A Cycle Identification Algorithm for enhanced LOng RAnge Navigation Signal Based on Skywave Reconstruction Technology
-
摘要: 针对增强型罗兰(eLORAN)系统在信号处理中的核心问题——周期识别,该文提出一种应对强天波干扰及低信噪比(SNR)等恶劣环境的联合算法。该方法首先在改进窗函数的基础上利用频谱相除技术估计信号特征参数,并根据大数理论的思想实现了天地波识别;其次,提出天地波时延差及幅度比的自适应2阶网格搜索匹配算法,在节省计算量的同时准确重构并去除天波;最后利用伪地波信号准确实现周期识别。仿真结果分析表明,该算法能够成功地克服现有技术中的一些弊端,实现小时延差及大强度天波干扰下的天波识别及分离,同时结合频谱相除技术的稳定性极大提高周期识别的正确率,进而为后续解调解码等流程提供保障。Abstract: To solve the core problem in signal processing of the enhanced LOng RAnge Navigation (eLORAN) system—cycle-identification, a joint algorithm for harsh condition such as high intensity skywave interference and low Signal-Noise-Ratio (SNR) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, based on the improved window function in this method, the characteristic parameters of signal are estimated by spectral division technology, and then the identification of ground and sky wave is realized according to the thought of large number theory. Secondly, in order to reconstruct accurately and remove the skywave while saving the computation, a two-stage adaptive searching and matching algorithm of the characteristic parameters is proposed. Finally, the cycle-identification is realized accurately by the output pseudo-groundwave. The analysis of simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can successfully overcome some disadvantages of the prior art, and realize the recognition and separation of skywave in the environment of low time-delay and high level skywave. In addition, the accuracy rate of cycle-identification is greatly improved combining with the stability of spectral division technology, so as to provide a guarantee for the subsequent demodulation and decoding processes.
-
表 1 周期识别错误次数及准确率(SGR=0 dB)
SNR(dB) $\Delta $τ (μs) 准确率(%) 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60 0 6 21 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 99.74 2 1 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 99.99 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 表 2 天地波分离后周期识别错误次数及准确率(SGR=18 dB)
SNR(dB) $\Delta $τ (μs) 准确率(%) 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60 0 19 9 4 13 16 1 11 5 8 0 1 7 99.22 2 10 3 0 10 7 0 6 0 1 0 0 3 99.67 4 2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 99.97 6 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 99.98 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 表 3 天地波分离后周期识别错误次数及准确率(SGR=24 dB)
SNR(dB) $\Delta $τ (μs) 准确率(%) 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60 0 11 7 2 25 11 2 25 3 6 29 0 12 98.89 2 6 4 1 18 2 0 8 0 1 6 0 6 99.57 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 0 0 3 0 0 99.93 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100.00 -
[1] 吴德伟. 无线电导航系统[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015: 86–88.WU Dewei. Radio Navigation System[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2015: 86–88. [2] SALLY B, JOSEPH C, RON D, et al. Enhanced loran (eLORAN) definition document[R]. International Loran Association, 2007. [3] 海杭. 罗兰-C使用手册[M]. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 1996: 48–50.HAI Hang. Loran-C Manual[M]. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 1996: 48–50. [4] RTCM. Minimum performance standards for marine eloran receiving equipment[S]. RTCM Special Committee, 2016. [5] 吴苗, 李方能, 苏晓庆, 等. 基于高斯平滑滤波的罗兰C周期识别新方法[J]. 海洋测绘, 2013, 33(6): 80–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2013.06.023WU Miao, LI Fangneng, SU Xiaoqing, et al. The new method of loran c cycle identification based on Gaussian smoothing filter[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2013, 33(6): 80–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2013.06.023 [6] QIN Honglei, JIN Xiaoqin, CONG Li, et al. MEDLL-based method of ground-wave and cycle identification for Loran-C signal[C]. 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Changsha, China, 2019: 114–123. [7] 雷文华, 李勇, 胡海冰. 罗兰C信号TOA高精度估计算法[J]. 电子设计工程, 2020, 28(11): 132–136,141. doi: 10.14022/j.issn1674-6236.2020.11.030LEI Wenhua, LI Yong, and HU Haibing. High precision TOA estimation method for Loran C signal[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2020, 28(11): 132–136,141. doi: 10.14022/j.issn1674-6236.2020.11.030 [8] 隋景鹏, 靳小琴, 舒东亮, 等. 改进优化包络罗兰C天地波周期联合识别算法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2020, 43(17): 115–119. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2004756SUI Jingpeng, JIN Xiaoqin, SHU Dongliang, et al. Improved Loran-C joint identification algorithm for sky-ground wave and cycle based on optimized envelope[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2020, 43(17): 115–119. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2004756 [9] 孙晶, 战兴华, 陈俊喆. 增强型罗兰信号周期检测方法[J]. 现代导航, 2021, 12(1): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7976.2021.01.005SUN Jing, ZHAN Xinghua, and CHEN Junzhe. Detection method of enhanced loran signal cycle[J]. Modern Navigation, 2021, 12(1): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7976.2021.01.005 [10] 信息产业部(电子). GB/T 12752-1991 船用罗兰C接收设备通用技术条件[S]. 北京: 国家技术监督局, 1991.Ministry of Information Industry (Electronics). GB/T 12752-1991 Generial specification for marine loran-C receiving equipment[S]. Beijing: China State Bureau of Technology Supervision, 1991. [11] MOHAMMED A F and LAST D. Loran-C skywave delay detection using ARMA algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 1998, 34(17): 1654–1655. doi: 10.1049/el:19981180 [12] 胡东亮, 杨迎春, 范菊红. 基于MUSIC算法的罗兰C接收机天地波自动识别方法研究[J]. 海军工程大学学报, 2006, 18(3): 7–9,22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2006.03.002HU Dongliang, YANG Yingchun, and FAN Juhong. Loran-C receiver sky-wave detection based on MUSIC algorithms[J]. Journal of Naval University of Engineering, 2006, 18(3): 7–9,22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3486.2006.03.002 [13] 熊伟, 胡永辉, 钱建立, 等. 靶场时统中自适应Loran-C接收机的研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2008, 31(3): 303–306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2008.03.025XIONG Wei, HU Yonghui, QIAN Jianli, et al. Research on Loran-C adaptive receiver in range time series system[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2008, 31(3): 303–306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2008.03.025 [14] 吴苗, 许江宁, 陈志勇, 等. 基于现代信号处理的罗兰C天波延迟估计研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2011, 31(2): 49–51,64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2011.02.014WU Miao, XU Jiangning, CHEN Zhiyong, et al. Skywave delay estimation of loran C based on modern signal processing methods[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2011, 31(2): 49–51,64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2011.02.014 [15] ZHANG Kai, WAN Guobin, and XI Xiaoli. Enhanced Loran skywave delay estimation based on artificial neural network in low SNR environment[J]. IET Radar Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(1): 127–132. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0222 [16] ZHANG Kai, WAN Guobin, PU Yurong, et al. Loran-C skywave delay estimation using hybrid-WRELAX algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(21): 1426–1427. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.2892 [17] ZHANG Kai, WAN Guobin, LI Minchao, et al. Skywave delay estimation in enhanced loran based on extended invariance principle weighted fourier transform and relaxation algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(8): 1344–1349. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5651 [18] MOHAMMED A F. Effect of Loran-C signal parameters on skywave delay estimation of IFFT technique[J]. Electronics Letters, 2003, 39(14): 1091–1093. doi: 10.1049/el:20030670 [19] 张田仓, 唐争. 用于罗兰C接收机天波识别的IFFT频谱相除技术探讨[J]. 信息与电子工程, 2004, 2(4): 274–278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2892.2004.04.009ZHANG Tiancang and TANG Zheng. IFFT spectral-division technique for skywave identification receivers[J]. Information and Electronic Engineering, 2004, 2(4): 274–278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2892.2004.04.009 -





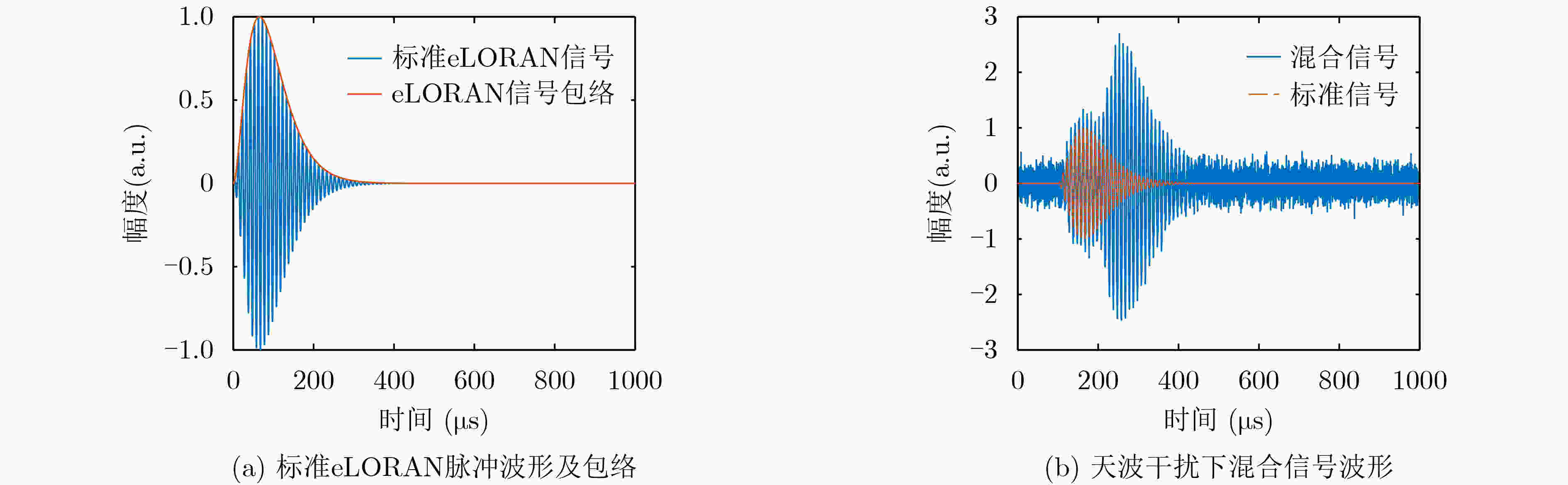
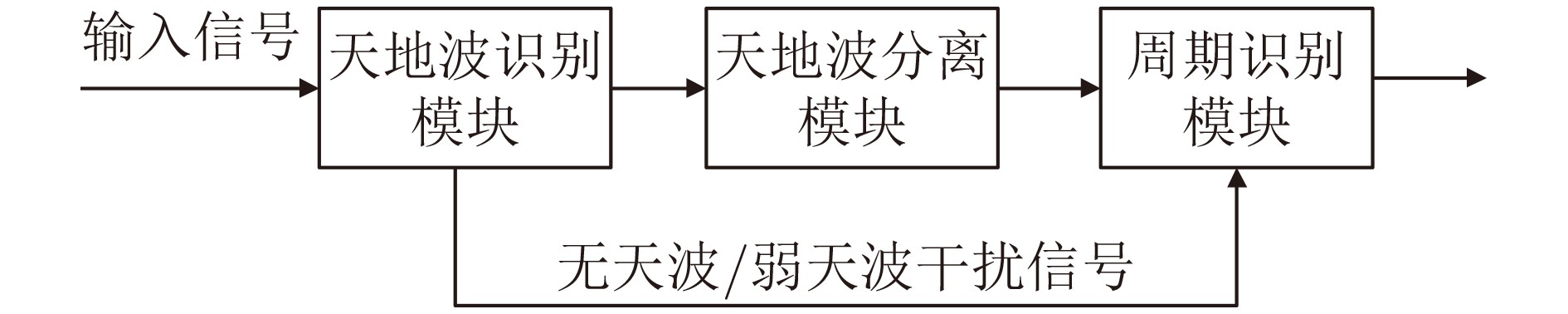
 下载:
下载:
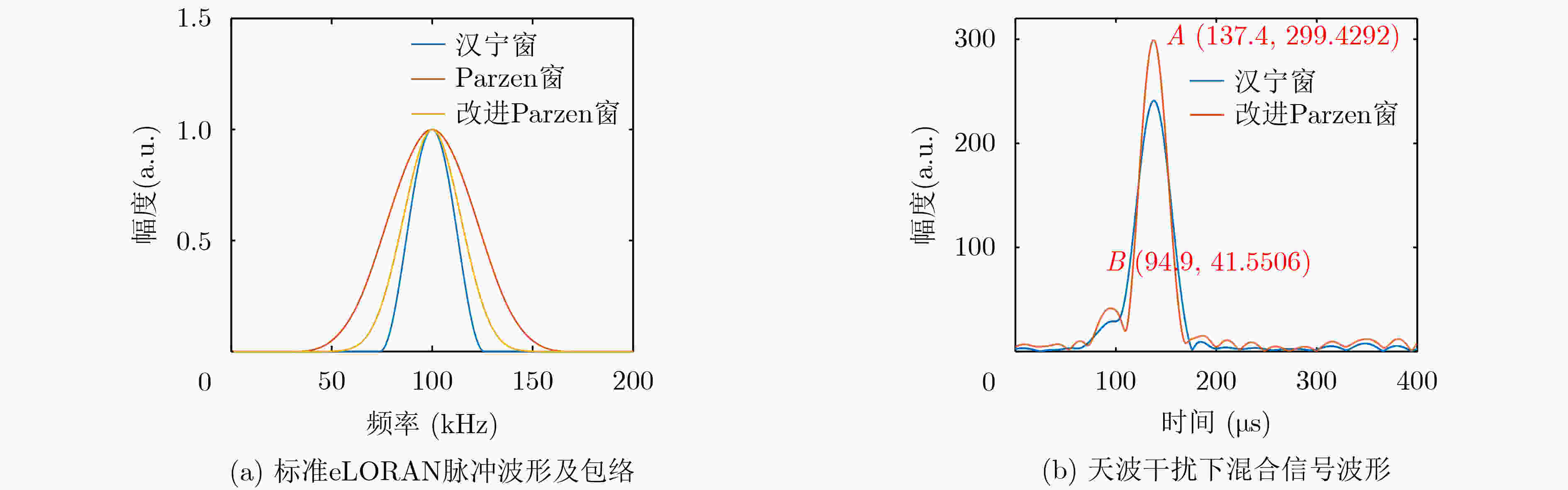
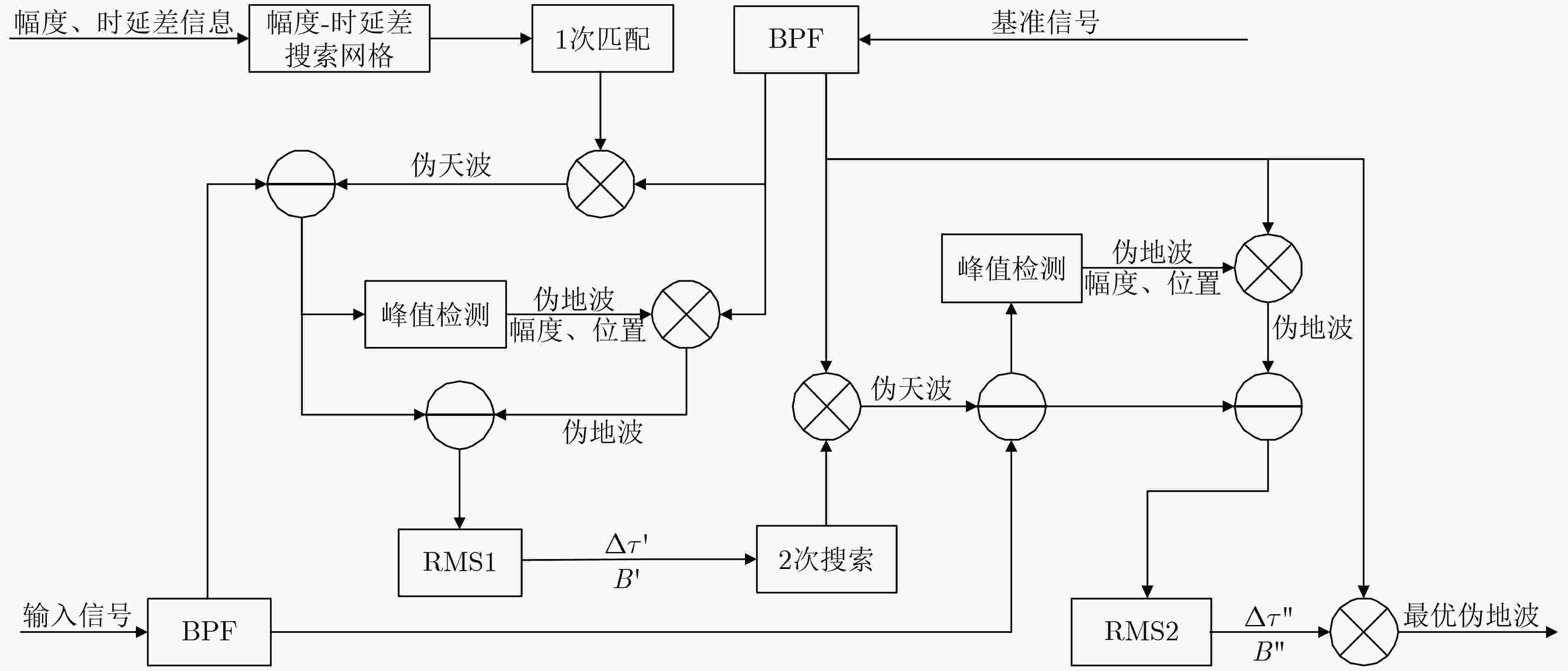
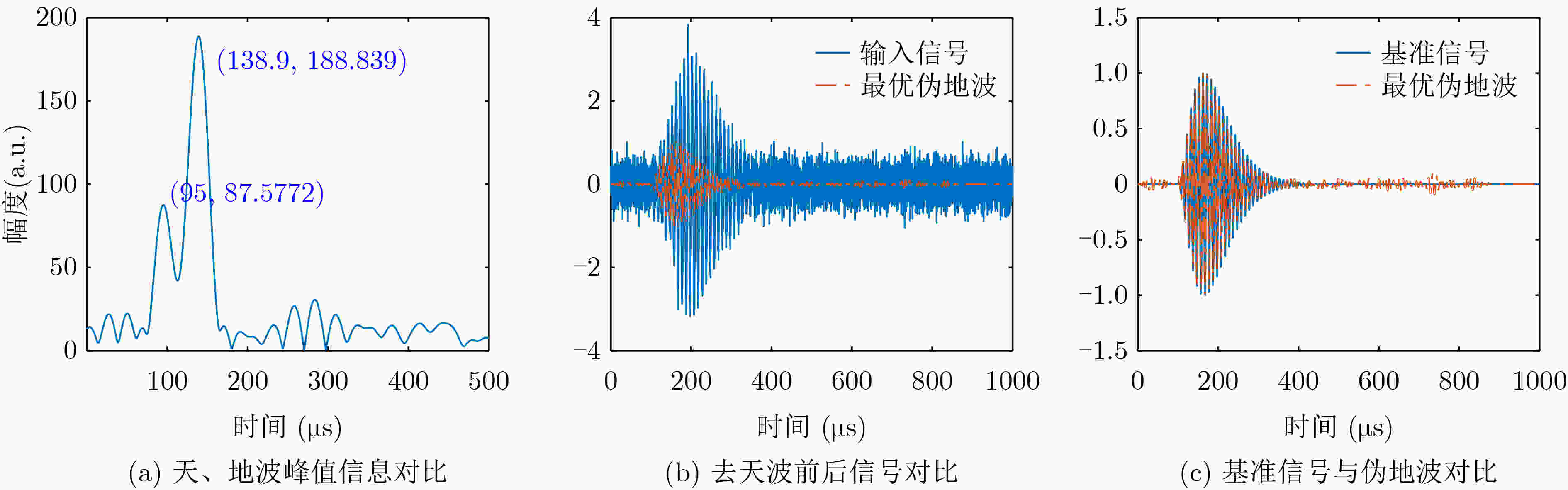
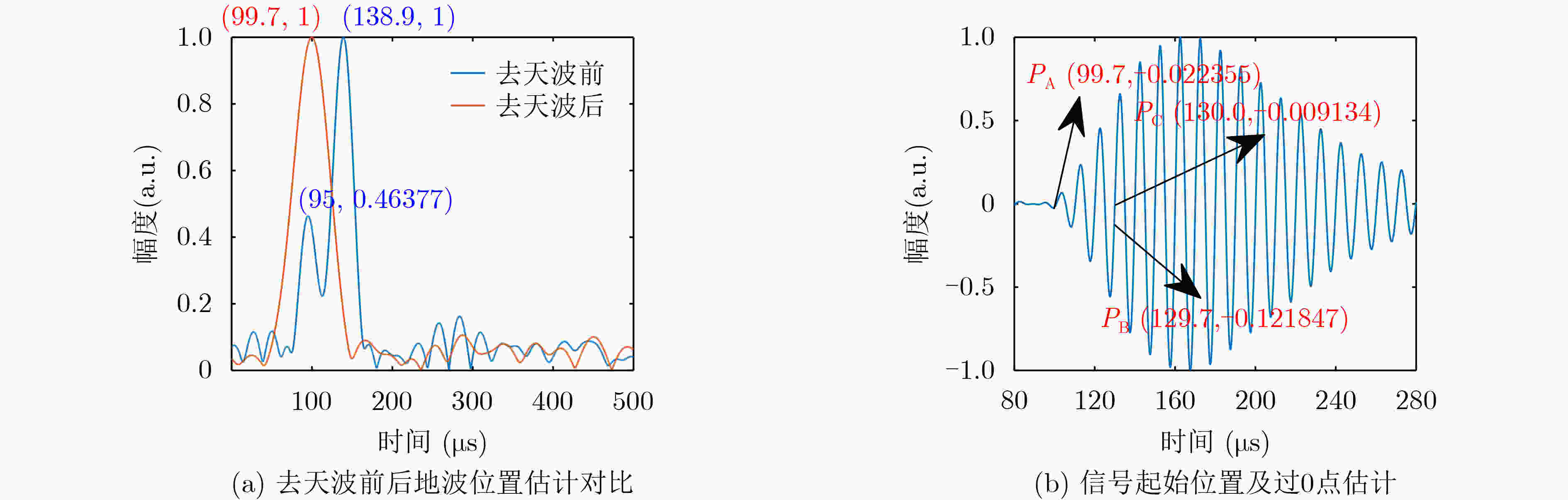
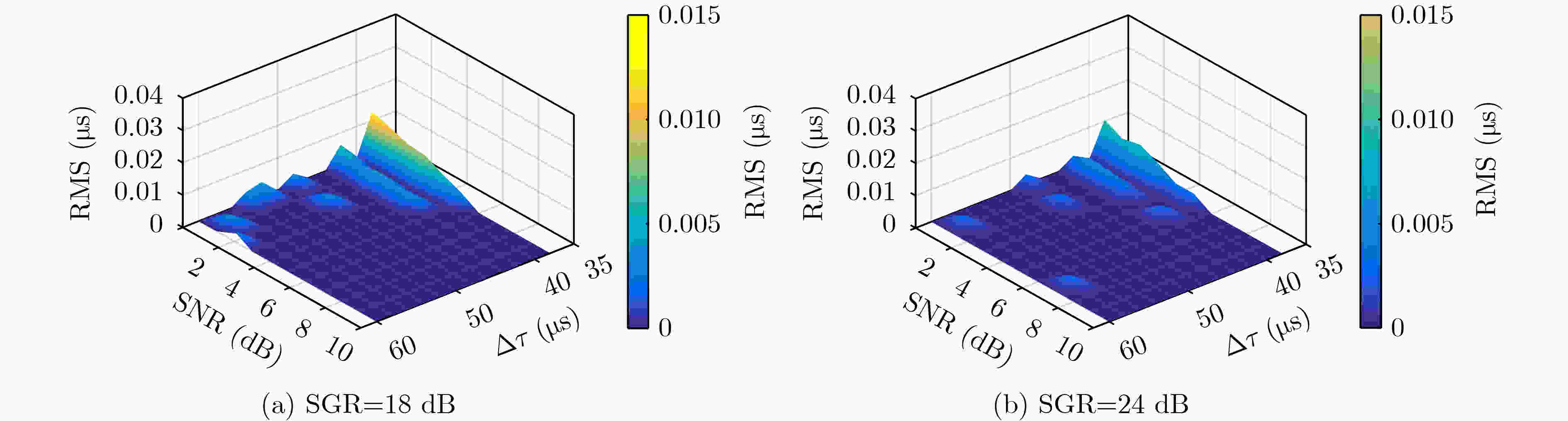
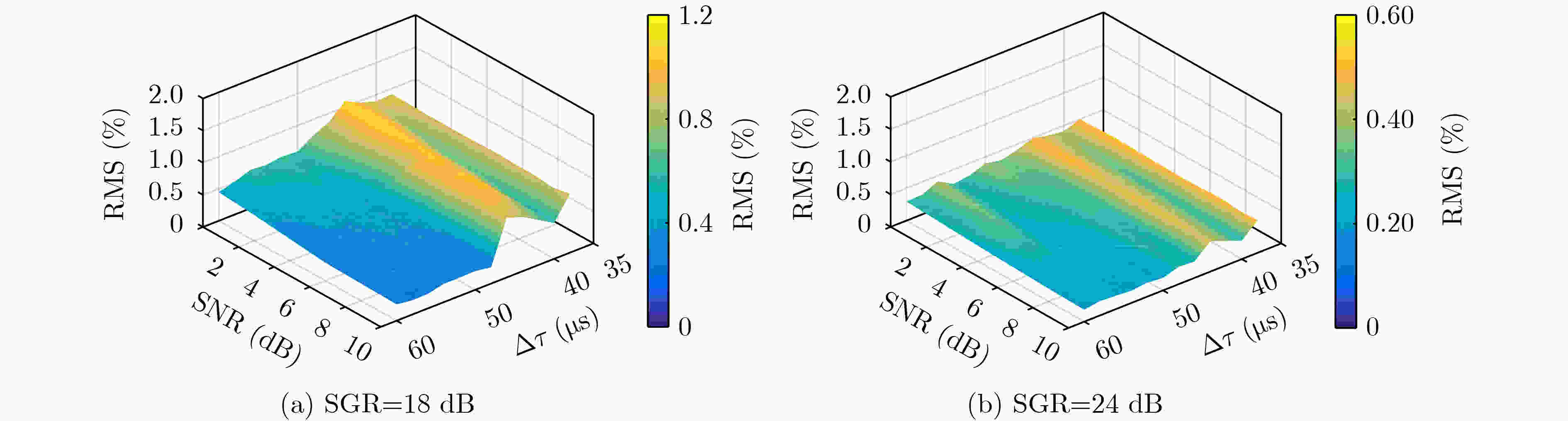


 下载:
下载:
