Modeling and Analysis of User Awareness and Information Coupling Propagation in D2D Communications
-
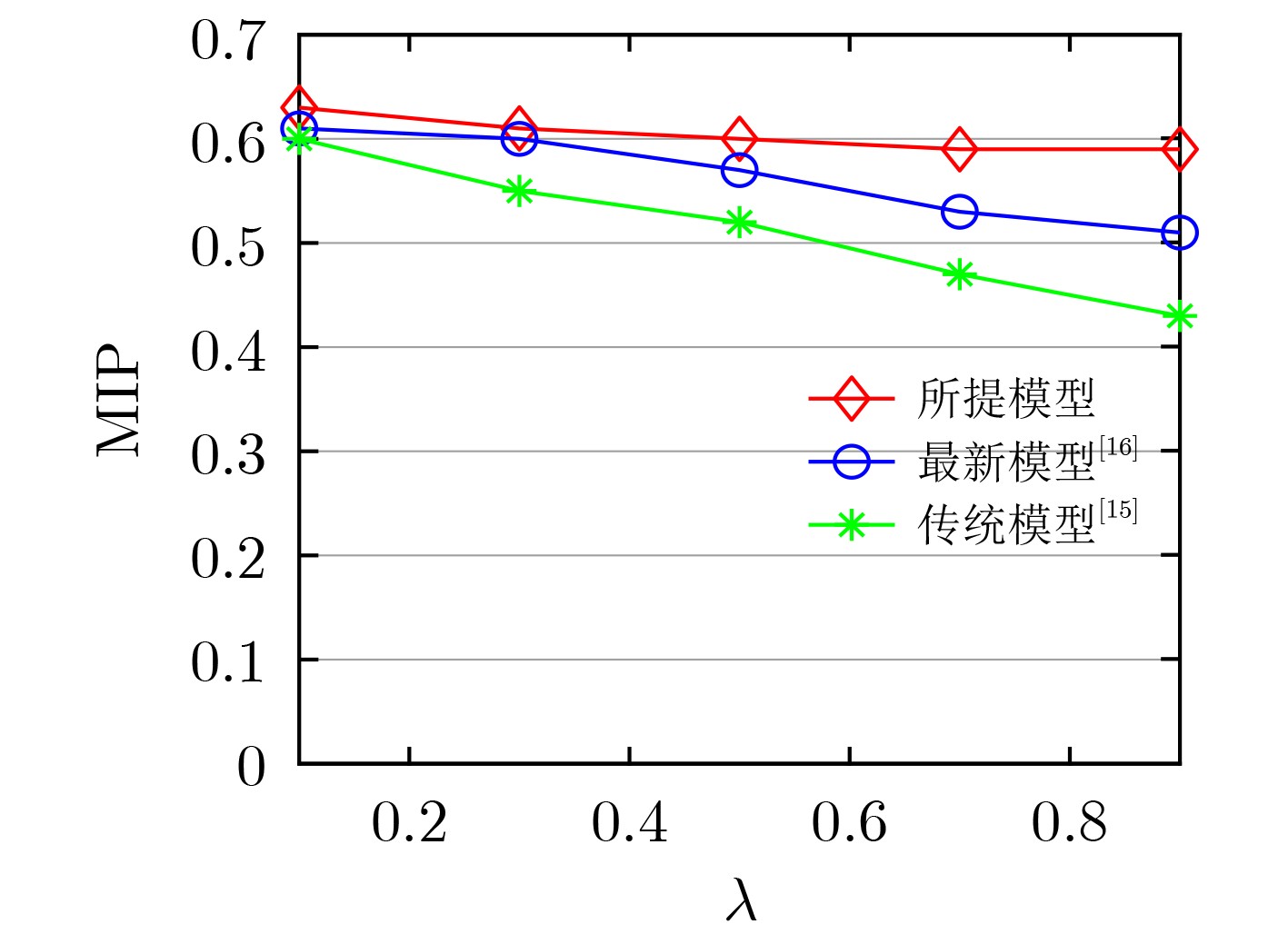
摘要: 设备到设备(D2D)通信中信息传输过程不仅受物理通信条件影响,还与用户动态属性密切相关。为探讨信息传输与用户意识扩散之间的内在关系,该文将信息传输与用户意识扩散视作两种传播过程,并引入过程影响因子刻画两者相互作用。进一步地,建立了一种信息与用户意识耦合传播动力学模型,并进行了全面分析。其中,理论分析证明了模型平衡点的存在唯一性及其全局稳定性,这揭示了D2D通信中信息与用户意识耦合传播的最终状态。实验分析也验证了该理论结果。同时,与传统模型和未考虑过程影响的传播模型对比发现所提模型能扩大信息传播规模且能更准确刻画信息传播过程。Abstract: The information transmission process in Device to Device (D2D) communications is not only affected by physical communication conditions but also closely related to the dynamic properties of users. To explore the internal relationship between information transmission and user awareness diffusion, they are regarded as two propagation processes, and the interprocess interaction factors are introduced to describe the interaction in this paper. Furthermore, a coupling propagation dynamical model of information and user awareness is established and analyzed comprehensively. Specifically, the existence and uniqueness of the equilibrium and its global stability are proved through theoretical analysis, which reveals the final state of coupling propagation between information and user awareness in D2D communications. The theoretical results are also verified by experimental analysis. Meanwhile, compared with the traditional model and the propagation model without considering the interaction of process, the scale of information propagation can be expanded and the information propagation process can be described more accurately by the proposed model.
-
表 1 系统参数
参数 含义 $ {\beta _1} $ 单位时间用户与相邻用户交互而得知信息的概率 $ {\beta _2} $ 单位时间用户通过查看持有设备得知信息的概率 $ \alpha $ 单位时间设备间物理传输率,即设备间感染率 $ \lambda $ 单位时间设备转发信息的概率 $ \eta $ 单位时间设备停止转发但保留信息的概率 $ \gamma $ 单位时间信息被从设备中删除的概率 $ {\delta _1} $ 单位时间新连入的S状态的设备数量 $ {\delta _2} $ 单位时间新连入的I状态的设备数量 $ {\delta _3} $ 单位时间新连入的R状态的设备数量 $ \mu $ 单位时间D2D连接中断的概率 $ {L_1} $ 设备信息传输对用户意识扩散的过程影响因子 $ {L_{\text{2}}} $ 用户意识扩散对设备信息传输的过程影响因子 表 2 参数设置
参数 值 $ {\beta _{\text{1}}} $ 0.002 $ {\beta _{\text{2}}} $ 0.012 $ \alpha $ 0.02 $ \lambda $ 0.02 $ \eta $ 0.02 $ \gamma $ 0.08 $ \mu $ 0.08 $ {\delta _{\text{1}}} $ 4 $ {\delta _{\text{2}}} $ 3 $ {\delta _{\text{3}}} $ 2 -
[1] CAO Jin, MA Maode, LI Hui, et al. A survey on security aspects for 3GPP 5G networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(1): 170–195. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2951818 [2] PEDHADIYA M K, JHA R K, and BHATT H G. Device to device communication: A survey[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2019, 129: 71–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2018.10.012 [3] NITTI M, STELEA G A, POPESCU V, et al. When social networks meet D2D communications: A survey[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(2): 396. doi: 10.3390/s19020396 [4] 王璐, 王熠晨. 具有社交意识的D2D网络安全协作传输策略[C]. 2017-2019年“学术金秋”获奖论文集, 西安, 2020: 110–114.WANG Lu and WANG Yichen. D2D network security cooperative transmission strategy with social awareness[C]. 2017-2019 "Academic Autumn" Award Collection, Xi’an, China, 2020: 110–114. [5] 张灿, 史鑫, 王萌. 社交感知的D2D内容安全缓存算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(10): 167–172. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.180901776ZHANG Can, SHI Xin, and WANG Meng. Social-aware D2D secure caching algorithm[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(10): 167–172. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.180901776 [6] ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Zufan, ZENG Tian, et al. Modeling and analysis of dynamic social ties in D2D collaborative video transmission[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2020, 2020: 1915840. doi: 10.1155/2020/1915840 [7] YI Yinxue, ZHANG Zufan, YANG L T, et al. Reemergence modeling of intelligent information diffusion in heterogeneous social networks: the dynamics perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 828–840. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.2975112 [8] 徐少毅, 张鹏. D2D协作通信网络中基于社交信息的中继选择和功率分配[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1142–1149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160746XU Shaoyi and ZHANG Peng. Social network information based relay selection and power allocation in D2D communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1142–1149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160746 [9] SCATÀ M, DI STEFANO A, LA CORTE A, et al. A multiplex social contagion dynamics model to shape and discriminate D2D content dissemination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(2): 581–593. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3027697 [10] ZHANG Zufan, LIU Anqi, YI Yinxue, et al. Exploring the dynamical behavior of information diffusion in D2D communication environment[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2020, 2020: 8848576. doi: 10.1155/2020/8848576 [11] SANG Chunyan and LIAO Shigen. Modeling and simulation of information dissemination model considering user’s awareness behavior in mobile social networks[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2020, 537: 122639. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.122639 [12] ZHOU Yinzuo, ZHOU Jie, CHEN Guanrong, et al. Effective degree theory for awareness and epidemic spreading on multiplex networks[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2019, 21(3): 035002. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/ab0458 [13] 魏静, 黄阳江豪, 朱恒民. 基于耦合网络的社交网络舆情传播模型研究[J]. 现代情报, 2019, 39(10): 110–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2019.10.013WEI Jing, HUANG Yangjianghao, and ZHU Hengmin. Research on public opinion communication model of social network based on coupling network[J]. Journal of Modern Information, 2019, 39(10): 110–118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0821.2019.10.013 [14] YI Yinxue, ZHANG Zufan, and GAN Chenquan. The outbreak threshold of information diffusion over social–physical networks[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019, 526: 121128. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.121128 [15] ZHANG Yuexia and PAN Dawei. Layered SIRS model of information spread in complex networks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2021, 411: 126524. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2021.126524 [16] YI Yinxue, ZHANG Zufan, YANG L T, et al. Social interaction and information diffusion in social Internet of Things: Dynamics, cloud-edge, traceability[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(4): 2177–2199. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3026995 [17] WANG Zhishuang, GUO Quantong, SUN Shiwen, et al. The impact of awareness diffusion on SIR-like epidemics in multiplex networks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2019, 349: 134–147. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2018.12.045 [18] XIA Chengyi, WANG Zhishuang, ZHENG Chunyuan, et al. A new coupled disease-awareness spreading model with mass media on multiplex networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 471: 185–200. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.08.050 [19] HÉBERT-DUFRESNE L, MISTRY D, and ALTHOUSE B M. Spread of infectious disease and social awareness as parasitic contagions on clustered networks[J]. Physical Review Research, 2020, 2(3): 033306. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.2.033306 [20] ROBINSON R C. An Introduction to Dynamical Systems: Continuous and Discrete[M]. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2004. [21] THIEME H R. Asymptotically autonomous differential equations in the plane[J]. Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics, 1993, 24(1): 351–380. doi: 10.1216/rmjm/1181072470 [22] GAN Chenquan, LI Xiaoke, WANG Lisha, et al. The impact of user behavior on information diffusion in D2D communications: A discrete dynamical model[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2018, 2018: 3745769. doi: 10.1155/2018/3745769 -





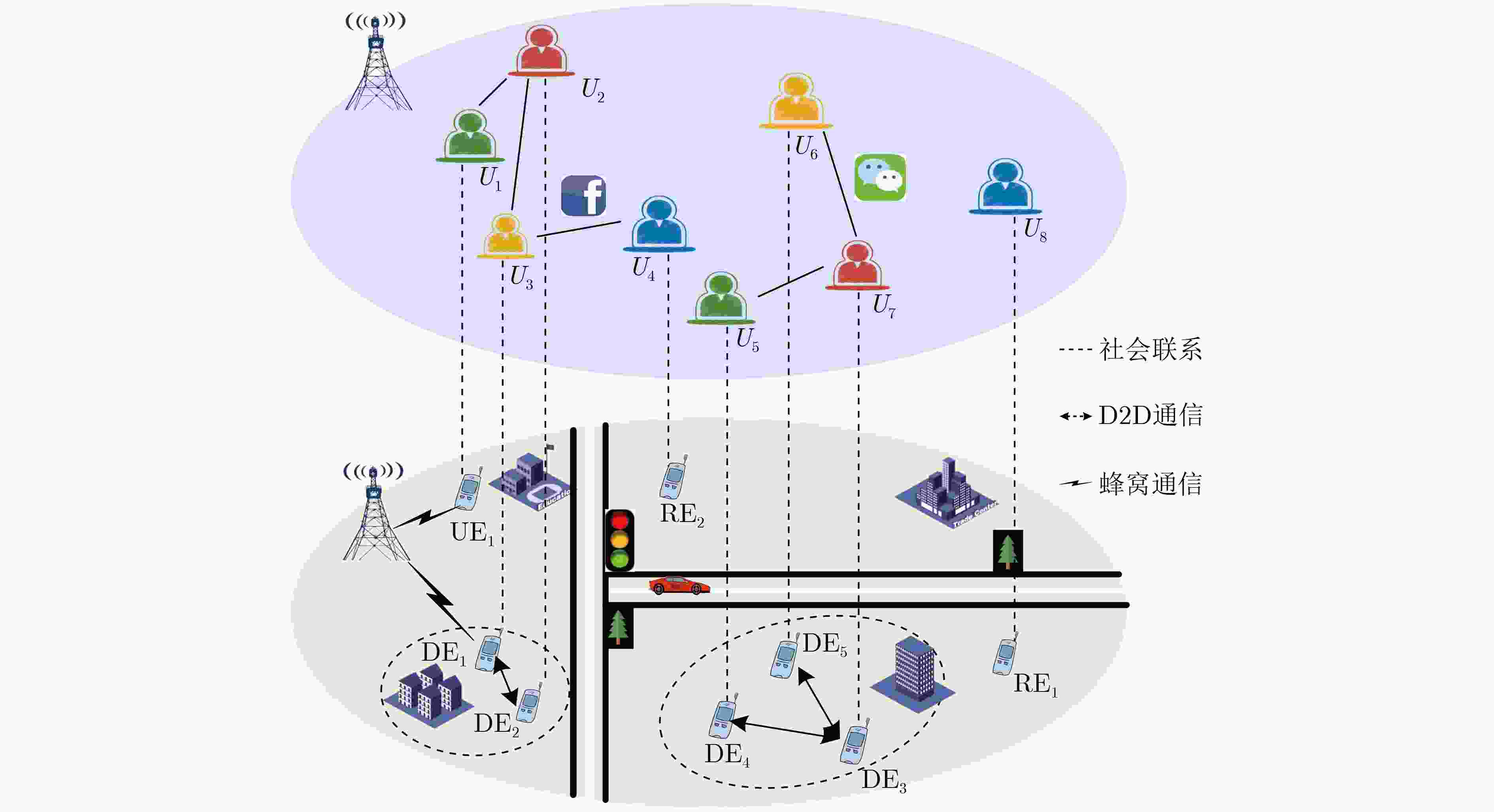
 下载:
下载:
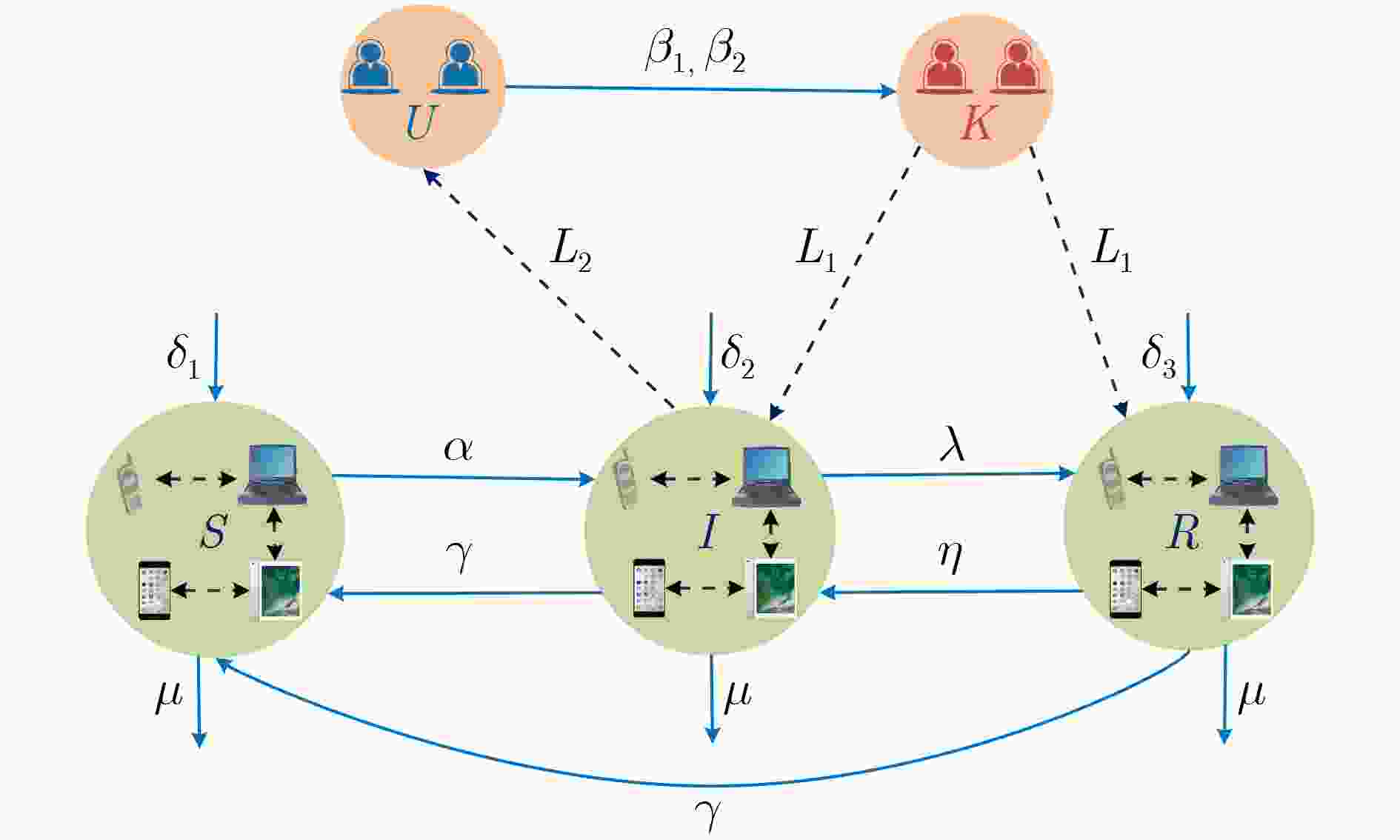
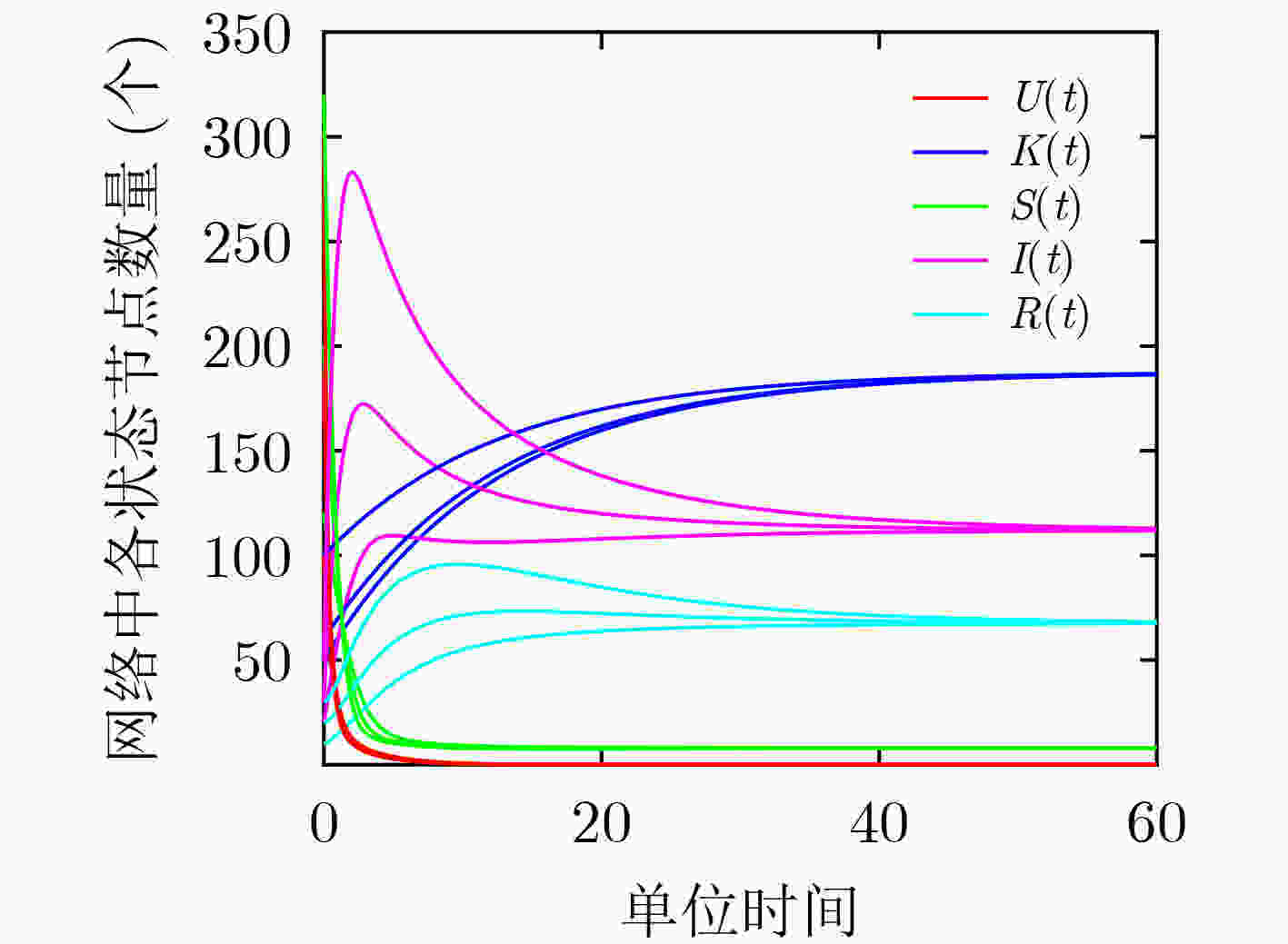

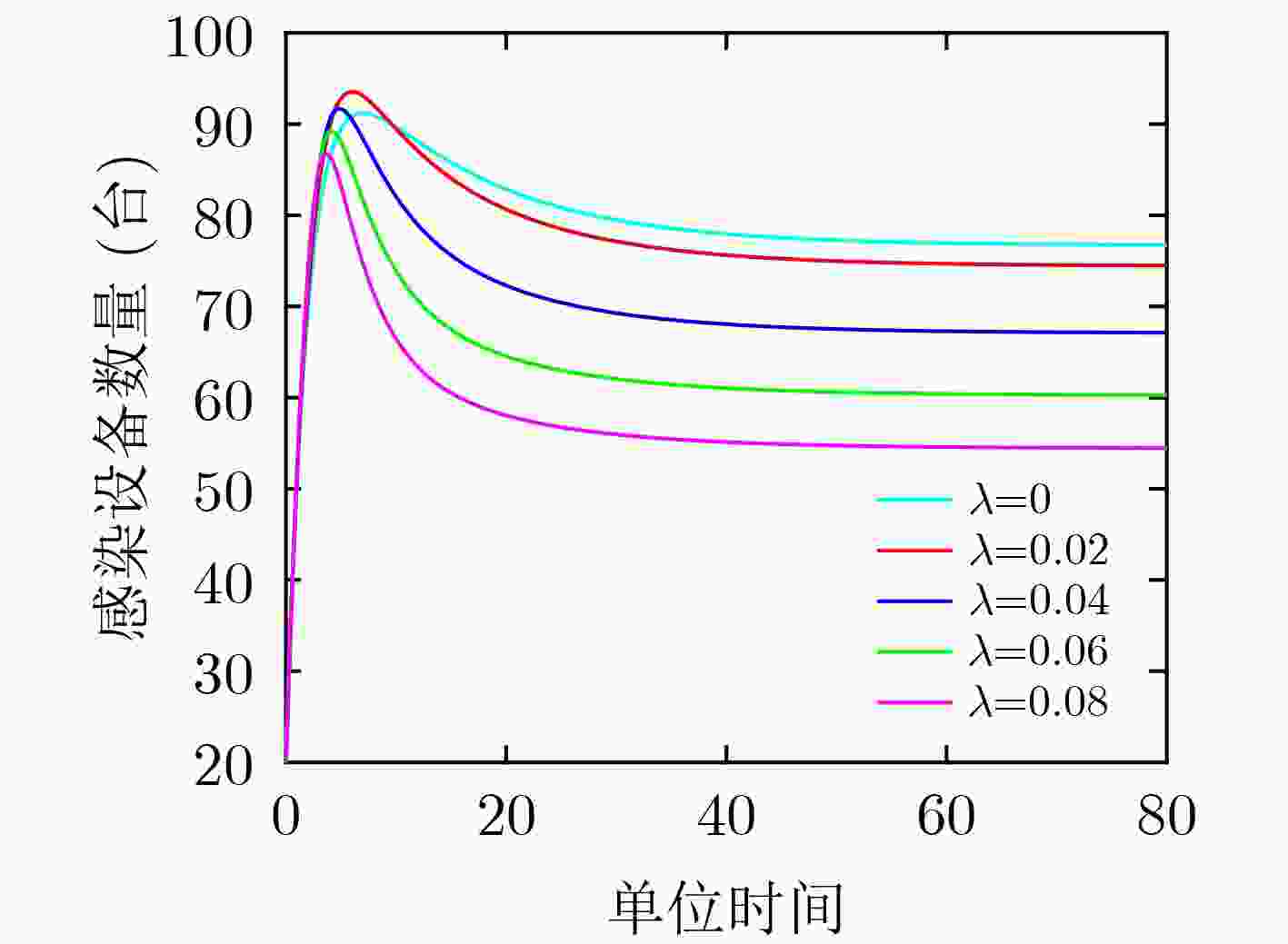

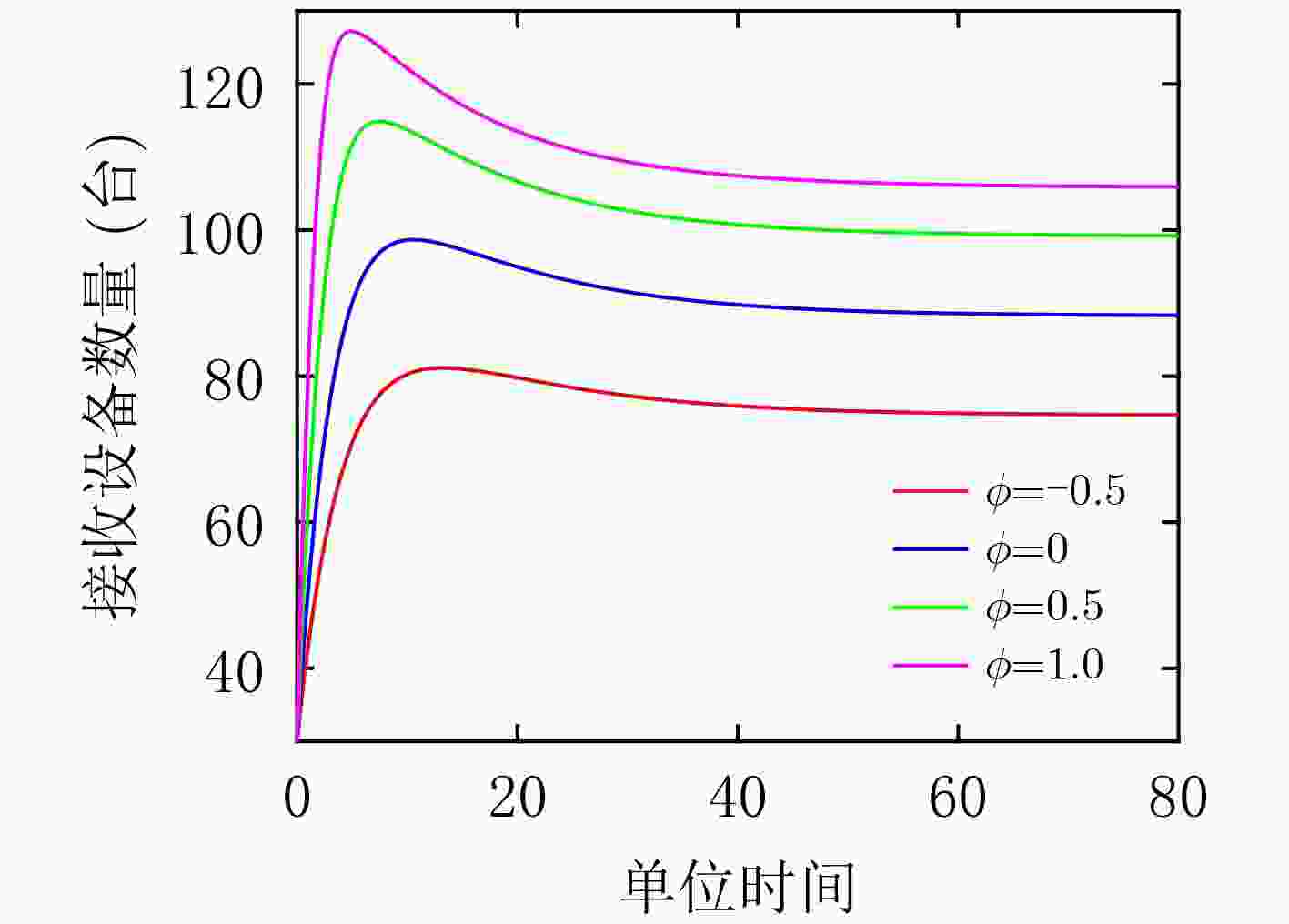



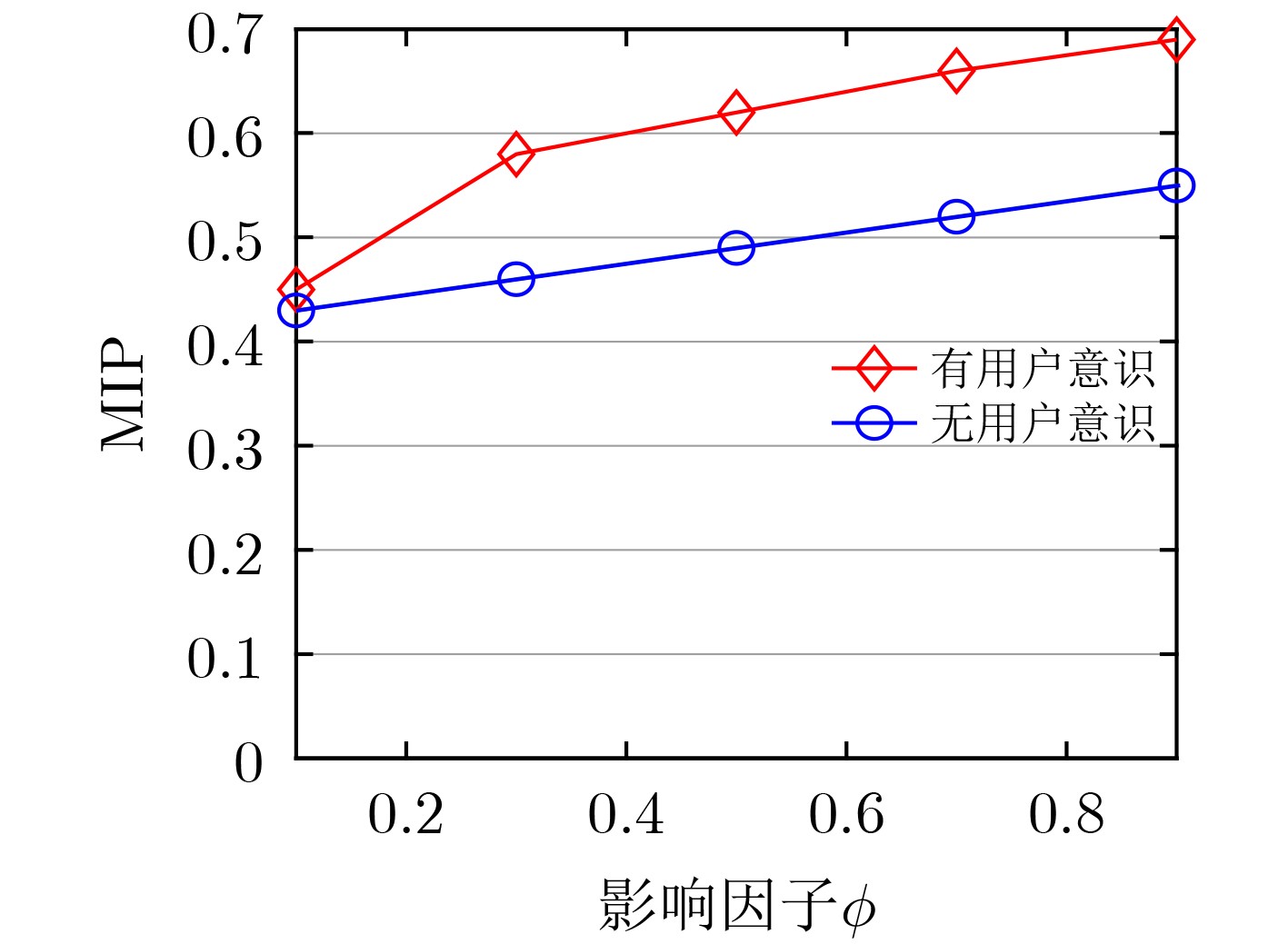
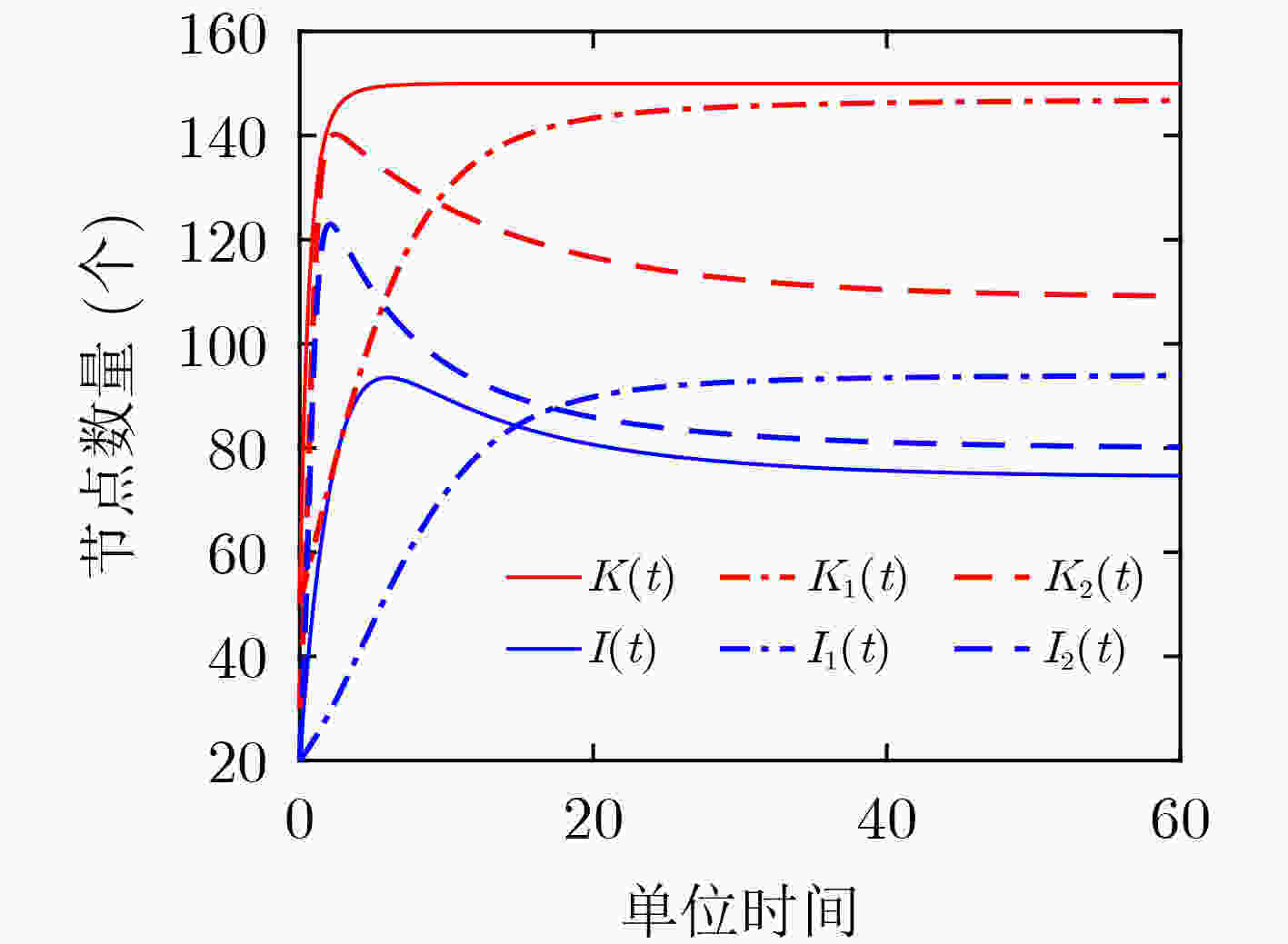
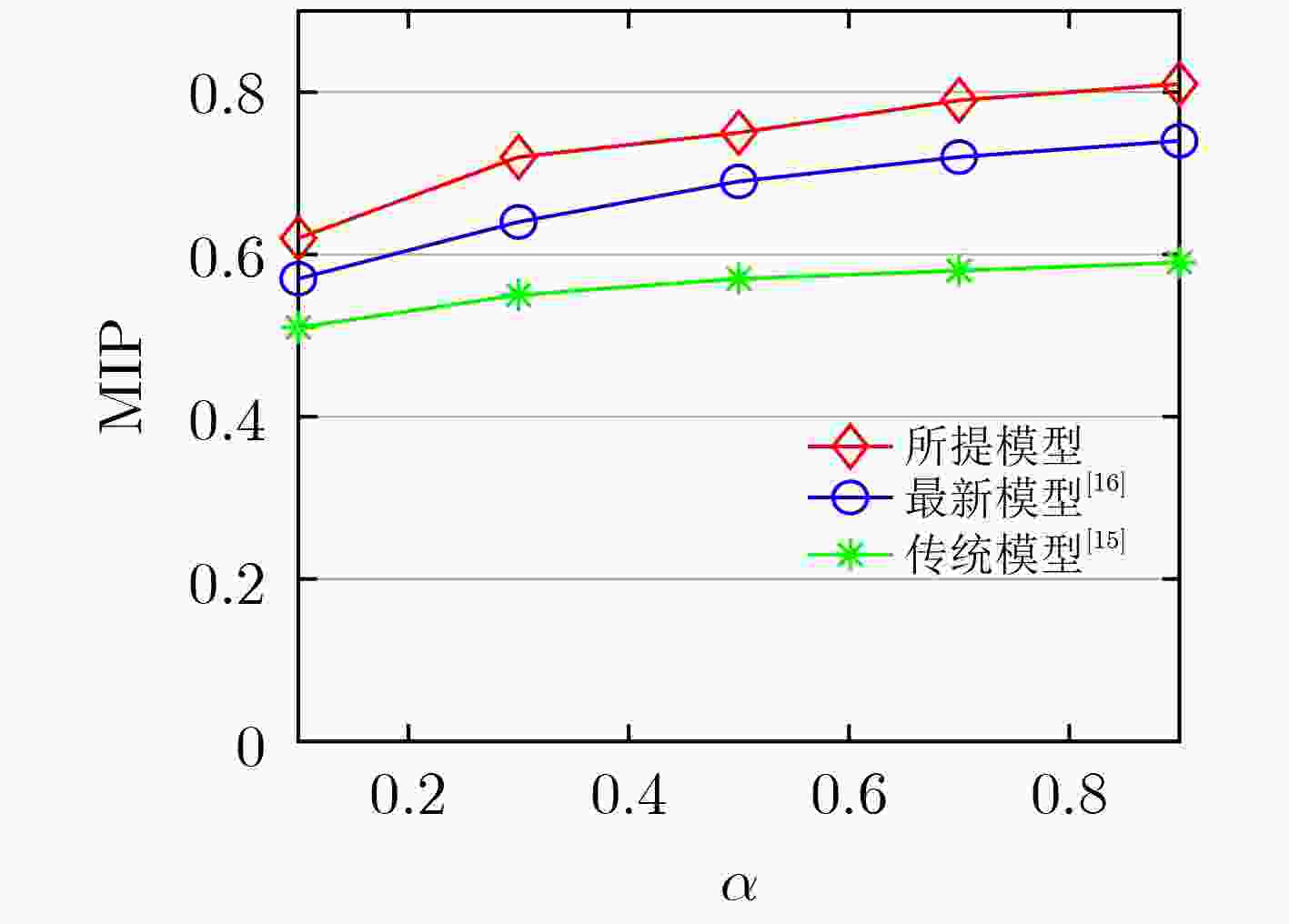




 下载:
下载:
