ANN Feature Vector Extraction Based Attack Method for Flip-Flop Based Arbiter Physical Unclonable Function
-
摘要: 为评估物理不可克隆函数(PUF)的安全性,需针对不同的PUF结构设计相应的攻击方法。该文通过对强PUF电路结构和工作机理的研究,利用人工神经网络(ANN)提出一种针对触发器-仲裁器物理不可克隆函数(FF-APUF)的有效攻击方法。首先,根据FF-APUF电路结构,利用多维数组构建电路延时模型;然后,对FF-APUF的二进制激励进行邻位划分,将划分后的激励转换为十进制并表示为行向量,实现特征向量提取;最后,基于提取的特征向量利用ANN构建攻击模型并通过后向传播算法获得最优参数。实验结果表明,相同条件下攻击预测率均高于其他3种常用的机器学习方法,尤其当激励响应对(CRP)数量较少、激励位数较多时,优势更加明显。当激励位数为128、CRP个数为100和500时,平均攻击预测率分别提高36.0%和16.1%。此外,该方法具有良好的鲁棒性和可扩展性,不同噪声系数下攻击预测率与可靠性相差最大仅0.32%。
-
关键词:
- 物理不可克隆函数 /
- 触发器-仲裁器物理不可克隆函数 /
- 人工神经网络 /
- 特征向量提取
Abstract: In order to evaluate the security of Physical Unclonable Function (PUF), it is necessary to put forward corresponding attack methods for different PUF structures. By studying the structure and working mechanism of Flip-Flop based Arbiter Physical Unclonable Function (FF-APUF), an effective attack method against FF-APUF is proposed based on Artificial Neural Network (ANN) in this paper. Firstly, according to the circuit structure, the delay model of FF-APUF is established by using multidimensional array. Secondly, all binary challenge bits are divided by two adjacent bits which are converted to a decimal, and then the challenges are expressed as a row vector to extract the feature vector. Finally, based on the extracted feature vectors, the attack model is constructed by ANN, and the optimal parameters are obtained by back propagation algorithm. The experimental results show that the prediction accuracy of the proposed method is higher than other three common machine learning methods under the same conditions. The attack advantage is more obvious, especially when the number of Challenge Response Pairs (CRP) is less and the bit number of challenges is large. For example, when the number of challenge bit is 128, and the number of CRPs is 100 and 500, the average attack prediction accuracy increased by 36.0% and 16.1% respectively. In addition, the proposed method has good robustness and scalability, and the maximum difference of attack prediction rate and reliability is only 0.32% under different noise. -
表 1 ANN特性参数及选取
特性参数 参数选取 初始化权值 随机正态分布 初始化偏置 零向量 优化器 Adam或RMSProp 损失函数 最小均方误差 正则化 L2 输出层激活函数 Sigmoid 表 2 攻击方法及预测率(%)
CRP个数 激励位数 APUF FF-APUF LR SVM GNB 本文方法 LR SVM GNB 本文方法 100 32 81.7 83.7 82.7 90.1 77.3 76.0 73.6 81.4 64 77.7 74.6 78.6 80.3 66.4 77.0 75.7 80.1 128 74.0 70.3 73.3 76.1 59.6 57.3 57.0 78.8 500 32 94.0 95.5 87.0 97.1 93.1 92.4 87.4 96.8 64 93.7 92.4 84.6 96.2 88.3 87.1 82.4 95.7 128 85.5 85.5 80.9 89.6 79.9 76.8 74.1 89.2 1000 32 97.5 97.9 92.2 99.5 97.0 97.3 90.2 99.0 64 95.8 95.1 89.9 97.5 94.3 93.1 86.9 95.5 128 93.4 91.7 86.2 93.5 89.2 87.1 81.5 91.5 2000 32 98.7 98.4 93.4 99.3 98.3 98.4 92.1 99.5 64 97.8 97.1 92.8 98.8 96.7 96.8 90.3 97.8 128 95.4 95.4 89.4 97.0 94.2 93.2 85.8 96.5 5000 32 99.4 99.2 95.6 99.7 99.0 99.2 95.5 99.6 64 99.0 98.8 93.4 99.2 98.5 98.5 94.1 98.9 128 98.2 98.2 92.5 98.7 97.7 97.1 90.7 97.9 10000 32 99.7 99.4 96.7 99.9 99.4 99.4 94.7 99.7 64 99.3 99.1 95.8 99.6 99.2 99.2 94.4 99.6 128 99.0 98.9 95.2 99.4 98.6 98.7 94.0 99.0 表 3 所提方法相比其他方法预测率的提升比例(%)
CRP个数 激励位数 APUF FF-APUF LR SVM GNB 平均值 LR SVM GNB 平均值 100 32 10.3 7.6 8.9 9.0 5.3 7.1 10.6 7.7 64 3.3 7.6 2.2 4.4 20.6 4.0 5.8 10.2 128 2.8 8.3 3.8 5.0 32.2 37.5 38.2 36.0 500 32 3.3 1.7 11.6 5.5 4.0 4.8 10.8 6.5 64 2.7 4.1 13.7 6.8 8.4 9.9 16.1 11.5 128 4.8 4.8 10.8 6.8 11.6 16.1 20.4 16.1 1000 32 2.1 1.6 7.9 3.9 2.1 1.7 9.8 4.5 64 1.8 2.5 8.5 4.3 1.3 2.6 9.9 4.6 128 0.1 2.0 8.5 3.5 2.6 5.1 12.3 6.6 2000 32 0.6 0.9 6.3 2.6 1.2 1.1 8.0 3.5 64 1.0 1.8 6.5 3.1 1.1 1.0 8.3 3.5 128 1.7 1.7 8.5 4.0 2.4 3.5 12.5 6.2 5000 32 0.3 0.5 4.3 1.7 0.6 0.4 4.3 1.8 64 0.2 0.4 6.2 2.3 0.4 0.4 5.1 2.0 128 0.5 0.5 6.7 2.6 0.2 0.8 7.9 3.0 10000 32 0.2 0.5 3.3 1.3 0.3 0.3 5.3 2.0 64 0.3 0.5 4.0 1.6 0.4 0.4 5.5 2.1 128 0.4 0.5 4.4 1.8 0.4 0.3 5.3 2.0 表 4 不同噪声条件下FF-APUF可靠性和攻击预测率
CRP个数 激励位数 噪声系数α 0 0.0125 0.025 0.050 0.100 0.150 0.200 可靠性(%) 32 100.00 99.67 99.20 98.85 96.38 95.40 93.42 64 100.00 99.68 99.16 98.33 96.14 95.57 93.39 128 100.00 99.58 99.21 98.23 96.20 95.14 93.28 预测率(%) 32 99.94 99.57 98.91 98.57 96.11 94.28 93.31 64 99.86 99.41 98.09 98.08 95.68 95.54 93.12 128 99.80 99.59 99.10 98.27 95.23 95.06 92.62 -
[1] LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, MA Xuejiao, et al. A multimode configurable physically unclonable function with bit-instability-screening and power-gating strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2021, 29(1): 100–111. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3030945 [2] YAN Wei, TEHRANIPOOR F, and CHANDY J A. PUF-based fuzzy authentication without error correcting codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2017, 36(9): 1445–1457. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2016.2638445 [3] USMANI M A, KESHAVARZ S, MATTHEWS E, et al. Efficient PUF-based key generation in FPGAs using per-device configuration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2019, 27(2): 364–375. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2877438 [4] 汪鹏君, 李乐薇, 郑雁公, 等. 基于气敏传感器的高稳态物理不可克隆函数发生器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(6): 1596–1602. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201104WANG Pengjun, LI Lewei, ZHENG Yangong, et al. High steady-state physical unclonable function generator based on gas sensors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(6): 1596–1602. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201104 [5] 徐金甫, 吴缙, 李军伟, 等. 基于敏感度混淆机制的控制型物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1601–1609. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180775XU Jinfu, WU Jin, LI Junwei, et al. Controlled physical unclonable function research based on sensitivity confusion mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1601–1609. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180775 [6] LIM D. Extracting secret keys from integrated circuits[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2004. [7] RÜHRMAIR U, SÖLTER J, SEHNKE F, et al. PUF modeling attacks on simulated and silicon data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2013, 8(11): 1876–1891. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2013.2279798 [8] SUH G E and DEVADAS S. Physical unclonable functions for device authentication and secret key generation[C]. The 44th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Diego, USA, 2007: 9–14. doi: 10.1145/1278480.1278484. [9] MAITI A and SCHAUMONT P. Improving the quality of a physical unclonable function using configurable ring oscillators[C]. 2009 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Prague, Czech Republic, 2009: 703–707. doi: 10.1109/FPL.2009.5272361. [10] SAHOO D P, NGUYEN P H, MUKHOPADHYAY D, et al. A case of lightweight PUF constructions: Cryptanalysis and machine learning attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2015, 34(8): 1334–1343. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2448677 [11] NGUYEN P H, SAHOO D P, JIN Chenglu, et al. The interpose PUF: Secure PUF design against state-of-the-art machine learning attacks[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2019, 2019(4): 243–290. doi: 10.13154/tches.v2019.i4.243-290 [12] SAHOO D P, MUKHOPADHYAY D, CHAKRABORTY R S, et al. A multiplexer-based arbiter PUF composition with enhanced reliability and security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2018, 67(3): 403–417. doi: 10.1109/TC.2017.2749226 [13] GU Chongyan, LIU Weiqiang, CUI Yijun, et al. A Flip-Flop based Arbiter Physical Unclonable Function (APUF) design with high entropy and uniqueness for FPGA implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, To be published. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2019.2935465. [14] AWANO H, IIZUKA T, and IKEDA M. PUFNet: A deep neural network based modeling attack for physically unclonable function[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Sapporo, Japan, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2019.8702431. [15] SANTIKELLUR P and CHAKRABORTY R S. A computationally efficient tensor regression network-based modeling attack on XOR arbiter PUF and its variants[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2021, 40(6): 1197–1206. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.3032624 [16] SHI Junye, LU Yang, and ZHANG Jiliang. Approximation attacks on strong PUFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2020, 39(10): 2138–2151. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2019.2962115 [17] CHATTERJEE D, MUKHOPADHYAY D, and HAZRA A. Interpose PUF can be PAC learned[OL]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343524875_Interpose_PUF_can_be_PAC_Learned?channel=doi&linkId=5f2e86d5458515b7290d567f&showFulltext=true. 2020. [18] CHAKRABORTY R S, JELDI R R, SAHA I, et al. Binary decision diagram assisted modeling of FPGA-based physically unclonable function by genetic programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2017, 66(6): 971–981. doi: 10.1109/TC.2016.2603498 -





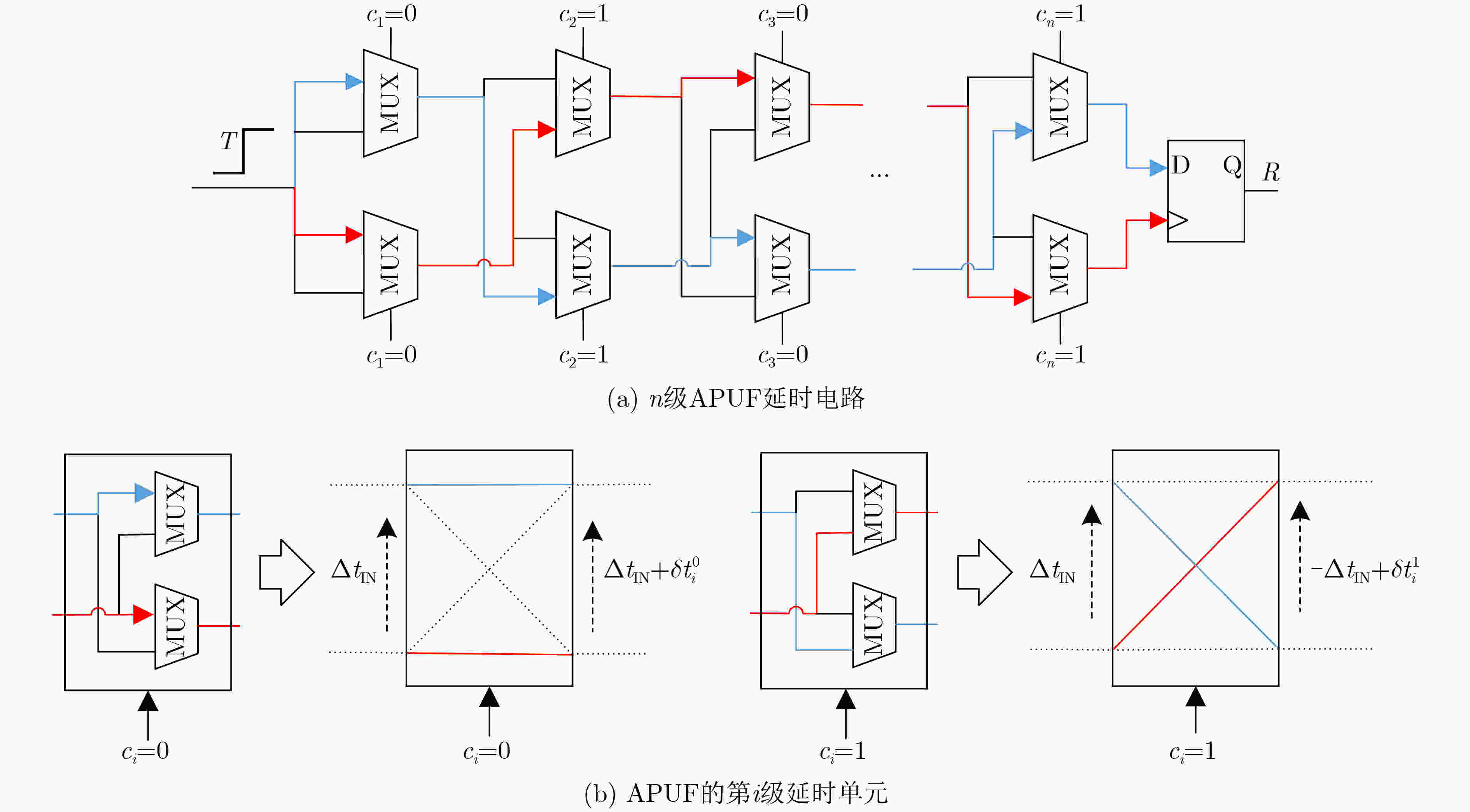
 下载:
下载:
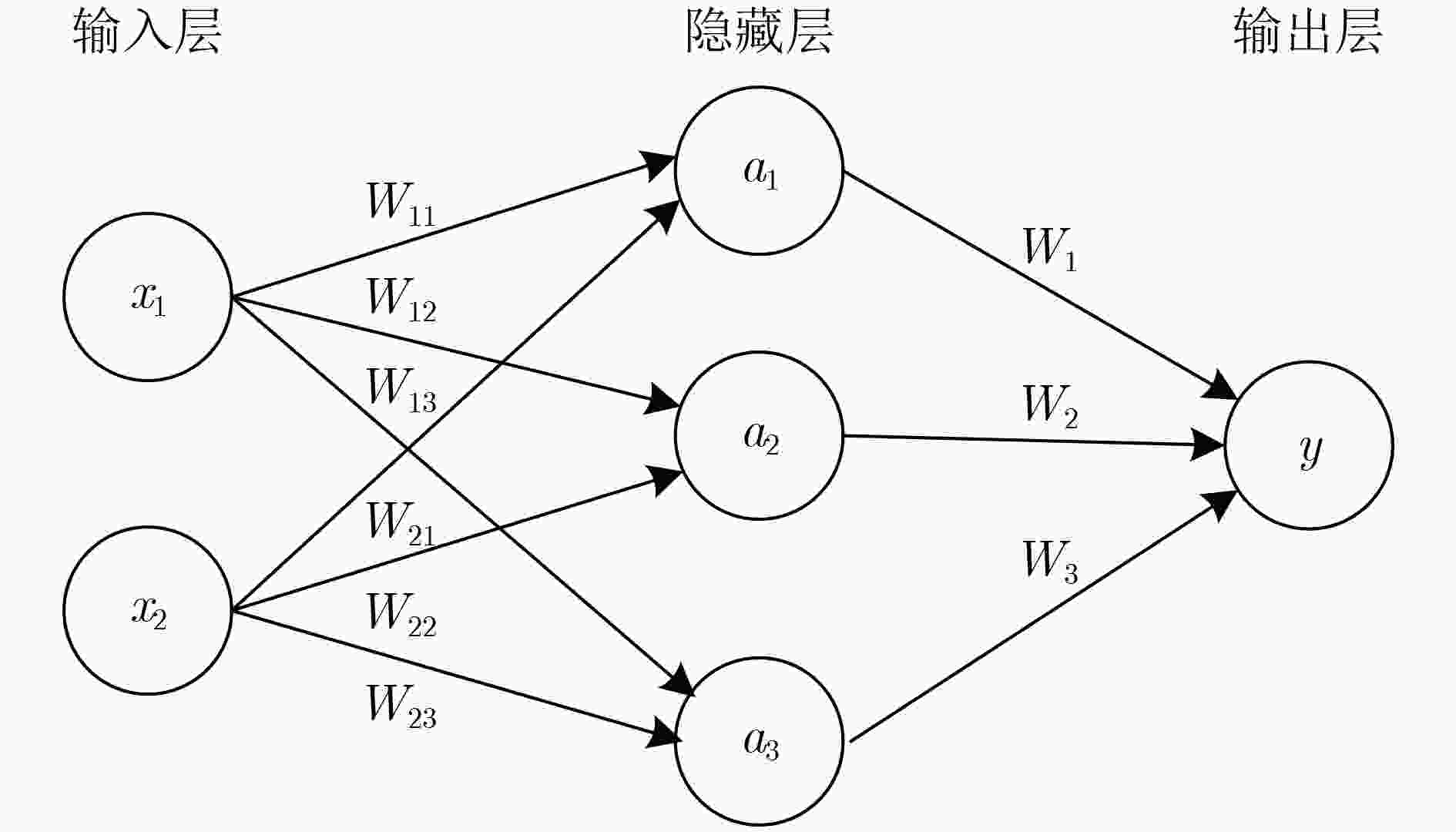
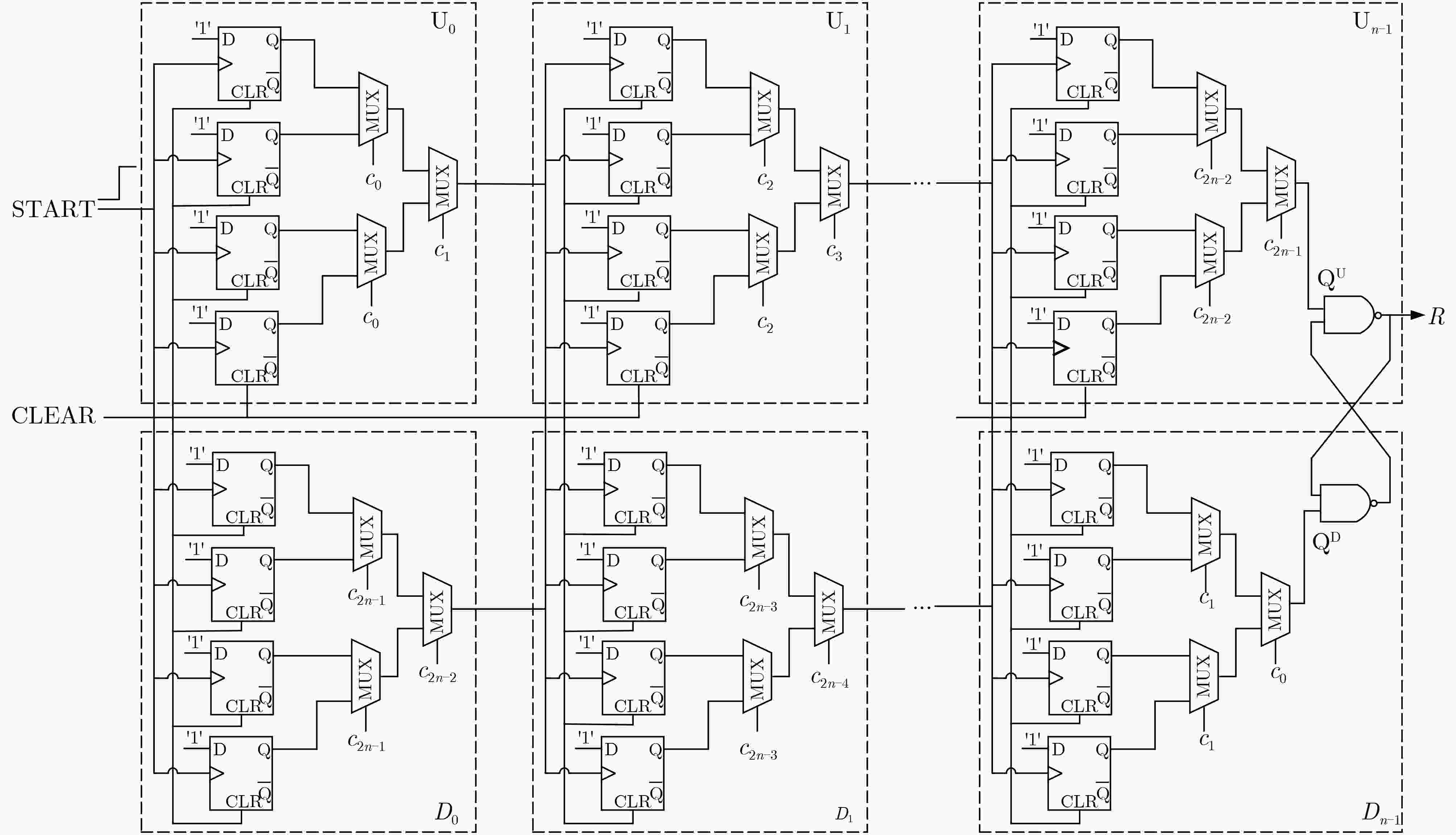
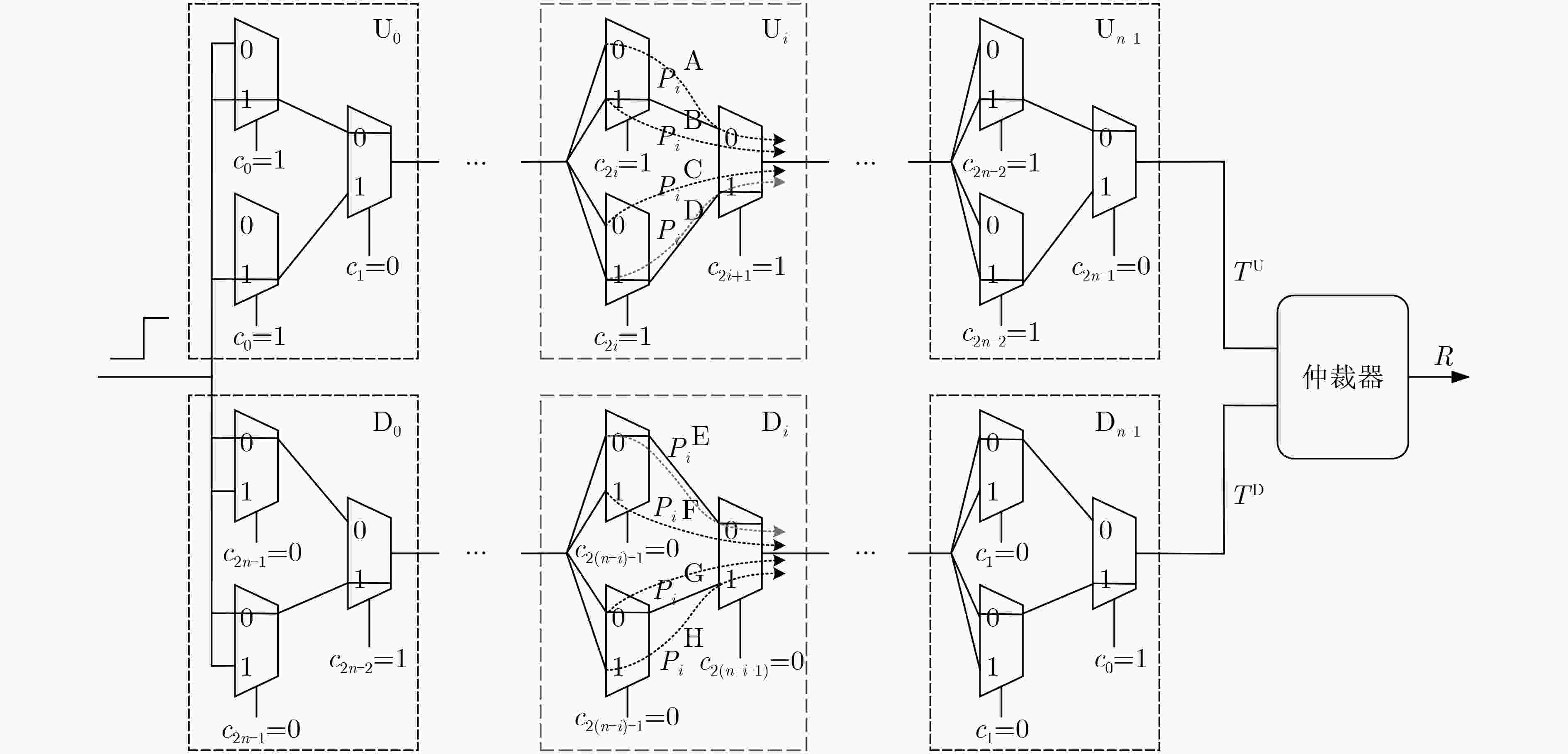
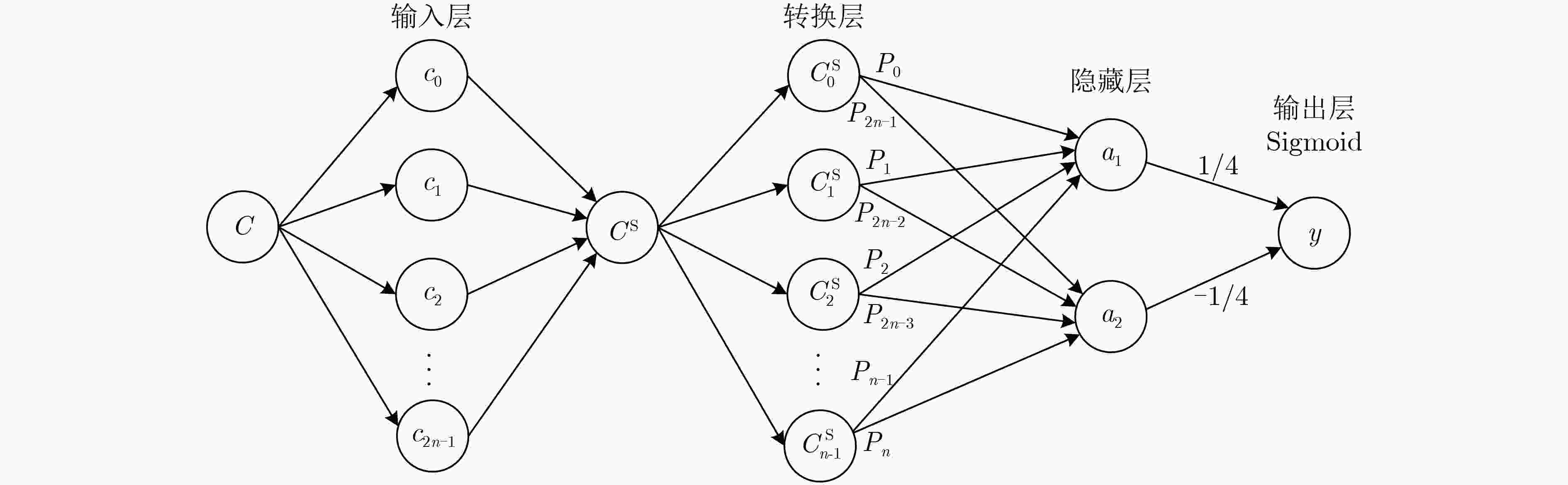
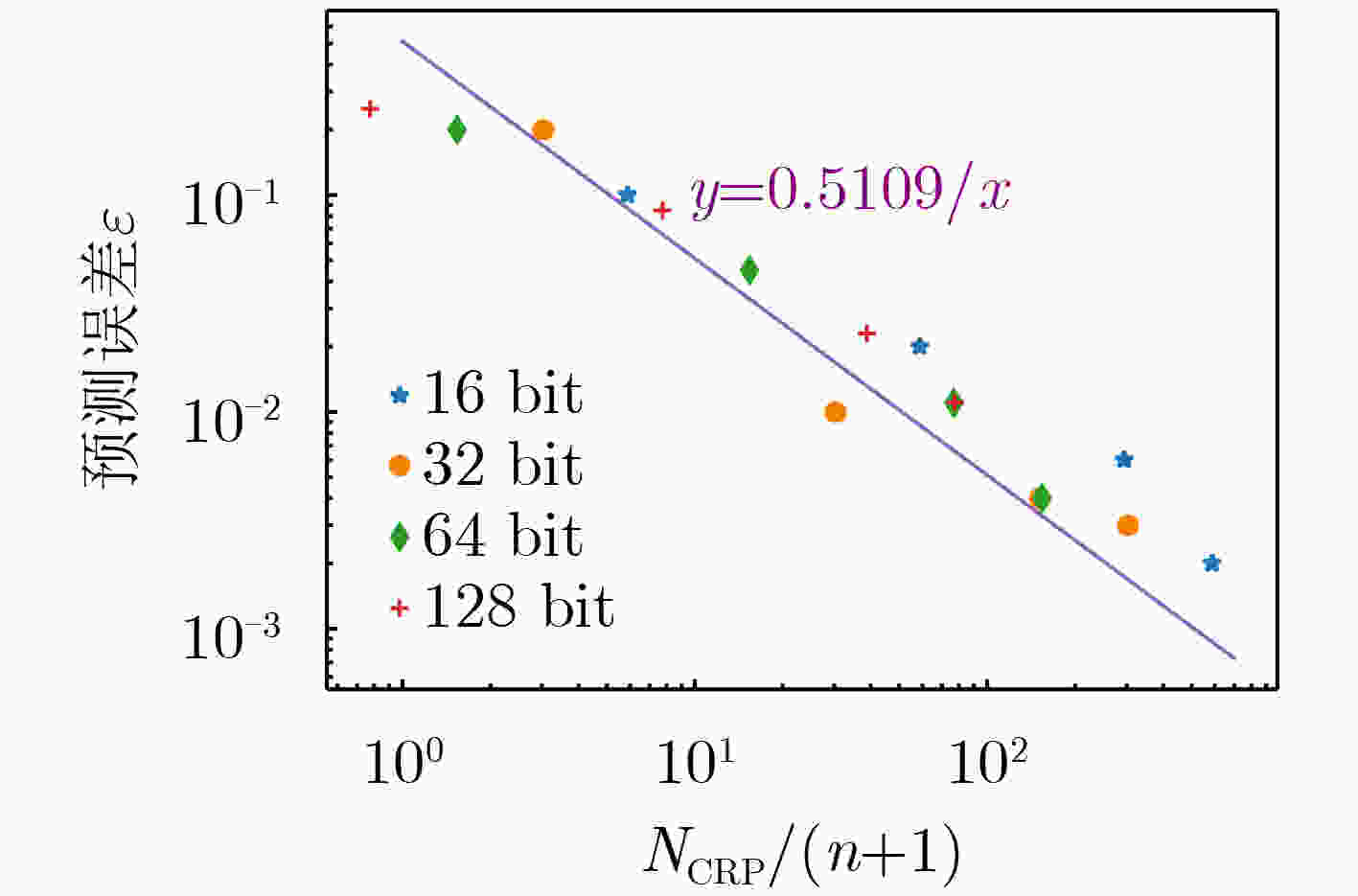
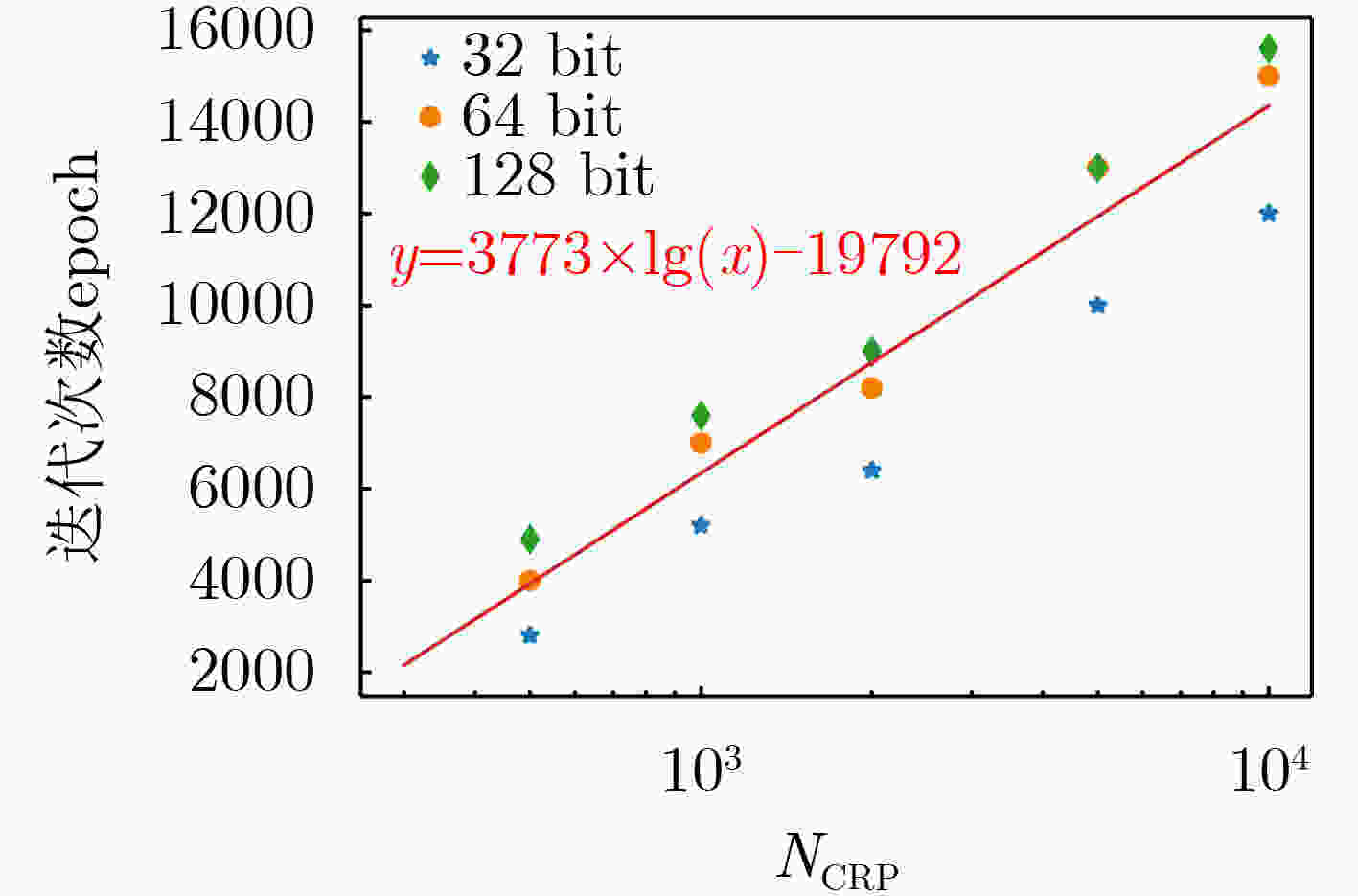


 下载:
下载:
