Research on Non-ideal Wireless Orbital Angular Momentum Multiplexing Communication System Based on Phase Compensation
-
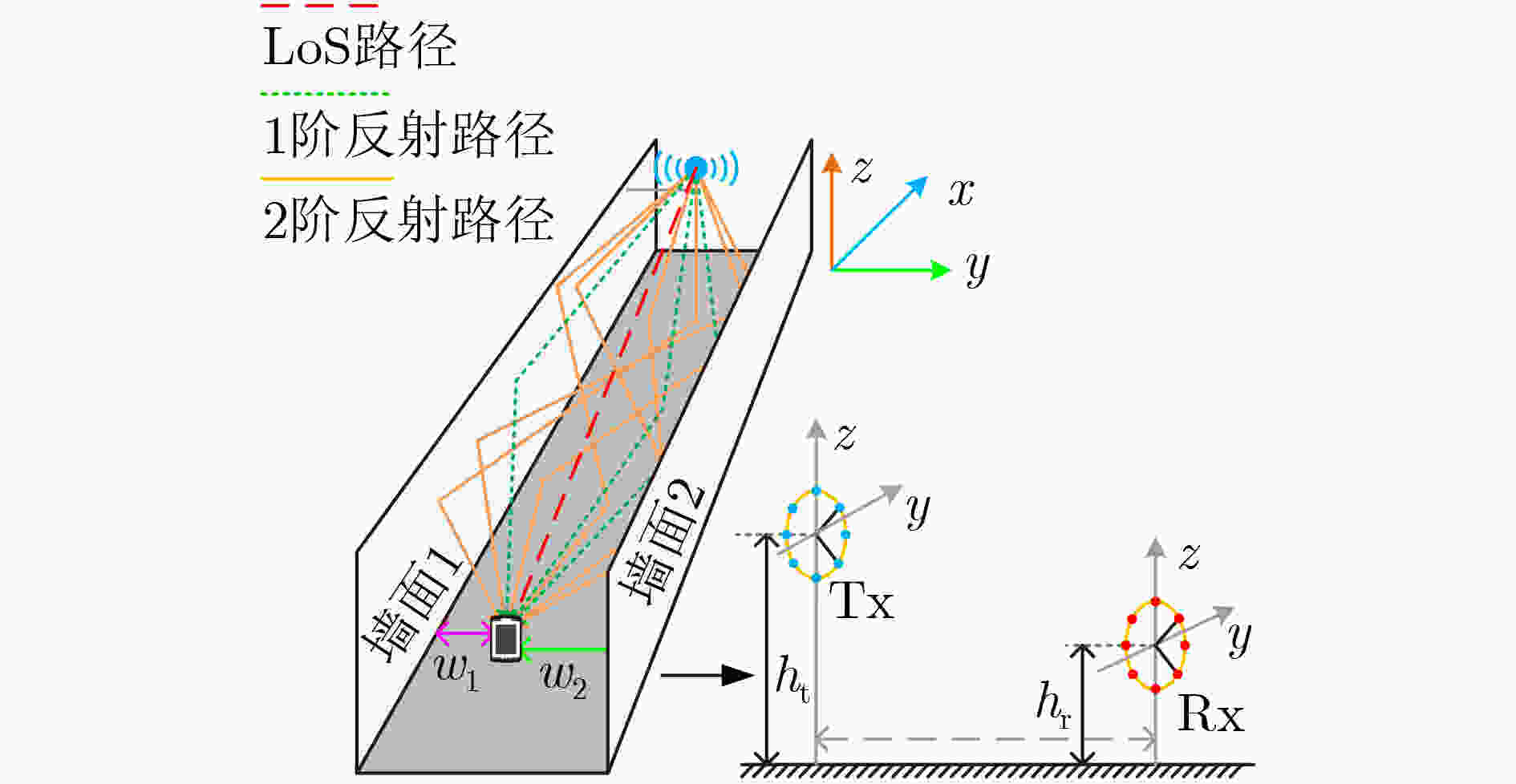
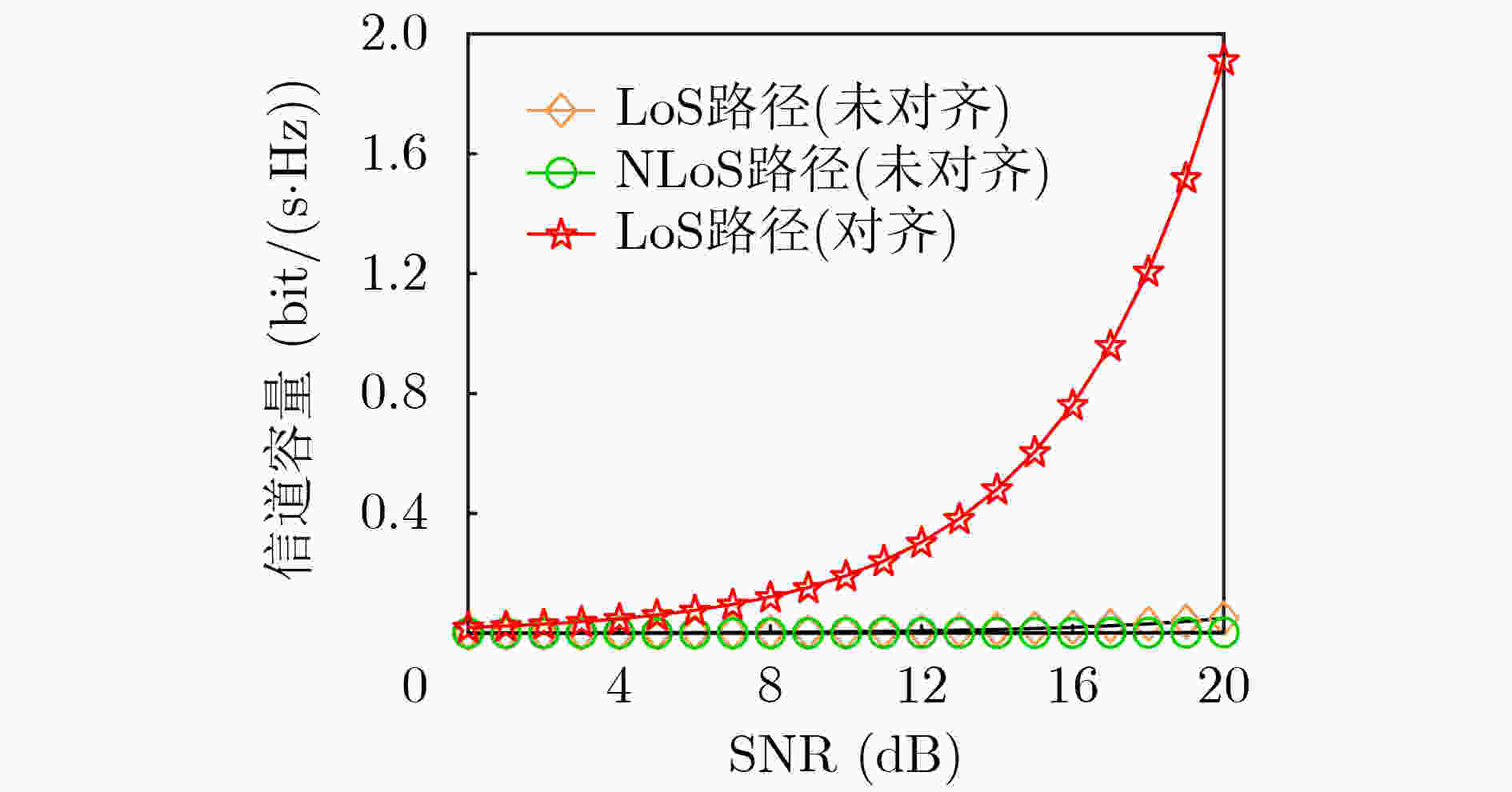
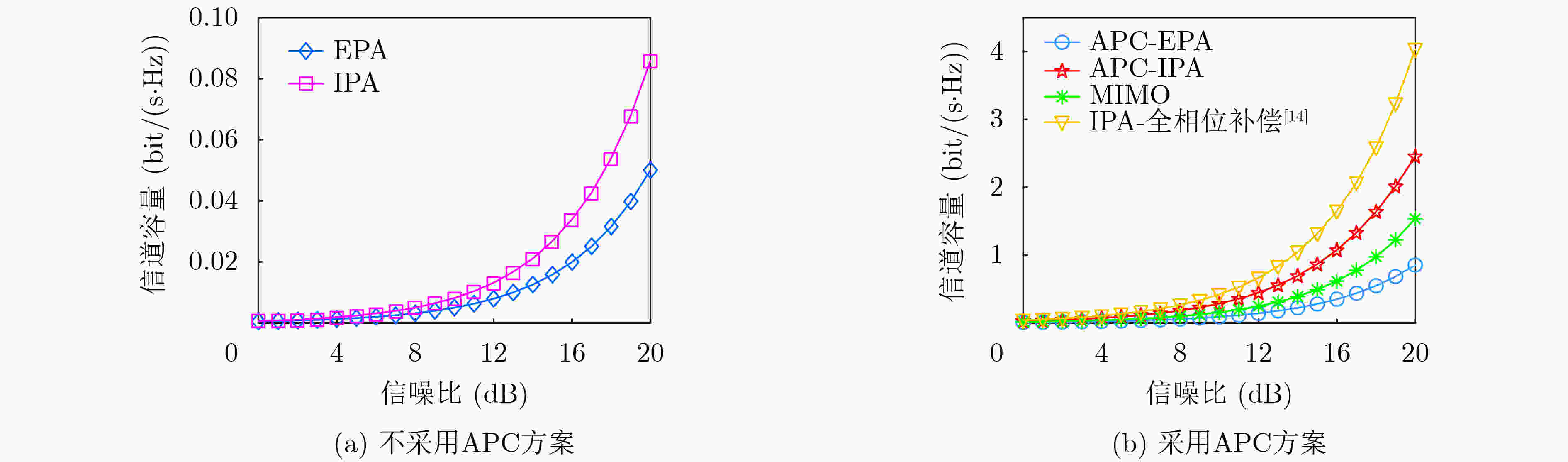
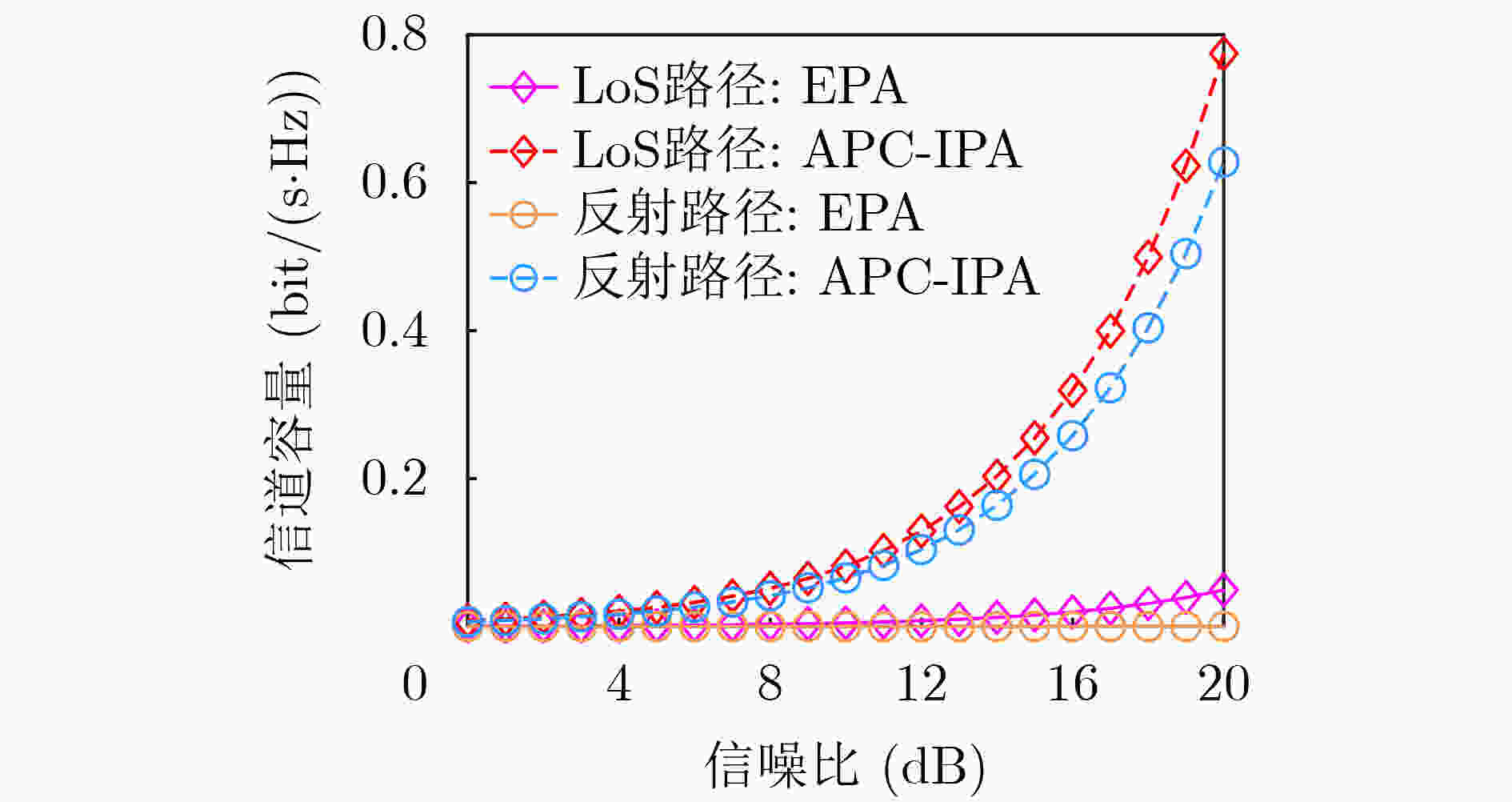
摘要: 电磁波轨道角动量各模态间满足严格正交性,为无线通信系统提供了一个新的复用维度。当前无线轨道角动量通信的研究仍集中于理想视距(LoS)场景,在实际通信场景中,多径效应和非对齐效应等非理想传输情况通常是无法避免的,这会使得无线轨道角动量多入多出(OAM-MIMO)通信系统的性能遭受较大损失。为提升非理想无线OAM-MIMO通信系统性能,该文建模了一种更加符合实际传输场景的毫米波OAM-MIMO 10射线信道模型;然后评估了多径效应和非对齐效应带来的性能损失问题;最后,提出了一种低复杂度的平均相位补偿与迭代功率分配(APC-IPA)联合优化方案来消除非对齐和多径效应造成的相位偏差,提升系统信道容量。仿真结果表明:在同时遭受非对齐和多径效应时,所提APC-IPA联合方案能够有效地提升系统信道容量。Abstract: The Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) satisfies orthogonality between each mode, which provides a new multiplexing dimension for wireless communication systems. At present, OAM communication still focuses on the Line of Sight (LoS) scenarios. The OAM Multiple Input Multiple Output (OAM-MIMO) communication system performance can be deteriorated by the non-ideal transmission conditions such as multipath and misalignment effects in the real scenarios. In order to improve the performance of the OAM-MIMO communication system, a millimeter-wave OAM-MIMO ten-rays channel in the actual transmission scenario is modelled in this paper; Then, the performance loss caused by multipath and misalignment effects are evaluated; Finally, a low-complexity Average Phase Compensation and Iterative Power Allocation (APC-IPA) joint optimization scheme is proposed to eliminate the phase deviation from the misalignment and multipath effects, and improve the capacity. The simulation results show that the proposed APC-IPA joint scheme increase effectively the channel capacity of the system when suffering from misalignment and multipath effects.
-
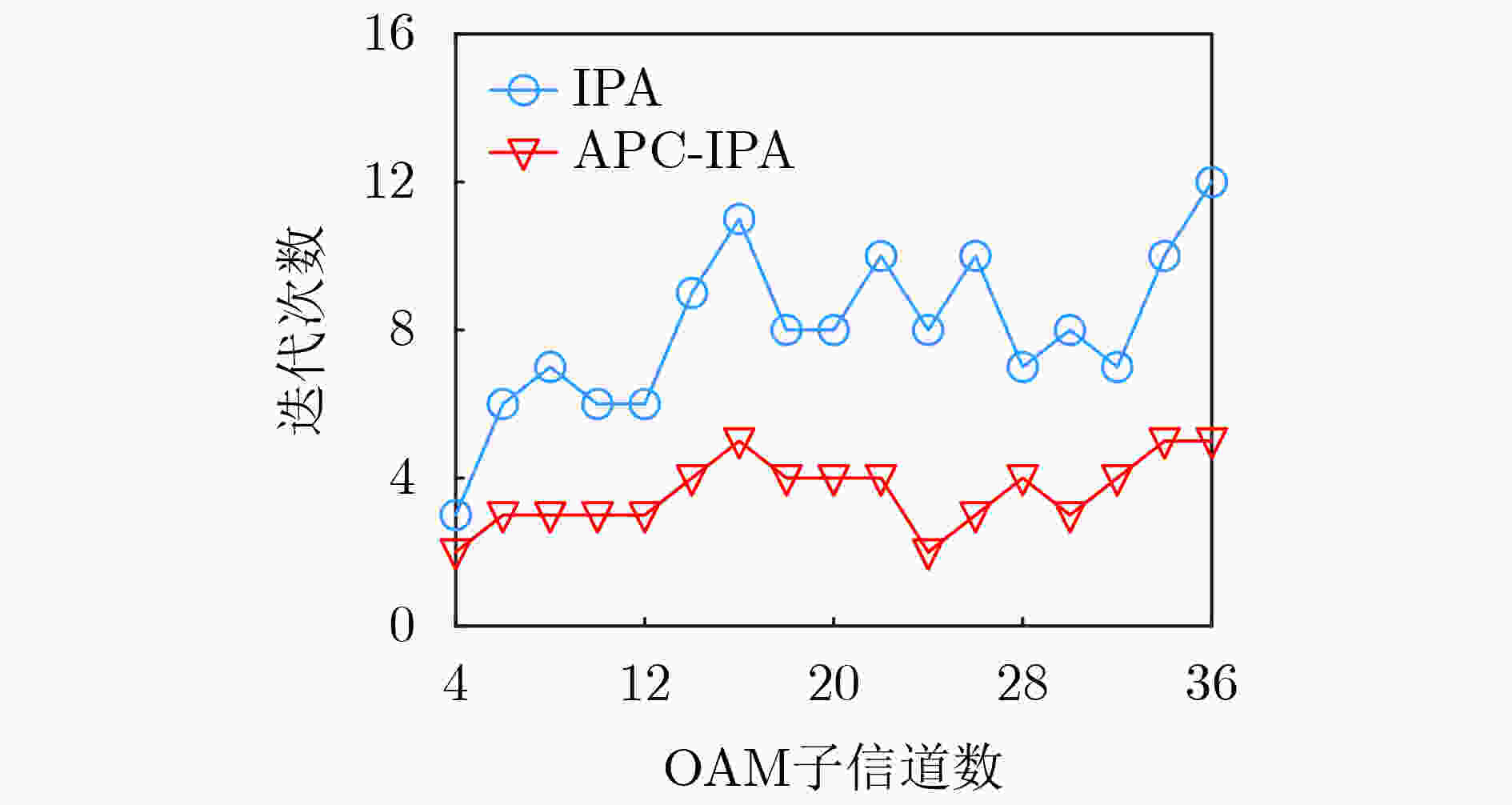
表 1 IPA算法
初始化:L, $ {P_{\text{t}}} $, $ {{\mathbf{H}}_{{\text{OAM}}}} $, ε, i = 1 (1) 根据式(30)计算相位补偿矩阵Q; (2) 根据式(31)更新OAM信道矩阵$ {{\mathbf{H}}_{{\text{OAM}}}} $; (3) For l = 1:L (4) 计算$ \rho _l^{(0)} = {{{P_{\text{t}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{P_{\text{t}}}} N}} \right. } N} $,根据式(16)计算$ {\text{SINR}}_l^{(0)} $; (5) End for (6) 根据式(17)和式(32)计算$ {C^{(0)}} $和$ {u^{(0)}} $; (7) For l = 1:L (8) 根据式(16)和式(33)更新$ {\text{SINR}}_l^{(i)} $和$ \rho _l^{(i)} $; (9) End for (10) 根据式(17)更新$ {C^{(i)}} $; (11) If $ {C^{(i)}} - {C^{(i - 1)}} > \varepsilon $,then (12) 根据式(32)更新$ {u^{(i)}} $; (13) i = i+1,回到步骤(7); (14) Else (15) Break; (16) End if (17) 输出最终的功率分配方案$ \left\{ {{\rho _1},{\rho _2},\cdots,{\rho _L}} \right\} $。 -
[1] 孙学宏, 李强, 庞丹旭, 等. 轨道角动量在无线通信中的研究新进展综述[J]. 电子学报, 2015, 43(11): 2305–2314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.11.025SUN Xuehong, LI Qiang, PANG Danxu, et al. New research progress of the orbital angular momentum technology in wireless communication: A survey[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(11): 2305–2314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.11.025 [2] 廖希, 周晨虹, 王洋, 等. 面向无线通信的轨道角动量关键技术研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1666–1677. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190372LIAO Xi, ZHOU Chenhong, WANG Yang, et al. A survey of orbital angular momentum in wireless communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1666–1677. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190372 [3] WANG Chengxiang, HUANG Jie, WANG Haiming, et al. 6G wireless channel measurements and models: Trends and challenges[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2020, 15(4): 22–32. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2020.3018436 [4] 赵林军, 张海林, 刘乃安. 涡旋电磁波无线通信技术的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(11): 3075–3085. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200899ZHAO Linjun, ZHANG Hailin, and LIU Naian. Research status of vortex electromagnetic wave wireless communication technologies[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(11): 3075–3085. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200899 [5] EDFORS O and JOHANSSON A J. Is orbital angular momentum (OAM) based radio communication an unexploited area?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(2): 1126–1131. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2011.2173142 [6] 王洋, 崔健, 廖希, 等. 基于信号检测的光无线轨道角动量复用系统研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(11): 3156–3165. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200955WANG Yang, CUI Jian, LIAO Xi, et al. Research on optical wireless orbital angular momentum multiplexing system based on signal detection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(11): 3156–3165. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200955 [7] ALLEN L, BEIJERSBERGEN M W, SPREEUW R J C, et al. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(11): 8185–8189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.8185 [8] THIDÉ B, THEN H, SJÖHOLM J, et al. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(8): 087701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.087701 [9] TAMBURINI F, MARI E, SPONSELLI A, et al. Encoding many channels on the same frequency through radio vorticity: First experimental test[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2012, 14: 033001. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/14/3/033001 [10] OPARE K A and KUANG Yujun. Performance of an ideal wireless orbital angular momentum communication system using multiple-input multiple-output techniques[C]. 2014 International Conference on Telecommunications and Multimedia, Heraklion, Greece, 2014: 144–149. [11] REN Yongxiong, LI Long, XIE Guodong, et al. Line-of-sight millimeter-wave communications using orbital angular momentum multiplexing combined with conventional spatial multiplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(5): 3151–3161. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2675885 [12] JIE Wenjun, WANG Yang, HU Tao, et al. Propagation model for UCA-based OAM communications in six-ray canyon channels[C]. The 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020: 1–4. [13] YAN Yan, LI Long, XIE Guodong, et al. Multipath effects in millimetre-wave wireless communication using orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 33482. doi: 10.1038/srep33482 [14] LIANG Liping, CHENG Wenchi, ZHANG Wei, et al. Joint OAM multiplexing and OFDM in sparse multipath environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 3864–3878. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2966787 [15] SHIN D, PARK E, KANG J, et al. Identification of non-ideal receiver condition for orbital angular momentum transmission[C]. The 2014 IEEE 79th Vehicular Technology Conference, Seoul, Korea, 2014: 1–5. [16] CHEN Rui, XU Hui, MORETTI M, et al. Beam steering for the misalignment in UCA-based OAM communication systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(4): 582–585. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2797931 [17] JING Haiyue, CHENG Wenchi, and XIA Xianggen. A simple channel independent beamforming scheme with parallel uniform circular array[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(3): 414–417. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2892114 [18] ZHENG Shilie, DONG Ruofan, ZHANG Zhuofan, et al. Non-line-of-sight channel performance of plane spiral orbital angular momentum MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 25377–25384. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2766078 [19] HU Tao, WANG Yang, LIAO Xi, et al. OAM-based beam selection for indoor millimeter wave MU-MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(5): 1702–1706. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3049457 [20] HU Tao, WANG Yang, MA Bo, et al. Orbit angular momentum MIMO with mode selection for UAV-assisted A2G networks[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(8): 2289. doi: 10.3390/s20082289 [21] ZHANG Weite, ZHENG Shilie, HUI Xiaonan, et al. Mode division multiplexing communication using microwave orbital angular momentum: An experimental study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(2): 1308–1318. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2645199 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
