Anonymous Online Registration and Secure Authentication Protocol in Intelligent Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks
-
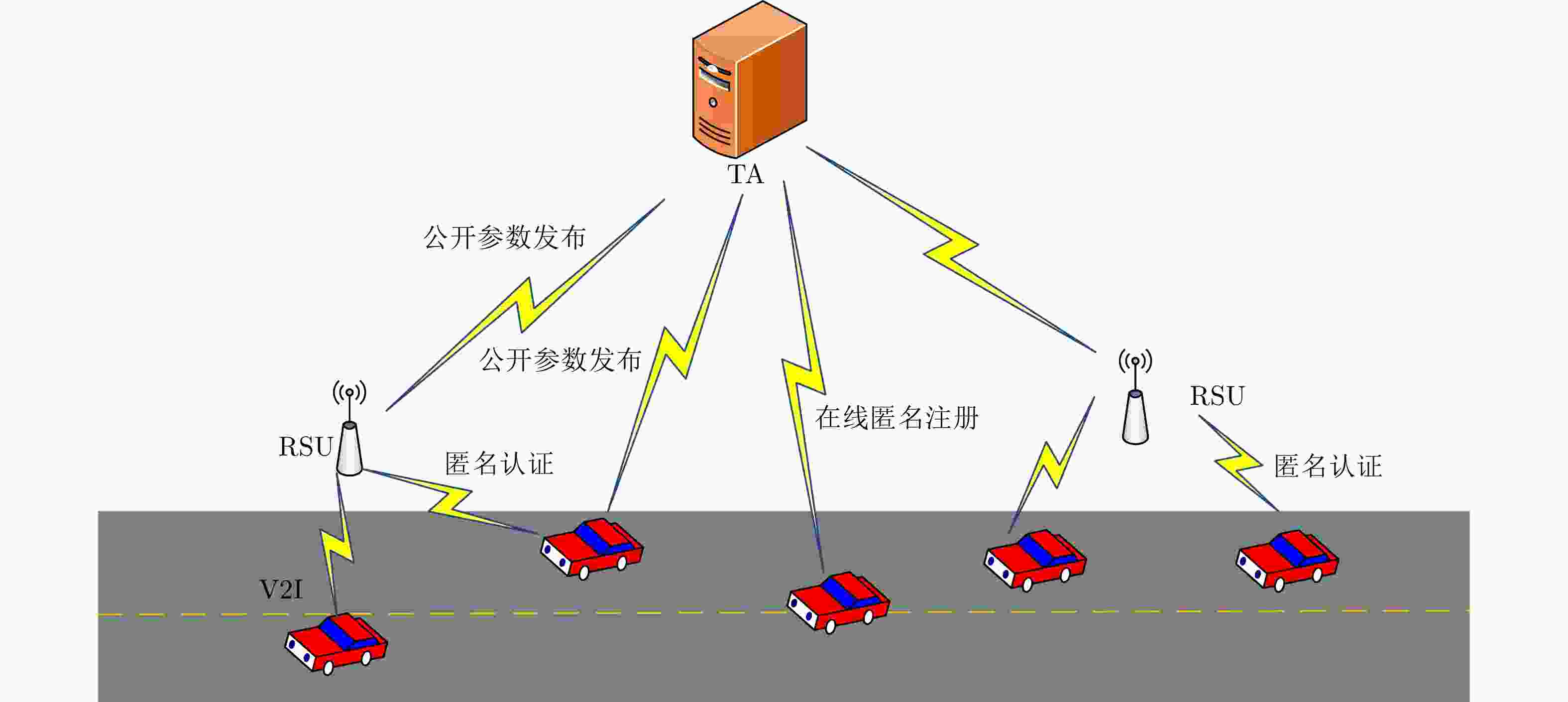
摘要: 随着智能交通系统(ITS)的建立,车载自组织网络(VANETs)在提高交通安全和效率方面发挥着重要的作用。由于车载自组织网络具有开放性和脆弱性特点,容易遭受各种安全威胁与攻击,这将阻碍其广泛应用。针对当前车载自组织网络传输中数据的认证性与完整性,以及车辆身份的隐私保护需求,该文提出一种智能车载自组织网络中的匿名在线注册与安全认证协议。协议让智能车辆在公开信道以匿名的方式向交通系统可信中心(TA)在线注册。可信中心证实智能车辆的真实身份后,无需搭建安全信道,在开放网络中颁发用于安全认证的签名私钥。车辆可以匿名发送实时交通信息到附近路边基站单元(RSU),并得到有效认证与完整性检测。该协议使得可信中心可以有效追踪因发送伪造信息引起交通事故的匿名车辆。协议可以让路边基站单元同时对多个匿名车辆发送的交通信息进行批量认证。该协议做了详细的安全性分析和性能分析。性能比较结果表明,该协议在智能车辆端的计算开销以及在路边基站单元端的通信开销都具有明显优势,而且无需搭建安全信道就能够实现匿名在线注册,因此可以安全高效地部署在智能车载自组织网络环境。Abstract: With the establishment of the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), Vehicular Ad-hoc NETworks (VANETs) play great roles in improving traffic safety and efficiency. However, due to the openness and fragility of VANETs, they are vulnerable to various network threats and attacks, and thereby hindering the wide applications of VANETs. To address the requirements for authentication and integrity of transmitted data, identity privacy-preservation, an anonymous online registration and secure authentication protocol is proposed in intelligent VANETs. The protocol enables a vehicle to execute anonymous online registration in transportation systems Trusted Authority (TA) via a public channel. Once validating the real identity, TA can return the private key to the vehicle for subsequent secure authentication via public channel. Thus, the vehicle can generate an authenticated traffic message to a nearby RoadSide Unit (RSU) in real time, so that RSU performs the authentication and integrity verification. This protocol supports anonymous identity traceability, thus TA can revoke the real identity of a malicious vehicle, which has generated some forged messages and caused traffic jams or accidents. In addition, this protocol supports batch authentication and verification of those transmitted traffic messages from different anonymous vehicles. The detailed security analysis and performance evaluation have been conducted. The results demonstrate that the protocol has outstanding advantages on the computational costs of each vehicle and the communication overhead of RSU, and can realize anonymous online registration without establishing secure channel. Therefore, the protocol could be securely and efficiently deployed in intelligent VANETs.
-
表 1 车辆匿名在线注册流程
(1) 计算$ {\text{UP}}{{\text{W}}_{{i}}}{\text{ = }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{(UI}}{{\text{D}}_{{i}}}{\text{||PW}}{{\text{D}}_{{i}}}{\text{)}} $; (2) 随机选取${s_i} \leftarrow {{Z} }_{\text{q} }^{\text{*} }$,计算${Q_i} = { {{H} }_2}({\text{UPW} }{}_{ {i} }{\text{||tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{ {i} } }{\text{||} }{s_i}||{T_i})P$; (3) 计算$Q_i^* = { {{H} }_{\text{2} } }{\text{(UPW} }{}_{ {i} }{\text{||tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{ {i} } }{\text{||} }{s_{ {i} } }{\text{|} }|{T_i}){\text{P} }{ {\text{K} }_{ {\text{TA} } } }$, ${\text{PSI} }{ {\text{D} }_{ {i} } }{\text{ = En} }{ {\text{c} }_{ {{Q} }_{ {{i,y} } }^{\text{*} } } }{\text{(RID} }{}_{ {i} }{\text{||P} }{ {\text{K} }_{ {\text{TA} } } }{\text{|} }|{T_i}|{\text{|request)} }$; (4)计算${\text{Aut} }{ {\text{h} }_{ {i} } }{\text{ = } }{ {{H} }_{\text{3} } }{\text{(PSID} }{}_{ {i} }{\text{||} }{ {{Q} }_{ {i} } }{\text{||tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{ {i} } }{\text{||} }{T_i}|{\text{|RI} }{ {\text{D} }_{ {i} } }{\text{)} }$; Vehicles $\overrightarrow {{\text{Re} }{ {\text{g} }_{{i} } }{\text{ = \{ PSI} }{ {\text{D} }_{_{{i} } } },{Q_i},{\text{tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{{i} } }{\text{,Aut} }{ {\text{h} }_{{i} } }\}}$ TA (a) 判断时间戳是否满足${\text{tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{{j} } }{\text{ - tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{ {i} } } \le { {\Delta {\rm{time} } } }$; (b) 计算$ Q_i^* = s{Q_i} $,解密得到$ {\text{RI}}{{\text{D}}_{{i}}},{T_i} $; (c) 计算${\text{Auth} }'_{ {i} }{\text{ = } }{ { {H} }_{\text{3} } }{\text{(PSI} }{ {\text{D} }_{ {i} } }||Q{}_i||{\text{tim} }{ {\text{e} }_{ {i} } }||{T_i}||{\text{RI} }{ {\text{D} }_{ {i} } }{\text{)} }$; (d) 判断${\text{Auth} }'_{ {i} }{\text{ = Auth} }$是否相等; (e) 选择$ {t_i} \leftarrow Z_q^* $,计算$ {R_i} = {t_i}P $,
$ {\text{s}}{{\text{k}}_{{i}}} = {t_i} + s{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(PSI}}{{\text{D}}_i}||{R_i}) $;(f) ${F_i}{\text{ = En} }{ {\text{c} }_{ {{Q} }_{ {{i,y} } }^{\text{*} } } }{\text{(s} }{ {\text{k} }_{ {i} } }{\text{||} }{T_i}||{\text{request} })$。 $\overleftarrow{ {\text{\{ } }{ {{F} }_i},{R_i}\} }$ 表 2 匿名认证验证流程
Vehicle RSU (1)选择$ {t_i} \leftarrow Z_q^* $,计算$ {U_i} = {r_i}P = ({\xi _i},{\zeta _i}) $; (2)计算$ {\eta _i} = {H_5}({\text{PSI}}{{\text{D}}_{{i}}}||{M_i}||{\text{time}}'_{{i}}) $; (3)进行签名$ {\mu }_{i}={\xi }_{i}\mathrm{mod}q,{\nu }_{i}=({\text{sk}}_{{i}}+{\mu }_{i}{r}_{i}{\eta }_{i})\mathrm{mod}q $; Vehicles $\overrightarrow{ {\text{Ms} }{ {\text{g} }_{{i} } }{\text{ = } }({M_i},{U_i},{\nu _i},{\text{PSI} }{ {\text{D} }_{{i} } }{\text{,time} }'_{{i} },{R_i})}$ RSU (a) 判断时间戳是否满足${\rm{time} }'_j-{\text{time} }'_i \le { {\Delta } }{ {\text{time} }' }$; (b) 计算$ {\eta }_{i}={H}_{5}({\text{PSID}}_{{i}}|\left|{M}_{i}\right||{\text{time}}'_{{i}}),{\mu }_{i}={\xi }_{i}\mathrm{mod}q $; (c) 验证$ {\nu _i}P = {\mu _i}{\eta _i}{U_i} + {R_i} + {H_4}({\text{PSI}}{{\text{D}}_{{i}}}||{R_i}){\text{P}}{{\text{K}}_{{\text{TA}}}} $是否相等。 表 3 密码模块运算时间实验参数
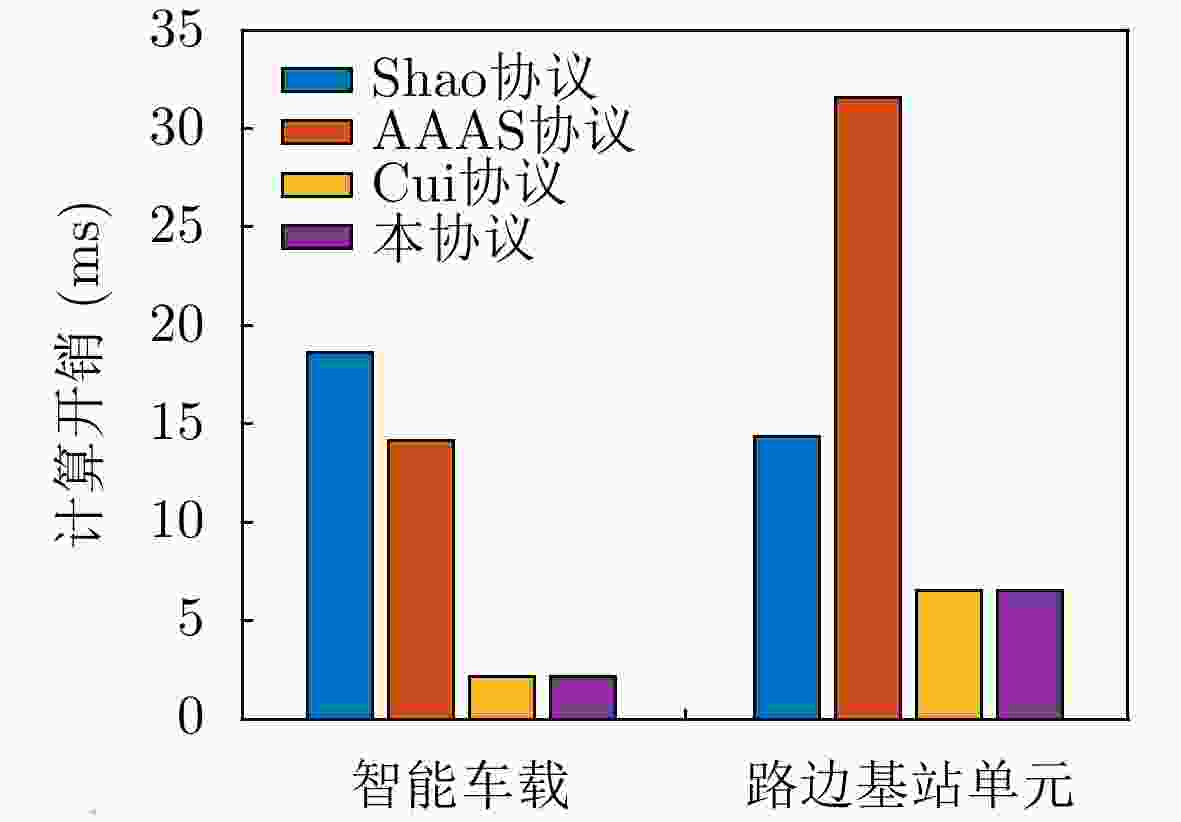
操作类型 符号表示 时间(ms) 双线性对运算 $ {\text{Pair}} $ 5.427 普通模指数运算 $ {\text{Exp}} $ 1.17 椭圆曲线倍点运算 $ {\text{Mult}} $ 2.1652 普通模乘法运算 $ {\text{mult}} $ 0.0009 映射到循环群的哈希运算 $ {\text{Hash}} $ 5.493 普通哈希运算 $ {\text{hash}} $ 0.0078 椭圆曲线上的加法运算 $ {\text{Add}} $ 0.0132 模逆运算 $ {\text{Inv}} $ 0.631 表 4 智能车载和RSU端计算开销比较
协议 智能车载通信模块 路边基站单元(RSU) AAAS协议 $ {\text{4Mult + Inv + Add + Hash}} \approx {\text{14}}{\text{.78 ms}} $ ${\text{3Pair + 2Mult + mult + 2Hash}} \approx {\text{26}}{\text{.11 ms}}$ Shao协议 ${\text{2Exp + 3Pair + mult}} \approx {\text{18}}{\text{.63 ms}}$ $ {\text{3Exp + 2Pair + mult}} \approx 14.37{\text{ ms}} $ Cui协议 $ {\text{Mult + hash + mult}} \approx 2.17{\text{ ms}} $ ${\text{3Mult + 2Add + 2hash}} \approx 6.54{\text{ ms}}$ 本协议 $ {\text{Mult + hash + 2mult}} \approx 2.18{\text{ ms}} $ ${\text{3Mult + 2Add + 2hash}} \approx 6.54{\text{ ms}}$ 表 5 通信开销比较
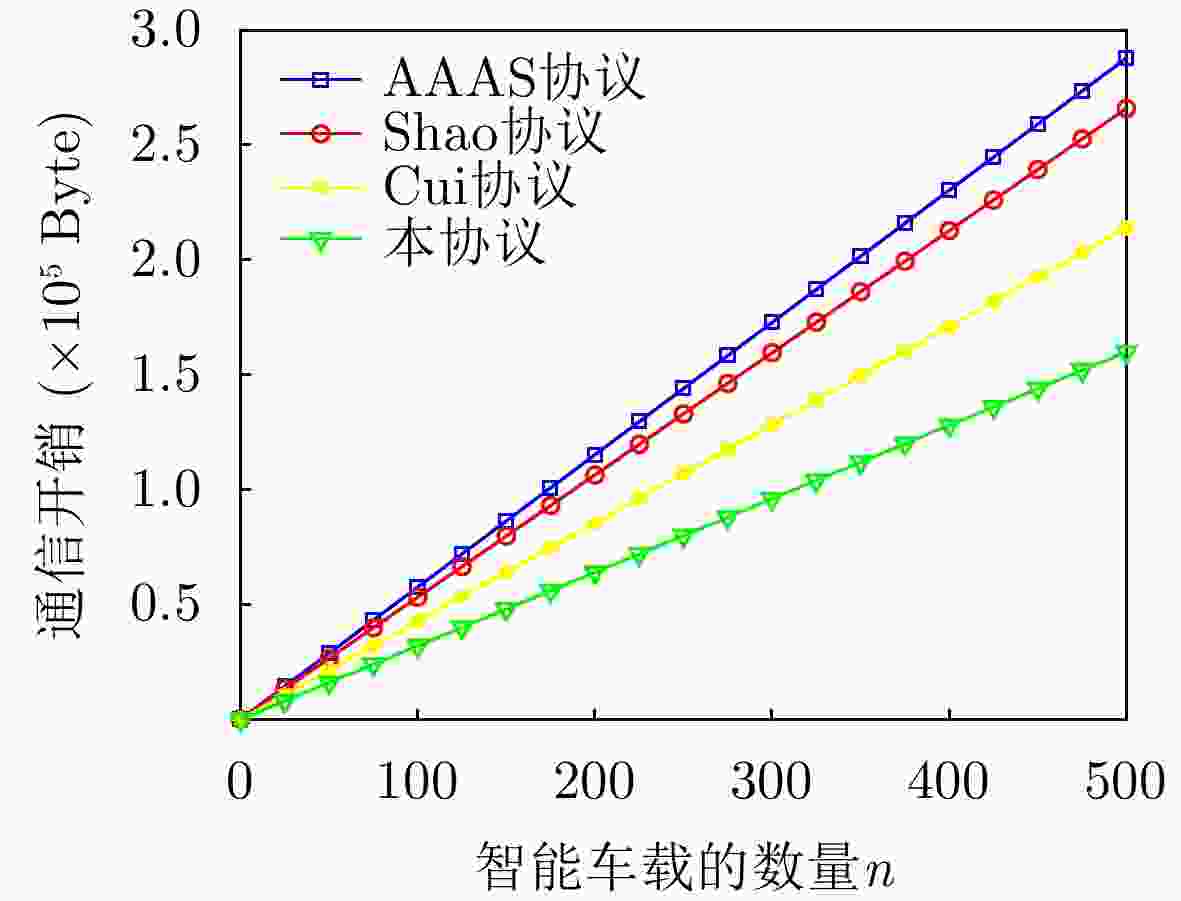
协议 单个智能车载认证 $ n $个智能车载认证 AAAS协议 $2\left| q \right| + 2\left| {{\text{ts}}} \right| + 2\left| {{\text{ex}}} \right| + 2\xi + 4\left| \mathbb{G} \right|$ $2n\left| q \right| + 2n\left| {{\text{ts}}} \right| + 2n\left| {{\text{ex}}} \right| + 2n\xi + 4n\left| \mathbb{G} \right|$ Shao协议 $4\left| \mathbb{G} \right| + \left| q \right|$ $4n\left| \mathbb{G} \right| + n\left| q \right|$ Cui协议 $3|\mathbb{G}| + 2\left| q \right| + \left| {{\text{ts}}} \right|$ $3n|\mathbb{G}| + 2n\left| q \right| + n\left| {{\text{ts}}} \right|$ 本协议 $2|\mathbb{G}| + 3\left| q \right| + \left| {{\text{ts}}} \right|$ $2n|\mathbb{G}| + 3n\left| q \right| + n\left| {{\text{ts}}} \right|$ -
[1] ZHANG Lei, HU Chuanyan, WU Qianhong, et al. Privacy-preserving vehicular communication authentication with hierarchical aggregation and fast response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(8): 2562–2574. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2485225 [2] 李兴华, 钟成, 陈颖, 等. 车联网安全综述[J]. 信息安全学报, 2019, 4(3): 17–33. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2019.05.02LI Xinghua, ZHONG Cheng, CHEN Ying, et al. Survey of internet of vehicles security[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2019, 4(3): 17–33. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2019.05.02 [3] 宋昊辰, 杨林, 徐华伟, 等. 智能网联汽车信息安全综述[J]. 信息安全与通信保密, 2020(7): 106–114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2020.07.013SONG Haochen, YANG Lin, XU Huawei, et al. Overview of the intelligent connected vehicles cyber security[J]. Information Security and Communications Privacy, 2020(7): 106–114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2020.07.013 [4] WU Qianhong, DOMINGO-FERRER J, GONZALEZ-NICOLAS Ú, et al. Balanced trustworthiness, safety, and privacy in vehicle-to-vehicle communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2010, 59(2): 559–573. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2009.2034669 [5] ZHANG Xiaojun, WANG Wenchen, MU Liming, et al. Efficient privacy-preserving anonymous authentication protocol for vehicular ad-hoc networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2021, 120(4): 3171–3187. doi: 10.1007/s11277-021-08605-x [6] QU Fengzhong, WU Zhihui, WANG Feiyue, et al. A security and privacy review of VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(6): 2985–2996. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2439292 [7] LU Rongxing, LIN Xiaodong, LUAN T H, et al. Pseudonym changing at social spots: An effective strategy for location privacy in VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2012, 61(1): 86–96. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2011.2162864 [8] MANVI S S and TANGADE S. A survey on authentication schemes in VANETs for secured communication[J]. Vehicular Communications, 2017, 9: 19–30. doi: 10.1016/j.vehcom.2017.02.001 [9] ALFADHLI S A, LU Songfeng, CHEN Kai, et al. MFSPV: A Multi-factor secured and lightweight privacy-preserving authentication scheme for VANETs[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 142858–142874. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3014038 [10] FOTOUHI M, BAYAT M, DAS A K, et al. A lightweight and secure two-factor authentication scheme for wireless body area networks in health-care IoT[J]. Computer Networks, 2020, 177: 107333. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107333 [11] LI Jie, LU Huang, and GUIZANI M. ACPN: A novel authentication framework with conditional privacy-preservation and non-repudiation for VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2015, 26(4): 938–948. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2014.2308215 [12] YING Bidi, MAKRAKIS D, and MOUFTAH H T. Privacy preserving broadcast message authentication protocol for VANETs[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2013, 36(5): 1352–1364. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2012.05.013 [13] WANG Yimin, ZHONG Hong, XU Yan, et al. Efficient extensible conditional privacy-preserving authentication scheme supporting batch verification for VANETs[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2016, 9(18): 5460–5471. doi: 10.1002/sec.1710 [14] JIANG Yanji, GE Shaocheng, and SHEN Xueli. AAAS: An anonymous authentication scheme based on group signature in VANETs[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 98986–98998. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2997840 [15] AZEES M, VIJAYAKUMAR P, and DEBOARH L J. EAAP: Efficient anonymous authentication with conditional privacy-preserving scheme for vehicular ad hoc networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(9): 2467–2476. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2634623 [16] SHAO Jun, LIN Xiaodong, LU Rongxing, et al. A threshold anonymous authentication protocol for VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(3): 1711–1720. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2405853 [17] XIONG Wanjun, WANG Ruomei, WANG Yujue, et al. CPPA-D: Efficient conditional privacy-preserving authentication scheme with double-Insurance in VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(4): 3456–3468. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3064337 [18] CUI Jie, ZHANG Jing, ZHONG Hong, et al. An efficient certificateless aggregate signature without pairings for vehicular ad hoc networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 451–452: 1–15. [19] 曾萍, 郭瑞芳, 马英杰, 等. 车载自组网中可证明安全的无证书认证方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 2873–2881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190883ZENG Ping, GUO Ruifang, MA Yingjie, et al. Provable security certificateless authentication scheme for vehicular Ad hoc network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 2873–2881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190883 [20] LIU Jingwei, LI Qingqing, SUN Rong, et al. An efficient anonymous authentication scheme for internet of vehicles[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–6. [21] CUI Jie, WU Di, ZHANG Jing, et al. An efficient authentication scheme based on semi-trusted authority in VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 2972–2986. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2896018 [22] JIANG Shunrong, ZHU Xiaoyan, and WANG Liangmin. An efficient anonymous batch authentication scheme based on HMAC for VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(8): 2193–2204. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2517603 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
