3D Model Classification Based on Viewpoint Differences and Multiple Classifiers
-
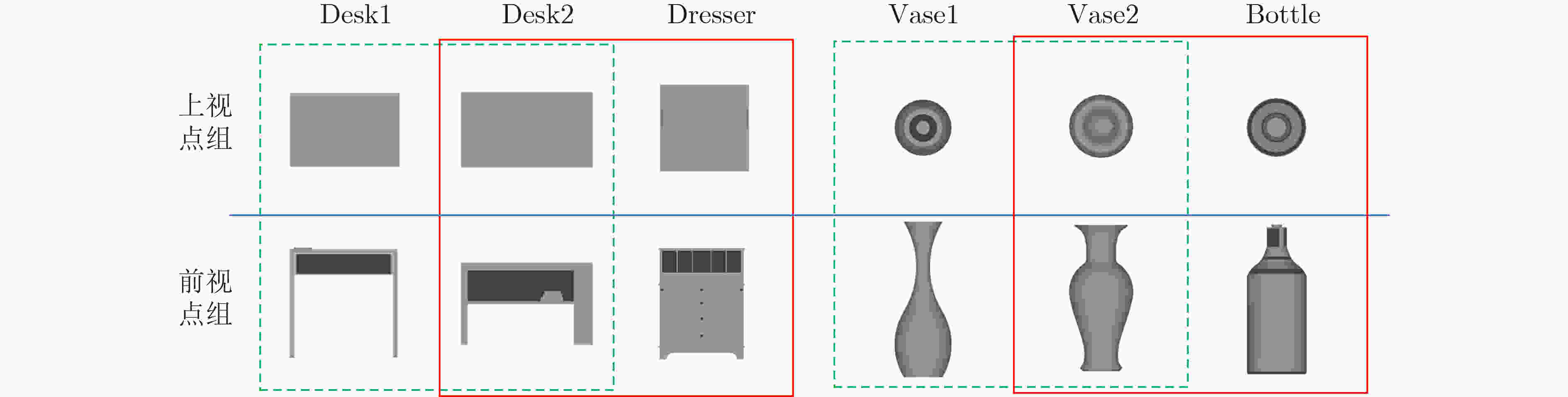
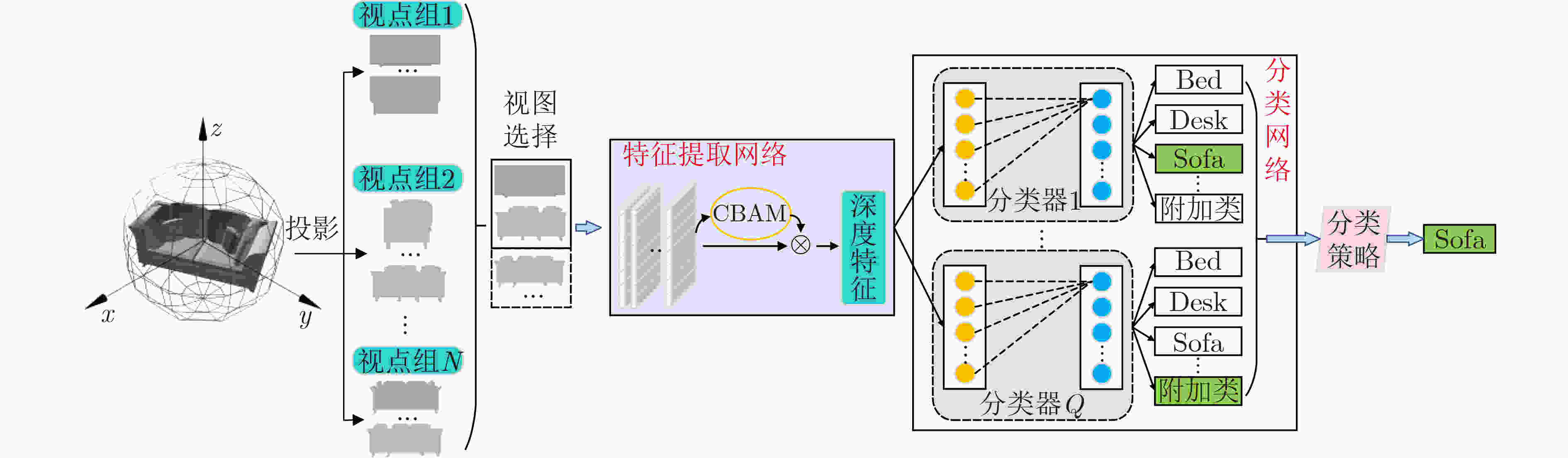
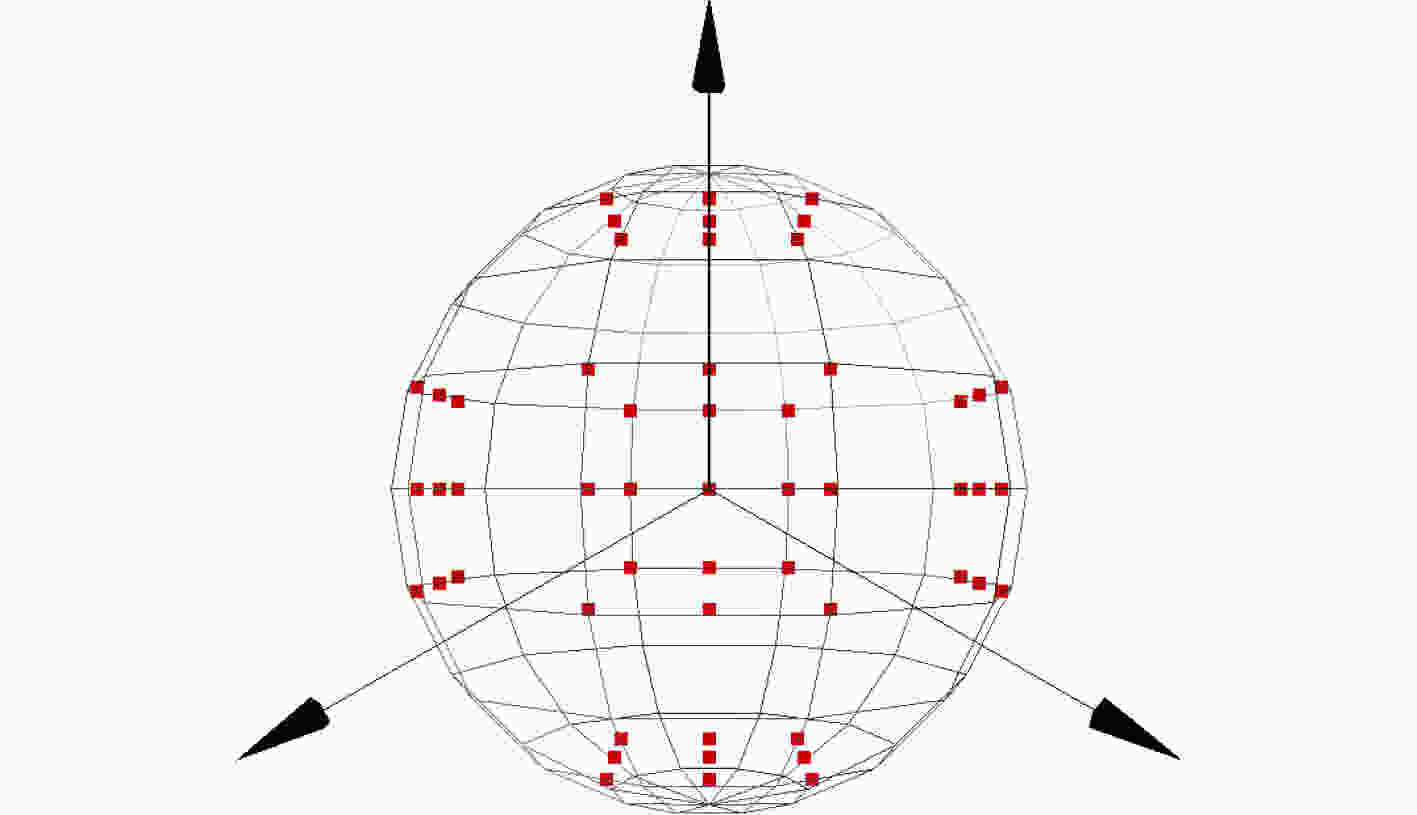
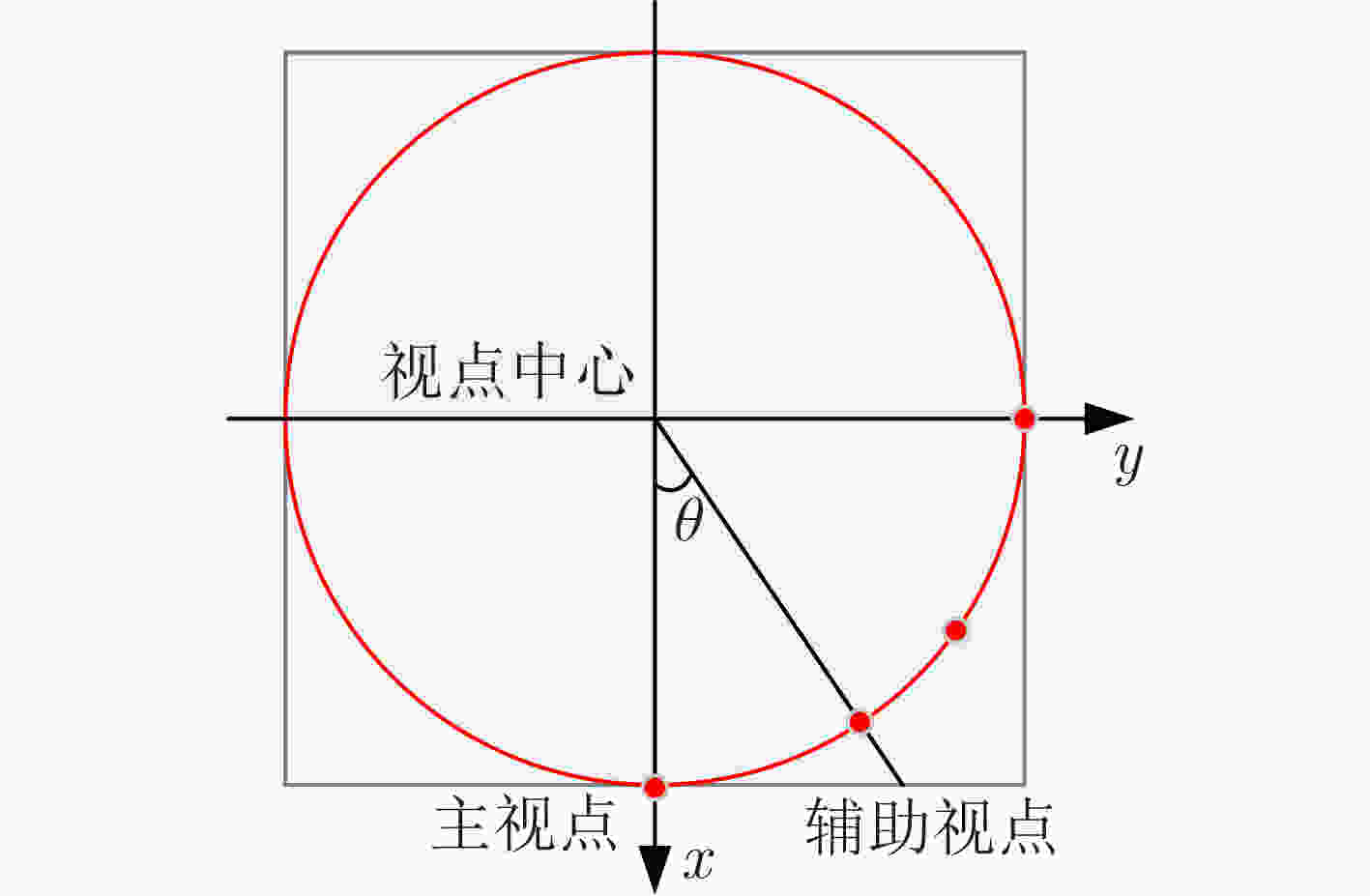
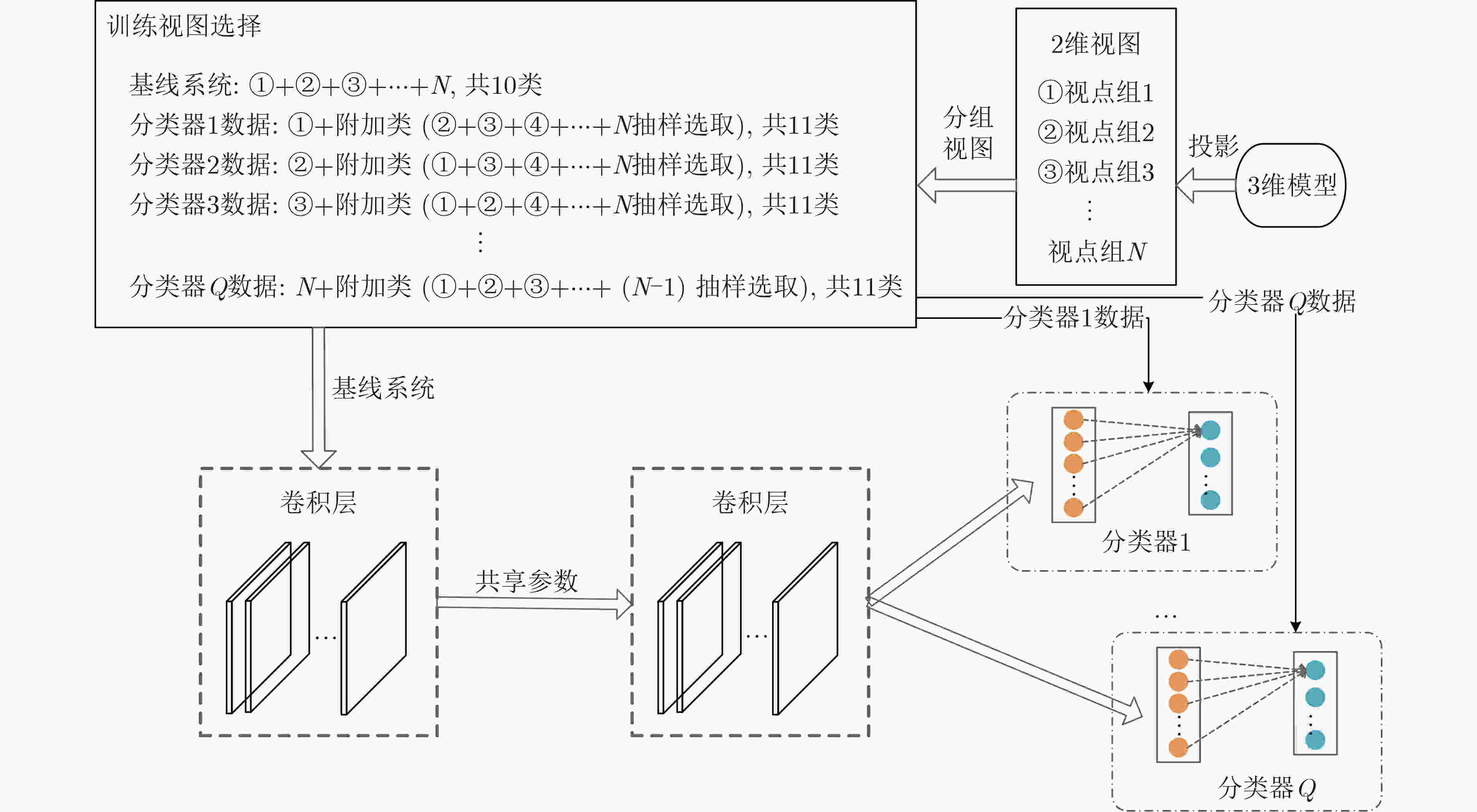
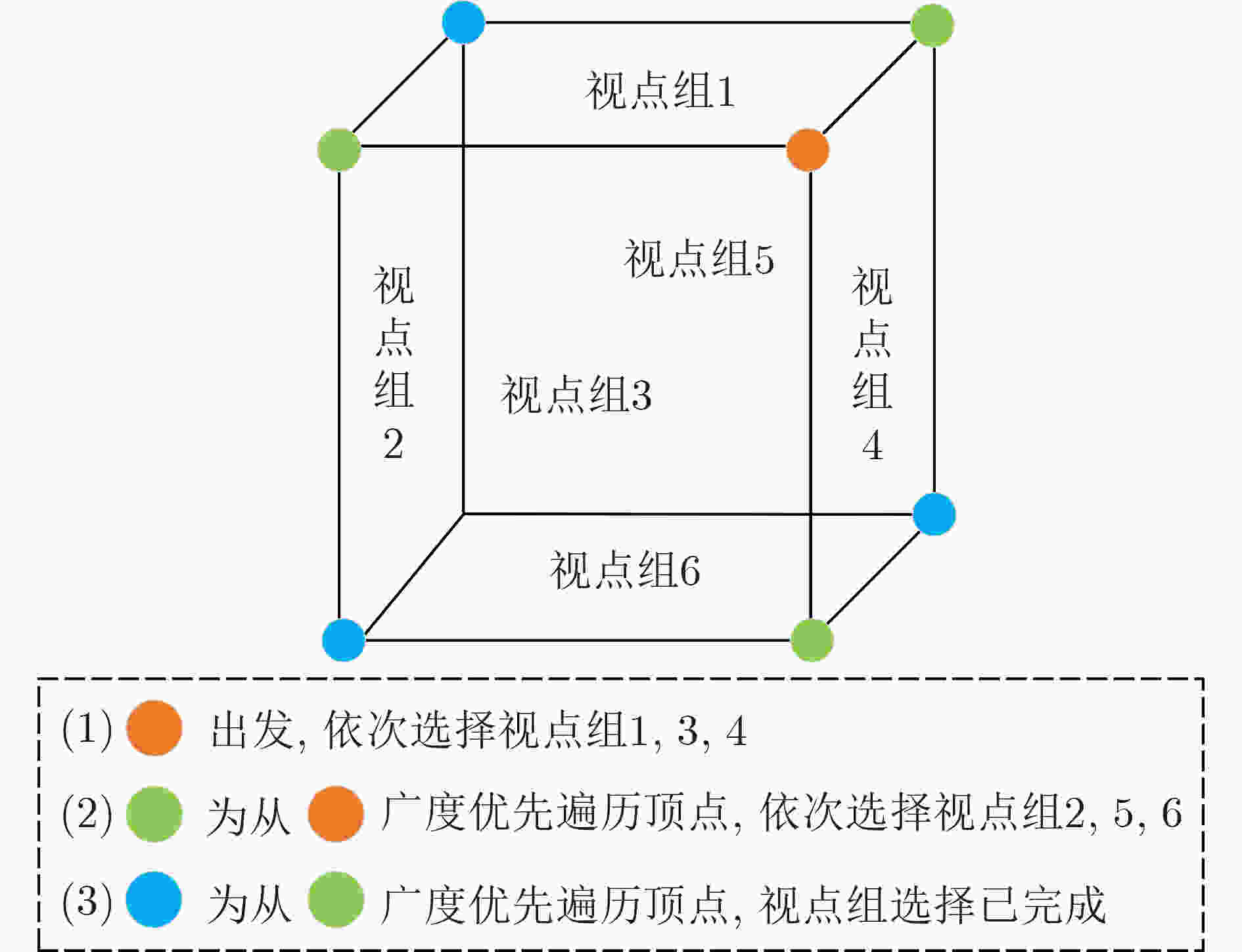
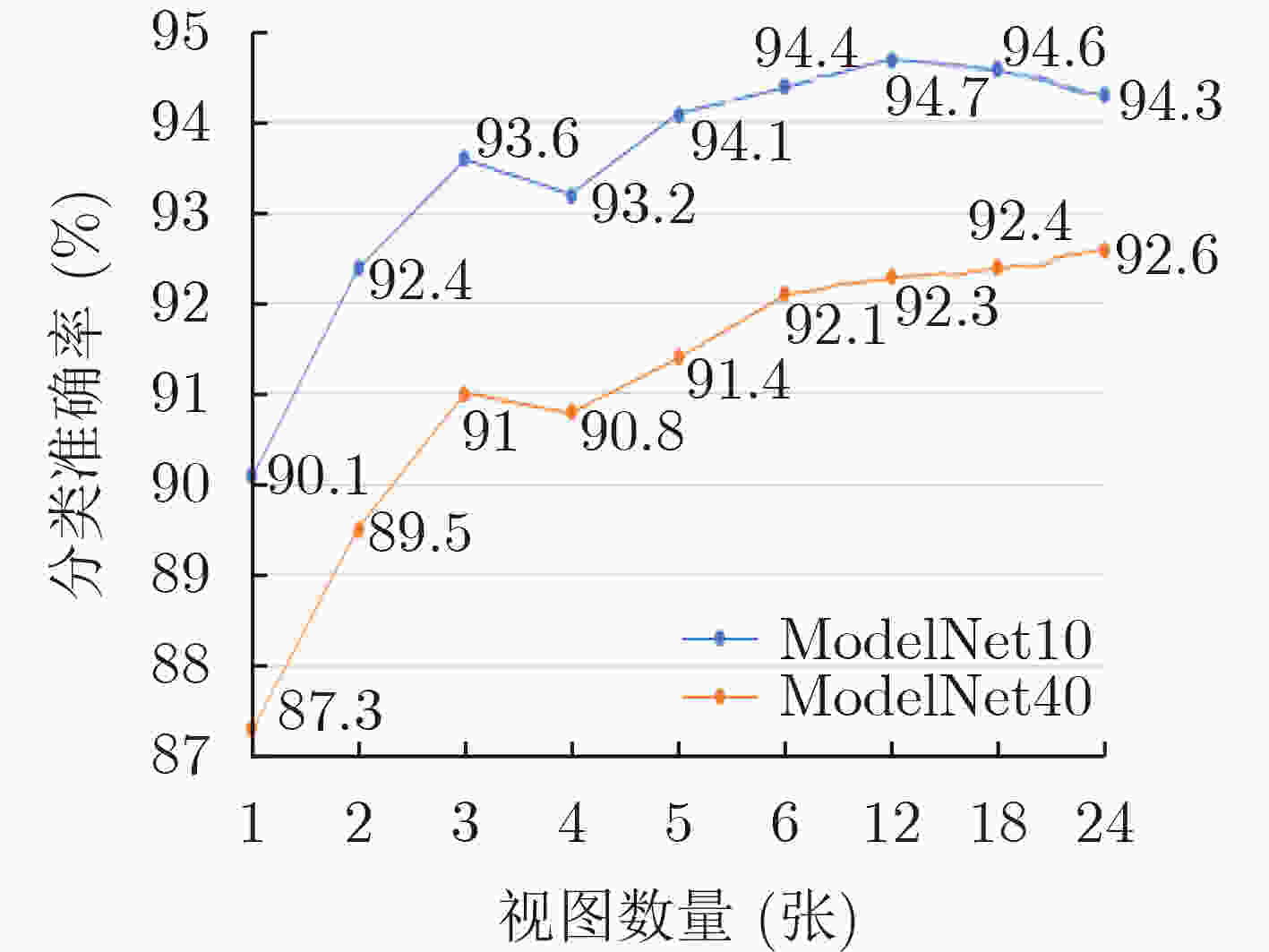
摘要: 基于视图的3维模型分类方法与深度学习融合能有效提升模型分类的准确率。但目前的方法将相同类别的3维模型所有视点上的视图归为一类,忽略了不同视点上的视图差异,导致分类器很难学习到一个合理的分类面。为解决这一问题,该文提出一个基于深度神经网络的3维模型分类方法。该方法在3维模型的周围均匀设置多个视点组,为每个视点组训练1个视图分类器,充分挖掘不同视点组下的3维模型深度信息。这些分类器共享1个特征提取网络,但却有各自的分类网络。为了使提取的视图特征具有区分性,在特征提取网络中加入注意力机制;为了对非本视点组的视图建模,在分类网络中增加了附加类。在分类阶段首先提出一个视图选择策略,从大量视图中选择少量视图用于分类,以提高分类效率。然后提出一个分类策略通过分类视图实现可靠的3维模型分类。在ModelNet10和ModelNet40上的实验结果表明,该方法在仅用3张视图的情况下分类准确率高达93.6%和91.0%。Abstract: The integration of view-based 3D model classification and deep learning can effectively improve the classification accuracy. However, current methods consider that the views from different viewpoints of 3D model with same category belong to the same category and ignore the view differences, which makes it difficult for the classifier to learn a reasonable classification surface. To solve this problem, a 3D model classification method based on deep neural network is proposed. The multiple viewpoint groups are set evenly around the 3D model in this method, and the view classifier for each viewpoint group is trained for fully mining the deep information of the 3D model in different viewpoint groups. These classifiers share a feature extraction network, but have their own classification network. In order to extract the discriminative view features, the attention mechanism is added to the feature extraction network; In order to model the views of the non-viewpoint group, additional classes are added to the classification network. In the classification stage, a view selection strategy is first proposed, which can use a small number of views to classify the 3D model and improve classification efficiency. Then a classification strategy is proposed to achieve reliable 3D model classification through classification view. Experimental results on ModelNet10 and ModelNet40 show that the classification accuracy can reach up to 93.6% and 91.0% with only 3 views.
-
表 1 ModelNet10数据集
分类器类型 测试集 训练集 前10类 前10类平均视图数 第11类 前10类 前10类平均视图数 第11类 视图分类器 8172 817 3632 35919 3592 15964 基线系统 49032 4903 – 215514 21551 – 表 2 视图分类准确率(%)
CBAM 附加类 数据集 视点组1(上) 视点组2(左) 视点组3(前) 视点组4(右) 视点组5(后) 视点组6(下) 无 无 训练 94.95 95.71 96.28 95.49 95.95 94.62 测试 85.88 87.21 89.72 86.73 89.03 83.92 有 训练 95.03 94.14 95.53 93.21 95.84 95.16 测试 89.61 87.25 89.74 87.03 88.91 88.41 有 无 训练 94.95 95.86 96.91 95.91 95.13 93.93 测试 89.18 89.37 90.82 89.35 88.67 86.94 有 训练 94.99 92.94 93.17 92.99 91.49 94.64 测试 91.52 90.41 90.93 90.02 89.19 90.38 表 3 分类准确率比较(%)
表 4 视图被分到附加类的数量统计
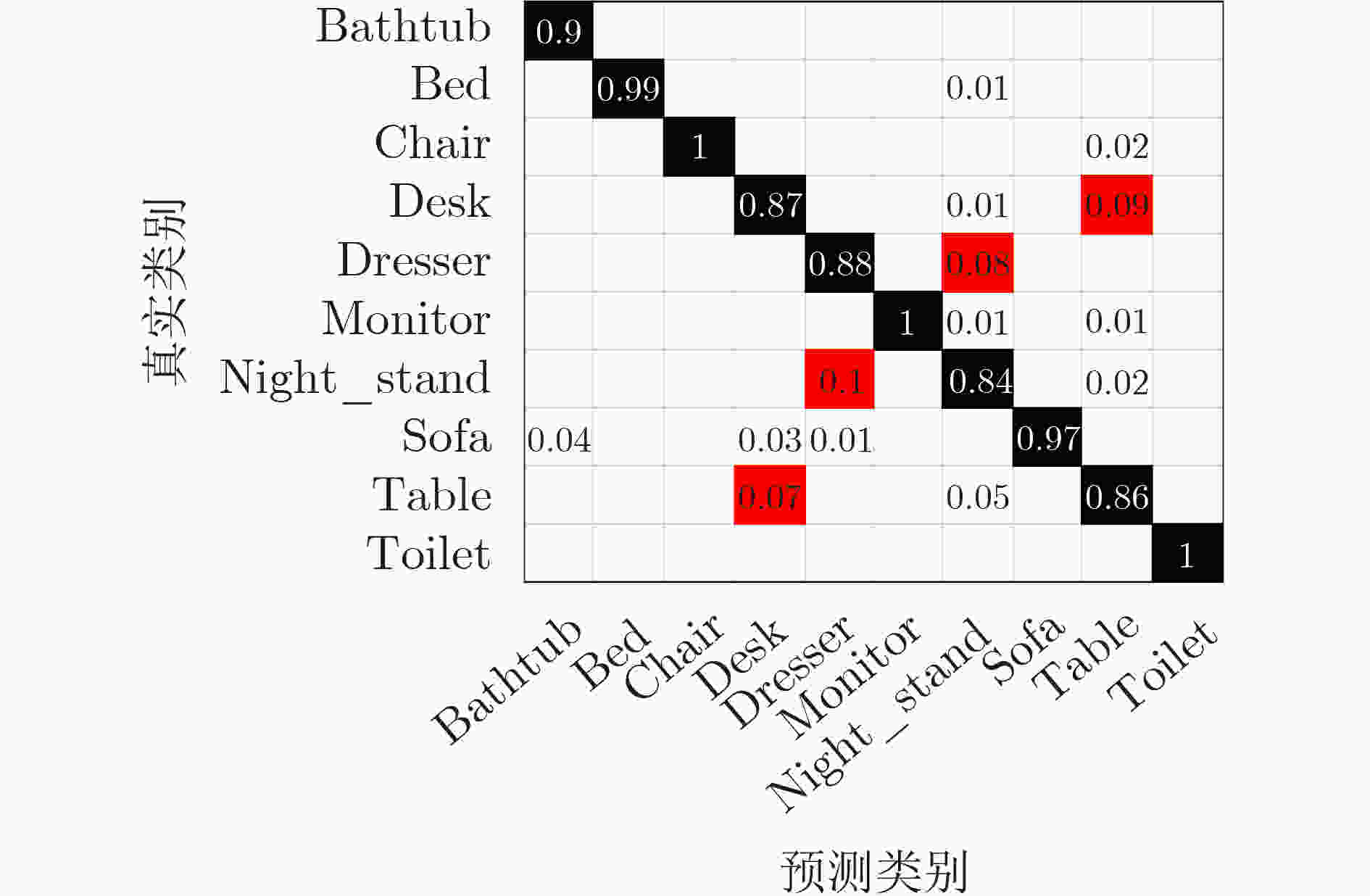
类别 总视图数/分到附加类张数 比例(%) 类别 总视图数/分到附加类张数 比例(%) Bathtub 2700/25 0.9 Monitor 5400/18 0.3 Bed 5400/30 0.6 Night_stand 4644/47 1.0 Chair 5400/9 0.2 Sofa 5400/15 0.3 Desk 4644/45 1.0 Table 5400/22 0.4 Dresser 4644/17 0.4 Toilet 5400/8 0.1 -
[1] 韩丽, 刘书宁, 徐圣斯, 等. 自适应稀疏编码融合的非刚性三维模型分类算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(11): 1898–1907. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17759HAN Li, LIU Shuning, XU Shengsi, et al. Non-rigid 3D model classification algorithm based on adaptive sparse coding fusion[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(11): 1898–1907. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17759 [2] 周文, 贾金原. 一种SVM学习框架下的Web3D轻量级模型检索算法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(1): 92–99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.01.012ZHOU Wen and JIA Jinyuan. Web3D lightweight for sketch-based shape retrieval using SVM learning algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(1): 92–99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.01.012 [3] 王栋. 面向三维模型检索的多视图特征学习方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019: 1–15.WANG Dong. Research on multi-view feature learning for 3D model retrieval[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019: 1–15. [4] SU Hang, MAJI S, KALOGERAKIS E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 945–953. [5] LIU Anan, GUO Fubin, ZHOU Heyu, et al. Semantic and context information fusion network for view-based 3D model classification and retrieval[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 155939–155950. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3018875 [6] GAO Zan, XUE Haixin, and WAN Shaohua. Multiple discrimination and pairwise CNN for view-based 3D object retrieval[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 125: 290–302. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.02.017 [7] HEGDE V and ZADEH R. FusionNet: 3D object classification using multiple data representations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.05695, 2016. [8] LIU Anan, ZHOU Heyu, LI Mengjie, et al. 3D model retrieval based on multi-view attentional convolutional neural network[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(7-8): 4699–4711. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-7521-8 [9] LIANG Qi, WANG Yixin, NIE Weizhi, et al. MVCLN: Multi-view convolutional LSTM network for cross-media 3D shape recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 139792–139802. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012692 [10] MA Yanxun, ZHENG Bin, GUO Yulan, et al. Boosting multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D object recognition via view saliency[C]. The 12th Chinese Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies, Beijing, China, 2017: 199–209. [11] 白静, 司庆龙, 秦飞巍. 基于卷积神经网络和投票机制的三维模型分类与检索[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(2): 303–314. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17160BAI Jing, SI Qinglong, and QIN Feiwei. 3D model classification and retrieval based on CNN and voting scheme[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(2): 303–314. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17160 [12] KANEZAKI A, MATSUSHITA Y, and NISHIDA Y. RotationNet: Joint object categorization and pose estimation using multiviews from unsupervised viewpoints[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 5010–5019. [13] SHI Baoguang, BAI Song, ZHOU Zhichao, et al. DeepPano: Deep panoramic representation for 3-D shape recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(12): 2339–2343. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2480802 [14] SINHA A, BAI Jing, and RAMANI K. Deep learning 3D shape surfaces using geometry images[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 223–240. [15] SFIKAS K, THEOHARIS T, and PRATIKAKIS I. Exploiting the PANORAMA representation for convolutional neural network classification and retrieval[C]. The 10th Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval, Lyon, France, 2017: 1–7. [16] HAN Zhizhong, SHANG Mingyang, LIU Zhenbao, et al. SeqViews2SeqLabels: Learning 3D global features via aggregating sequential views by RNN with attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(2): 658–672. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2868426 [17] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [18] WOO S M, LEE S H, YOO J S, et al. Improving color constancy in an ambient light environment using the phong reflection model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 1862–1877. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2785290 [19] SHILANE P, MIN P, KAZHDAN M, et al. The Princeton shape benchmark[C]. Shape Modeling Applications, 2004, Genova, Italy, 2004: 167–178. -





 下载:
下载:

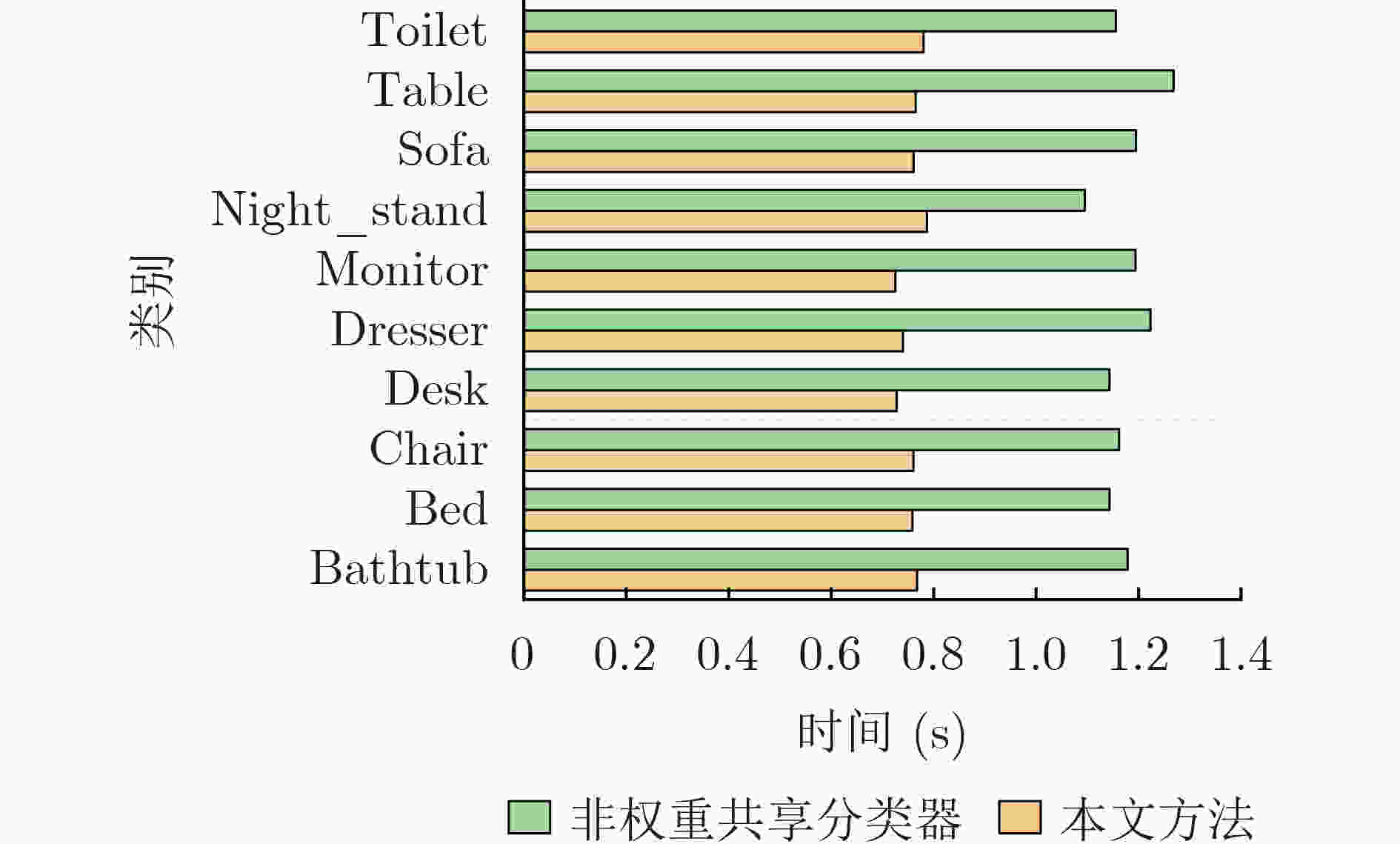


 下载:
下载:
