An Overview on Calibration Techniques for Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits
-
摘要: 射频集成电路(RFICs)对工艺偏差、器件失配、器件非线性等引入的静态非理想因素以及温度变化、增益改变、输入/输出频率变动等引入的动态非理想因素所表现出的鲁棒性较差。该文深入挖掘影响射频集成电路性能的关键因素,并对典型的校准算法进行归纳和总结,为高性能射频集成电路设计提供理论支撑。Abstract: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFICs) show poor robustness to static non-ideal factors introduced by process deviations, device mismatches, device nonlinearities, and dynamic non-ideal factors introduced by temperature changes, gain changes, and input/output frequency changes. The key factors that affect the performance of RFICs are excavated deeply, and typical calibration algorithms are summarized to provide theoretical support for the design of high-performance RFICs.
-
表 1 本文校准技术总结
降级原因 降级现象 产生原因 校准技术 出现场景 射频
收发
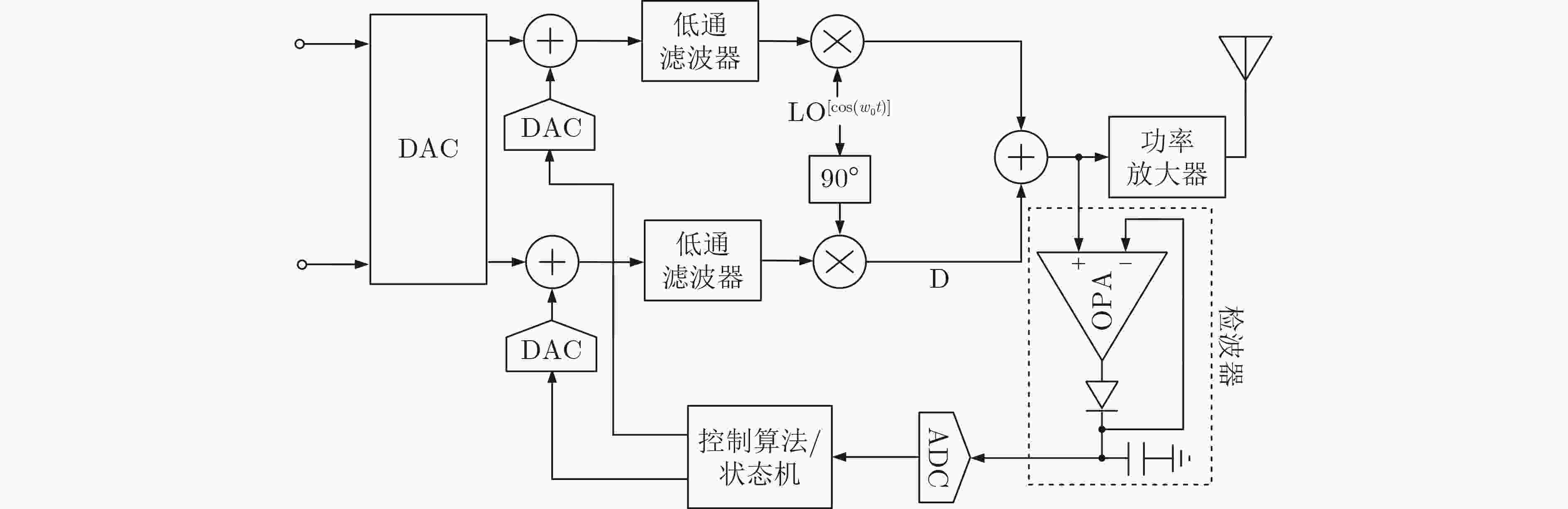
链路直流偏移 接收链路饱和 自混频/外部强干扰/
工艺偏差、温度变化直流偏移校准 接收链路 偶次非线性失真 降低信号信噪比 器件非线性、器件失配 偶次非线性失真校准 零中频接收链路 I/Q失配 星座图旋转 工艺偏差、温度变化 I/Q失配校准 收发链路 谐波干扰 降低信号信噪比 混频器开关效应的奇次谐波 谐波抑制技术 超宽带接收链路 滤波器带宽偏移 信号混叠效应或者抑制
周期性频谱能力减弱工艺偏差、温度变化 滤波器带宽偏移校准 收发链路 本振泄露 星座图水平/垂直移动 器件失配 本振泄露校准 发射链路 PA非线性 发射频谱增生 器件非线性 数字预失真 发射链路 频率综合器 KVCO过大 本振杂散增强、锁定时间长 频率综合器固有属性 自动频率校准 频率综合器 稳定性降级 环路自激 外部输入/输出频率变化 稳定性校准 多通道
射频收发多通道
幅相失配波束畸形成形 器件失配导致多通道幅相失配 多片同步校准技术 相控阵等多通道
应用场景 -
[1] HUANG Minyu, CHI Taiyun, LI Sensen, et al. A 24.5–43.5-GHz ultra-compact CMOS receiver front end with calibration-free instantaneous full-band image rejection for multiband 5G massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(5): 1177–1186. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2959495 [2] 贾海昆, 池保勇. 硅基毫米波雷达芯片研究现状与发展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 173–190. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190666JIA Haikun and CHI Baoyong. The status and trends of silicon-based millimeter-wave radar SoCs[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 173–190. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190666 [3] KUMAR T B, MA Kaixue, and YEO K S. A 4 GHz 60 dB variable gain amplifier with tunable DC offset cancellation in 65 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2015, 25(1): 37–39. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2014.2361676 [4] 李松亭. CMOS射频接收集成电路关键技术研究与设计实现[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2015.LI Songting. Research of key techniques and implementation on CMOS rf receiving integrated circuits[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015. [5] SHIH H Y, KUO C N, CHEN W H, et al. A 250 MHz 14 dB-NF 73 dB-Gain 82 dB-DR analog baseband chain with digital-assisted DC-offset calibration for ultra-wideband[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(2): 338–350. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2036320 [6] LI Songting, LI Jiancheng, GU Xiaochen, et al. A continuously and widely tunable 5 dB-NF 89.5 dB-Gain 85.5 dB-DR CMOS TV receiver with digitally-assisted calibration for multi-standard DBS applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(11): 2762–2774. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2281691 [7] JIN Jing, LIU Xiaoming, YAN Taotao, et al. Fully configurable capacitor-less oversampling DC offset cancellation for direct conversion receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2019, 66(10): 1683–1687. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2019.2921895 [8] RETZ G, SHANAN H, MULVANEY K, et al. A highly integrated low-power 2.4GHz transceiver using a direct-conversion diversity receiver in 0.18 μm CMOS for IEEE802.15. 4 WPAN[C]. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, USA, 2009: 414–415. [9] BRANDOLINI M, ROSSI P, SANZOGNI D, et al. A +78 dBm IIP2 CMOS direct downconversion mixer for fully integrated UMTS receivers[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(3): 552–559. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.864123 [10] DUFRENE K, BOOS Z, and WEIGEL R. Digital adaptive IIP2 calibration scheme for CMOS downconversion mixers[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(11): 2434–2445. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2005453 [11] JIANG Peichen, LU Zhijian, GUAN Rui, et al. All-digital adaptive module for automatic background IIP2 calibration in CMOS downconverters with fast convergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2013, 60(7): 427–431. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2013.2261171 [12] DANILOVIC D, MILOVANOVIC V, CATHELIN A, et al. Low-power inductorless RF receiver front-end with IIP2 calibration through body bias control in 28nm UTBB FDSOI[C]. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 87–90. [13] XIA Bing, QI Nan, FU Jian, et al. A blocker-tolerant ZigBee transceiver with on-chip balun and CR/IQ/IIP2 self-calibrations for home automation[J]. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 2016, 86(1): 11–23. doi: 10.1007/s10470-015-0636-6 [14] KACZMAN D, SHAH M, ALAM M, et al. A single-chip 10-band WCDMA/HSDPA 4-band GSM/EDGE SAW-less CMOS receiver with DigRF 3G interface and +90 dBm IIP2[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(3): 718–739. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2009.2013762 [15] ELAHI I and MUHAMMAD K. IIP2 calibration by injecting DC offset at the mixer in a wireless receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2007, 54(12): 1135–1139. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2007.905376 [16] VAHIDFAR M B and SHOAEI O. A high IIP2 mixer enhanced by a new calibration technique for zero-IF receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2008, 55(3): 219–223. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2008.918998 [17] ZHANG Weifeng, HE Hongyin, and WANG Riyan. A 2.0 GHz IQ imbalance compensator with programmable switch biases in a passive mixer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2018, 65(8): 989–993. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2799571 [18] KO J, KIM J, CHO S, et al. A 19-mW 2.6-mm2 L1/L2 dual-band CMOS GPS receiver[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(7): 1414–1425. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.847326 [19] CHOO H, SESTOK C, ZHANG Xiaoxi, et al. Joint TX and feedback RX IQ mismatch compensation for integrated direct conversion transmitters[C]. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 53–56. [20] QI Nan, XU Yang, CHI Baoyong, et al. A dual-channel Compass/GPS/GLONASS/Galileo reconfigurable GNSS receiver in 65 nm CMOS with on-chip I/Q calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2012, 59(8): 1720–1732. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2206502 [21] LI Songting, LI Jiancheng, GU Xiaochen, et al. Reconfigurable all-band RF CMOS transceiver for GPS/GLONASS/Galileo/Beidou with digitally assisted calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2015, 23(9): 1814–1827. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2014.2348593 [22] ZHANG Cheng, WANG Lifang, TAN Xi, et al. Adaptive IF selection and IQ mismatch compensation in a low-IF GSM receiver[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(6): 065005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/6/065005 [23] YE Hui, LI Bin, HUANG Mo, et al. A digital IQ imbalance self-calibration in FDD transceiver[C]. International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test, Hsinchu, China, 2017: 1–4. [24] KHANDELWAL A and VERMA A. A Novel gain, phase and offset calibration scheme for wideband direct-conversion transmitters[C]. IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference, Glasgow, UK, 2015: 1–5. [25] LI Chunshu, LI Min, POLLIN S, et al. Reduced complexity on-chip IQ-imbalance self-calibration[C]. IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems, Quebec City, Canada, 2012: 31–36. [26] KAWAI S, YAMAGISHI T, HAGIWARA Y, et al. A 1024-QAM capable WLAN receiver with –56.3 dB image rejection ratio using self-calibration technique[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–4. [27] PANG Jian, MAKI S, KAWAI S, et al. A 50.1-Gb/s 60-GHz CMOS transceiver for IEEE 802.11ay with calibration of LO feedthrough and I/Q imbalance[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(5): 1375–1390. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2886338 [28] 陈雷, 岳光荣, 唐俊林, 等. 基于数字预失真的发射机I/Q不平衡矫正[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(4): 847–853. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160581CHEN Lei, YUE Guangrong, TANG Junlin, et al. Calibration of transmitter I/Q imbalance based on digital Pre-distortion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(4): 847–853. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160581 [29] KAWAI S, ITO R, NAKATA K, et al. An 802.11ax 4×4 high-efficiency WLAN AP transceiver SoC supporting 1024-QAM with frequency-dependent IQ calibration and integrated interference analyzer[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(12): 3688–3699. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2877168 [30] BAZRAFSHAN A, TAHERZADEH-SANI M, and NABKI F. A 0.8-4 GHz software-defined radio receiver with improved harmonic rejection through non-overlapped clocking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2018, 65(10): 3186–3195. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2815720 [31] WU Liang, NG A W L, ZHENG Shiyuan, et al. A 0.9-5.8 GHz software-defined receiver RF front-end with transformer-based current-gain boosting and harmonic rejection calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2017, 25(8): 2371–2382. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2017.2695719 [32] CHA H K, KWON K, CHOI J, et al. A CMOS wideband RF front-end with mismatch calibrated harmonic rejection mixer for terrestrial digital TV tuner applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2010, 58(8): 2143–2151. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2010.2053072 [33] DE BOER P T, ALINK M S O, and KLUMPERINK E A M. Simplified harmonic rejection mixer analysis and design based on a filtered periodic impulse model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2021, 68(7): 2292–2296. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3051769 [34] SHEHATA M A, ROY V, BRESLIN J, et al. A 32-42-GHz RTWO-based frequency quadrupler achieving >37 dBc harmonic rejection in 22-nm FD-SOI[J]. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters, 2021, 4: 72–75. doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2021.3055628 [35] EL-AASSAR O, KIBAROGLU K, and REBEIZ G M. A 16 path all-passive harmonic rejection mixer with watt-level in-band IIP3 in 45-nm CMOS SOI[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2020, 30(8): 790–793. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2020.3004546 [36] GEBHARD A, SADJINA S, TERTINEK S, et al. A harmonic rejection strategy for 25% duty-cycle IQ-mixers using digital-to-time converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2020, 67(7): 1229–1233. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2019.2937654 [37] KANG H, HO W G, SINGH V K, et al. A wideband receiver employing PWM-based harmonic rejection downconversion[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(5): 1398–1410. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2784764 [38] HAQ F U, ENGLUND M, ANTONOV Y, et al. A blocker-tolerant two-stage harmonic-rejection RF front-end[C]. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Boston, USA, 2019: 203–206. [39] FORBES T, HO W G, and GHARPURE R. Design and analysis of harmonic rejection mixers with programmable LO frequency[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(10): 2363–2374. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2275652 [40] WU Hao, MURPHY D, and DARABI H. A harmonic-selective multi-band wireless receiver with digital harmonic rejection calibration[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(3): 796–807. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2885546 [41] KIM S, JEONG M, KIM Y, et al. A complex band-pass filter for low-IF conversion DAB/T-DMB tuner with I/Q mismatch calibration[C]. IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 2008: 473–476. [42] LE VU H, LUU H T T, TRAN L D, et al. Implementation of CMOS tunable on-chip Gm-C IF filter in RF front-end IC for SDR transceiver[C]. 7th International Conference on Integrated Circuit, Design, and Verification, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2017: 46–51. [43] HUANG Mo, CHEN Dihu, GUO Jianping, et al. A CMOS delta-sigma PLL transmitter with efficient modulation bandwidth calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2015, 62(7): 1716–1725. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2015.2441965 [44] LIANG Zhen, LI Bin, HUANG Mo, et al. A four-band TD-LTE transmitter with wide dynamic range and LPF bandwidth calibration[C]. International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test, Hsinchu, China, 2017: 1–4. [45] CHEN Fangxiong, LIN Min, CHEN Bei, et al. Design of an active-RC low-pass filter with accurate tuning architecture[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2008, 29(11): 2238–2244. [46] LI Songting, CHEN Lihu, and ZHAO Yong. Reconfigurable active-RC LPF with self-adaptive bandwidth calibration for software-defined radio in 130 nm CMOS[C]. 14th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology, Qingdao, China, 2018: 1–3. [47] 吴建辉, 周明杰, 陈超, 等. 一种用于Gm-C滤波器的主从结构频率校准电路[P]. 中国专利, 103905037A, 2014.WU Jianhui, ZHOU Mingjie, CHEN Chao, et al. Principal and subordinate structure frequency calibration circuit used for Gm-C filter[P]. China Patent. 103905037A, 2014. [48] 李巍, 高亭, 陈云峰, 等. 一种用于Gm-C滤波器的频率自调谐电路[P]. 中国专利, 101867354B, 2014.LI Wei, GAO Ting, CHEN Yunfeng, et al. Frequency self-tuning circuit used for Gm-C filter[P]. China Patent. 101867354B, 2014. [49] ADI. AD9361 user guide[EB/OL]. https://www.analog.com/cn/products/ad9361.html, 2021. [50] WU C, WANG Yanjie, NIKOLI B, et al. An interference-resilient wideband mixer-first receiver with LO leakage suppression and I/Q correlated orthogonal calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2016, 64(4): 1088–1101. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2532867 [51] SHIH H Y and WANG C W. A highly-integrated 3-8 GHz Ultra-wideband RF transmitter with digital-assisted carrier leakage calibration and automatic transmit power control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2012, 20(8): 1357–1367. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2011.2157842 [52] PANG Jian, MAKI S, KAWAI S, et al. 24.9 A 128-QAM 60GHz CMOS transceiver for IEEE802.11ay with calibration of LO feedthrough and I/Q imbalance[C]. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 424–425. [53] 张飞飞, 彭程, 荣兴帅, 等. 基于射频收发芯片的发射本振泄露数字校准系统及方法[P]. 中国专利, 111181594A, 2020.ZAHNG Feifei, PENG Cheng, RONG Xingshuai, et al. Transmitting local oscillator leakage digital calibration system and method based on radio frequency transceiver chip[P]. China Patent. 111181594A, 2020. [54] 蓝翱华, 周瑞兴. 一种进行IQ信号实时校准的方法和装置[P]. 中国专利, 102223330A, 2011.LAN Aohua and ZHOU Ruixing. Method and device for IQ (intelligence quotient) signal real-time calibration[P]. China Patent. 102223330A, 2011. [55] SETH S, KWON D H, VENUGOPALAN S, et al. A dynamically biased multiband 2G/3G/4G cellular transmitter in 28 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(5): 1096–1108. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2510023 [56] O'SULLIVAN C, NERAD J, BURYANEC J, et al. Carrier leak calibration scheme on a 0.18µm transmitter[C]. IET Irish Signals and Systems Conference, Cork, Ireland, 2010: 141–146. [57] PRAVEEN M V and KRISHNAPURA N. An automatic LO leakage calibration method for class-AB power mixer based RF transmitters[C]. IEEE Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Florence, Italy, 2018: 1–5. [58] 曹韬, 刘友江, 杨春, 等. 高效宽带包络跟踪系统电路性能优化及非线性行为校正[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 787–794. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190275CAO Tao, LIU Youjiang, YANG Chun, et al. Circuits optimization and system linearization for high efficiency and wideband envelope tracking architecture[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 787–794. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190275 [59] YOO S W, HUNG S C, and YOO S M. A Watt-level quadrature class-G switched-capacitor power amplifier with linearization techniques[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(5): 1274–1287. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2904209 [60] CHO K and GHARPUREY R. An efficient class-G stage for switching RF power amplifier applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2019, 66(4): 597–601. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2870277 [61] BANERJEE A, DING Lei, and HEZAR R. A high efficiency multi-mode outphasing RF power amplifier with 31.6 dBm peak output power in 45nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(3): 815–828. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2954068 [62] JUNG D, LI Sensen, PARK J S, et al. A CMOS 1.2-V hybrid current- and voltage-mode three-way digital Doherty PA with built-in phase nonlinearity compensation[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(3): 525–535. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2953832 [63] HUNG S C, YOO S W, and YOO S M. A quadrature class-G complex-domain Doherty digital power amplifier[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(7): 2029–2039. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3040973 [64] OTA T, KAWASAKI T, KIMURA S, et al. A novel multi-band look-up table based digital predistorter with a single common feedback loop[C]. Proceedings of 2018 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Kyoto, Japan, 2018: 551–553. [65] REN Jijun. Digital predistorter for short-wave power amplifier with improving index accuracy of lookup table based on FPGA[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 182881–182885. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2960092 [66] WANG Siqi, ROGER M, SARRAZIN J, et al. An efficient method to study the tradeoff between power amplifier efficiency and digital predistortion complexity[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2019, 29(11): 741–744. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2019.2939911 [67] CAMPO P P, LAMPU V, ANTTILA L, et al. Closed-loop sign algorithms for low-complexity digital predistortion: Methods and performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(1): 1048–1062. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3038316 [68] SALEH A A M. Frequency-independent and frequency-dependent nonlinear models of TWT amplifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1981, 29(11): 1715–1720. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1981.1094911 [69] MANSELL A R and BATEMAN A. Adaptive predistortion with reduced feedback complexity[J]. Electronics Letters, 1996, 32(13): 1153–1154. doi: 10.1049/el:19960785 [70] WHITE G P, BURR A G, and JAVORNIK T. Modelling of nonlinear distortion in broadband fixed wireless access systems[J]. Electronics Letters, 2003, 39(8): 686–687. doi: 10.1049/el:20030462 [71] CAVERS J K. The effect of quadrature modulator and demodulator errors on adaptive digital predistorters for amplifier linearization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1997, 46(2): 456–466. doi: 10.1109/25.580784 [72] EUN C and POWERS E J. A new Volterra predistorter based on the indirect learning architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(1): 223–227. doi: 10.1109/78.552219 [73] ISAKSSON M, WISELL D, and RONNOW D. A comparative analysis of behavioral models for RF power amplifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2006, 54(1): 348–359. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.860500 [74] VUONG X T and GUIBORD A F. Modelling of nonlinear elements exhibiting frequency-dependent AM/AM and AM/PM transfer characteristics[J]. Canadian Electrical Engineering Journal, 1984, 9(3): 112–116. doi: 10.1109/CEEJ.1984.6593795 [75] DING Lei, ZHOU G T, MORGAN D R, et al. A robust digital baseband predistorter constructed using memory polynomials[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2004, 52(1): 159–165. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2003.822188 [76] KU H, MCKINLEY M D, and KENNEY J S. Quantifying memory effects in RF power amplifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(12): 2843–2849. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2002.805196 [77] ISAKSSON M, WISELL D, and RONNOW D. Wide-band dynamic modeling of power amplifiers using radial-basis function neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(11): 3422–3428. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.855742 [78] DING Lei, MUJICA F, and YANG Zigang. Digital predistortion using direct learning with reduced bandwidth feedback[C]. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Seattle, USA, 2013: 1–3. [79] ZHANG Qian, CHEN Wenhua, and FENG Zhenghe. Reduced cost digital predistortion only with in-phase feedback signal[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2018, 28(3): 257–259. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2018.2797541 [80] 兰榕, 胡欣, 邹峰, 等. 基于循环平稳特性的欠采样宽带数字预失真研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1274–1280. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190105LAN Rong, HU Xin, ZOU Feng, et al. Research of low sampling frequency broadband digital predistortion with cyclostationary characteristics[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1274–1280. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190105 [81] NG E, BELTAGY Y, SCARLATO G, et al. Digital predistortion of millimeter-wave RF beamforming arrays using low number of steering angle-dependent coefficient sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2019, 67(11): 4479–4492. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2019.2924893 [82] TERVO N, KHAN B, KURSU O, et al. Digital predistortion of phased-array transmitter with shared feedback and far-field calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(1): 1000–1015. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.3038193 [83] PHAM Q A, LÓPEZ-BUENO D, WANG Teng, et al. Partial least squares identification of multi look-up table digital predistorters for concurrent dual-band envelope tracking power amplifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2018, 66(12): 5143–5150. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2018.2857819 [84] HUANG Hai, XIA Jingjing, and BOUMAIZA S. Novel parallel-processing-based hardware implementation of baseband digital predistorters for linearizing wideband 5G transmitters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(9): 4066–4076. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.2993236 [85] SURYASARMAN P, LIU Peng, and SPRINGER A. Optimizing the identification of digital predistorters for improved power amplifier linearization performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2014, 61(9): 671–675. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2014.2331095 [86] HU Xin, LIU Ting, LIU Zhijun, et al. A novel single feedback architecture with time-interleaved sampling for multi-band DPD[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(6): 1033–1036. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2910812 [87] ZHOU Dayong and DEBRUNNER V. A novel adaptive nonlinear predistorter based on the direct learning algorithm[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 2004: 2362–2366. [88] NAGATA Y. Linear amplification technique for digital mobile communications[C]. Vehicular Technology Conference, San Francisco, USA, 1989: 159–164. [89] 吴溪. 基于自主标准的UHF RFID读写器的设计与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014.WU Xi. Design and realization of the UHF RFID reader based on independent standard[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014. [90] CAVERS J K. Amplifier linearization using a digital predistorter with fast adaptation and low memory requirements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1990, 39(4): 374–382. doi: 10.1109/25.61359 [91] FAULKNER M and JOHANSSON M. Adaptive linearization using predistortion-experimental results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1994, 43(2): 323–332. doi: 10.1109/25.293651 [92] SHIN J and SHIN H. A fast and high-precision VCO frequency calibration technique for wideband ΔΣ fractional-N frequency synthesizers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2010, 57(7): 1573–1582. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2009.2036057 [93] LEE D S, JANG J H, PARK H G, et al. A wide-locking-range dual injection-locked frequency divider with an automatic frequency calibration loop in 65-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2015, 62(4): 327–331. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2014.2387591 [94] ZHOU Jin, LI Wei, HUANG Deping, et al. A 0.4-0.6-GHz frequency synthesizer using dual-mode VCO for software-defined radio[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(2): 848–859. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2233493 [95] SHIN J and SHIN H. A 1.9-3.8 GHz ΔΣ fractional-N PLL frequency synthesizer with fast auto-calibration of loop bandwidth and VCO frequency[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(3): 665–675. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2179733 [96] HU Ang, LIU Dongsheng, ZHANG Kefeng, et al. A 0.045- to 2.5-GHz frequency synthesizer with TDC-based AFC and phase switching multi-modulus divider[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(12): 4470–4483. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.2997598 [97] DING Xin, WU Jianhui, and CHEN Chao. An agile automatic frequency calibration technique for PLL[C]. IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications, Beijing, China, 2018: 32–33. [98] RYU H, SUNG E T, PARK S, et al. Fast automatic frequency calibrator using an adaptive frequency search algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2017, 25(4): 1490–1496. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2016.2627578 [99] MOON Y J, ROH Y S, JEONG C Y, et al. A 4.39-5.26 GHz LC-tank CMOS voltage-controlled oscillator with small VCO-gain variation[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2009, 19(8): 524–526. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2009.2024846 [100] LIU Xiaolong, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Li, et al. A 3.01-3.82 GHz CMOS LC voltage-controlled oscillator with 6.29% VCO-gain variation for WLAN applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(7): 075002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/075002 [101] LU Lei, CHEN Jinghong, YUAN Lu, et al. An 18-mW 1.175-2-GHz frequency synthesizer with constant bandwidth for DVB-T tuners[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2009, 57(4): 928–937. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2014449 [102] WU Ting, HANUMOLU P K, MAYARAM K, et al. Method for a constant loop bandwidth in LC-VCO PLL frequency synthesizers[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(2): 427–435. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2010792 [103] 李国儒, 孙庭波. 针对射频收发芯片的同步系统及方法[P]. 中国专利, 111245472A, 2020.LI Guoru and SUN Tingbo. Radio frequency transceiver chip, and synchronization system and method for radio frequency transceiver chip[P]. China Patent. 111245472A, 2020. [104] YU Sunquan, CHEN Lihu, LI Songting, et al. Adaptive multi-beamforming for space-based ADS-B[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2019, 72(2): 359–374. doi: 10.1017/S0373463318000735 [105] YU Sunquan, CHEN Lihu, FAN Chengguang, et al. Integrated antenna and receiver system with self-calibrating digital beamforming for space-based ADS-B[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 170: 480–486. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.02.001 [106] WANG Yun, WU Rui, PANG Jian, et al. A 39-GHz 64-element phased-array transceiver with built-in phase and amplitude calibrations for large-array 5G NR in 65-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(5): 1249–1269. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.2980509 [107] SONG Zheng, LIU Xiliang, ZHAO Xiaokun, et al. A low-power NB-IoT transceiver with digital-polar transmitter in 180-nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2017, 64(9): 2569–2581. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2707412 [108] 廖怀林. 硅基射频集成电路和系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 167–173. [109] BEN-BASSAT A, GROSS S, LANE A, et al. A 10.5 fully integrated 27 dBm dual-band all-digital polar transmitter supporting 160 MHz for WiFi 6 applications[C]. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 180–182. [110] GHAHREMANI A, ANNEMA A J, and NAUTA B. A +20 dBm highly efficient linear outphasing class-E PA without AM/AM and AM/PM characterization requirements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2019, 66(7): 1149–1153. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2877708 [111] 廖怀林, 杨帆, 王润华, 等. 一种高线性度的数控相位插值器[P]. 中国专利, 106027037A, 2016.LIAO Huailin, YANG Fan, WANG Runhua, et al. High-linearity digitally phase interpolator[P]. China Patent. 106027037A, 2016. [112] STASZEWSKI R B, LEIPOLD D, MUHAMMAD K, et al. Digitally controlled oscillator (DCO)-based architecture for RF frequency synthesis in a deep-submicrometer CMOS process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 2003, 50(11): 815–828. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2003.819128 [113] 俞思辰. 无线射频领域中宽带全数字频率综合器的研究与设计[D]. [博士论文], 复旦大学, 2014. -





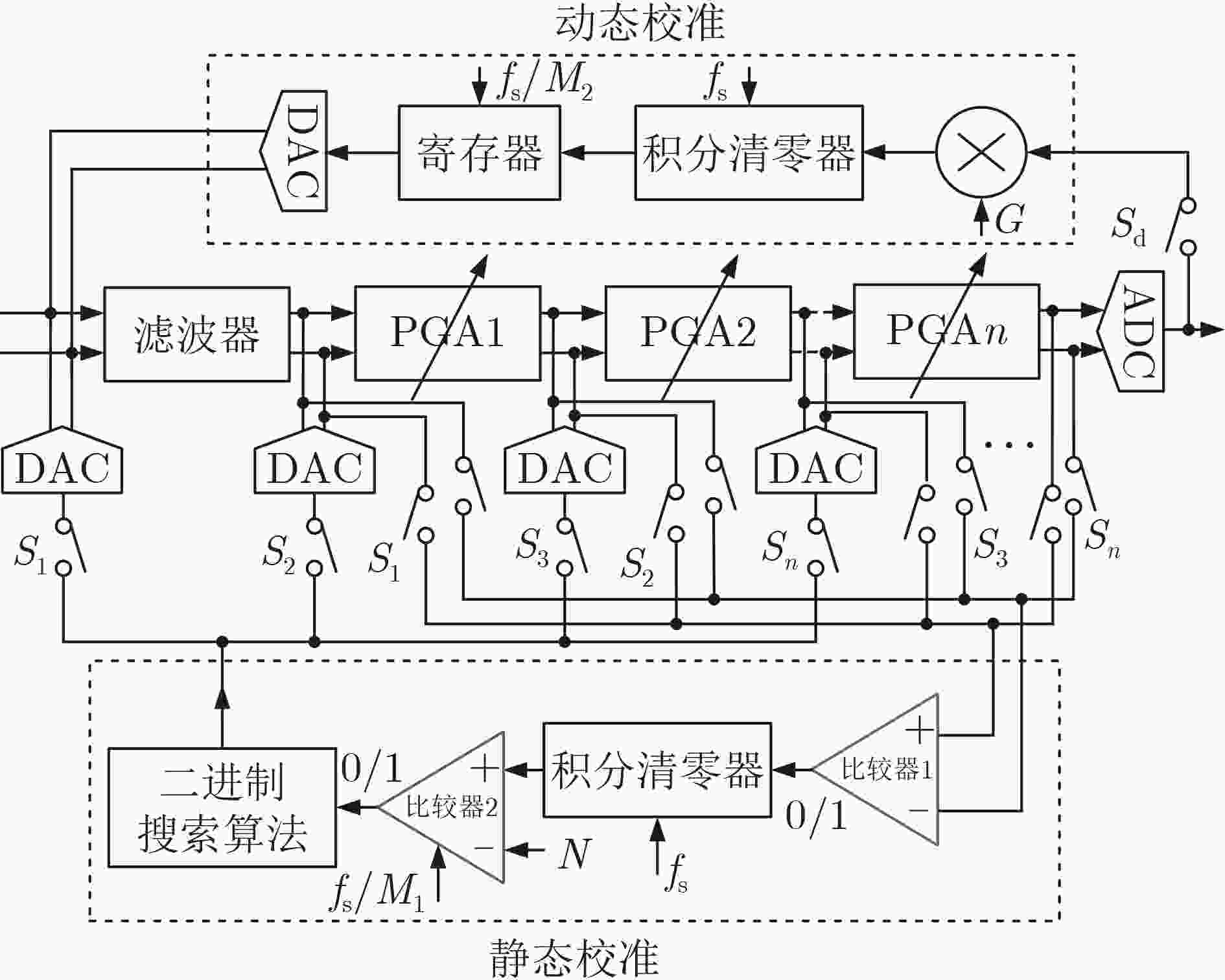
 下载:
下载:
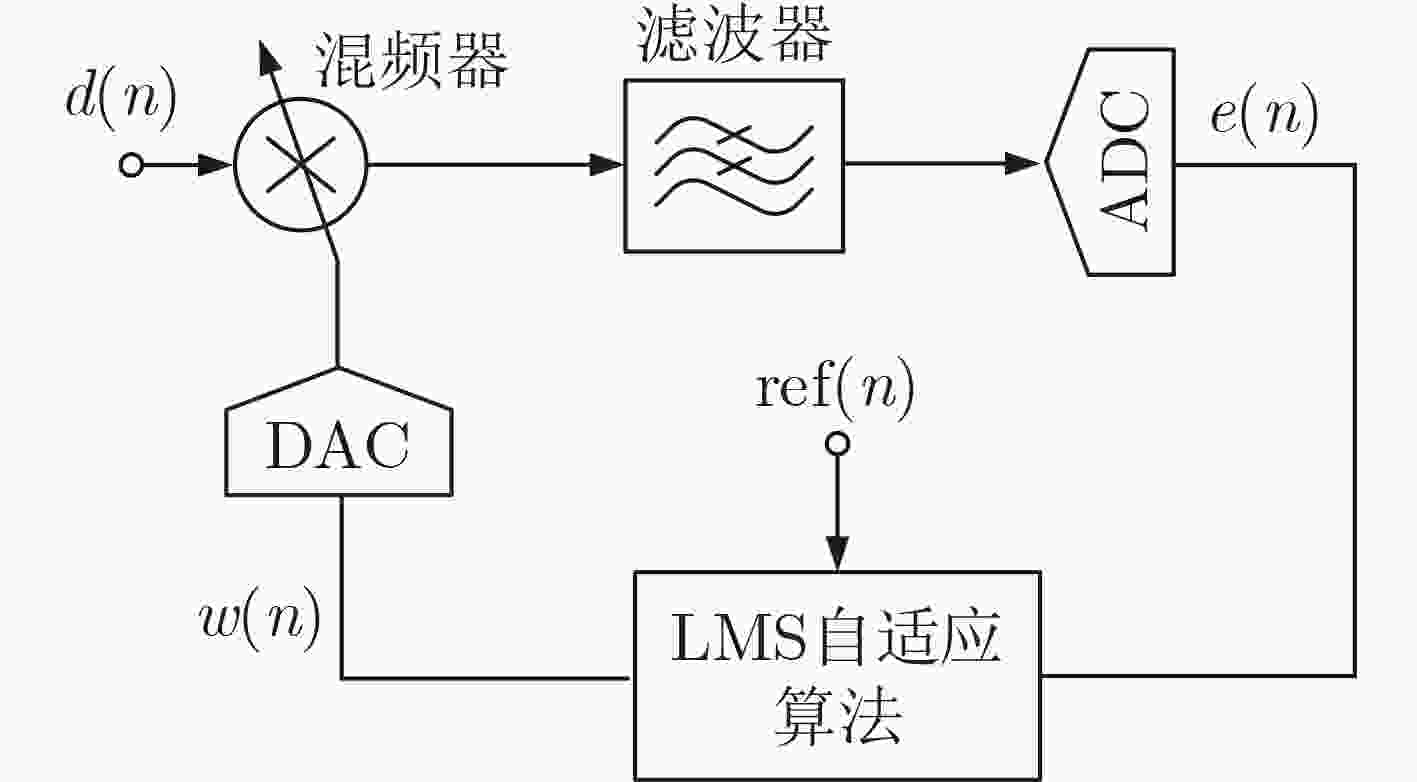


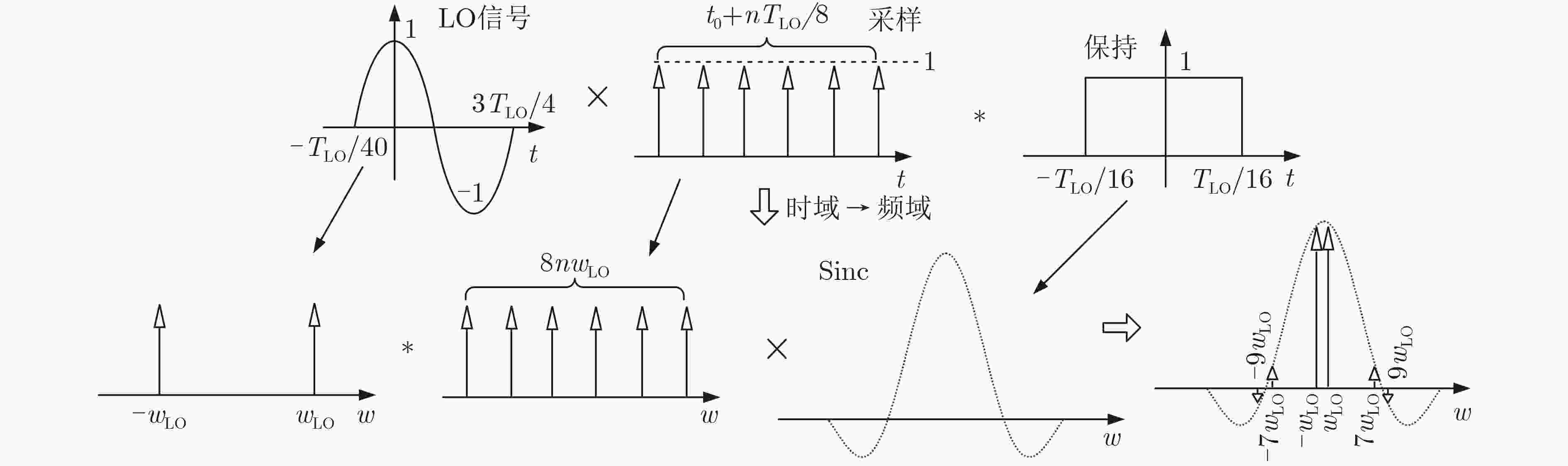
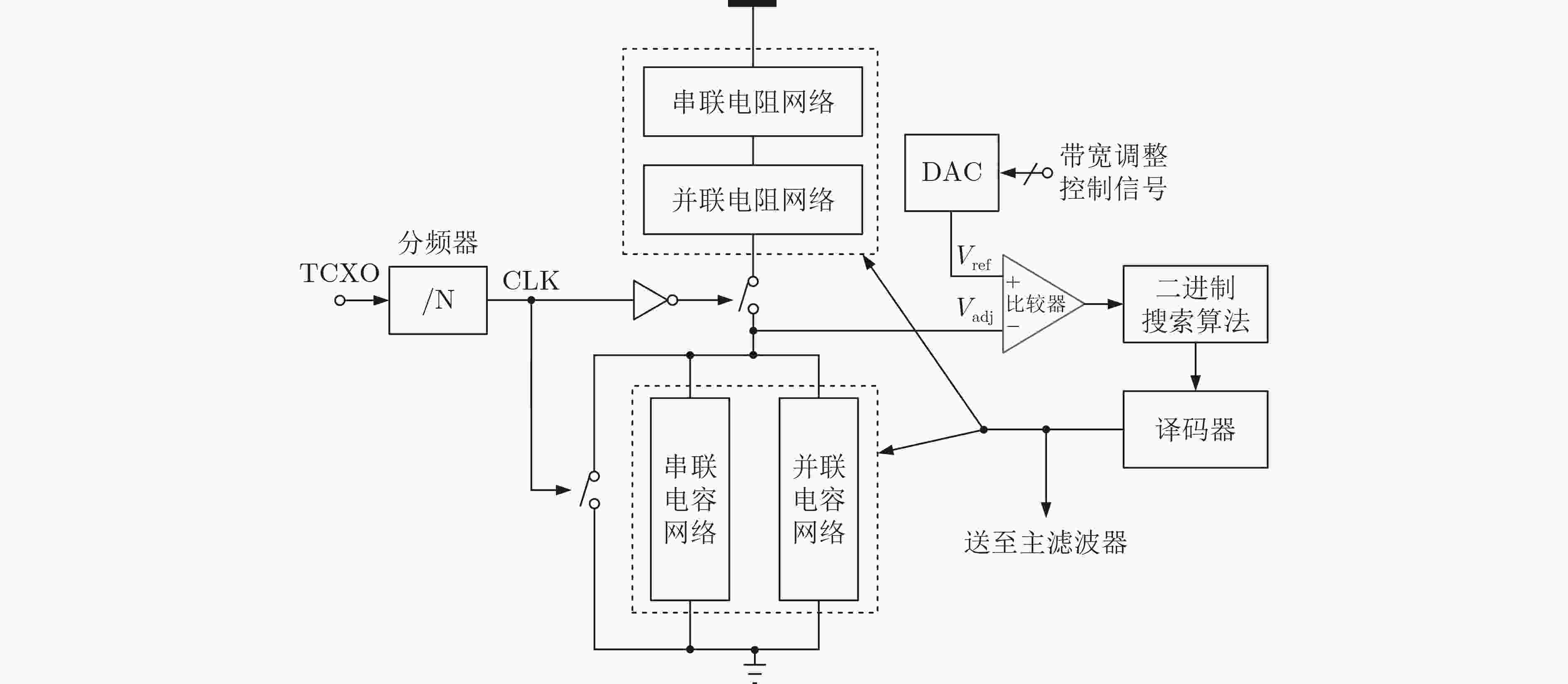


 下载:
下载:
