A Reservation and Reuse Combined Q-learning Semi Persistent Scheduling for C-V2X Communication
-
摘要: 第3代合作伙伴计划(3GPP)模式4提供了一种直连通信的接入方式,以支持车联网C-V2X应用。然而V2X网络动态变化的业务负载和车辆移动性导致信道质量不稳定,加剧了传输过程中分组碰撞问题。为了满足高可靠低时延的V2X通信需求,该文针对动态负载环境下的高效分布式资源分配策略,提出一种预留-重用联合的Q学习型半持续调度(RRC-QSPS)算法。该文首先对模式4中现有的半持续调度(SPS)算法分组碰撞问题进行理论建模,分析了影响碰撞概率的关键参数,继而提出了动态业务环境下车辆智能体的强化Q学习模型,建立包括预留-重用联合的动作空间与Q目标函数,并通过
$ \varepsilon $ -贪心算法求解,智能决策动态负载环境下无线资源的预留与重用。仿真对比结果表明,相比于已有的Lookahead-SPS优化算法,RRC-QSPS算法在高速高负载场景下分组接收率提高了7%,数据包更新时延降低了10%。Abstract: The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) mode 4 provides a direct communication mode to support the C-V2X applications. However, the dynamic traffic load and vehicle mobility lead to uncertainty of channel quality with serious packet collision problem. In order to meet the demand of ultra reliability and low latency of V2X communication. A Reservation-Reuse Combined Q-learning Semi Persistent Scheduling (RRC-QSPS) algorithm is proposed for efficient distributed resource allocation in dynamic load environment. Firstly, the theoretical model of the collision probability of Semi Persistent Scheduling (SPS) algorithm is built. Then, the Q-learning model of vehicle agent in dynamic load environment is proposed with the reservation-reuse combined action and Q function. By using$ \varepsilon $ -greedy method, the optimal reservation and reuse of wireless resources in dynamic load environment can be solved. The simulation results show that compared with the existing Lookahead-SPS optimization algorithms, the packet reception ratio of RRC-QSPS is improved by 7% and the update packet delay is reduced by 10% in high speed and high load scenarios. -
表 1 5G网络技术及优势
5G网络技术 优势 软件定义网络技术 提升数据网络灵活性 网络功能虚拟化技术 提升网络运维效率 网络切片技术 满足不同应用场景需求 大规模MIMO技术 提升网络的通信容量 设备到设备通信技术 支持直连通信,降低端到端时延 表 2 算法1 RRC-QSPS
输入:C1,C2,NCAMRs, Q(st, at) 输出:CAMRid (1) 初始化Q学习参数和SPS算法参数RC←random(C1,C2),
CAMRid←random(1, NCAMRs)(2) 观察当前状态st (3) LOOP (4) IF RC /= 0 THEN (5) RC←RC–1 (6) ELSE (7) 由式(18)选择动作at并执行,即更新RC和RP值,保持或
重选CAMRid(8) ELSE IF (9) 观察后续状态st+1,并由式(16)计算回报函数Rt (10) 根据式(17)更新Q(st, at)值 (11) END LOOP 表 3 仿真参数和配置
参数 参数值 仿真时间 50 s 仿真区域中的车辆数(ρ) 100 平均车速 120 km/h(方差=3) 道路长度 1000 m 车道数 2(每个方向1个) CAM大小 190 Bytes 发包率 5~50 pps 感测距离(raw) 150 m 发射功率 15 dBm 传播模型 WINNER+, B1 阴影衰落方差 3 dB 路径损耗指数(β) 2.75 调制和编码方案 MCS 7 (QPSK) -
[1] JEON Y and KIM H. An explicit reservation-augmented resource allocation scheme for C-V2X Sidelink mode 4[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 147241–147255. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3015549 [2] BAZZI A, CECCHINI G, ZANELLA A, et al. Study of the impact of PHY and MAC parameters in 3GPP C-V2V mode 4[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 71685–71698. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2883401 [3] NAIK G, CHOUDHURY B, and PARK J M. IEEE 802.11 bd & 5G NR V2X: Evolution of radio access technologies for V2X communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 70169–70184. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2919489 [4] WANG Shuai, LIU Yan, ZHU Jie, et al. A novel collision supervision and avoidance algorithm for scalable MAC of vehicular networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2021, 30(1): 164–170. doi: 10.1049/cje.2020.12.001 [5] MOLINA-MASEGOSA R and GOZALVEZ J. LTE-V for sidelink 5G V2X vehicular communications: A new 5G technology for short-range vehicle-to-everything communications[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(4): 30–39. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2752798 [6] GONZALEZ-MARTÍN M, SEPULCRE M, MOLINA-MASEGOSA R, et al. Analytical models of the performance of C-V2X mode 4 vehicular communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(2): 1155–1166. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2888704 [7] JUNG S Y, CHEON H R, and KIM J H. Reducing consecutive collisions in sensing based semi persistent scheduling for cellular-V2X[C]. 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, USA, 2019: 1–5. [8] JEON Y, KUK S, and KIM H. Reducing message collisions in sensing-based semi-persistent scheduling (SPS) by using reselection lookaheads in cellular V2X[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4388. doi: 10.3390/s18124388 [9] BONJORN N, FOUKALAS F, and POP P. Enhanced 5G V2X services using sidelink device-to-device communications[C]. 2018 17th Annual Mediterranean ad HOC Networking Workshop (Med-Hoc-Net), Capri, Italy, 2018: 1–7. [10] HONNAIAH P J, MATURO N, and CHATZINOTAS S. Foreseeing semi-persistent scheduling in mode-4 for 5G enhanced V2X communication[C]. 2020 IEEE 17th Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 1–2. [11] 余翔, 陈晓东, 王政, 等. 基于LTE-V2X的车联网资源分配算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(2): 188–193.YU Xiang, CHEN Xiaodong, WANG Zheng, et al. Resource allocation algorithm for internet of vehicles based on LTE-V2X[J]. Computer Engineering, 2021, 47(2): 188–193. [12] 金久一, 邱恭安. C-V2X通信中资源分配与功率控制联合优化[J/OL]. 计算机工程, 2020: 1–10. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=JSJC20201014004&v=fpDLQvPDFGcn3qeXmuRIceO0Zyyaau3ClfB8VIRe3GnypH%25mmd2FWjA8xWhfkjlUBdOBz, 2020.JIN Jiuyi and QIU Gongan. Joint optimization of resource allocation and power control in C-V2X communications[J/OL]. Computer Engineering, 2020: 1–10. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=JSJC20201014004&v=fpDLQvPDFGcn3qeXmuRIceO0Zyyaau3ClfB8VIRe3GnypH%25mmd2FWjA8xWhfkjlUBdOBz, 2020. [13] CAMPOLO C, MOLINARO A, ROMEO F, et al. 5G NR V2X: On the impact of a flexible numerology on the autonomous sidelink mode[C]. 2019 IEEE 2nd 5G World Forum (5GWF), Dresden, Germany, 2019: 102–107. [14] BONJORN N, FOUKALAS F, CAÑELLAS F, et al. Cooperative resource allocation and scheduling for 5G eV2X services[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 58212–58220. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2889190 [15] HAIDER A and HWANG S H. Adaptive transmit power control algorithm for sensing-based semi-persistent scheduling in C-V2X mode 4 communication[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(8): 846. doi: 10.3390/electronics8080846 [16] YE Hao, LI G Y, and JUANG B H F. Deep reinforcement learning based resource allocation for V2V communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3163–3173. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2897134 [17] 陈前斌, 管令进, 李子煜, 等. 基于深度强化学习的异构云无线接入网自适应无线资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1468–1477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190511CHEN Qianbin, GUAN Lingjin, LI Ziyu, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive wireless resource allocation algorithm for heterogeneous cloud wireless access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1468–1477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190511 [18] SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: An introduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1998, 9(5): 1054. [19] CECCHINI G, BAZZI A, MASINI B M, et al. LTEV2Vsim: An LTE-V2V simulator for the investigation of resource allocation for cooperative awareness[C]. 2017 5th IEEE International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Naples, Italy, 2017: 80–85. -







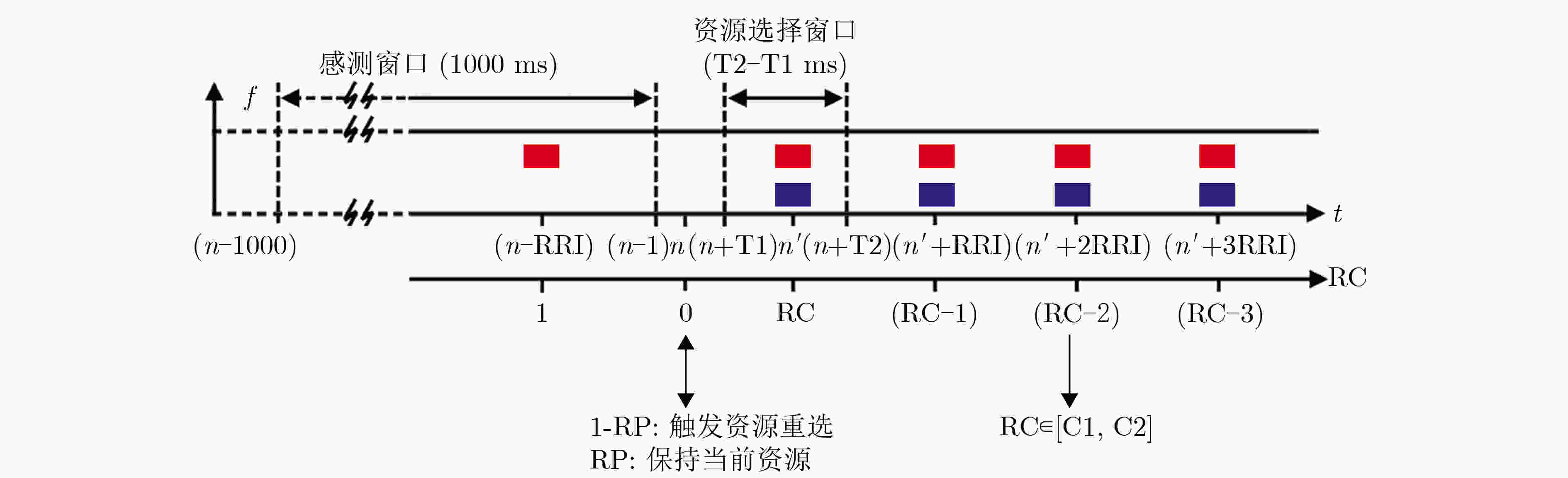
 下载:
下载:
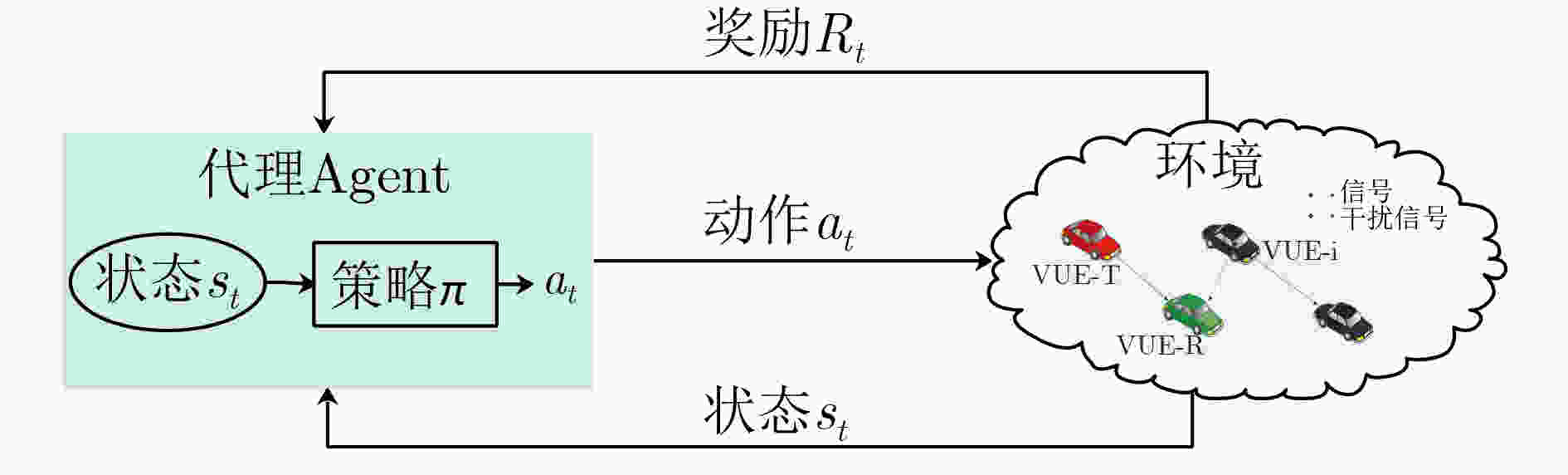
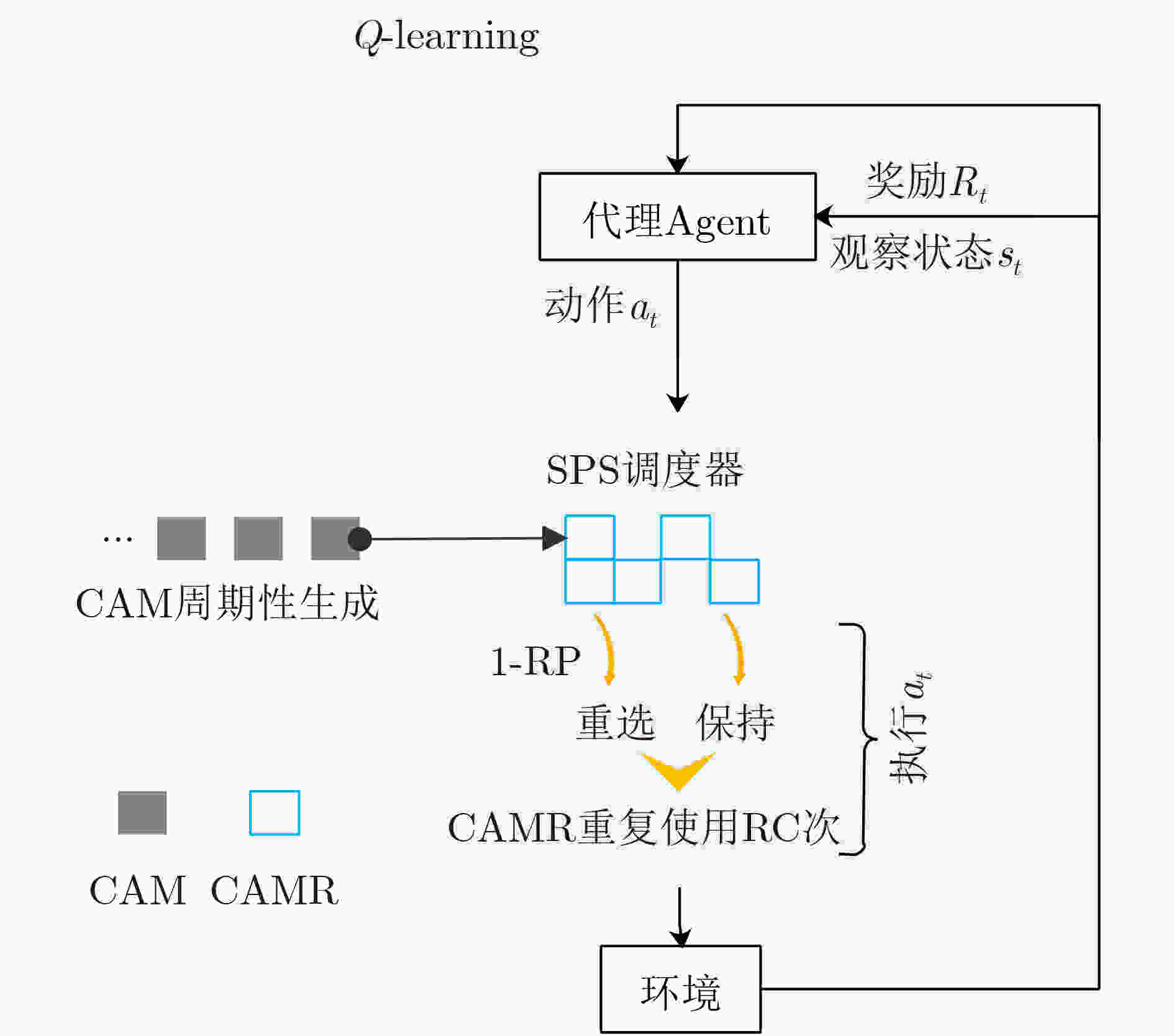
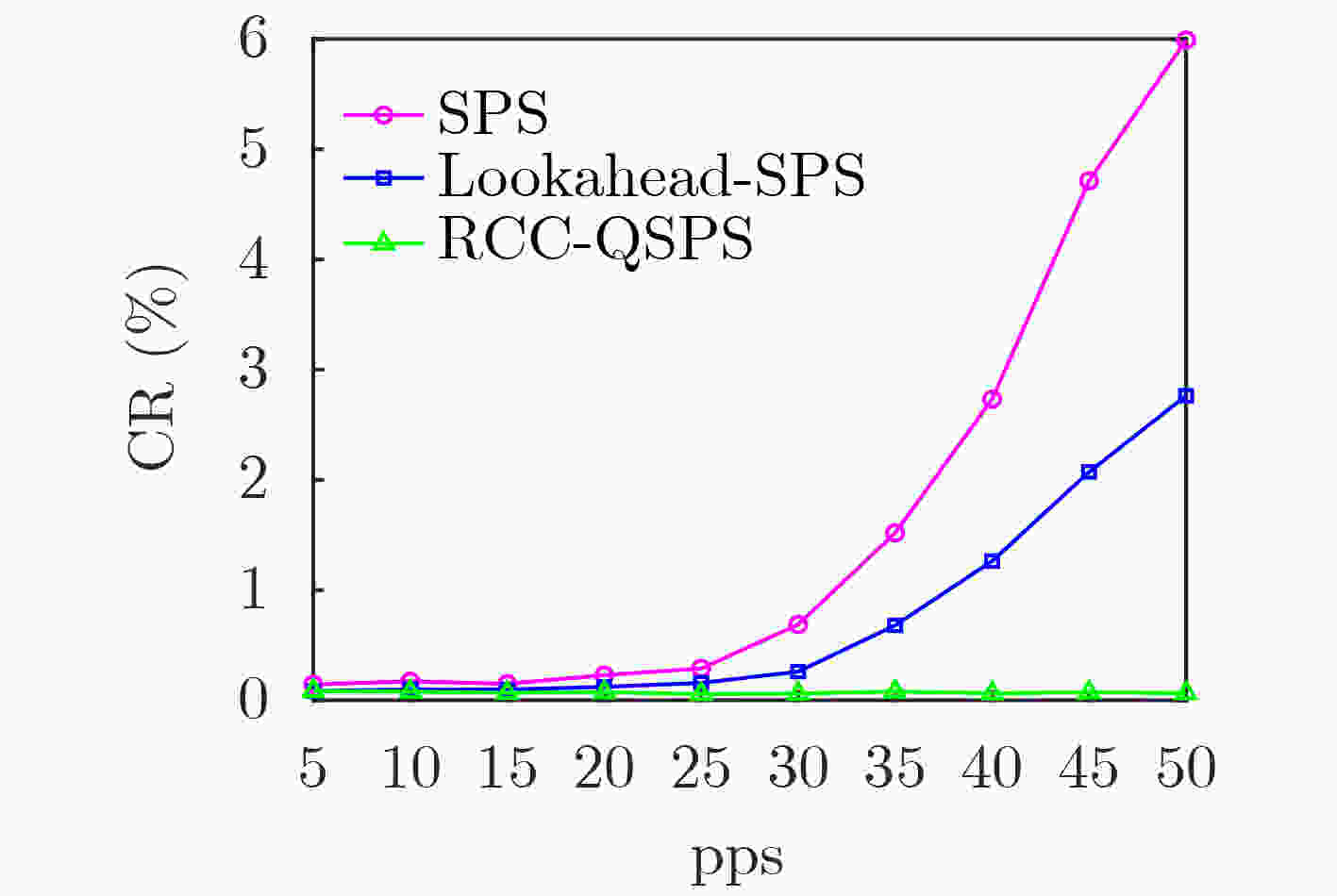
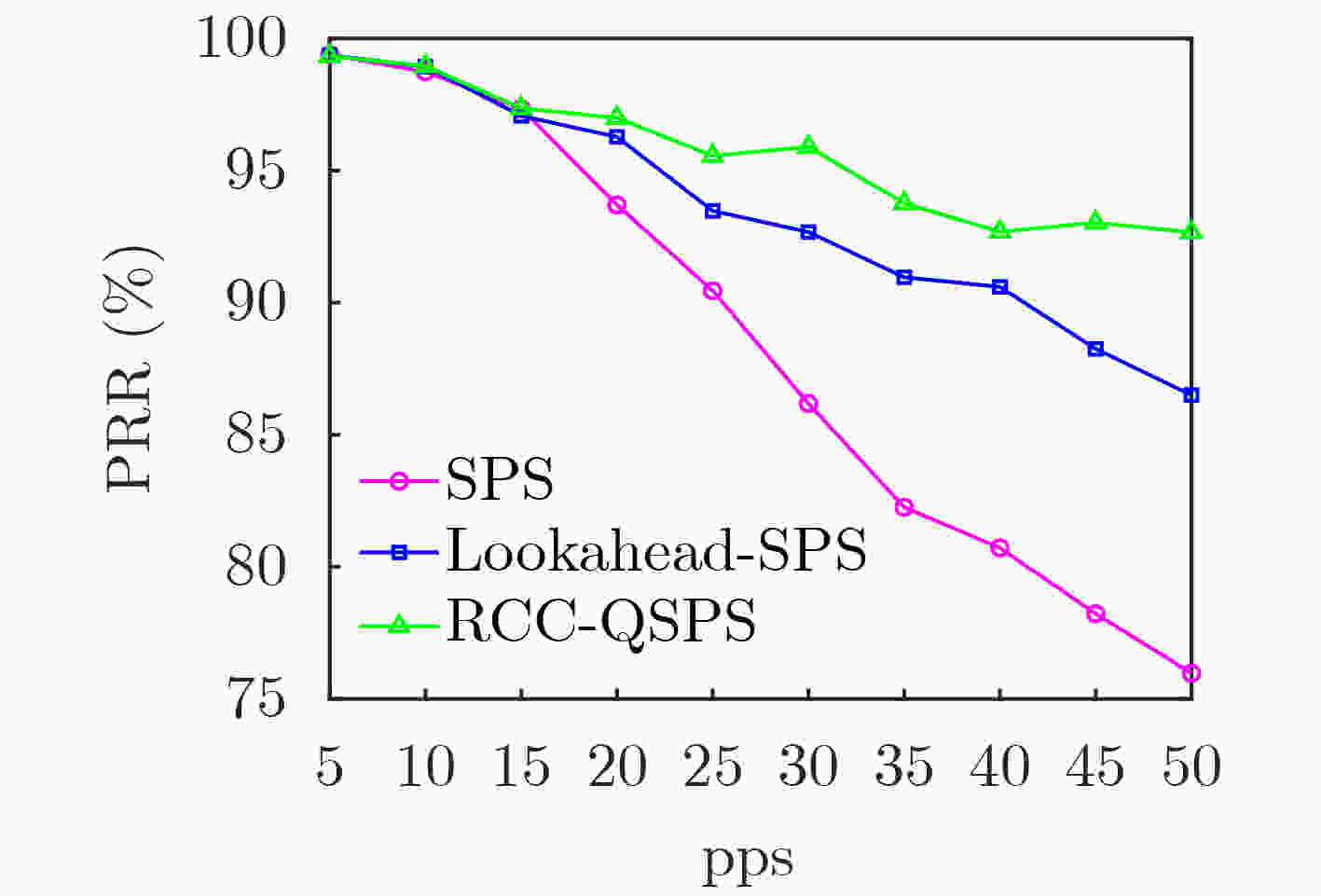
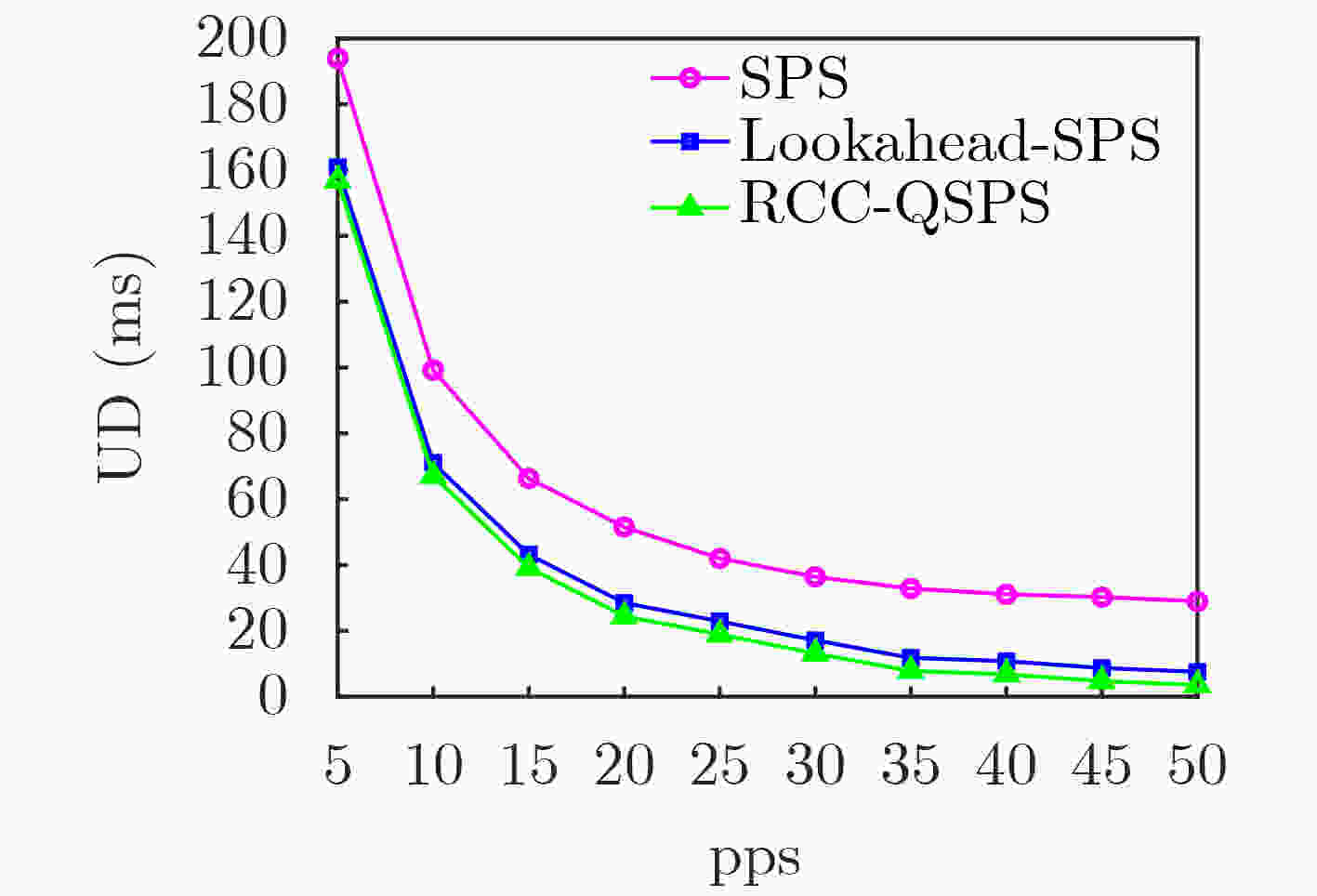
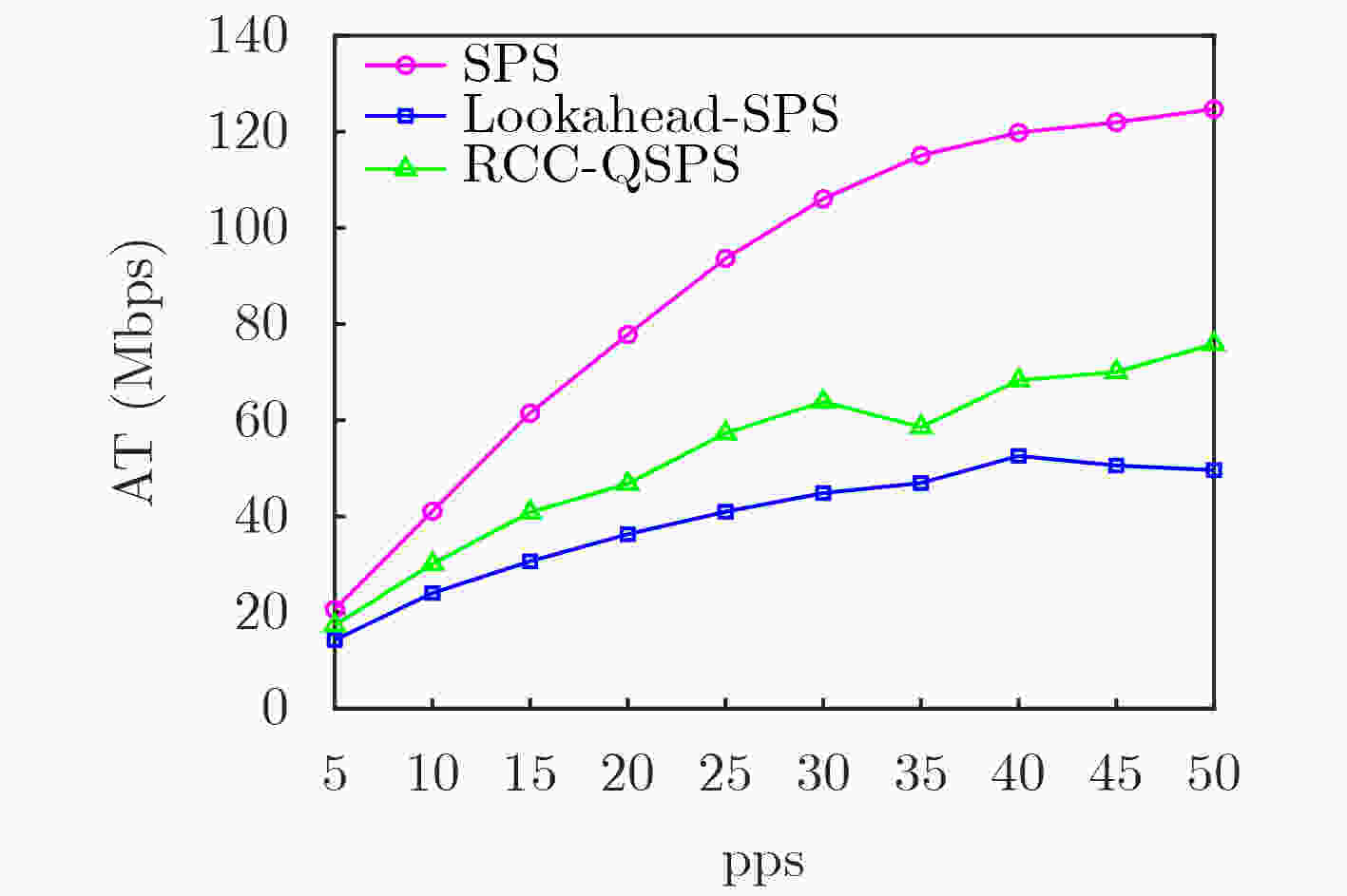


 下载:
下载:
