Underdetermined Blind Source Separation Based on Third-order Statistics
-
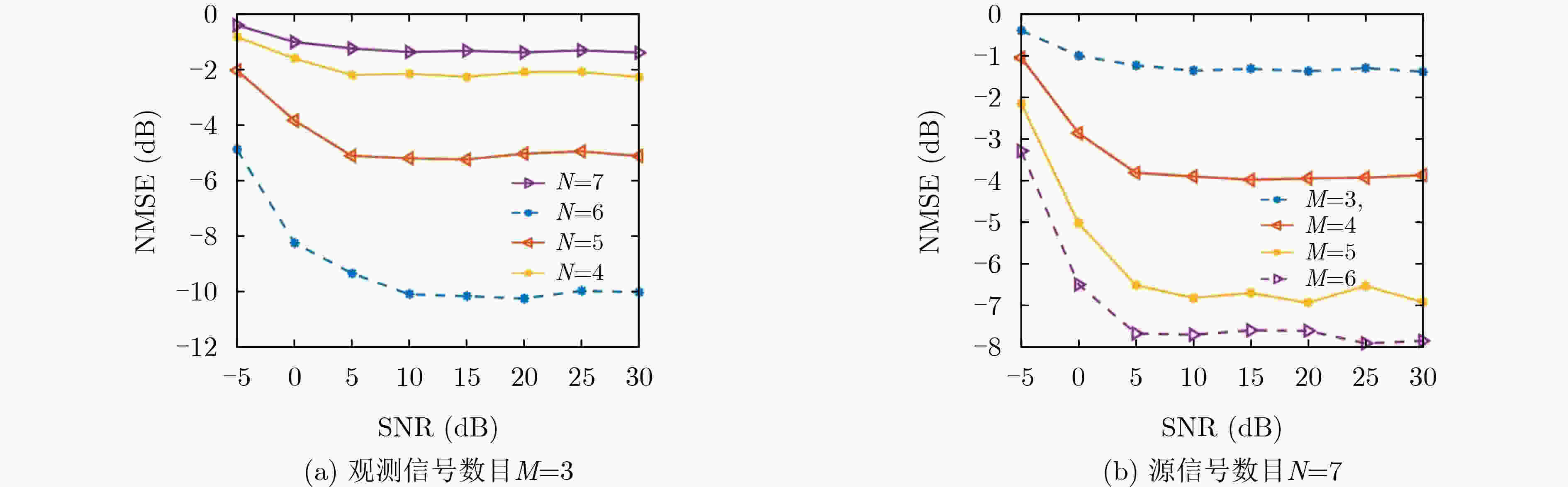
摘要: 盲源分离(BSS)在缺失源信号信息及信息混合方式信息的情况下,仅利用观测信号实现源信号恢复,是信号处理中的重要手段。欠定盲源分离(UBSS)中观测信号少于源信号数目,因此,相较于正定/超定情形,其更接近现实情况。然而,观测信号往往受到噪声干扰,传统基于2阶统计量和信号稀疏性的欠定盲源分离结果对噪声较为敏感。鉴于3阶统计量在处理对称分布噪声时的优势,该文利用观测信号的3阶统计信息实现混合矩阵的估计。考虑到源信号的自相关特性,计算多时延下观测信号一系列的3阶统计信息,并堆叠成4阶张量,进而将混合矩阵估计问题转化为4阶张量的典范双峰分解问题。该文进一步利用广义高斯模型和期望最大算法实现源信号的恢复。1000次蒙特卡罗实验表明该文算法能够有效抑制噪声的影响。针对3×4混合模型,当信噪比为15 dB时,该文算法对混合矩阵的平均估计误差达到–20.35 dB,所恢复出的源信号与真实源信号之间的平均绝对相关系数达0.84,与现有方法相比,取得了最好的分离结果。Abstract: Blind Source Separation (BSS) aims to separate the source signals from the mixed observations without any information about the mixing process and the source signals, which is a major area in the signal processing field. In Underdetermined Blind Source Separation (UBSS), the number of observed signals is less than the number of source signals, and thus UBSS is much closer to reality than the determined/overdetermined BSS. However, the observations are always disturbed by noise, deteriorating the performance of traditional underdetermined blind source separation based on second-order statistics and signal sparsity. Taking the advantage of third-order statistics in dealing with symmetric noise, a novel mixing matrix estimation method based on the third-order statistics of the observations is proposed. Considering the autocorrelations of the sources, a sequence of third-order statistics of the observations corresponding to multiple delays are calculated and stacked into a fourth-order tensor. Then the mixing matrix is estimated via the canonical polyadic decomposition of the fourth-order tensor. Furthermore, the generalized Gaussian distribution is employed to characterize the sources and the expectation-maximum algorithm is utilized to recover the sources. The results from 1000 Monte Carlo experiments demonstrate that the proposed method is robust to the noise. The proposed method archives the normalized mean square error of –20.35 dB and the mean absolute correlation coefficient between the recovered sources and the real ones of 0.84 when the signal to noise ratios equal to 15 dB for the cases with 3×4 mixing matrices. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm yields superior performances in comparing with state-of-the-art underdetermined blind source separation methods.
-
表 1 本文算法步骤
输入:${{M}}$维观测信号${\boldsymbol{X}}$。 输出:混合矩阵${\boldsymbol{A}}$和恢复的源信号$\hat {\boldsymbol{S}}$。 步骤1 计算观测信号的3阶统计量。 步骤2 通过对观测信号进行延时,计算出不同的3阶张量,并将
这些3阶张量堆叠成4阶张量。步骤3 通过张量的CP分解,计算出混合矩阵${{\boldsymbol{A}}^{(1)} },{{\boldsymbol{A}}^{(2)} },{{\boldsymbol{A}}^{(3)} }$。 步骤4 通过奇异值分解优化混合矩阵的估计$\hat {\boldsymbol{A}}$ 。 步骤5 通过信号恢复算法对信号进行恢复,获得恢复信号$\hat {\boldsymbol{S}}$。 表 2 各算法恢复出的源信号与真实源信号间的平均绝对皮尔逊相关系数
信噪比(dB) –5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 文献[13] 0.2538 0.3966 0.5395 0.6206 0.6799 0.7250 0.7427 0.7662 文献[14] 0.2350 0.3832 0.5380 0.6616 0.7326 0.7951 0.8306 0.8439 文献[15] 0.2080 0.2933 0.3803 0.4752 0.6472 0.7065 0.7135 0.7441 文献[16] 0.2586 0.3781 0.4923 0.6563 0.7805 0.8196 0.8350 0.8288 文献[17] 0.2556 0.4214 0.5958 0.7103 0.7879 0.8149 0.8178 0.8339 文献[18] 0.2925 0.4595 0.6330 0.7465 0.8210 0.8475 0.8696 0.8691 本文算法 0.3005 0.4866 0.6598 0.7775 0.8441 0.8672 0.8816 0.8887 -
[1] BRIDWELL D A, RACHAKONDA S, SILVA R F, et al. Spatiospectral decomposition of multi-subject EEG: Evaluating blind source separation algorithms on real and realistic simulated data[J]. Brain Topography, 2018, 31(1): 47–61. doi: 10.1007/s10548-016-0479-1 [2] 周媛媛, 常莹, 陈浩, 等. 基于参考台的盲源分离法在抑制地磁场近场噪音中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(2): 572–586. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0551ZHOU Yuanyuan, CHANG Ying, CHEN Hao, et al. Application of reference-based blind source separation method in the reduction of near-field noise of geomagnetic measurements[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(2): 572–586. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0551 [3] DU Bo, WANG Shaodong, XU Chang, et al. Multi-task learning for blind source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4219–4231. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2836324 [4] 张天骐, 张华伟, 刘董华, 等. 基于区域增长校正的频域盲源分离排序算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(3): 580–587. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180386ZHANG Tianqi, ZHANG Huawei, LIU Donghua, et al. Frequency domain blind source separation permutation algorithm based on regional growth correction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(3): 580–587. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180386 [5] 王泽林, 陈锴, 卢晶. 车载场景结合盲源分离与多说话人状态判决的语音抽取[J]. 声学学报, 2020, 45(5): 696–706. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2020.05.009WANG Zelin, CHEN Kai, and LU Jing. Speech extraction based on blind source separation and multi-talker status tracking in automobile environment[J]. Acta Acustica, 2020, 45(5): 696–706. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2020.05.009 [6] COMON P. Independent component analysis, a new concept?[J]. Signal Processing, 1994, 36(3): 287–314. doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(94)90029-9 [7] HYVÄRINEN A and OJA E. A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(7): 1483–1492. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.7.1483 [8] 季策, 穆文欢, 耿蓉. 基于A-DBSCAN的欠定盲源分离算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(12): 2676–2683. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.12.02JI Ce, MU Wenhuan, and GENG Rong. Underdetermined blind source separation algorithm based on A-DBSCAN[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(12): 2676–2683. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.12.02 [9] 李红光, 郭英, 张东伟, 等. 基于欠定盲源分离的同步跳频信号网台分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920LI Hongguang, GUO Ying, ZHANG Dongwei, et al. Synchronous frequency hopping signal network station sorting based on underdetermined blind source separation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 319–328. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190920 [10] CUI Wei, GUO Shuxu, REN Lin, et al. Underdetermined blind source separation for linear instantaneous mixing system in the non-cooperative wireless communication[J]. Physical Communication, 2021, 45: 101255. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101255 [11] YILMAZ O and RICKARD S. Blind separation of speech mixtures via time-frequency masking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(7): 1830–1847. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.828896 [12] ABRARD F and DEVILLE Y. Blind separation of dependent sources using the “time-frequency ratio of mixtures” approach[C]. The Seventh International Symposium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Paris, France, 2003: 81–84. [13] REJU V G, KOH S N, and SOON Y I. An algorithm for mixing matrix estimation in instantaneous blind source separation[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 89(9): 1762–1773. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.03.017 [14] KIM S G and YOO C D. Underdetermined blind source separation based on subspace representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(7): 2604–2614. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2017570 [15] ZHEN Liangli, PENG Dezhong, YI Zhang, et al. Underdetermined blind source separation using sparse coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(12): 3102–3108. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2610960 [16] ZHEN Liangli, PENG Dezhong, ZHANG Haixian, et al. Underdetermined mixing matrix estimation by exploiting sparsity of sources[J]. Measurement, 2020, 152: 107268. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107268 [17] DE LATHAUWER L and CASTAING J. Blind identification of underdetermined mixtures by simultaneous matrix diagonalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(3): 1096–1105. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.908929 [18] ZOU Liang, CHEN Xun, and WANG Z J. Underdetermined joint blind source separation for two datasets based on tensor decomposition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(5): 673–677. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2546687 [19] 吕晓德, 孙正豪, 刘忠胜, 等. 基于二阶统计量盲源分离算法的无源雷达同频干扰抑制研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1288–1296. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190178LÜ Xiaode, SUN Zhenghao, LIU Zhongsheng, et al. Research on suppressing co-channel interference of passive radar based on blind source separation using second order statistics[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1288–1296. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190178 -





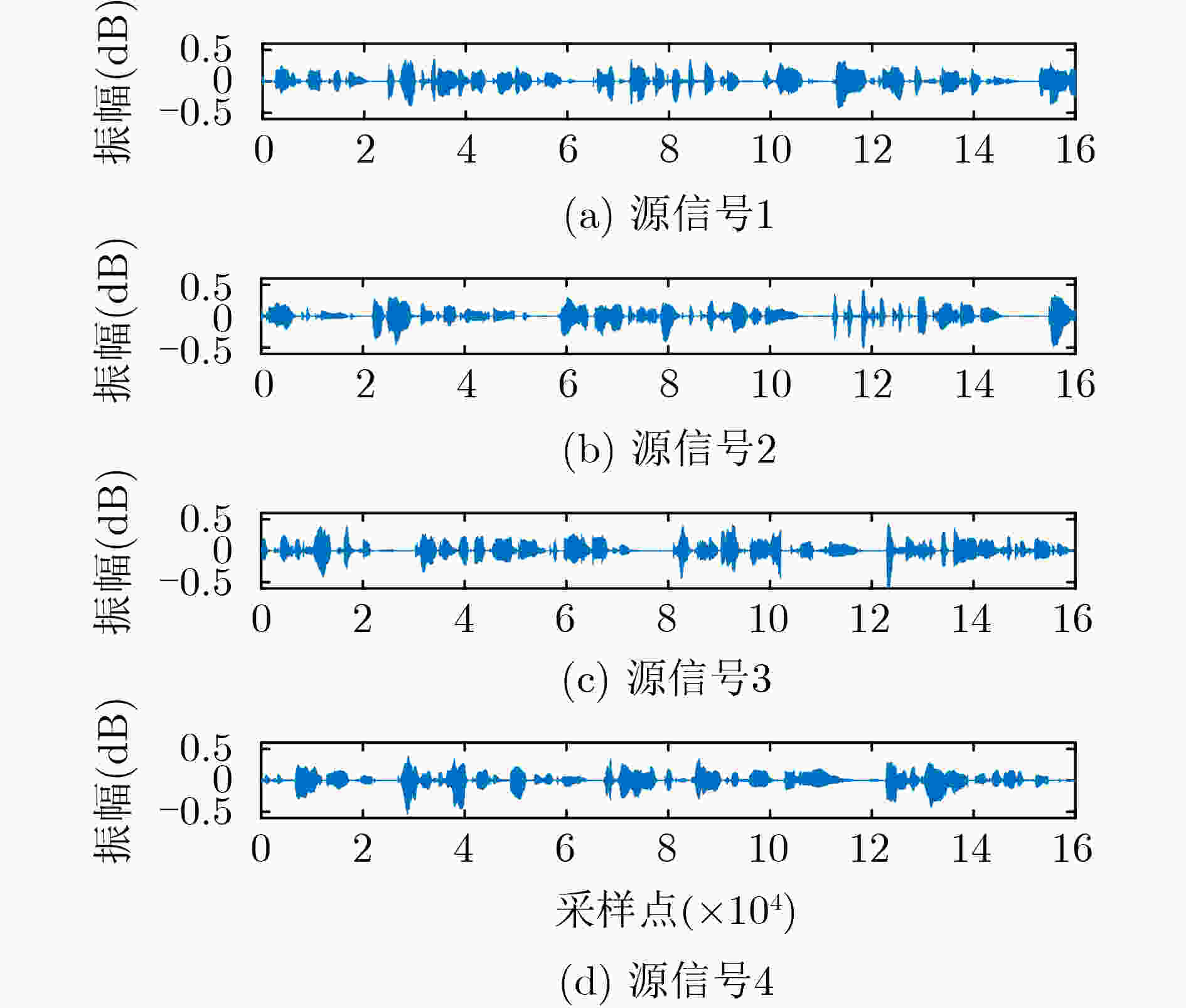
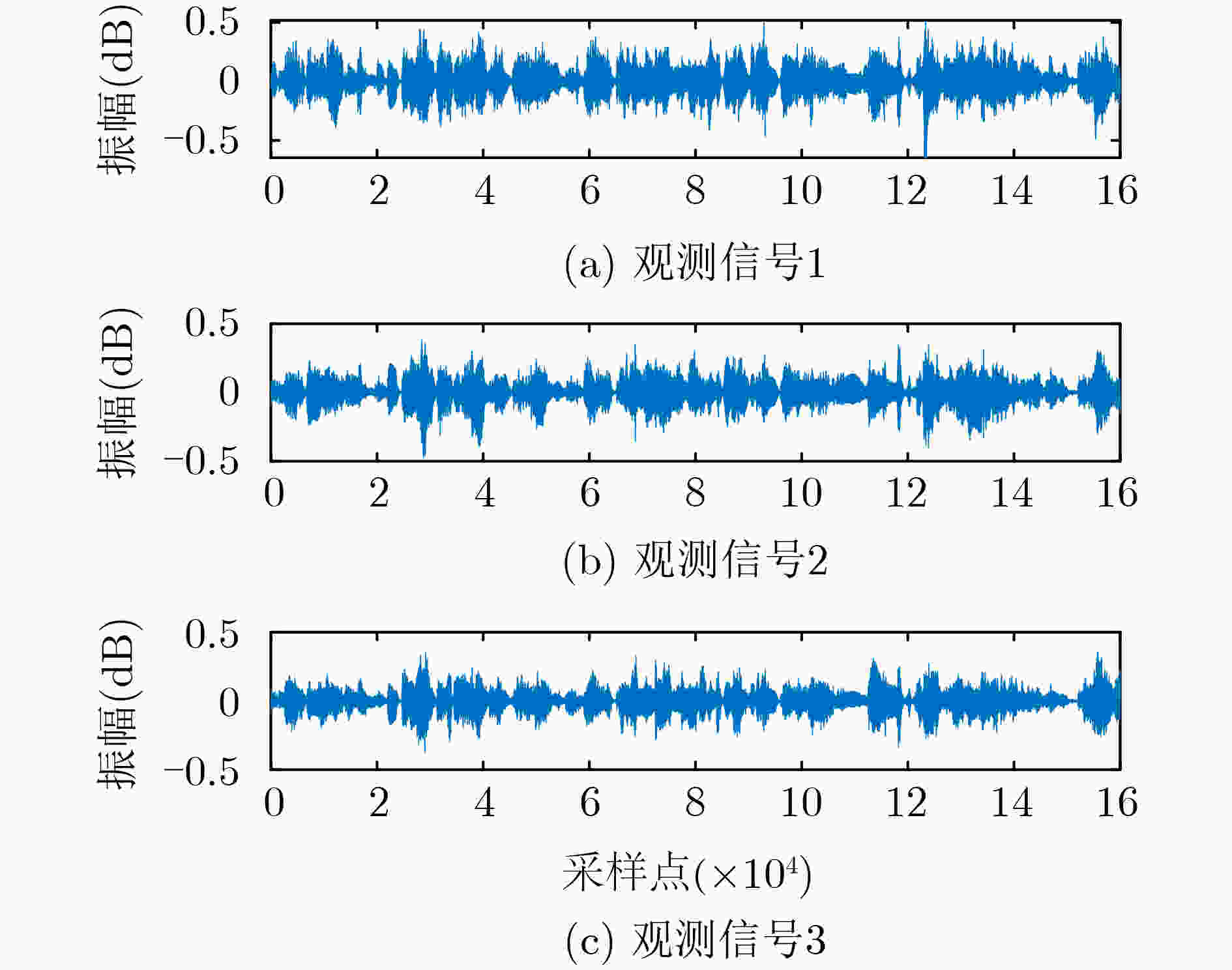
 下载:
下载:
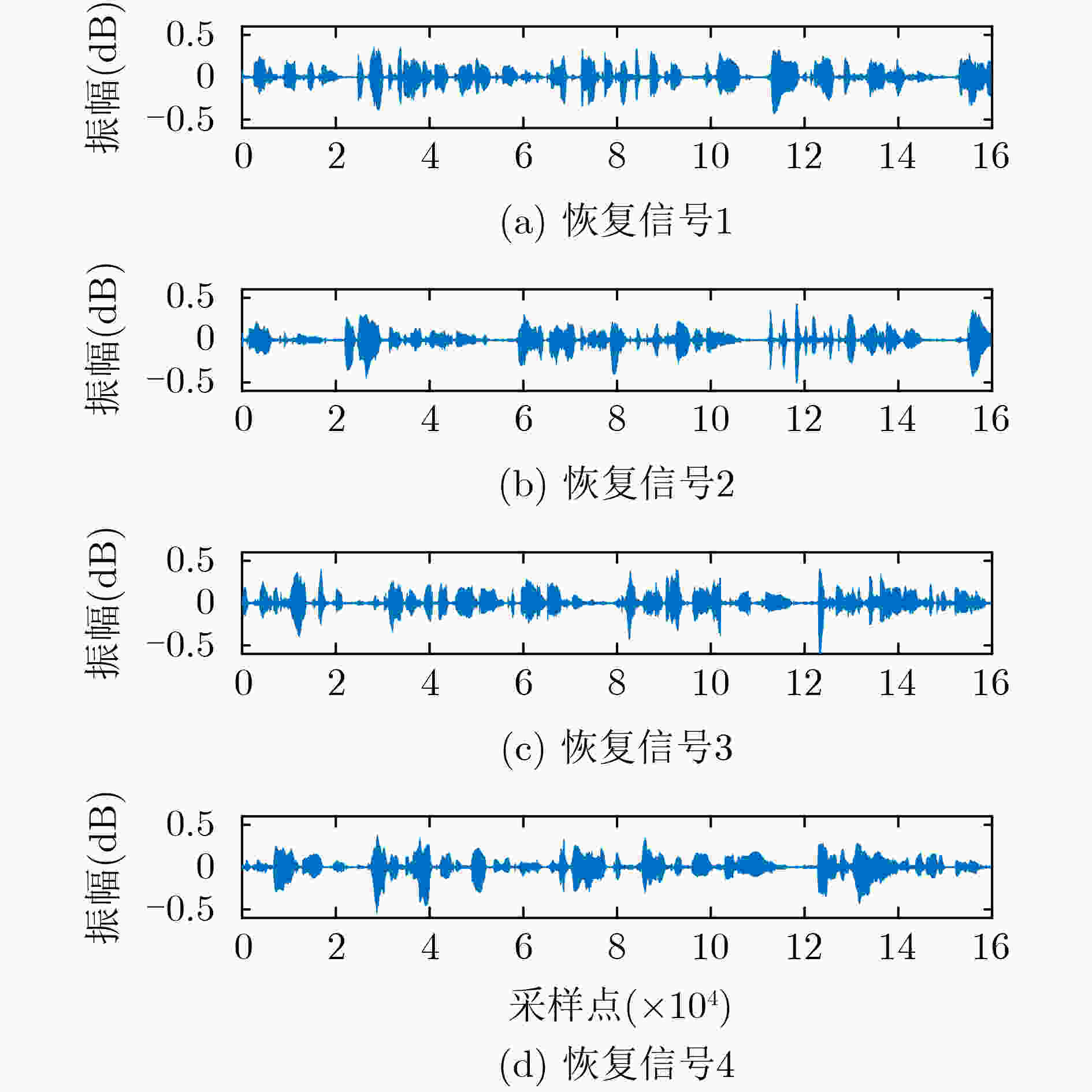
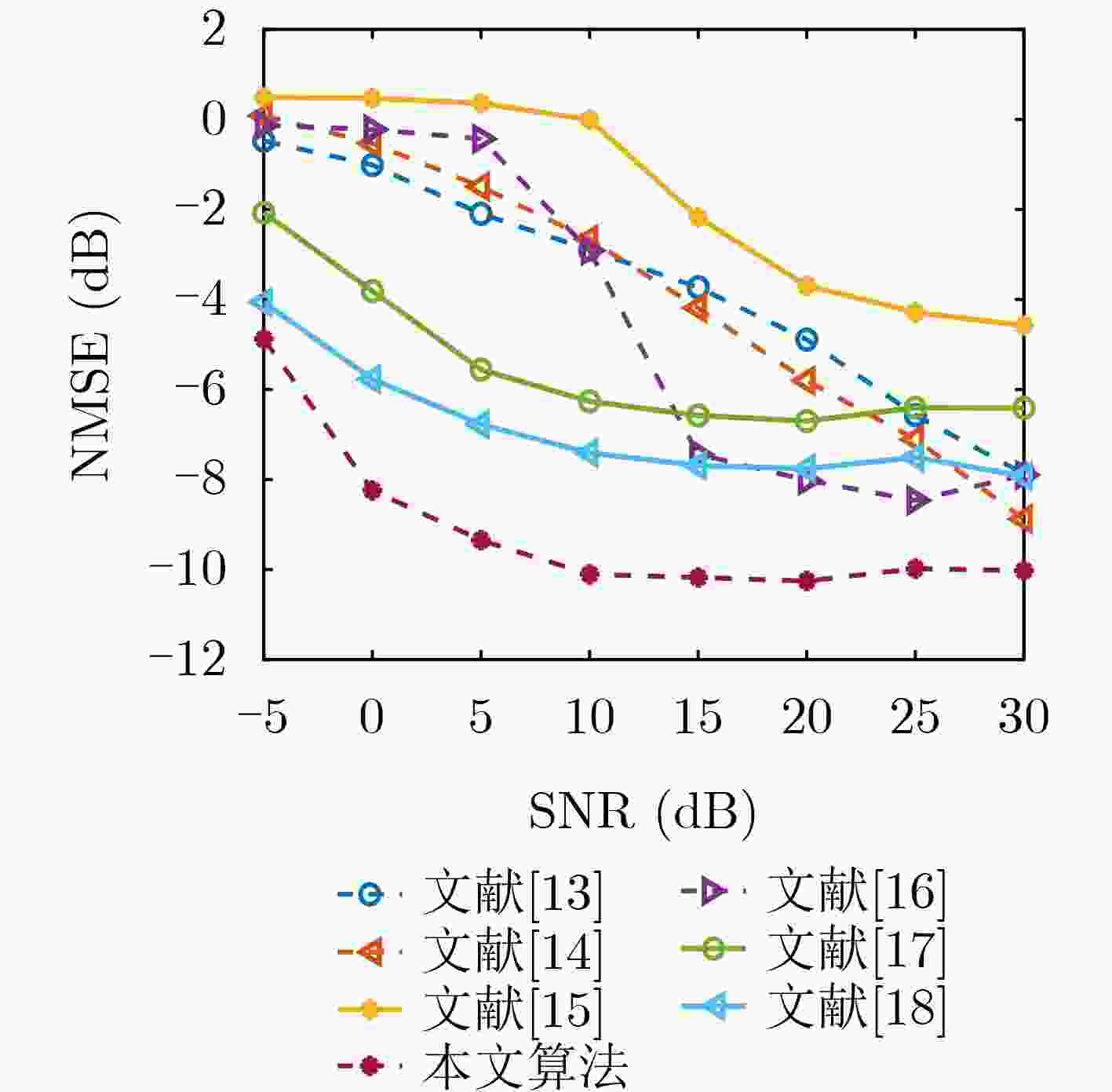


 下载:
下载:
