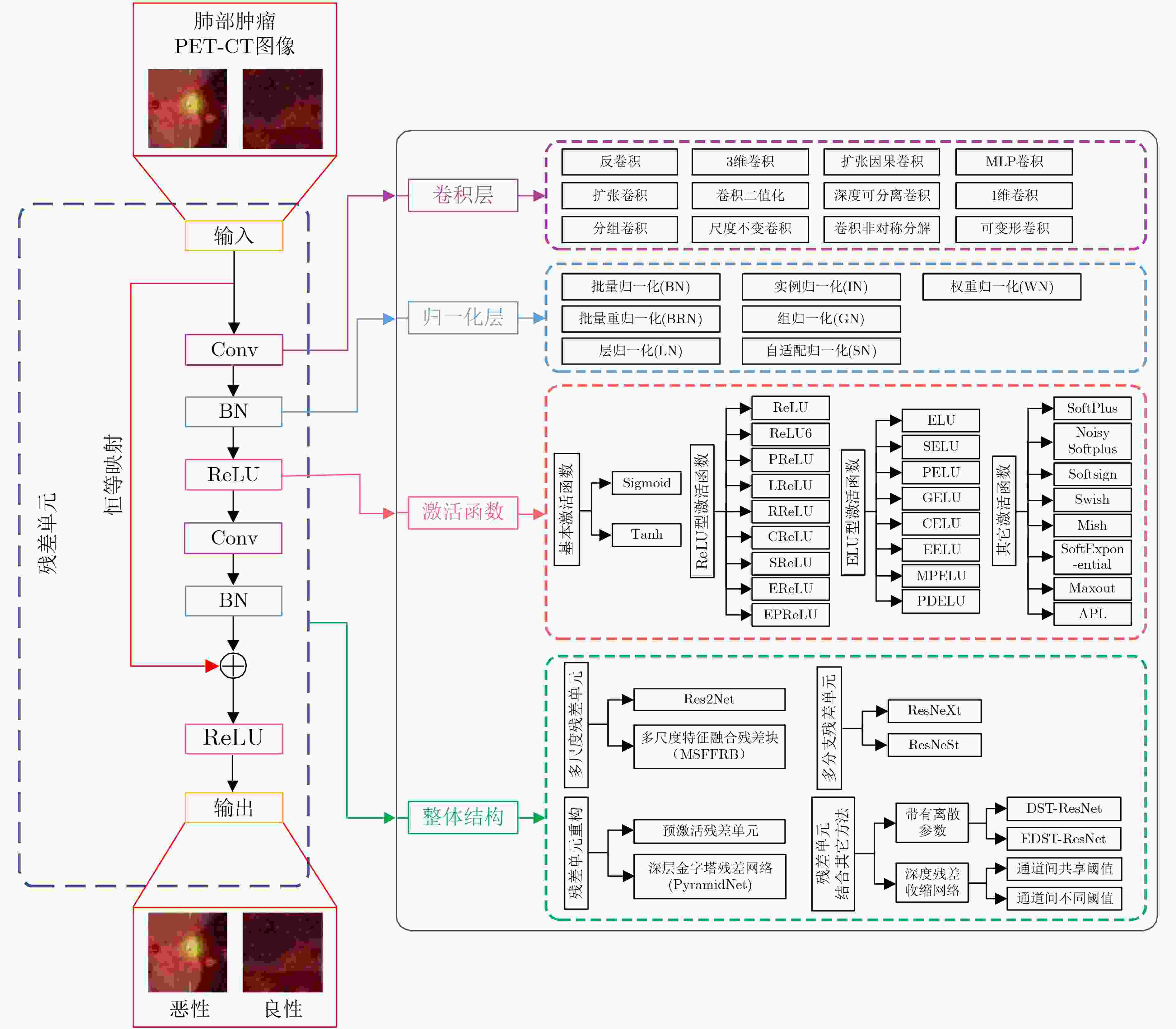
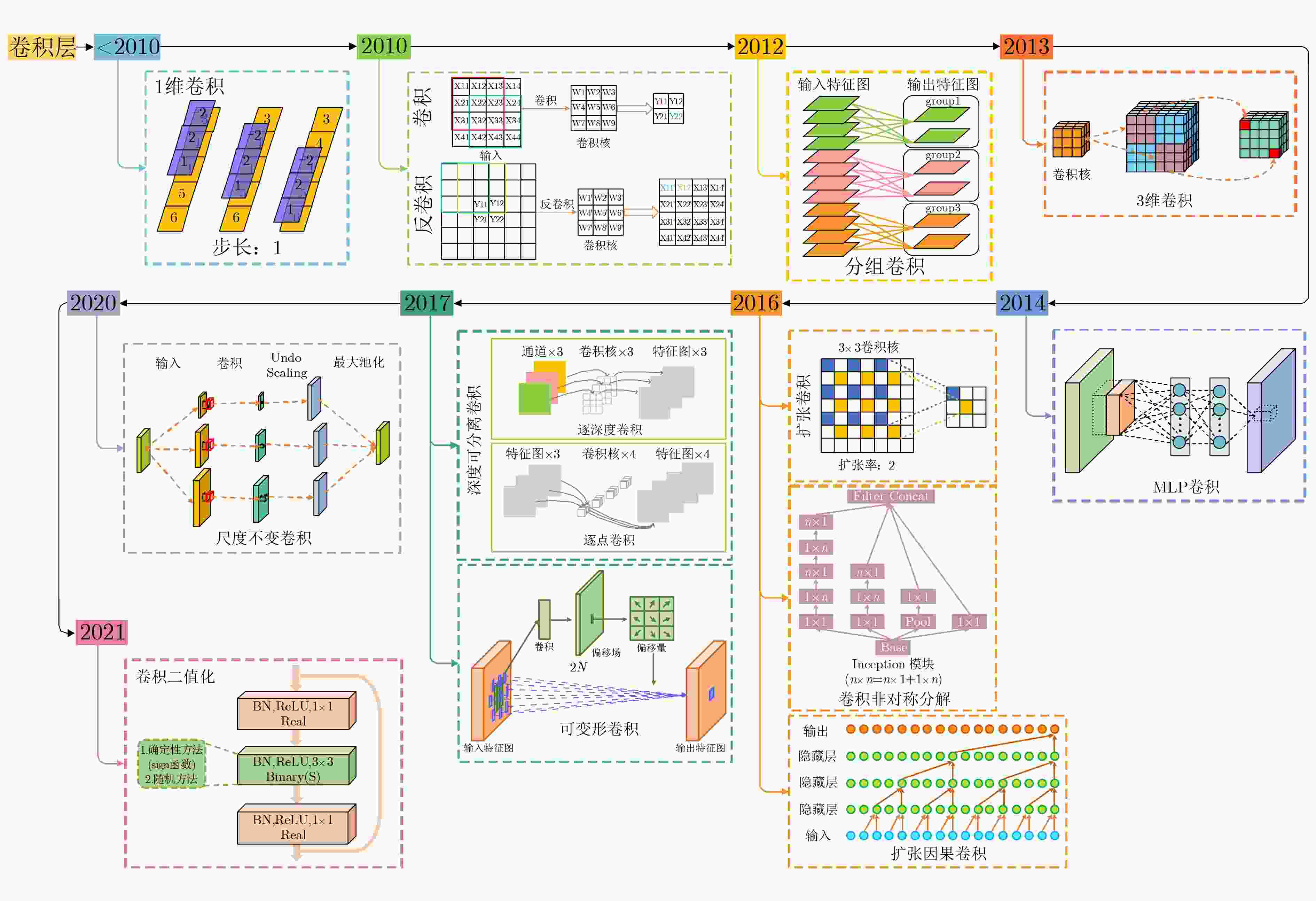
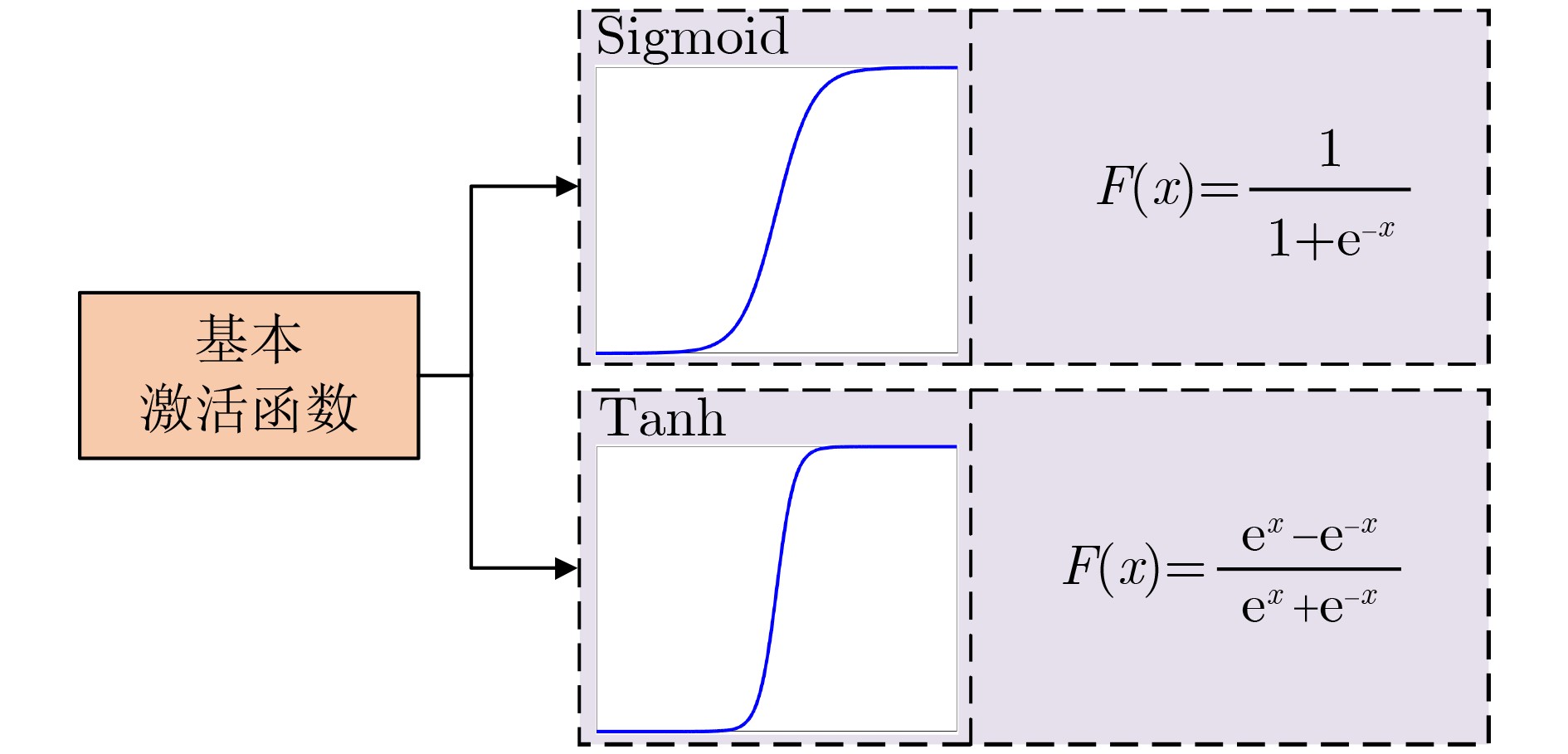
摘要: 残差神经网络(ResNet)是深度学习领域的研究热点,广泛应用于医学图像处理领域。该文对残差神经网络从以下几个方面进行综述:首先,阐述残差神经网络的基本原理和模型结构;然后,从残差单元、残差连接和网络整体结构3方面总结了残差神经网络的改进机制;其次,从与DenseNet, U-Net, Inception结构和注意力机制结合4方面探讨残差神经网络在医学图像处理领域中的广泛应用;最后,讨论ResNet在医学图像处理领域中面临的主要挑战,并对未来的发展方向进行展望。该文系统梳理了残差神经网络的最新研究进展,以及在医学图像处理中的应用,对残差神经网络的研究具有重要的参考价值。Abstract: Residual neural Network (ResNet) is a hot topic in deep learning research, which is widely used in medical image processing. The residual neural network is reviewed in this paper from the following aspects: Firstly, the basic principles and model structure of residual neural network are explained; Secondly, the improvement mechanisms of residual neural network are summarized from three aspects of residual unit, residual connection and the entire network structure; Thirdly, the wide applications of residual neural network to medical image processing are discussed from four aspects combining DenseNet, U-Net, Inception structure and attention mechanism; Finally, the main challenges that ResNet faces in medical image processing are discussed, and the future development direction is prospected. In this paper, the latest research progress of residual neural network and its application to medical image processing are systematically sorted out, which has important reference value for the research of residual neural network.
-
表 1 归一化算法总结
归一化算法 归一化对象 归一化维度 计算的元素数量 与批量大小是否有关 批量归一化(BN) 激活值 一批数据的单通道 N × H × W 有关 批量重归一化(BRN) 激活值 一批数据的单通道 N × H × W 有关 层归一化(LN) 激活值 一层数据的全部通道 C × H × W 无关 实例归一化(IN) 激活值 单一通道的数据 H × W 无关 组归一化(GN) 激活值 一层数据的通道子集 |C/G| × H × W 无关 自适配归一化(SN) 激活值 结合通道、层和小批量 — 有关 权重归一化(WN) 权重 单个卷积核的参数 — 无关 -
[1] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, United States, 2012: 1106–1114. [2] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, United States, 2015: 1–14. [3] 杨淑莹, 桂彬彬, 陈胜勇. 基于小波分解和1D-GoogLeNet的心律失常检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 3018–3027. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200774YANG Shuying, GUI Binbin, and CHEN Shengyong. Arrhythmia detection based on wavelet decomposition and 1D-GoogLeNet[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 3018–3027. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200774 [4] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [5] 周涛, 霍兵强, 陆惠玲, 等. 残差神经网络及其在医学图像处理中的应用研究[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(7): 1436–1447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.07.024ZHOU Tao, HUO Bingqiang, LU Huiling, et al. Research on residual neural network and its application on medical image processing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(7): 1436–1447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.07.024 [6] WU Nan, PHANG J, PARK J, et al. Deep neural networks improve radiologists' performance in breast cancer screening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(4): 1184–1194. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2945514 [7] KARTHIK R, MENAKA R, and HARIHARAN M. Learning distinctive filters for COVID-19 detection from chest X-ray using shuffled residual CNN[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 99: 106744. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106744 [8] LU Yan, QIN Xuejun, FAN Haoyi, et al. WBC-Net: A white blood cell segmentation network based on UNet++ and ResNet[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 101: 107006. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.107006 [9] NAZIR A, CHEEMA M N, SHENG Bin, et al. OFF-eNET: An optimally fused fully end-to-end network for automatic dense volumetric 3D intracranial blood vessels segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7192–7202. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2999854 [10] MA Danying, SHANG Linwei, TANG Jinlan, et al. Classifying breast cancer tissue by Raman spectroscopy with one-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2021, 256: 119732. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119732 [11] FANG Lingling and WANG Xin. COVID-19 deep classification network based on convolution and deconvolution local enhancement[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 135: 104588. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104588 [12] ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHOU Xinyu, LIN Mengxiao, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6848–6856. [13] CAO Feilong and GUO Wenhui. Deep hybrid dilated residual networks for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 384: 170–181. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.11.092 [14] LIN Min, CHEN Qiang, and YAN Shuicheng. Network in network[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.4400, 2013. [15] LU Zhenyu, BAI Yanzhong, CHEN Yi, et al. The classification of gliomas based on a Pyramid dilated convolution resnet model[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 133: 173–179. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2020.03.007 [16] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. [17] YAN Jining, MU Lin, WANG Lizhe, et al. Temporal convolutional networks for the advance prediction of ENSO[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 8055. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65070-5 [18] HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, 2017. [19] PRASETYO E, SUCIATI N, and FATICHAH C. Multi-level residual network VGGNet for fish species classification[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, To be published. [20] DAI Jifeng, QI Haozhi, XIONG Yuwen, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 764–773. [21] SIKDAR A and CHOWDHURY A S. Scale-invariant batch-adaptive residual learning for person re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 129: 279–286. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.11.032 [22] LIU Xuejing, LI Liang, WANG Shuhui, et al. Local-binarized very deep residual network for visual categorization[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 430: 82–93. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.11.041 [23] LOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [24] LOFFE S. Batch renormalization: Towards reducing minibatch dependence in batch-normalized models[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1945–1953. [25] TIAN Chunwei, XU Yong, and ZUO Wangmeng. Image denoising using deep CNN with batch renormalization[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 121: 461–473. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.08.022 [26] BA J L, KIROS J R, and HINTON G E. Layer normalization[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450, 2016. [27] 王志扬, 袁旭, 沈项军, 等. 深度网络去相关层归一化技术研究[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2021.01.001WANG Zhiyang, YUAN Xu, SHEN Xiangjun, et al. Research on decorrelate layer normalization in deep network[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2021.01.001 [28] ULYANOV D, VEDALDI A, and LEMPITSKY V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08022v3, 2016. [29] CASELLA A, MOCCIA S, PALADINI D, et al. A shape-constraint adversarial framework with instance-normalized spatio-temporal features for inter-fetal membrane segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 70: 102008. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102008 [30] WU Yuxin and HE Kaiming. Group normalization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(3): 742–755. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01198-w [31] LUO Ping, REN Jiamin, PENG Zhanglin, et al. Differentiable learning-to-normalize via switchable normalization[C]. The 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2019. [32] ZHONG Zhen, XIAO Guobao, ZENG Kun, et al. TSSN-Net: Two-step sparse switchable normalization for learning correspondences with heavy outliers[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 452: 159–168. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.093 [33] SALIMANS T and KINGMA D P. Weight normalization: A simple reparameterization to accelerate training of deep neural networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 901–909. [34] HUANG Lei, LIU Xianglong, QIN Jie, et al. Projection based weight normalization: Efficient method for optimization on oblique manifold in DNNs[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 105: 107317. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107317 [35] GLOROT X, BORDES A, and BENGIO Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[C]. The 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2011: 315–323. [36] XU Bing, WANG Naiyan, CHEN Tianqi, et al. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.00853v2, 2015. [37] JIANG Xiaoheng, PANG Yanwei, LI Xuelong, et al. Deep neural networks with elastic rectified linear units for object recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 1132–1139. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.09.056 [38] SHANG Wenling, SOHN K, ALMEIDA D, et al. Understanding and improving convolutional neural networks via concatenated rectified linear units[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016. [39] CLEVERT D, UNTERTHINER T, and HOCHREITER S. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs)[C]. The 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016. [40] KLAMBAUER G, UNTERTHINER T, MAYR A, et al. Self-Normalizing neural networks[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 972–981. [41] TROTTIER L, GIGUERE P, and CHAIB-DRAA B. Parametric exponential linear unit for deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Cancun, Mexico, 2017: 207–214. [42] BARRON J T. Continuously differentiable exponential linear units[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.07483, 2017. [43] KIM D, KIM J, and KIM J. Elastic exponential linear units for convolutional neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 406: 253–266. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.051 [44] LI Yang, FAN Chunxiao, LI Yong, et al. Improving deep neural network with multiple parametric exponential linear Units[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 301: 11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.01.084 [45] CHENG Qishang, LI HongLiang, WU Qingbo, et al. Parametric deformable exponential linear units for deep neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 125: 281–289. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.02.012 [46] 杜进, 陈云华, 张灵, 等. 基于改进深度残差网络的低功耗表情识别[J]. 计算机科学, 2018, 45(9): 303–307,319. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2018.09.051DU Jin, CHEN Yunhua, ZHANG Ling, et al. Energy-efficient facial expression recognition based on improved deep residual networks[J]. Computer Science, 2018, 45(9): 303–307,319. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2018.09.051 [47] GOODFELLOW I J, WARDE-FARLEY D, MIRZA M, et al. Maxout networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, USA, 2013. [48] AGOSTINELLI F, HOFFMAN M D, SADOWSKI P J, et al. Learning activation functions to improve deep neural networks[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [49] YILDIZ C, ACIKGOZ H, KORKMAZ D, et al. An improved residual-based convolutional neural network for very short-term wind power forecasting[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 228: 113731. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113731 [50] YAN Jiajia, LI Chaofeng, ZHENG Yuhui, et al. MMP-Net: A multi-scale feature multiple parallel fusion network for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 25431–25441. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971092 [51] TARIQ S, LOY-BENITEZ J, NAM K, et al. Transfer learning driven sequential forecasting and ventilation control of PM2.5 associated health risk levels in underground public facilities[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 406: 124753. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124753 [52] GAO Shanghua, CHENG Mingming, ZHAO Kai, et al. Res2Net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(2): 652–662. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938758 [53] QIN Jinghui, HUANG Yongjie, and WEN Wushao. Multi-scale feature fusion residual network for single image super-resolution[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 379: 334–342. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.076 [54] XIE Saining, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5987–5995. [55] ZHANG Hang, WU Chongruo, ZHANG Zhongyue, et al. ResNeSt: Split-attention networks[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.08955v2, 2020. [56] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 630–645. [57] HAN D, KIM J, and KIM J. Deep pyramidal residual networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6307–6315. [58] ZHOU Yue, LI Guoqi, and LI Huiqi. Automatic cataract classification using deep neural network with discrete state transition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(2): 436–446. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2928229 [59] ZHAO Minghang, ZHONG Shisheng, FU Xuyun, et al. Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4681–4690. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2943898 [60] LIU Shuaiqi, WANG Jie, LU Yucong, et al. Multi-Focus image fusion based on residual network in non-subsampled shearlet domain[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 152043–152063. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947378 [61] ARSALAN M, KIM D S, OWAIS M, et al. OR-Skip-Net: Outer residual skip network for skin segmentation in non-ideal situations[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 141: 112922. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112922 [62] JIA Haozhe, XIA Yong, SONG Yang, et al. 3D APA-Net: 3D adversarial pyramid anisotropic convolutional network for prostate segmentation in MR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(2): 447–457. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2928056 [63] ALOTAIBI B and ALOTAIBI M. A hybrid deep resNet and inception model for hyperspectral image classification[J]. PFG-Journal of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Science, 2020, 88(6): 463–476. doi: 10.1007/s41064-020-00124-x [64] LIU Bing, LIU Qiao, ZHANG Taiping, et al. MSSTResNet-TLD: A robust tracking method based on tracking-learning-detection framework by using multi-scale spatio-temporal residual network feature model[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 362: 175–194. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.024 [65] LU Zhenyu, XU Bin, SUN Le, et al. 3-D channel and spatial attention based multiscale spatial-spectral residual network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4311–4324. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3011992 [66] ZHANG Buyi, QING Chunmei, XU Xiangmin, et al. Spatial residual blocks combined parallel network for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 74513–74524. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988553 [67] FU Jun, LI Weisheng, DU Jiao, et al. A multiscale residual pyramid attention network for medical image fusion[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 66: 102488. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102488 [68] MA Yangyang, QI Fugui, WANG Pengfei, et al. Multiscale residual attention network for distinguishing stationary humans and common animals under through-wall condition using ultra-wideband radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 121572–121583. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006834 [69] HUANG Gao, SUN Yu, LIU Zhuang, et al. Deep networks with stochastic depth[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 646–661. [70] ZHANG Jinpeng, ZHANG Jinming, HU Guyue, et al. Scalenet: A convolutional network to extract multi-scale and fine-grained visual features[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 147560–147570. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2946425 [71] LIU Hong, CAO Haichao, SONG Enmin, et al. A cascaded dual-pathway residual network for lung nodule segmentation in CT images[J]. Physica Medica, 2019, 63: 112–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2019.06.003 [72] ZAGORUYKO S and KOMODAKIS N. Wide residual networks[C]. The 2016 British Machine Vision Conference, York, UK, 2016: 1–12. [73] SHI Jun, LI Zheng, YING Shihui, et al. MR image super-resolution via wide residual networks with fixed skip connection[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(3): 1129–1140. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2843819 [74] TAI Ying, YANG Jian, and LIU Xiaoming. Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2790–2798. [75] JIN Zhi, IQBAL M Z, ZOU Wenbin, et al. Dual-Stream multi-path recursive residual network for JPEG image compression artifacts reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(2): 467–479. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2982174 [76] ZHANG Ke, SUN Miao, HAN T X, et al. Residual networks of residual networks: Multilevel residual networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(6): 1303–1314. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2654543 [77] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. [78] AMARANAGESWARAO G, DEIVALAKSHMI S, and KO S B. Wavelet based medical image super resolution using cross connected residual-in-dense grouped convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2020, 70: 102819. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2020.102819 [79] DING Yi, GONG Linpeng, ZHANG Mingfeng, et al. A multi-path adaptive fusion network for multimodal brain tumor segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 412: 19–30. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.078 [80] SHAN Pufang, WANG Yiding, FU Chong, et al. Automatic skin lesion segmentation based on FC-DPN[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2020, 123: 103762. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103762 [81] CHEN Bingzhi, LI Jinxing, GUO Xiaobao, et al. DualCheXNet: Dual asymmetric feature learning for thoracic disease classification in chest X-rays[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2019, 53: 101554. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.04.031 [82] 吴宣言, 缑新科, 朱子重, 等. 深层聚合残差密集网络的超声图像左心室分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(9): 1930–1942. doi: 10.11834/jig.190552WU Xuanyan, GOU Xinke, ZHU Zizhong, et al. Left ventricular segmentation on ultrasound images using deep layer aggregation for residual dense networks[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(9): 1930–1942. doi: 10.11834/jig.190552 [83] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [84] YU Shuang, XIAO Di, FROST S, et al. Robust optic disc and cup segmentation with deep learning for glaucoma detection[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2019, 74: 61–71. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2019.02.005 [85] LU Lin, JIAN Liqiong, LUO Jun, et al. Pancreatic segmentation via ringed residual U-Net[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 172871–172878. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956550 [86] KONG Zhengmin, XIONG Feng, ZHANG Chenggang, et al. Automated maxillofacial segmentation in panoramic dental X-Ray images using an efficient encoder-decoder network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 207822–207833. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3037677 [87] PHAM V T, TRAN T T, WANG Pachun, et al. EAR-UNet: A deep learning-based approach for segmentation of tympanic membranes from otoscopic images[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2021, 115: 102065. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102065 [88] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–6. [89] CHEN Liang, BENTLEY P, MORI K, et al. DRINet for medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(11): 2453–2462. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2835303 [90] GAO Fei, WU T, CHU Xianghua, et al. Deep residual inception encoder–decoder network for medical imaging synthesis[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2020, 24(1): 39–49. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2912659 [91] ZONG Yongshuo, CHEN Jinling, YANG Lvqing, et al. U-Net based method for automatic hard exudates segmentation in fundus images using inception module and residual connection[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 167225–167235. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3023273 [92] HU Jie, SHEN Li, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-Excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [93] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [94] GUAN Qingji and HUANG Yaping. Multi-label chest X-ray image classification via category-wise residual attention learning[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 130: 259–266. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.10.027 [95] WANG Jun, BAO Yiming, WEN Yaofeng, et al. Prior-Attention residual learning for more discriminative COVID-19 screening in CT images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(8): 2572–2583. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2994908 [96] CHENG Junlong, TIAN Shengwei, YU Long, et al. ResGANet: Residual group attention network for medical image classification and segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 76: 102313. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102313 [97] XING Jie, CHEN Chao, LU Qinyang, et al. Using BI-RADS stratifications as auxiliary information for breast masses classification in ultrasound images[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2021, 25(6): 2058–2070. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3034804 [98] 乔思波, 庞善臣, 王敏, 等. 基于残差混合注意力机制的脑部CT图像分类卷积神经网络模型[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(5): 984–991. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200881QIAO Sibo, PANG Shanchen, WANG Min, et al. A convolutional neural network for brain CT image classification based on residual hybrid attention mechanism[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(5): 984–991. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200881 -






 下载:
下载:

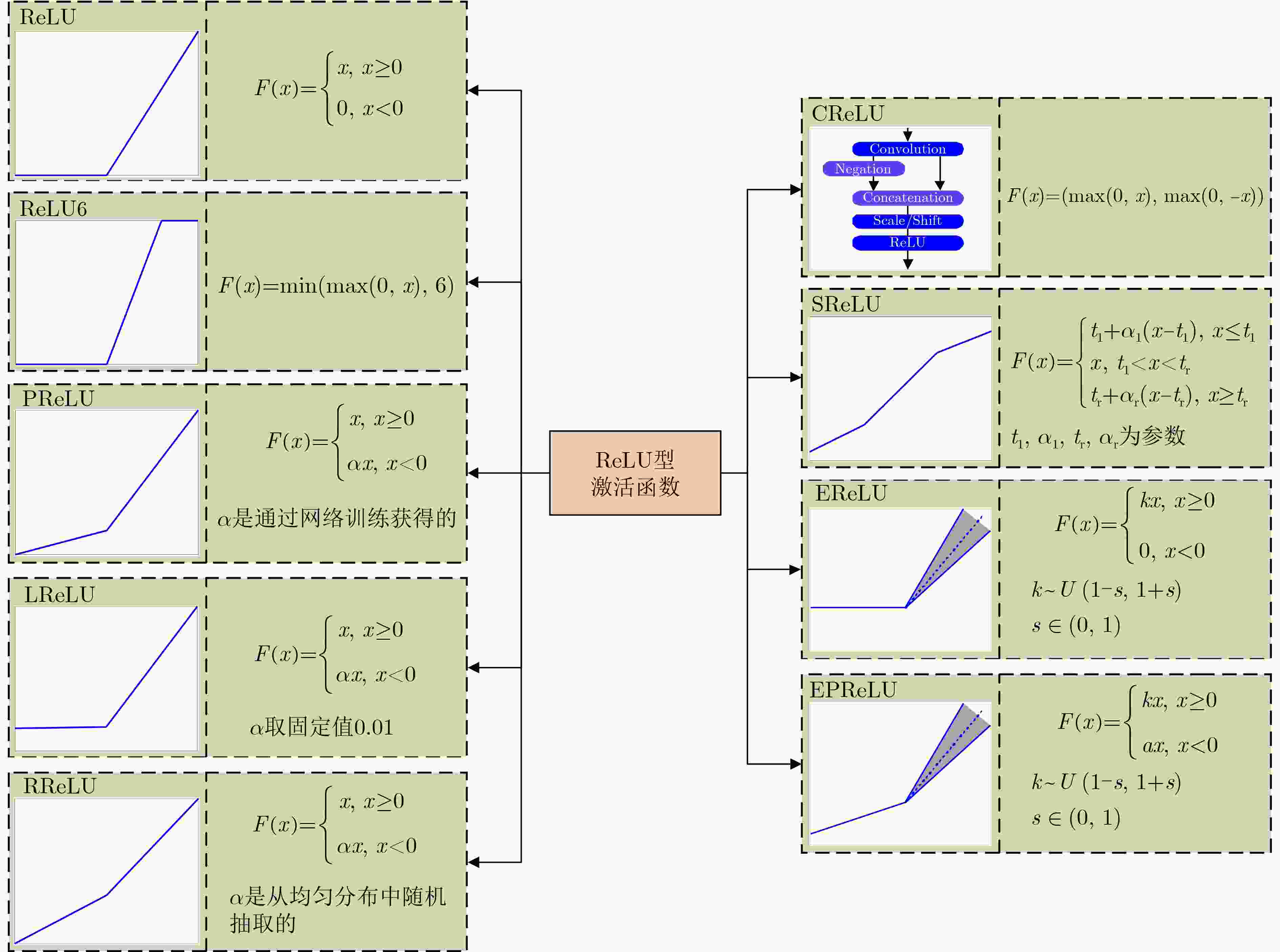
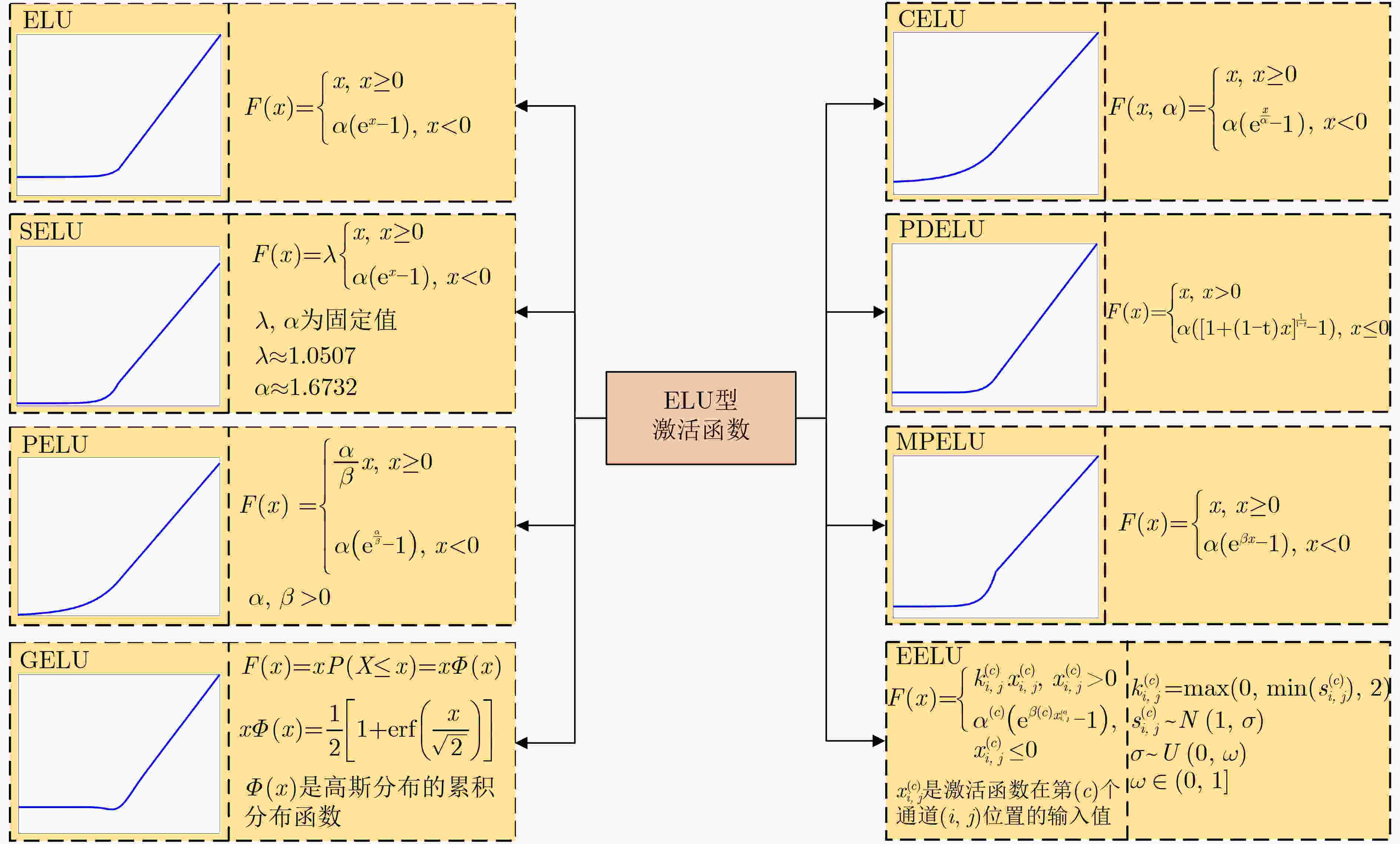
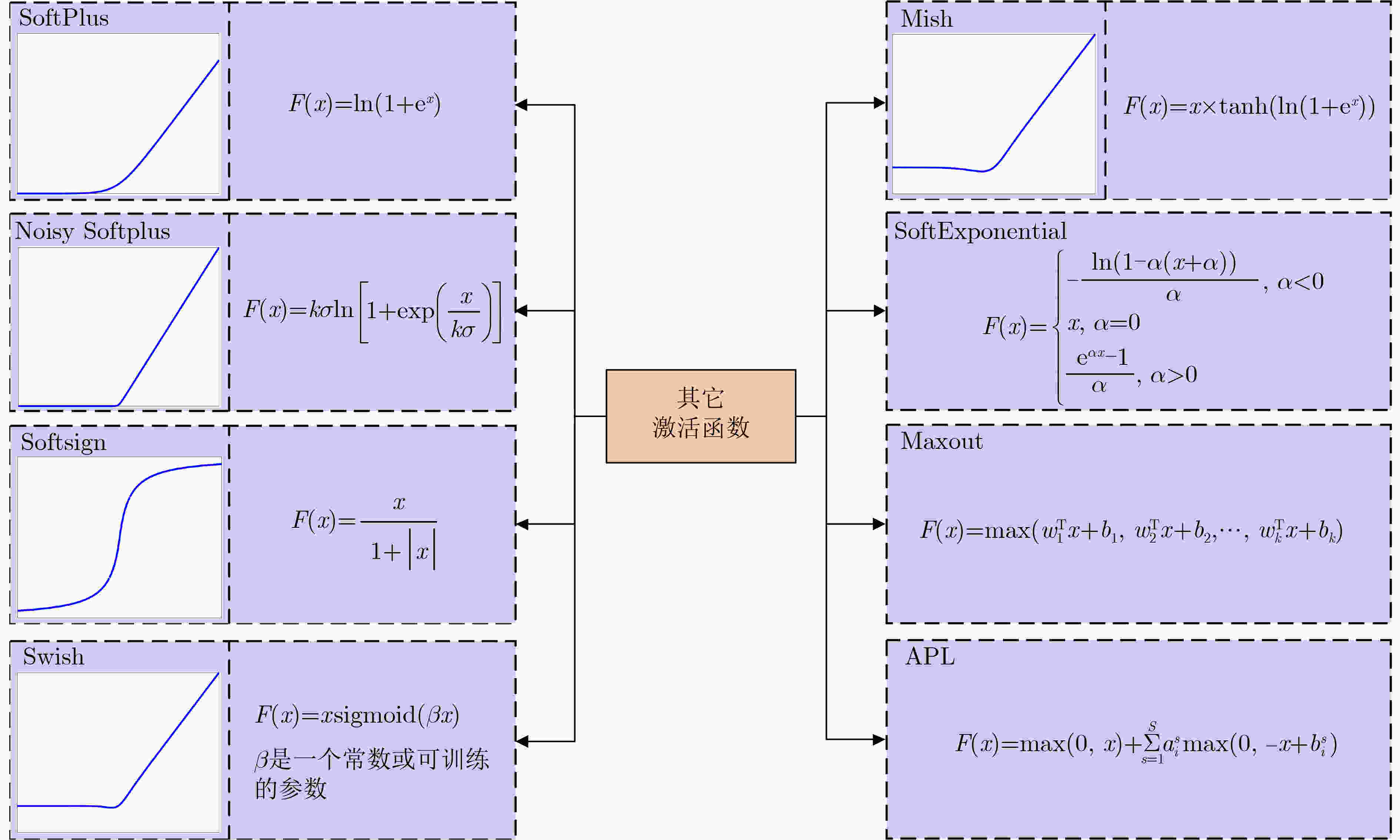
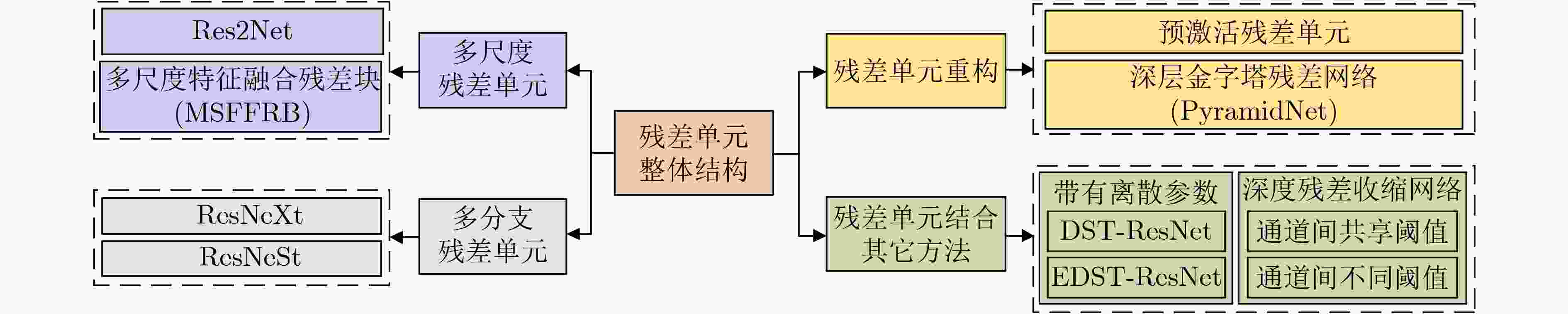
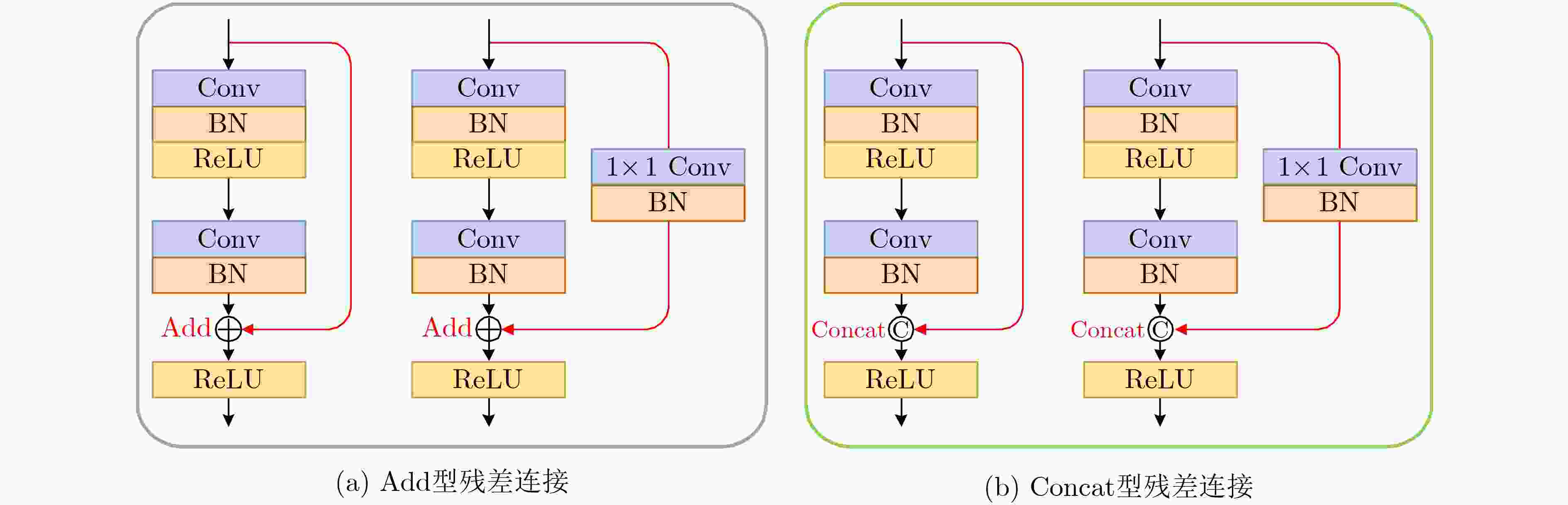
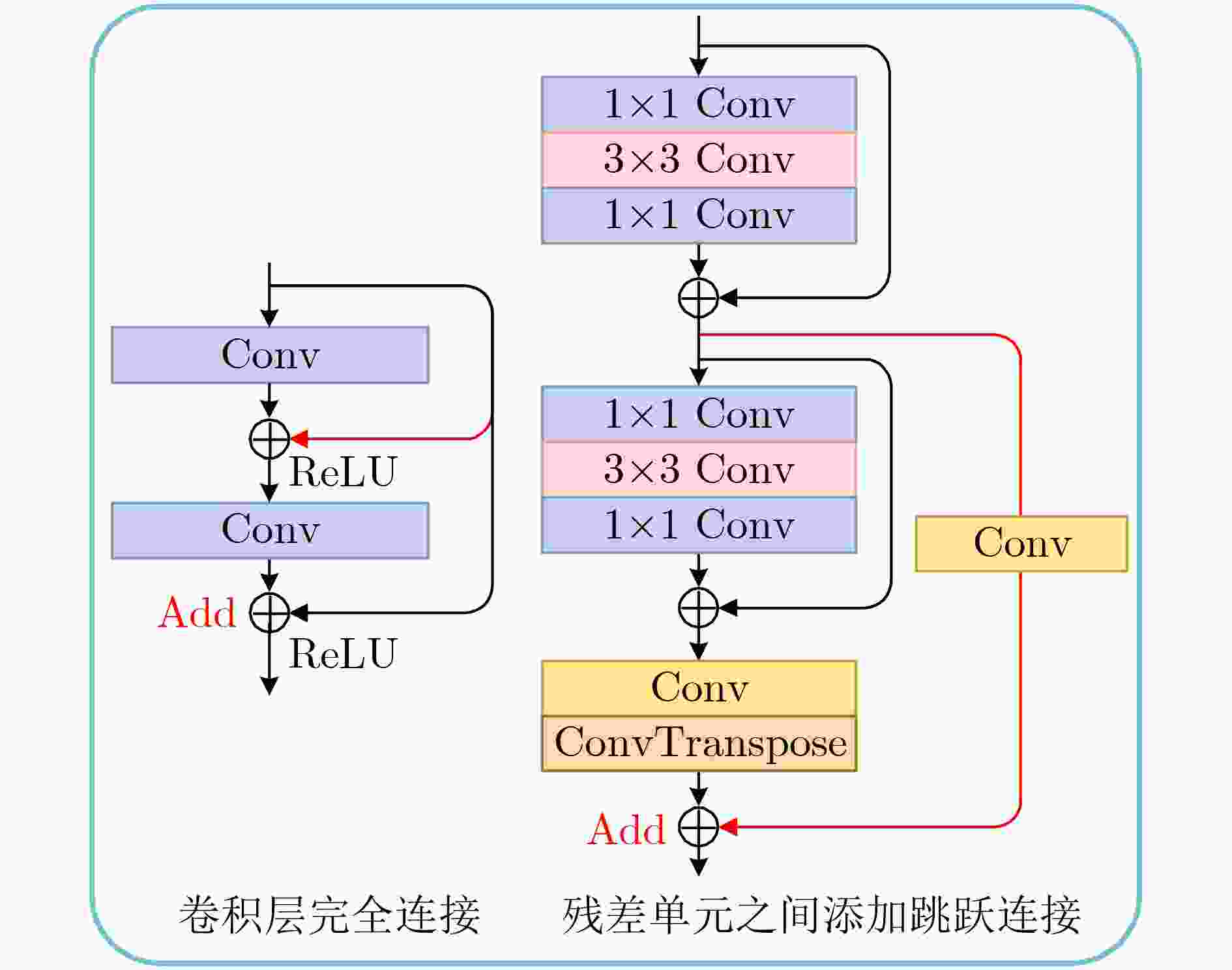
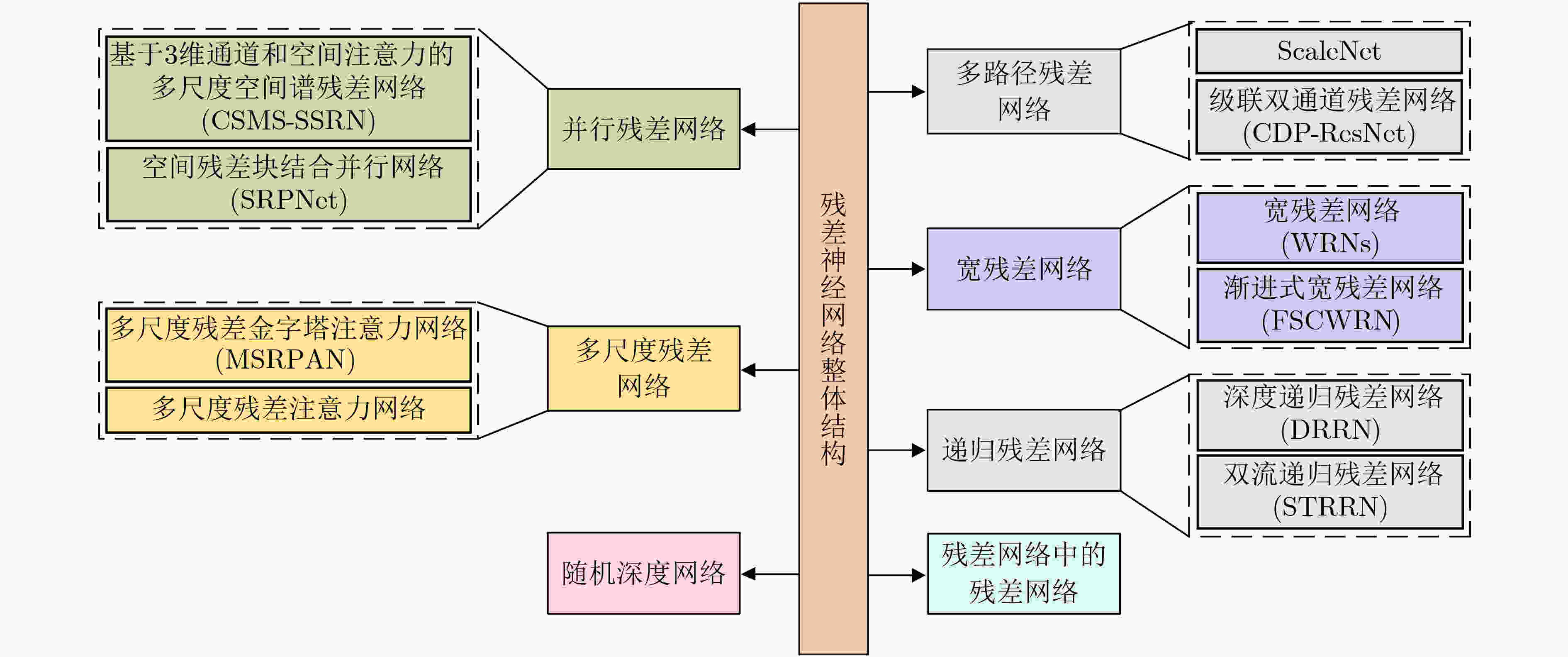


 下载:
下载:
