Cross-domain Chinese Word Segmentation Based on New Word Discovery
-
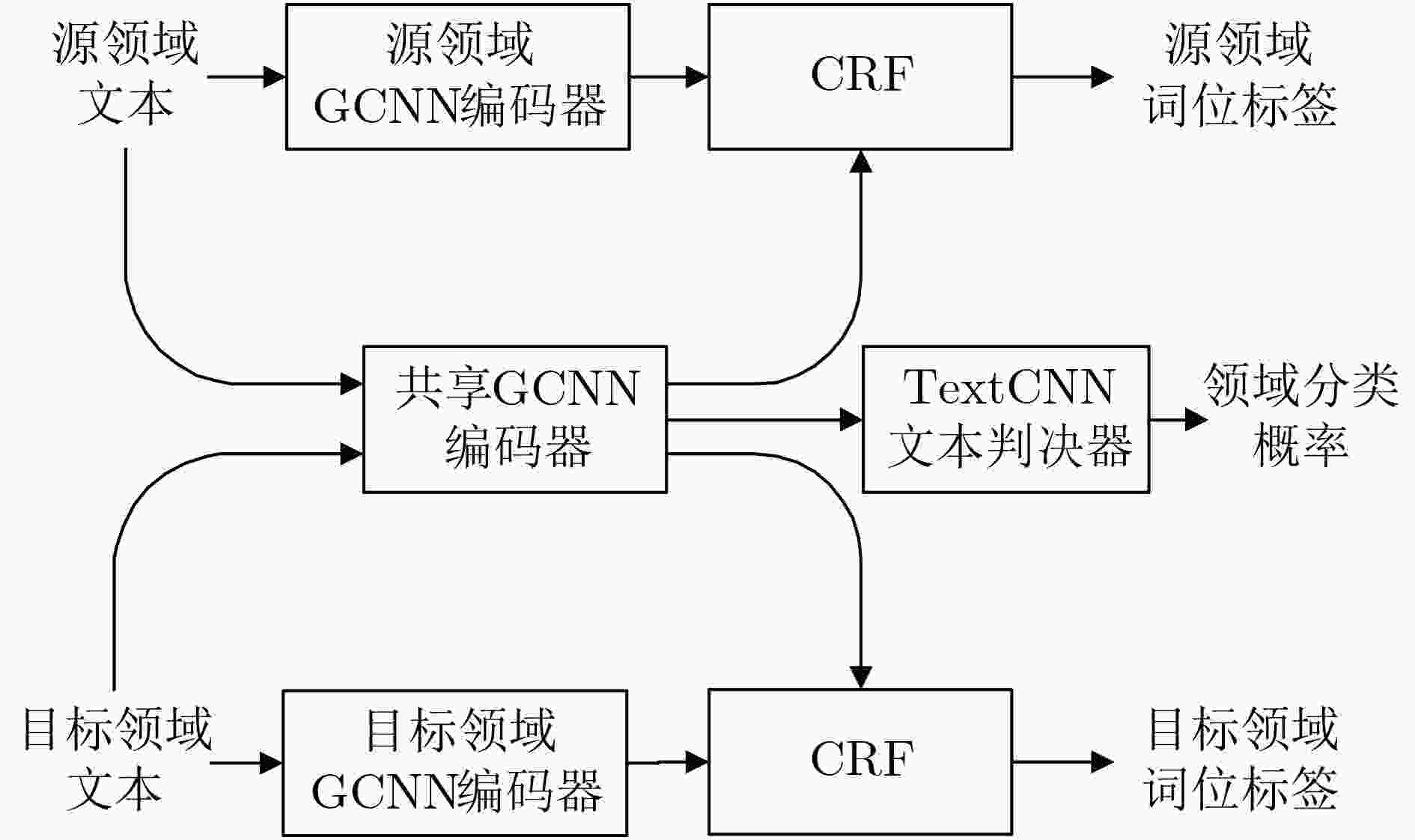
摘要: 深度神经网络(DNN)是目前中文分词的主流方法,但将针对某一领域训练的网络模型用于其他领域时,会因存在跨领域的未登录词(OOV)和表达鸿沟而造成性能显著下降,而在实际中对所有未知领域的训练语料进行人工标注和训练模型并不可行。为了解决这个问题,该文构建了一个基于新词发现的跨领域中文分词系统,可以自动完成从目标领域语料中提取新词、标注语料和训练网络模型的工作。此外,针对现有新词发现算法提取出的词表垃圾词串多以及自动标注语料中存在噪声样本的问题,提出了一种基于向量增强互信息和加权邻接熵的无监督新词发现算法以及一种基于对抗式训练的中文分词模型。实验中将使用北大开源新闻语料训练的网络模型提取出的特征迁移到医疗、发明专利和小说领域,结果表明该文所提方法在未登录词率、准确率、召回率和分词F值方面均优于现有方法。Abstract: Deep Neural Network (DNN) is the major method in current Chinese word segmentation. However, its performance is significantly degraded when the network trained for one domain is used in other domains due to the Out Of Vocabulary (OOV) words and expression gaps. In this paper, a cross domain Chinese word segmentation system based on new word discovery is built to handle the OOV word and expression gap problems. An unsupervised new word discovery algorithm based on vector enhanced mutual information and weighted adjacency entropy, and a Chinese word segmentation model based on adversarial training are also proposed to improve the performance of the baseline system. Experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to the conventional methods in the OOV rates, precisions, recalls and F-scores.
-
表 1 实验中使用的语料大小(Byte)
语料 句子(k) 词语(M) 字符(M) 新闻 53.7 1.3 2.1 医疗 32.0 0.7 1.2 《诛仙》 59.0 2.1 3.0 《斗罗》 40.0 2.0 0.9 发明专利 17.0 0.6 0.9 表 2 不同方法的未登录词率(%)
算法 无新词发现 MI+BE 本文方法 医疗 25.93 16.31 5.42 《诛仙》 15.52 8.24 1.43 《斗罗》 11.15 7.06 1.23 发明专利 18.39 11.27 3.45 表 3 前20个最频繁出现词中垃圾词串数(个)
语料 医疗 《诛仙》 《斗罗》 发明专利 MI+BE 4 5 7 6 本文方法 1 1 2 6 表 4 基于对抗式训练的分词算法效果
性能指标 准确率(%) 召回率(%) F值 算法 基线 GCNN_CRF 本文方法 基线 GCNN_CRF 本文方法 基线 GCNN_CRF 本文方法 医疗 71.7 80.7 82.4 74.3 82.0 83.7 73.0 81.4 83.0 《诛仙》 77.8 89.3 90.3 75.6 87.5 87.7 76.7 88.4 89.0 《斗罗》 81.7 92.1 92.8 81.7 91.9 92.4 81.0 92.0 92.6 发明专利 84.3 88.1 89.8 81.6 87.1 87.2 82.9 87.6 88.5 -
[1] 陈平, 刘晓霞, 李亚军. 基于字典和统计的分词方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2008, 44(10): 144–146. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2008.10.042CHEN Ping, LIU Xiaoxia, and LI Yajun. Chinese word segmentation based on dictionary and statistics[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2008, 44(10): 144–146. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2008.10.042 [2] WU Andi and JIANG Zixin. Word segmentation in sentence analysis[C]. 1998 International Conference on Chinese Information Processing, Beijing, China, 1998: 169–180. [3] 朱聪慧, 赵铁军, 郑德权. 基于无向图序列标注模型的中文分词词性标注一体化系统[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(3): 700–704. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00214ZHU Conghui, ZHAO Tiejun, and ZHENG Dequan. Joint Chinese word segmentation and POS tagging system with undirected graphical models[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(3): 700–704. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00214 [4] YUAN Zheng, LIU Yuanhao, YIN Qiuyang, et al. Unsupervised multi-granular Chinese word segmentation and term discovery via graph partition[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2020, 110: 103542. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103542 [5] DU Jinlian, MI Wei, and DU Xiaolin. Chinese word segmentation in electronic medical record text via graph neural network-bidirectional LSTM-CRF model[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Seoul, Korea, 2020: 985–989. [6] WANG Qi, ZHOU Yangming, RUAN Tong, et al. Incorporating dictionaries into deep neural networks for the Chinese clinical named entity recognition[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2019, 92: 103133. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103133 [7] XU Jingjing, MA Shuming, ZHANG Yi, et al. Transfer deep learning for low-resource Chinese word segmentation with a novel neural network[C]. The 6th National CCF Conference on Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, Dalian, China, 2017: 721–730. [8] BELLEGARDA J R. Statistical language model adaptation: Review and perspectives[J]. Speech Communication, 2004, 42(1): 93–108. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2003.08.002 [9] 刘伟童, 刘培玉, 刘文锋, 等. 基于互信息和邻接熵的新词发现算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2019, 36(5): 1293–1296. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2017.11.0745LIU Weitong, LIU Peiyu, LIU Wenfeng, et al. New word discovery algorithm based on mutual information and branch entropy[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2019, 36(5): 1293–1296. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2017.11.0745 [10] 罗桂琼, 费洪晓, 戴弋. 基于反序词典的中文分词技术研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2008, 18(1): 80–83.LUO Guiqiong, FEI Hongxiao, and DAI Yi. Research of Chinese segmentation based on converse segmentation dictionary[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2008, 18(1): 80–83. [11] YAO Yushi and HUANG Zheng. Bi-directional LSTM recurrent neural network for Chinese word segmentation[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 2016: 345–353. [12] LIU Liyuan, SHANG Jingbo, REN Xiang, et al. Empower sequence labeling with task-aware neural language model[C]. The Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, United States, 2018. [13] KAN Zhigang, QIAO Linbo, YANG Sen, et al. Event arguments extraction via dilate gated convolutional neural network with enhanced local features[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 123483–123491. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004378 [14] MIKOLOV T, CHEN Kai, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[C]. The 1st International Conference on Learning Representations, Scottsdale, Arizona, 2013. [15] KIM Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[C]. The 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1746–1751. [16] Beijing Universty, City University of Hong Kong, CKIP, et al. The second international Chinese word segmentation bakeoff data[EB/OL]. http://sighan.cs.uchicago.edu/bakeoff2005/, 2005. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
