A Method for Evaluating the Severity of Intermittent Faults of Electronic Systems Based on Variational Mode Decomposition-Gated Recurrent Units
-
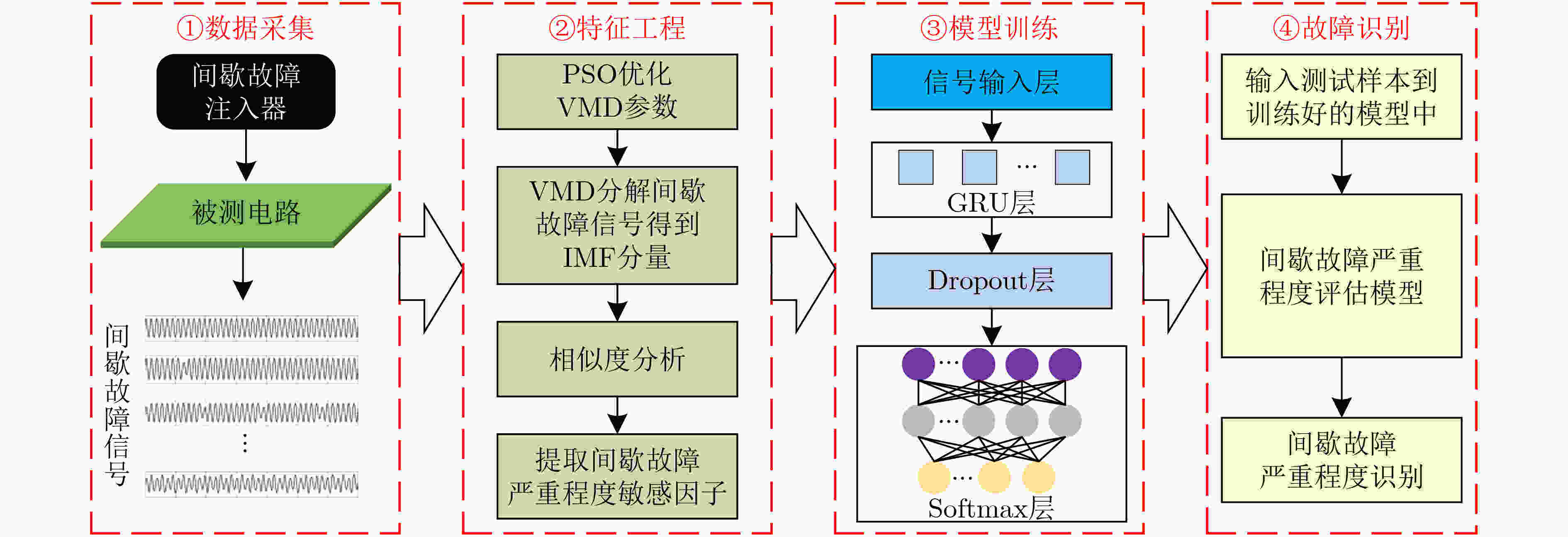
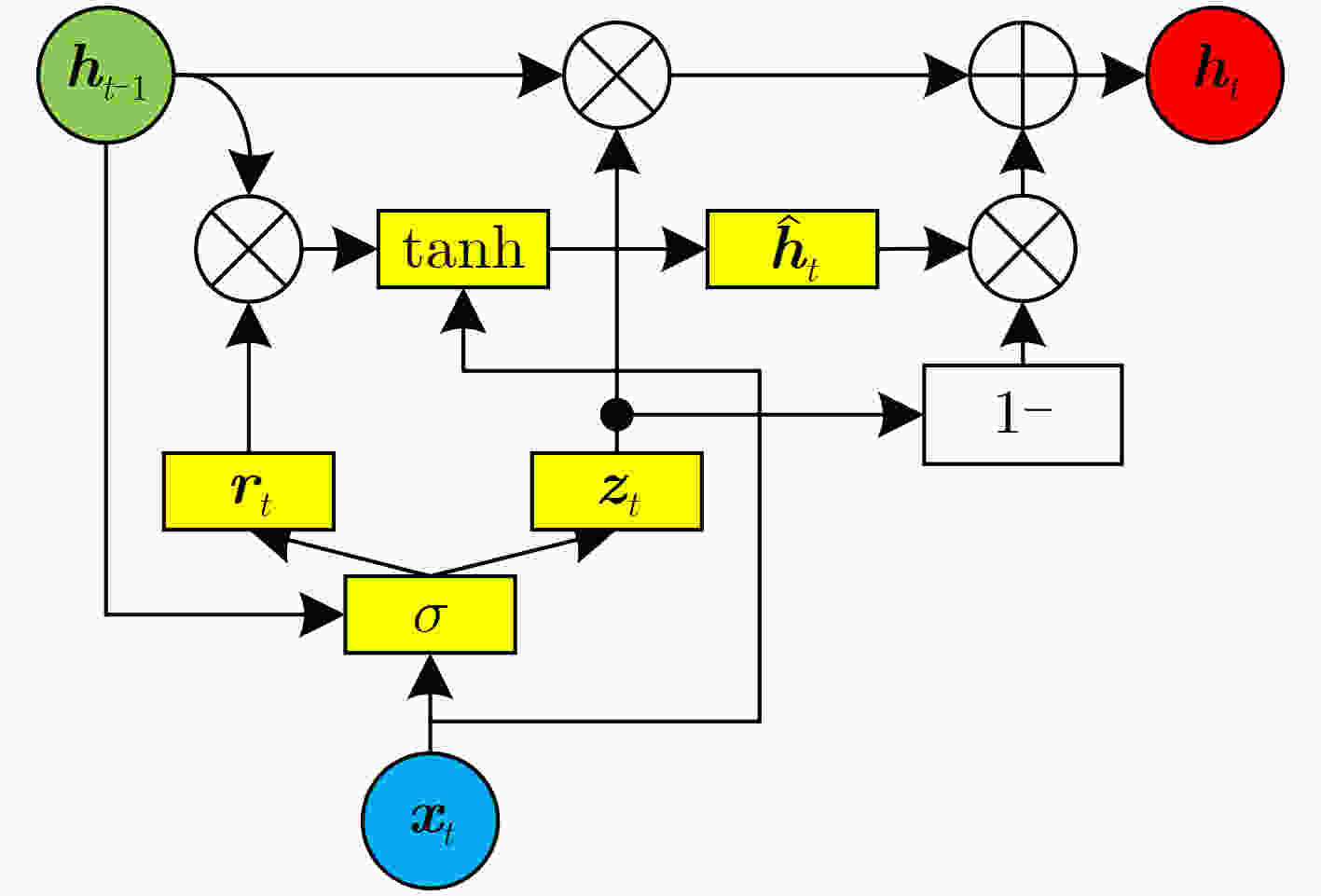
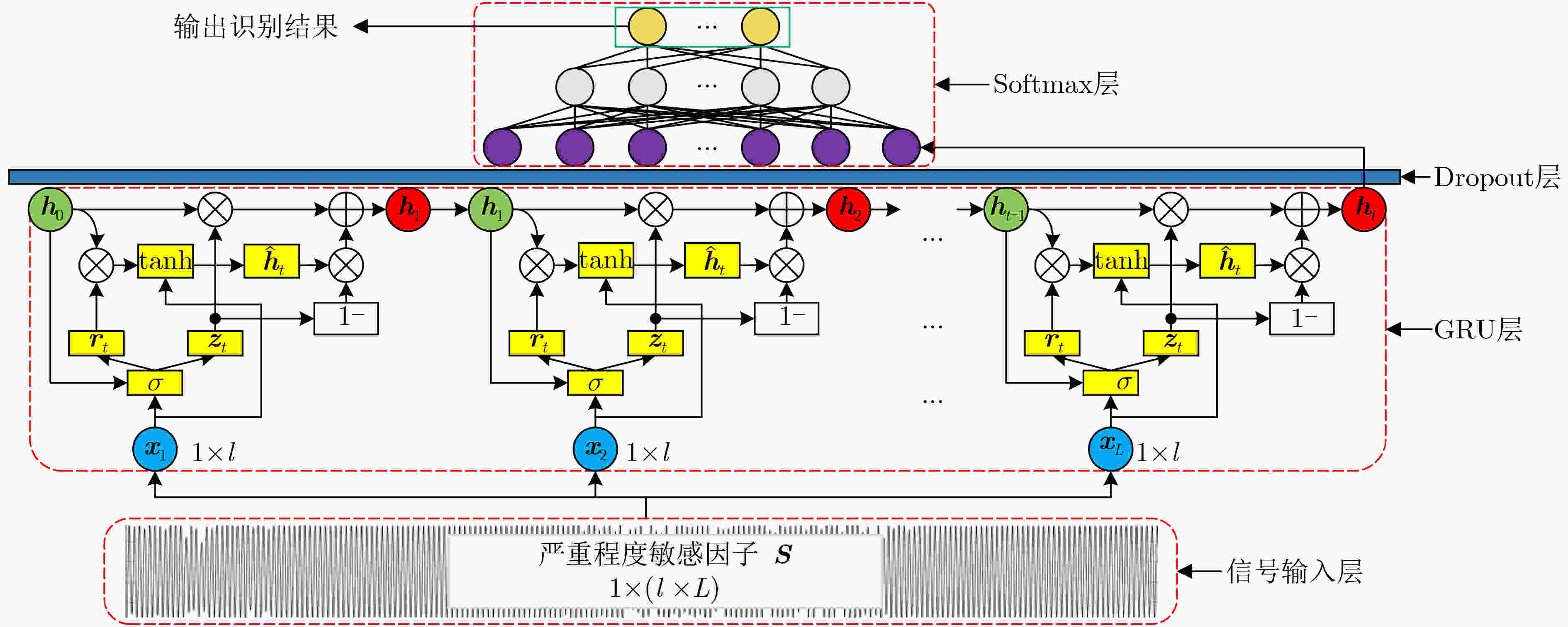
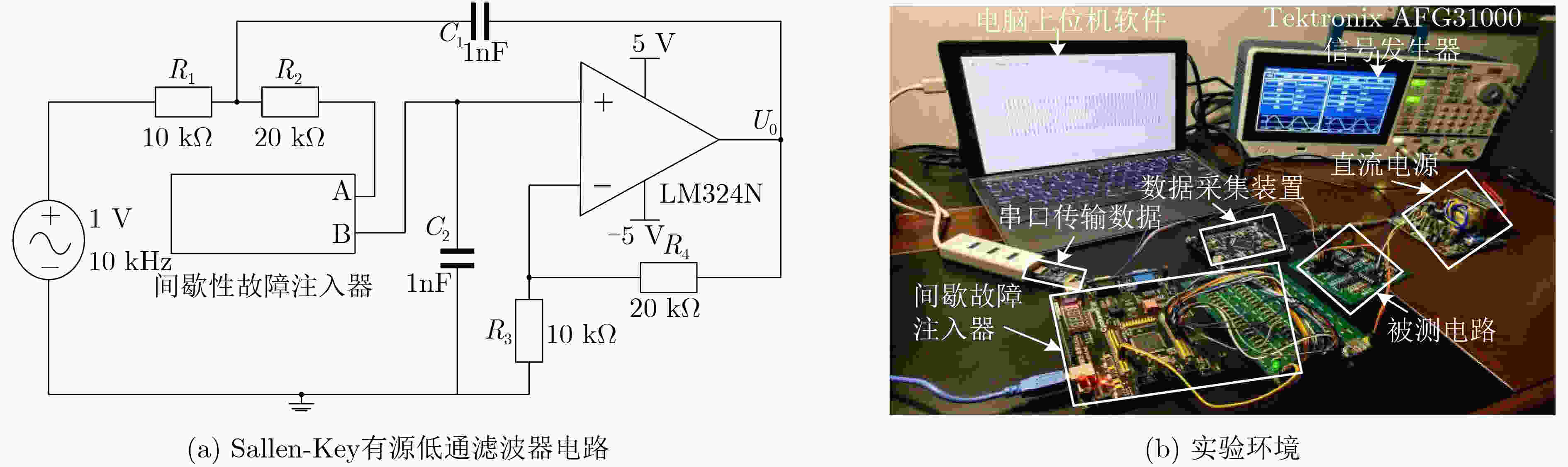
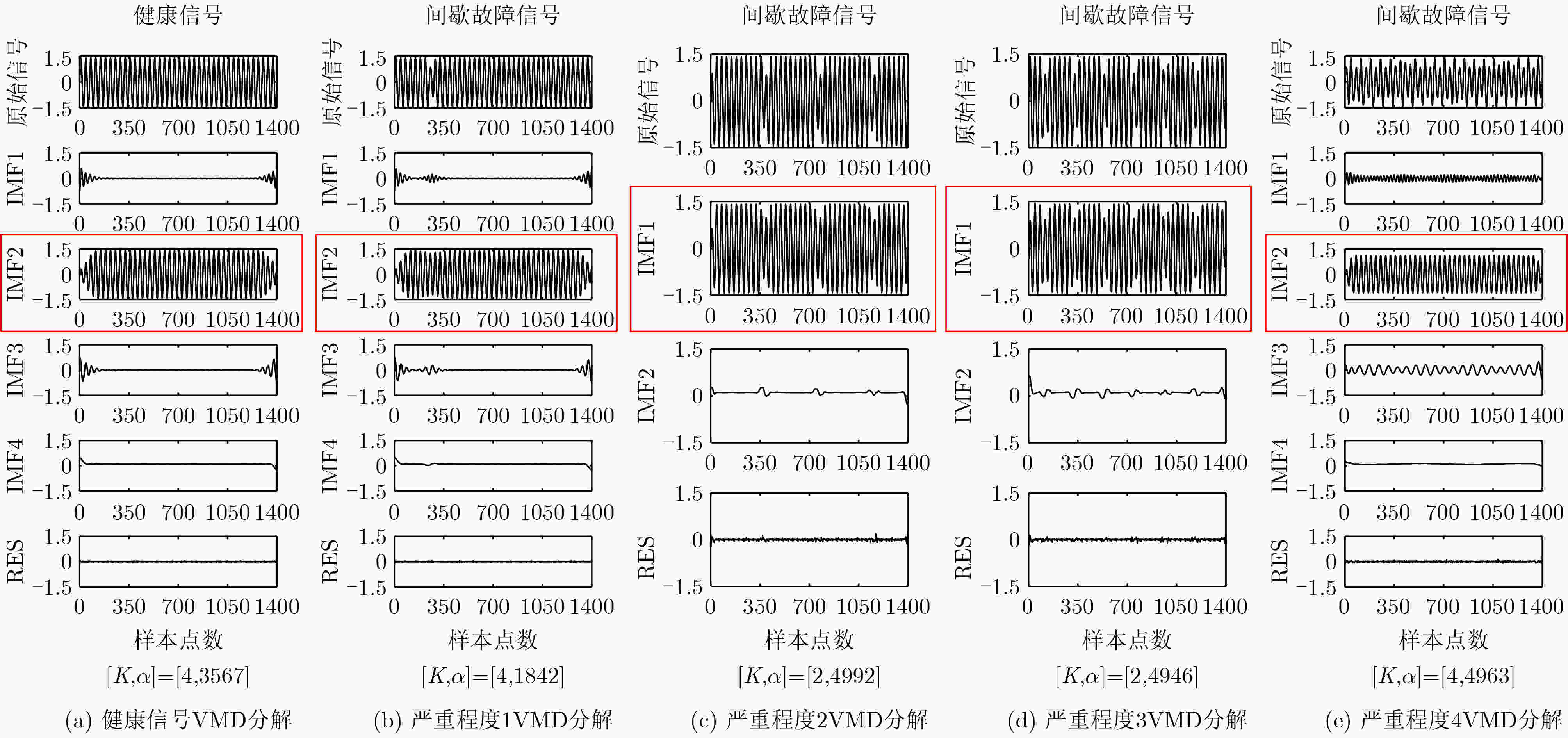
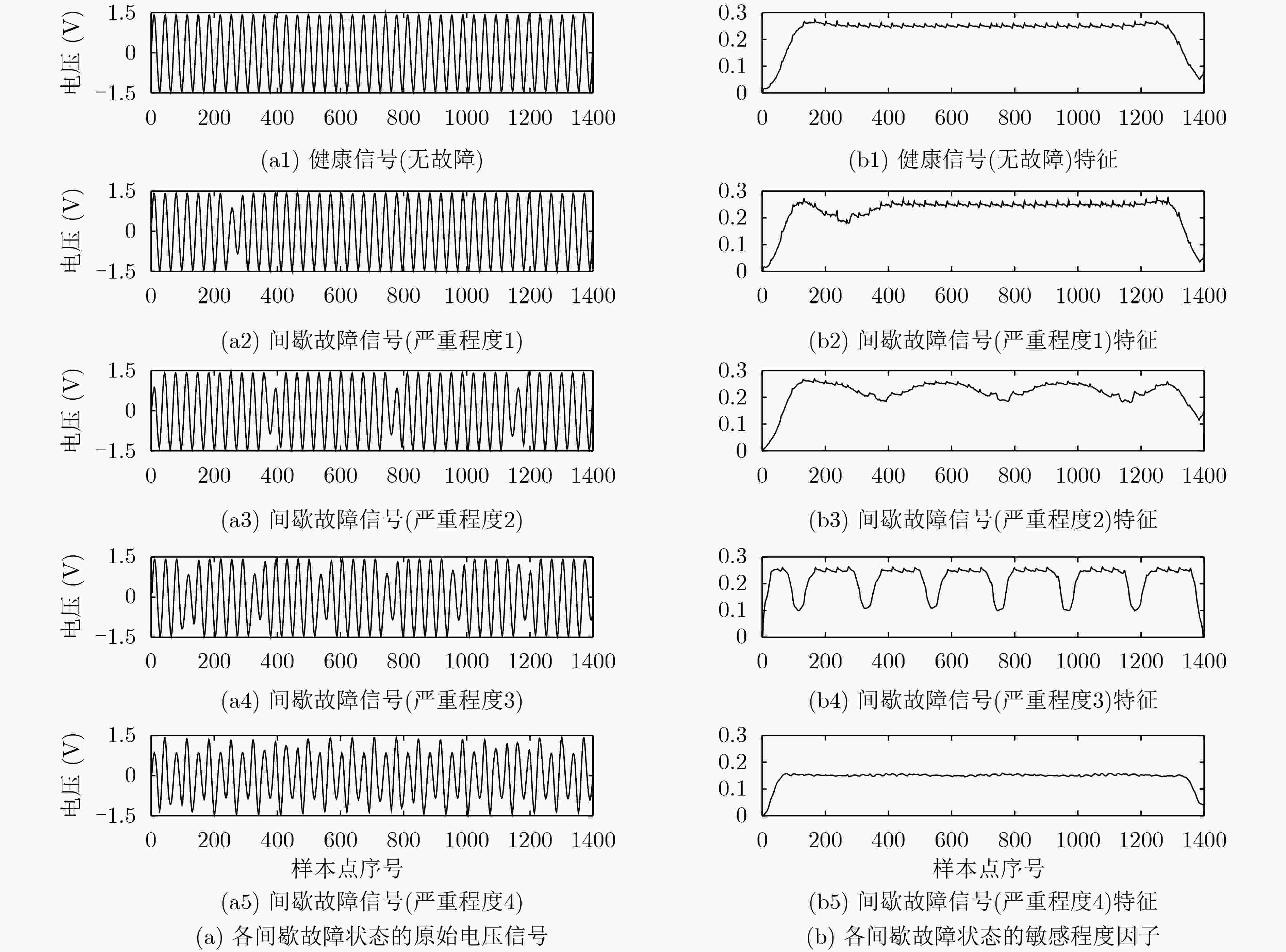
摘要: 针对电子系统间歇故障信号受噪声影响大且冗余信息多,导致深度神经网络模型对间歇故障严重程度评估能力受限的问题,该文提出一种基于变分模式分解和门循环单元(VMD-GRU)的间歇故障严重程度评估方法。先通过变分模式分解(VMD)对间歇故障信号进行自适应分解得到所有固有模式函数(IMF)分量,再对IMF分量进行相似度分析选择敏感分量,并利用微分增强型能量算子构建严重程度敏感因子。最后,利用严重程度敏感因子训练门循环单元(GRU)循环神经网络评估模型。通过对电子系统的关键电路注入不同严重程度的间歇故障进行评估,结果表明该方法有较强的间歇故障严重程度评估能力,评估结果更加准确有效。
-
关键词:
- 间歇故障 /
- 严重程度敏感因子 /
- 变分模式分解和门循环单元 /
- 故障注入 /
- 电子系统
Abstract: Considering the problem that the intermittent fault signal of the electronic system is greatly affected by noise and has a lot of redundant information, which results in the limitation of the deep neural network model to evaluate the severity of the intermittent fault. A method for evaluating the severity of intermittent faults based on Variational Mode Decomposition-Gated Recurrent Units (VMD-GRU) is proposed. Firstly, all Intrinsic Mode Function (IMF) components are adaptively decomposed on intermittent fault signals through Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD). Then the sensitivity analysis of the IMF components is performed to select the sensitive components, and the differential enhanced energy operator is used to construct the severity sensitivity factor. Finally, the severity sensitivity factor is used to train the Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) recurrent neural network severity evaluation model. Through the evaluation of intermittent faults of different severity injected into the key circuits of electronic systems, the results show that this method has a strong ability to evaluate the severity of intermittent faults, and is more accurate and effective in evaluating the severity of intermittent faults. -
表 1 模型基本参数设置
模型参数 数值 信号输入长度 20 GRU隐藏层数 200 全连接层神经元数 5 初始学习率 0.001 学习率下降系数 0.5 学习率下降周期 20 批量大小 20 最大周期数 200 表 2 Sallen-Key电路不同严重程度的间歇故障分类结果
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L1 49 – – – – L2 1 49 – – – L3 – 1 49 – – L4 – – – 50 – L5 – – 1 – 50 表 3 Sallen-Key电路不同严重程度间歇故障识别准确率(%)
评估方法 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 本文方法 98 98 98 100 100 表 4 文献[16]间歇故障状态分类结果
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L1 49 15 – – – L2 1 35 – – – L3 – – 50 37 – L4 – – – 13 – L5 – – – – 50 表 5 文献[17]间歇故障状态分类结果
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L1 31 – – – – L2 19 50 – – – L3 – – 50 – – L4 – – – 50 – L5 – – – – 50 表 6 文献[26]间歇故障状态分类结果
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L1 40 24 – – – L2 9 20 1 – – L3 1 6 49 20 – L4 – – – 26 – L5 – – – 4 50 表 7 文献[27]间歇故障状态分类结果
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L1 50 6 – – – L2 – 44 – – – L3 – – 50 6 – L4 – – – 44 – L5 – – – – 50 -
[1] IEEE. IEEE 100: The authoritative dictionary of IEEE standards terms, seventh edition[S]. USA: IEEE Press, 2000. [2] ZHOU Donghua, ZHAO Yinghong, WANG Zidong, et al. Review on diagnosis techniques for intermittent faults in dynamic systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(3): 2337–2347. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2907500 [3] RASHID L, PATTABIRAMAN K, and GOPALAKRISHNAN S. Characterizing the impact of intermittent hardware faults on programs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2015, 64(1): 297–310. doi: 10.1109/TR.2014.2363152 [4] SAVIR J. Testing for single intermittent failures in combinational circuits by maximizing the probability of fault detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 1980, C-29(5): 410–416. doi: 10.1109/TC.1980.1675595 [5] ZHANG Liangwei, LIN Jing, LIU Bin, et al. A review on deep learning applications in prognostics and health management[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 162415–162438. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2950985 [6] 刘惠, 刘振宇, 郏维强, 等. 深度学习在装备剩余使用寿命预测技术中的研究现状与挑战[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2021, 27(1): 34–52.LIU Hui, LIU Zhenyu, JIA Weiqiang, et al. Current research and challenges of deep learning for equipment remaining useful life prediction[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 27(1): 34–52. [7] GAO Zhiwei, CECATI C, and DING S X. A survey of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant techniques-part I: Fault diagnosis with model-based and signal-based approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3757–3767. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2417501 [8] GAO Zhiwei, CECATI C, and DING S X. A survey of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant techniques-Part II: Fault diagnosis with knowledge-based and hybrid/active approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3768–3774. [9] LIU Zhenbao, JIA Zhen, VONG C M, et al. Capturing high-discriminative fault features for electronics-rich analog system via deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(3): 1213–1226. doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2690940 [10] SHRESTHA A and MAHMOOD A. Review of deep learning algorithms and architectures[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 53040–53065. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2912200 [11] ZHENG Shuai, RISTOVSKI K, FARAHAT A, et al. Long short-term memory network for remaining useful life estimation[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, Dallas, USA, 2017: 88–95. [12] SHI Junyou, HE Qingjie, and WANG Zili. A transfer learning LSTM network-based severity evaluation for intermittent faults of an electrical connector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 11(1): 71–82. [13] DE BRUIN T, VERBERT K, and BABUŠKA R. Railway track circuit fault diagnosis using recurrent neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(3): 523–533. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2551940 [14] SHI Junyou, HE Qingjie, and WANG Zili. An LSTM-based severity evaluation method for intermittent open faults of an electrical connector under a shock test[J]. Measurement, 2021, 173: 108653. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108653 [15] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [16] ZHANG Yahui, ZHOU Taotao, HUANG Xufeng, et al. Fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on recurrent neural networks[J]. Measurement, 2021, 171: 108774. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108774 [17] TAO Ying, WANG Xiaodan, SÁNCHEZ R V, et al. Spur gear fault diagnosis using a multilayer gated recurrent unit approach with vibration signal[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 56880–56889. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914181 [18] QI Haiyu, GANESAN S, and PECHT M. No-fault-found and intermittent failures in electronic products[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2008, 48(5): 663–674. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2008.02.003 [19] KERKHOFF H G and EBRAHIMI H. Investigation of intermittent resistive faults in digital CMOS circuits[J]. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 2016, 25(3): 1640023. doi: 10.1142/S0218126616400235 [20] LIU Cang, WANG Jianye, ZHANG Antang, et al. Research on the fault diagnosis technology of intermittent connection failure belonging to FPGA solder-joints in BGA package[J]. Optik, 2014, 125(2): 737–740. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.07.044 [21] LI Huakang, LYU Kehong, ZHANG Yong, et al. Study of solder joint intermittent fault diagnosis based on dynamic analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 9(9): 1748–1758. doi: 10.1109/TCPMT.2019.2929752 [22] HUANG N E, SHEN Zheng, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903–995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [23] CARSON J R. Notes on the theory of modulation[J]. Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers, 1922, 10(1): 57–64. [24] LI Junning, CHEN Wuge, HAN Ka, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on GA-VMD and improved WOA-LSSVM[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 166753–166767. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3023306 [25] LI Yuxiao, ZHOU Xinglong, and LI Sheng. A intermittent fault injection strategy for electronic equipment health status recognition[C]. 2020 11th International Conference on Prognostics and System Health Management, Jinan, China: IEEE, 2020: 68–73. [26] MIAO Xiaodong, LI Shunming, ZHU Yanqi, et al. A novel real-time fault diagnosis method for planetary gearbox using transferable hidden layer[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(15): 8403–8412. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2965988 [27] LIAO Guoping, GAO Wei, YANG Gengjie, et al. Hydroelectric generating unit fault diagnosis using 1-D convolutional neural network and gated recurrent unit in small hydro[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(20): 9352–9363. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2926095 -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
