Salient Target Extraction from Low Depth of Field Images Based on Diversity Measure in Singular Value Decomposition Domain
-
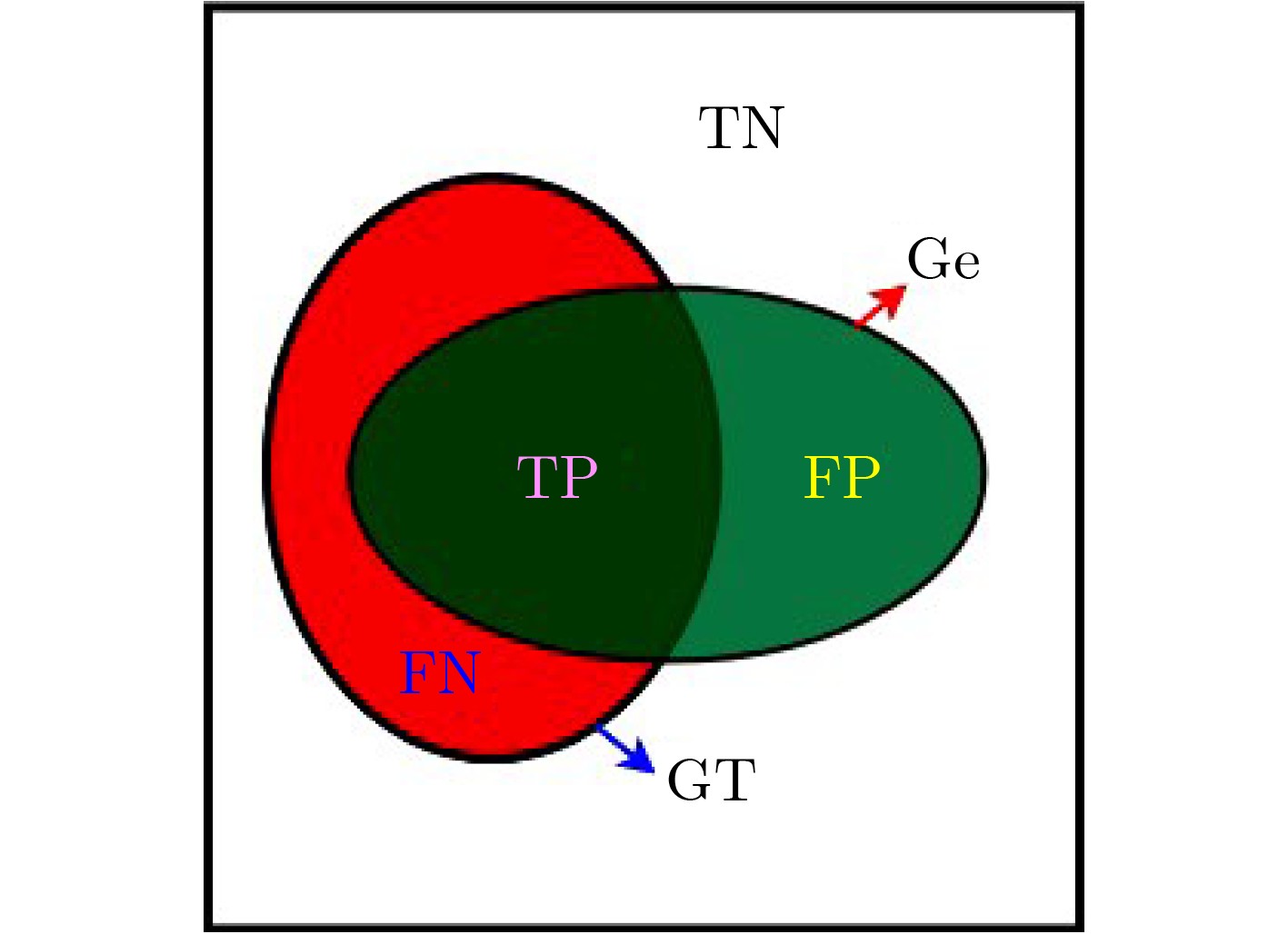
摘要: 针对低景深图像(DOF)目标提取过程中,容易出现目标提取不完整或背景被误识为目标等现象,该文提出一种奇异值分解 (SVD)域差异性度量的低景深图像目标提取方法。先对低景深图像进行高斯模糊,以图像中每一个像素点为中心,利用滑动窗口分别截取模糊前后图像上相同位置的图像块并进行奇异值分解,再构造两奇异值之间的差异特征向量,针对此向量定义低中高全频段信息加权的差异性度量算子,计算对应像素点的显著性特征值,逐像素处理得到显著性结果图并进行阈值化处理,实现低景深图像目标的有效提取。对大量低景深图像进行处理,并与几种现有方法进行比较,提出方法的F度量值最大可提高54%,平均绝对误差减少76%~87%,可完整提取目标并有效去除背景,具有较强的可靠性。Abstract: In the process of target extraction in low Depth Of Field (DOF) image, it is easy to get incomplete target extraction or the background is mistakenly recognized as a target. A low DOF image target extraction method based on Singular Value Difference (SVD) measurement is proposed. Firstly, Gaussian blur is applied to the low DOF image. Taking the current pixel as the center, the image blocks at the same position on the image before and after blur are intercepted by using the sliding window, and singular value decomposition is carried out. Then, the difference feature vector between the two singular values is constructed. Based on this vector, the difference measurement operator is defined to calculate the characteristic intensity value of the corresponding pixel. The feature salient map is obtained by pixel by pixel processing, and the threshold processing is carried out to realize the effective extraction of low DOF image targets. A large number of low DOF images are processed, and compared with several existing methods, the maximum F measure can be increased by 54%, and the average absolute error can be reduced by 76%~87%. The proposed method can completely extract the target and effectively remove the background, and has strong reliability.
-
表 1 像素特征度量值计算
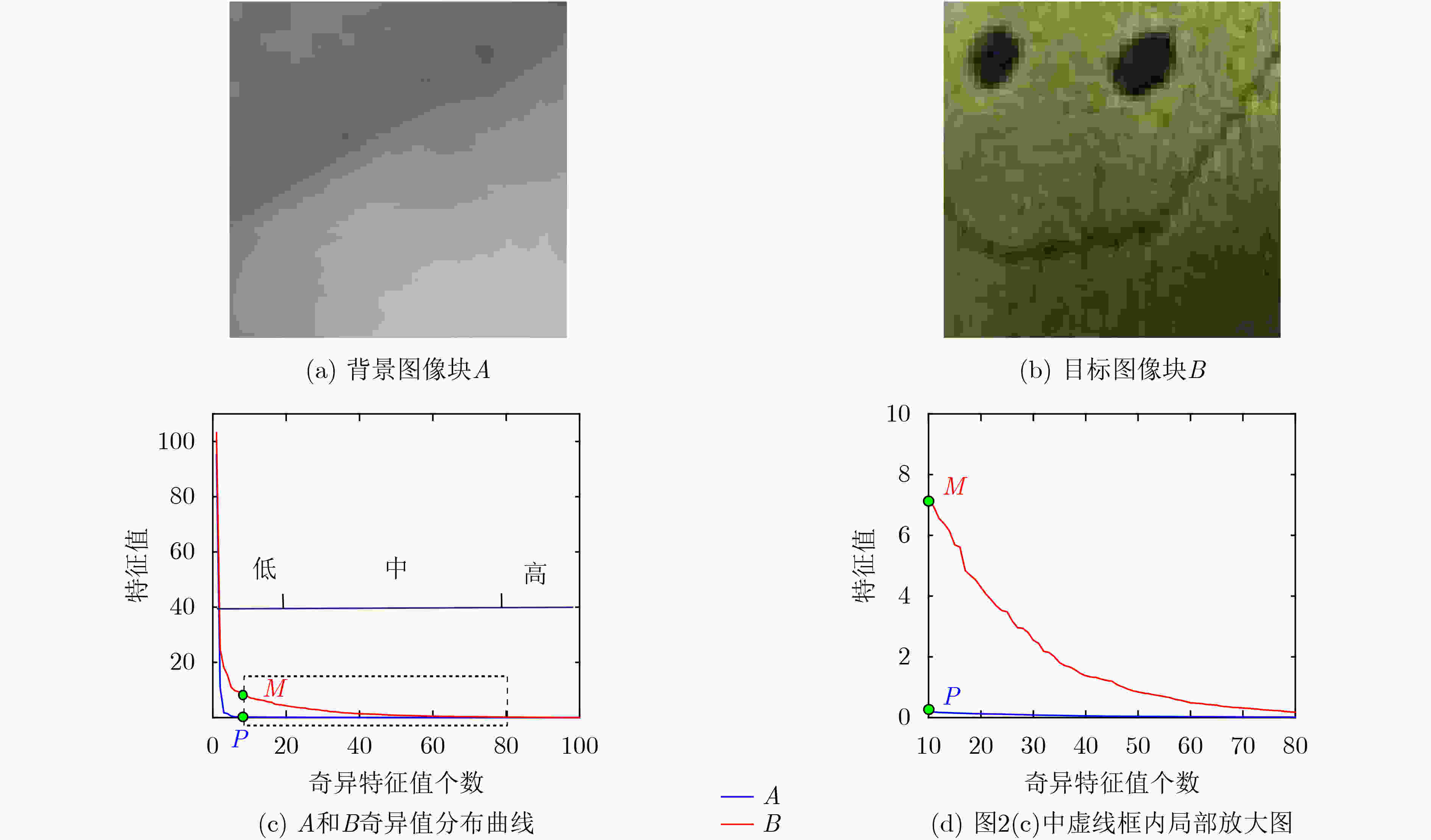
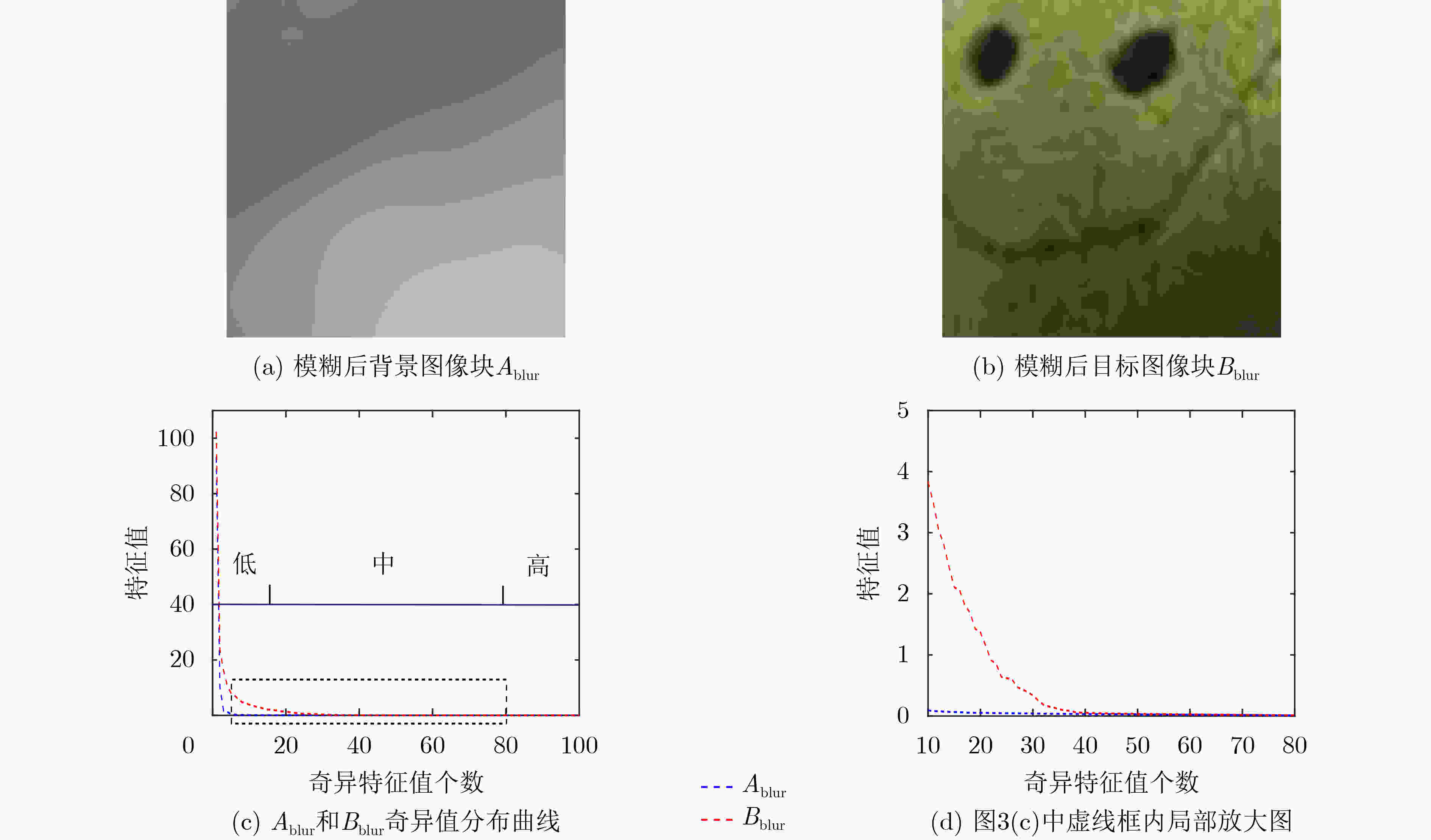
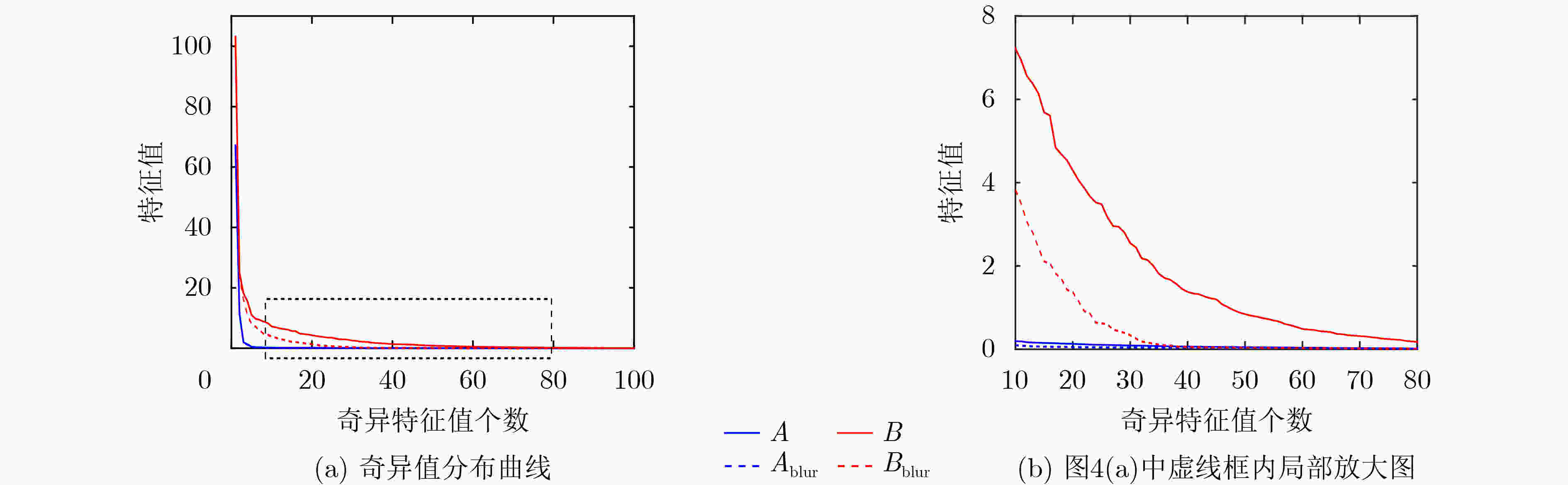
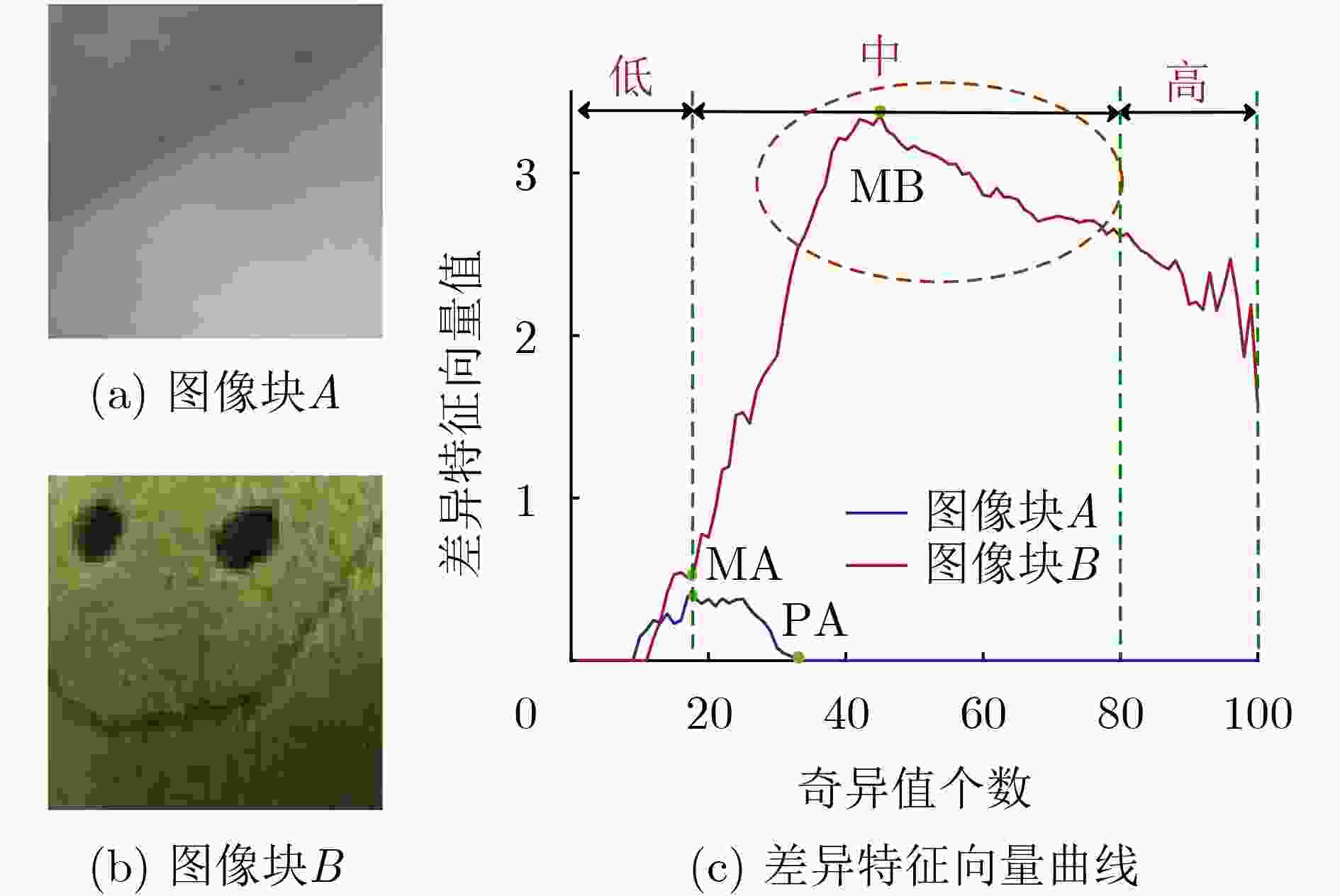
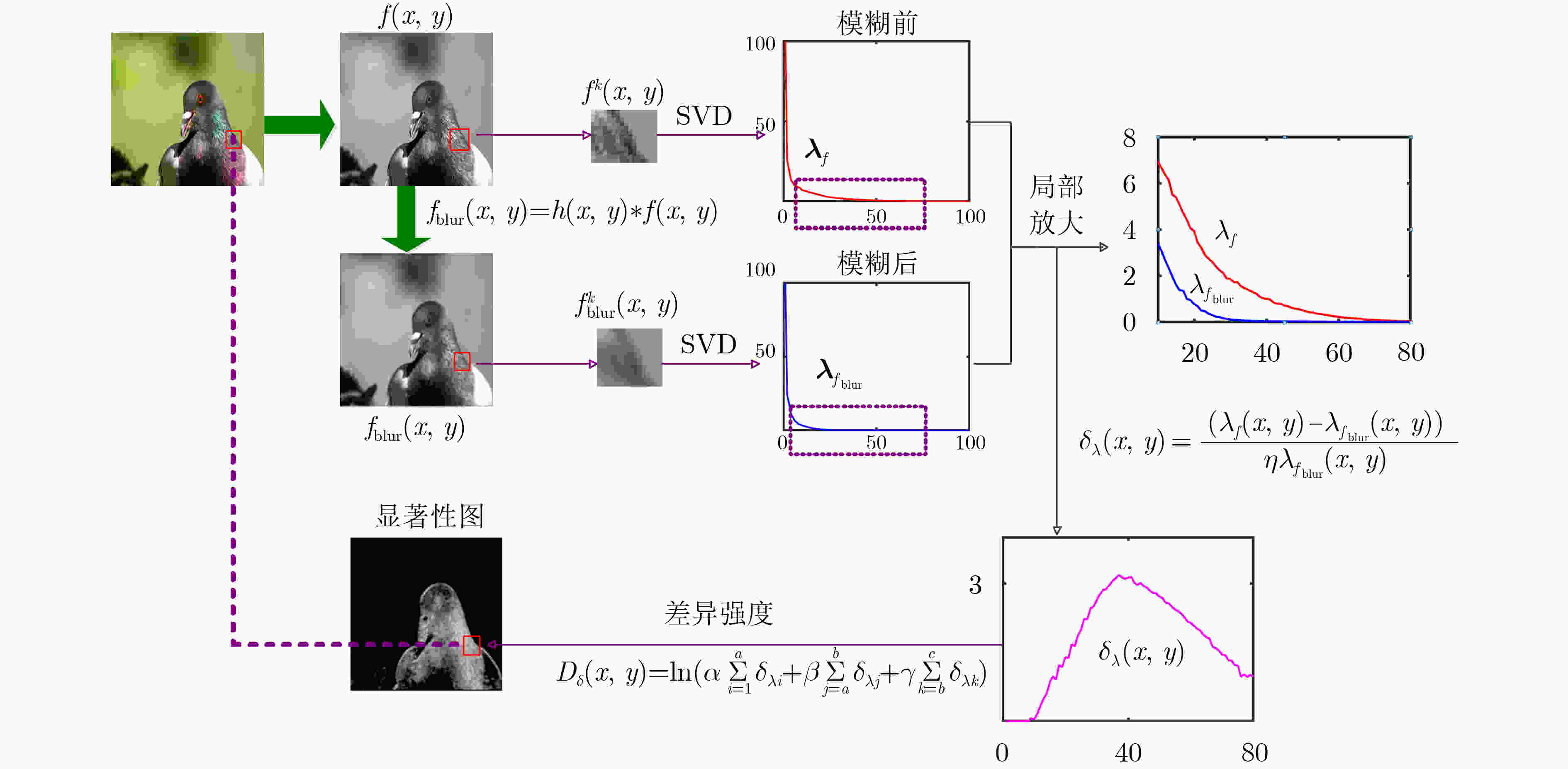
(1) 输入低景深图像$ f(x,y) $ (2) 对$ f(x,y) $进行高斯模糊处理得到图像${f_{{\rm{blur}}} }(x,y)$ (3) x=1:M 循环 (4) y=1:N 循环 (5) 式(5)、式(6),计算以(x,y)为中心的窗口大小图像块
$ {f^k}(x,y) $和$f_{{\rm{blur}}}^k(x,y)$的SVD奇异值(6) 式(7), 计算两图像块奇异值差异特征向量$ {{\mathbf{\delta }}_\lambda } $ (7) 利用度量式(8), 计算(x,y)像素点的特征度量值 (8) 终止循环(4) (9) 终止循环(3) (10) 利用式(9)进行阈值化,得到目标提取结果图像 表 2 不同方法的F-measure值
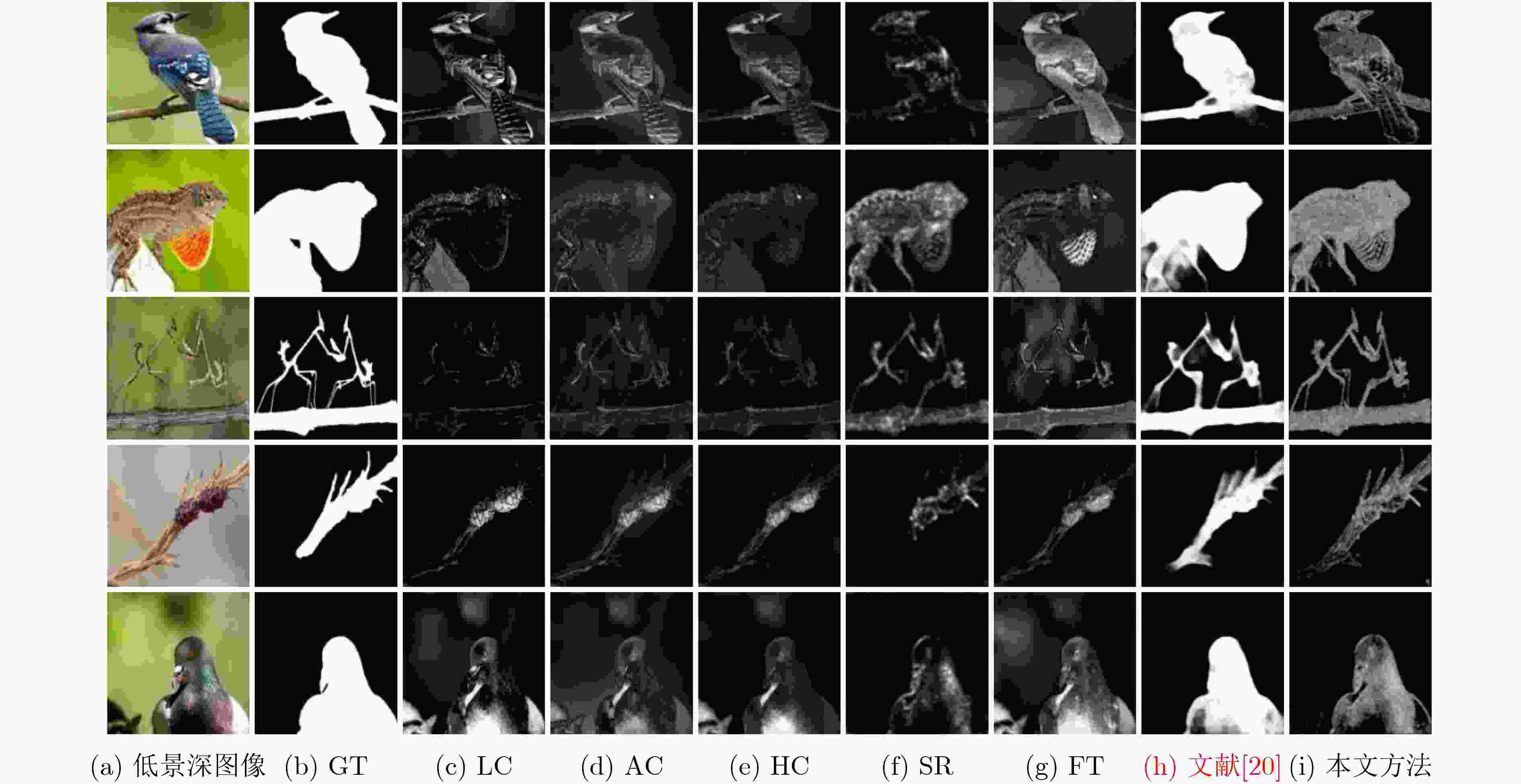
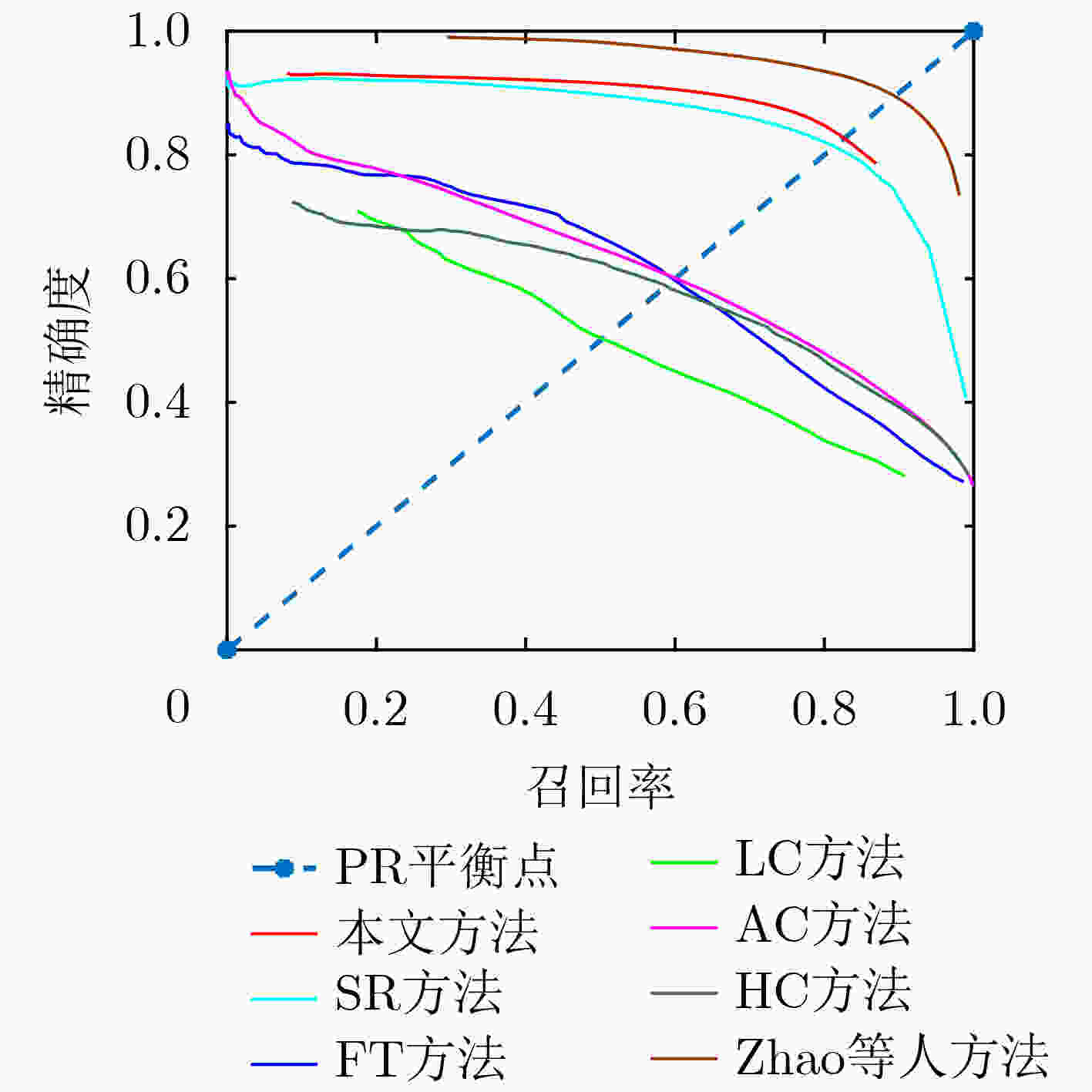
LC FT AC HC SR 文献[20] SVD-DM F-measure 0.5867 0.6069 0.5588 0.4955 0.7094 0.8942 0.7639 表 3 不同方法对应的平均绝对误差值
LC FT AC HC SR 文献[20] SVD-DM MAE 0.6415 0.6993 0.7320 0.6629 0.3983 0.0728 0.0957 -
[1] XU Guodong, QUAN Yuhui, and HUI Ji. Estimating defocus blur via rank of local patches[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5381–5389. [2] XIAN Ke, PENG Juewen, ZHANG Chao, et al. Ranking-based salient object detection and depth prediction for shallow depth-of-field[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(5): 1815. doi: 10.3390/s21051815 [3] RAFIEE G, DLAY S S, and WOO W L. Region-of-interest extraction in low depth of field images using ensemble clustering and difference of Gaussian approaches[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(10): 2685–2699. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.03.006 [4] WIRTH T, NABER A, and NAHM W. Combination of color and focus segmentation for medical images with low depth-of-field[J]. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 4(1): 345–349. doi: 10.1515/cdbme-2018-0083 [5] LIU Zhi, LI Weiwei, SHEN Liquan, et al. Automatic segmentation of focused objects from images with low depth of field[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2010, 31(7): 572–581. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2009.11.016 [6] HASSAN H, BASHIR A K, ABBASI R, et al. Single image defocus estimation by modified gaussian function[J]. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 2019, 30(6): e3611. doi: 10.1002/ett.3611 [7] LI Nianyi, YE Jinwei, JI Yu, et al. Saliency detection on light field[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1605–1616. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2610425 [8] BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, JIANG Huaizu, et al. Salient object detection: A benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5706–5722. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2487833 [9] ZHAI Yun and SHAH M. Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues[C]. The 14th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Santa Barbara, USA, 2006: 815–824. [10] ACHANTA R, ESTRADA F, WILS P, et al. Salient region detection and segmentation[C]. The 6th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, Santorini, Greece, 2008: 66–75. [11] CHENG Mingming, MITRA N J, HUANG Xiaolei, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569–582. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401 [12] CHENG Mingming, ZHANG Guoxin, MITRA N J, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[C]. 2011 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, USA, 2011: 409–416. [13] HOU Xiaodi and ZHANG Liqing. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1–8. [14] GUO Chenlei, MA Qi, and ZHANG Liming. Spatio-temporal saliency detection using phase spectrum of quaternion Fourier transform[C]. 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. [15] ACHANTA R, HEMAMI S, ESTRADA F, et al. Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 1597–1604. [16] KIM J, HAN D, TAI Y W, et al. Salient region detection via high-dimensional color transform and local spatial support[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(1): 9–23. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2495122 [17] BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, HOU Qibin, et al. Salient object detection: A survey[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(2): 117–150. doi: 10.1007/s41095-019-0149-9 [18] AHN S and CHONG J. Segmenting a noisy low-depth-of-field image using adaptive second-order statistics[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(3): 275–278. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2357792 [19] 邓小玲, 倪江群, 李震, 等. 多特征融合的低景深图像前景提取算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(6): 846–851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00846DENG Xiaoling, NI Jiangqun, LI Zhen, et al. Foreground extraction from low depth-of-field images based on colour-texture and HOS Features[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6): 846–851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00846 [20] ZHAO Wenda, ZHAO Fan, WANG Dong, et al. Defocus blur detection via multi-stream bottom-top-bottom network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 1884–1897. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2906588 [21] WANG Lijun, SHEN Xiaohui, ZHANG Jianming, et al. DeepLens: Shallow depth of field from a single image[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37(6): 245. doi: 10.1145/3272127.3275013 [22] WANG Wenguan, LAI Qiuxia, FU Huazhu, et al. Salient object detection in the deep learning era: An in-depth survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43: 1–20. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3051099. [23] 季正燕, 陈辉, 张佳佳, 等. 一种基于奇异值分解的解相干算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 1913–1918. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161157JI Zhengyan, CHEN Hui, ZHANG Jiajia, et al. Decorrelation algorithm based on singular value decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 1913–1918. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161157 [24] LI Ping, WANG Hua, LI Xuemei, et al. An image denoising algorithm based on adaptive clustering and singular value decomposition[J]. IET Image Processing, 2021, 15(3): 598–614. doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12017 [25] SANG Qingbing, YANG Yunshuo, LIU Lixiong, et al. Image quality assessment based on quaternion singular value decomposition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 75925–75935. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989312 [26] XIAO Huimei, LU Wei, LI Ruipeng, et al. Defocus blur detection based on multiscale SVD fusion in gradient domain[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2019, 59: 52–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.12.048 -
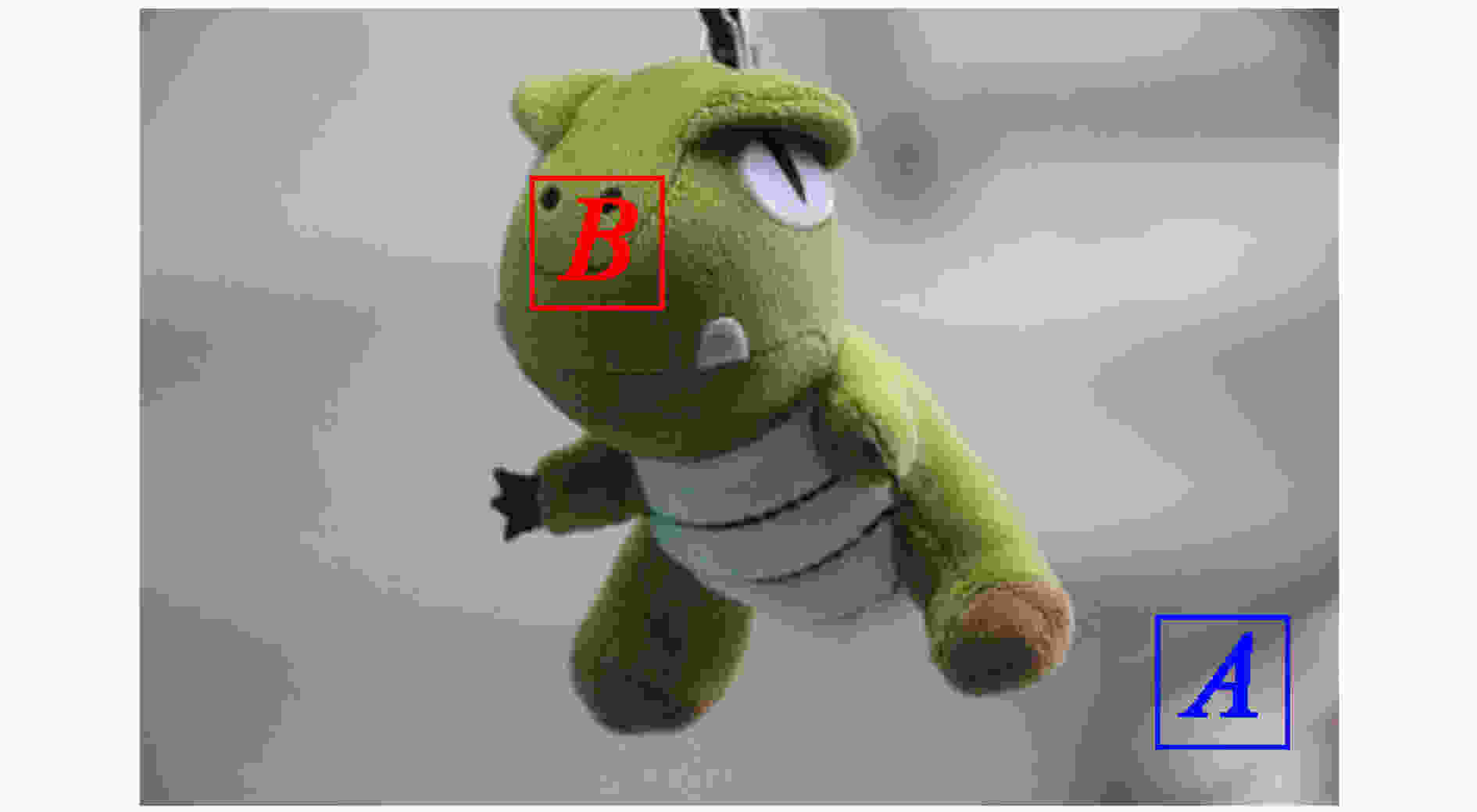






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
