Radar Signal Recognition Method Based on Knowledge Distillation and Attention Map
-
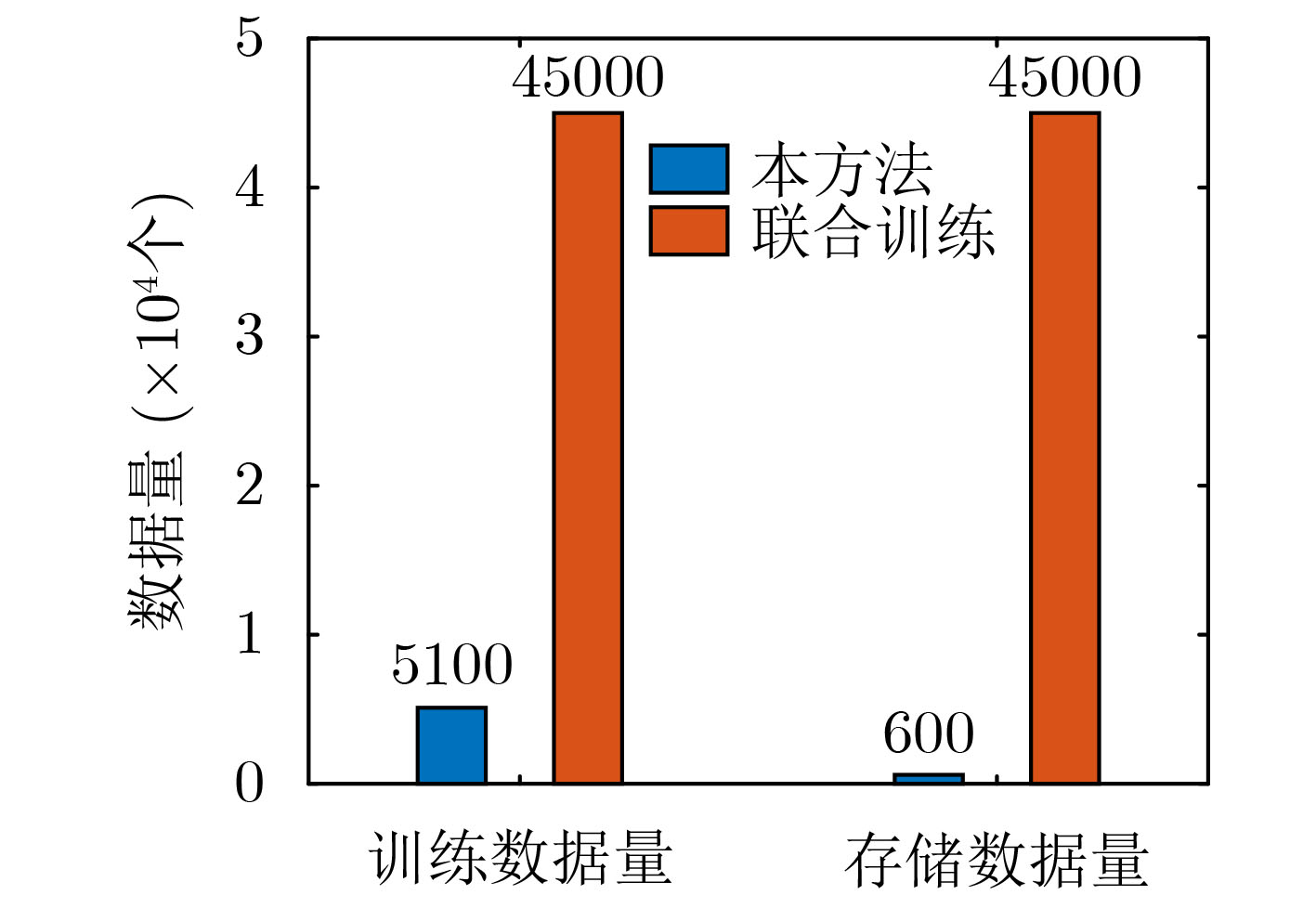
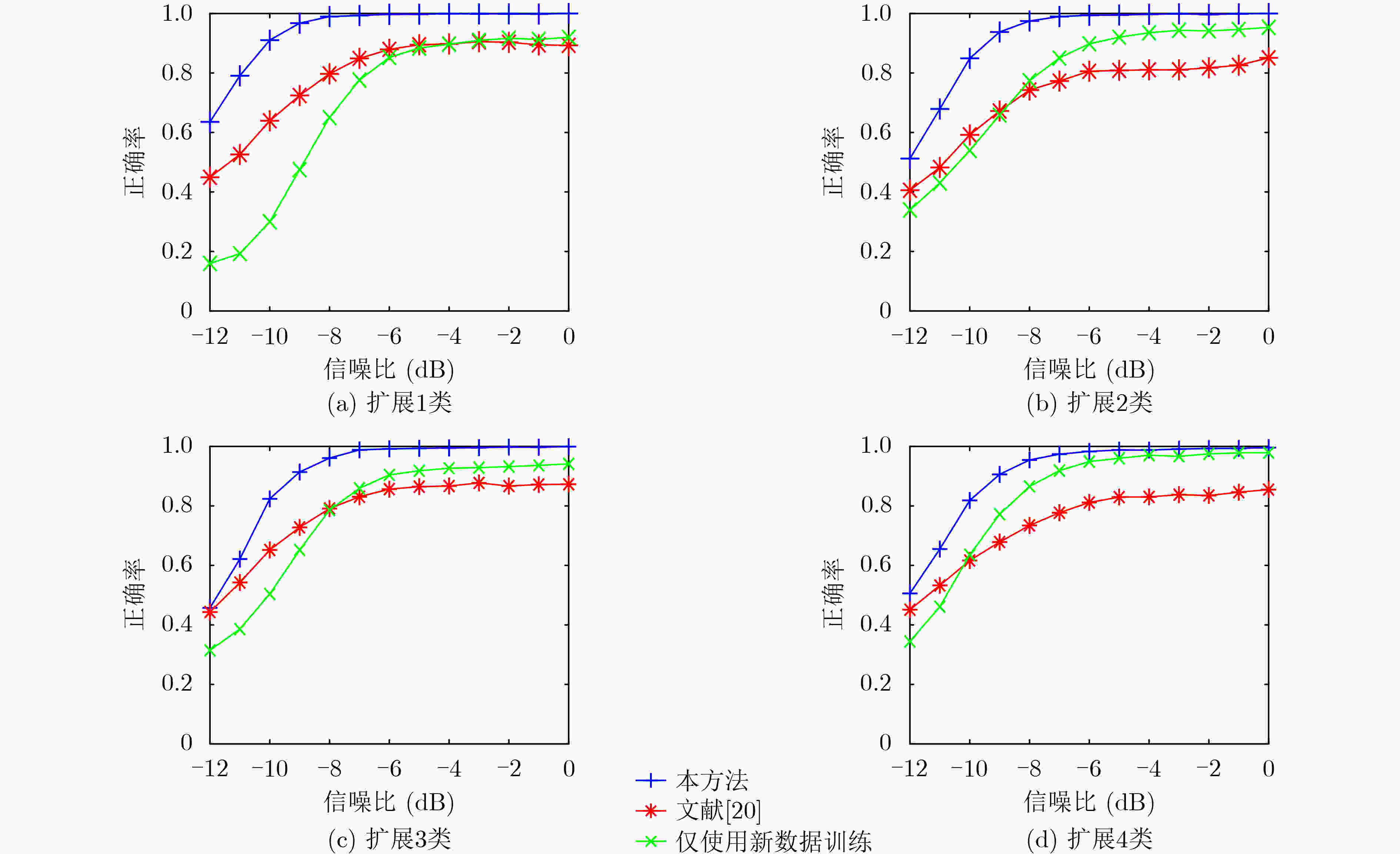
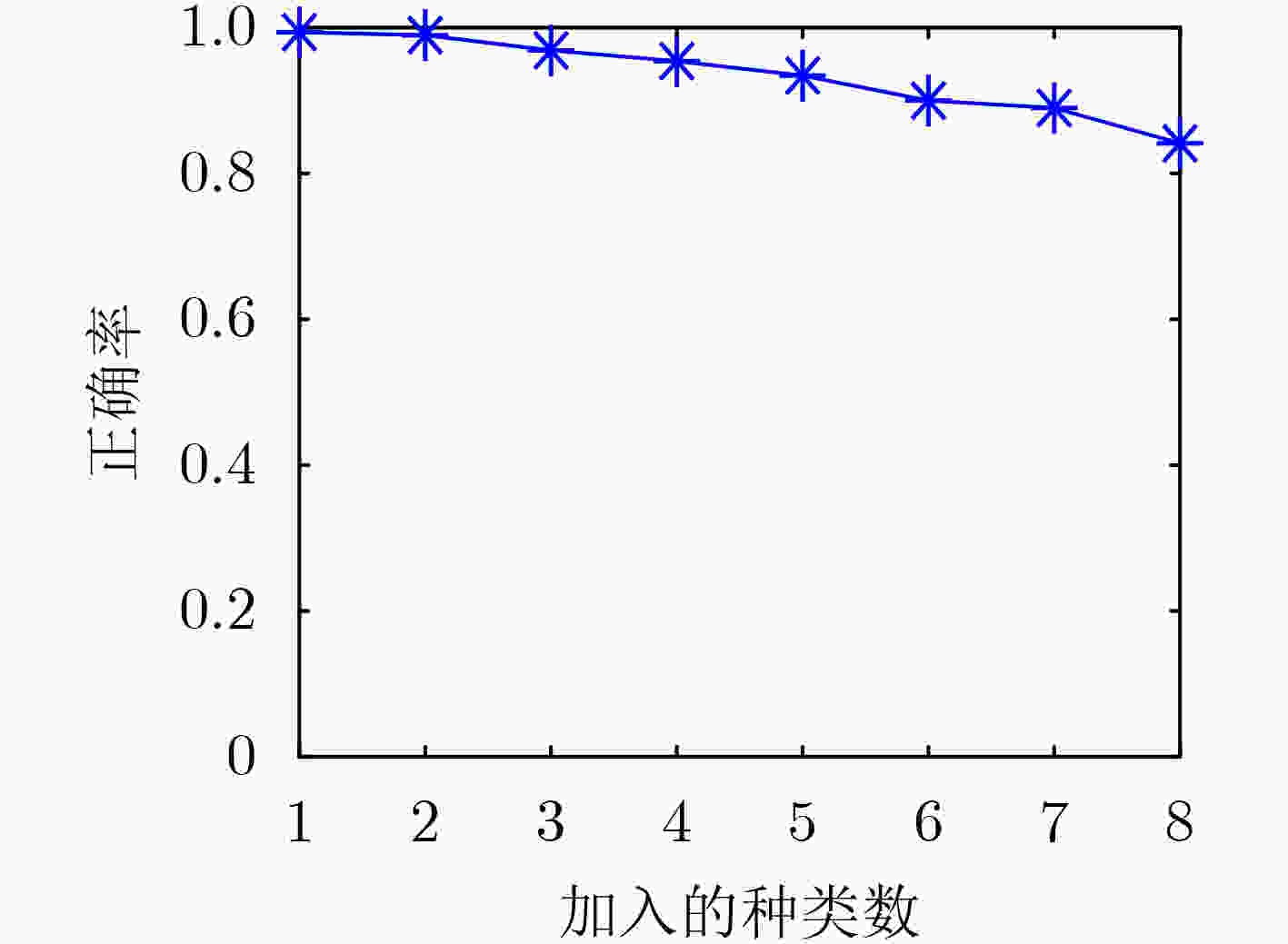
摘要: 针对传统雷达信号识别方法无法有效进行识别类型扩展问题,该文提出一种基于知识蒸馏与注意力图的雷达信号识别方法。首先将雷达信号的平滑伪Wigner-Ville分布(SPWVD)作为输入;然后设计了基于残差网络的增量学习网络结构,利用基于知识蒸馏与注意力图的损失函数,缓解类别增量过程中的灾难性遗忘;最后采用基于样本特征均值距离的方法对数据集进行管理,有效降低存储资源占用空间。实验表明,该方法能在存储资源有限的情况下,对扩展分类的信号快速完成训练,且对原有分类和扩展分类信号均有良好的识别准确率。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that traditional radar signal recognition methods can not effectively expand the recognition types, a radar signal recognition method based on knowledge distillation and attention map is proposed. Firstly, the Smooth Pseudo Wigner-Ville Distribution (SPWVD) of the radar signal is used as input; Then, the incremental learning network structure based on residual network is designed, and the loss function based on knowledge distillation and attention map is used to alleviate the catastrophic forgetting in the process of category increment; Finally, a method based on the mean distance of sample features is used to manage the data set, which reduces effectively the occupied storage resources. Experiments show that this method can quickly complete the training of the extended classification signal under the condition of limited storage resources, and has good recognition accuracy for the original classification and the extended classification signal.
-
表 1 已识别信号参数设置
信号类型 参数 变化范围 LFM 初始频率$ {f_c} $
带宽$\Delta f$0.01~0.45
0.02~0.40Frank 载频${f_0}$
相位数0.10~0.45
[4, 5, 6, 7, 8]BPSK Barker码
载频${f_0}$
码长${T_b}$[5, 7, 11, 13]
0.10~0.45
(1/32~1/16)NDLFM 初始频率${f_c}$
带宽$\Delta f$0.01~0.41
0.05~0.45EQFM 最小频率${f_{{\rm{min}}} }$
最大频率${f_{{\rm{max}}} }$
带宽$\Delta f$0.01~0.45
0.01~0.45
0.05~0.40SFM 最小频率${f_{{\rm{min}}} }$
最大频率${f_{{\rm{max}}} }$
带宽$\Delta f$0.01~0.18
0.20~0.45
0.02~0.44表 2 扩展类型信号参数设置
信号类型 参数 变化范围 2FSK 载频${f_1}$,$ {f_2} $
码宽${T_b}$0.10~0.45
(1/32~1/8)N4FSK 载频${f_1}$~$ {f_4} $
码宽${T_b}$0.10~0.45
(1/32~1/8)NLFM-SFM 初始频率${f_c}$
最小频率${f_{{\rm{min}}} }$
最大频率${f_{{\rm{max}}} }$0.01~0.45
0.08~0.18
0.20~0.30MLFM 载频${f_0}$
带宽$ \Delta f $0.01~0.25
0.10~0.45P1, P2 载频${f_0}$
步进频率$M$0.10~0.45
[4,5,6,7,8], P2取偶数P3, P4 载频${f_0}$
压缩比0.10~0.45
16~64 -
[1] 王星, 周一鹏, 周东青, 等. 基于深度置信网络和双谱对角切片的低截获概率雷达信号识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2972–2976. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160031WANG Xing, ZHOU Yipeng, ZHOU Dongqing, et al. Research on low probability of intercept radar signal recognition using deep belief network and bispectra diagonal slice[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2972–2976. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160031 [2] ZHANG Chunhong, HAN Yuetao, ZHANG Ping, et al. Research on modern radar emitter modelling technique under complex electromagnetic environment[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019(20): 7134–7138. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0579 [3] 徐玉芬. 现代雷达信号处理的数字脉冲压缩方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2007, 29(7): 61–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2007.07.018XU Yufen. Methods of digital pulse compression in modern radar signal processing[J]. Modern Radar, 2007, 29(7): 61–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2007.07.018 [4] 曲志昱, 毛校洁, 侯长波. 基于奇异值熵和分形维数的雷达信号识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 303–307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.10QU Zhiyu, MAO Xiaojie, and HOU Changbo. Radar signal recognition based on singular value entropy and fractal dimension[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 303–307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.10 [5] 肖易寒, 王亮, 郭玉霞. 基于去噪卷积神经网络的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2300–2307. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200506XIAO Yihan, WANG Liang, and GUO Yuxia. Radar signal modulation type recognition based on denoising convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2300–2307. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200506 [6] QU Zhiyu, WANG Wenyang, HOU Changbo, et al. Radar signal intra-pulse modulation recognition based on convolutional denoising autoencoder and deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 112339–112347. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935247 [7] 郭立民, 寇韵涵, 陈涛, 等. 基于栈式稀疏自编码器的低信噪比下低截获概率雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 875–881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170588GUO Limin, KOU Yunhan, CHEN Tao, et al. Low probability of intercept radar signal recognition based on stacked sparse auto-encoder[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 875–881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170588 [8] 石礼盟, 杨承志, 吴宏超. 基于深层残差网络和三元组损失的雷达信号识别方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(11): 2506–2512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.11.12SHI Limeng, YANG Chengzhi, and WU Hongchao. Radar signal recognition method based on deep residual network and triplet loss[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(11): 2506–2512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.11.12 [9] PARISI G I, KEMKER R, PART J L, et al. Continual lifelong learning with neural networks: A review[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 113: 54–71. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.01.012 [10] DHAR P, SINGH R V, PENG K C, et al. Learning without memorizing[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5133–5141. [11] HINTON G, VINYALS O, and DEAN J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 14(7): 38–39. [12] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. [13] ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921–2929. [14] LI Zhizhong and HOIEM D. Learning without forgetting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(12): 2935–2947. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2773081 [15] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [16] CASTRO F M, MARÍN-JIMÉNEZ M J, GUIL N, et al. End-to-end incremental learning[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 241–257. [17] REBUFFI S A, KOLESNIKOV A, SPERL G, et al. iCaRL: Incremental classifier and representation learning[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5533–5542. [18] 郭立民, 陈鑫, 陈涛. 基于AlexNet模型的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(3): 1000–1008. doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20171056GUO Limin, CHEN Xin, and CHEN Tao. Radar signal modulation type recognition based on AlexNet model[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition, 2019, 49(3): 1000–1008. doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20171056 [19] 秦鑫, 黄洁, 查雄, 等. 基于扩张残差网络的雷达辐射源信号识别[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(3): 456–462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.03.006QIN Xin, HUANG Jie, ZHA Xiong, et al. Radar emitter signal recognition based on dilated residual network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(3): 456–462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.03.006 [20] KÄDING C, RODNER E, FREYTAG A, et al. Fine-tuning deep neural networks in continuous learning scenarios[C]. The 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, China, 2016: 588–605. -





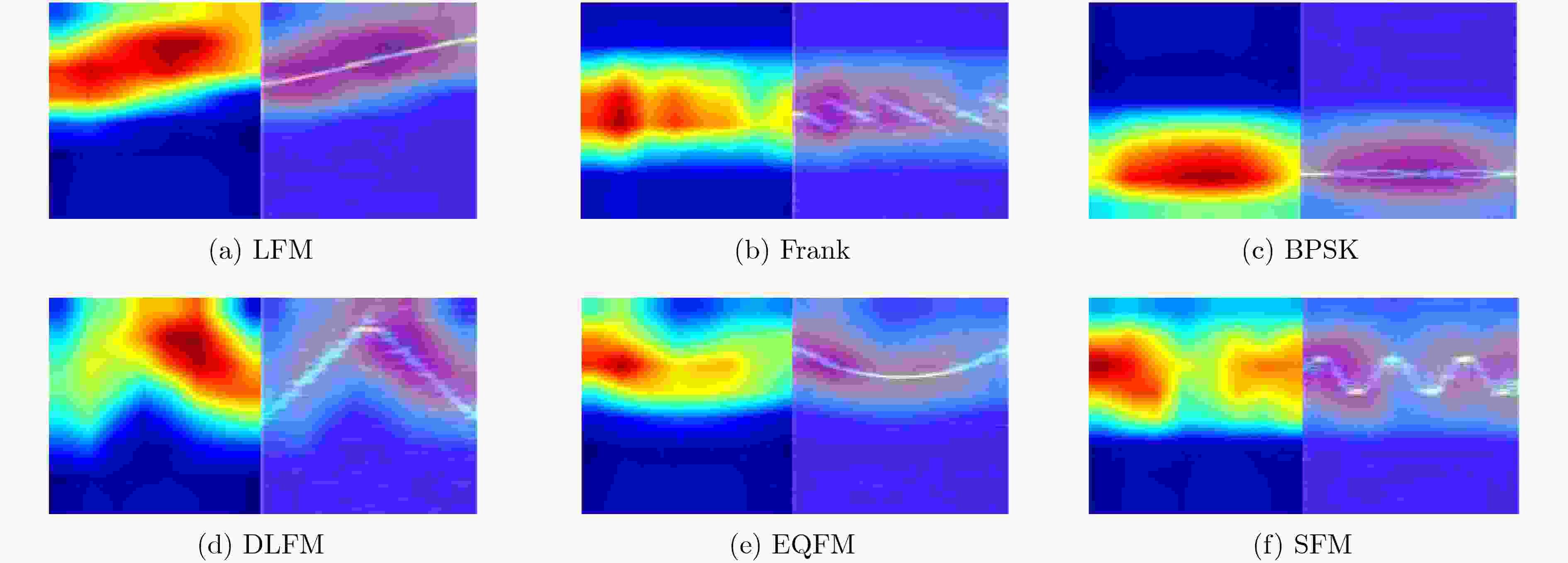
 下载:
下载:
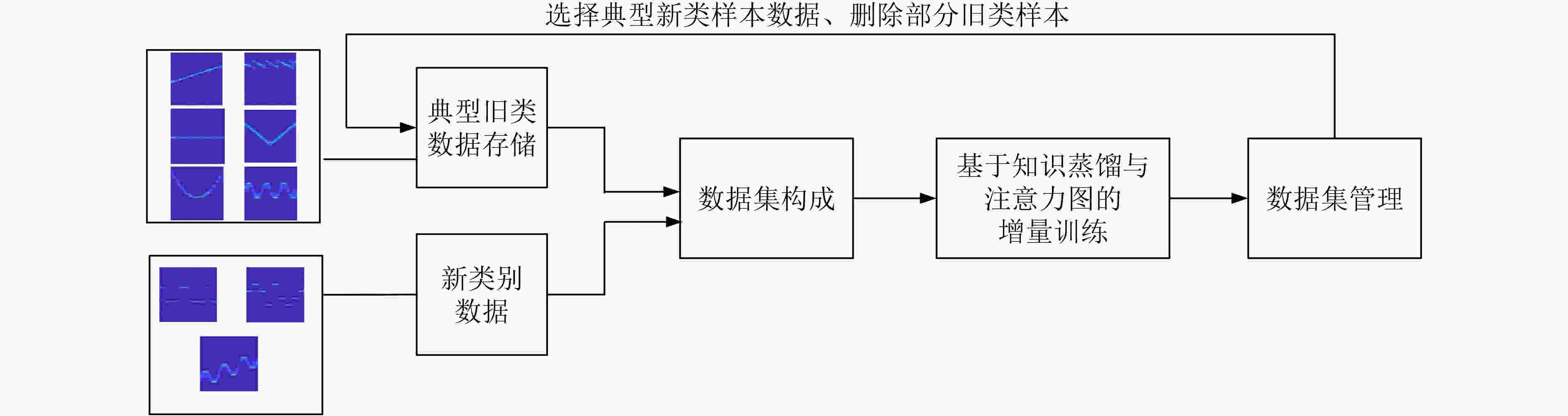
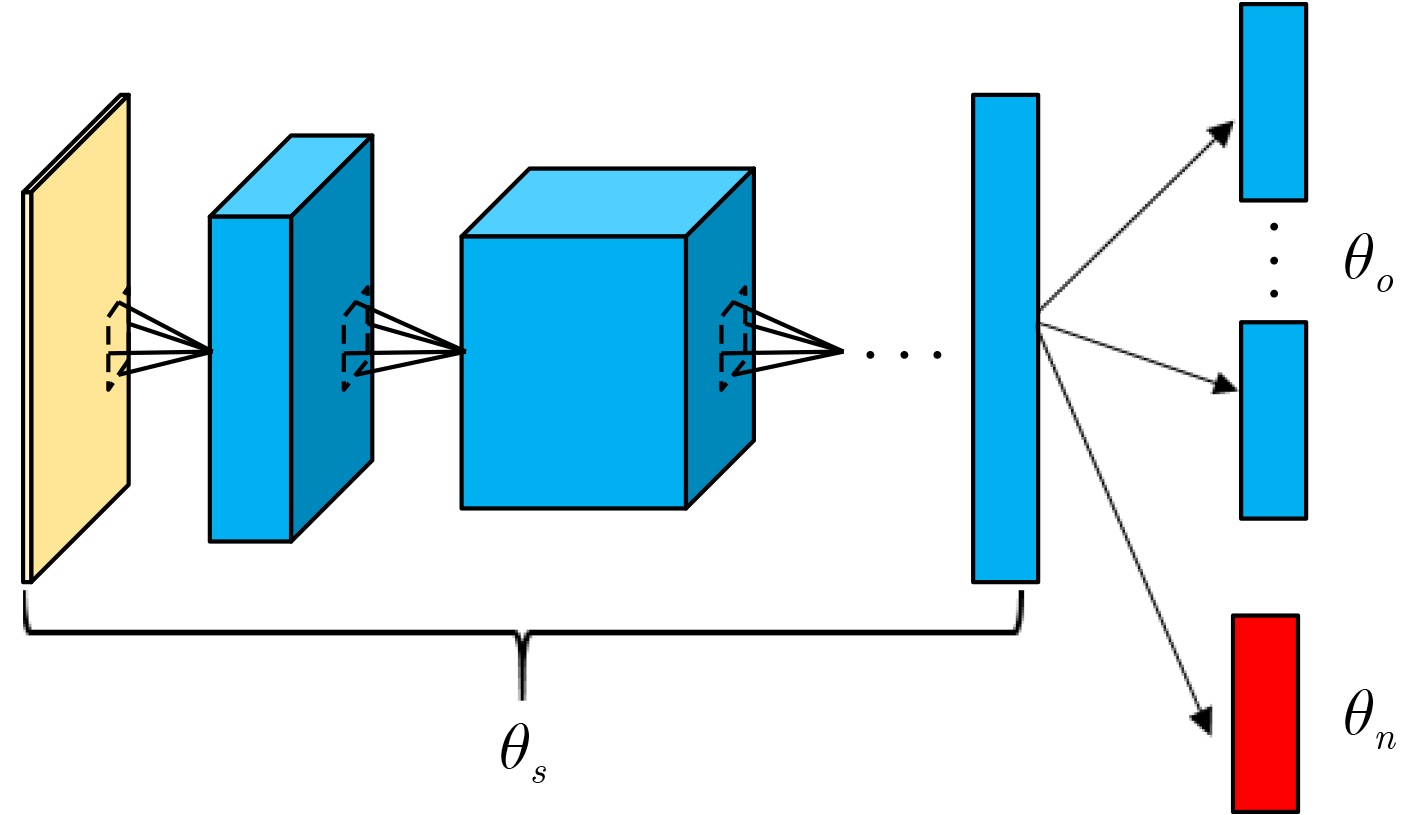

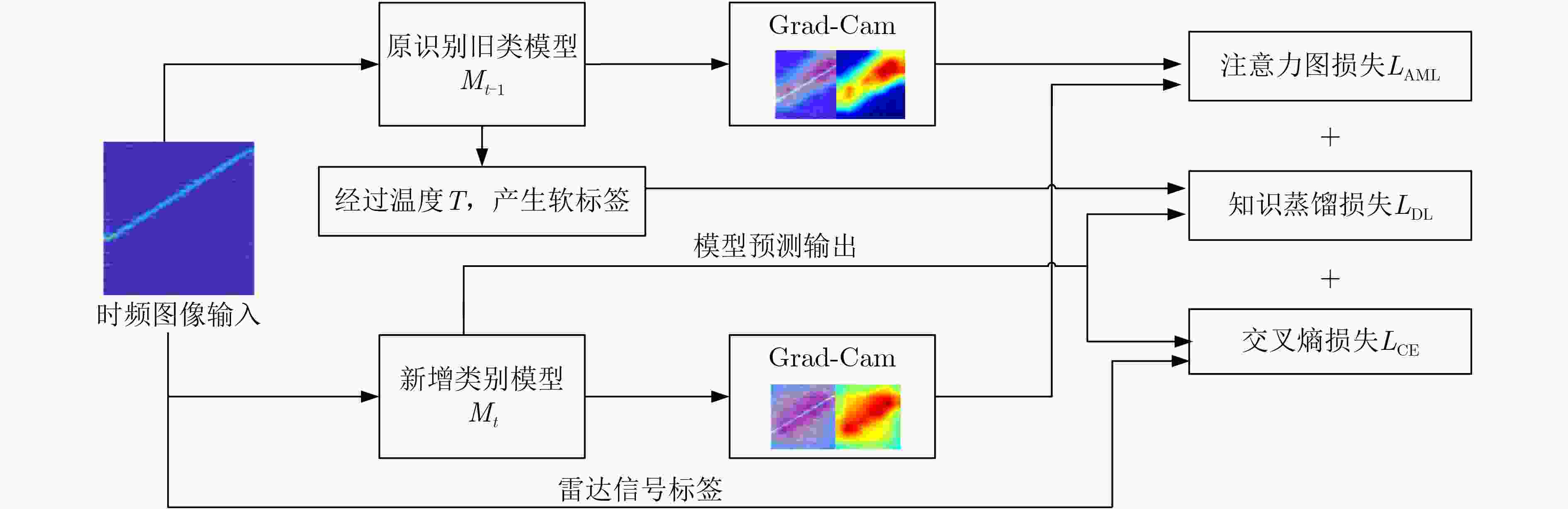
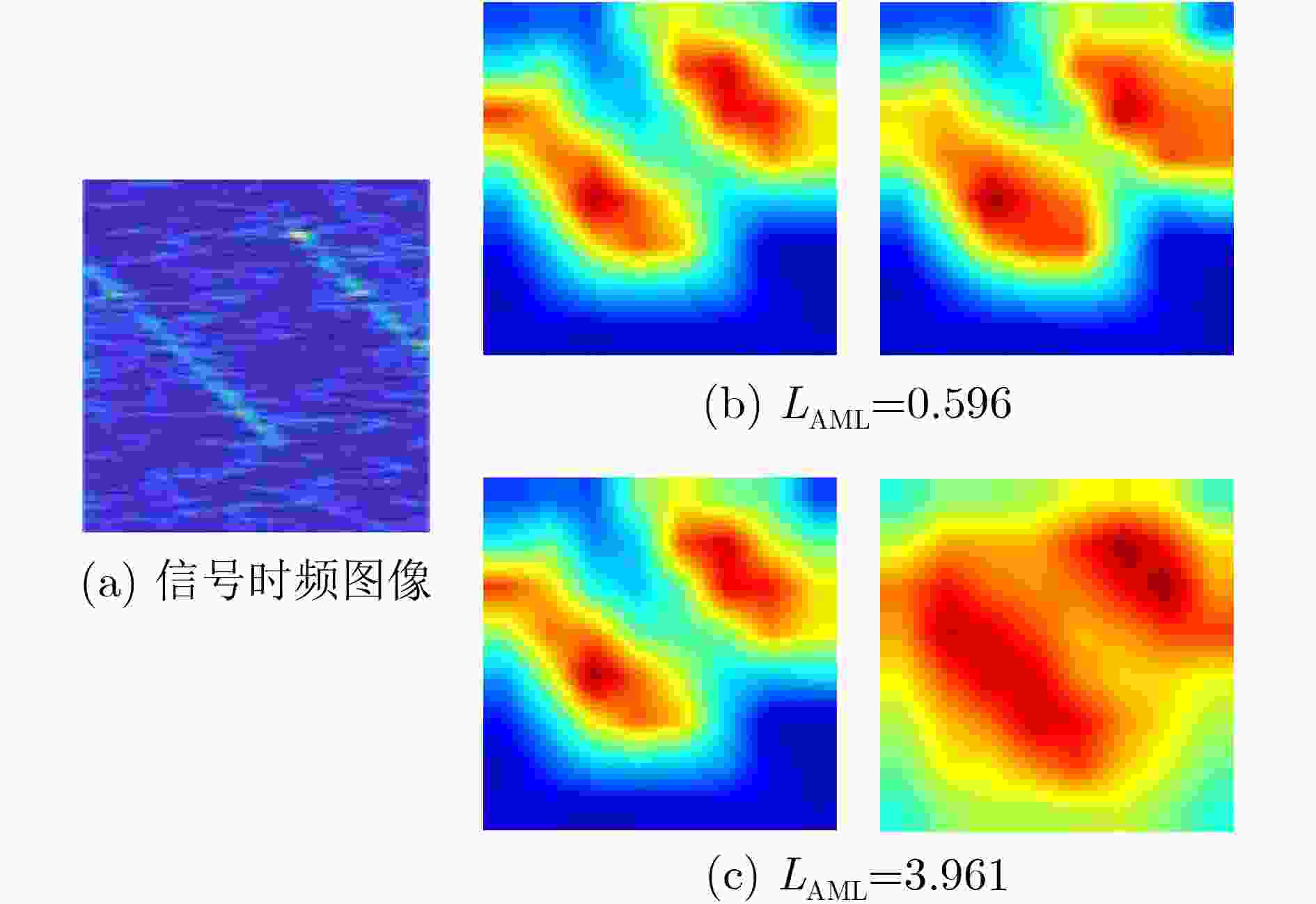
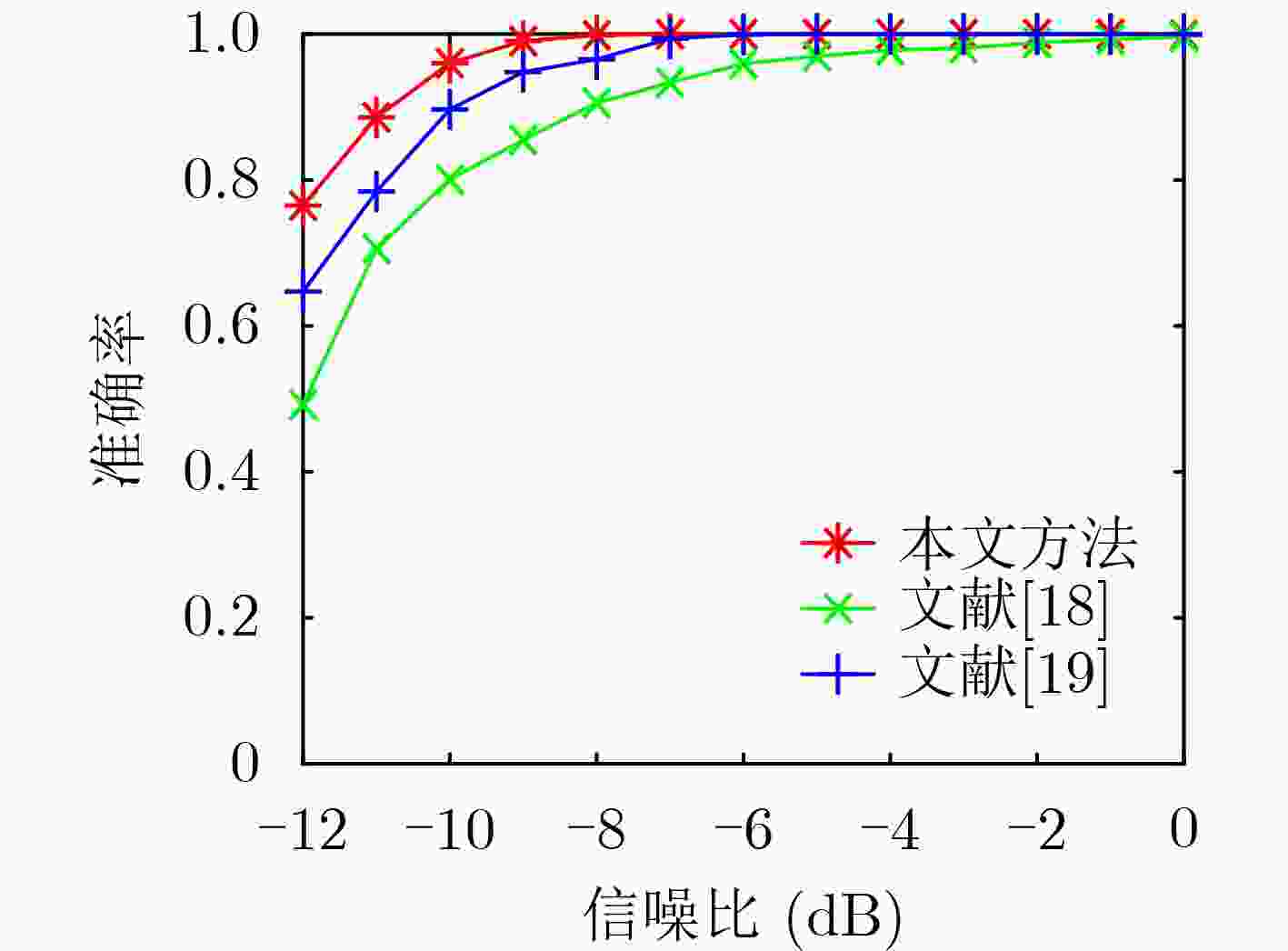
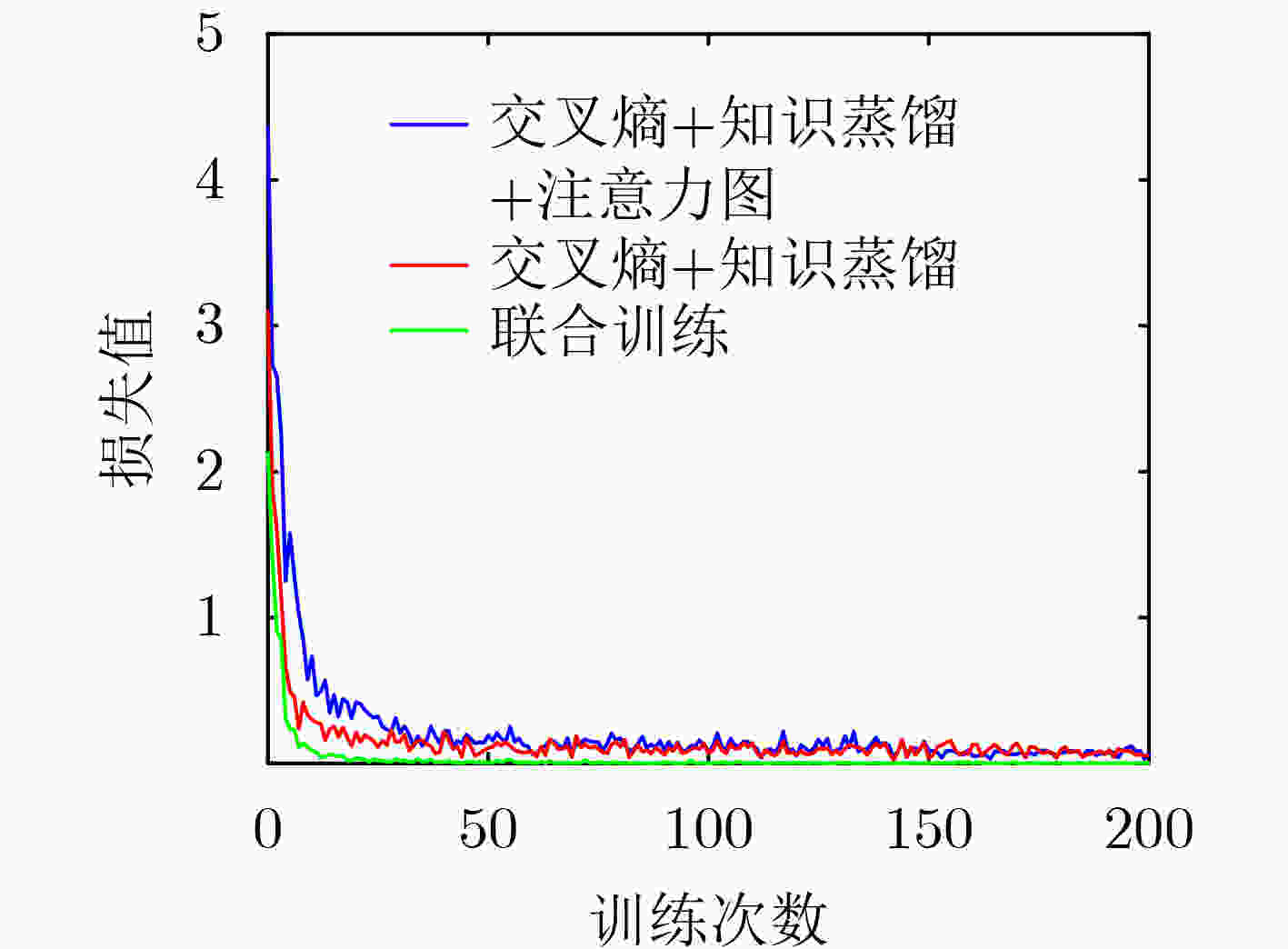
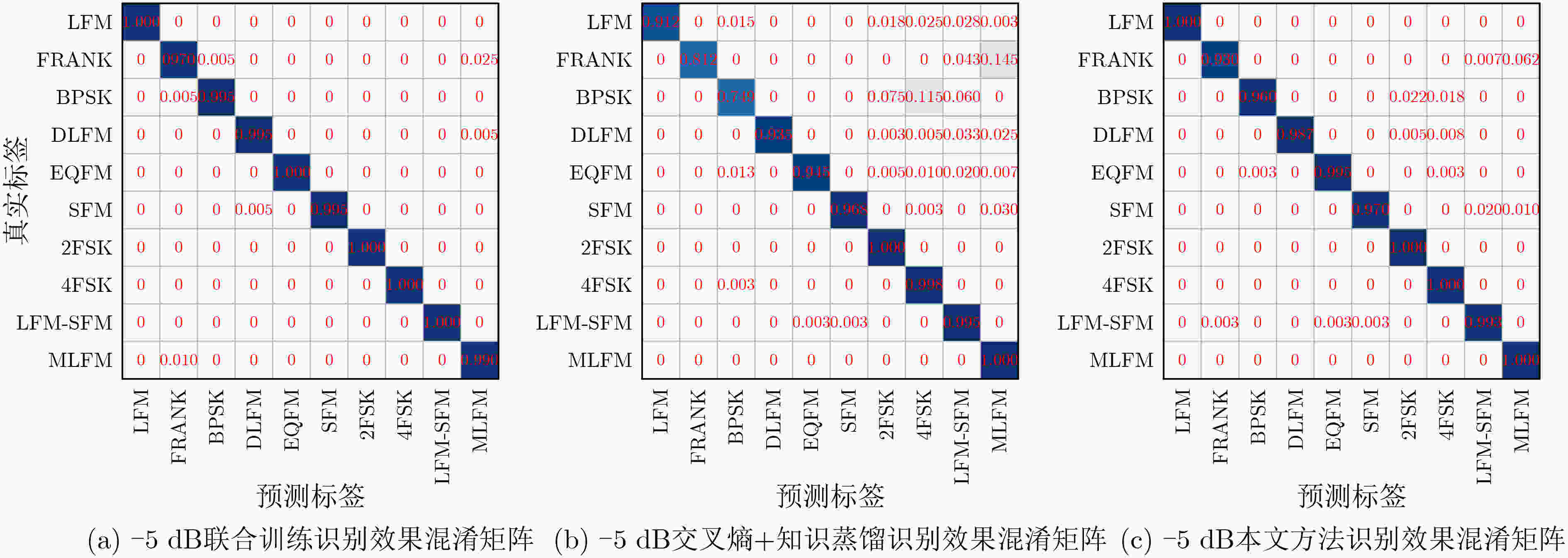


 下载:
下载:
