Online Estimation for Phased Array Seeker Pointing Error Slope Using Rao-Blackwellised Particle Filters
-
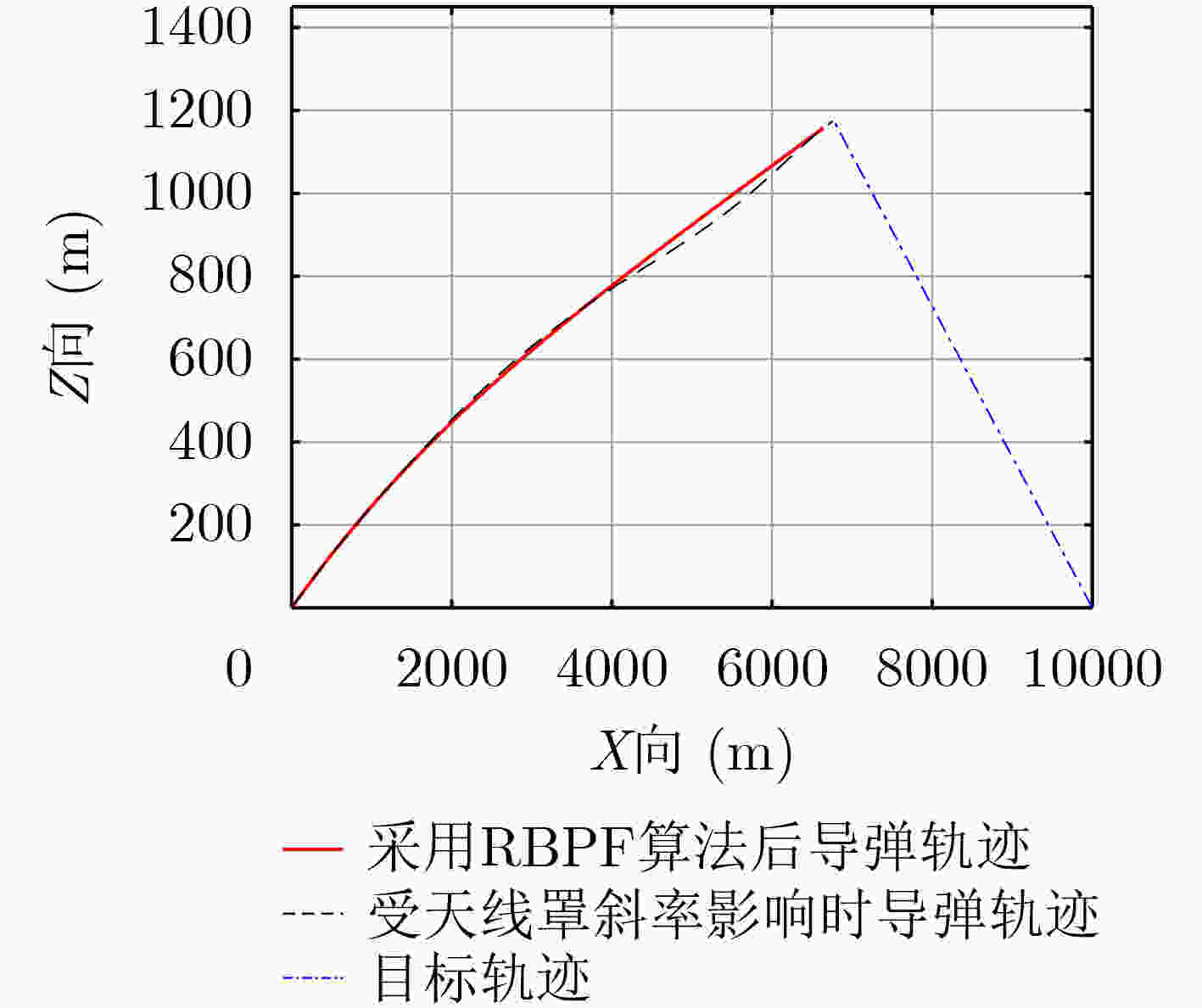
摘要: 针对相控阵导引头指向误差斜率对导弹制导系统带来的寄生回路振荡问题,该文提出一种指向误差斜率在线估计的算法,并能同步估计出目标状态。基于Rao-Blackwellised粒子滤波(RBPF),将指向误差斜率和目标状态同步估计问题分解为两个问题:一个是指向误差斜率的后验估计问题,另一个是以指向误差斜率估计为条件的目标状态估计问题。该文给出了算法的推导过程,并进行了数字仿真验证。仿真结果表明,该文所提算法对于相控阵导引头指向误差斜率的估计性能优良;并能同时准确估计出目标状态信息。采用此信息形成导引指令,可以消除指向误差斜率对制导系统的不利影响,提高系统的稳定性和制导精度。
-
关键词:
- 相控阵导引头 /
- 指向误差斜率 /
- 目标状态 /
- 在线同步估计 /
- Rao-Blackwellised粒子滤波
Abstract: Considering the problem of parasitic loop oscillation caused by pointing error slope of phased array seeker for missile guidance system, an estimation algorithm of pointing error slope is proposed, and target state can be estimated synchronously. Based on the Rao-Blackwellised Particle Filters (RBPF), the simultaneous estimation of pointing error slope and target state is decomposed into two problems: one is the posterior estimation of pointing error slope, the other is the target state estimation conditional on the estimation of pointing error slope. The derivation process of the algorithm is given and the numerical simulation is carried out. The simulation results show that the algorithm proposed has better performance in estimating the pointing error slope of phased array seeker, and the target state information can be estimated accurately at the same time. Using this information to form the guidance command can eliminate the adverse effects of pointing error slope on the guidance system, and improve system stability and guidance accuracy. -
表 1 仿真初始条件
符号 定义 取值 ${V_{\rm{T}}}$ 目标速度 300 m/s ${V_{\rm{M}}}$ 导弹速度 600 m/s ${D_0}$ 导弹目标初始距离 10000 m ${\theta _{\rm{M}}}$ 导弹初始偏角 15° ${\theta _{\rm{T}}}$ 目标飞行偏角 160° 表 2 仿真参数
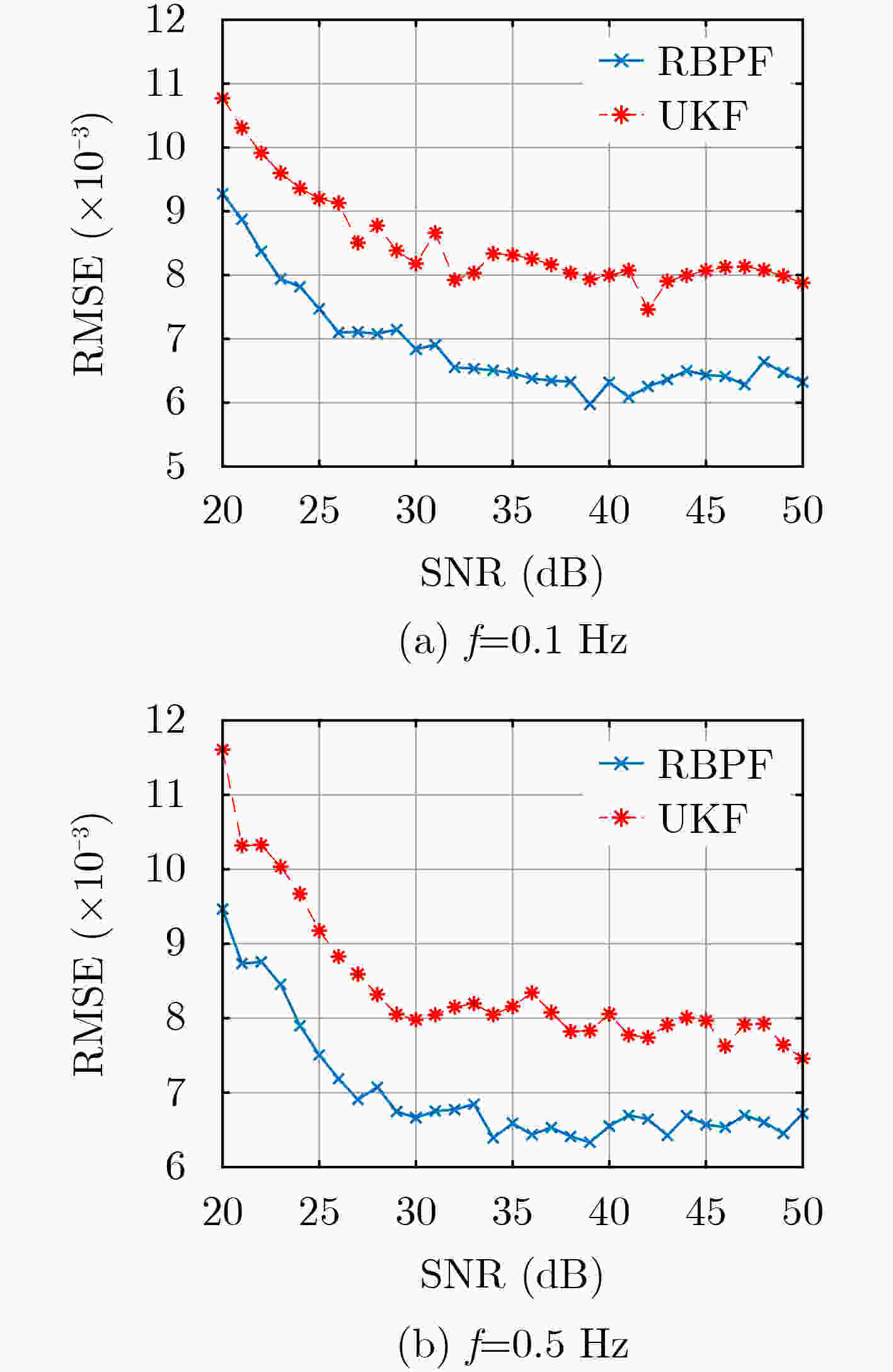
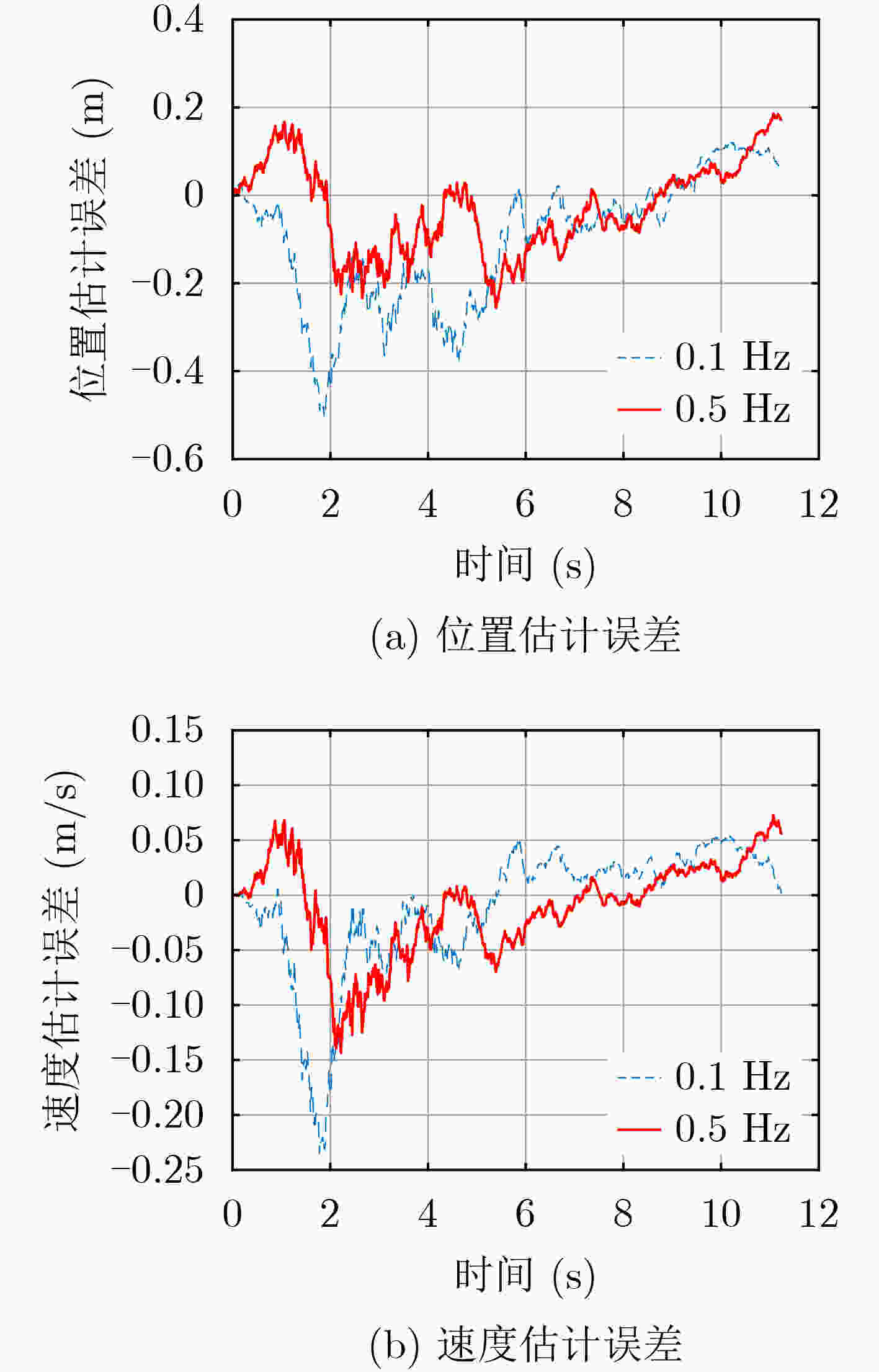
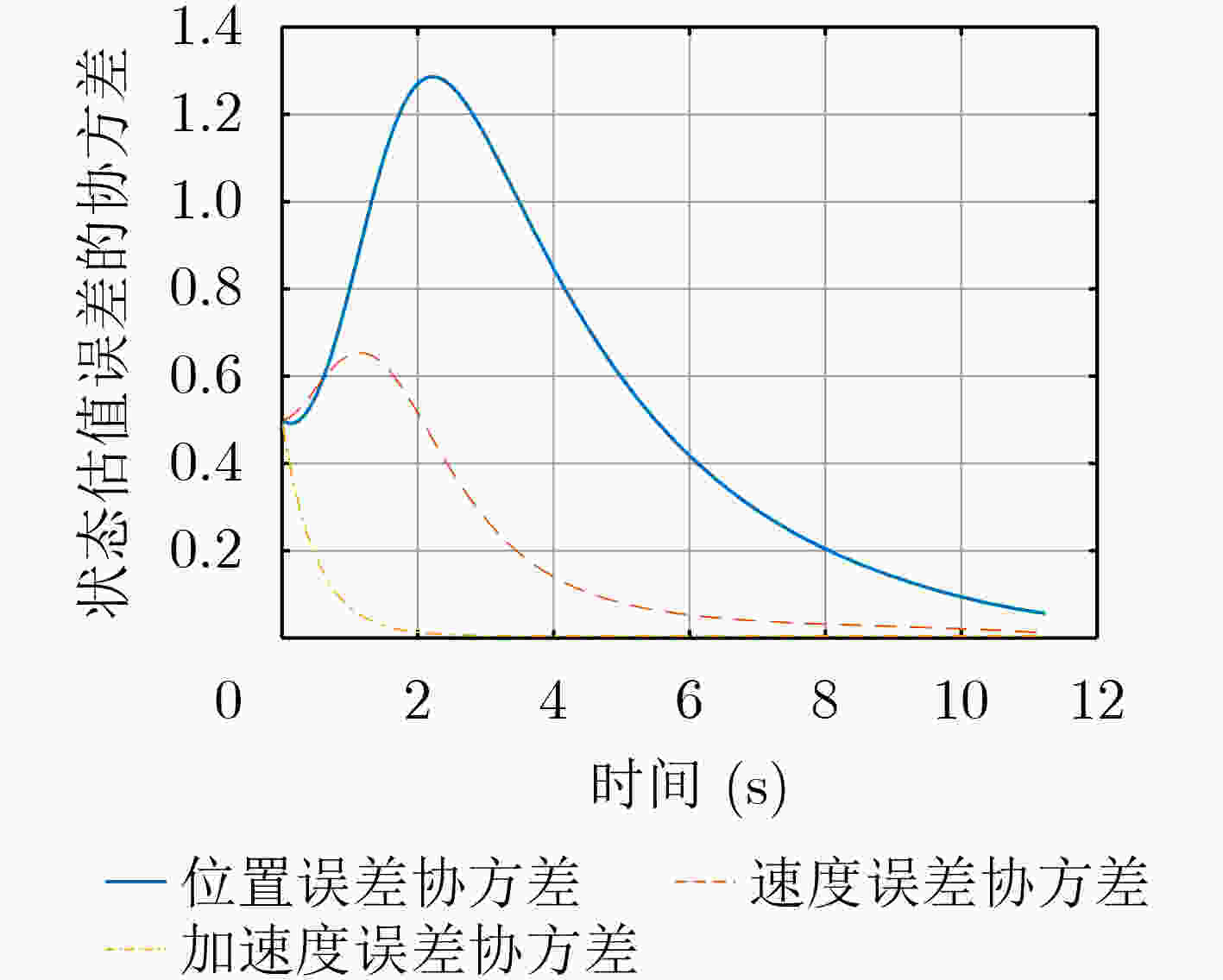
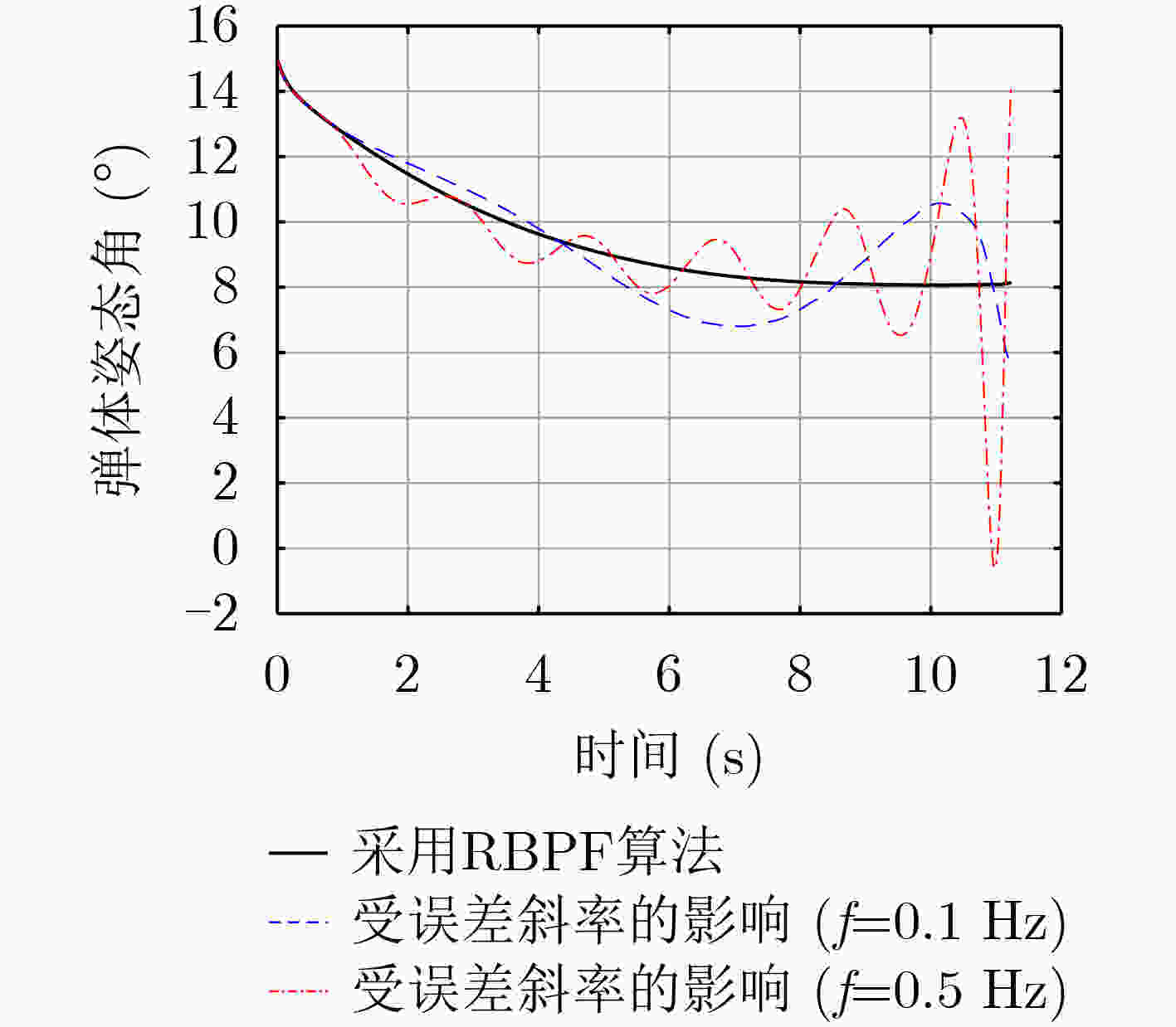
符号 定义 取值 SNR 信噪比 25 dB ${\sigma _R}$ 导引头角度测量噪声 1 mrad M 粒子数 100 [a,b] 均匀分布区间 [–0.06, 0.06] -
[1] MANCUSO Y, GREMILLET P, and LACOMME P. T/R-Modules technological and technical trends for phased array antennas[C]. 2005 European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 2006: 4. [2] 樊会涛, 闫俊. 相控阵制导技术发展现状及展望[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(9): 2807–2814.FAN Huitao and YAN Jun. Development and Outlook of active electronically scanned array guidance technology[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 2807–2814. [3] 赵鸿燕. 国外相控阵雷达导引头技术发展研究[J]. 航空兵器, 2018(3): 11–17.ZHAO Hongyan. Research on overseas phased array radar seeker technology development[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2018(3): 11–17. [4] NESLINE F W and ZARCHAN P. Line-of-sight reconstruction for faster homing guidance[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1985, 8(1): 3–8. doi: 10.2514/3.19927 [5] 王迪, 王雪梅, 何岷, 等. 基于有源单元方向图等效法的弹载相控阵天线互耦补偿[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(32): 194–198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.32.028WANG Di, WANG Xuemei, HE Min, et al. Mutual coupling compensation of missile-loaded phased array antenna based on active element pattern equivalent method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(32): 194–198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.32.028 [6] 廖志忠, 王琪. 雷达导引头指向误差对导弹制导的影响与对策[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(2): 519–525.LIAO Zhizhong and WANG Qi. Influence and countermeasures of radar seeker pointing error on missile guidance[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(2): 519–525. [7] YU Jing, LU Zhiyi, LI Xiangping, et al. Performance analysis of beam error parasitic loop of phased array radar seeker[J]. Icg, 2018, 14(11): 2752–2759. [8] WILLMAN W. Radome compensation using adaptive dither[R]. AAAI-98-4415, 1998. [9] ZARCHAN P and GRATT H. Adaptive Radome compensation using dither[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1999, 22(1): 51–57. doi: 10.2514/2.4370 [10] YUEH W R. Adaptive estimation scheme for radome error calibration[C]. The 22nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Antonio, USA, 1983: 546–551. [11] LIN J M and CHAU Y F. Radome slope compensation using multiple-model Kalman filters[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1995, 18(3): 637–640. doi: 10.2514/3.21438 [12] 曹晓瑞, 董朝阳, 王青, 等. 基于EKF的天线罩误差斜率多模型估计方法[J]. 航空学报, 2010, 31(8): 1608–1613.CAO Xiaorui, DONG Chaoyang, WANG Qing, et al. Radome slope estimation using multiple model based on EKF[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2010, 31(8): 1608–1613. [13] 周荻, 李君龙, 袁宇祺. 一种雷达导引头天线罩斜率误差实时估计方法[J]. 现代防御技术, 2020, 48(5): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2020.05.001ZHOU Di, LI Junlong, and YUAN Yuqi. An real-time estimation algorithm for slope error of Radome of radar seeker[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2020, 48(5): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2020.05.001 [14] 宗睿, 林德福, 兰玲, 等. 考虑天线罩误差的雷达导引头隔离度影响与UKF在线补偿[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2016, 36(12): 1269–1278.ZONG Rui, LIN Defu, LAN Ling, et al. Influence of radar seeker disturbance rejection rate with Radome error and on-line compensation with UKF[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016, 36(12): 1269–1278. [15] 金鹏飞, 于剑桥, 艾晓琳, 等. 基于模型参考自适应的天线罩误差斜率估计[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2018, 38(6): 135–139.JIN Pengfei, YU Jianqiao, AI Xiaolin, et al. Estimation of Radome boresight error slope based on model reference adaptive system[J]. Journal of Projectiles,Rockets,Missiles and Guidance, 2018, 38(6): 135–139. [16] LIN S Y, LIN Defu, and WANG Wei. A Novel online estimation and compensation method for strapdown phased array seeker disturbance rejection effect using extended state Kalman filter[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 172330–172340. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956256 [17] JIA Danping, DUAN Guangxue, WANG Nan, et al. Simultaneous localization and mapping based on Lidar[C]. The 2019 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Nanchang, China, 2019: 5528–5532. [18] DOUCET A, DE FREITAS N, MURPHY K P, et al. Rao-Blackwellised particle filtering for dynamic Bayesian networks[C]. The 16th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2000: 176–183. [19] MONTEMERLO M, THRUN S, KOLLER D, et al. . FastSLAM: A factored solution to the simultaneous localization and mapping problem[C]. The Eighteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Edmonton, Canada, 2002: 593–598. [20] GRISETTI G, STACHNISS C, and BURGARD W. Improved techniques for grid mapping with Rao-Blackwellized particle filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2007, 23(1): 34–46. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2006.889486 [21] BAILEY T, NIETO J, and NEBOT E. Consistency of the FastSLAM algorithm[C]. 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, USA, 2006: 424–429. [22] ZARCHAN P. Tactical and Strategic Missile Guidance[M]. 6th ed. Virginia: AIAA Inc. , 2012: 656–660. [23] SINGER R A and STEIN J J. An optimal tracking filter for processing sensor data of imprecisely determined origin in surveillance systems[C]. 1971 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Miami, USA, 1971: 171–175. [24] ARULAMPALAM M S, MASKELL S, GORDON N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. doi: 10.1109/78.978374 [25] DOUC R and CAPPE O. Comparison of resampling schemes for particle filtering[C]. ISPA 2005. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis, Zagreb, Croatia, 2005: 64–69. [26] JULIER S J and UHLMANN J K. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2004, 92(3): 401–422. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2003.823141 -





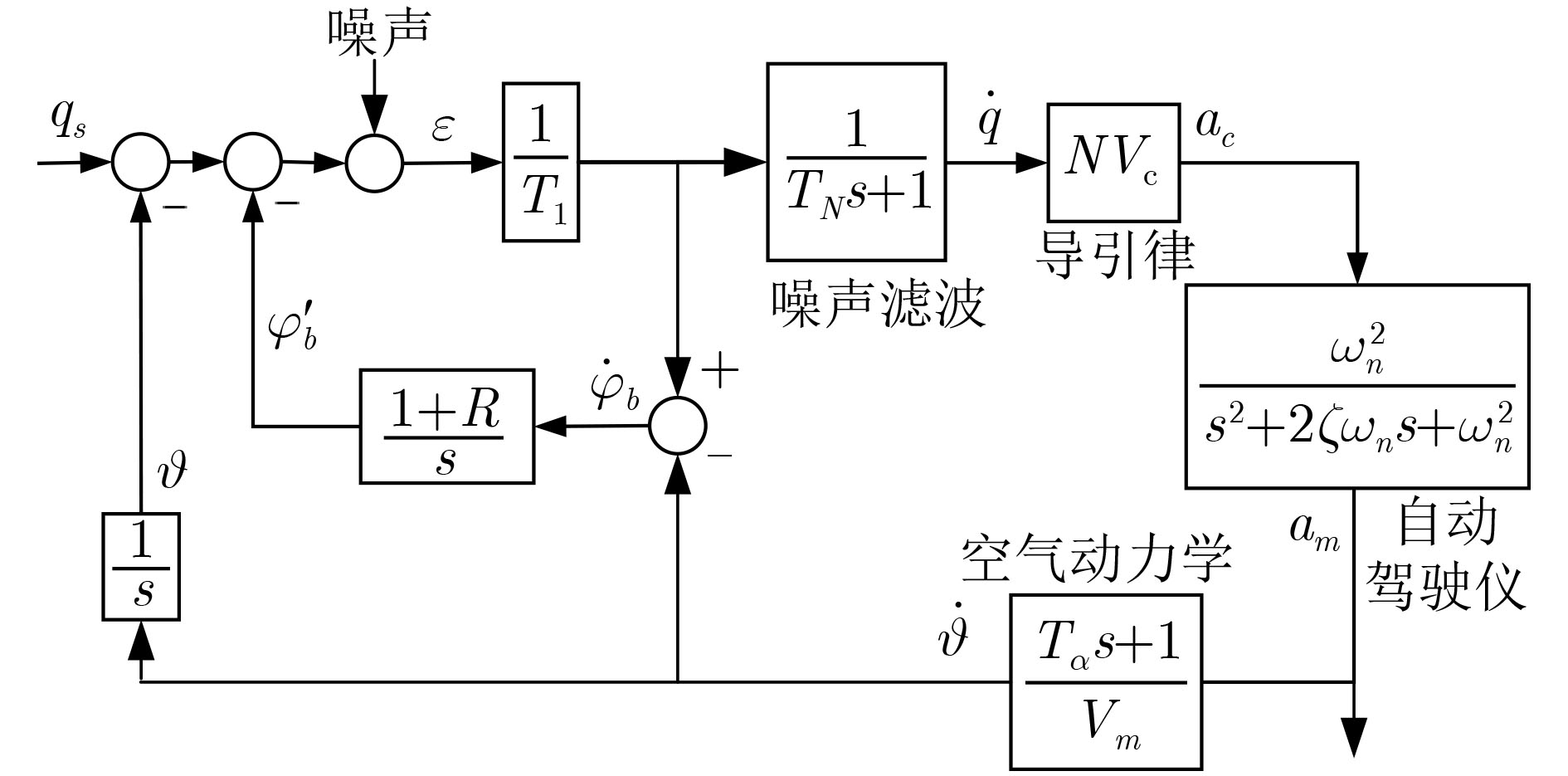
 下载:
下载:
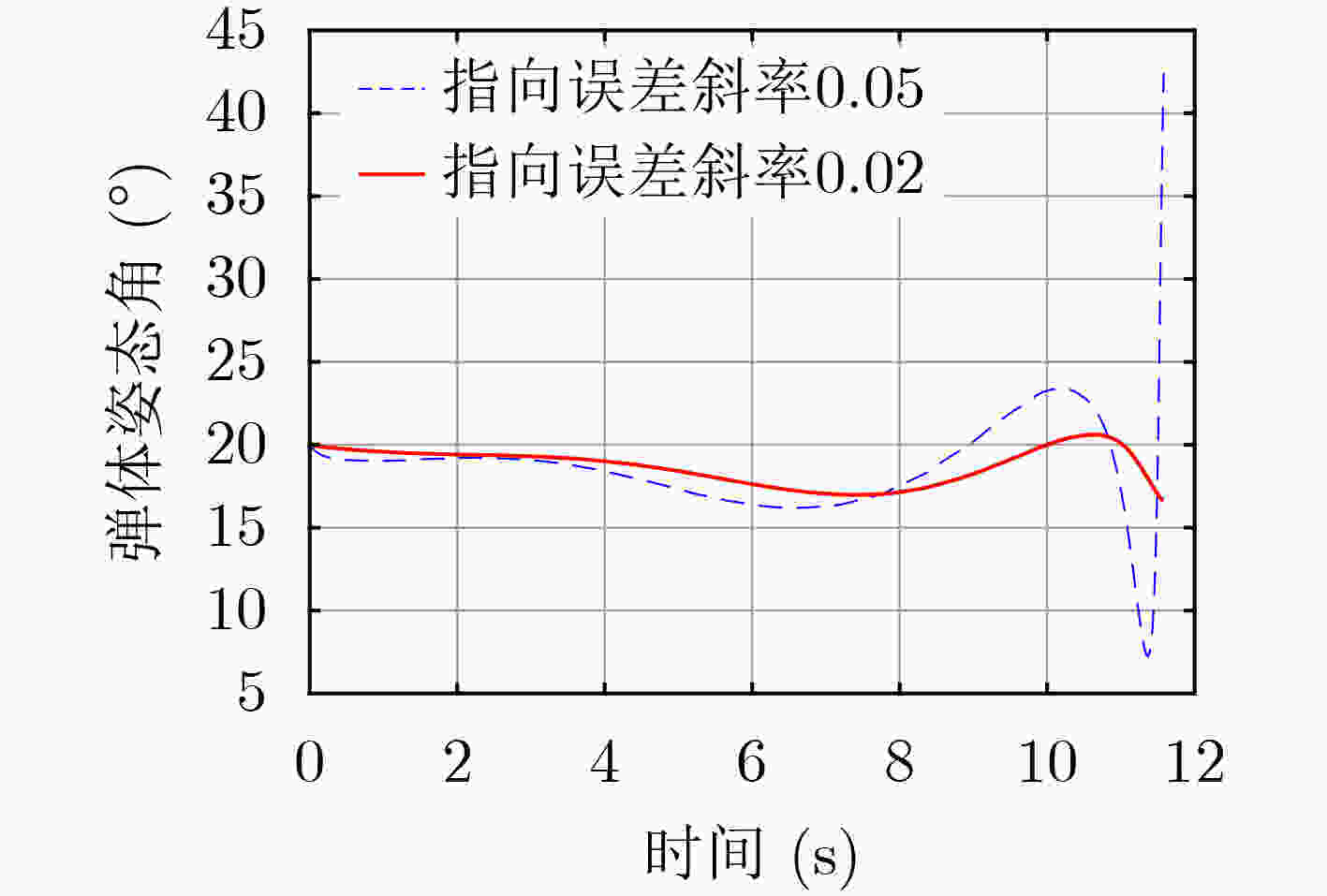
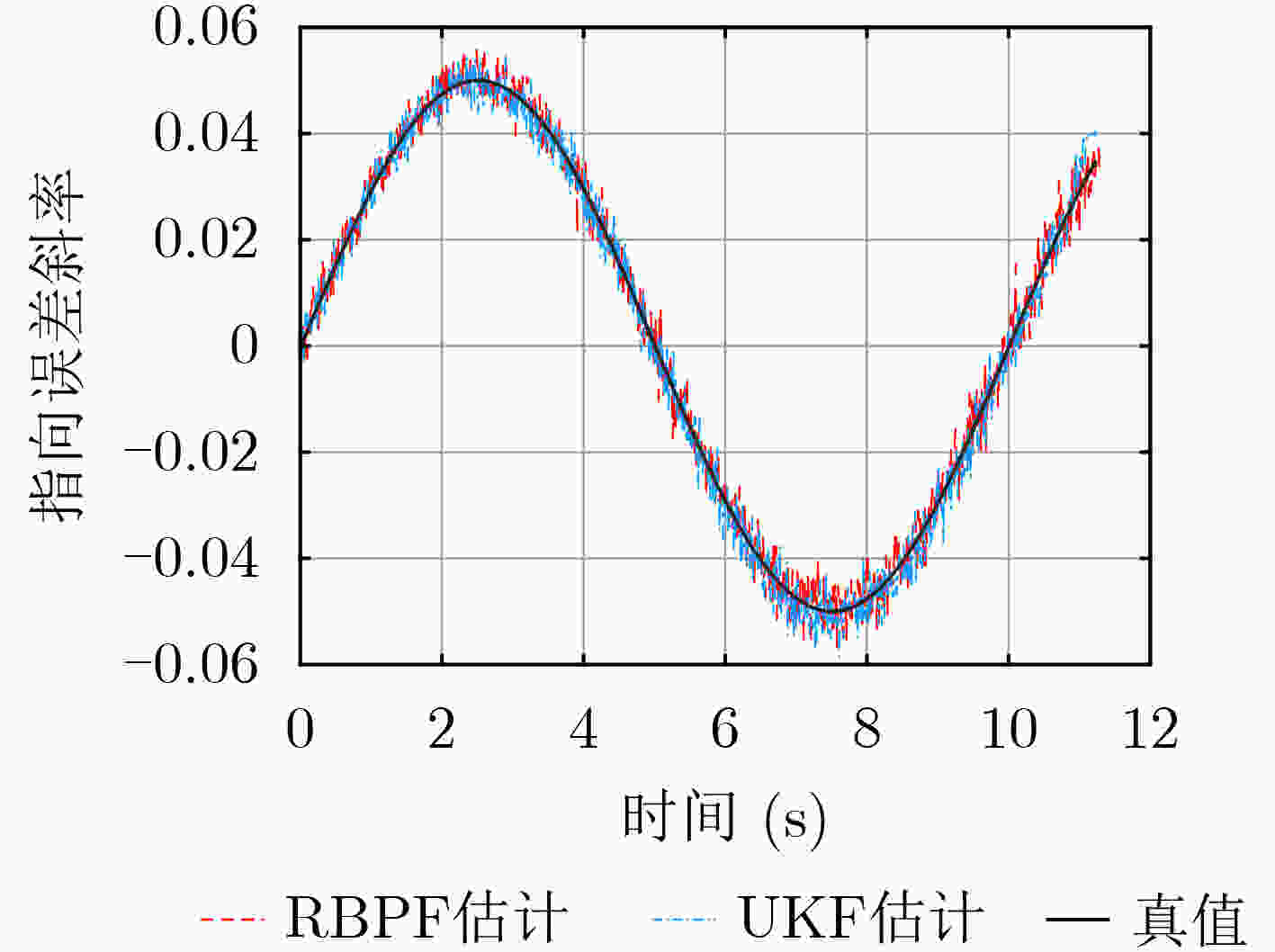

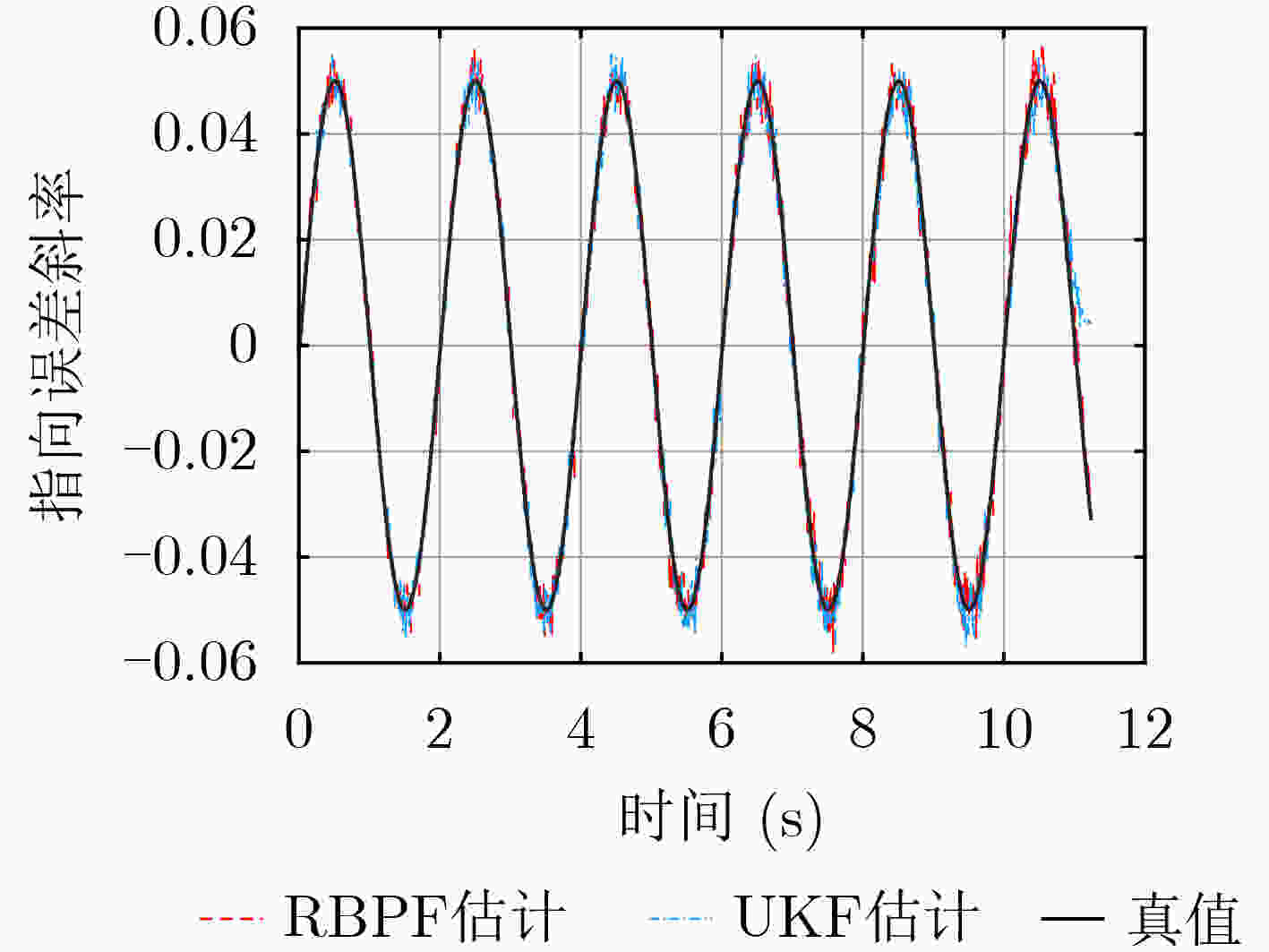




 下载:
下载:
