Solution of Graph Coloring Problem Based on FPGA
-
摘要: 图着色问题是在满足相邻顶点不能分配相同颜色且颜色数最少的约束条件下,将图的顶点划分为不相交的集合,且每个集合中的顶点分配相同的颜色。由于图着色问题属于NP-完全问题,求解图着色问题的算法复杂度会随顶点个数的增加呈指数级增长。当顶点个数非常大时,通用处理器求解图着色问题的性能将会显著下降。因此,该文基于现场可编程逻辑门阵列(FPGA)实现求解图着色算法的专用硬件加速器。首先依据FPGA模块化的设计思路提出并实现了基于回溯法的图着色问题求解的硬件架构;其次分析了FPGA内部消耗资源与图着色顶点数之间的关系;最后利用通用异步收发传输器协议实现了通用处理器与FPGA的通信。实验结果表明,相比于在通用处理器上利用软件实现图着色算法,基于FPGA所实现的图着色算法运行时间减少了一个数量级。除此之外,FPGA内部消耗资源数与顶点个数呈线性关系,且每次迭代时FPGA运算所消耗的时间与顶点个数无关。Abstract: Graph coloring problem divides the vertices of the graph into disjoint sets and the vertices in each set are assigned by the same color under the constraints that adjacent vertices can not be assigned the same color and the number of colors is the smallest. Since graph coloring problem belongs to the class of NP-complete problems, the complexity for solving the graph coloring problem increases exponentially with the number of vertices. The performance of solving graph coloring problem by general-purpose processors decreases significantly when the number of vertices is large enough. This paper implements a dedicated hardware accelerator for solving graph coloring problem based on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). Firstly, by utilizing the rule of FPGA modular design, the hardware architecture for solving graph coloring problem based on the backtracking is proposed and implemented. Secondly, the relationship between the resource consumption of FPGA and the number of vertices is analyzed. Finally, the general-purpose processor and FPGA can communicate through universal asynchronous transmitter-receiver protocol. The experimental results show that the running time of graph coloring algorithm based on FPGA is about an order of magnitude smaller than that of graph coloring algorithm based on software on general-purpose processors. Besides, the resource consumption of FPGA is linear with the number of vertices and the time consumption at each iteration is independent of the number of vertices.
-
Key words:
- Graph coloring problem /
- Backtracking /
- FPGA
-
表 1 FPGA资源消耗
图的顶点个数 12 16 32 64 128 256 512 LE 499 547 717 1045 1700 2997 5580 寄存器 262 323 439 667 1119 2019 3815 -
[1] GUO Jianding. Theoretical research on graph coloring: Application to resource allocation in device-to-device 4G radio system (LTE)[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté, 2018. [2] ELUMALAI A. Graph theory applications in computer science and engineering[J]. Malaya Journal of Matematik, 2020, S(2): 4025–4027. doi: 10.26637/MJM0S20/1043 [3] PODDAR N and MONDAL B. An instruction on course timetable scheduling applying graph coloring approach[J]. International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 2018, 9(2): 23939–23945. doi: 10.24327/ijrsr.2018.0902.1567 [4] DE LIMA A M and CARMO R. Exact algorithms for the graph coloring problem[J]. Revista de Informática Teórica e Aplicada, 2018, 25(4): 57–73. doi: 10.22456/2175-2745.80721 [5] VENKATASUBRAMANIAN M. Failure evasion: Statistically solving the NP complete problem of testing difficult-to-detect faults[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Auburn University, 2016. [6] LAWLER E L. A note on the complexity of the chromatic number problem[J]. Information Processing Letter, 1976, 5(3): 66–67. doi: 10.1016/0020-0190(76)90065-X [7] EPPSTEIN D. Small maximal independent sets and faster exact graph coloring[J]. Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applications, 2003, 7(2): 131–140. doi: 10.7155/jgaa.00064 [8] BYSKOV J M. Chromatic number in time O(2.4023n): Using maximal independent sets[R]. BRICS Report Series RS-02-45, 2002. [9] BRÉLAZ D. New methods to color the vertices of a graph[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(4): 251–256. doi: 10.1145/359094.359101 [10] MEHROTRA A and TRICK M A. A column generation approach for graph coloring[J]. Informs Journal on Computing, 1996, 8(4): 344–354. doi: 10.1287/ijoc.8.4.344 [11] MARAPPAN R and SETHUMADHAVAN G. Complexity analysis and stochastic convergence of some well-known evolutionary operators for solving graph coloring problem[J]. Mathematics, 2020, 8(3): 303. doi: 10.3390/math8030303 [12] GUI Chuangyi, ZHENG Long, HE Bingsheng, et al. A survey on graph processing accelerators: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2019, 34(2): 339–371. doi: 10.1007/s11390-019-1914-z [13] BROWN S. FPGA architectural research: A survey[J]. IEEE Design & Test of Computers, 1996, 13(4): 9–15. doi: 10.1109/54.544531 [14] CHINNERY D and KEUTZER K. Closing the Gap Between ASIC & Custom: Tools and Techniques for High-Performance ASIC Design[M]. Boston, USA: Springer, 2002: 1–414. [15] BESTA M, STANOJEVIC D, DE FINE LICHT J, et al. Graph processing on FPGAs: Taxonomy, survey, challenges[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06697.pdf, 2021. [16] 许进. 极大平面图理论(上册: 结构-构造-着色)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.XU Jin. Theory of Maximal Planar Graph (Volume One: Structure-Construction-Colorings)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. [17] FAZAKAS A, NEAG M, and FESTILA L. Block RAM versus distributed RAM implementation of SVM Classifier on FPGA[C]. Proceedings of 2006 International Conference on Applied Electronics, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 2006: 43–46. [18] JUNGK B and STÖTTINGER M. Serialized lightweight SHA-3 FPGA implementations[J]. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2019, 71: 102857. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2019.102857 [19] CLIFFORD W. Introduction to FPGA acceleration[EB/OL]. https://www.stemmer-imaging.com/media/uploads/websites/documents-/tech-tips/en_GB-TechTip-_Intoduction-to-FPGA-acceleration-20110211.pdf, 2021. [20] TRIMBERGER S, ROWSON J, LANG C, et al. A structured design methodology and associated software tools[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 1981, 28(7): 618–634. doi: 10.1109/TCS.1981.1085035 [21] LEWIS D, AHMED E, BAECKLER G, et al. The stratix II logic and routing architecture[C]. Proceedings of the 2005 ACM/SIGDA 13th International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, USA, 2005: 14–20. [22] Intel stratix 10 GX/SX product table[EB/OL]. https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/programmable/us/en/pdfs/literature/pt/stratix-10-product-table.pdf, 2021. -





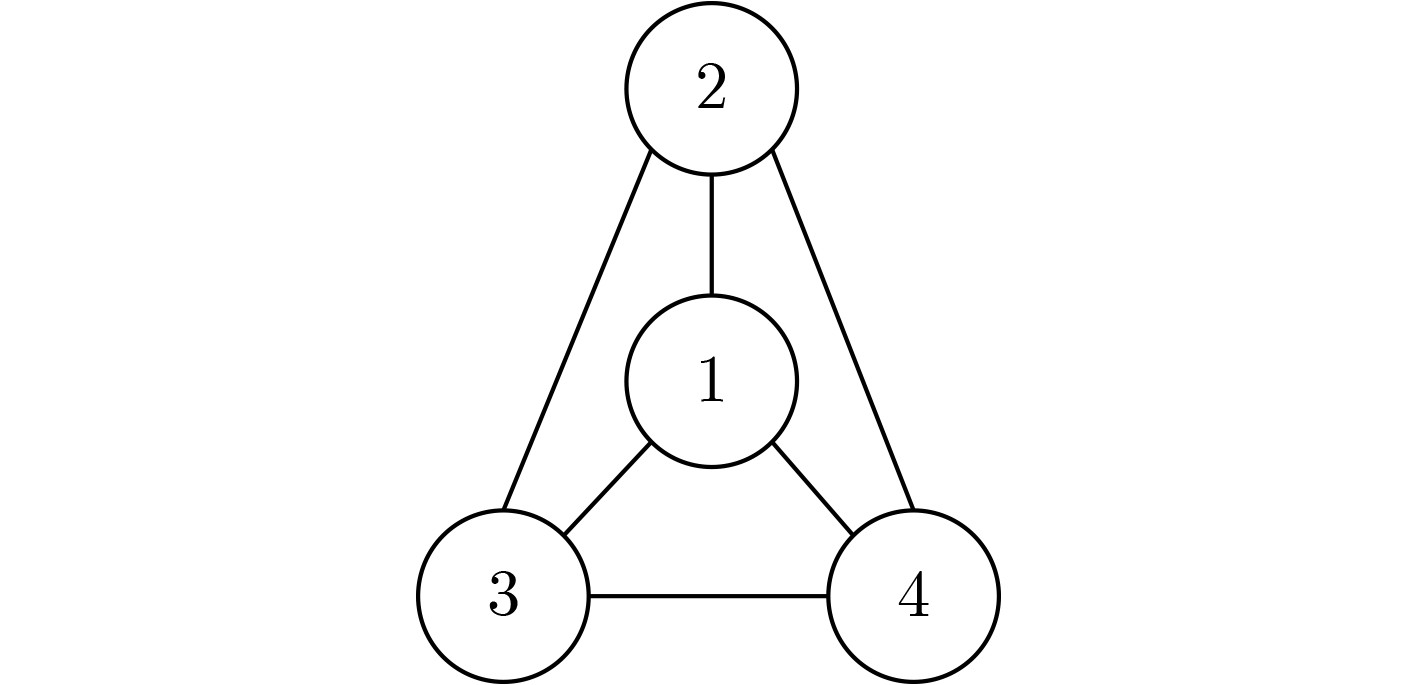
 下载:
下载:
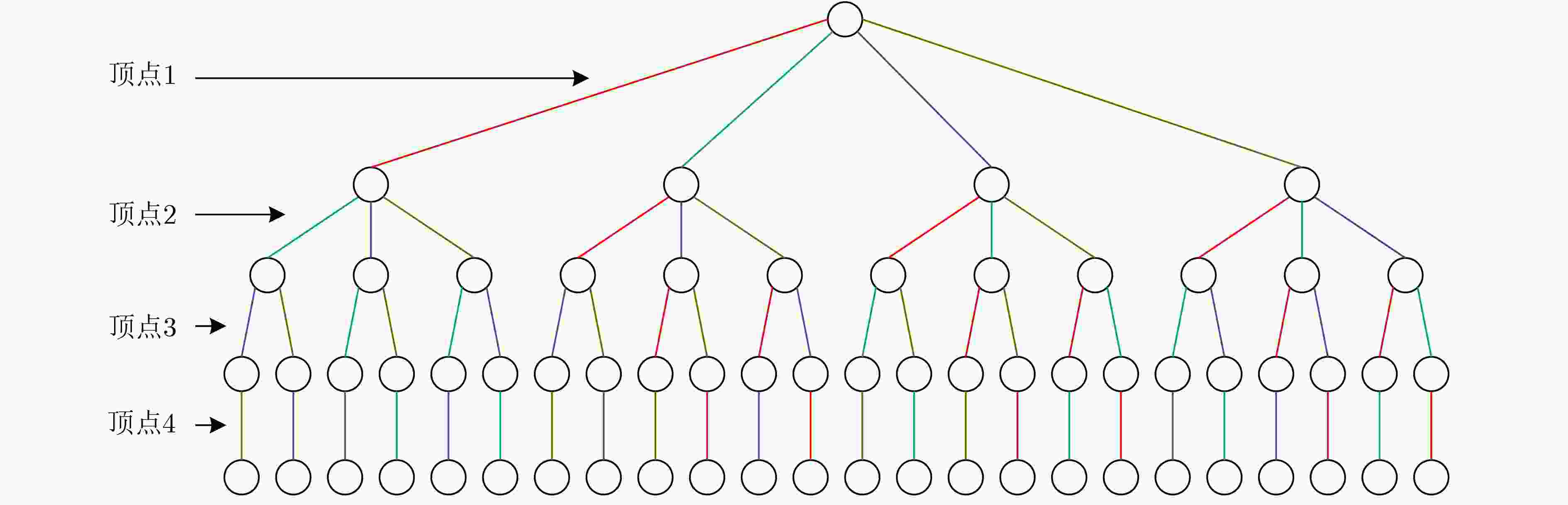
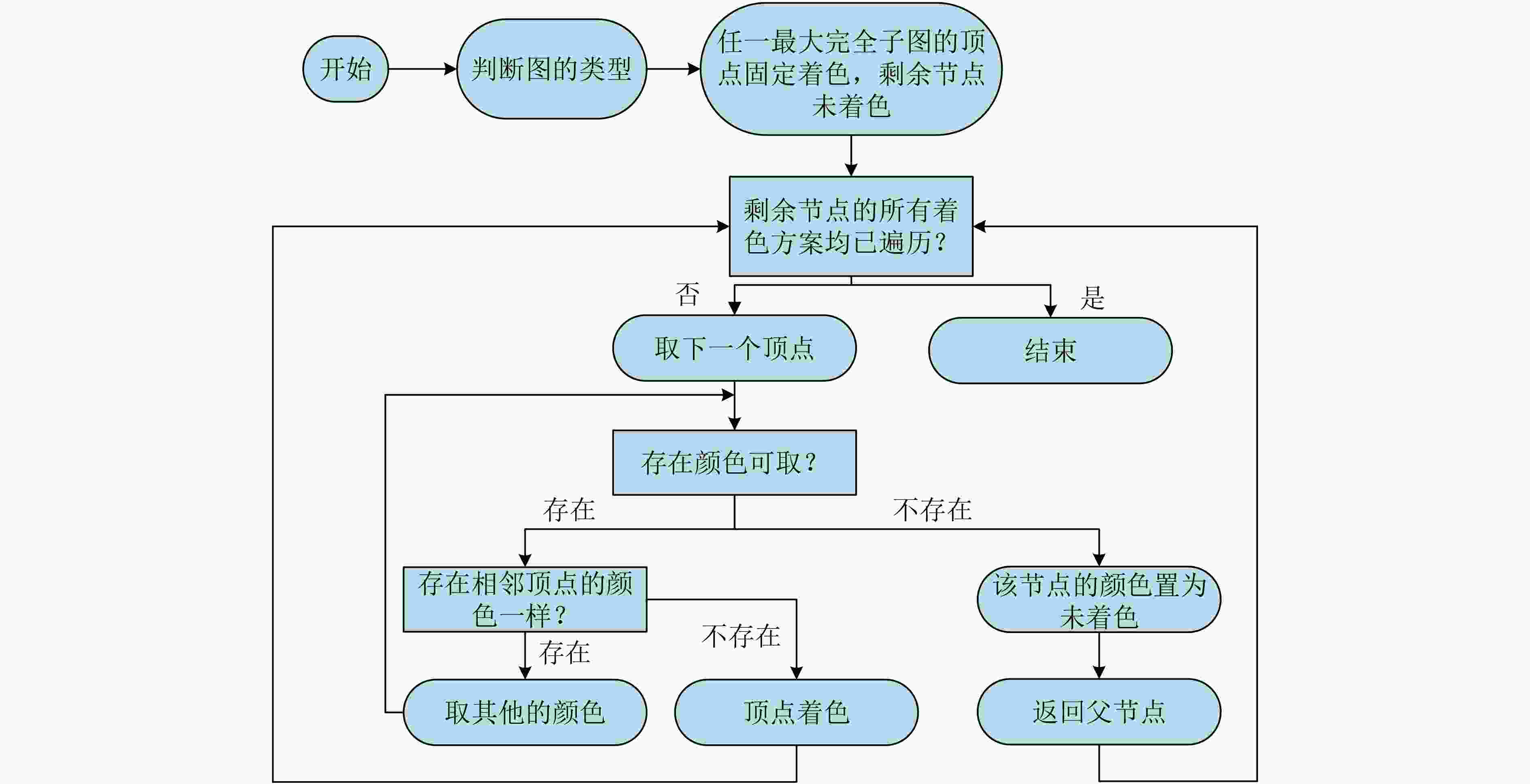
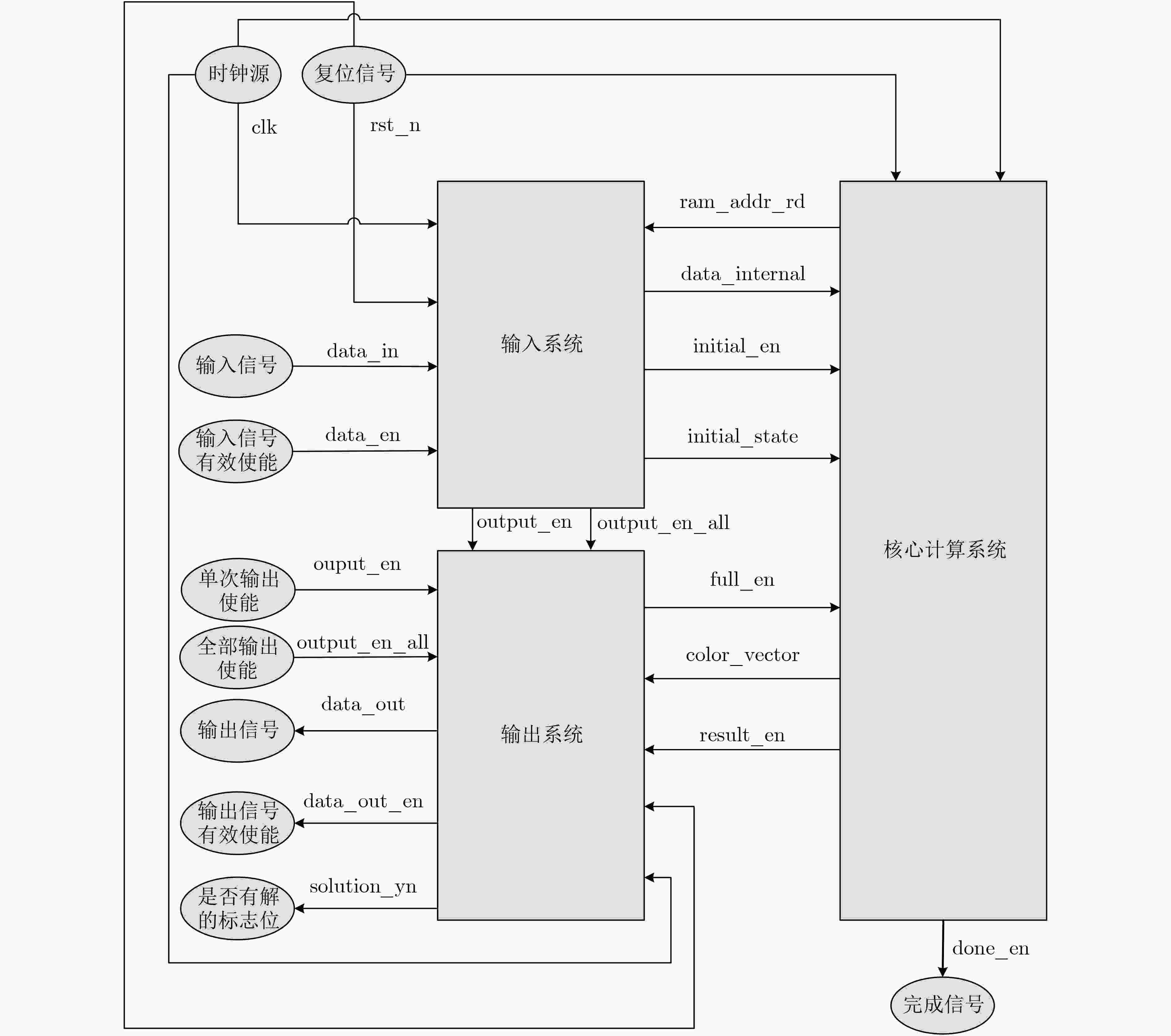




 下载:
下载:
