Resource Rllocation for UAV-assisted D2D Communications with Energy Harvesting
-
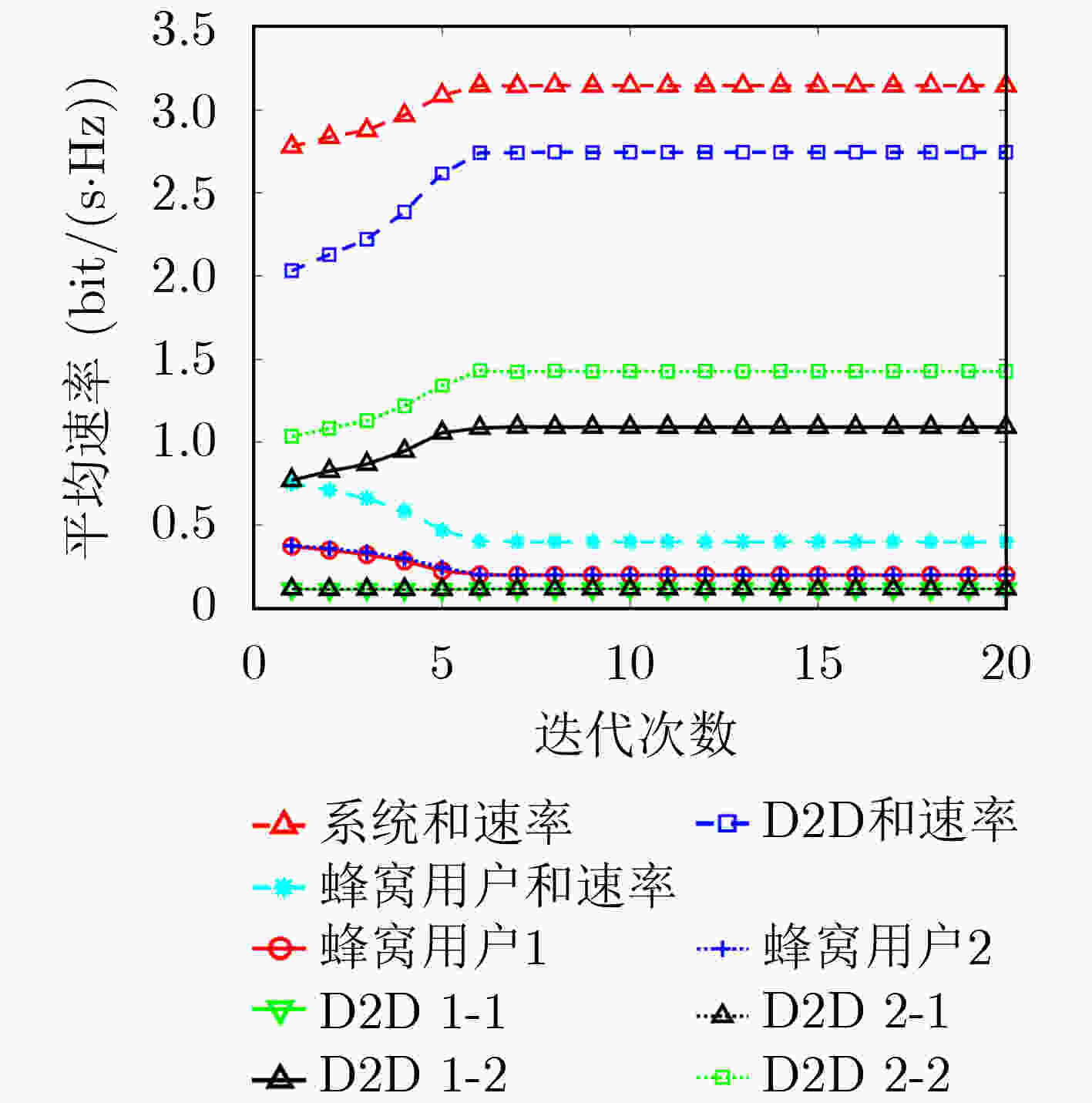
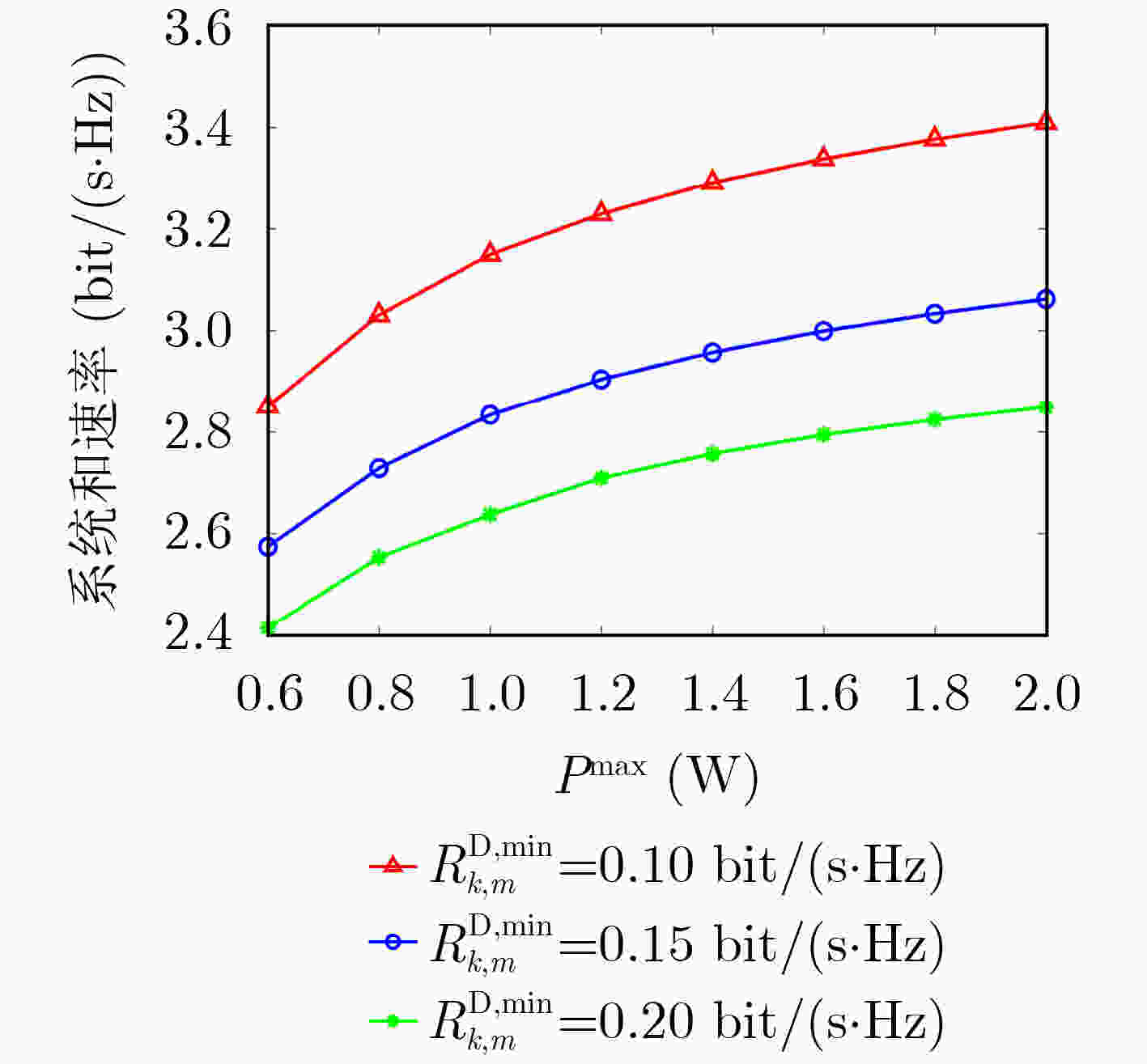
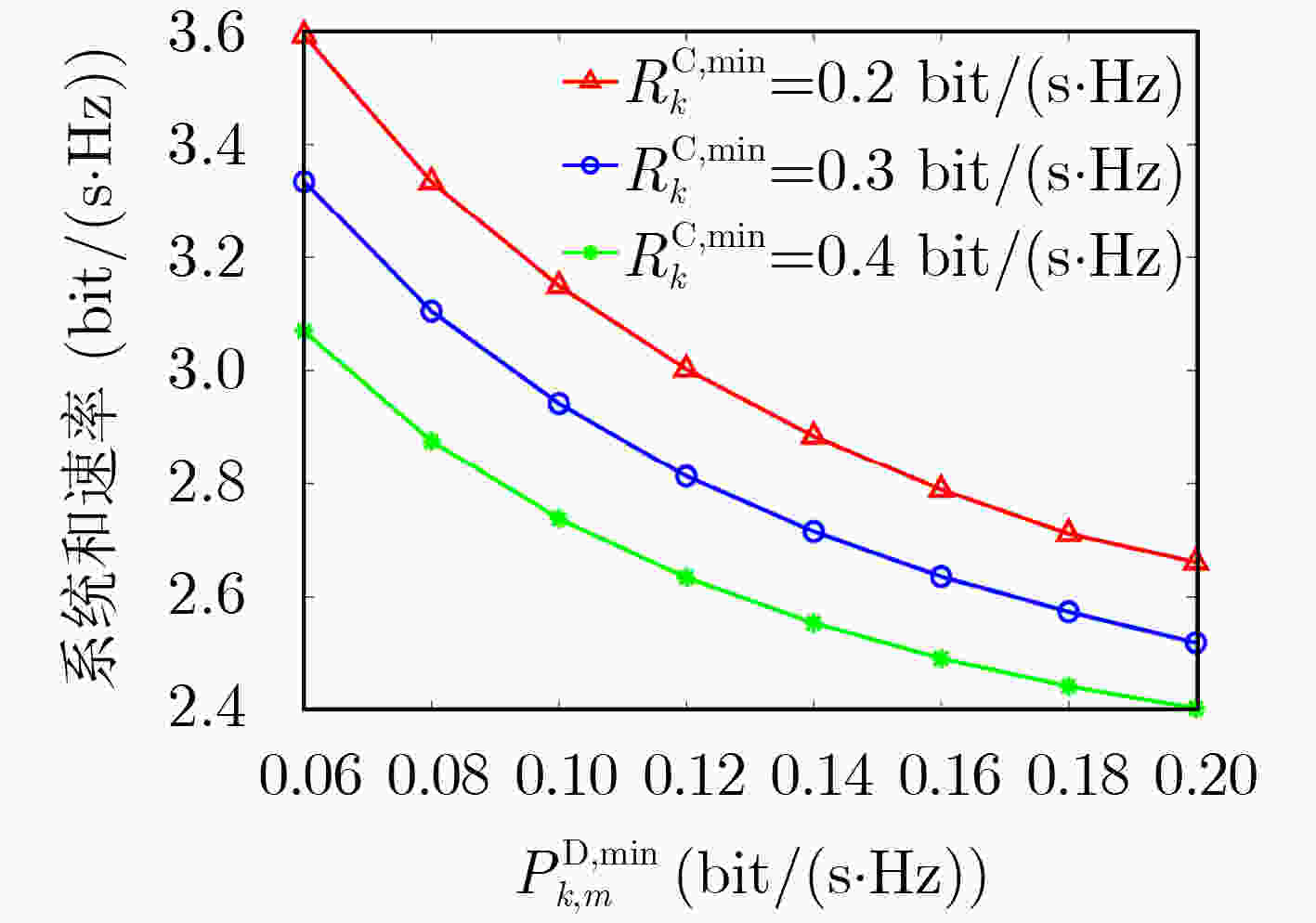
摘要: 为更好地利用周围环境中的射频信号能量,提升终端直连(D2D)通信的运行时间和无人机(UAV)通信的频谱利用率,该文提出一种基于能量收集的UAV-D2D网络资源分配算法。考虑UAV最大发射功率和移动性约束,蜂窝用户和D2D用户的最小速率约束,建立了系统和速率最大化的多变量耦合资源分配问题。利用连续凸近似和变量替换方法将混合整数非线性规划问题转化为凸优化问题,并利用拉格朗日对偶方法获得闭式解。仿真结果表明,所提算法具有良好的收敛性能,并能够有效提升系统容量。Abstract: In order to utilize better the surrounding radio-frequency energy and improve the operation lifetime of Device-to-Device (D2D) communications as well as the spectrum efficiency of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) communication, a resource allocation algorithm is proposed for UAV-D2D networks with energy harvesting. Considering the constraints of the maximum transmit power and the mobility of the UAV, the minimum rate requirements of both cellular users and D2D users, a multivariable coupling resource allocation problem is formulated to maximize the sum rates of both cellular users and D2D users. The mixed-integer nonlinear programming problem is transformed into a convex optimization problem by using the successive convex approximation and variable substitution methods, where the closed-form solutions are obtained by the using Lagrange dual method. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has good convergence performance and higher system capacity.
-
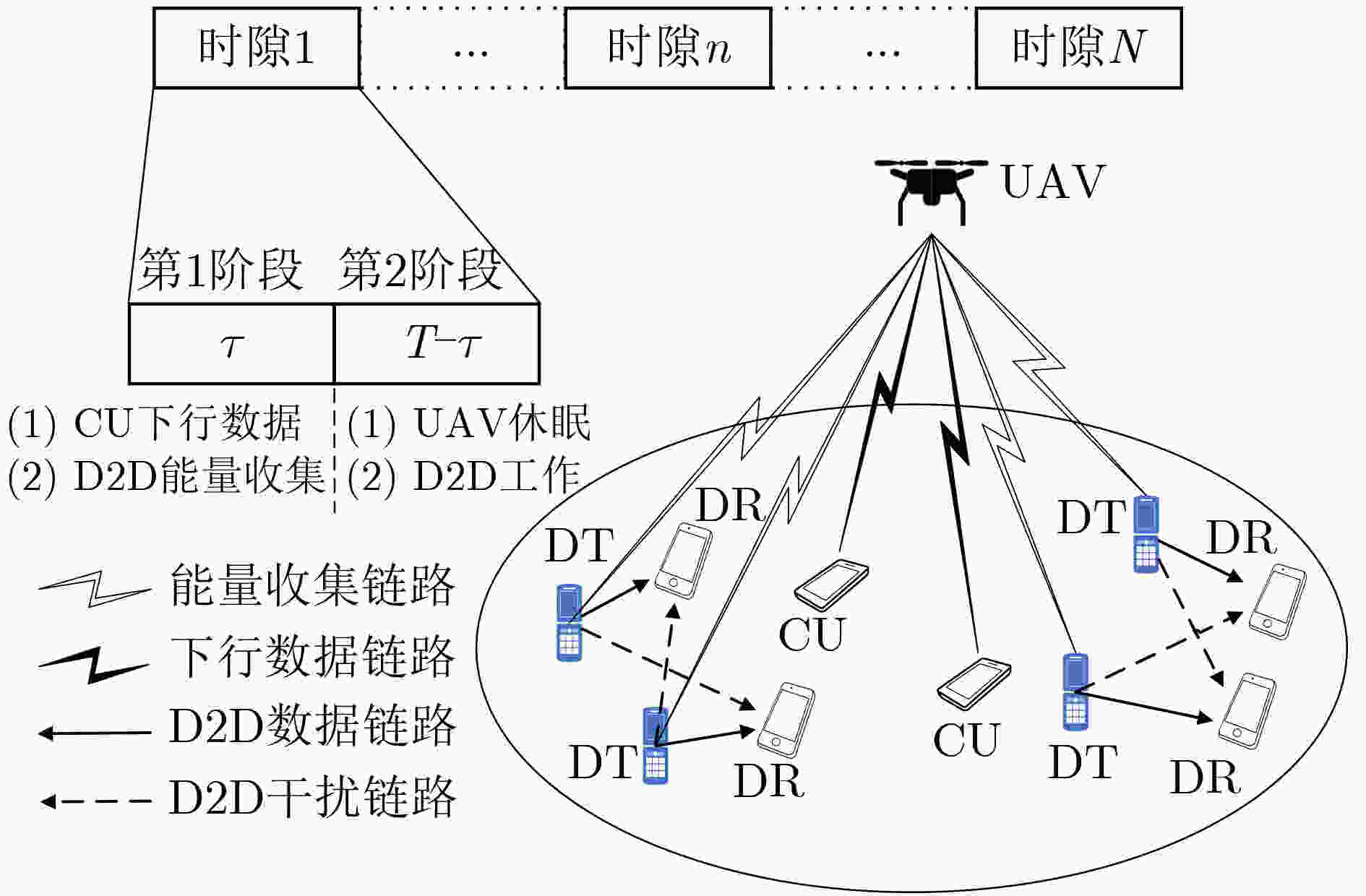
表 1 基于交替迭代的资源分配算法
初始化系统参数:用户簇个数、用户簇内D2D对数、D2D发射
机功率和UAV轨迹$ {{\mathbf{q}}_n} $;设置迭代收敛精度为$ \varepsilon $,最大迭代次数
$ {L_{\rm max}} $;穷尽搜索$ N $个时隙UAV与用户簇连接情况。(1) 循环; (2) 迭代次数更新$ l = l + 1 $; (3) 通过问题式(18)得到$ {\tau _{k,n}} $和$ p_{k,n}^{\rm C} $; (4) 通过问题式(35)得到$ p_{k,n,m}^{\rm D} $; (5) 通过问题式(47)得到$ {{\mathbf{q}}_n} $; (6) 直到算法满足收敛条件或达到最大迭代次数,即
$ R\left( {l + 1} \right) - R\left( l \right) \le \varepsilon $或$l = {L_{{\rm{max}}} }$。 -
[1] MOZAFFARI M, SAAD W, BENNIS M, et al. A tutorial on UAVs for wireless networks: Applications, challenges, and open problems[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(3): 2334–2360. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2902862 [2] ZENG Yong, ZHANG Rui, and LIM T J. Wireless communications with unmanned aerial vehicles: Opportunities and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(5): 36–42. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7470933 [3] ZHANG Haijun, ZHANG Jianmin, and LONG Keping. Energy efficiency optimization for NOMA UAV network with imperfect CSI[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(12): 2798–2809. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3005489 [4] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [5] ZHAO Nan, LU Weidang, SHENG Min, et al. UAV-assisted emergency networks in disasters[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(1): 45–51. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2018.1800160 [6] WANG Feiran, XU Chen, SONG Lingyang, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation for device-to-device underlay communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(4): 2082–2092. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2379653 [7] 徐勇军, 刘子腱, 李国权, 等. 基于NOMA的无线携能D2D通信鲁棒能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175XU Yongjun, LIU Zijian, LI Guoquan, et al. Robust energy efficiency optimization algorithm for NOMA-based D2D communication with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175 [8] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Robust secure energy-efficiency optimization in SWIPT-aided heterogeneous networks with a nonlinear energy-harvesting model[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(19): 14908–14919. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3072965 [9] ZHANG Haijun, FENG Mengting, LONG Keping, et al. Energy efficient resource management in SWIPT enabled heterogeneous networks with NOMA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(2): 835–845. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2948874 [10] HUANG Jun, XING Congcong, and GUIZANI M. Power allocation for D2D communications with SWIPT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(4): 2308–2320. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2963833 [11] YANG H H, LEE J, and QUEK T Q S. Heterogeneous cellular network with energy harvesting-based D2D communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(2): 1406–1419. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2489651 [12] ZHONG Xijian, GUO Yan, LI Ning, et al. Joint optimization of relay deployment, channel allocation, and relay assignment for UAVs-aided D2D networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2020, 28(2): 804–817. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2020.2970744 [13] WANG Haichao, WANG Jinlong, DING Guoru, et al. Resource allocation for energy harvesting-powered D2D communication underlaying UAV-assisted networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2018, 2(1): 14–24. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2017.2767203 [14] JI Jiequ, ZHU Kun, NIYATO D, et al. Joint trajectory design and resource allocation for secure transmission in cache-enabled UAV-relaying networks with D2D communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(3): 1557–1571. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3013647 [15] JI Jiequ, ZHU Kun, NIYATO D, et al. Probabilistic cache placement in UAV-assisted networks with D2D connections: Performance analysis and trajectory optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(10): 6331–6345. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3006908 [16] HUANG Wenhuan, YANG Zhaohui, PAN Cunhua, et al. Joint power, altitude, location and bandwidth optimization for UAV with underlaid D2D communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 524–527. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2878706 [17] WANG Baoji, ZHANG Rongqing, CHEN Chen, et al. Graph-based file dispatching protocol with D2D-enhanced UAV-NOMA communications in large-scale networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(9): 8615–8630. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2994549 [18] HUQ K M S, MUMTAZ S, ZHOU Zhenyu, et al. Energy-efficiency maximization for D2D-enabled UAV-aided 5G networks[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. [19] LIU Xiaonan, LI Zan, ZHAO Nan, et al. Transceiver design and multihop D2D for UAV IoT coverage in disasters[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1803–1815. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2877504 [20] NGUYEN H T, TUAN H D, DUONG T Q, et al. Joint D2D assignment, bandwidth and power allocation in cognitive UAV-enabled networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(3): 1084–1095. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.2969623 [21] XIE Lifeng, XU Jie, and ZHANG Rui. Throughput maximization for UAV-enabled wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1690–1703. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875446 [22] NGUYEN M N, NGUYEN L D, DUONG T Q, et al. Real-time optimal resource allocation for embedded UAV communication systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 225–228. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2867775 [23] ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Yanxia, XIANG Lin, et al. Robust energy-efficient transmission for wireless-powered D2D communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7951–7965. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3095626 [24] BOSHKOVSKA E, NG D W K, ZLATANOV N, et al. Robust resource allocation for MIMO wireless powered communication networks based on a non-linear EH model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(5): 1984–1999. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2664860 [25] 徐勇军, 谷博文, 陈前斌, 等. 基于能效最大的无线供电反向散射网络资源分配算法[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(10): 202–210. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020132XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, CHEN Qianbin, et al. Energy efficiency maximization resource allocation algorithm in wireless-powered backscatter communication network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(10): 202–210. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020132 [26] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [27] XU Yongjun, HU Yuan, LI Guoquan, et al. Robust resource allocation for heterogeneous wireless network: A worst-case optimisation[J]. IET Communications, 2018, 12(9): 1064–1071. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2017.0626 -





 下载:
下载:
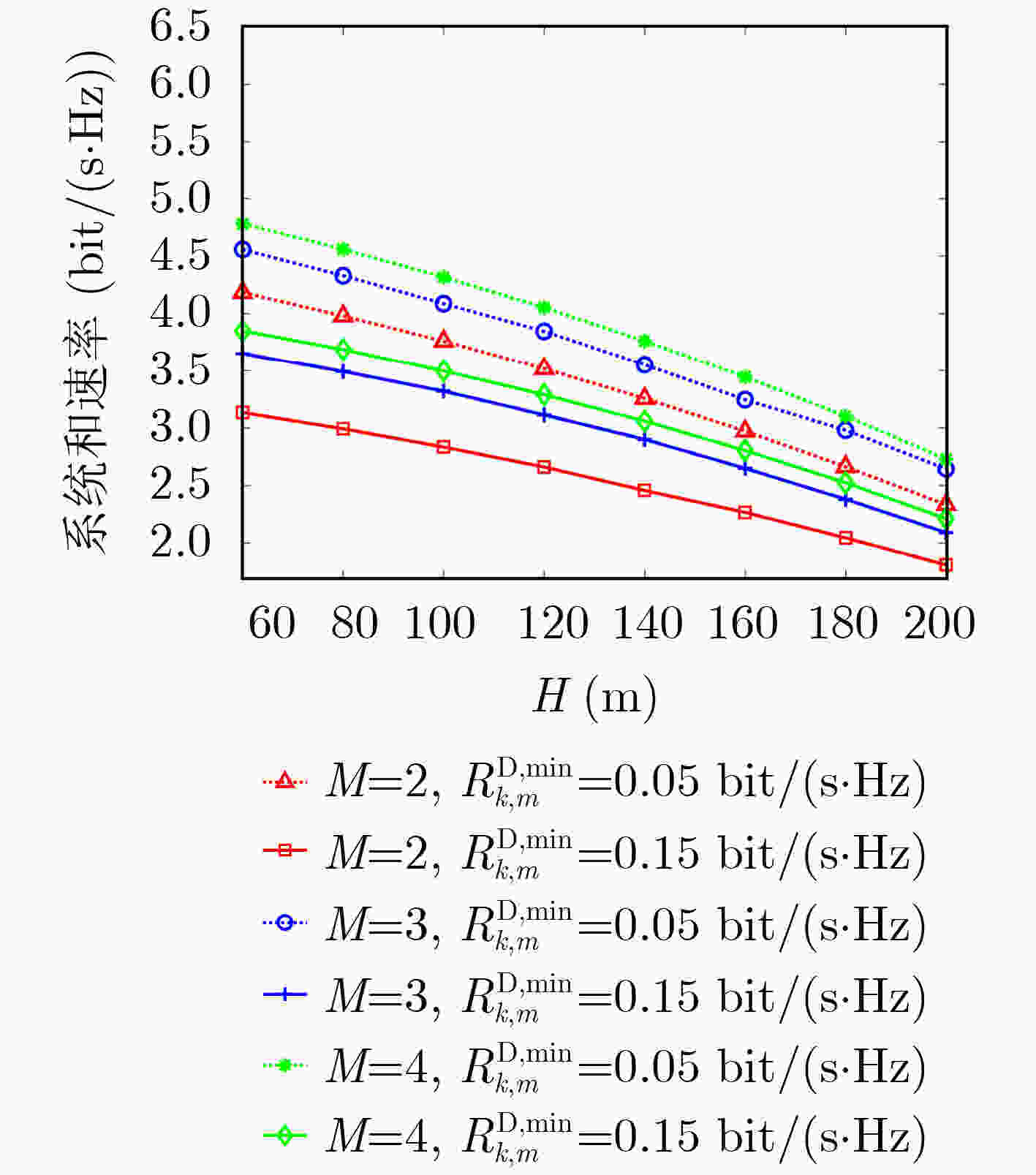
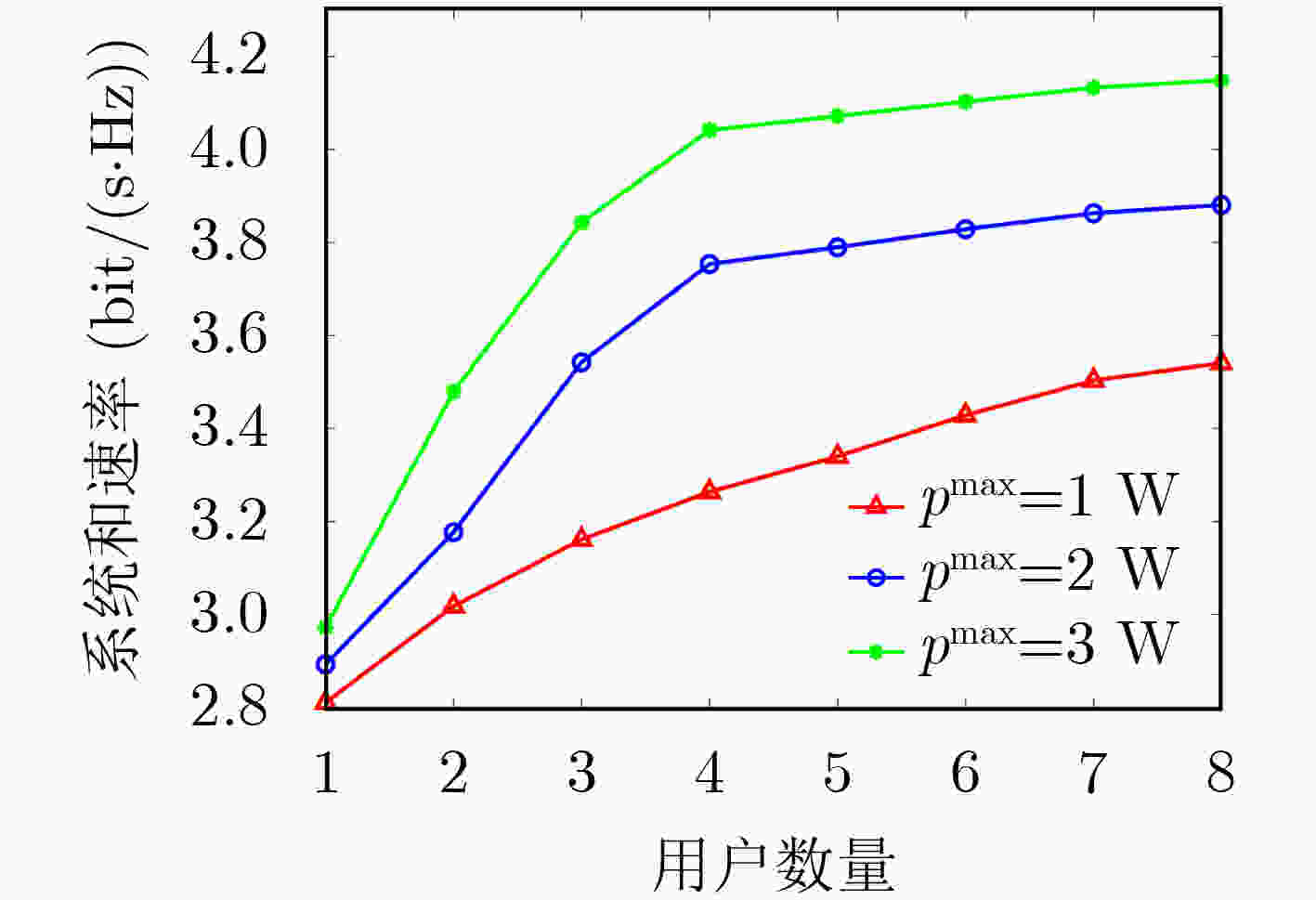
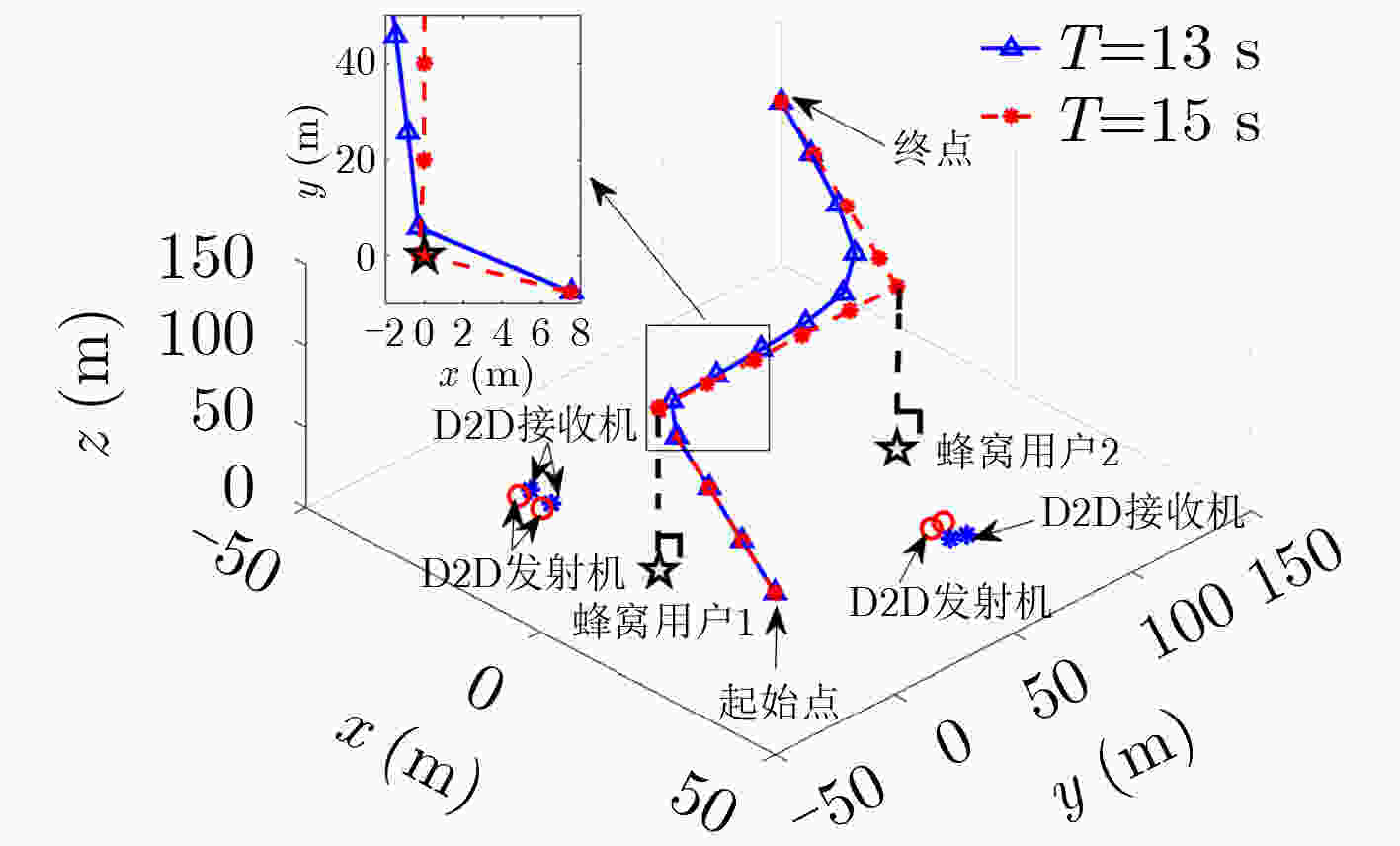
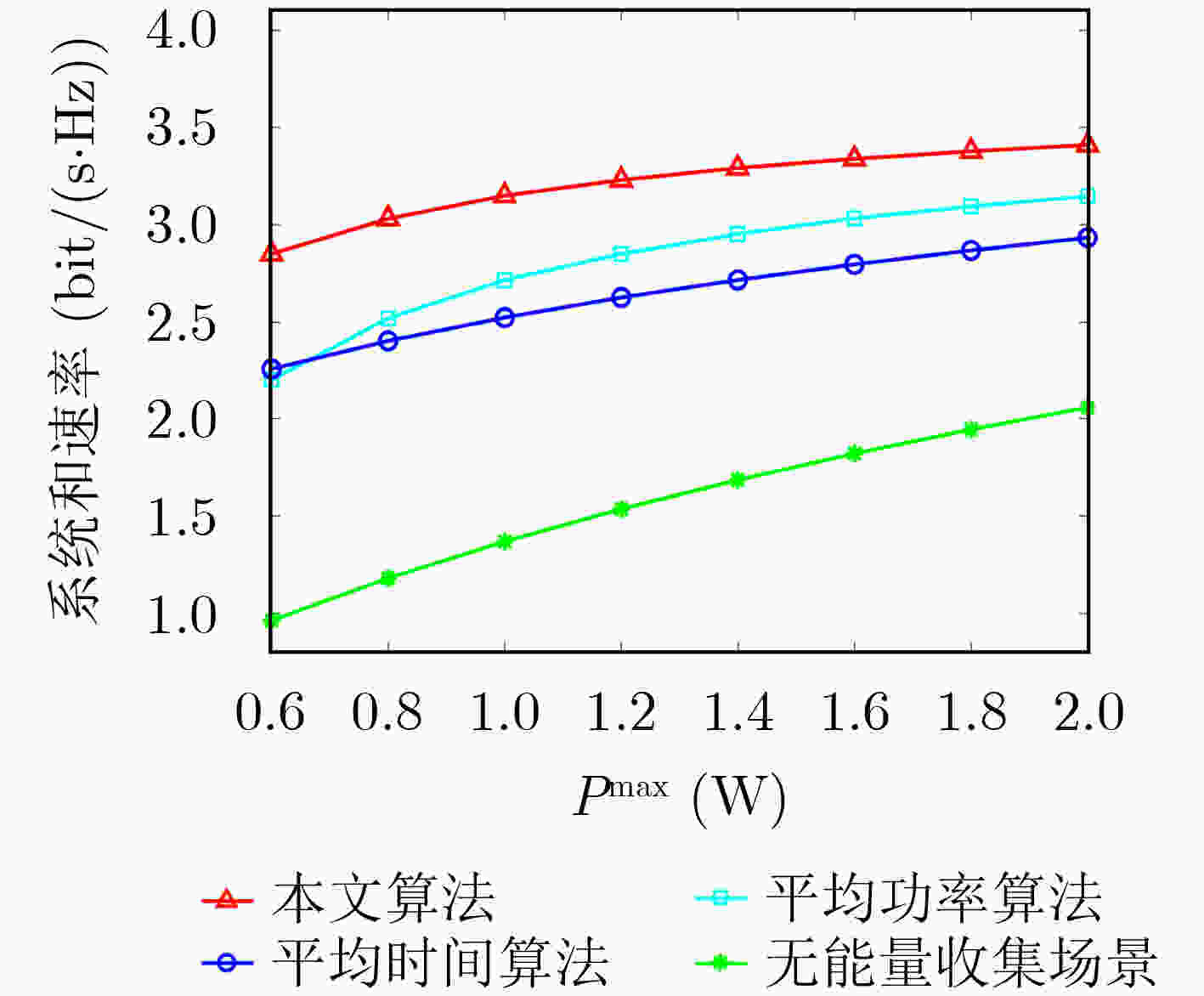
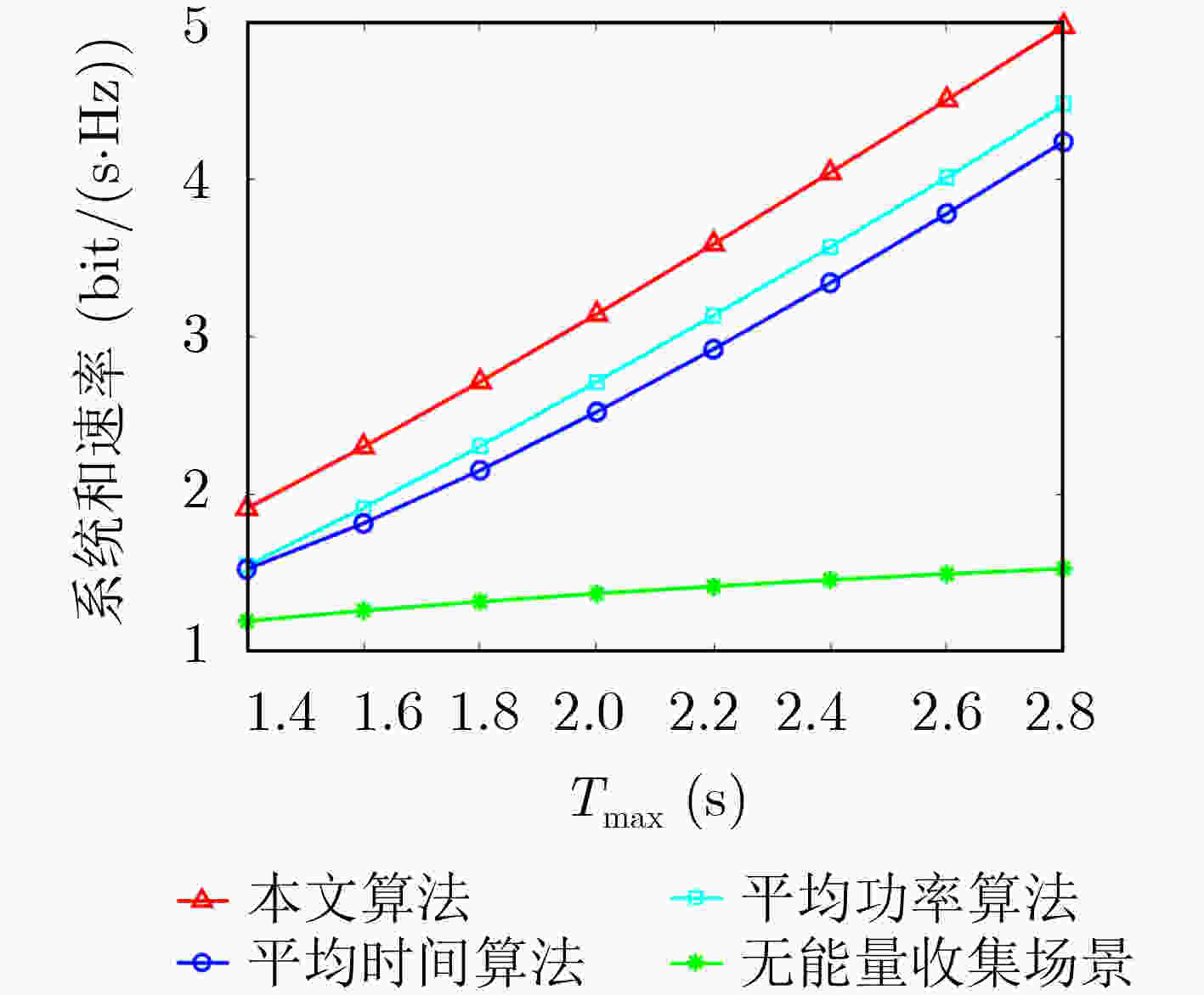


 下载:
下载:
