Adaptive and Efficient Time Synchronization Optimization Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Networks
-
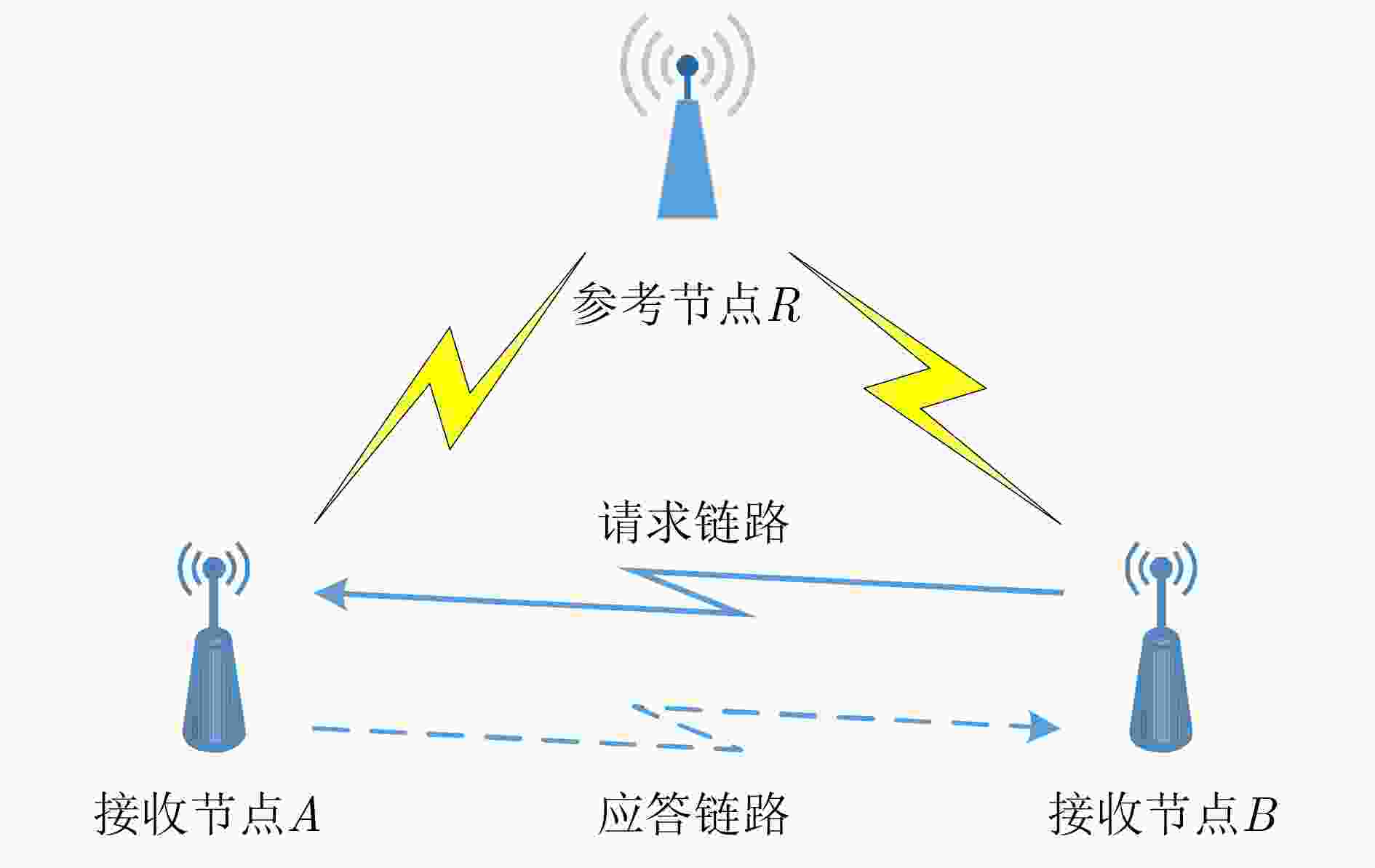
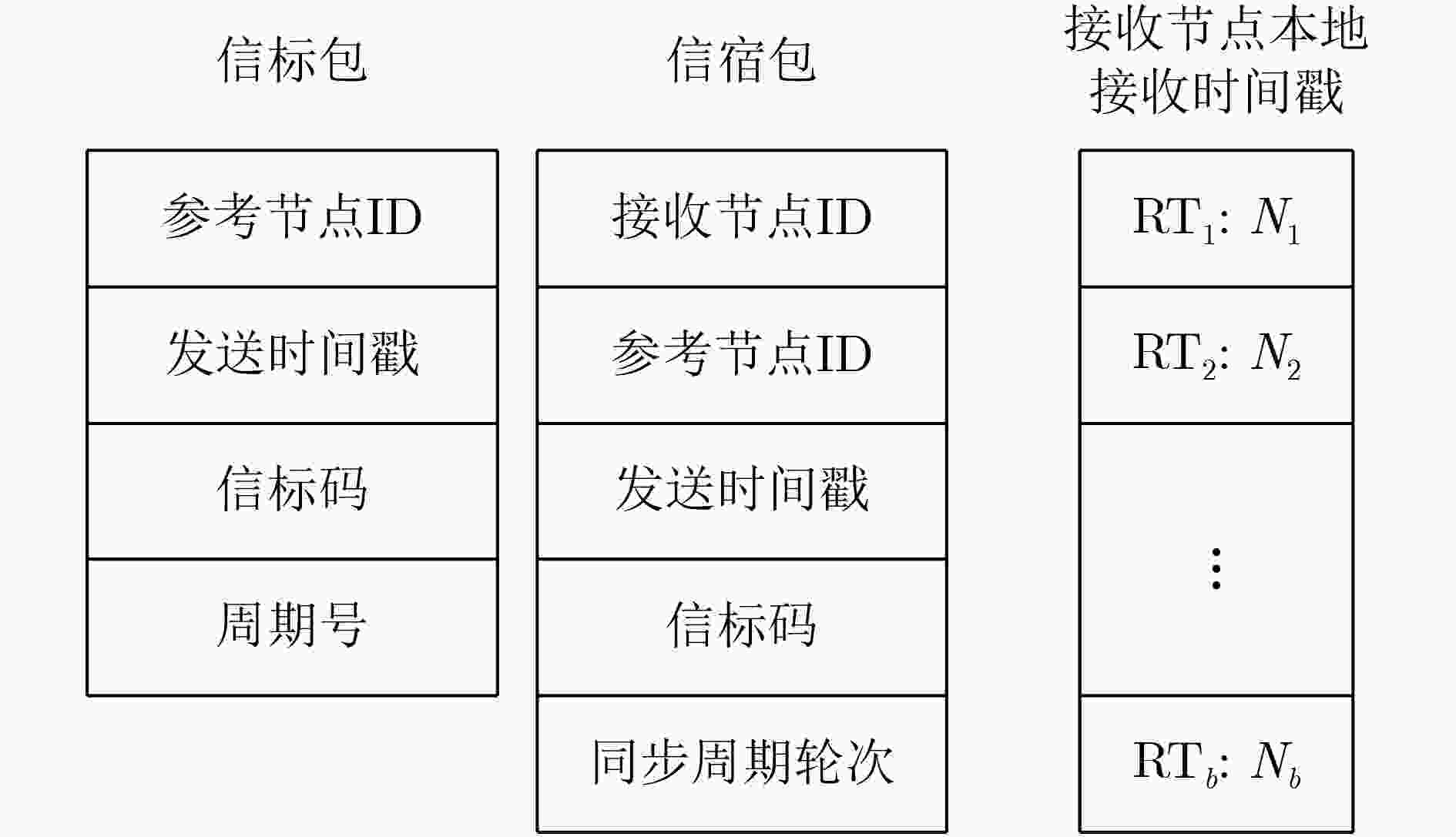
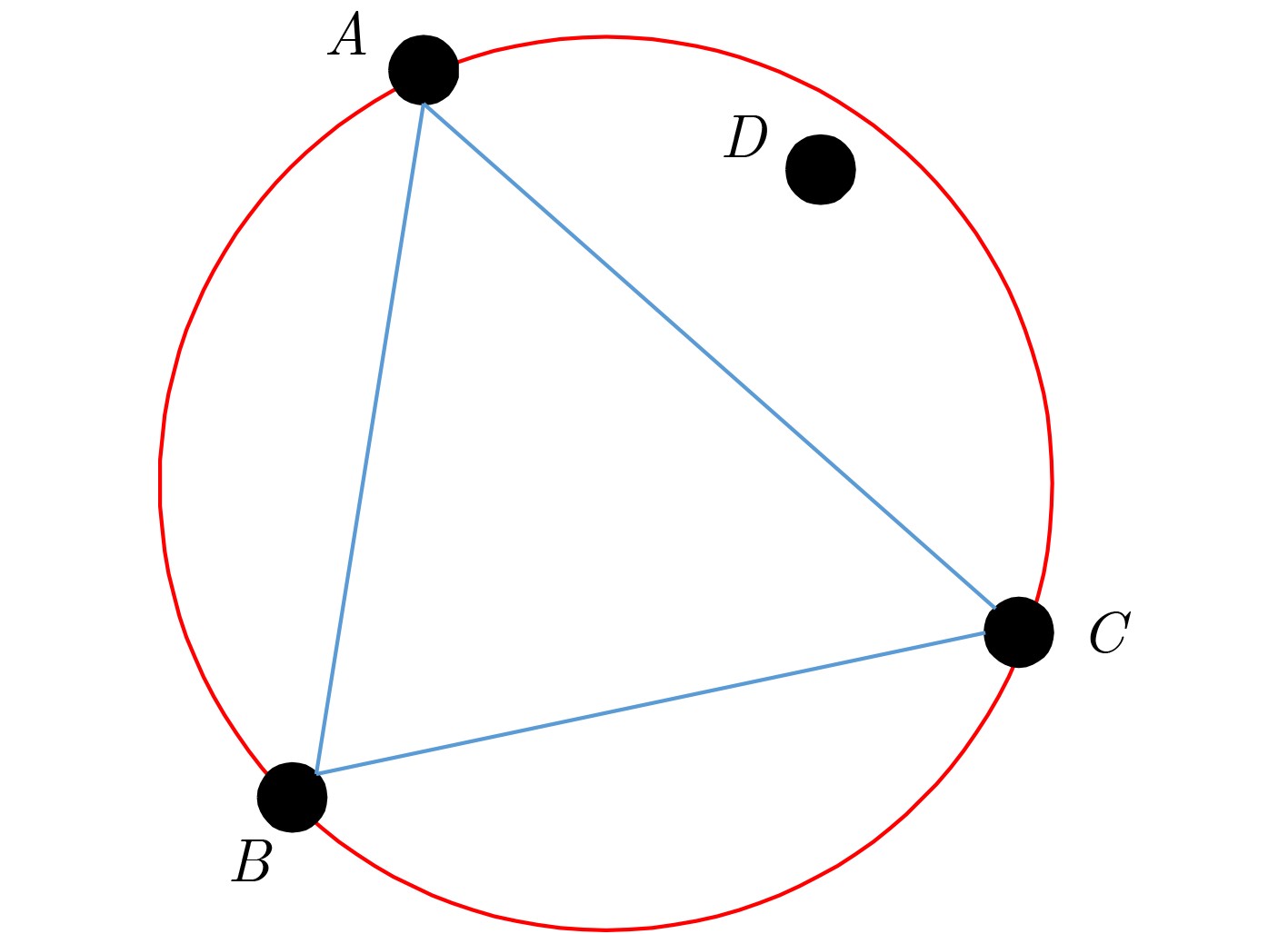
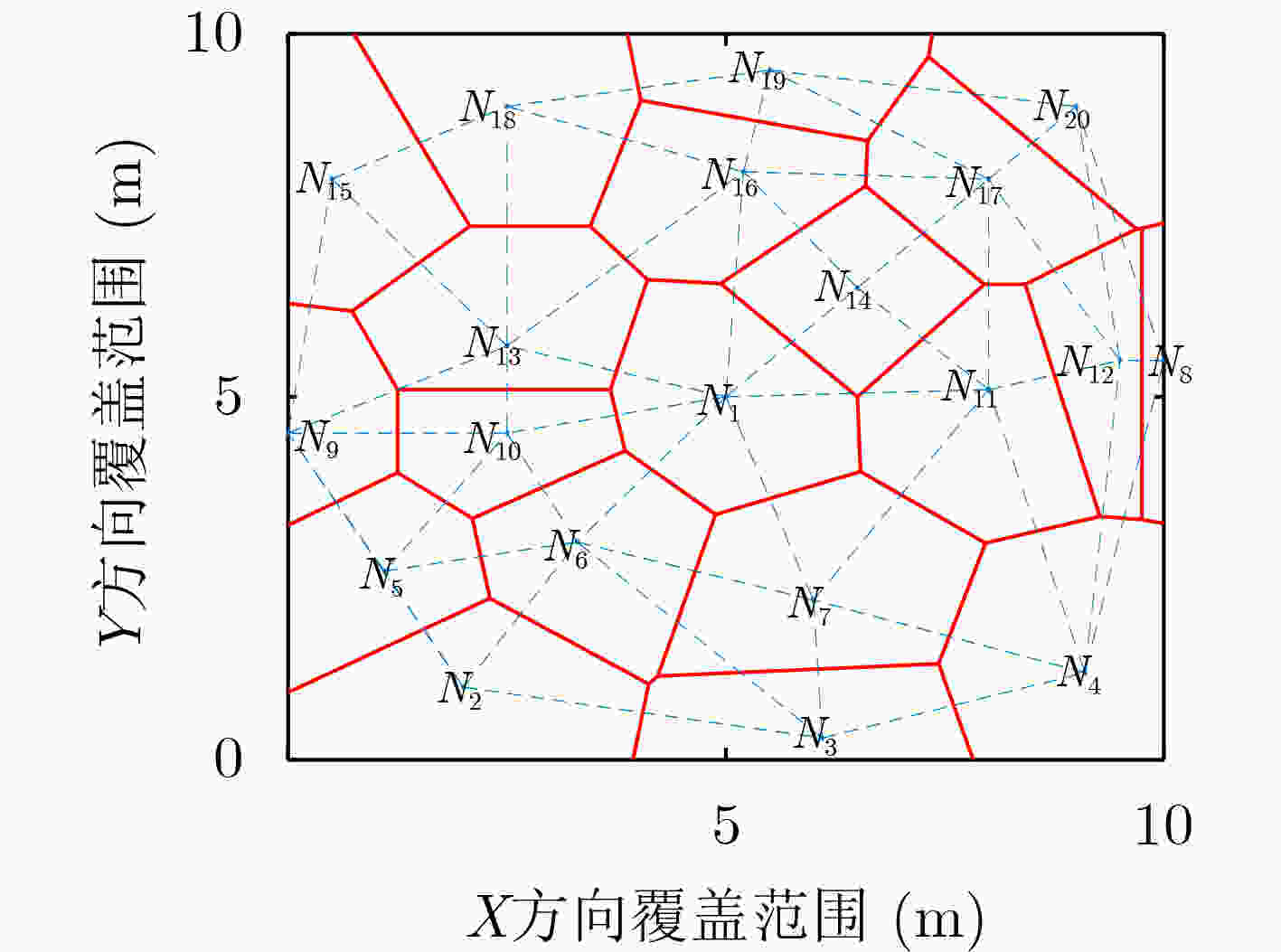
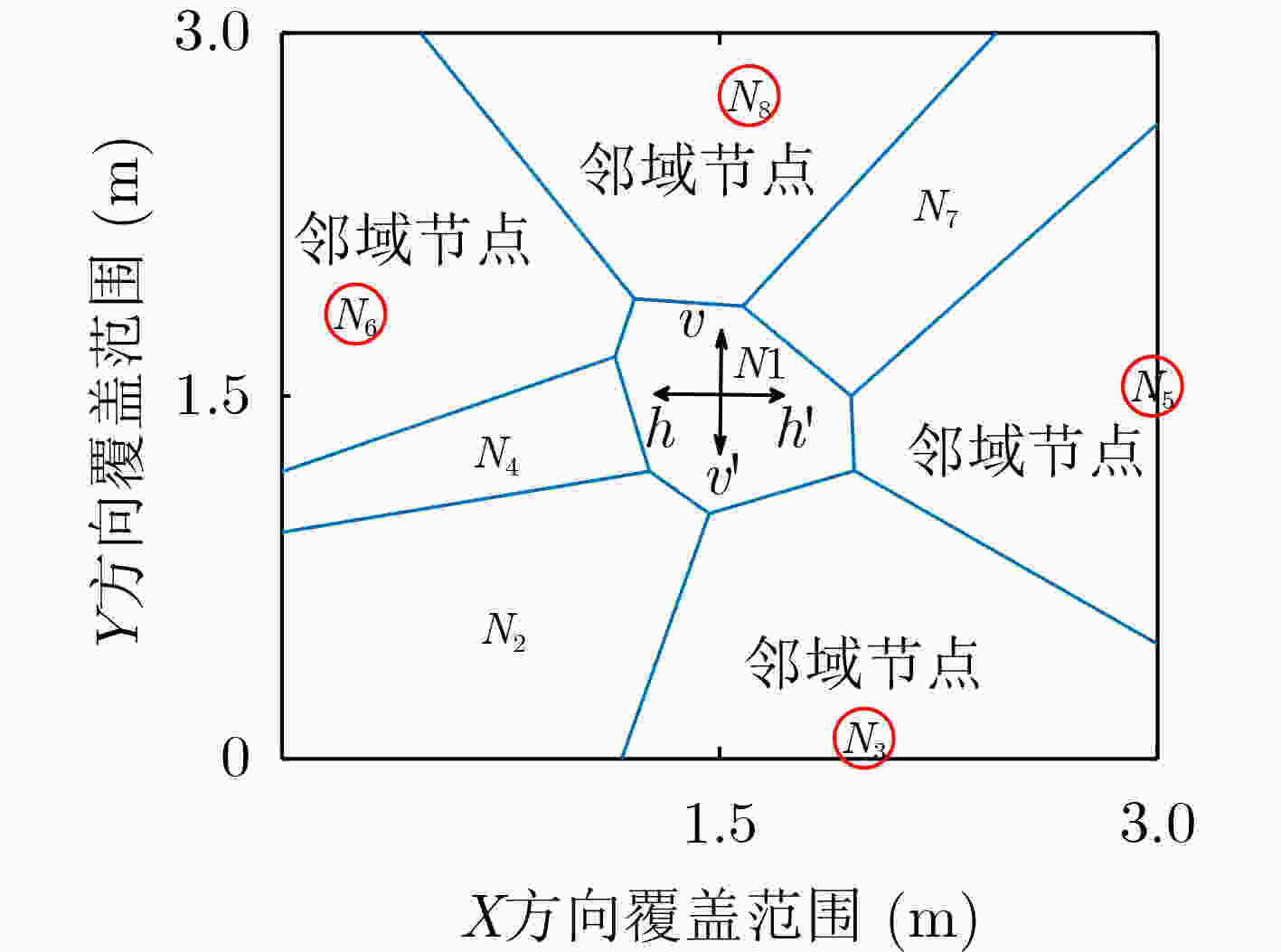
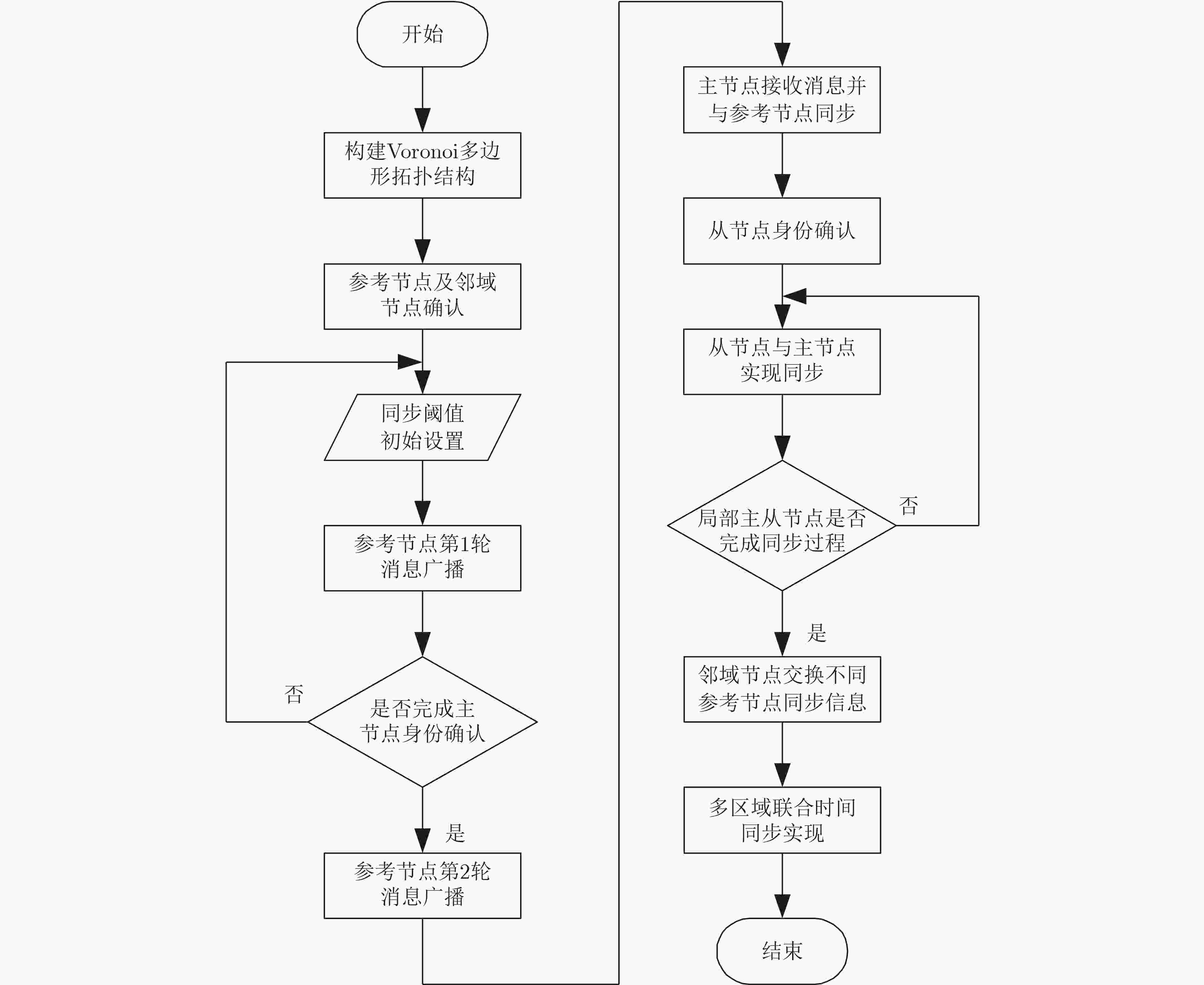
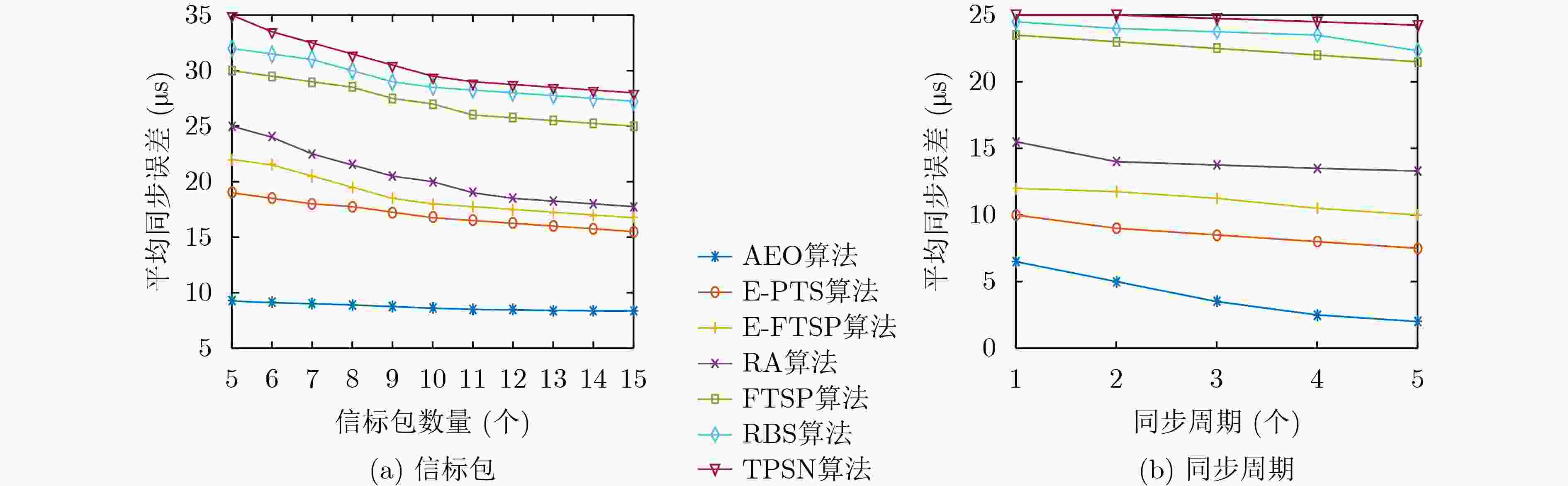
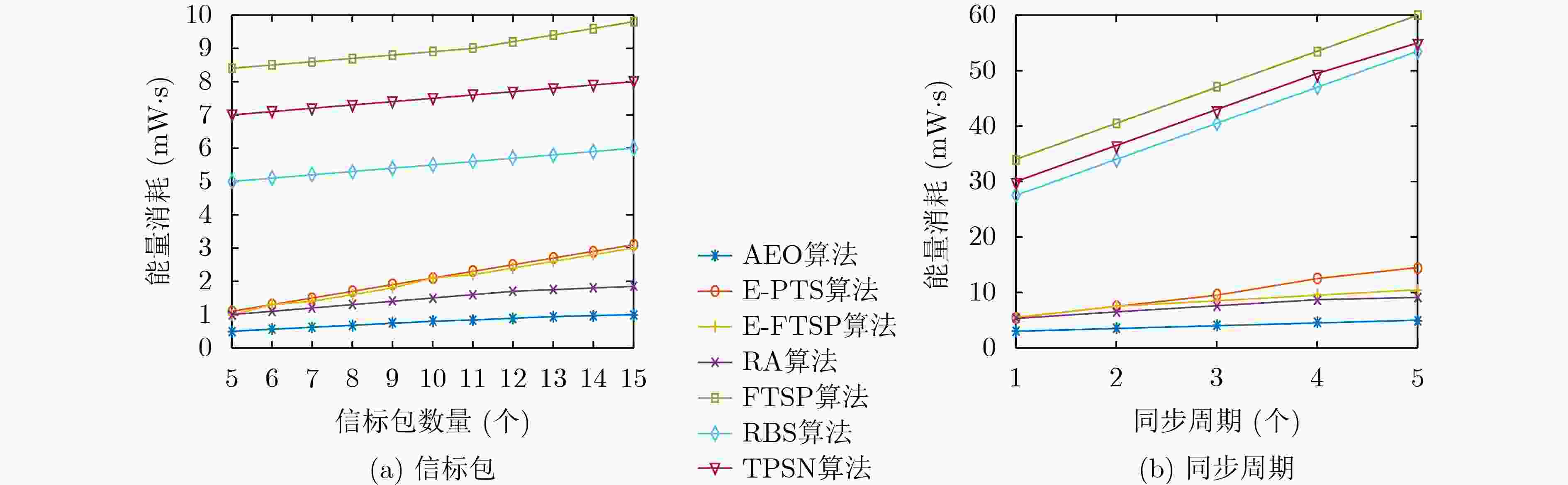
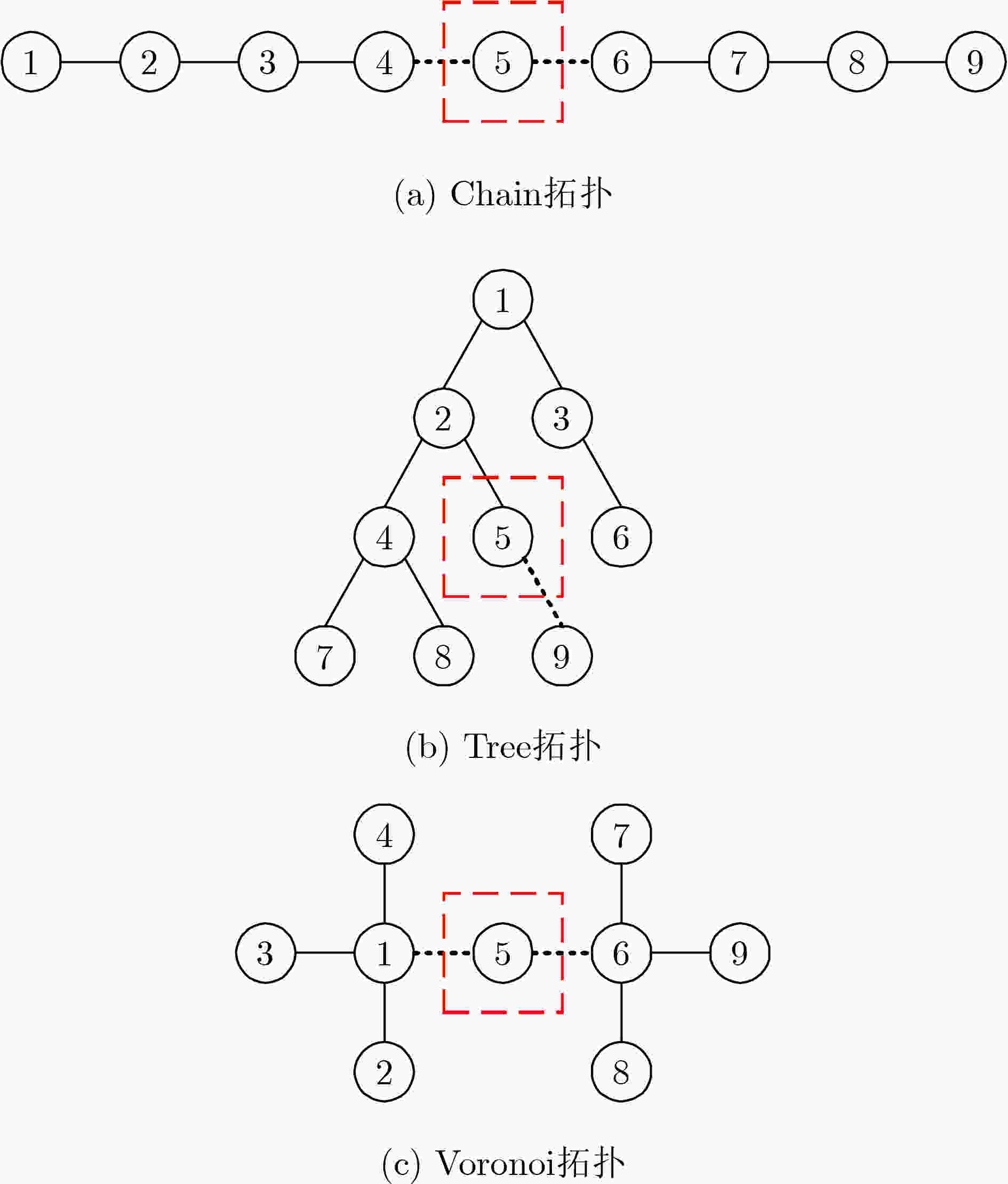
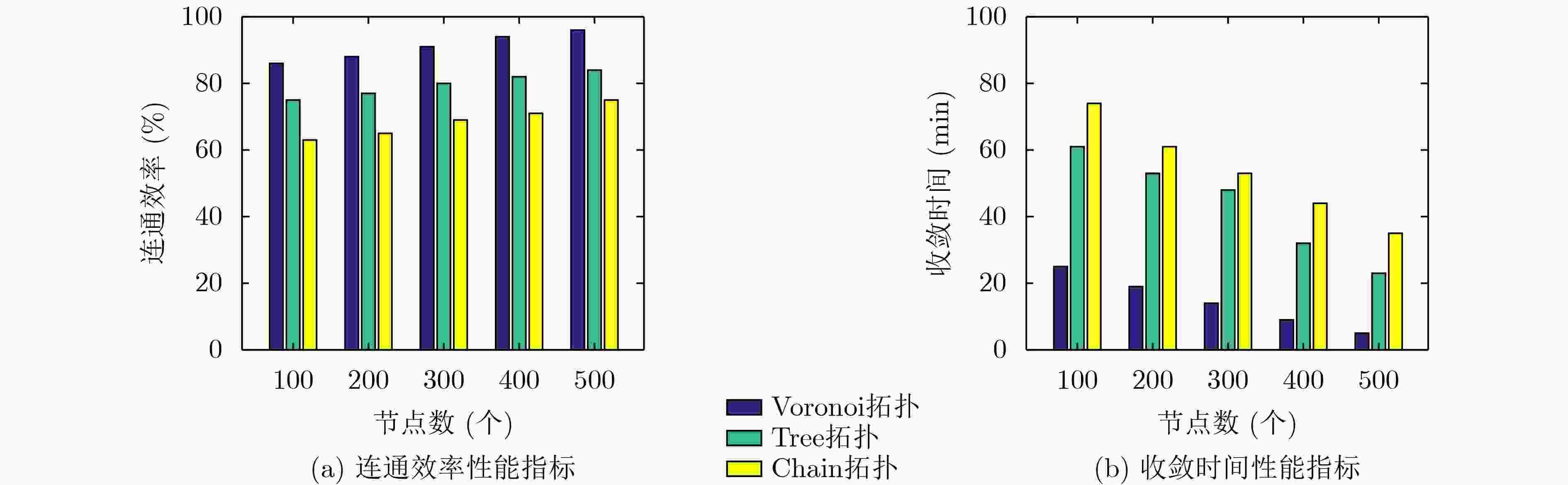
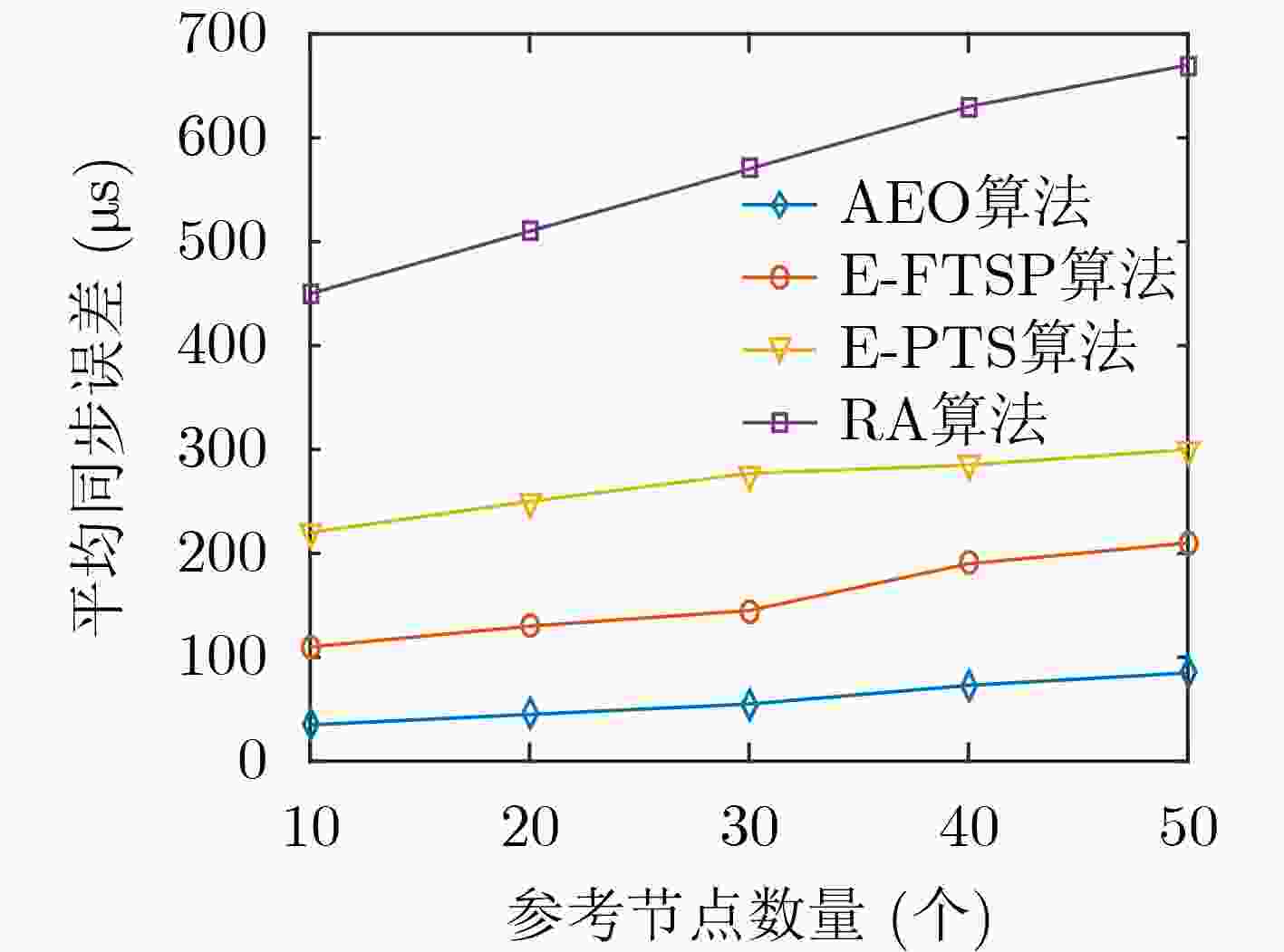
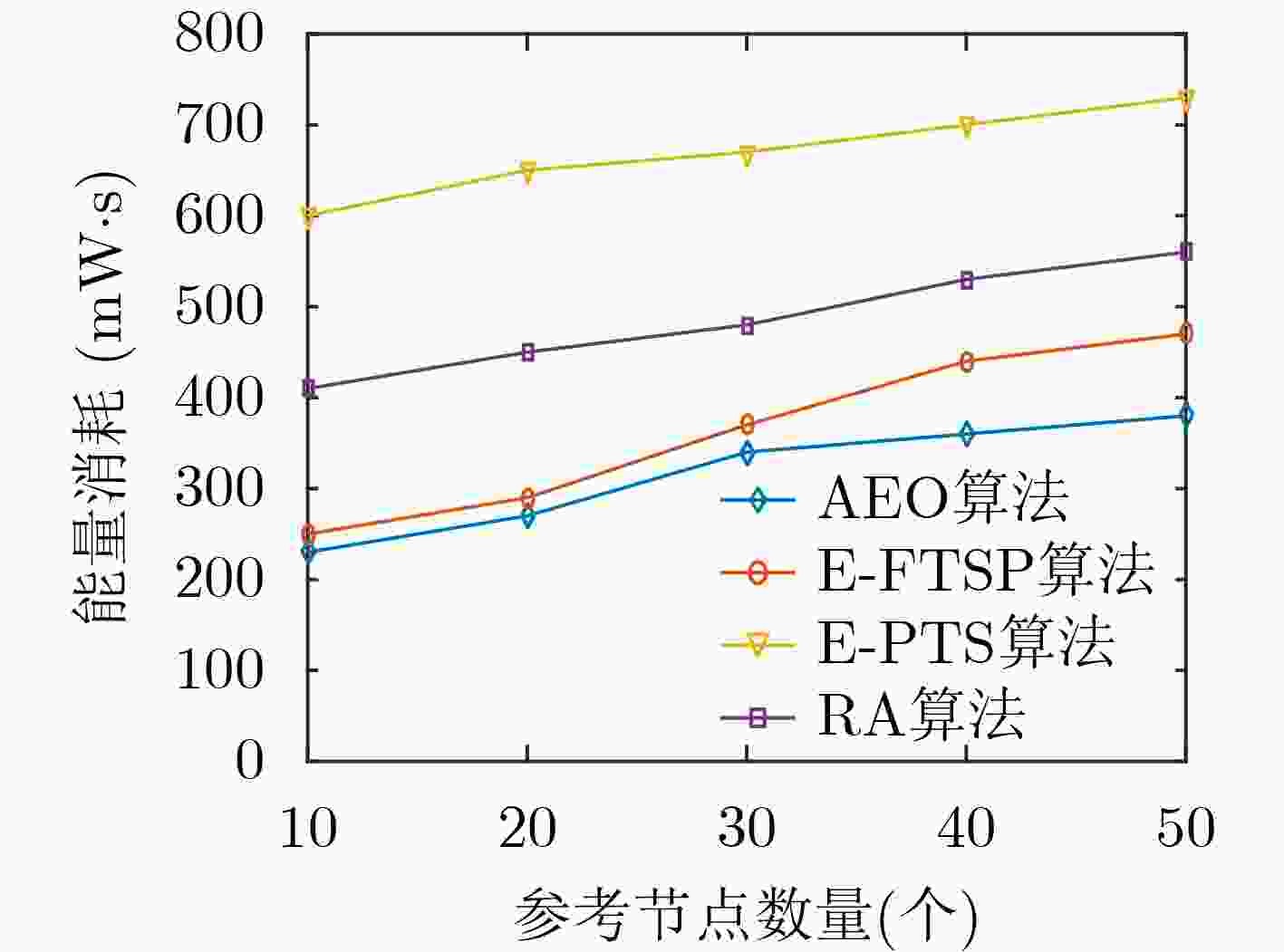
摘要: 针对无线传感器网络全网多跳自适应时间同步效率低的问题,在接收端与接收端同步模型基础上,该文提出一种自适应高效无线传感器网络时间同步优化算法(AEO)。首先,双节点同步时,从节点接收来自参考节点的同步消息并进行确认,在同步周期结束后通过拟合估计和数据更新完成时间修正,构建交互参数同步包,并与主节点进行信息交换完成同步过程。其次,全网同步时,建立Voronoi多边形拓扑结构,认定拓扑结构中参考节点和邻域节点身份(ID),参考节点覆盖区域间通过邻域节点交换同步信息,实现自适应多区域节点联合时间同步。仿真结果表明该算法在双节点时间同步中能够保证同步误差较小,网络能耗较低;同时,Voronoi拓扑相较于其他典型拓扑,在连通效率和收敛时间方面均有所改进。Abstract: To solve the problem of low efficiency for multiple-hop adaptive time synchronization in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), an Adaptive and Efficient time synchronization Optimization (AEO) algorithm is proposed based on receiver-receiver time synchronization model. Firstly, in pairwise time synchronization, slave node receives the synchronization message from reference node and confirmed. After the synchronization period, the time correction is realized by fitting estimation and data update. Then the interactive parameter synchronization package is constructed. The slave node exchanges interactive parameter synchronization package with the master to realize pairwise synchronization. Secondly, the Voronoi polygon topology is established. The network also identifies the IDentification (ID) of reference nodes and neighbor nodes in the topology. The coverage area of reference nodes exchange synchronization information by neighboring nodes to realize adaptive regions joint time synchronization. The simulation results show that the algorithm has less synchronization errors and lower network energy consumption in pairwise time synchronization. Meanwhile, the Voronoi topology improves connectivity efficiency and convergence time compared with other typical topologies.
-
表 1 仿真参数
参数 设置值 最大数据报大小 127 Byte 最大网络范围 500 m × 500 m 网络节点数量 100~500 最大感知半径 20 m 最大通信半径 40 m 参考节点数量 10~50 信标包数量 5~15 信标间隔 1 s 周期数 1~5 仿真时间 5 h 节点初始能量 5 W·s 发送端能量消耗 50 nW·s/bit 接收端能量消耗 50 nW·s/bit -
[1] YADAV D K, JAYANTH S, DAS S K, et al. Critical review on slope monitoring systems with a vision of unifying WSN and IoT[J]. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 2019, 9(4): 167–180. doi: 10.1049/iet-wss.2018.5197 [2] GUO Jun and JAFARKHANI H. Movement-efficient sensor deployment in wireless sensor networks with limited communication range[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(7): 3469–3484. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2914199 [3] GRICHI H, MOSBAHI O, KHALGUI M, et al. New power-oriented methodology for dynamic resizing and mobility of reconfigurable wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2018, 48(7): 1120–1130. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2645401 [4] AL-SHAIKHI A and MASOUD A. Efficient, single hop time synchronization protocol for randomly connected WSNs[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2017, 6(2): 170–173. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2017.2650223 [5] ELSON J, GIROD L, and ESTRIN D. Fine-grained network time synchronization using reference broadcasts[C]. The 5th Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, Boston, USA, 2002: 147–163. [6] KASHYAP D and JAIN T K. Comparative analysis of time synchronization schemes for wireless sensor networks[C]. 2014 International Conference on Signal Propagation and Computer Technology, Ajmer, India, 2014: 1–4. [7] 王义君, 钱志鸿, 王桂琴, 等. 无线传感器网络能量有效时间同步算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(9): 2174–2179. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00236WANG Yijun, QIAN Zhihong, WANG Guiqin, et al. Research on energy-efficient time synchronization algorithm for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(9): 2174–2179. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00236 [8] SHI Fanrong, TUO Xianguo, RAN Lili, et al. Fast convergence time synchronization in wireless sensor networks based on average consensus[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(2): 1120–1129. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2936518 [9] SUN Xianbo, SU Yixin, HUANG Yong, et al. Design and development of a wireless sensor network time synchronization system for photovoltaic module monitoring[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2020, 16(5): 1–8. doi: 10.1177/1550147720927341 [10] UPADHYAY D, DUBEY A K, and THILAGAM P S. Application of non-linear gaussian regression-based adaptive clock synchronization technique for wireless sensor network in agriculture[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(10): 4328–4335. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2818302 [11] HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R, and FRIEDMAN J. The Elements of Statistical Learning[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2009: 349. [12] 刘大鹍, 陈桂芬, 王义君. 无线自组织网络协作时间同步优化算法[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(4): 702–710. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.04.009LIU Dakun, CHEN Guifen, and WANG Yijun. Cooperative time synchronization optimization algorithm for wireless ad hoc Networks[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(4): 702–710. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.04.009 [13] LIU Yuanxin and SNOEYINK J. A comparison of five implementations of 3D Delaunay tessellation[J]. Combinatorial and Computational Geometry, 2005, 52(2005): 439–458. [14] MARÓTI M, KUSY B, SIMON G, et al. The flooding time synchronization protocol[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Baltimore, USA, 2004: 39–49. [15] PHAN L A, KIM T, KIM T, et al. Performance analysis of time synchronization protocols in wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(13): 3020. doi: 10.3390/s19133020 [16] GANERIWAL S, KUMAR R, and SRIVASTAVA M B. Timing-sync protocol for sensor networks[C]. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Los Angeles, USA, 2003: 138–149. [17] CHO H, KIM J, and BAEK Y. Enhanced precision time synchronization for wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(8): 7625–7643. doi: 10.3390/s110807625 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
