A Review of YOLO Object Detection Based on Deep Learning
-
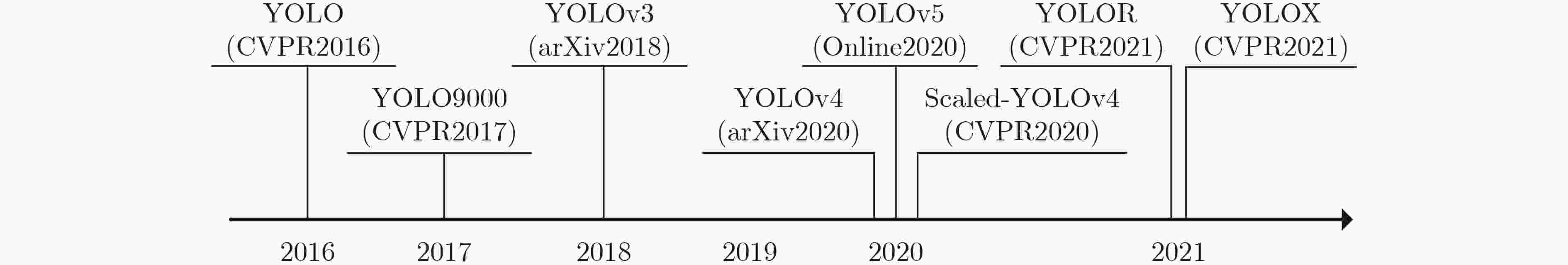
摘要: 目标检测是计算机视觉领域的一个基础任务和研究热点。YOLO将目标检测概括为一个回归问题,实现端到端的训练和检测,由于其良好的速度-精度平衡,近几年一直处于目标检测领域的领先地位,被成功地研究、改进和应用到众多不同领域。该文对YOLO系列算法及其重要改进、应用进行了详细调研。首先,系统地梳理了YOLO家族及重要改进,包含YOLOv1-v4, YOLOv5, Scaled-YOLOv4, YOLOR和最新的YOLOX。然后,对YOLO中重要的基础网络,损失函数进行了详细的分析和总结。其次,依据不同的改进思路或应用场景对YOLO算法进行了系统的分类归纳。例如,注意力机制、3D、航拍场景、边缘计算等。最后,总结了YOLO的特点,并结合最新的文献分析可能的改进思路和研究趋势。Abstract: Object detection is one of the basic tasks and research hotspots in the field of computer vision. The YOLO (You Only Look Once) frames object detection is a regression problem to implement end-to-end training and detection. YOLO becomes the leading object detector due to its good speed-accuracy balance, which has been successfully studied, improved, and applied to many different fields. YOLO series and its important improvements and applications are investigated in detail. Firstly, the YOLO family and important improvements are systematically summarized, including YOLOv1-v4, YOLOv5, Scaled-YOLOv4, YOLOR, and the latest YOLOX. Then, important backbone and loss functions in YOLO are analyzed and summarized in detail. Next, the application of YOLO is systematically classified and summarized according to different improvement ideas or scenarios, such as attention mechanisms, three-dimensional scenes, aerial scenes, edge computing, etc. Finally, the characteristics of the YOLO series are summarized and the possible improvement ideas and research trends are analyzed in combination with the latest literature.
-
Key words:
- Object detection /
- YOLO /
- Deep learning /
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
-
图 5 VisDrone2019数据集示例[37]
表 1 YOLO系列在VOC2012的检测结果
表 2 各类YOLO算法在COCO test2017上的表现
检测框架 主干网络 尺寸 fps AP AP50 AP75 APS APM APL GPU YOLOv3[12], arXiv2018 Darknet-53 416 35 31.0 55.3 32.3 15.2 33.2 42.8 Maxwell GPU YOLOv3-tiny[12], arXiv2018 Darknet Ref 416 330 – 33.1 – – – – GTX 1080Ti GC-YOLOv3[31], MDPI2020 Darknet 53 416 28 – 55.5 – – – – GTX 1080Ti YOLOv4-CSP[13], arXiv2020 CSPDarknet-53 640 70 47.5 66.2 51.7 28.2 51.2 59.8 Volta GPU YOLOv5-S[14] Modified CSP v5 640 156.3 36.7 55.4 – – – – Volta GPU YOLOv5-X[14] Modified CSP v5 640 82.6 50.4 68.8 – – – – Volta GPU PP-YOLOv2[40], arXiv2021 ResNet50-vd-dcn[28] 640 68.9 49.5 68.2 54.4 30.7 52.9 61.2 Volta GPU YOLOR-P6[9], arXiv2021 – 1280 49 52.6 70.6 57.6 34.7 56.6 64.2 Volta GPU YOLOX-X[10], arXiv2021 Modified CSP v5 640 57.8 51.2 69.6 55.7 31.2 56.1 66.1 Volta GPU -
[1] LIU Li, OUYANG Wanli, WANG Xiaogang, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261–318. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 [2] ZOU Zhengxia, SHI Zhenwei, GUO Yuhong, et al. Object detection in 20 years: A survey[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1905.05055, 2019. [3] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. [4] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [5] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [6] JIAO Licheng, ZHANG Fan, LIU Fang, et al. A survey of deep learning-based object detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 128837–128868. doi: 10.1109/access.2019.2939201 [7] WU Xiongwei, SAHOO D, and HOI S C H. Recent advances in deep learning for object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 396: 39–64. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.01.085 [8] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [9] WANG C Y, YEH I H, and LIAO H Y M. You only learn one representation: Unified network for multiple tasks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2105.04206, 2021. [10] GE Zheng, LIU Songtao, WANG Feng, et al. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO series in 2021[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2107.08430, 2021. [11] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517–6525. [12] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [13] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. [14] JOCHER G, STOKEN A, BOROVEC J, et al. Ultralytics/YOLOv5: V3.1 - bug fixes and performance improvements[EB/OL].https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4154370, 2020. [15] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, and LIAO H Y M. Scaled-YOLOv4: Scaling cross stage partial network[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13024–13033. [16] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [17] 罗会兰, 陈鸿坤. 基于深度学习的目标检测研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(6): 1230–1239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.06.026LUO Huilan and CHEN Hongkun. Survey of object detection based on deep learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(6): 1230–1239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.06.026 [18] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. [19] EVERINGHAM M, ESLAMI S M A, VAN GOOL L, et al. The PASCAL visual object classes challenge: A retrospective[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(1): 98–136. doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0733-5 [20] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [21] WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, WU Y H, et al. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1571–1580. [22] MISRA D. Mish: A self regularized non-monotonic activation function[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1908.08681, 2019. [23] LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifang, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759–8768. [24] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [25] GHIASI G, LIN T Y, and LE Q V. NAS-FPN: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7029–7038. [26] ELFWING S, UCHIBE E, and DOYA K. Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcement learning[J]. Neural Networks, 2018, 107: 3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2017.12.012 [27] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN Bo, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1314–1324. [28] MA Ningning, ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHENG Haitao, et al. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]. 2018 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 122–138. [29] 李成跃, 姚剑敏, 林志贤, 等. 基于改进YOLO轻量化网络的目标检测方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(14): 141003. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.141003LI Chengyue, YAO Jianmin, LIN Zhixian, et al. Object detection method based on improved YOLO lightweight network[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(14): 141003. doi: 10.3788/LOP57.141003 [30] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [31] YANG Yang and DENG Hongmin. GC-YOLOv3: You only look once with global context block[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(8): 1235. doi: 10.3390/electronics9081235 [32] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. 2018 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [33] ZHENG Zhaohui, WANG Ping, LIU Wei, et al. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression[C]. The 34th 2020 AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12993–13000. [34] REZATOFIGHI H, TSOI N, GWAK J Y, et al. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 658–666. [35] BODLA N, SINGH B, CHELLAPPA R, et al. Soft-NMS--improving object detection with one line of code[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5562–5570. [36] CHEN Zhiming, CHEN Kean, LIN Weiyao, et al. PIoU loss: Towards accurate oriented object detection in complex environments[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 195–211. [37] DU Dawei, ZHU Pengfei, WEN Longyin, et al. VisDrone-DET2019: The vision meets drone object detection in image challenge results[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 213–226. [38] University of Saskatchewan. Kaggle competition: Global wheat detection[EB/OL]. https://www.kaggle.com/c/global-wheat-detection, 2020. [39] HUANG Zhanchao, WANG Jianlin, FU Xuesong, et al. DC-SPP-YOLO: Dense connection and spatial pyramid pooling based YOLO for object detection[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 522: 241–258. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.02.067 [40] HUANG Xin, WANG Xinxin, LV Wenyu, et al. PP-YOLOv2: A practical object detector[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2104.10419, 2021. [41] DING Jian, XUE Nan, XIA Guisong, et al. Object detection in aerial images: A large-scale benchmark and challenges[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2102.12219, 2021. [42] TEKIN B, SINHA S N, and FUA P. Real-time seamless single shot 6D object pose prediction[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 292–301. [43] SIMON M, AMENDE K, KRAUS A, et al. Complexer-YOLO: Real-time 3D object detection and tracking on semantic point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1190–1199. [44] TAKAHASHI M, JI Y, UMEDA K, et al. Expandable YOLO: 3D object detection from RGB-D images[C]. 2020 21st International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM), Cracow, Poland, 2020: 1–5. [45] DING Caiwen, WANG Shuo, LIU Ning, et al. REQ-YOLO: A resource-aware, efficient quantization framework for object detection on FPGAs[C]. 2019 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Seaside, USA, 2019: 33–42. [46] LEE Y, LEE C, LEE H J, et al. Fast detection of objects using a YOLOv3 network for a vending machine[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), Hsinchu, China, 2019: 132–136. [47] AZIMI S M. ShuffleDet: Real-time vehicle detection network in on-board embedded UAV imagery[C]. 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Munich, Germany, 2019: 88–99. [48] TIJTGAT N, VAN RANST W, VOLCKAERT B, et al. Embedded real-time object detection for a UAV warning system[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2110–2118. [49] ZHANG Pengyi, ZHONG Yunxin, and LI Xiaoqiong. SlimYOLOv3: Narrower, faster and better for real-time UAV applications[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 37–45. [50] HENDRY and CHEN R C. Automatic license plate recognition via sliding-window darknet-YOLO deep learning[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2019, 87: 47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2019.04.007 [51] TU Renwei, ZHU Zhongjie, BAI Yongqiang, et al. Improved YOLO v3 network-based object detection for blind zones of heavy trucks[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2020, 29(5): 053002. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.29.5.053002 [52] YANG Shuo, ZHANG Junxing, BO Chunjuan, et al. Fast vehicle logo detection in complex scenes[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 110: 196–201. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.08.007 [53] YANG Fan, YANG Deming, HE Zhiming, et al. Automobile fine-grained detection algorithm based on multi-improved YOLOv3 in smart streetlights[J]. Algorithms, 2020, 13(5): 114. doi: 10.3390/a13050114 [54] LI Min, ZHANG Zhijie, LEI Liping, et al. Agricultural greenhouses detection in high-resolution satellite images based on convolutional neural networks: Comparison of faster R-CNN, YOLO v3 and SSD[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(17): 4938. doi: 10.3390/s20174938 [55] WU Dihua, LV Shuaichao, JIANG Mei, et al. Using channel pruning-based YOLO v4 deep learning algorithm for the real-time and accurate detection of apple flowers in natural environments[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 178: 105742. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105742 [56] XU Zhifeng, JIA Ruisheng, SUN Hongmei, et al. Light-YOLOv3: Fast method for detecting green mangoes in complex scenes using picking robots[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2020, 50(12): 4670–4687. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-01818-w [57] SHARIF M, AMIN J, SIDDIQA A, et al. Recognition of different types of leukocytes using YOLOv2 and optimized bag-of-features[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 167448–167459. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3021660 [58] ZHUANG Zhemin, LIU Guobao, DING Wanli, et al. Cardiac VFM visualization and analysis based on YOLO deep learning model and modified 2D continuity equation[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2020, 82: 101732. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2020.101732 [59] KYRKOU C. YOLOpeds: Efficient real-time single-shot pedestrian detection for smart camera applications[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2020, 14(7): 417–425. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2019.0897 [60] 赵斌, 王春平, 付强. 显著性背景感知的多尺度红外行人检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(10): 2524–2532. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190761ZHAO Bin, WANG Chunping, and FU Qiang. Multi-scale pedestrian detection in infrared images with salient background-awareness[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(10): 2524–2532. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190761 [61] KRIŠTO M, IVASIC-KOS M, and POBAR M. Thermal object detection in difficult weather conditions using YOLO[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 125459–125476. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3007481 [62] LIU Peng, SONG Changlin, LI Junmin, et al. Detection of transmission line against external force damage based on improved YOLOv3[J]. International Journal of Robotics and Automation, 2020, 35(6): 460–468. [63] XIE Yiqun, CAI Jiannan, BHOJWANI R, et al. A locally-constrained YOLO framework for detecting small and densely-distributed building footprints[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2020, 34(4): 777–801. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2019.1624761 [64] LUO Yanyang, SHAO Yanhua, CHU Hongyu, et al. CNN-based blade tip vortex region detection in flow field[C]. SPIE 11373, Eleventh International Conference on Graphics and Image Processing (ICGIP 2019), Hangzhou, China, 2020: 113730P. -





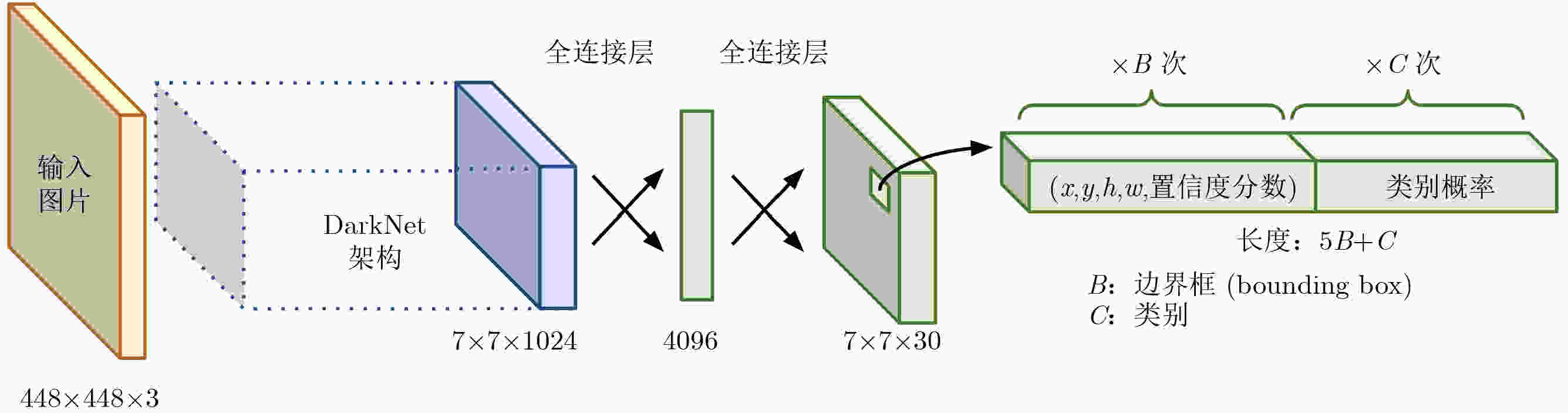
 下载:
下载:
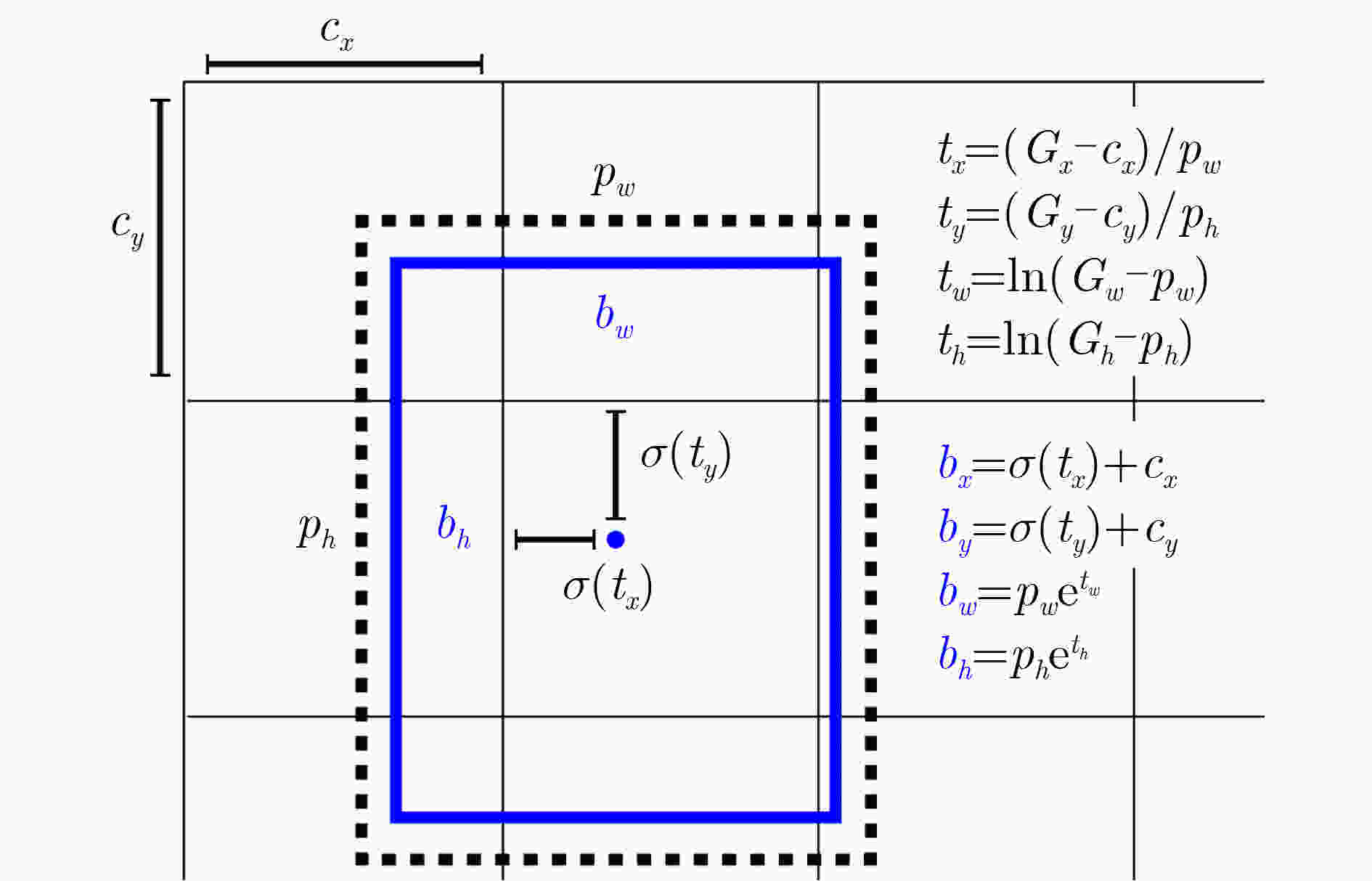
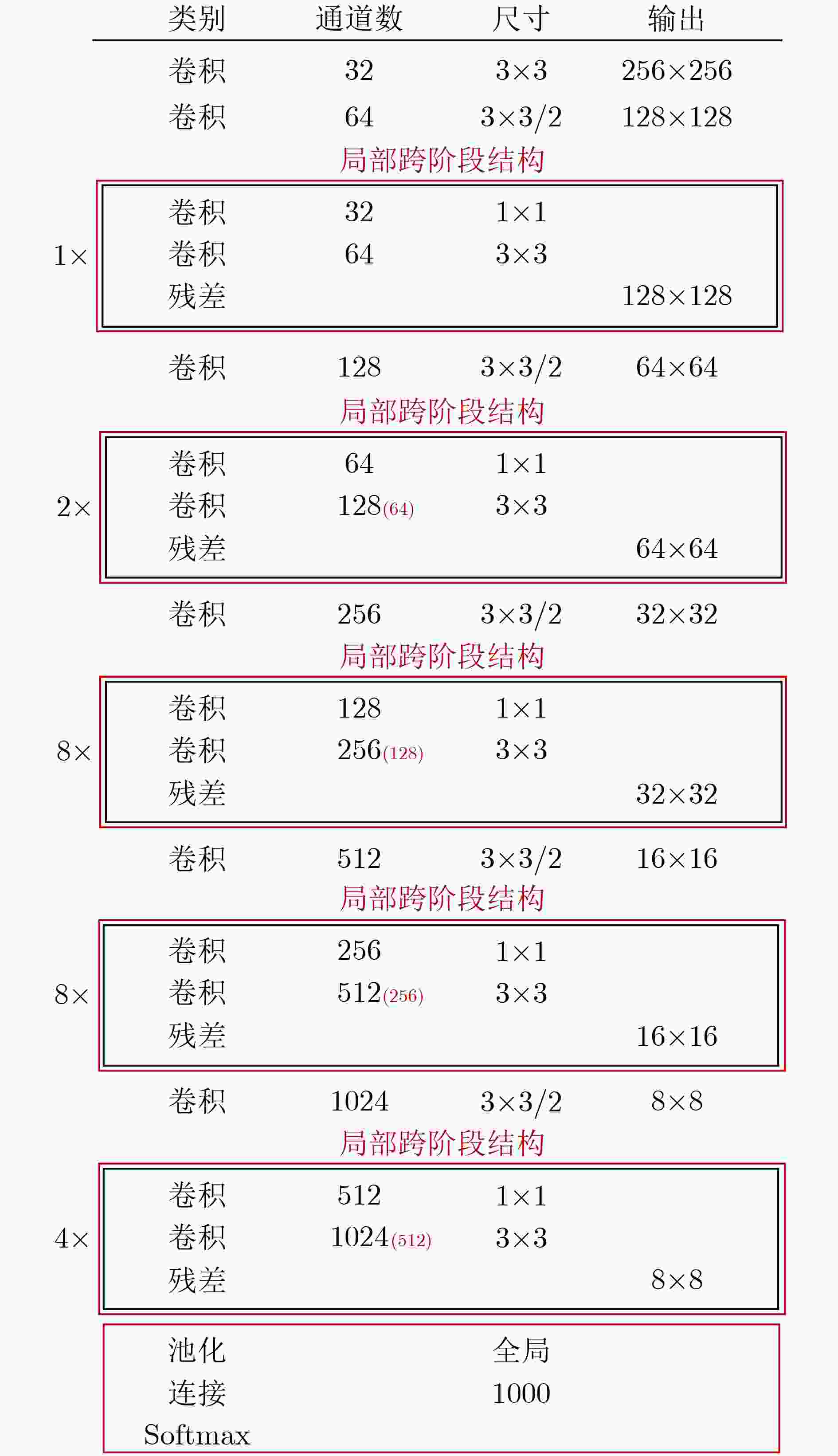




 下载:
下载:
