Object Detection Method for Multi-scale Full-scene Surveillance Based on Attention Mechanism
-
摘要: 针对复杂城市监控场景中由于目标尺寸变化大、目标遮挡、天气影响等原因导致目标特征不明显的问题,该文提出一种基于注意力机制的多尺度全场景监控目标检测方法。该文设计了一种基于Yolov5s模型的多尺度检测网络结构,以提高网络对目标尺寸变化的适应性。同时,构建了基于注意力机制的特征提取模块,通过网络学习获得特征的通道级别权重,增强了目标特征,抑制了背景特征,提高了特征的网络提取能力。通过K-means聚类算法计算全场景监控数据集的初始锚框大小,加速模型收敛同时提升检测精度。在COCO数据集上,与基本网络相比,平均精度均值(mAP)提高了3.7%,mAP50提升了4.7%,模型推理时间仅为3.8 ms。在整个场景监控数据集中,mAP50达到89.6%,处理监控视频时为154 fps,满足监控现场的实时检测要求。Abstract: Focusing on the problem that the object features are not obvious in complex urban surveillance scenes due to large object size changes, object occlusion and weather influence, a multi-scale full-scene surveillance object detection method based on attention mechanism is proposed. In this paper, a multi-scale detection network structure based on Yolov5s model is designed to improve the adaptability of the network to the changes of object size. Meanwhile, a feature extraction module based on attention mechanism is constructed to obtain channel level weight of features through network learning, which enhances the object features, suppresses the background features, and improves the network extraction capability of features. The initial anchor frame size of the full-scene surveillance dataset is calculated by the K-means clustering algorithm to accelerate the model convergence while improving the detection accuracy. On the COCO dataset, the mean Average Precision (mAP) is improved by 3.7%, and the mAP50 is improved by 4.7% compared with the basic network, and the model inference time is only 3.8 ms. In the full-scene surveillance dataset, the mAP50 reaches 89.6% and the fps is 154 frames per second when processing the surveillance video, which meets the real-time detection requirements of the surveillance scene.
-
Key words:
- Object detection /
- Full-scene surveillance /
- Multi-scale detection /
- Attention mechanism
-
表 1 COCO数据集上的消融实验结果
方法 mAP50 mAP 推理时间(ms) Yolov5s 55.4 36.7 3.0 Yolov5s+Attention1 55.7 35.4 3.3 Yolov5s +Attention2 56.8 37.4 3.2 Yolov5s +Attention3 53.1 33.0 2.9 Yolov5s +Attention4 54.2 33.5 2.8 Yolov5s +Multi-scale 59.0 39.3 3.5 MODN-BAM 60.1 40.4 3.8 表 2 Open Images v6数据集上的消融实验结果
方法 mAP50 mAP Yolov5s 71.2 49.8 Yolov5s+Attention2 72.1 51.3 Yolov5s+ Multi-scale 74.6 55.5 MODN-BAM 75.7 56.3 表 3 COCO数据集上与其他算法的对比结果
方法 Size mAP mAP50 mAP75 mAPs mAPm mAPl fps RetinaNet-ResNet101 800×800 37.8 57.5 40.8 20.2 41.1 49.2 11 YOLOF 800×* 37.7 56.9 40.6 19.1 42.5 53.2 32 YOLOF-ResNet101 800×* 39.8 59.4 42.9 20.5 44.5 54.9 21 RDSNet 800×800 38.1 58.5 40.8 21.2 41.5 48.2 10.9 Yolov3 608×608 33.0 57.9 34.4 18.3 35.4 41.9 20 Yolov3-SPP 608×608 36.2 60.6 38.2 20.6 37.4 46.1 73 NAS-FPN 640×640 39.9 – – – – – 24 EfficientDet-D1 640×640 39.6 58.6 42.3 17.9 44.3 56.0 50 Yolov5s 640×640 36.7 55.4 39.0 21.1 41.9 45.5 204 MODN-BAM 640×640 40.4 60.1 43.3 22.5 45.0 54.9 175 表 4 全场景监控数据集上的消融实验结果
方法 frame size mAP50 fps Yolov5s 1920×1080 85.7 182 Yolov5s+Attention2 1920×1080 87.6 176 Yolov5s+ Multi-scale 1920×1080 88.4 163 MODN-BAM 1920×1080 89.6 154 -
[1] 陈勇, 刘曦, 刘焕淋. 基于特征通道和空间联合注意机制的遮挡行人检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1486–1493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190606CHEN Yong, LIU Xi, and LIU Huanlin. Occluded pedestrian detection based on joint attention mechanism of channel-wise and spatial information[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1486–1493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190606 [2] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. [3] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [4] 董小伟, 韩悦, 张正, 等. 基于多尺度加权特征融合网络的地铁行人目标检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 2113–2120. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200450DONG Xiaowei, HAN Yue, ZHANG Zheng, et al. Metro pedestrian detection algorithm based on multi-scale weighted feature fusion network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 2113–2120. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200450 [5] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [6] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [7] DAI Jifeng, LI Yi, HE Kaiming, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 379–387. [8] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [9] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [10] 刘革, 郑叶龙, 赵美蓉. 基于RetinaNet改进的车辆信息检测[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(3): 854–858. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019071262LIU Ge, ZHENG Yelong, and ZHAO Meirong. Vehicle information detection based on improved RetinaNet[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(3): 854–858. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019071262 [11] DUAN Kaiwen, BAI Song, XIE Lingxi, et al. CenterNet: Keypoint triplets for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6568–6577. [12] ZHOU Xingyi, ZHUO Jiacheng, and KRÄHENBUHL P. Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 850–859. [13] WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, WU Y H, et al. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1571–1580. [14] WANG Wenhai, XIE Enze, SONG Xiaoge, et al. Efficient and accurate arbitrary-shaped text detection with pixel aggregation network[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8439–8448. [15] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [16] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. [17] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [18] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [19] 陈鸿坤, 罗会兰. 多尺度语义信息融合的目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 2087–2095. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200147CHEN Hongkun and LUO Huilan. Multi-scale semantic information fusion for object detection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 2087–2095. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200147 [20] ROBBINS H and MONRO S. A stochastic approximation method[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1951, 22(3): 400–407. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729586 [21] ZHENG Zhaohui, WANG Ping, LIU Wei, et al. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12993–13000. [22] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. [23] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. [24] CHEN Qiang, WANG Yingming, YANG Tong, et al. You only look one-level feature[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13034–13043. [25] WANG Shaoru, GONG Yongchao, XING Junliang, et al. RDSNet: A new deep architecture for reciprocal object detection and instance segmentation[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12208–12215. [26] GHIASI G, LIN T Y, and LE Q V. NAS-FPN: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7029–7038. [27] TAN Mingxing, PANG Ruoming, and LE Q V. EfficientDet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10778–10787. -





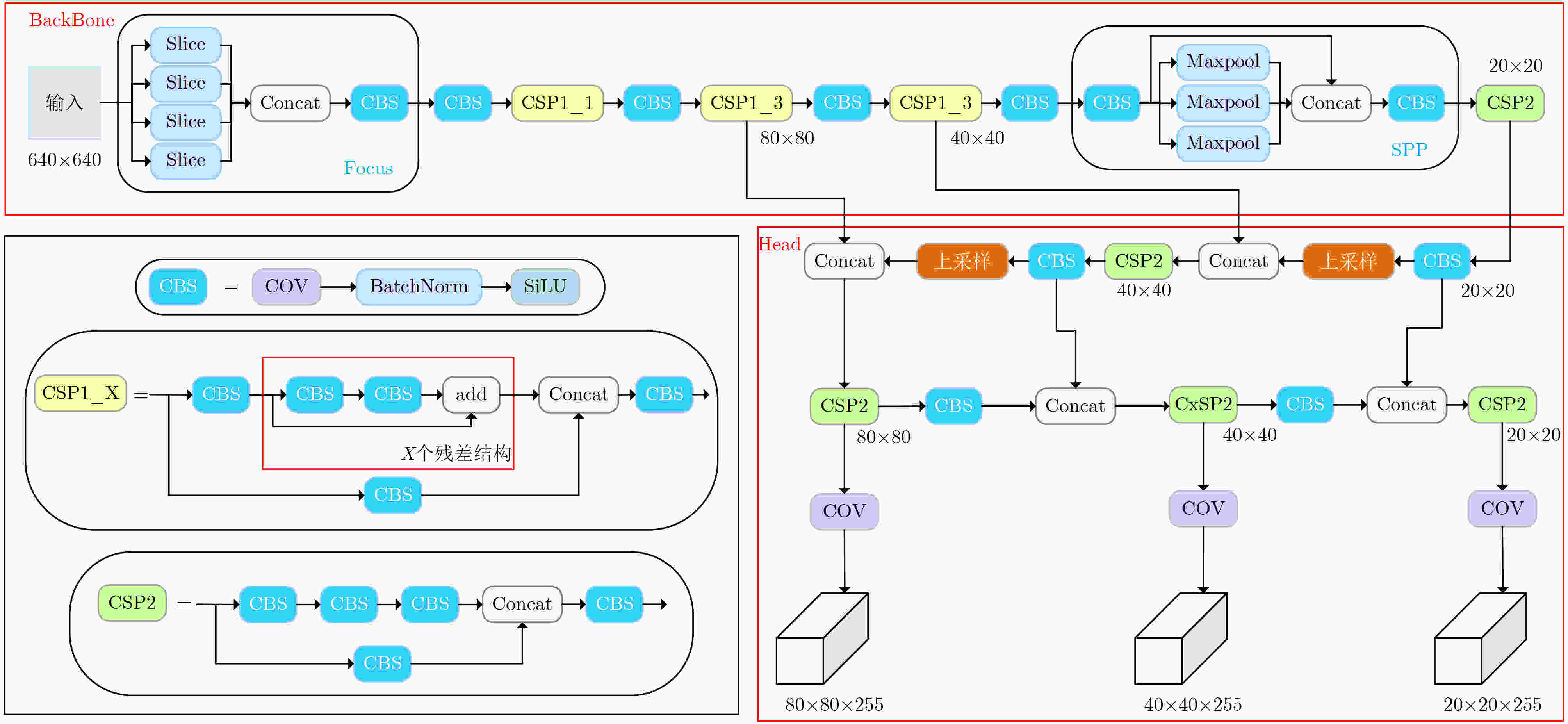
 下载:
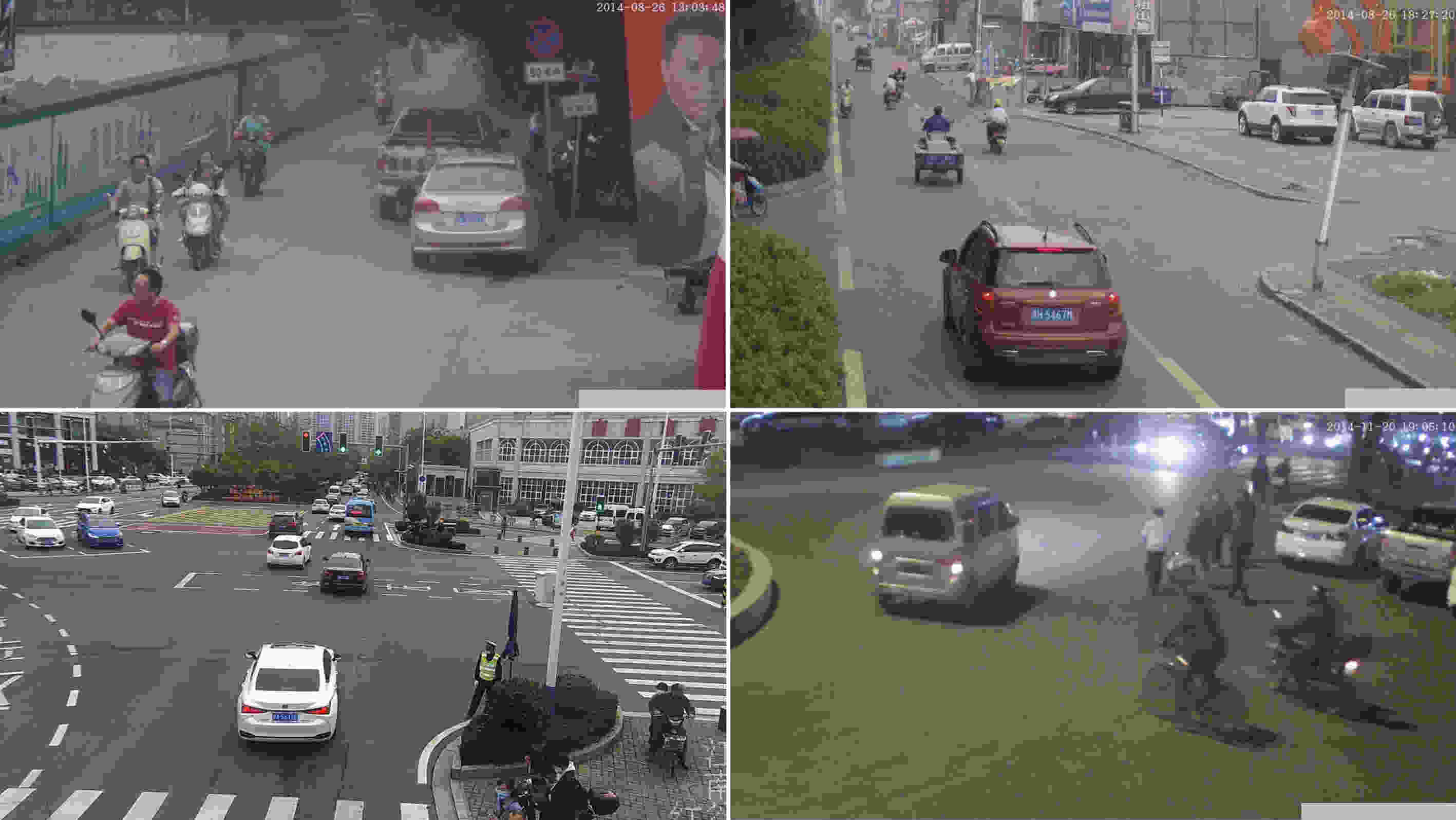
下载:
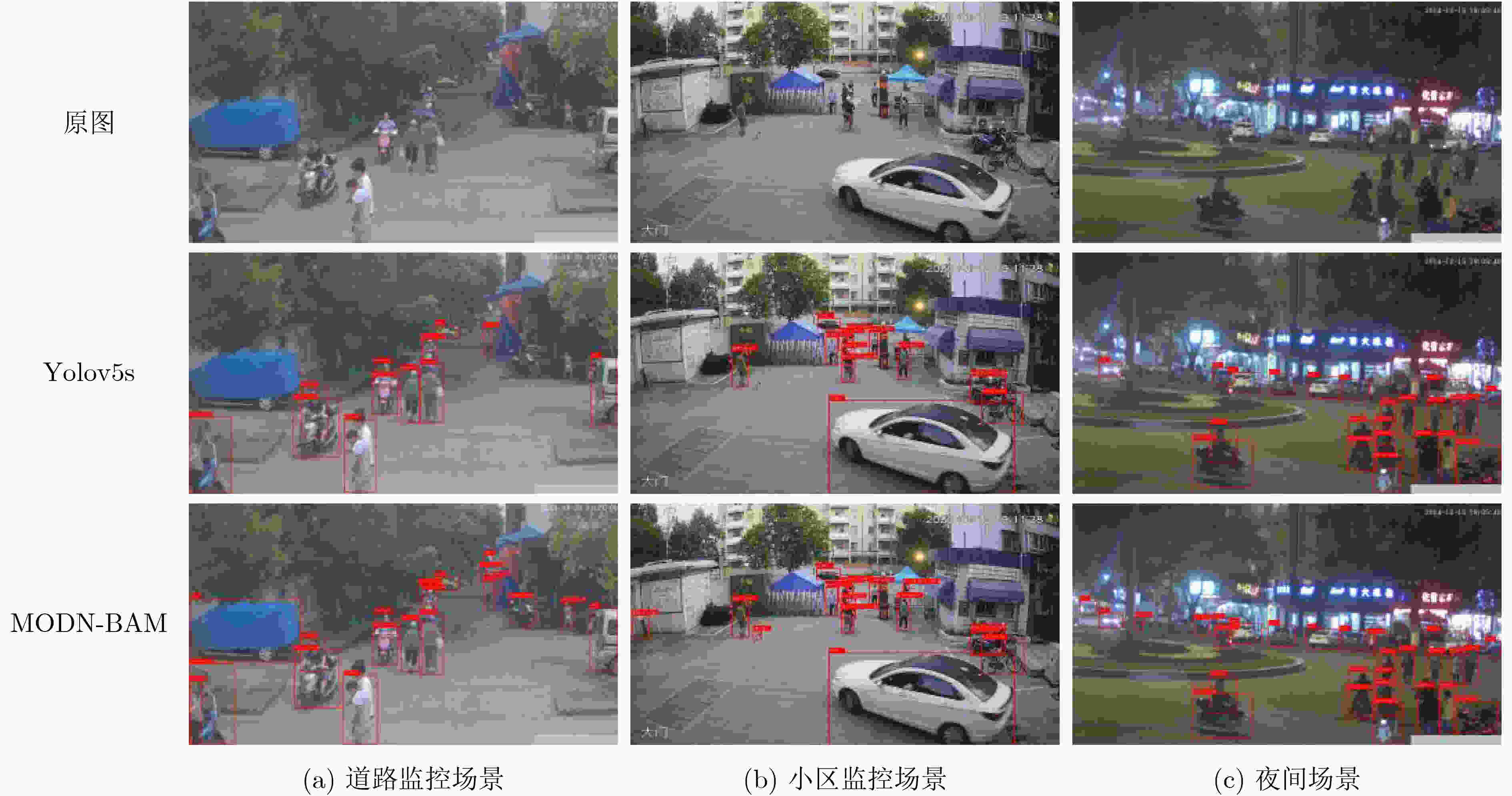
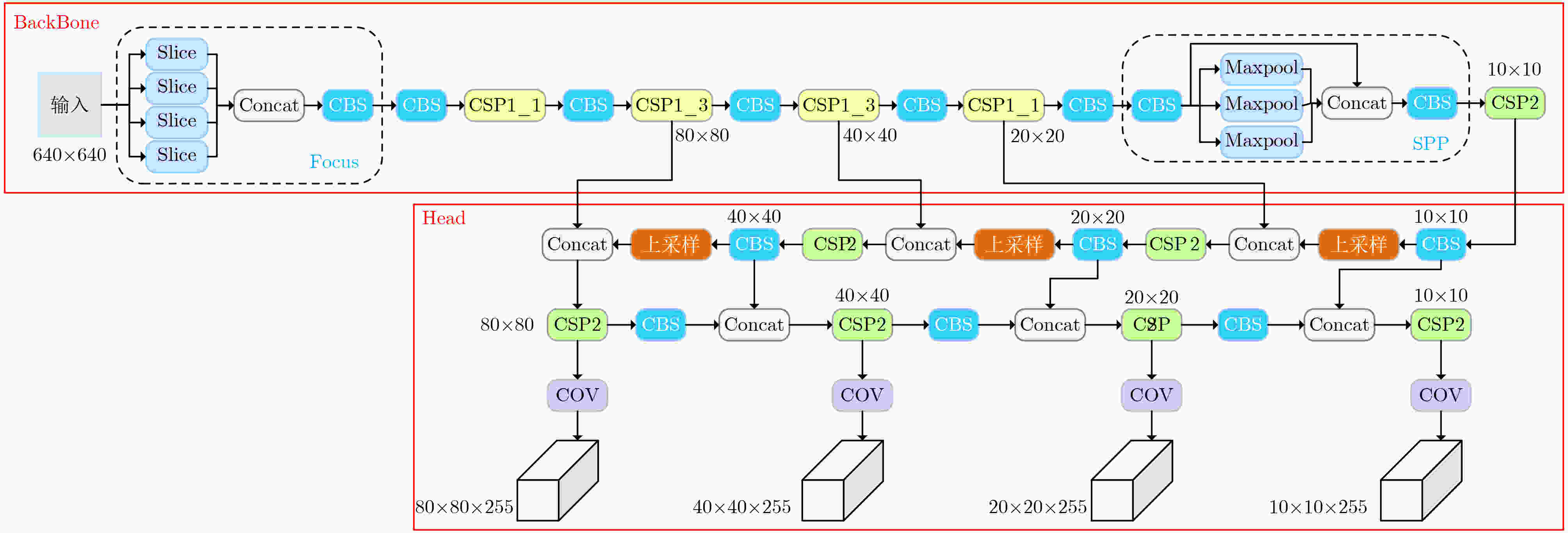
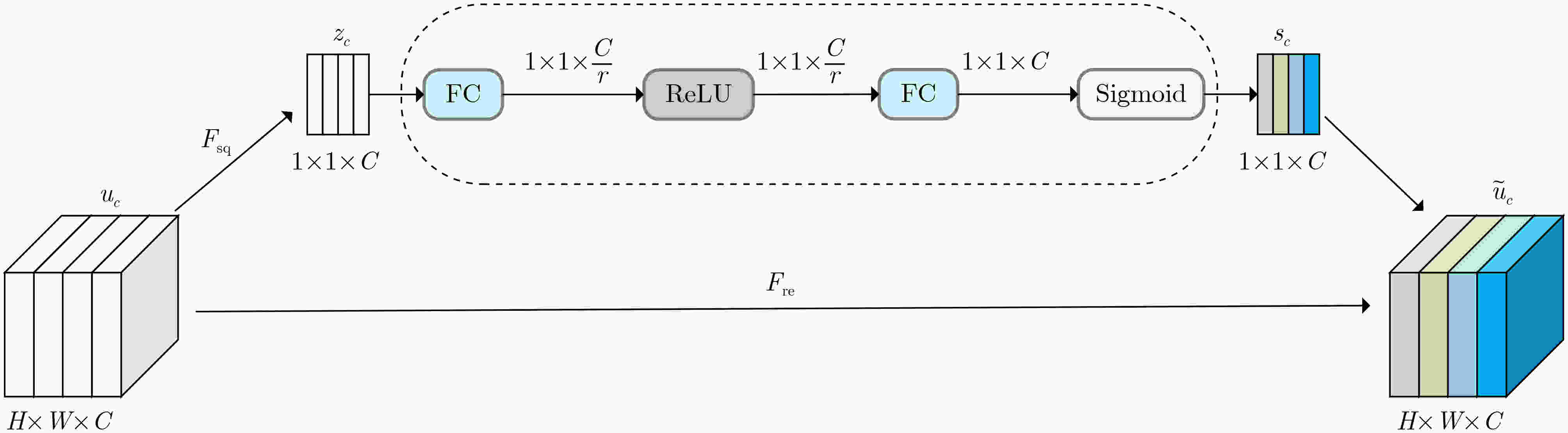
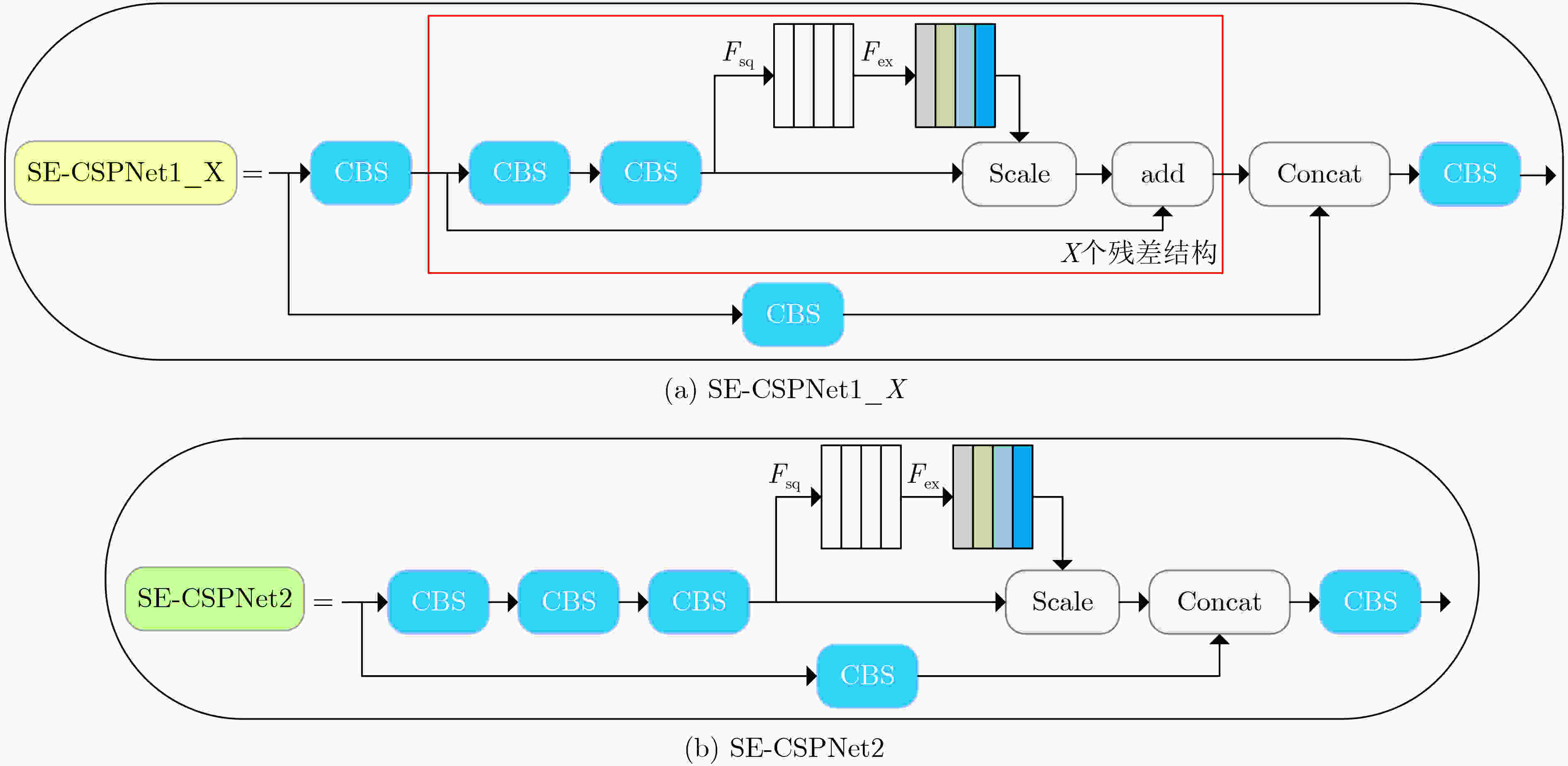




 下载:
下载:
