Depth Estimation Based on Semantic Guidance for Light Field Image
-
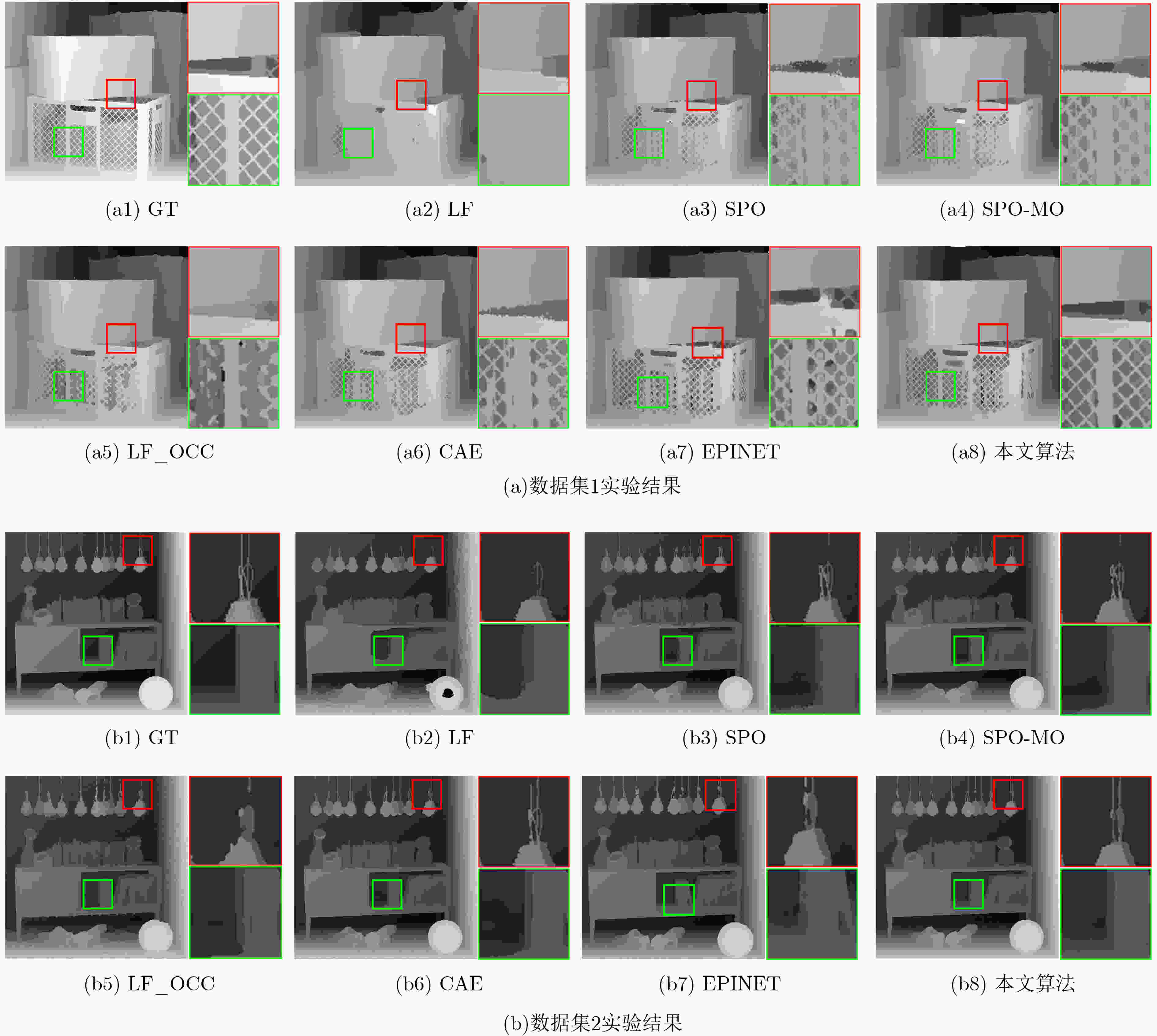
摘要: 光场图像的深度估计是3维重建、自动驾驶、对象跟踪等应用中的关键技术。然而,现有的深度学习方法忽略了光场图像的几何特性,在边缘、弱纹理等区域表现出较差的学习能力,导致深度图像细节的缺失。该文提出了一种基于语义导向的光场图像深度估计网络,利用上下文信息来解决复杂区域的不适应问题。设计了语义感知模块的编解码结构来重构空间信息以更好地捕捉物体边界,空间金字塔池化结构利用空洞卷积增大感受野,挖掘多尺度的上下文内容信息;通过无降维的自适应特征注意力模块局部跨通道交互,消除信息冗余的同时有效融合多路特征;最后引入堆叠沙漏串联多个沙漏模块,通过编解码结构得到更加丰富的上下文信息。在HCI 4D光场数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法表现出较高的准确性和泛化能力,优于所比较的深度估计的方法,且保留较好的边缘细节。Abstract: Light Field Depth Estimation(LFDE) is critical to the related applications such as 3D reconstruction, automatic driving and object tracking. However, the existing depth learning-based methods bring details lost on the edge, weak texture and other complex areas, because of ignoring the geometric characteristics of the light field image in the learning network. This paper proposes a semantic guided LFDE network, which utilizes contextual information of light field images to solve ill posed problems in complex regions. Encoder-decoder structure of semantic perception module is designed to reconstruct the spatial information for better obtaining the object boundary. The spatial pyramid pooling structure uses the atrous convolution to increase the receptive field and capture the multi-scale contextual information. Then, an adaptive local cross-channel interaction feature attention module without dimensionality reduction is used to eliminate information redundancy, and multi-channels are effectively fused. Finally, the stacked hourglass is introduced to connect multiple hourglass modules in series, and more rich context information is obtained by using the encoder-decoder structure. The experimental results on 4D light field dataset new HCI demonstrate that the proposed method has higher accuracy and generalization ability, which is superior to the depth estimation method compared, and retains better edge details.
-
Key words:
- Light field image /
- Depth estimation /
- Semantic perception /
- Attention mechanism
-
表 1 MSE指标对比
算法 Boxes Cotton Dino Sideboard Backgammon Pyramids Stripes Avg LF 17.43 9.168 1.163 5.071 13.01 0.273 17.45 9.08 SPO 9.107 1.313 0.311 1.024 4.587 0.043 6.955 3.33 LF_OCC 9.593 1.074 0.9441 2.073 22.78 0.077 7.942 6.35 CAE 8.427 1.506 0.382 0.876 6.074 0.048 3.556 2.98 FSNET 11.82 0.881 0.893 1.961 6.585 0.015 1.798 3.42 EPINET 5.904 0.282 0.169 0.849 2.579 0.012 0.286 1.44 本文算法 4.739 0.259 0.125 0.615 1.541 0.007 0.516 1.12 表 2 BP指标对比
算法 Boxes Cotton Dino Sideboard Backgammon Pyramids Stripes Avg LF 23.02 7.829 19.03 21.98 5.516 12.35 35.74 17.9 SPO 15.89 2.594 2.184 9.297 3.781 0.861 14.98 7.08 LF_OCC 26.52 6.218 14.91 18.49 19.07 3.172 18.41 15.2 CAE 17.88 3.369 4.968 9.845 3.924 1.681 7.872 7.07 FSNET 14.34 0.575 2.526 5.402 4.341 0.288 3.722 4.45 EPINET 12.24 0.543 1.319 4.921 2.231 0.283 1.063 3.23 本文算法 12.32 0.342 1.346 3.941 1.722 0.231 2.359 3.18 表 3 各算法的运行时间(s)对比
算法 Boxes Cotton Dino Sideboard LF 962.1 984.5 1130 987.4 SPO 2128 2025 2024 2073 LF_OCC 10408 6325 10099 13531 CAE 826.9 814.2 832.8 861.5 FSNET 85.05 84.91 85.63 84.78 EPINET 2.031 2.036 2.035 2.046 本文算法 6.001 5.874 5.981 5.856 表 4 模块消融实验的定量结果比较
模块 MSE BP SP_block FA_block SH_block – – × × × 1.47 4.07 √ × × 1.36 3.53 √ × √ 1.21 3.67 √ √ √ 1.12 3.18 -
[1] MENG N, LI K, LIU J Z, et al. Light field view synthesis via aperture disparity and warping confidence map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 3908–3921. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3066293 [2] ZHANG M, JI W, PIAO Y R, et al. LFNet: Light field fusion network for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 6276–6287. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2990341 [3] LI X, YANG Y B, ZHAO Q J, et al. Spatial pyramid based graph reasoning for semantic segmentation[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8947–8956. [4] 武迎春, 王玉梅, 王安红, 等. 基于边缘增强引导滤波的光场全聚焦图像融合[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2293–2301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190723WU Yingchun ,WANG Yumei, WANG Anhong. Light field all-in-focus image fusion based on edge enhanced guided filtering[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2293–2301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190723 [5] JEON H G, PARK J, CHOE G, et al. Accurate depth map estimation from a lenslet light field camera[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA, 2015: 1547–1555. [6] CHEN C, LIN H T, YU Z, et al. Light field stereo matching using bilateral statistics of surface cameras[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 1518–1525. [7] WANNER S and GOLDLUECKE B. Globally consistent depth labeling of 4D light field[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 41–48. [8] ZHANG S, SHENG H, LI C, et al. Robust depth estimation for light field via spinning parallelogram operator[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 145: 148–159. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2015.12.007 [9] TAO M W, SRINIVASAN P P, MALIK J, et al. Depth from shading, defocus, and correspondence using light-field angular coherence[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1940–1948. [10] WANG T C, EFROS A A, and RAMAMOORTHI R. Occlusion-aware depth estimation using light-field cameras[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3487–3495. [11] WILLIEM W and PARK I K. Robust light field depth estimation for noisy scene with occlusion[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4396–4404. [12] HEBER S, YU W, and POCK T. Neural EPI-volume networks for shape from light field[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2271–2279. [13] LUO Y X, ZHOU W H, FANG J P, et al. EPI-patch based convolutional neural network for depth estimation on 4D light field[C]. 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Guangzhou, China, 2017: 642–652. [14] SHIN C, JEON H G, YOON Y, et al. EPINET: A fully-convolutional neural network using epipolar geometry for depth from light field images[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Lake City, USA, 2018: 4748–4757. [15] TSAI Y J, LIU Y L, OUHYOUNG M, et al. Attention-Based view selection networks for light-field disparity estimation[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 12095–12103. doi: 10.1609/AAAI.v34i07.6888 [16] ZHOU W H, ZHOU E C, YAN Y X, et al. Learning depth cues from focal stack for light field depth estimation[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, China, 2019: 1074–1078. [17] SHI J L, JIANG X R, and GUILLEMOT C. A framework for learning depth from a flexible subset of dense and sparse light field views[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(12): 5867–5880. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2923323 [18] GUO C L, JIN J, HOU J H, et al. Accurate light field depth estimation via an occlusion-aware network[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, London, UK, 2020: 1–6. [19] HU J, SHEN L, and SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [20] YE J W, WANG X C, JI Y X, et al. Amalgamating filtered knowledge: Learning task-customized student from multi-task teachers[C]. Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 2019: 4128–4134. [21] HONAUER K, JOHANNSEN O, KONDERMANN D, et al. A dataset and evaluation methodology for depth estimation on 4D light fields[C]. 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, China, 2016: 19–34. -





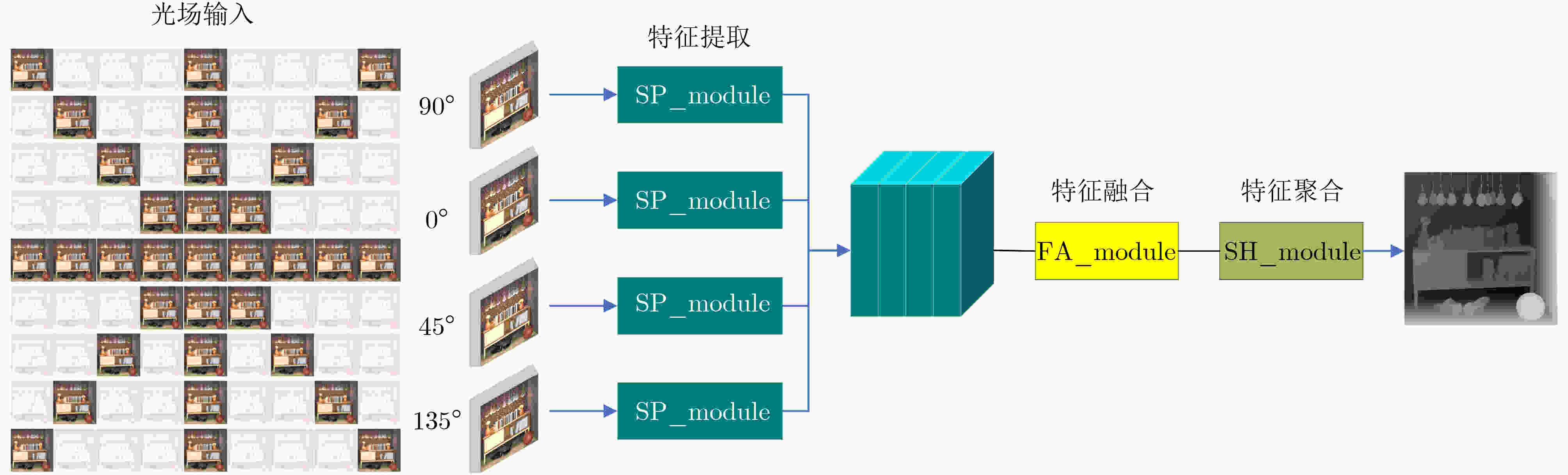
 下载:
下载:
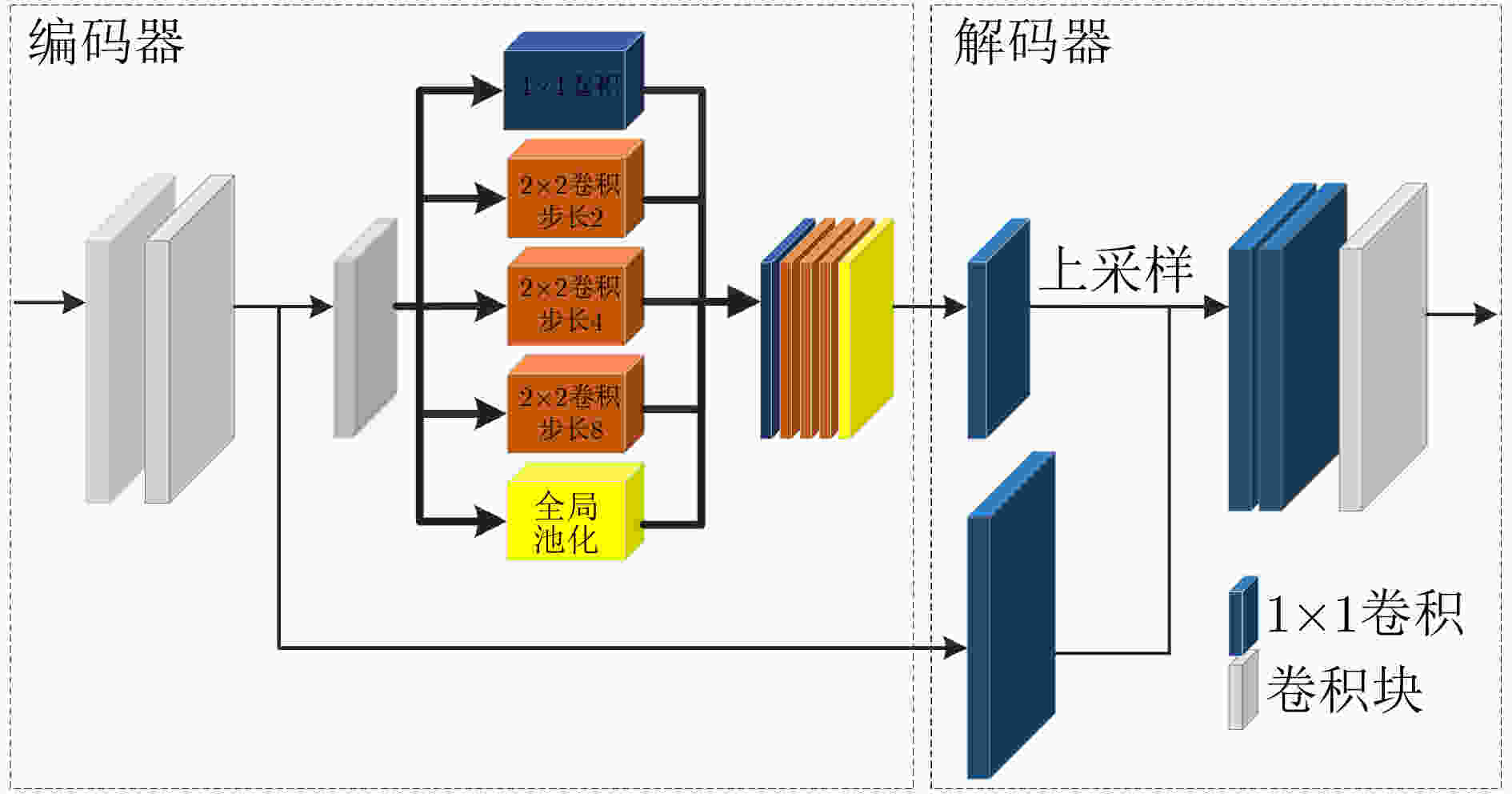
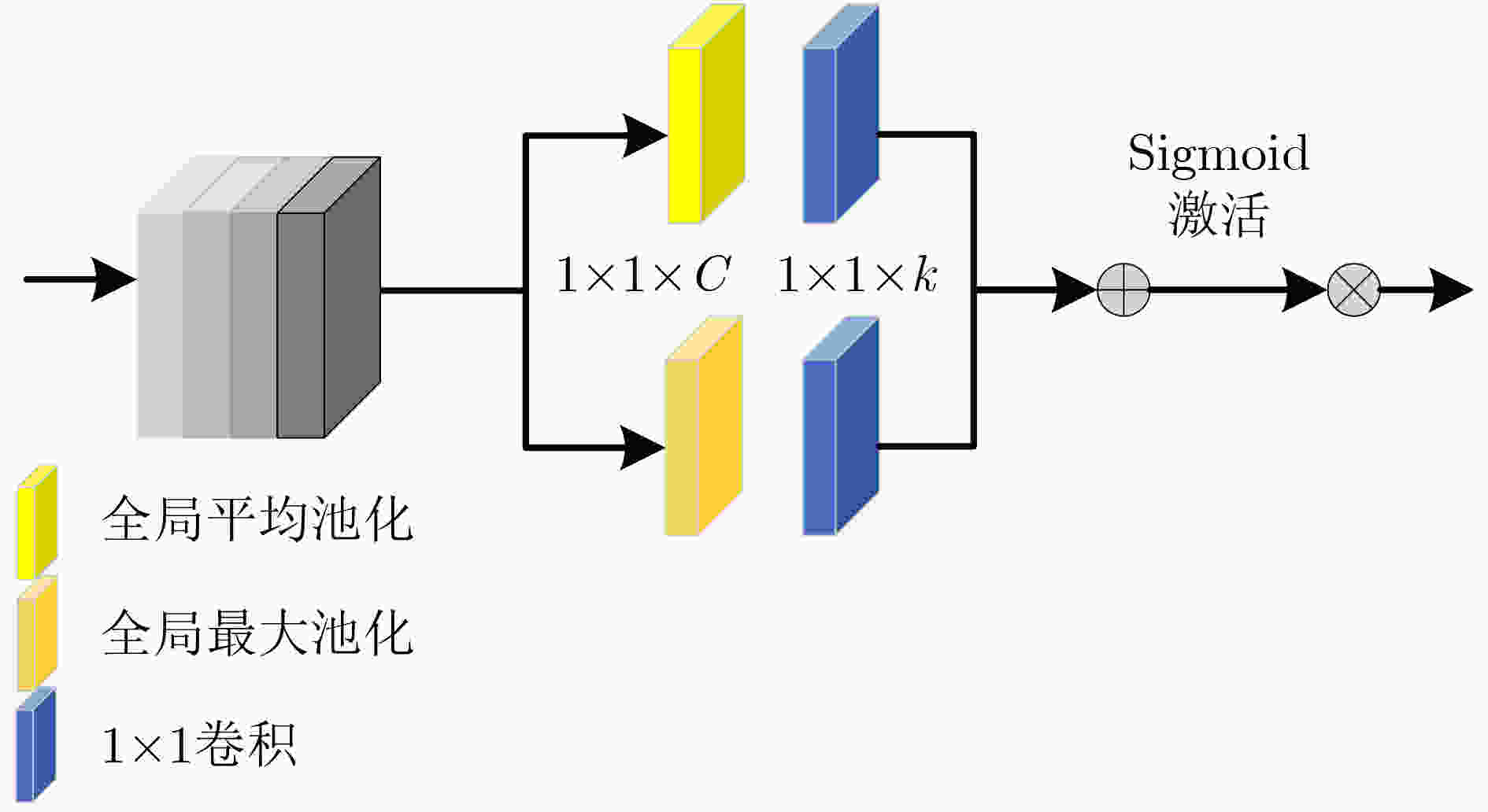
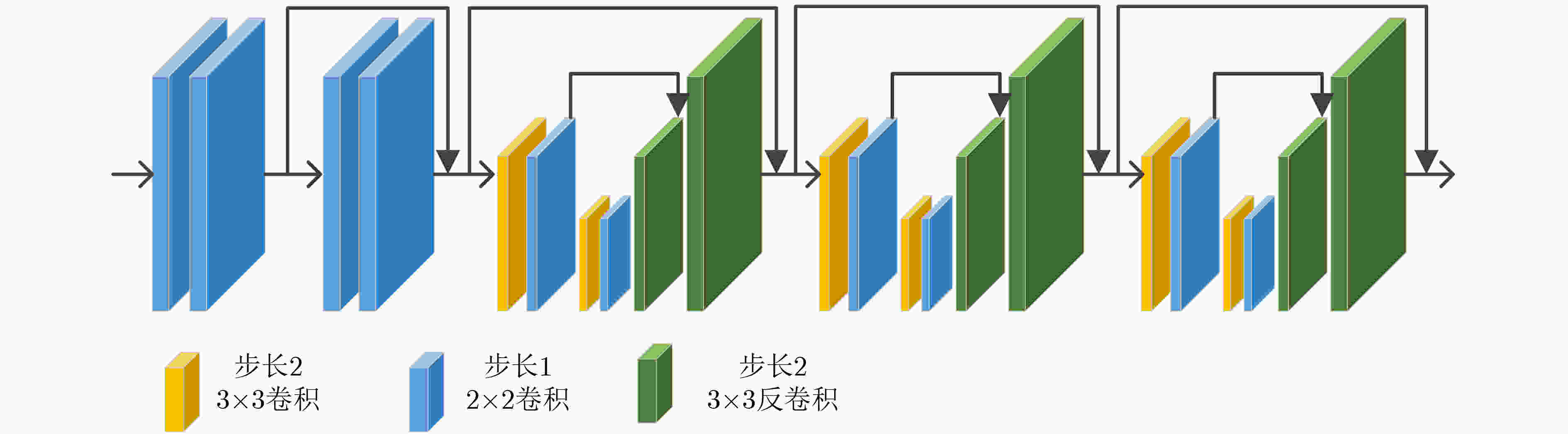



 下载:
下载:
