Robust Energy Efficiency Resource Allocation Algorithm in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-assisted Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Networks
-
摘要: 为提高非正交多址接入(NOMA)网络的鲁棒性和系统能效(EE),考虑了不完美信道状态信息,该文提出一种可重构智能表面(RIS)辅助的NOMA网络鲁棒能效最大资源分配算法。考虑用户信干噪比(SINR)中断概率约束、基站的最大发射功率约束以及连续相移约束,建立了一个非线性的能效最大化资源分配模型。用Dinkelbach方法将分式形式的目标函数转换为线性的参数相减的形式,利用S-procedure方法将含有信道不确定性的SINR中断概率约束转换成确定性形式,利用交替优化算法将多变量耦合的非凸优化问题分解成多个凸优化子问题,最后用CVX对分解出的子问题进行求解。仿真结果表明,在EE方面,所提算法比无可重构智能表面(RIS)算法提高了7.4%。在SINR中断概率方面,所提算法比非鲁棒算法降低了85.5%。Abstract: To improve the robustness and Energy Efficiency (EE) of Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA)-based networks, a robust EE maximization-based algorithm is proposed in a Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-assisted NOMA network with imperfect channel state information. Considering the outage probability constraints of users' Signal-to-Interference-to-Noise Ratio (SINR), the maximum transmit power constraints of the base station, and continuous phase shift constraints, a nonlinear EE maximization-based resource allocation model is established. By using Dinkelbach's method the fractional objective function is converted into a linear parameter subtraction form, the S-procedure method is used to transform the outage probability of SINR with channel uncertainty into deterministic form. By using the alternative optimization method, the non-convex optimization problem is converted into several convex optimization subproblems, then the CVX is used to solve the subproblems. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is 7.4% higher than the without Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) algorithm in terms of EE, the proposed algorithm is 85.5% lower than the non-robust algorithm in terms of the outage probability of SINR.
-
表 1 系统参数描述
参数 含义 参数 含义 $ K $ 用户数 $ \xi $ 发射功率放大器的效率 $ M $ 基站天线数 $ {s}_{k} $ 基站发给用户k的期望信号 $N$ RIS反射振元数 ${{\boldsymbol{w}}_k}$ 基站到用户k的波束成形向量 ${\boldsymbol{G}}$ BS到RIS的信道 $ {\rho _k} $ 用户k的SINR小于目标SINR的概率 ${{\boldsymbol{h}}_k}$ BS到用户k的信道 ${P_{{\text{BS}}}}$ BS总功率消耗 ${{\boldsymbol{r}}_k}$ RIS到用户k的信道 ${P_c}$ 系统总电路损耗 $ {\theta _n} $ 反射系数的相移 ${{\hat {\boldsymbol G}}}$ BS到RIS的估计信道 ${t_k}$,${\mu _k}$ 松弛变量 $\Delta {\boldsymbol{G}}$ BS到RIS的估计信道误差 ${\boldsymbol{\theta }}$ 相移对角矩阵 ${{{\hat {\boldsymbol r}}}_k}$ RIS到用户k的估计信道 $ \gamma _k^{{\text{tar}}} $ 用户k的目标SINR $\Delta {{\boldsymbol{r}}_k}$ RIS到用户k的估计信道误差 ${P_0}$ BS的最大传输功率 $ {{\boldsymbol{I}}_a} $ 大小为$a \times a$的单位矩阵 表 2 基于交替迭代的能效资源分配算法
初始化系统参数$i = 1$;给定${{\boldsymbol{\varTheta }}^{(0)}}$, $\beta _k^{(0)}$, ${\lambda ^{(0)}}$, ${\boldsymbol{W}}_k^{(0)}$;最大迭
代次数${i_{\max }}$;收敛精度$\varepsilon {\text{ = }}{10^{ - 6}}$;(1) for $i = 1,2,\cdots$ do
(2) 根据给定的${ {\boldsymbol{\varTheta } }^{(i{{ - } }1)} }$和$\beta _k^{(i{{ - } }1)}$求解问题式(31)得到主动波
束成形$\{ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_k}\} $以及$\mathcal{F}_i^1$;(3) 根据给定$\{ {\boldsymbol{W}}_k^{(i)}\} $和$ {{\boldsymbol{\varTheta }}^{(i - 1)}} $求解问题式(32)得到松弛变量
${\beta _k}$以及$ \mathcal{F}_i^2 $;
(4) 根据给定$\{ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_k}\} $和${\beta _k}$求解问题式(33)得到被动波束成形${\boldsymbol{\varTheta }}$;
(5) 计算$ ℱ{i}_{}({\lambda }^{(i)}) $, $\lambda _{}^{(i)} = {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{k = 1}^K { { {\log }_2}(1 + \beta _k^{(i)})} }/\xi \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{k = 1}^K$ ${ {\text{Tr} }\left( { {\boldsymbol{W} }_k^{(i)} } \right)} +{P_c}$;
(6) if $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{\left| {\mathcal{F}_i^1 - \mathcal{F}_{i - 1}^1} \right|}/ {\mathcal{F}_{i - 1}^1 \le \varepsilon }}} \\ \begin{gathered} {{\left| {\mathcal{F}_i^2 - \mathcal{F}_{i - 1}^2} \right|}/ {\mathcal{F}_{i - 1}^2 \le \varepsilon }} \\ {{\left| {{\mathcal{F}_i} - {\mathcal{F}_{i - 1}}} \right|}/{{\mathcal{F}_{i - 1}} \le \varepsilon }} \\ \end{gathered} \end{array}} \right. $ 或者$i = {i_{\max }}$则
(7) break;
(8) else(9) $i = i + 1$;
(10) end if(11) end for -
[1] ZHANG Shunqing, WU Qingqing, XU Shugong, et al. Fundamental green tradeoffs: Progresses, challenges, and impacts on 5G networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(1): 33–56. [2] AKYILDIZ I F, KAK A, and NIE S. 6G and beyond: The future of wireless communications systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 133995–134030. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010896 [3] XU Yongjun, GUAN Gui, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. [4] DING Zhiguo, PENG Mugen, and POOR H V. Cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access in 5G systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2015, 19(8): 1462–1465. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2015.2441064 [5] DING Zhiguo and POOR H V. A simple design of IRS-NOMA transmission[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(5): 1119–1123. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2974196 [6] ZENG Ming, LI Xingwang, LI Gen, et al. Sum rate maximization for IRS-assisted uplink NOMA[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(1): 234–238. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3025978 [7] MU Xidong, LIU Yuanwei, GUO Li, et al. Exploiting Intelligent reflecting surfaces in NOMA networks: Joint beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6884–6898. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3006915 [8] NI Wanli, LIU Xiao, LIU Yuanwei, et al. Resource allocation for multi-cell IRS-aided NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(7): 4253–4268. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3057232 [9] ZUO Jiakuo, LIU Yuanwei, QIN Zhijin, et al. The application of intelligent reflecting surface in downlink NOMA systems[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. [10] ZHU Jianyue, HUANG Yongming, WANG Jiaheng, et al. Power efficient IRS-assisted NOMA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(2): 900–913. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3029617 [11] ZHANG Zheng, LV Lu, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust and secure communications in intelligent reflecting surface assisted NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(3): 739–743. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3039811 [12] FANG Fang, XU Yanqing, PHAM Q V, et al. Energy-efficient design of IRS-NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 14088–14092. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3024005 [13] ZHAO Mingmin, LIU An, and ZHANG Rui. Outage-constrained robust beamforming for intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1301–1316. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3056899 [14] 徐勇军, 刘子腱, 李国权, 等. 基于NOMA的无线携能D2D通信鲁棒能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175XU Yongjun, LIU Zijian, LI Guoquan, et al. Robust energy efficiency optimization algorithm for NOMA-based D2D communication with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175 [15] SHENG Min, WANG Liang, WANG Xijun, et al. Energy efficient beamforming in MISO heterogeneous cellular networks with wireless information and power transfer[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(4): 954–968. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2544538 [16] GHARAVOL E A, LIANG Yingchang, and MOUTHAAN K. Robust downlink beamforming in multiuser MISO cognitive radio networks with imperfect channel-state information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2010, 59(6): 2852–2860. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2010.2049868 [17] WANG Kunyu, SO A M C, CHANG T H, et al. Outage constrained robust transmit optimization for multiuser MISO downlinks: Tractable approximations by conic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5690–5705. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2354312 [18] DINKELBACH W. On nonlinear fractional programming[J]. Management Science, 1967, 13(7): 492–498. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.13.7.492 [19] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 67–113. [20] SHEN Hong, XU Wei, JIN Shi, et al. Joint transmit and receive beamforming for multiuser MIMO downlinks with channel uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(5): 2319–2335. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2013.2290754 [21] AL-OBIEDOLLAH H M, CUMANAN K, THIYAGALINGAM J, et al. Energy efficient beamforming design for MISO non-orthogonal multiple access systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(6): 4117–4131. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2900634 -





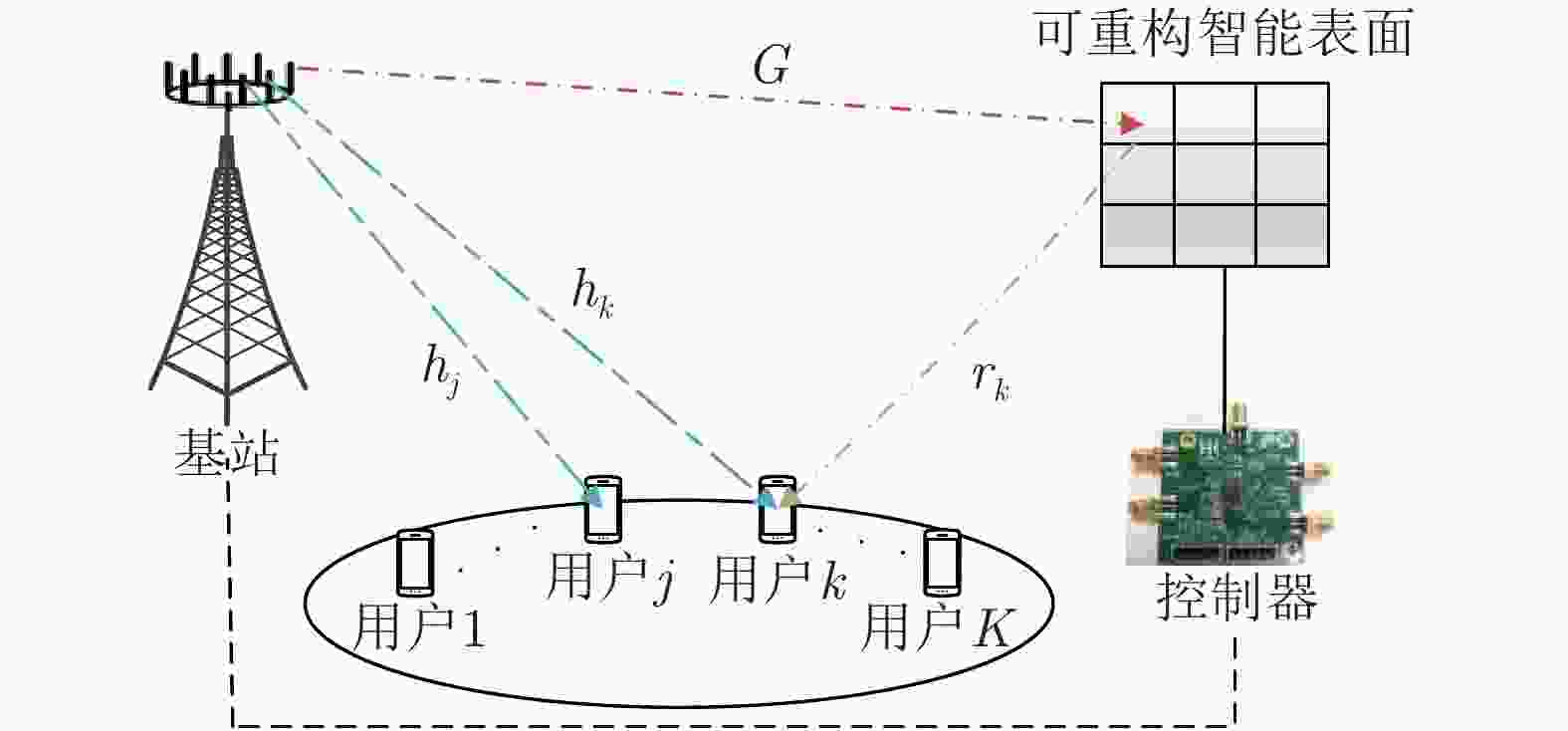
 下载:
下载:
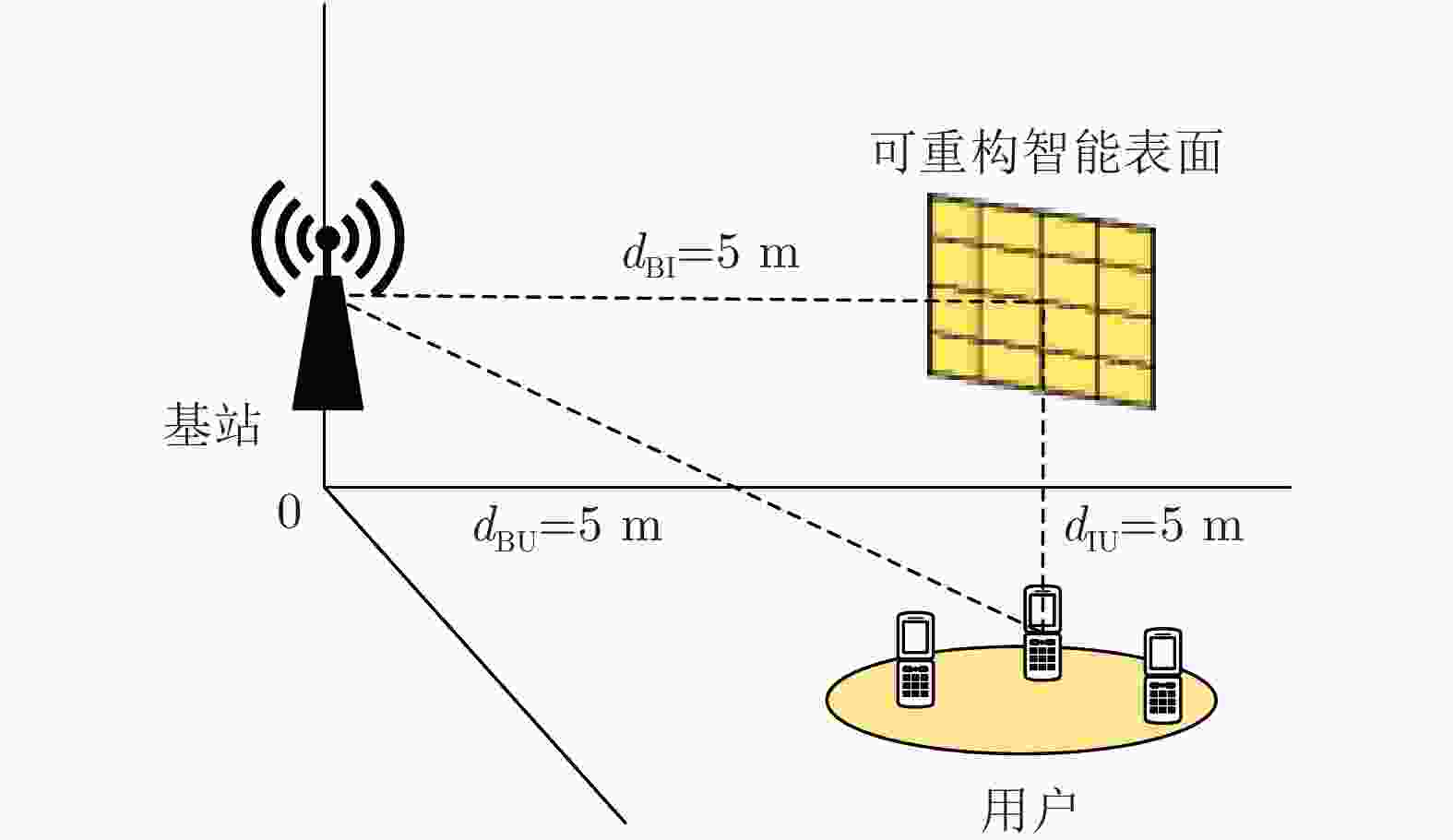
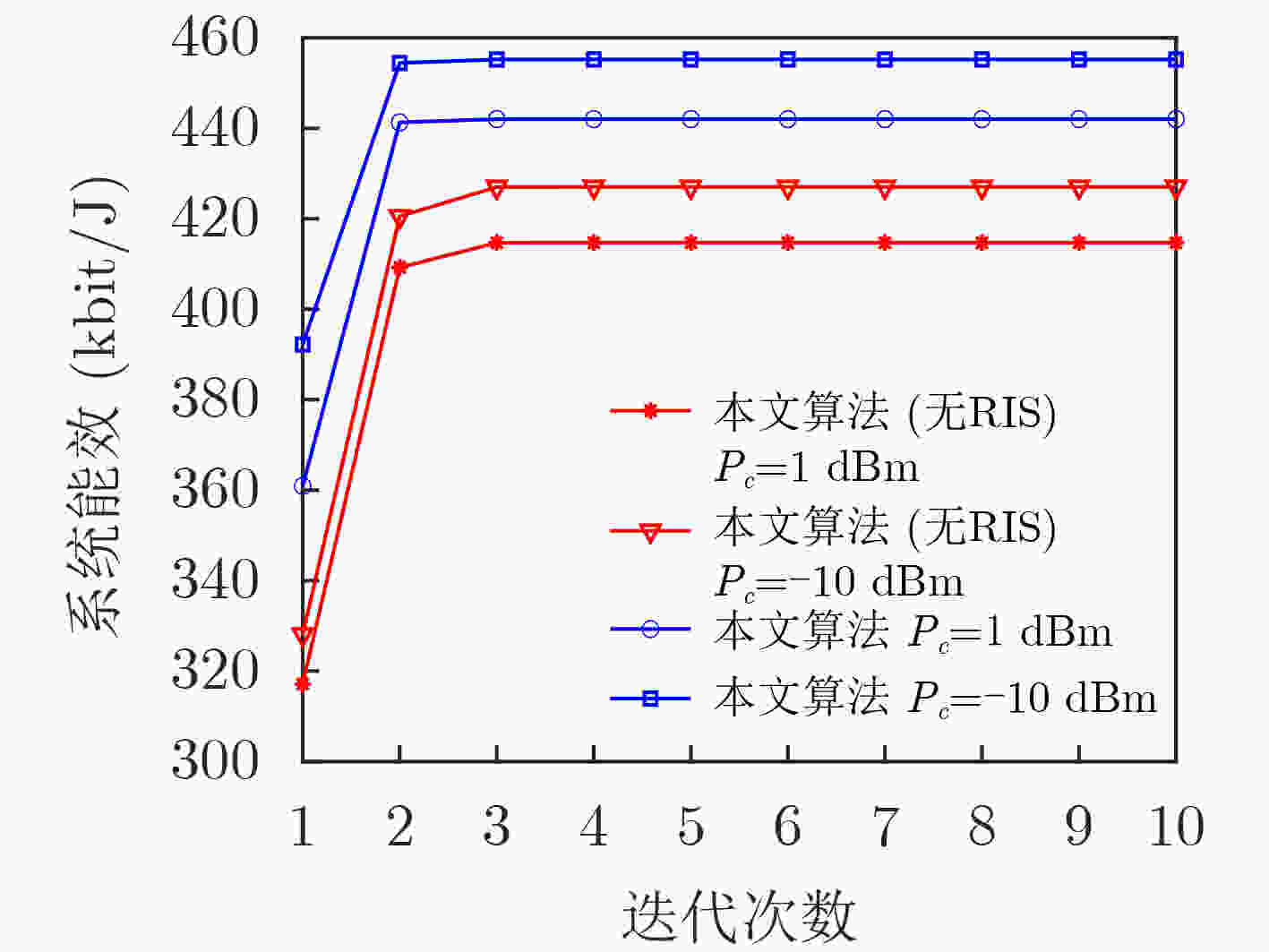
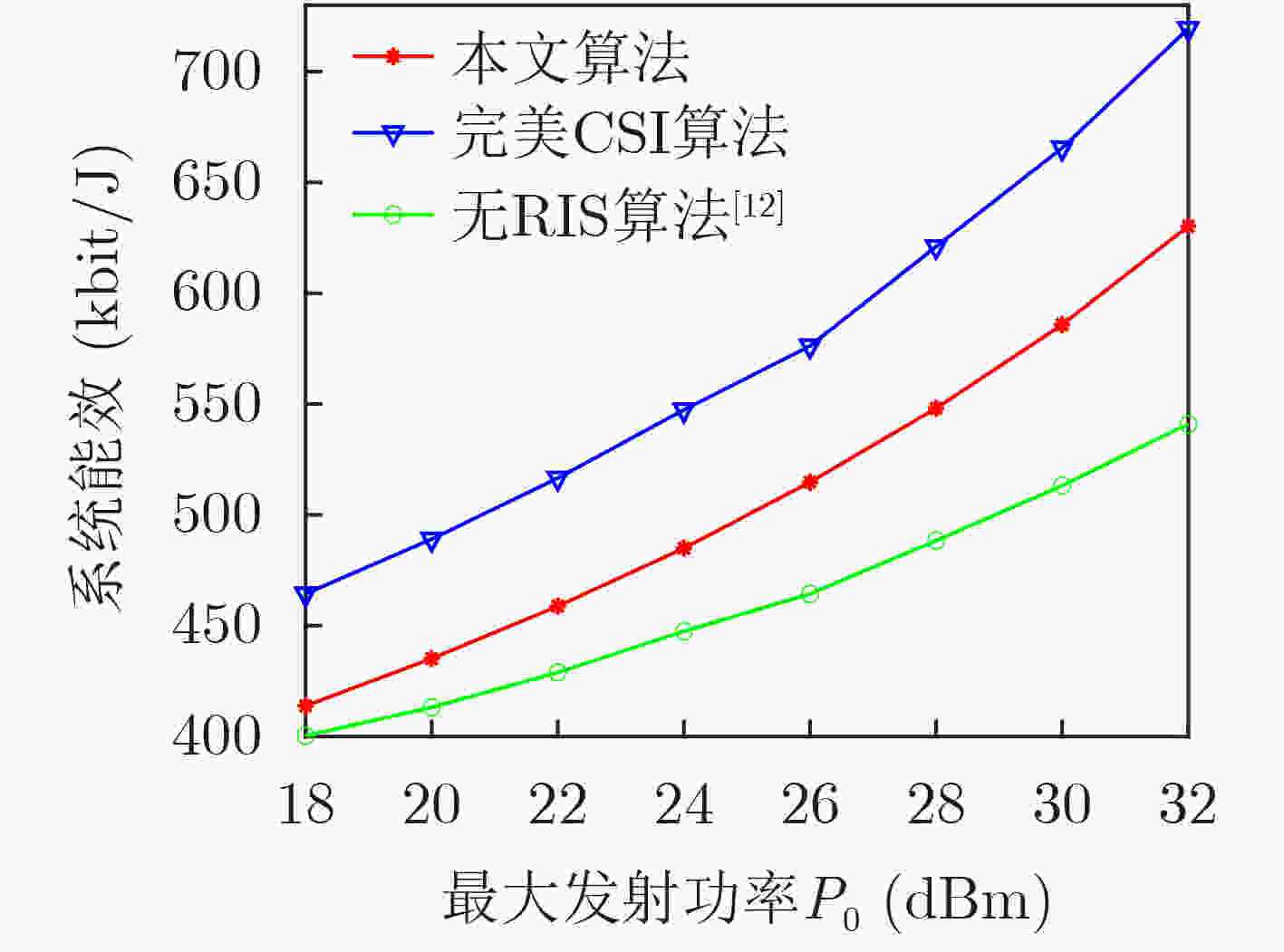
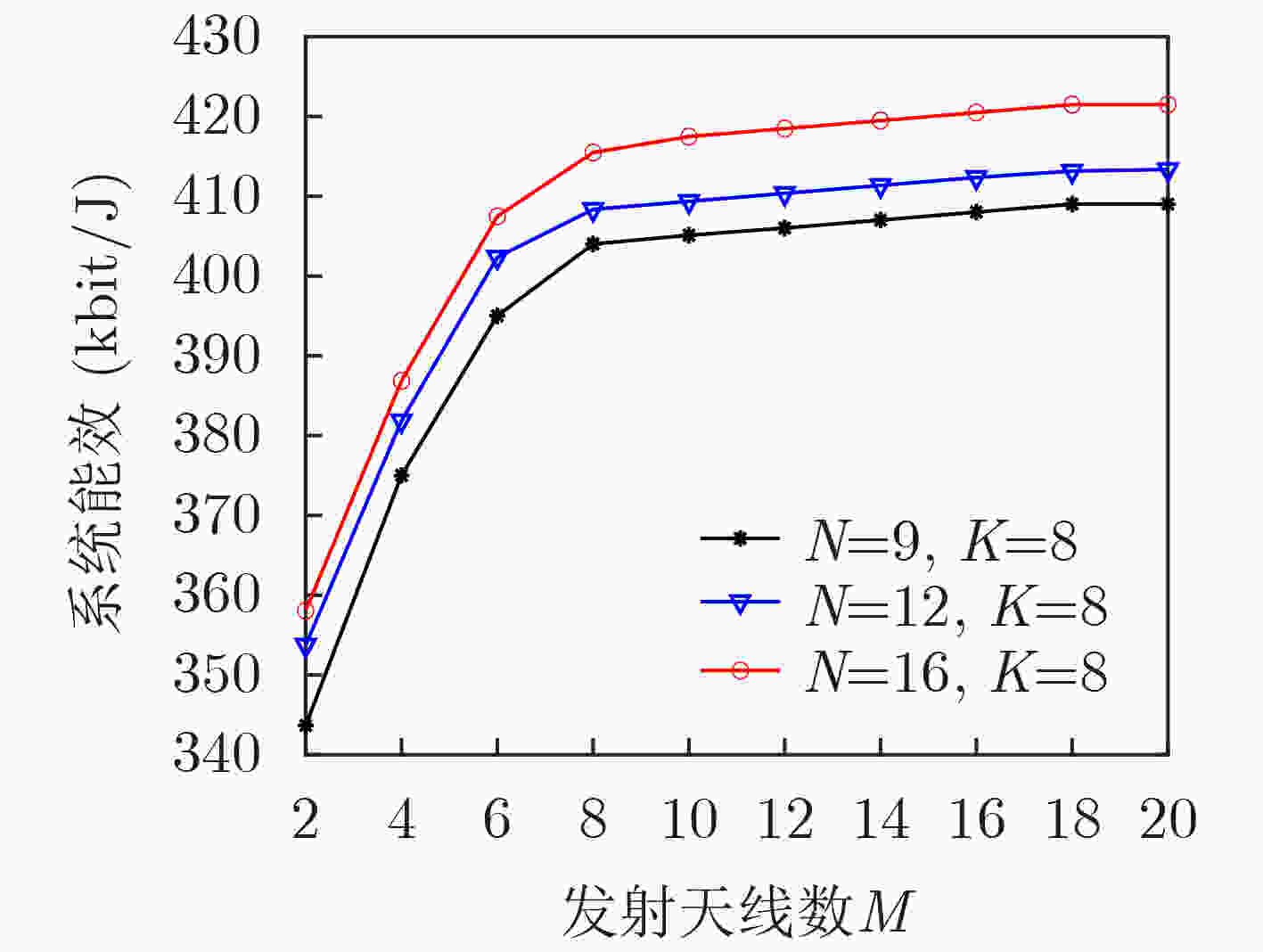
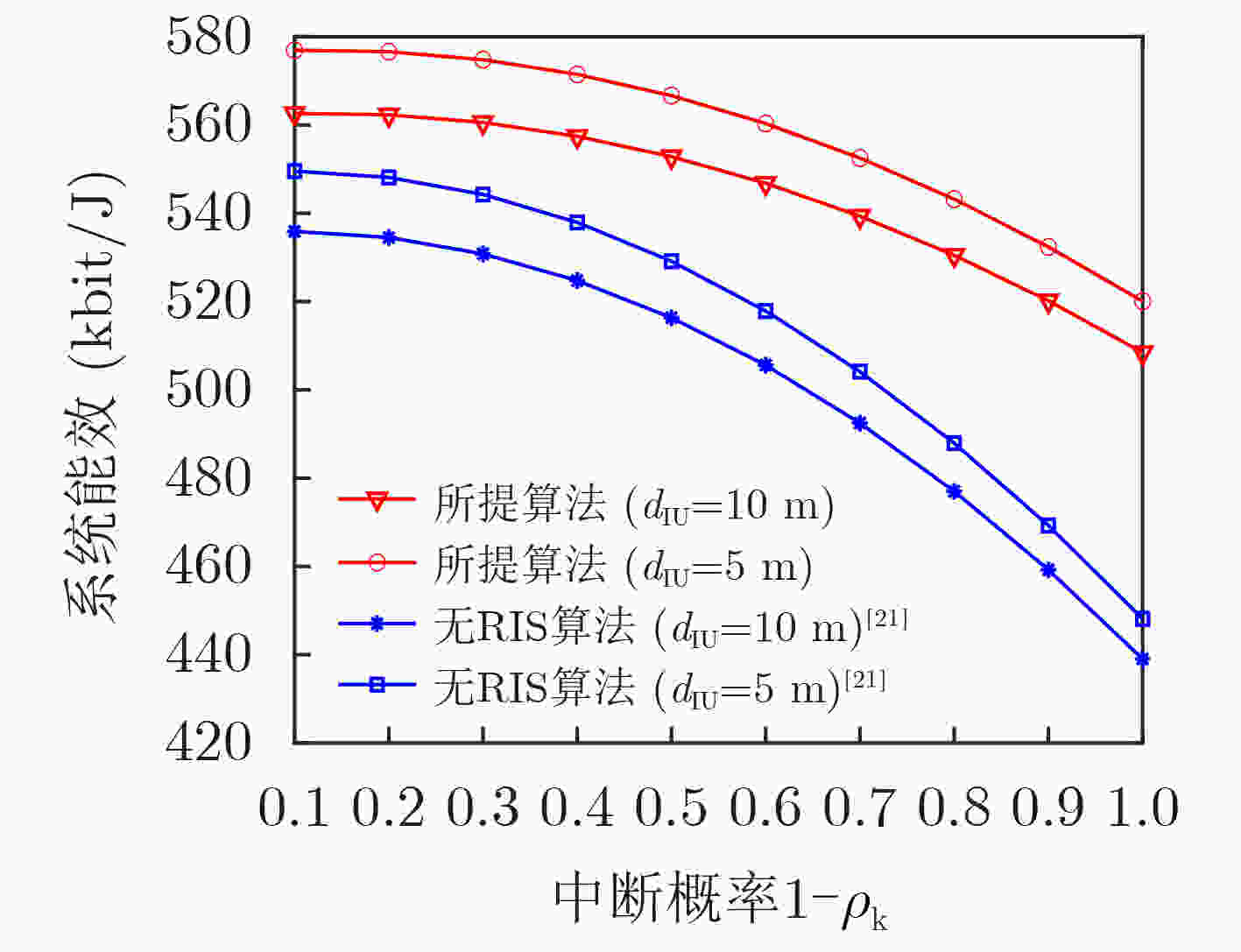
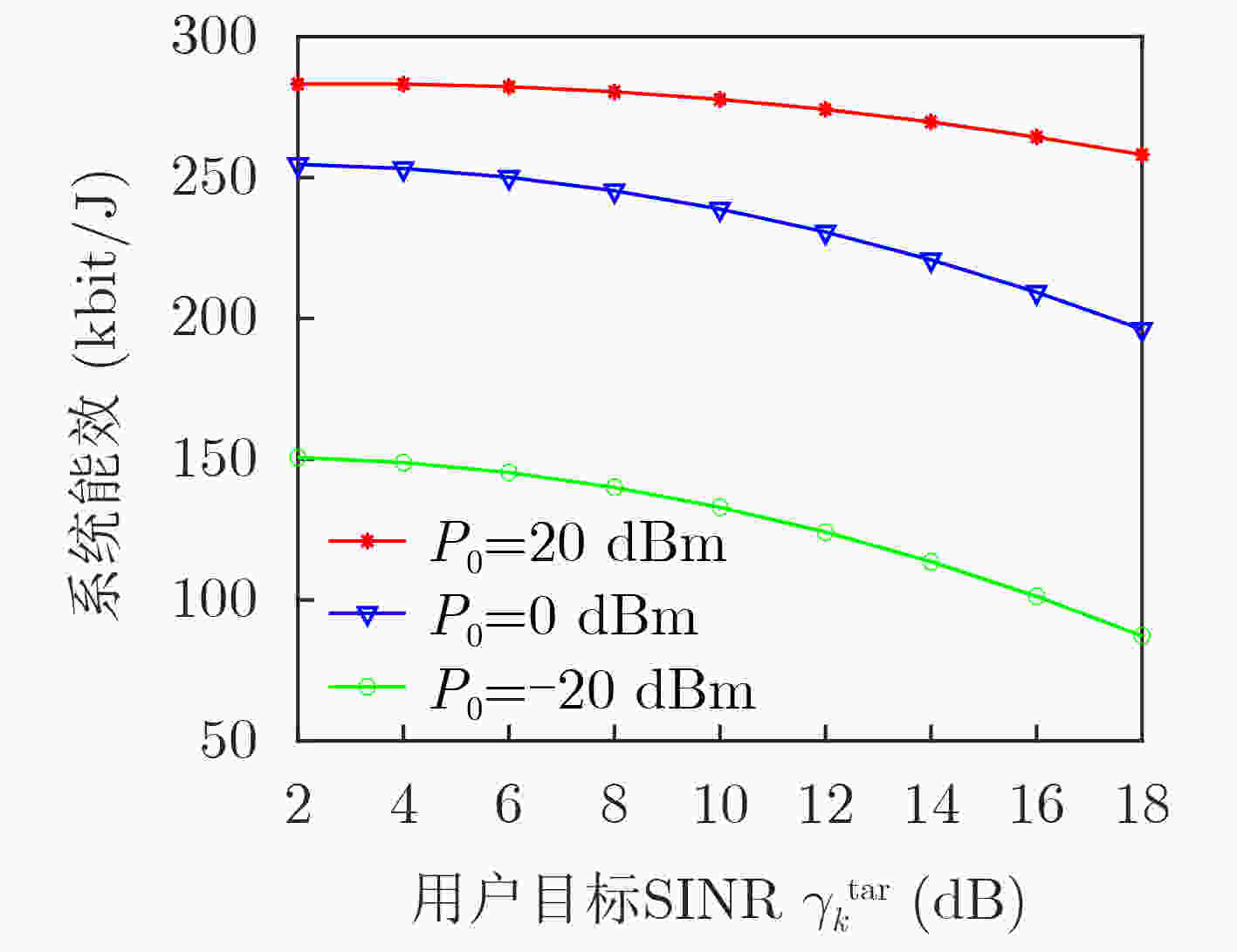
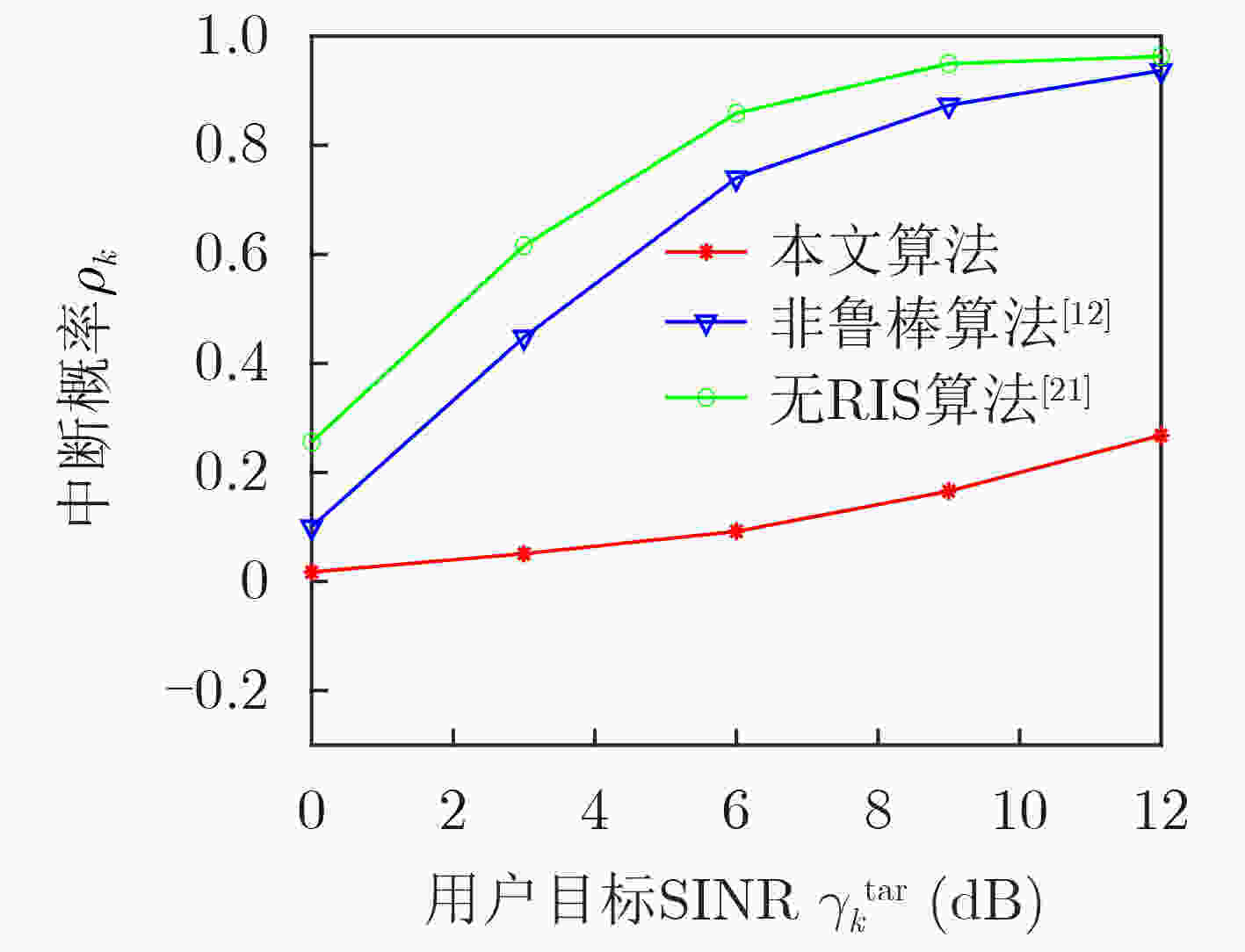


 下载:
下载:
