Energy-efficient Optimization Algorithm in Multi-tag Wireless-powered Backscatter Communication Networks
-
摘要: 为了提高物联网(IoT)节点的运行周期和能量利用率,该文提出一种多标签无线供电反向散射通信网络能效最大化资源分配算法。考虑传输速率约束、能量收集约束以及发射功率约束,建立了基于系统能效最大化的资源分配模型。利用Dinkelbach理论、2次变换以及变量替换法,将原分式非凸问题转化为可求解的凸优化问题。通过拉格朗日对偶理论求得优化问题的全局最优解。仿真结果表明,该算法具有较好的收敛性和能效。Abstract: To improve the operation cycle and energy utilization of Internet of Things (IoT) nodes, an energy-efficient maximization resource allocation algorithm is proposed for a multi-tag wireless-powered backscatter communication network. Specifically, a resource allocation model is developed to maximize the system energy efficiency under the transmission rate constraints, energy harvesting constraints, and transmit power constraints. The original fractional non-convex problem is transformed into a solvable convex optimization problem by using Dinkelbach's theory, a quadratic transformation method, and the variable substitution method. The globally optimal solutions of the considered problem are obtained by using Lagrange dual theory. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has better convergence and energy efficiency.
-
表 1 基于迭代的能效最大化资源分配算法
初始化系统参数$ K,{h_k},{g_k},h,{\sigma ^2},T{\text{,}}{P_{{\text{max}}}},R_k^{{\text{R}},\min },E_k^{\text{C}},E_k^{{\text{C,min}}} $;
给定初始化能效${\eta _{{\text{EE}}}}$,外层迭代次数$t = 0$;定义算法收敛精度$\varpi $,外层最大迭代次数为${T_{\max }}$; (1) while${\text{|} }\dfrac{ {R(t)} }{ { {E^{ {\text{total} } } }(t)} } - {\eta _{ {\text{EE} } } }{\text{(} }t - 1{\text{)|} } > \varpi$或$t \leq {T_{\max }}$, do (2) 初始化迭代步长和拉格朗日乘子,内层最大迭代次数$ {L_{\max }} $,
初始化内层迭代次数$ l{\text{ = }}0 $;(3) while 所有拉格朗日乘子的收敛精度大于$\varpi $,do (4) for $ k{\text{ = 1:}}K $ (5) 根据式(18)计算最优功率$P_k^*$; (6) 根据式(19)计算$\beta _k^*$; (7) 计算反射系数$\alpha _k^*$; (8) 根据式(20)—式(23)更新拉格朗日乘子
$ {\mu _k},{\omega _k},{\varepsilon _k},\nu $;(9) end for (10) 更新$l = l + 1$; (11) until 收敛或$l{\text{ = }}{L_{\max }}$; (12) end while
(13) 更新$ {\eta _{{\text{EE}}}}{\text{(}}t) = \dfrac{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {\tau _k^{}} R(t - 1)}}{{{E^{{\text{total}}}}(t - 1)}} $和$ t = t + 1 $;(14) end while (15) 输出所需优化变量$P_k^*,\beta _k^*,\alpha _k^*$。 -
[1] XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, and LI Dong. Robust energy-efficient optimization for secure wireless-powered backscatter communications with a non-linear EH model[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3209–3213. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3097737 [2] VAN HUYNH N, HOANG D T, LU Xiao, et al. Ambient backscatter communications: A contemporary survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(4): 2889–2922. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2841964 [3] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [4] 徐勇军, 刘子腱, 李国权, 等. 基于NOMA的无线携能D2D通信鲁棒能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175XU Yongjun, LIU Zijian, LI Guoquan, et al. Robust energy efficiency optimization algorithm for NOMA-based D2D communication with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175 [5] LIU Xiaolan, GAO Yue, and HU Fengye. Optimal time scheduling scheme for wireless powered ambient backscatter communications in IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2264–2272. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2889700 [6] RAMEZANI P and JAMALIPOUR A. Optimal resource allocation in backscatter assisted WPCN with practical energy harvesting model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(12): 12406–12410. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2946690 [7] YANG Gang, XU Xinyue, and LIANG Yingchang. Resource allocation in NOMA-enhanced backscatter communication networks for wireless powered IoT[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(1): 117–120. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2944369 [8] XIAO Sa, GUO Huayan, and LIANG Yingchang. Resource allocation for full-duplex-enabled cognitive backscatter networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 3222–3235. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2912203 [9] LYU Bin, HOANG D T, and YANG Zhen. User cooperation in wireless-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 632–635. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2890642 [10] LYU Bin, YOU Changsheng, YANG Zhen, et al. The optimal control policy for RF-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(3): 2804–2808. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2768667 [11] YE Yinghui, SHI Liqin, HU R Q, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation for wirelessly powered backscatter communications[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(8): 1418–1422. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2920834 [12] XU Yongjun, QIN Zhijin, GUI Guan, et al. Energy efficiency maximization in NOMA enabled backscatter communications with QoS guarantee[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(2): 353–357. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3031042 [13] YANG Haohang, YE Yinghui, and CHU Xiaoli. Max-min energy-efficient resource allocation for wireless powered backscatter networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 688–692. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2965942 [14] 王公仆, 熊轲, 刘铭, 等. 反向散射通信技术与物联网[J]. 物联网学报, 2017, 1(1): 67–75. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2017.00009WANG Gongpu, XIONG Ke, LIU Ming, et al. Backscatter communication technology and Internet of things[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2017, 1(1): 67–75. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2017.00009 [15] DINKELBACH W. On nonlinear fractional programming[J]. Management Science, 1967, 13(7): 492–498. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.13.7.492 [16] SHEN Kaiming and YU Wei. Fractional programming for communication systems—Part I: Power control and beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(10): 2616–2630. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2812733 [17] XU Yongjun, LI Guoquan, YANG Yang, et al. Robust resource allocation and power splitting in SWIPT enabled heterogeneous networks: A robust minimax approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10799–10811. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2941897 [18] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [19] ZAPPONE A and JORSWIECK E. Energy Efficiency in Wireless Networks via Fractional Programming Theory[M]. Boston-Delft: Now Foundations and Trends, 2015. [20] XU Yongjun and GUI Guan. Optimal resource allocation for wireless powered multi-carrier backscatter communication networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(8): 1191–1195. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2985010 [21] GAO Zhengnian, XU Yongjun, WANG Qianzhu, et al. Outage-constrained energy efficiency maximization for RIS-assisted WPCNs[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3370–3374. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3101657 -





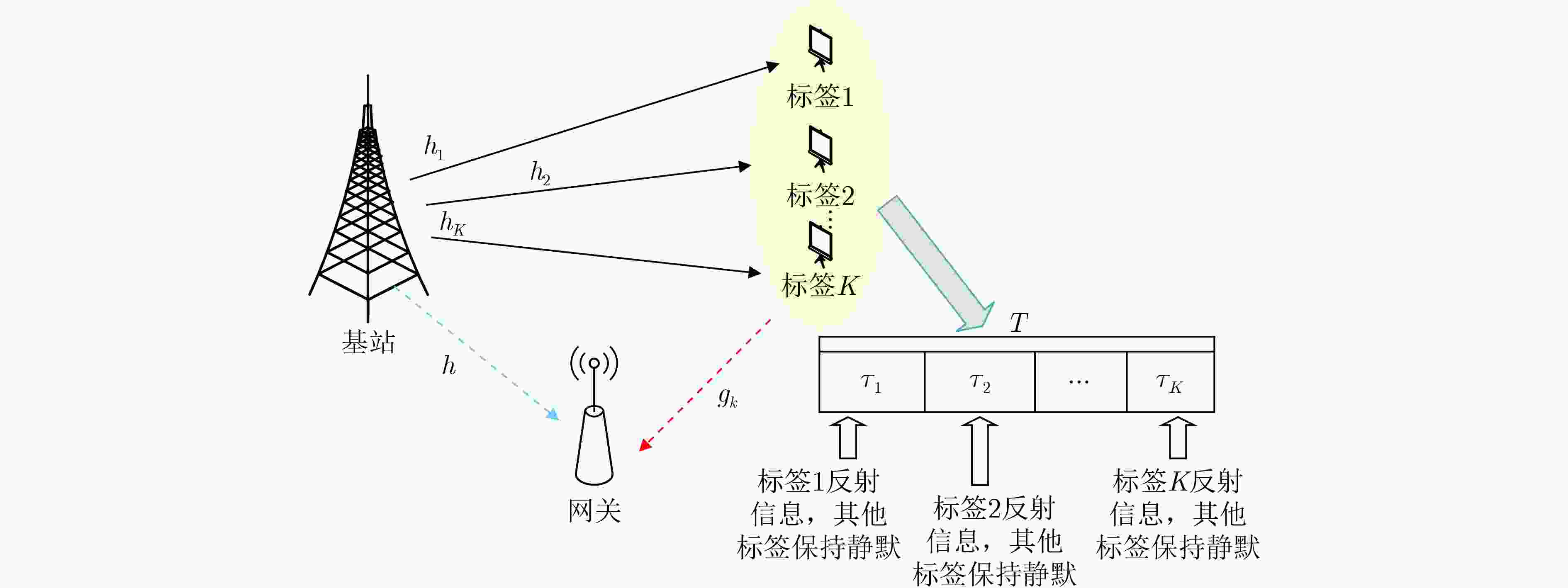
 下载:
下载:
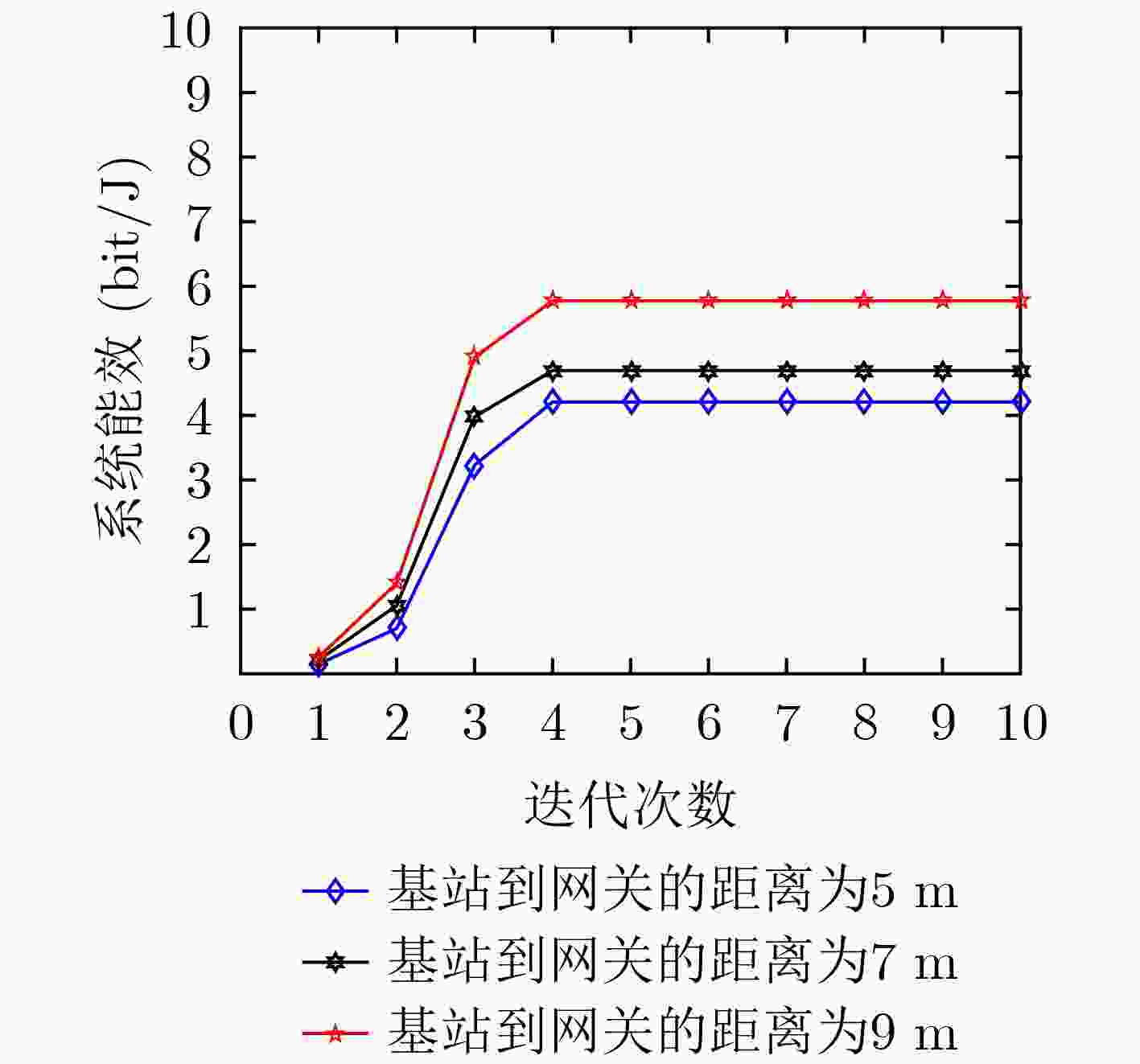
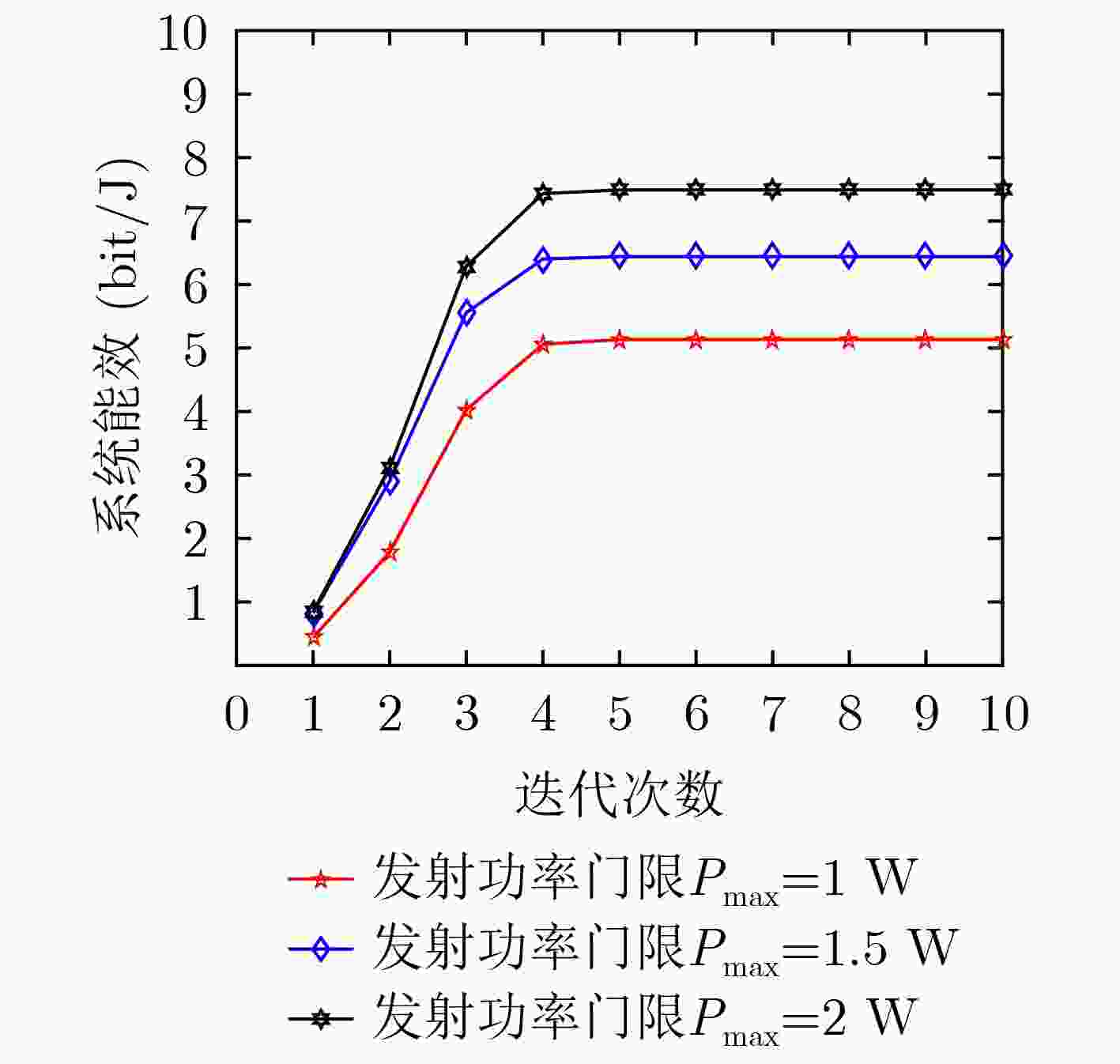
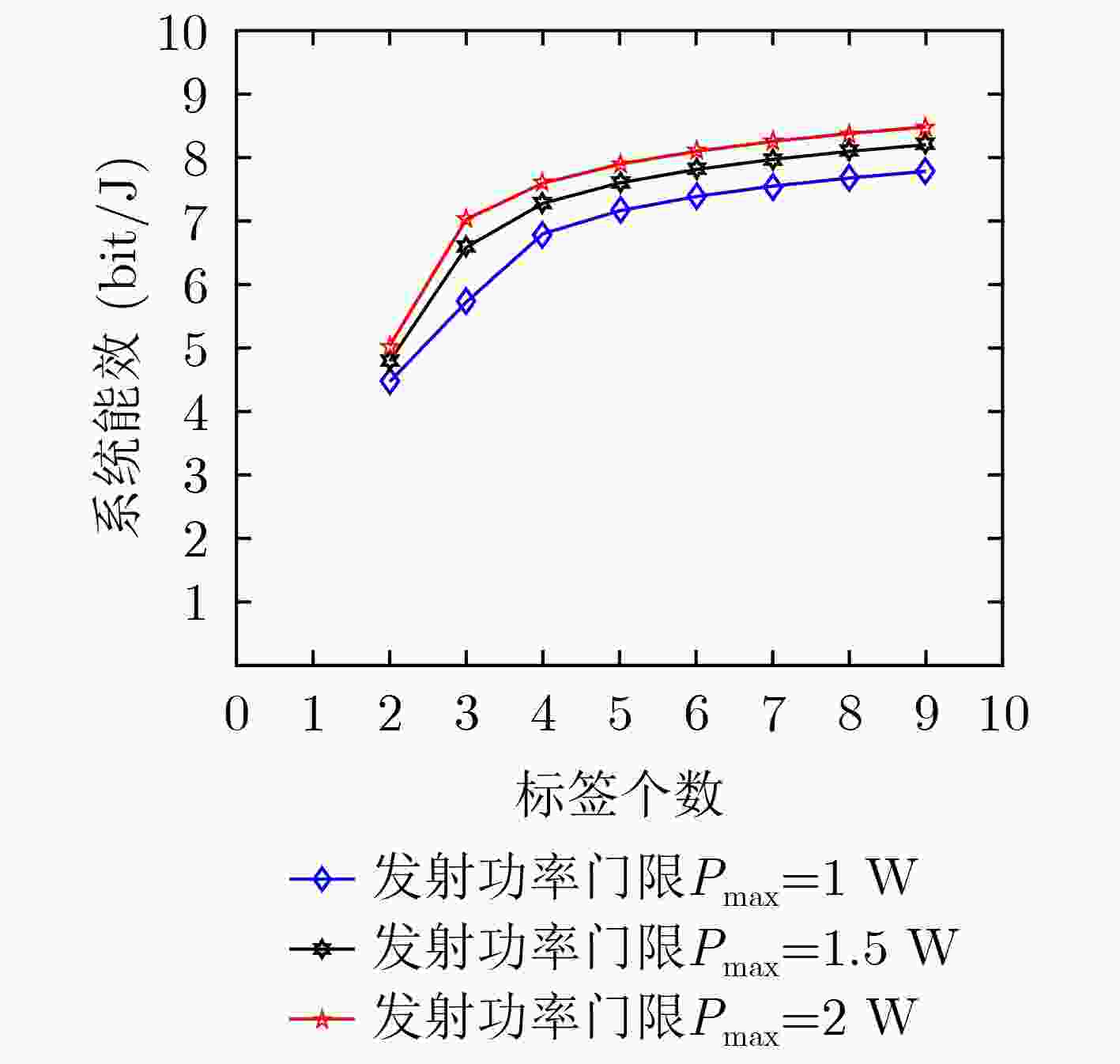
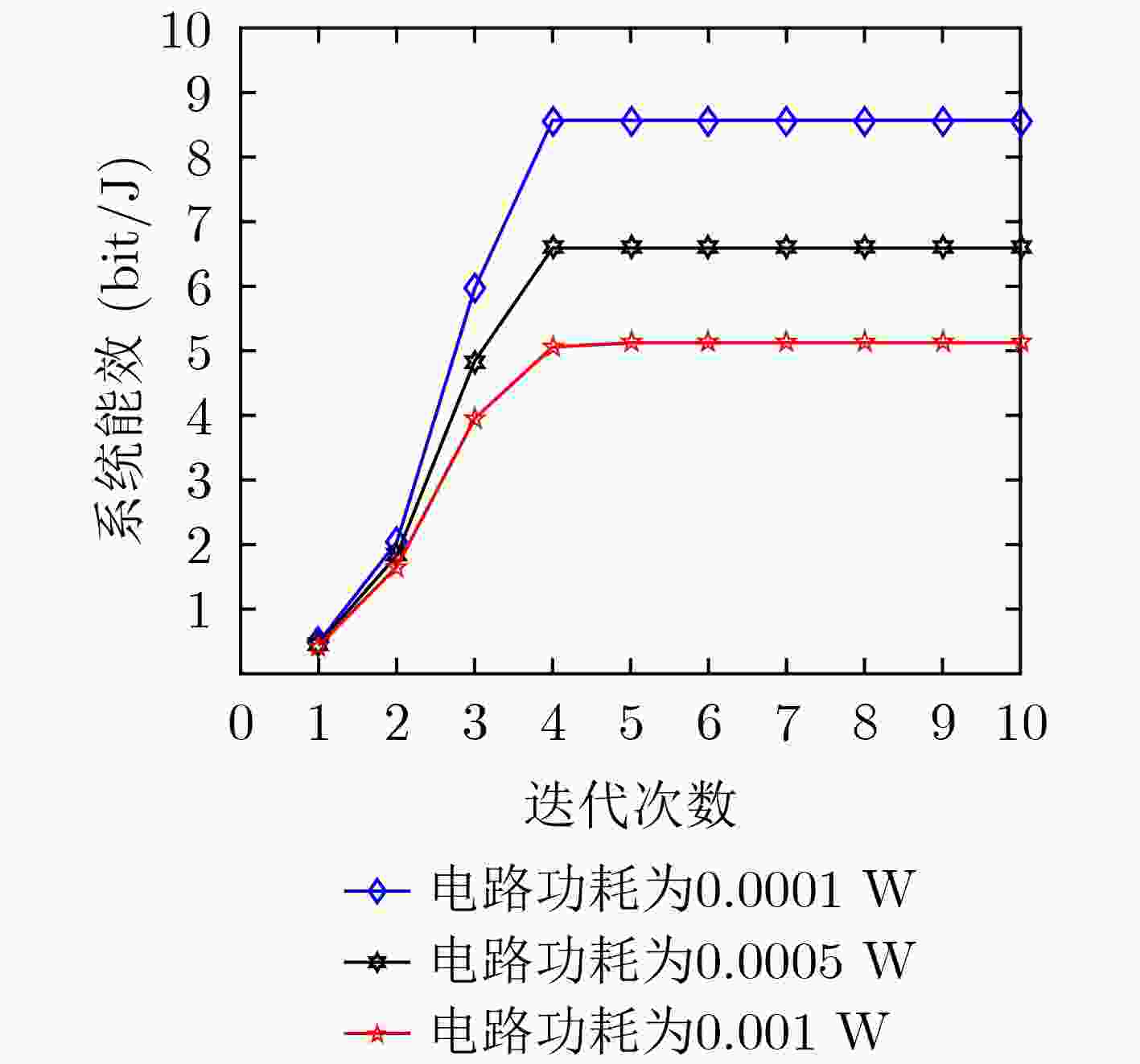
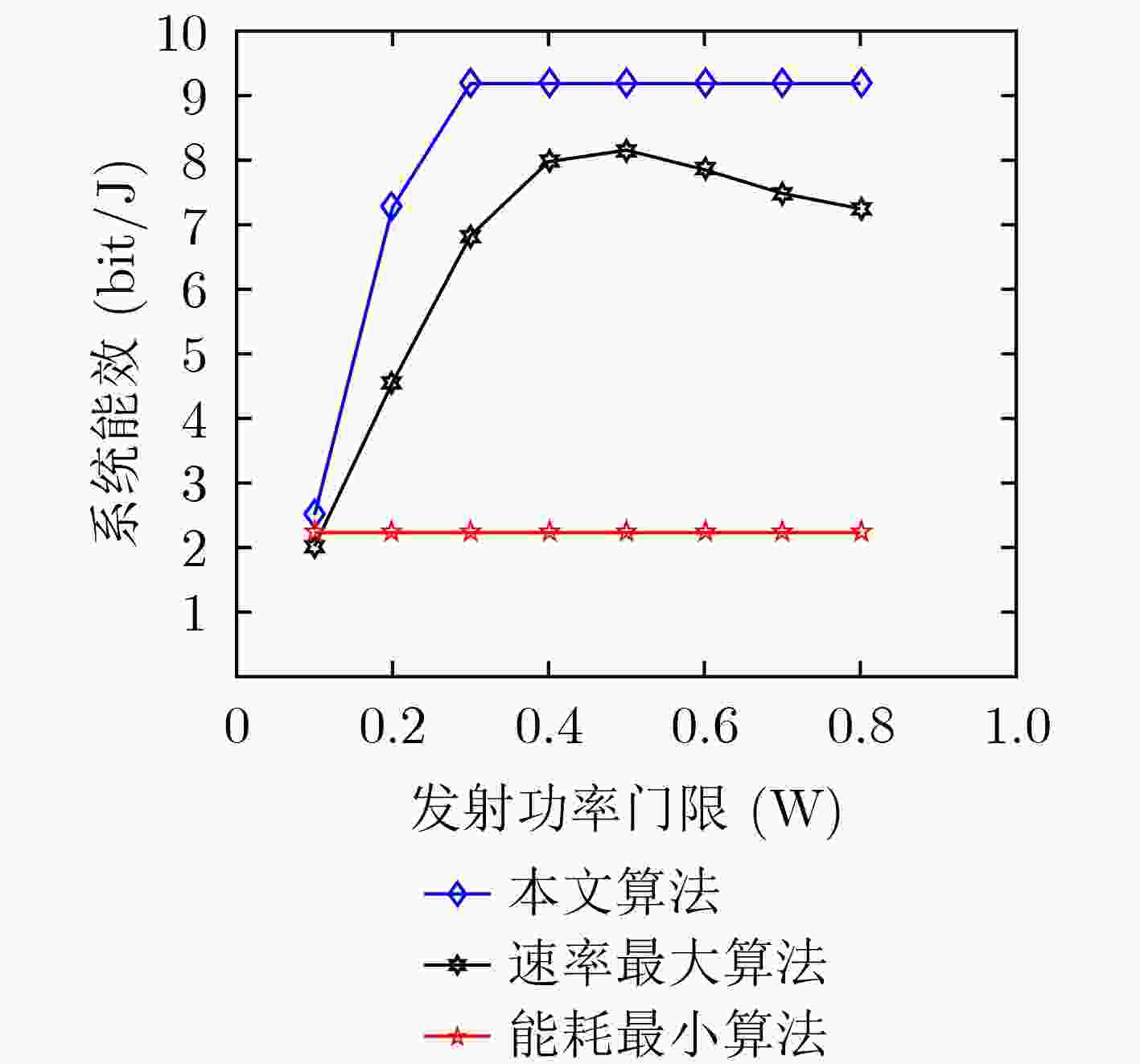
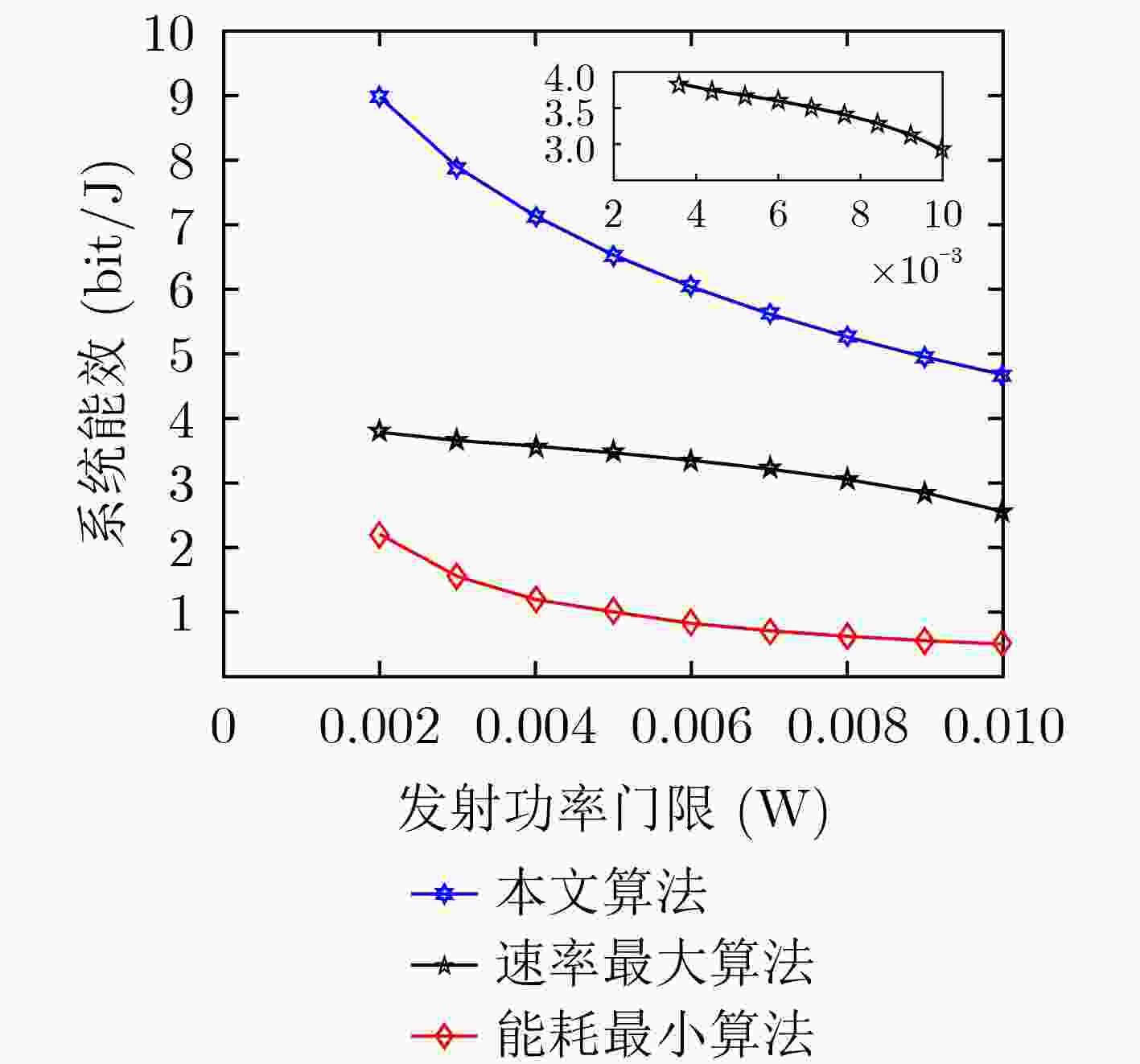


 下载:
下载:
