A Deep Learning Method for SSVEP Classification Based on Phase and Frequency Characteristics
-
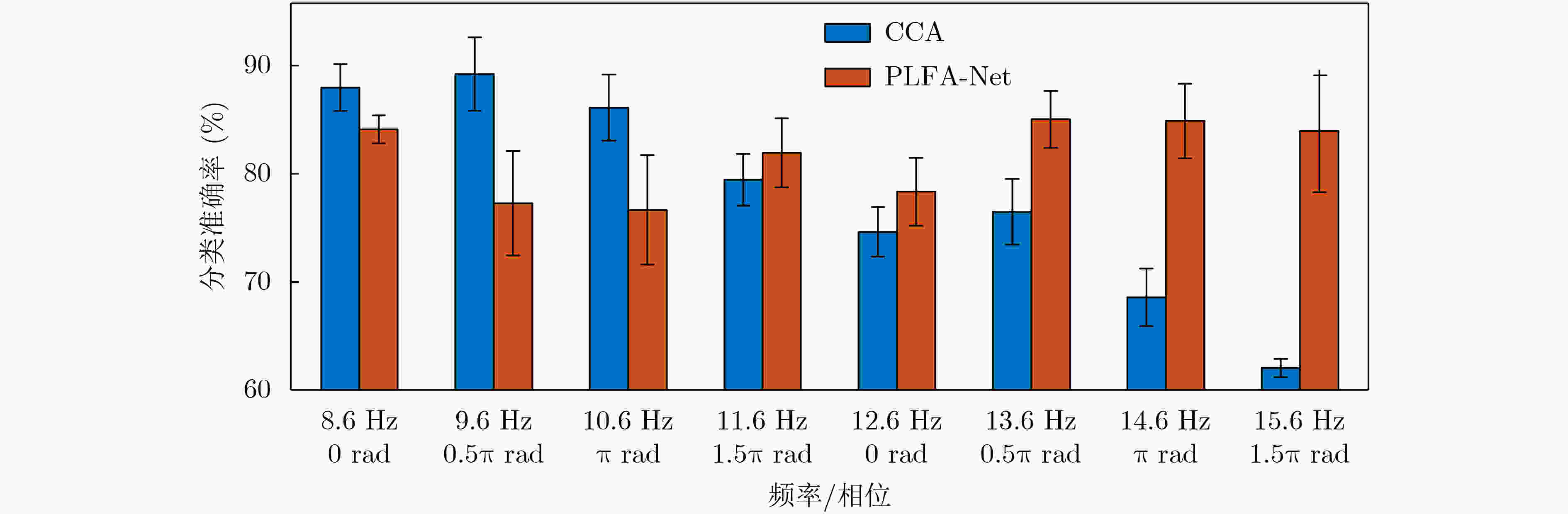
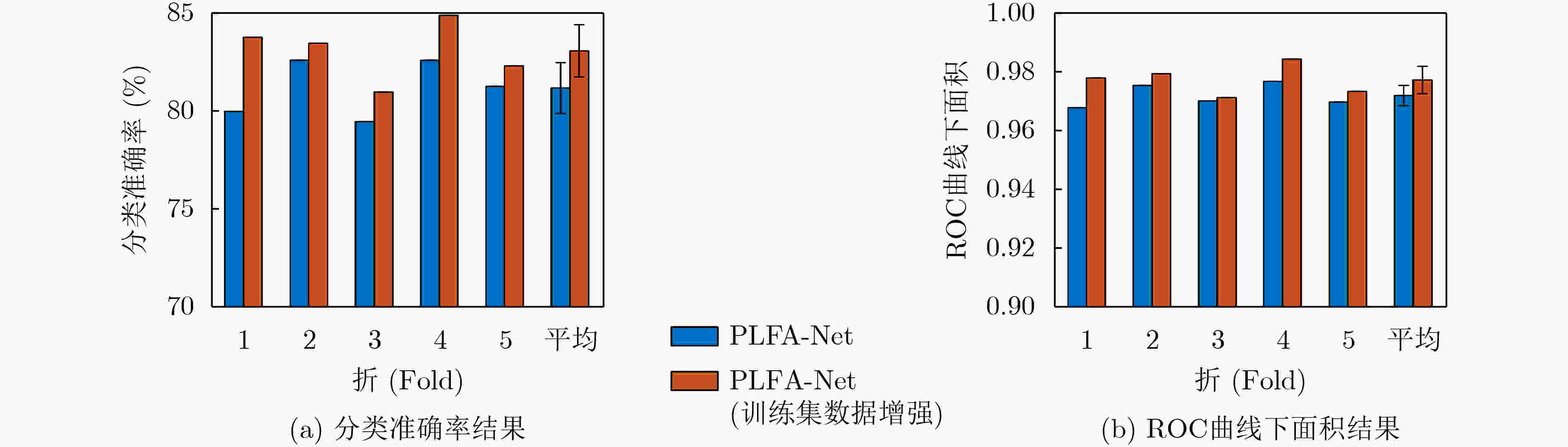
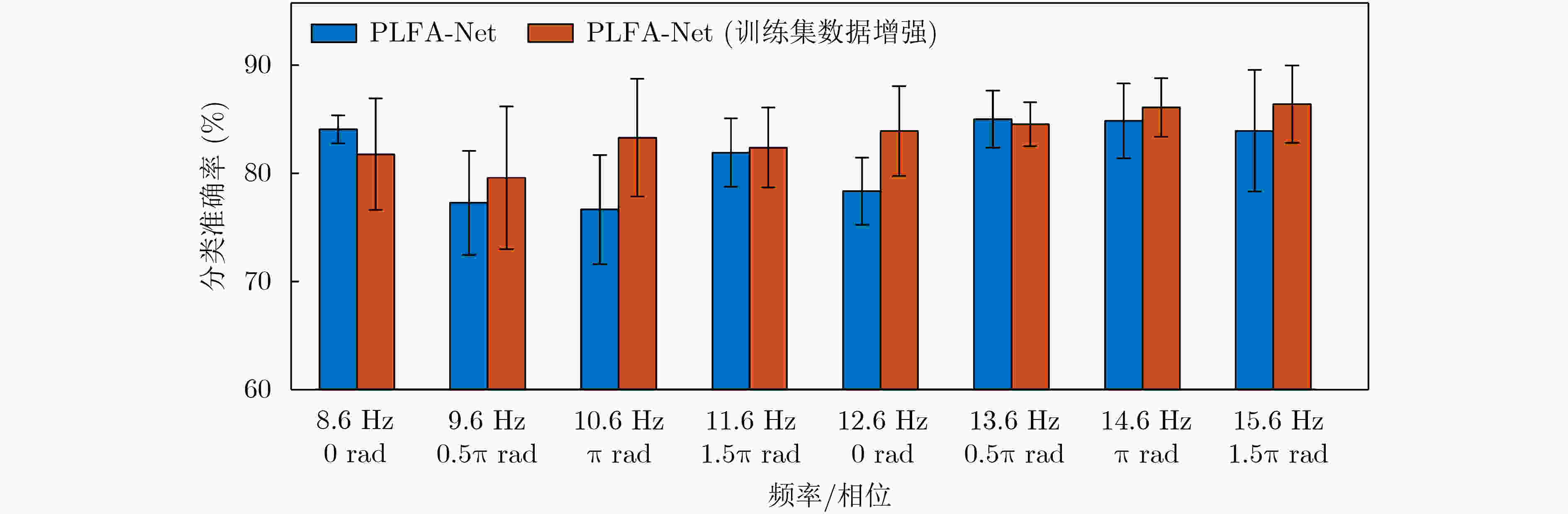
摘要: 针对现有深度学习分类方法对稳态视觉诱发电位相位与频率信息利用不充分的问题,该文提出一种用于稳态视觉诱发电位(SSVEP)分类的卷积神经网络模型。该模型以经过快速傅里叶变换后的复向量作为输入,首先对各个导联的实部向量和虚部向量进行卷积,学习相位信息;随后引入空间注意力机制,对判别频率信息进行增强;然后使用2维卷积和最大池化层进一步提取空域和频域信息;最后使用全连接层进行分类。实验结果表明利用该方法在跨受试情况下准确率可达到81.21%,通过在训练集增加标准正弦信号模板准确率可进一步提升至83.17%,相比典型相关分析方法获得了更好的分类效果。Abstract: A deep learning method for Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential (SSVEP) classification is proposed to solve the problem that phase and frequency information are not fully used in existing deep learning models. First, the proposed model uses complex vectors of fast Fourier transform as input and operates convolution on real and imaginary vectors to learn phase information, and then utilizes the spatial attention module to enhance discriminative frequency information. Next, two-dimensional convolution and max pooling are used to extract further spatial and frequency features. Finally, fully connected layers are utilized to classify. The accuracy of proposed model can reach 81.21% in the case of cross subject, and the accuracy can be further improved to 83.17% by adding the standard sinusoidal signal templates to the training set. The results show that the proposed model achieves better performance than canonical correlation analysis algorithm.
-
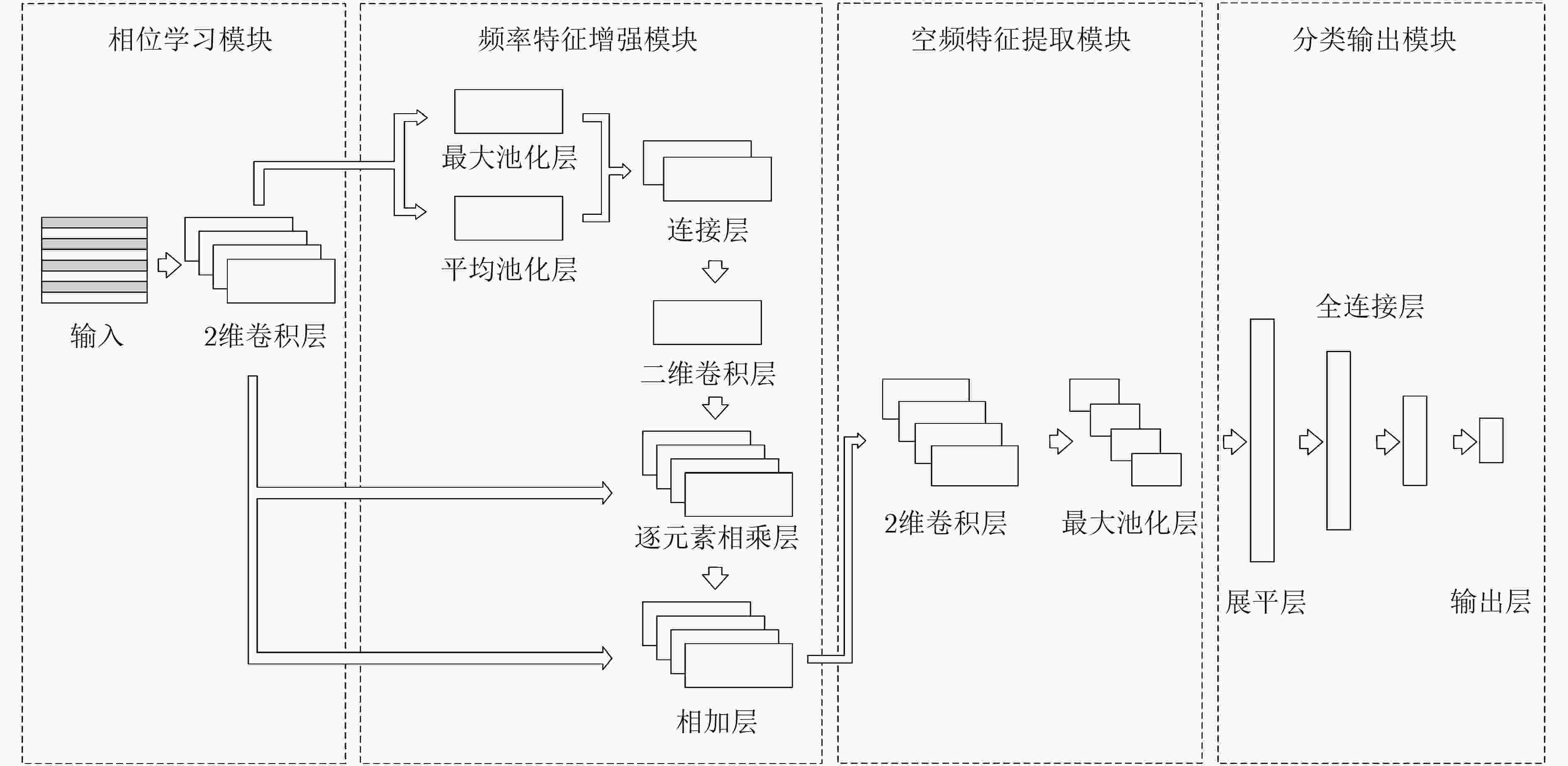
表 1 PLFA-Net模型详细结构及参数设置
模块 层 卷积核数量 卷积核大小 步长 输出维度 其他参数 相位学习 Input (60,188) Reshape (60,188,1) Conv2D 4 (2,1) (2,1) (30,188,4) max_norm=0.5 BN (30,188,4) Activation (30,188,4) ‘relu’ 频率特征增强 MaxPooling2D (1,1) (1,1) (30,188,1) axis=–1 AveragePooling2D (1,1) (1,1) (30,188,1) axis=–1 Concatenate (30,188,2) axis=–1 Conv2D 1 (5,5) (1,1) (30,188,1) padding=‘same’ Activation (30,188,1) ‘tanh’ Multiply (30,188,4) Add (30,188,4) 空频特征提取 Conv2D 4 (5,5) (1,1) (26,184,4) max_norm=0.5 BN (26,184,4) Activation (26,184,4) ‘relu’ MaxPooling2D (2,2) (13,92,4) SpatialDropout2D (13,92,4) p=0.5 分类输出 Flatten 4784 Dense 512 512 max_norm=0.5 Activation 512 ‘relu’ Dense 256 256 max_norm=0.5 Activation 256 ‘relu’ Dense 8 8 max_norm=0.5 Activation 8 ‘softmax’ 表 2 5折交叉验证PLFA-Net模型分类结果
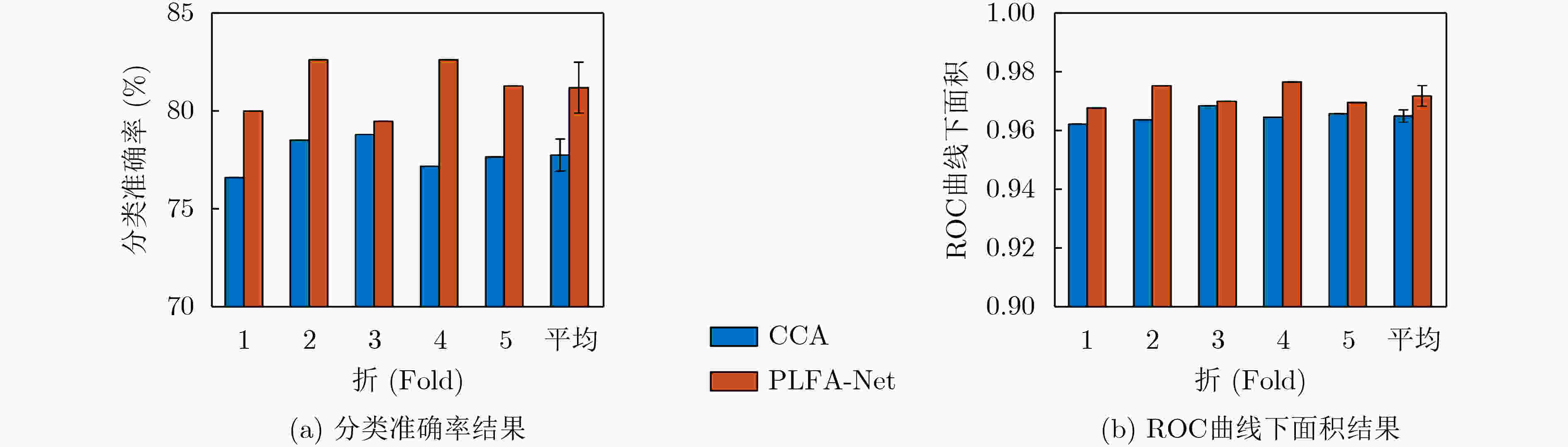
折 ACC (%) AUC 1st 80.02 0.9678 2nd 82.63 0.9754 3rd 79.48 0.9701 4th 82.63 0.9768 5th 81.30 0.9697 平均 81.21±0.81 0.9720±0.0034 -
[1] LIN Zhonglin, ZHANG Changshui, WU Wei, et al. Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCIs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(12): 2610–2614. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.886577 [2] 林中林, 张雅静, 高小榕, 等. 一种通过脑电信号实时检测双眼竞争的方法[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2007, 20(5): 381–384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0837.2007.05.016LIN Zhonglin, ZHANG Yajing, GAO Xiaorong, et al. A method for real-time detection of binocular rivalry through electroencephalogram[J]. Space Medicine &Medical Engineering, 2007, 20(5): 381–384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0837.2007.05.016 [3] NAKANISHI M, WANG Yijun, WANG Yute, et al. Enhancing unsupervised canonical correlation analysis-based frequency detection of SSVEPs by incorporating background EEG[C]. Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, USA, 2014: 3053–3056. [4] CHEN Xiaogang, WANG Yijun, NAKANISHI M, et al. High-speed spelling with a noninvasive brain-computer interface[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(44): E6058–E6067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508080112 [5] CHEN Xiaogang, WANG Yijun, Gao Shangkai, et al. Filter bank canonical correlation analysis for implementing a high-speed SSVEP-based brain-computer interface[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2015, 12(4): 046008. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/12/4/046008 [6] YIN Erwei, ZHOU Zongtan, JIANG Jun, et al. A dynamically optimized SSVEP brain-computer interface (BCI) speller[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 62(6): 1447–1456. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2320948 [7] 岳敬伟. 脑机协调控制理论与关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2015.YUE Jingwei. On brain-computer coordination control theory and key technologies[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015. [8] YANG Chen, HAN Xu, WANG Yijun, et al. A dynamic window recognition algorithm for SSVEP-based brain-computer interfaces using a spatio-temporal equalizer[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2018, 28(10): 1850028. doi: 10.1142/S0129065718500284 [9] BEVILACQUA V, TATTOLI G, BUONGIORNO D, et al. A novel BCI-SSVEP based approach for control of walking in virtual environment using a convolutional neural network[C]. Proceedings of 2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Beijing, China, 2014: 4121–4128. [10] KWAK N S, MÜLLER K R, and LEE S W. A convolutional neural network for steady state visual evoked potential classification under ambulatory environment[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0172578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172578 [11] ATTIA M, HETTIARACHCHI I, HOSSNY M, et al. A time domain classification of steady-state visual evoked potentials using deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Washington, USA, 2018: 766–769. [12] ATTIA M, HETTIARACHCHI I, MOHAMED S, et al. A frequency domain classifier of steady-state visual evoked potentials using deep separable convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Miyazaki, Japan, 2018: 2134–2139. [13] EL-FIQI H, WANG Min, SALIMI N, et al. Convolution neural networks for person identification and verification using steady state visual evoked potential[C]. Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Miyazaki, Japan, 2018: 1062–1069. [14] AZNAN N K N, BONNER S, CONNOLLY J, et al. On the classification of SSVEP-based dry-EEG signals via convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Miyazaki, Japan, 2018: 3726–3731. [15] 杜光景, 谢俊, 张玉彬, 等. 用于稳态视觉诱发电位脑机接口目标识别的深度学习方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2019, 53(11): 42–48. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201911006DU Guangjing, XIE Jun, ZHANG Yubin, et al. A deep learning method for target recognition in steady-state visual evoked potential–based brain-computer interface[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2019, 53(11): 42–48. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201911006 [16] LIU Bingchuan, HUANG Xiaoshan, WANG Yijun, et al. BETA: A large benchmark database toward SSVEP-BCI application[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2020, 14: 627. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00627 -





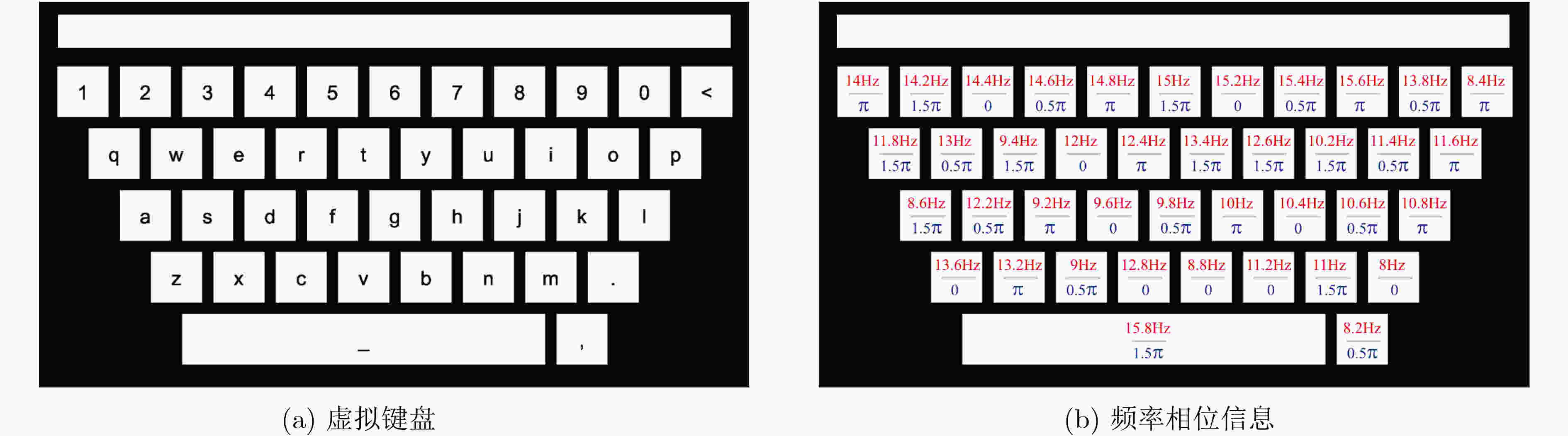
 下载:
下载:
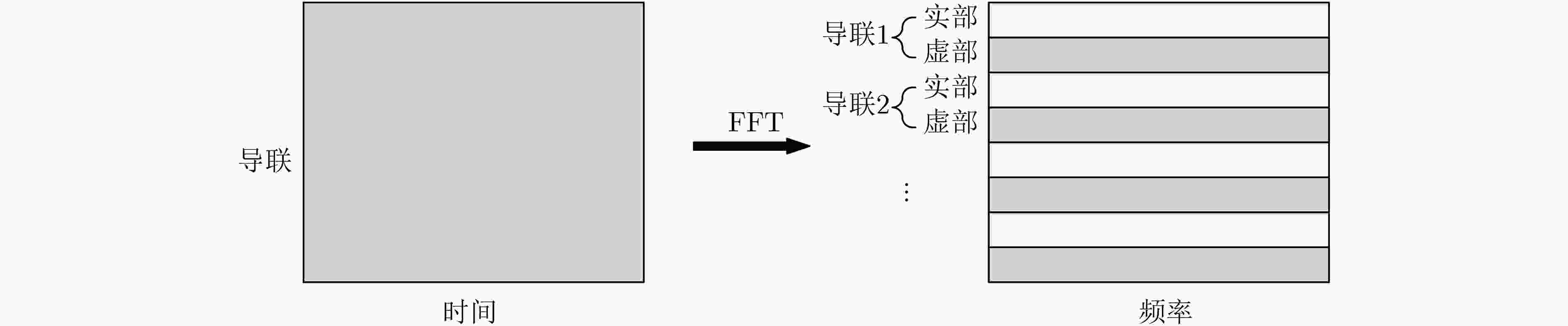
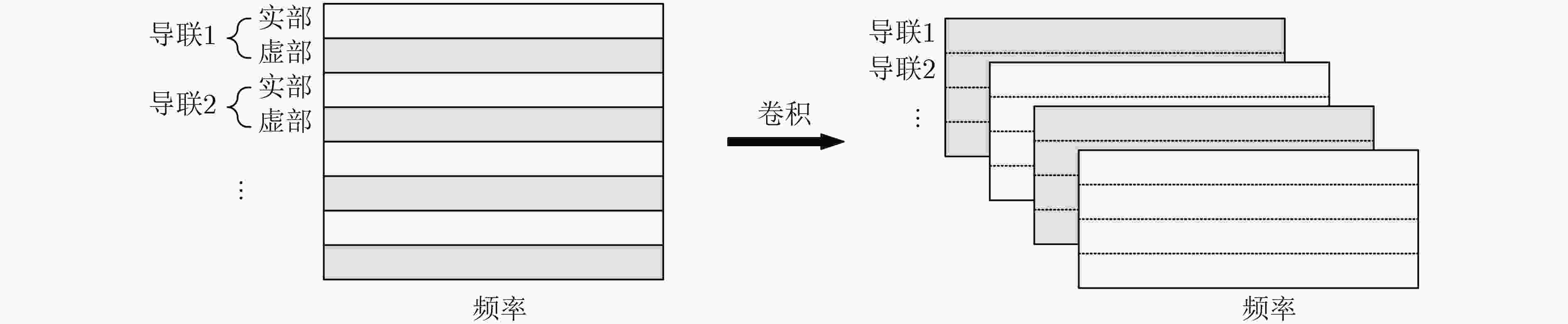
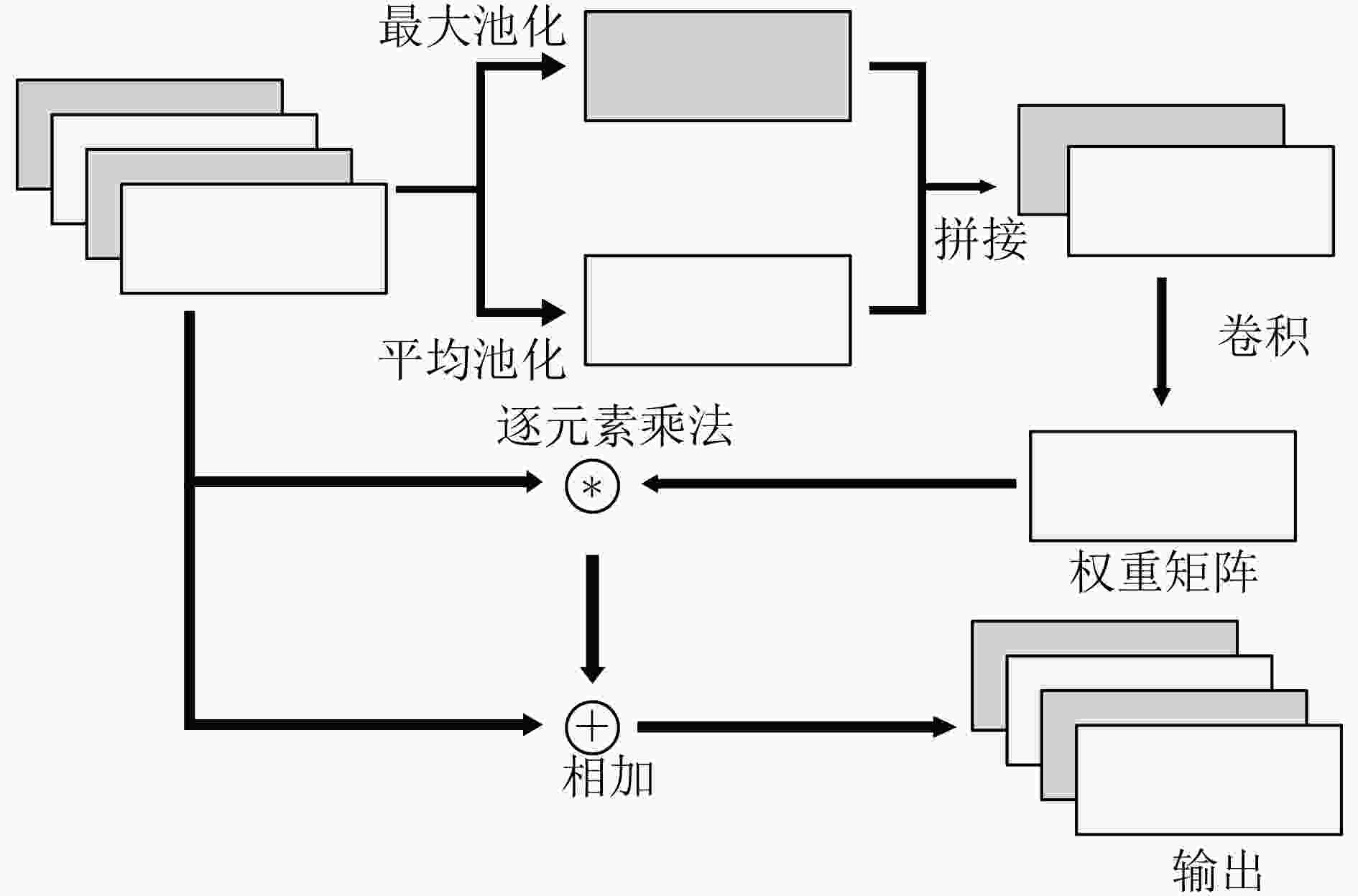


 下载:
下载:
