Sequence Cipher Based Machine Learning-Attack Resistance Method for Strong-PUF
-
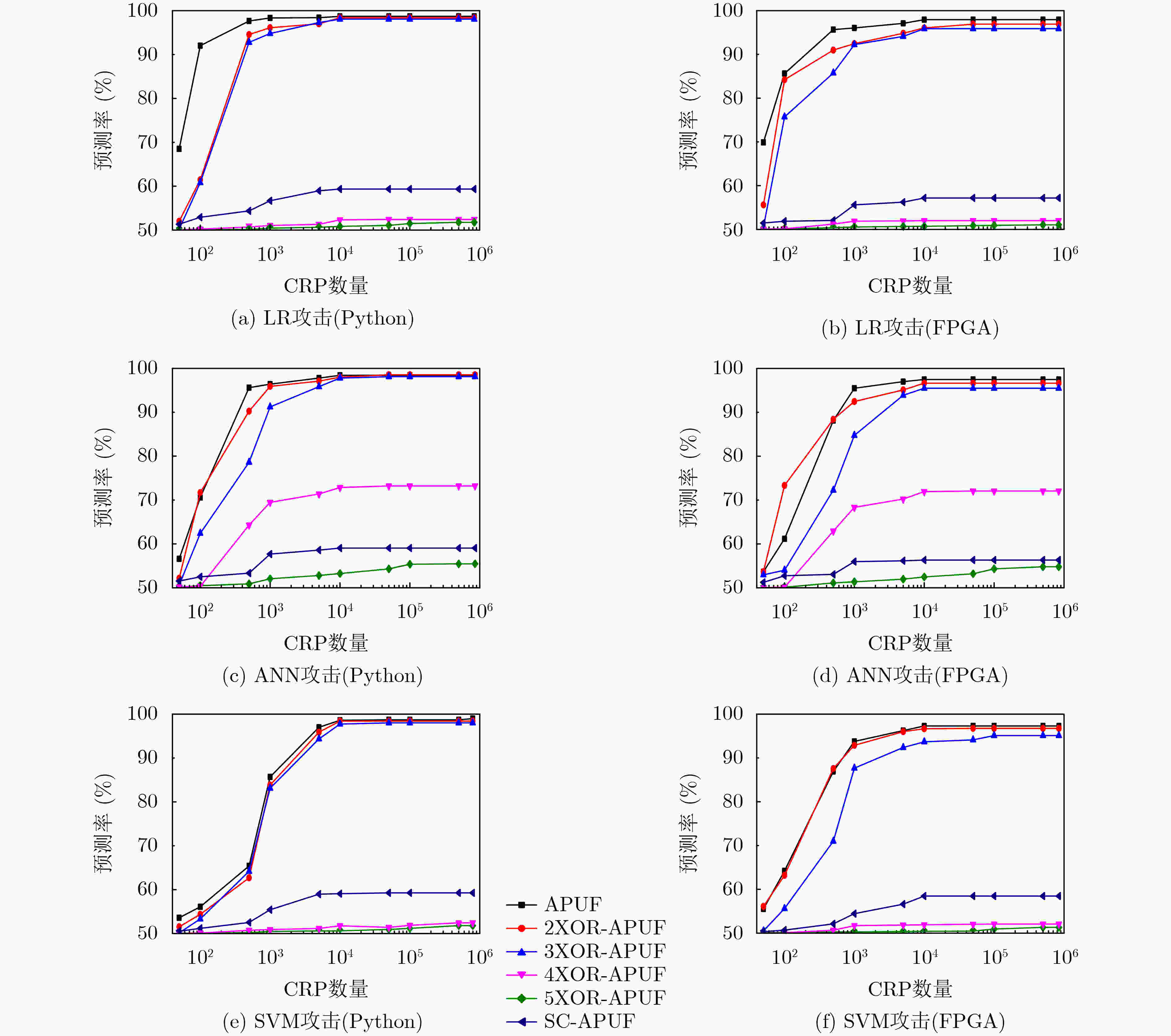
摘要: 物理不可克隆函数(Physical Unclonable Function, PUF)在信息安全领域具有极其重要的应用前景,然而也存在其自身安全受机器学习攻击等方面的不足。该文通过对PUF电路和密码算法的研究,提出一种基于序列密码的强PUF抗机器学习攻击方法。首先,通过构造滚动密钥生成器产生随机密钥,并与输入激励进行混淆;然后,将混淆后的激励通过串并转换电路作用于强PUF,产生输出响应;最后,利用Python软件仿真和FPGA硬件实现,并分析其安全性和统计特性。实验结果表明,当建模所用激励响应对(Challenge Response Pairs, CRPs)高达106组时,基于逻辑回归、人工神经网络和支持向量机的攻击预测率接近50%的理想值。此外,该方法通用性强、硬件开销小,且不影响PUF的随机性、唯一性以及可靠性。Abstract: Physical Unclonable Function (PUF) has extremely important application prospects to the field of information security, however, there are also shortcomings in its own security from machine learning attacks and other aspects. By studying PUF circuits and cryptographic algorithm, a method based on sequence cipher of strong-PUF is proposed to resist machine learning attacks. Firstly, the random key is generated by constructing a rolling key generator, which is obfuscated with the input challenge; Then the obfuscated challenge is applied to the strong-PUF through a series-parallel conversion circuit to generate the output response; Finally, Python software simulation and FPGA hardware implementation are used to analyze the safety and statistical properties. The experimental results show that the attack prediction rates based on logistic regression, artificial neural network and support vector machine are close to the ideal value of 50% when the CRPs used for modeling are up to 106 groups. In addition, this method has high versatile, low hardware overhead and does not affect the randomness, uniqueness and reliability of PUF.
-
表 1 预测率与统计特性的实验结果比较(%)
PUF结构 实现方法 硬件开销 随机性 唯一性 可靠性 LR ANN SVM APUF 仿真 – 50.21 49.76 98.86 98.69 98.43 98.71 FPGA 19-Slice 50.73 49.56 98.82 97.94 97.47 97.28 2XOR-APUF 仿真 – 49.67 50.61 98.92 98.38 98.54 98.41 FPGA 39-Slice 50.13 49.35 98.74 96.91 96.63 96.74 3XOR-APUF 仿真 – 49.63 49.12 98.37 98.06 98.10 98.01 FPGA 58-Slice 49.72 49.68 97.22 95.89 95.48 95.11 4XOR-APUF 仿真 – 50.22 49.36 95.18 52.41 73.21 52.43 FPGA 77-Slice 49.94 50.33 93.38 52.01 72.05 52.07 5XOR-APUF 仿真 – 49.28 49.52 93.61 51.76 55.46 51.79 FPGA 96-Slice 50.07 50.59 92.54 51.04 54.78 51.32 SC-APUF 仿真 – 50.19 50.69 98.73 59.34 59.06 59.27 FPGA 28-Slice 50.44 50.38 98.68 57.18 56.33 58.47 -
[1] 汪鹏君, 李乐薇, 郑雁公, 等. 基于气敏传感器的高稳态物理不可克隆函数发生器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1596–1602. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201104WANG Pengjun, LI Lewei, ZHENG Yangong, et al. High steady-state physical unclonable function generator based on gas sensors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1596–1602. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201104 [2] ZHANG Jiliang and QU Gang. Physical unclonable function-based key sharing via machine learning for IoT security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(8): 7025–7033. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2938462 [3] AMAN M N, TANEJA S, SIKDAR B, et al. Token-based security for the internet of things with dynamic energy-quality tradeoff[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2843–2859. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875472 [4] CHATTERJEE B, DAS D, MAITY S, et al. RF-PUF: Enhancing IoT security through authentication of wireless nodes using in-situ machine learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(1): 388–398. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2849324 [5] PAPPU R, RECHT B, TAYLOR J, et al. Physical one-way functions[J]. Science, 2002, 297(5589): 2026–2030. doi: 10.1126/science.1074376 [6] LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, MA Xuejiao, et al. A 215-F2 bistable physically unclonable function with an ACF of < 0.005 and a native bit instability of 2.05% in 65-nm CMOS process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2020, 28(11): 2290–2299. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3014892 [7] CUI Yijun, WANG Chenghua, LIU Weiqiang, et al. Lightweight configurable ring oscillator PUF based on RRAM/CMOS hybrid circuits[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Nanotechnology, 2020, 1: 128–134. doi: 10.1109/OJNANO.2020.3040787 [8] LIU Weiqiang, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Zhengran, et al. XOR-based low-cost reconfigurable PUFs for IoT security[J]. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2019, 18(3): 25. doi: 10.1145/3274666 [9] 徐金甫, 吴缙, 李军伟, 等. 基于敏感度混淆机制的控制型物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1601–1609. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180775XU Jinfu, WU Jin, LI Junwei, et al. Controlled physical unclonable function research based on sensitivity confusion mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1601–1609. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180775 [10] ZHANG Jiliang and SHEN Chaoqun. Set-based obfuscation for strong PUFs against machine learning attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, 68(1): 288–300. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3028508 [11] AVVARU S V S, ZENG Ziqing, and PARHI K K. Homogeneous and heterogeneous feed-forward XOR physical unclonable functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 2485–2498. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.2968113 [12] GAO Yansong, MA Hua, AL-SARAWI S F, et al. PUF-FSM: A controlled strong PUF[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(5): 1104–1108. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2740297 [13] 刘伟强, 崔益军, 王成华. 一种低成本物理不可克隆函数结构的设计实现及其RFID应用[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(7): 1772–1776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.07.036LIU Weiqiang, CUI Yijun, and WANG Chenghua. Design and implementation of a low-cost physical unclonable function and its application in RFID[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(7): 1772–1776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.07.036 [14] SANTIKELLUR P and CHAKRABORTY R S. A computationally efficient tensor regression network-based modeling attack on XOR arbiter PUF and its variants[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2021, 40(6): 1197–1206. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.3032624 [15] VIJAYAKUMAR A and KUNDU S. A novel modeling attack resistant PUF design based on non-linear voltage transfer characteristics[C]. Proceedings of 2015 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Grenoble, France, 2015: 653–658. doi: 10.7873/DATE.2015.0522. [16] AVVARU S V S and PARHI K K. Effect of loop positions on reliability and attack resistance of feed-forward PUFs[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Miami, USA, 2019: 366–371. doi: 10.1109/ISVLSI.2019.00073. [17] XU Yunhao, LAO Yingjie, LIU Weiqiang, et al. Mathematical modeling analysis of strong physical unclonable functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2020, 39(12): 4426–4438. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.2969645 [18] 李俊志, 关杰. 非线性反馈移存器型序列密码的完全性通用算法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(9): 2075–2080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.09.005LI Junzhi and GUAN Jie. Universal algorithm of full diffusion of stream cipher based on nonlinear feedback shift register[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(9): 2075–2080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.09.005 -





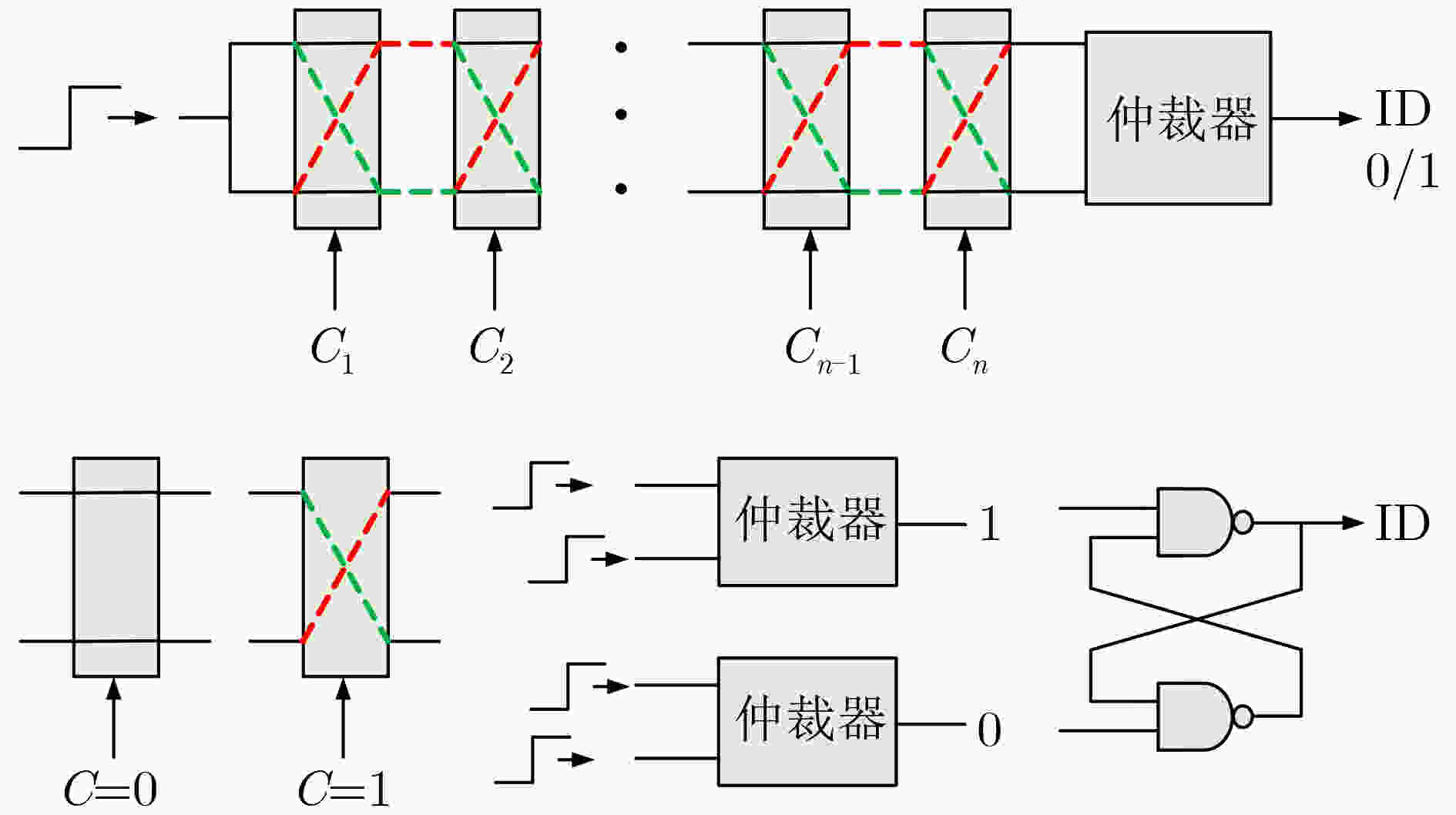
 下载:
下载:

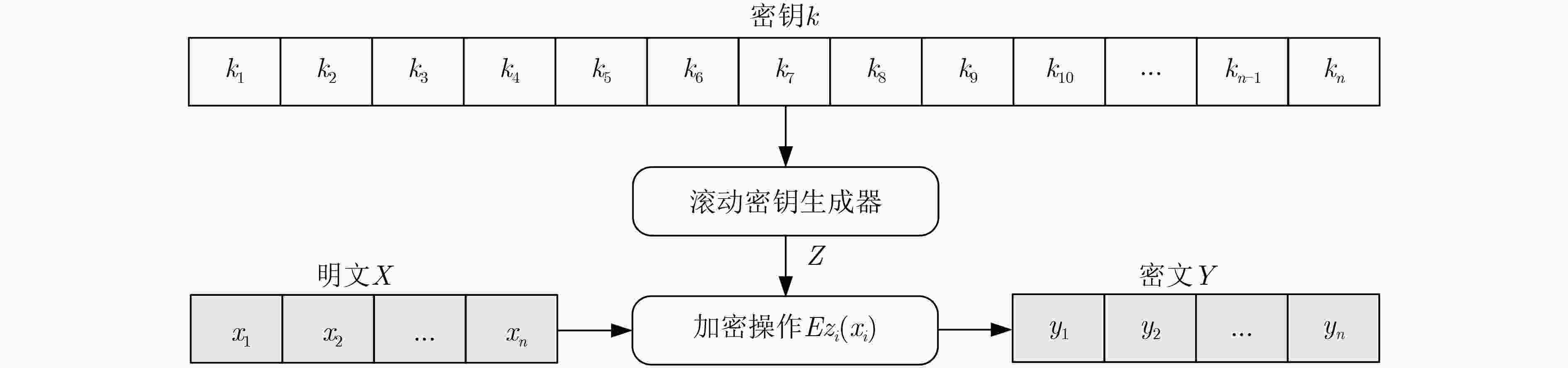
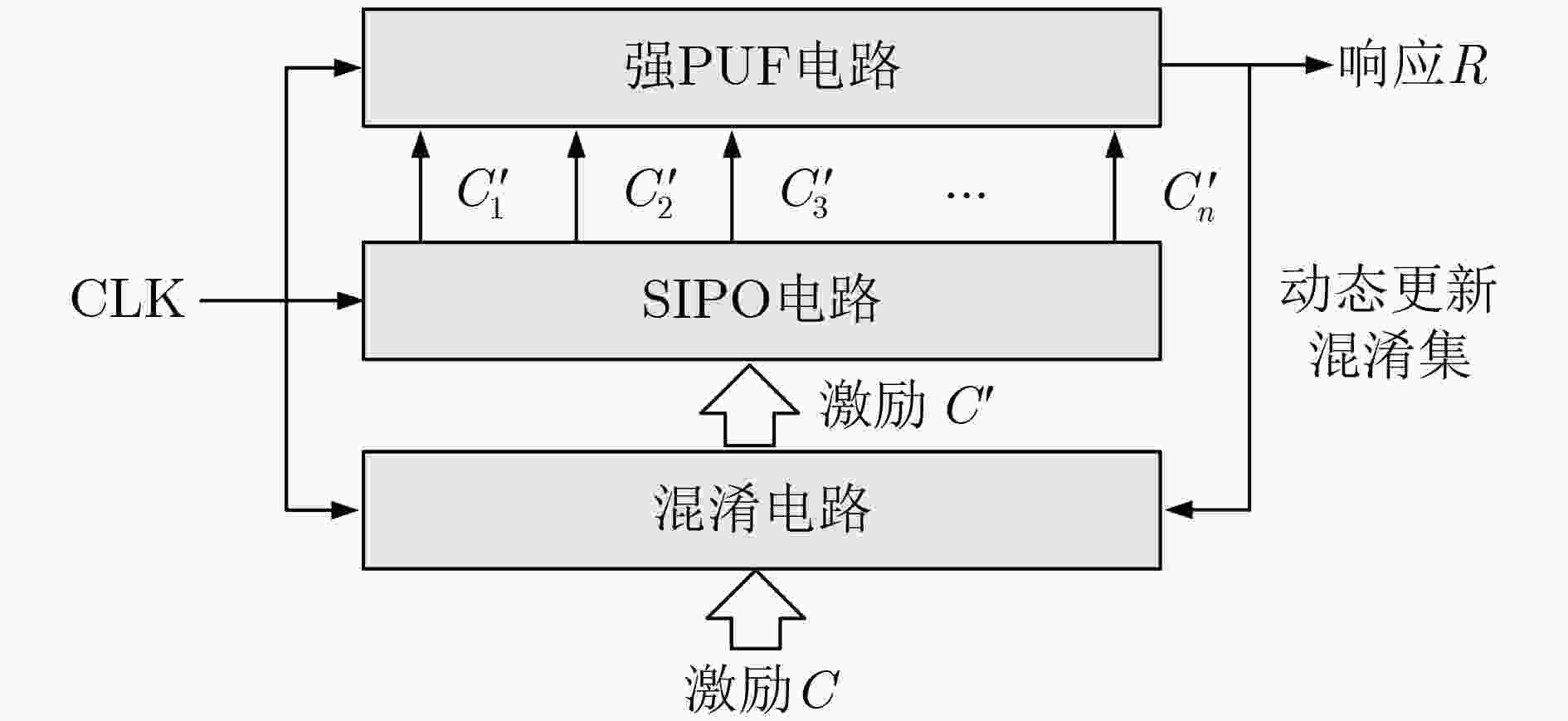

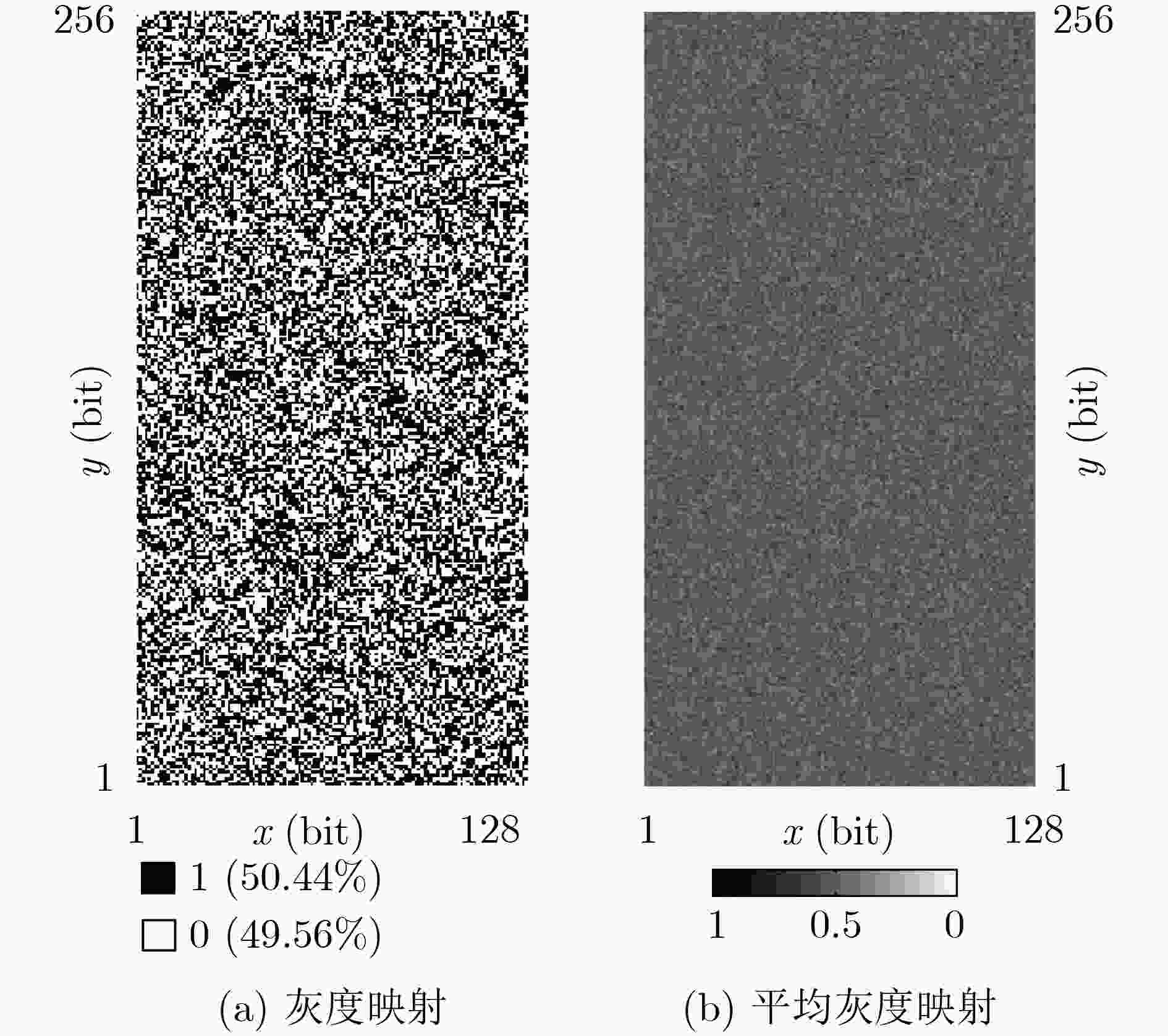
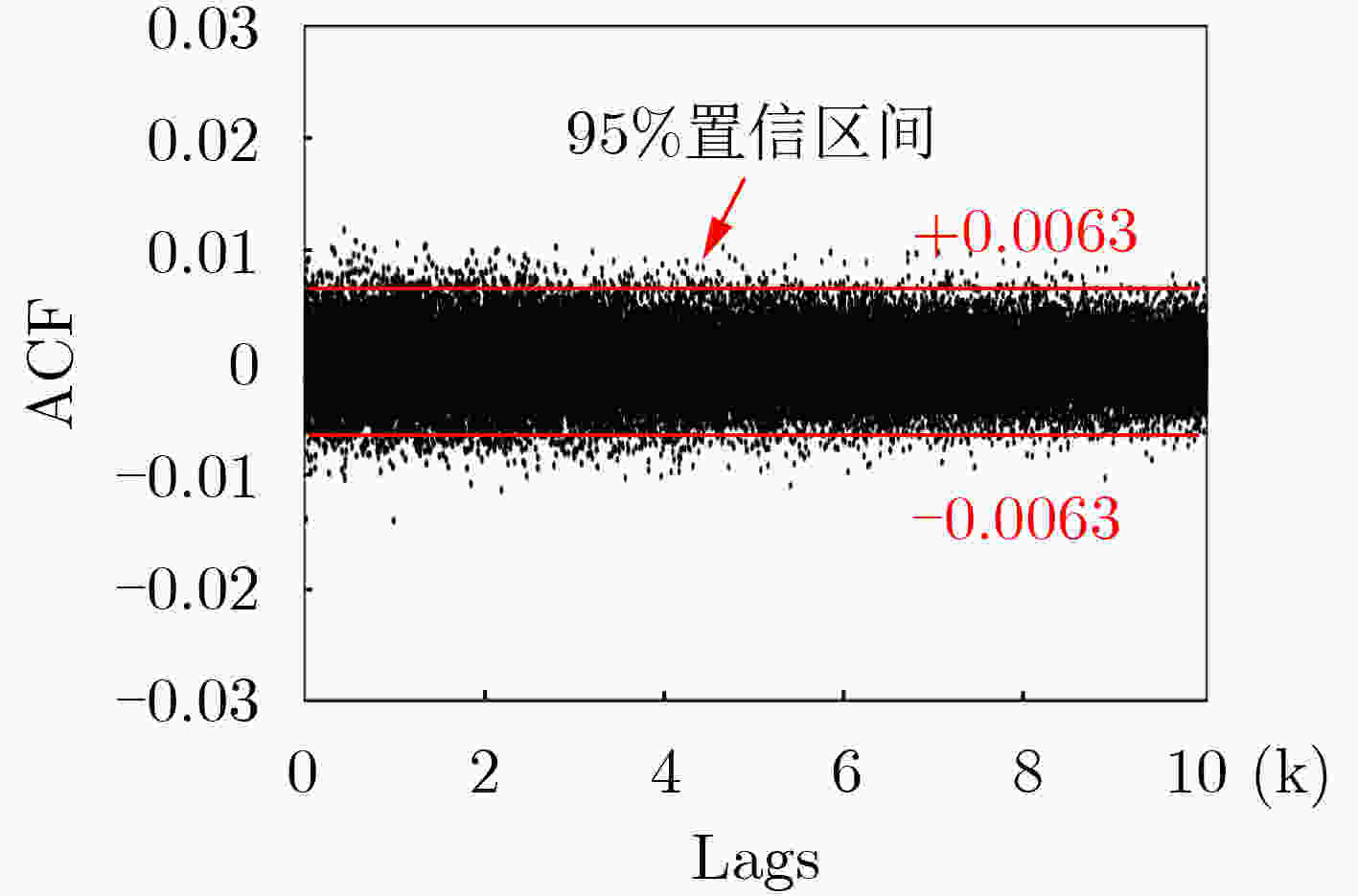
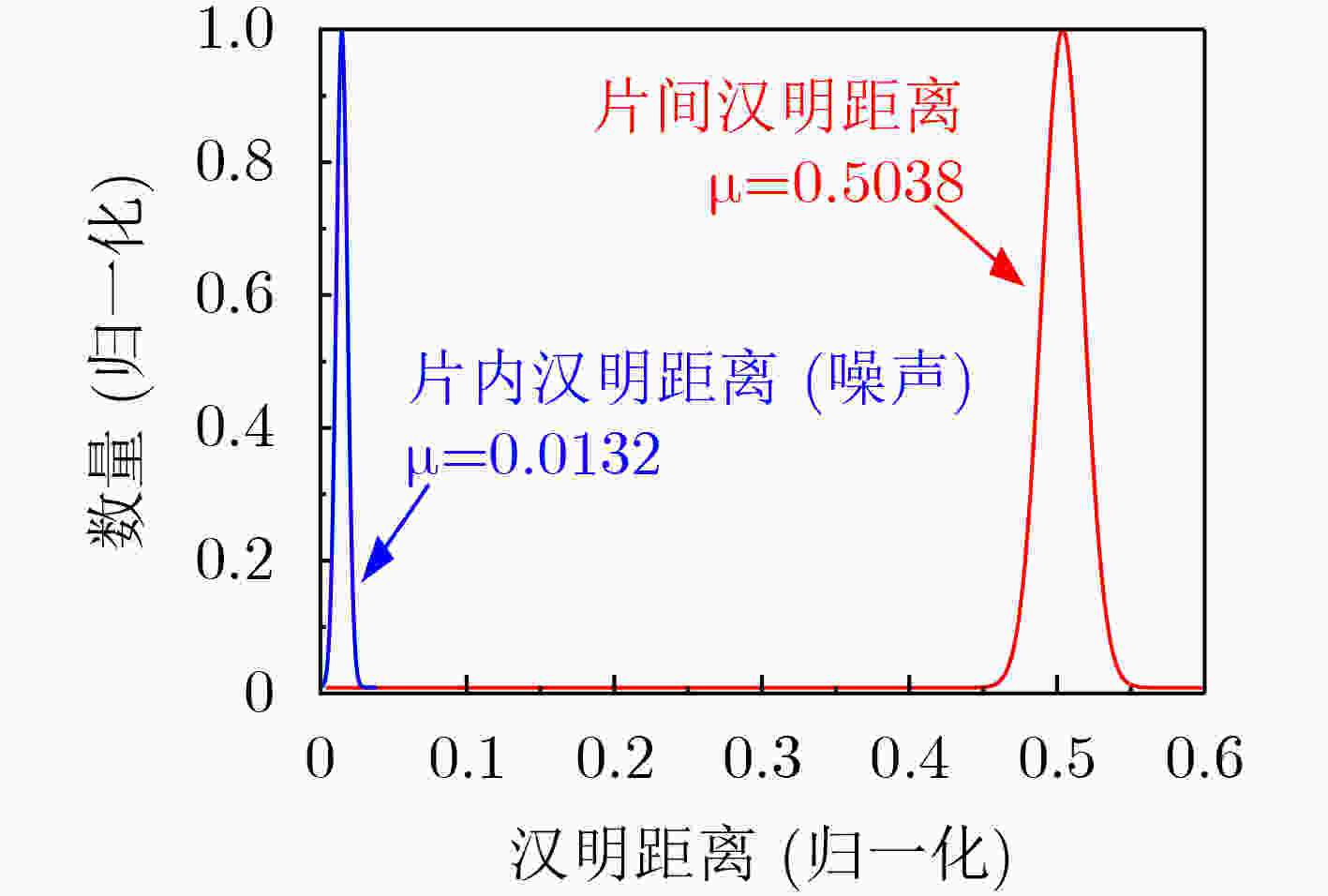


 下载:
下载:
