Virtual Machine Placement Algorithm for Supporting Multiple Applications to Mobile Edge Computing
-
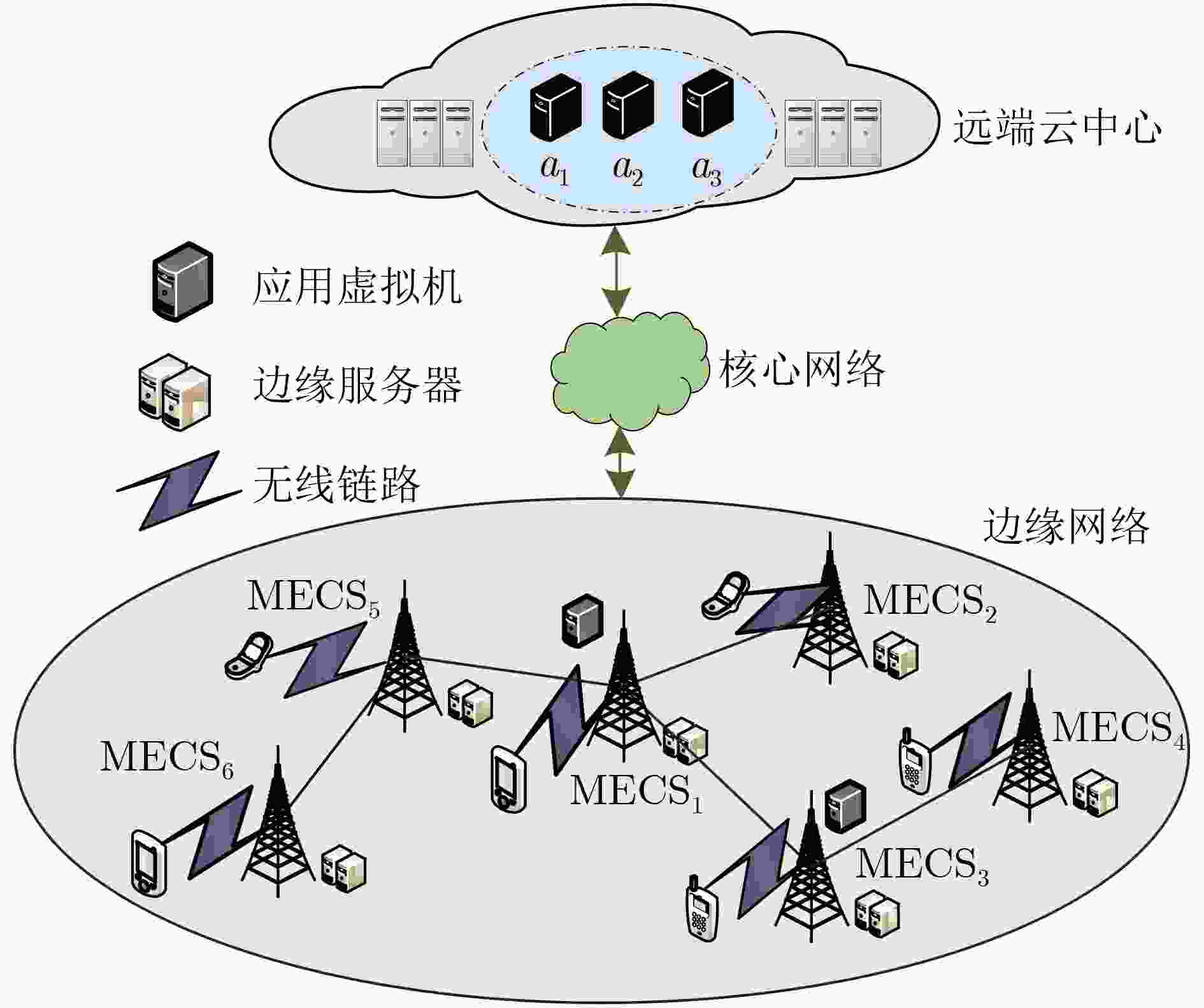
摘要: 移动边缘计算(MEC)通过在用户近端以虚拟机(VM)形式部署应用服务,能有效降低服务响应延迟并减少核心网络数据流量。然而,当前MEC中虚拟机部署的大多数研究尚未具体考虑用户对多种应用服务的需求。因此,该文针对MEC中多应用服务的虚拟机部署问题,提出两种启发式算法,即基于适应度的启发式部署算法(FHPA)和基于分治的启发式部署算法(DCBHPA),通过在边缘网络中配置支持多种应用服务的虚拟机来最大限度地减少网络中的数据流量。FHPA和DCBHPA分别基于边缘服务器的网络连接特征和用户对应用请求的差异性,定义了不同的适应度计算模型。在此基础上,通过子问题划分机制实现VM配置。仿真结果表明,相比于基准算法,所提算法能更好地控制系统数据流量,有效地提高边缘网络服务资源的利用率。Abstract: In Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) environment, deploying application services in the form of Virtual Machines (VM) at the edge of the network can effectively reduce the service response delay and reduce the data traffic of core network. There have been many solutions to the problem of optimal allocation of edge network resources, but few studies consider the optimal deployment of VM that provide users with multiple application services to mobile edge networks. To this end, two heuristic algorithms are proposed, Fitness-based Heuristic Placement Algorithm (FHPA) and Divide-and-Conquer Based Heuristic Placement Algorithm (DCBHPA). By distributing VMs that support multiple application services to the MEC network, these two algorithms aim to minimize the data traffic in MEC architecture. Besides, FHPA and DCBHPA define respectively different fitness computing models based on the network connection characteristics of edge servers, as well as the differences in users’ application requests. Thus, VM configuration can be realized through the sub-problem division mechanism. Compared with the baseline algorithms, the simulation results show that the proposed algorithms can better control the system data traffic and improve effectively the utility of edge network service resources.
-
表 1 聚类过程
初始化图$G$的直径$E$,根据适应度定义集合$ {X_i} $,令$ Y $为空集 (1) for $j \leftarrow 1$to $ E $ do (2) for $i \leftarrow 1$to $ k $ do (3) 对于距离集合$ {X_i} $中初始AS跳数为$ j $的元素$ y $ (4) if $ y \notin Y $ then (5) 更新集合$ Y \leftarrow Y \cup \{ y\} $ (6) 更新集合$ {X_i} \leftarrow {X_i} \cup \{ y\} $ (7) end if (8) end for (9) end for 表 2 基于适应度的启发式部署算法
输入:$ G,k,A,U,\delta ,E,X $ 输出:最优VM分配策略 (1)计算和极值正规化$ {\alpha _s},\forall s \in S,\forall \alpha \in F $ (2)根据式(9)计算熵权$ {\omega _\alpha },\alpha \in F $ (3)根据式(10)计算$ {W_s},\forall s \in S $ (4)对$ W $进行降序排序,选择前$ k $个MEC服务器分别分配到集合
${X_i},i = 1,2, \cdots, k$(5)执行表1中的聚类过程将所有MEC服务器划分到${X_i},i = 1,2\cdots, k$ (6)for $ a \in A $ do (7) for $ i \leftarrow 1 $ to $ k $ do (8) for $ s \in {X_i} $ do (9) 将应用$ a $的一个VM配置到$ s $上,通过式(2)计算集合
$ {X_i} $内的数据流量(10) end for (11) 将应用服务$ a $的一个VM部署在最小化$ {X_i} $内数据流量的边
缘服务器上(12) end for (13) end for 表 3 基于分治的启发式部署算法
输入:$ G,k,A,U,\delta ,E,X $ 输出:最优VM分配策略 (1)计算并归一化$ R_s^a,\forall s \in S,\forall a \in A $ (2) for $ a \in A $ do (3) $Y = \varnothing$ (4) for $ i \leftarrow 1 $ to $ k $ do (5) for $ s \in S $ do (6) 通过式(11)计算影响因子$ {\beta _s} $ (7) end for (8) $ P = \left\{ {{P_s} = 0,\forall s \in S} \right\} $ (9) for $ s \in S $ do (10) 根据式(12)计算$ {P_s} $ (11) end for (12) 对$ P $降序排序,选择第1个$ {P_s} $,将满足$ s \notin Y $的$ s $加入集合$ {X_i} $ (13) 更新集合$ Y = Y \cup \{ s\} $ (14) end for (15) 执行表1中的聚类过程将所有MEC服务器划分到
${X_i},i = 1,2, \cdots,k$(16) end for (17) 根据表2的步骤(7)—步骤(12)找到最优VM部署位置 (18) end for 表 4 网络拓扑表
拓扑图 节点数 链路数 spiralight 15 16 noel 19 25 agis 25 30 shentel 28 35 evolink 37 45 -
[1] JIANG Congfeng, FAN Tiantian, GAO Honghao, et al. Energy aware edge computing: A survey[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 151: 556–580. doi: 10.1016/J.COMCOM.2020.01.004 [2] KHAN W Z, AHMED E, HAKAK S, et al. Edge computing: A survey[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 219–235. doi: 10.1016/J.FUTURE.2019.02.050 [3] PAN Jianli and MCELHANNON J. Future edge cloud and edge computing for internet of things applications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(1): 439–449. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2767608 [4] ZHOU Yuchen, YU F R, CHEN Jian, et al. Resource allocation for information-centric virtualized heterogeneous networks with in-network caching and mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(12): 11339–11351. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2737028 [5] SUN Xiang and ANSARI N. EdgeIoT: Mobile edge computing for the internet of things[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(12): 22–29. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.1600492CM [6] HA K, ABE Y, EISZLER T, et al. You can teach elephants to dance: Agile VM handoff for edge computing[C]. The 2nd ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing, San Jose, USA, 2017: 12. [7] ZHAO Lei and LIU Jiajia. Optimal placement of virtual machines for supporting multiple applications in mobile edge networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 6533–6545. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2808171 [8] GAO Siyi, ZHOU Ao, CHEN Xican, et al. Redundant virtual machine placement in mobile edge computing[C]. The 1st International Conference on Blockchain and Trustworthy Systems, Guangzhou, China, 2019: 371–384. [9] SUN Xiang and ANSARI N. Latency aware workload offloading in the cloudlet network[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(7): 1481–1484. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2690678 [10] KUO J J, YANG H H, and TSAI M J. Optimal approximation algorithm of virtual machine placement for data latency minimization in cloud systems[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, Canada, 2014: 1303–1311. [11] ZENG Deze, GU Lin, GUO Song, et al. Joint optimization of task scheduling and image placement in fog computing supported software-defined embedded system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(12): 3702–3712. doi: 10.1109/TC.2016.2536019 [12] GU Lin, ZENG Deze, GUO Song, et al. Cost efficient resource management in fog computing supported medical cyber-physical system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2017, 5(1): 108–119. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2015.2508382 [13] 张海波, 刘香渝, 荆昆仑, 等. 车联网中基于NOMA-MEC的卸载策略研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 1072–1079. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200017ZHANG Haibo, LIU Xiangyu, JING Kunlun, et al. Research on NOMA-MEC-based offloading strategy in internet of vehicles[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 1072–1079. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200017 [14] 张海波, 李虎, 陈善学, 等. 超密集网络中基于移动边缘计算的任务卸载和资源优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592ZHANG Haibo, LI Hu, CHEN Shanxue, et al. Computing offloading and resource optimization in ultra-dense networks with mobile edge computation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592 [15] YANG Song, LI Fan, SHEN Meng, et al. Cloudlet placement and task allocation in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 5853–5863. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2907605 [16] AGRYZKOV T, TORTOSA L, VICENT J F, et al. A centrality measure for urban networks based on the eigenvector centrality concept[J]. Environment and Planning B:Urban Analytics and City Science, 2019, 46(4): 668–689. doi: 10.1177/2399808317724444 [17] WANG Yamin, CAO Zhiying, ZHANG Xiuguo, et al. Clustering-based algorithm for services deployment in mobile edge computing environment[C]. The 2019 IEEE 25th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Tianjin, China, 2019: 963–966. [18] CHIN T L, CHEN Y S, and LYU K Y. Queuing model based edge placement for work offloading in mobile cloud networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 47295–47303. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2979479 [19] KNIGHT S, NGUYEN H X, FALKNER N, et al. The internet topology zoo[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(9): 1765–1775. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2011.111002 [20] ZHAO Lei, LIU Jiajia, SHI Yongpeng, et al. Optimal placement of virtual machines in mobile edge computing[C]. 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 2017: 1–6. [21] JIA Mike, CAO Jiannong, and LIANG Weifa. Optimal cloudlet placement and user to cloudlet allocation in wireless metropolitan area networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2017, 5(4): 725–737. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2015.2449834 -





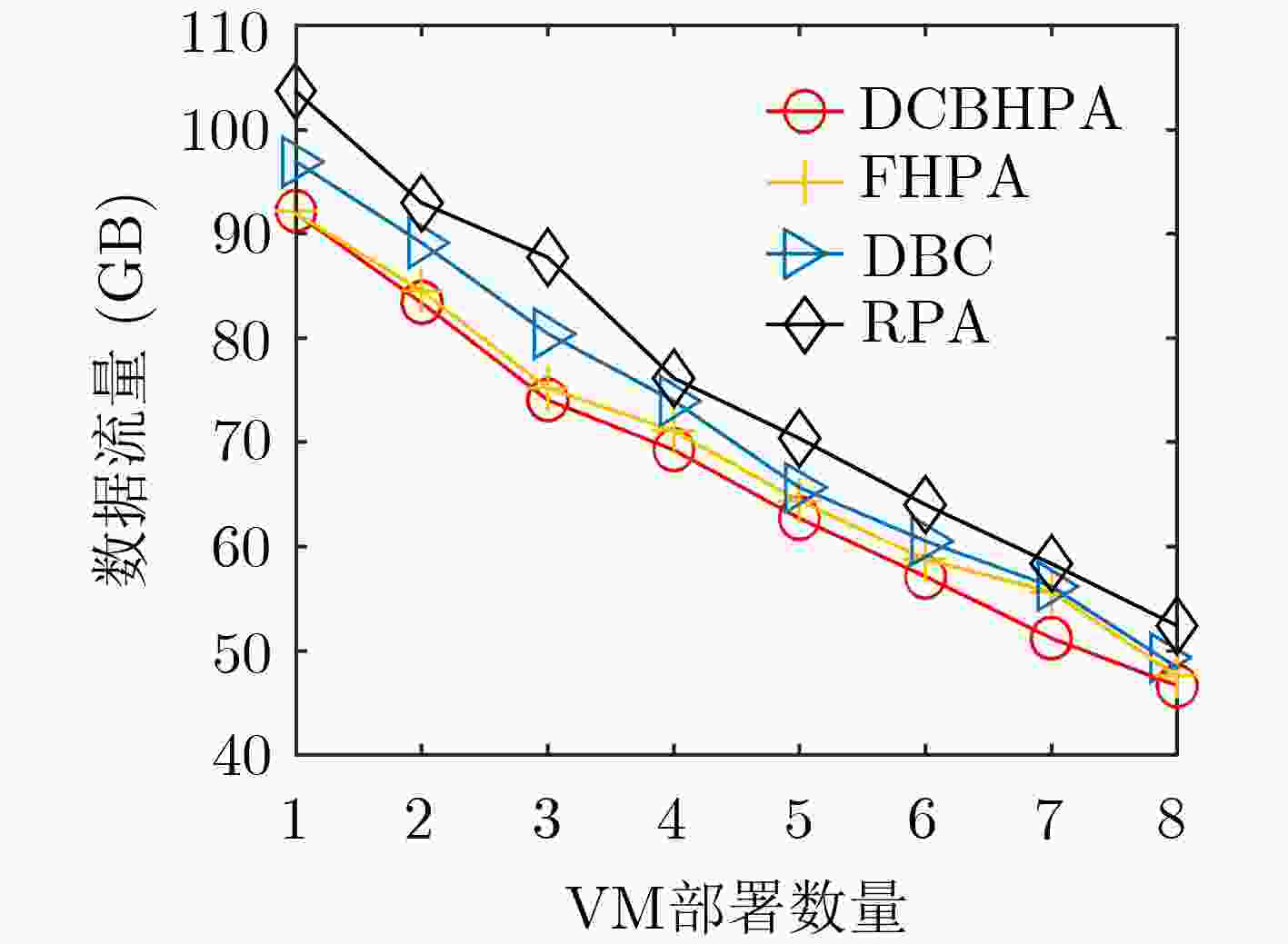
 下载:
下载:
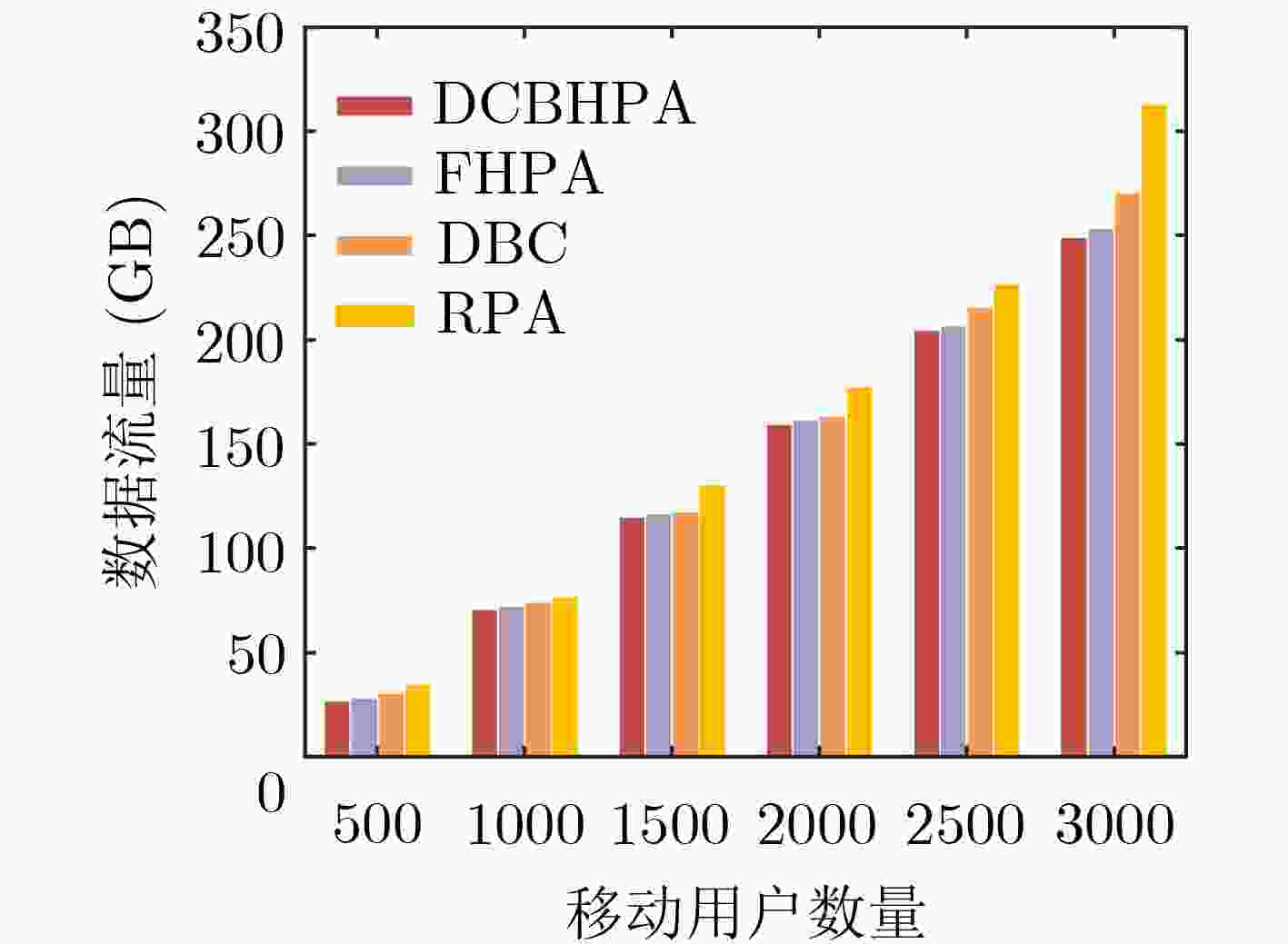
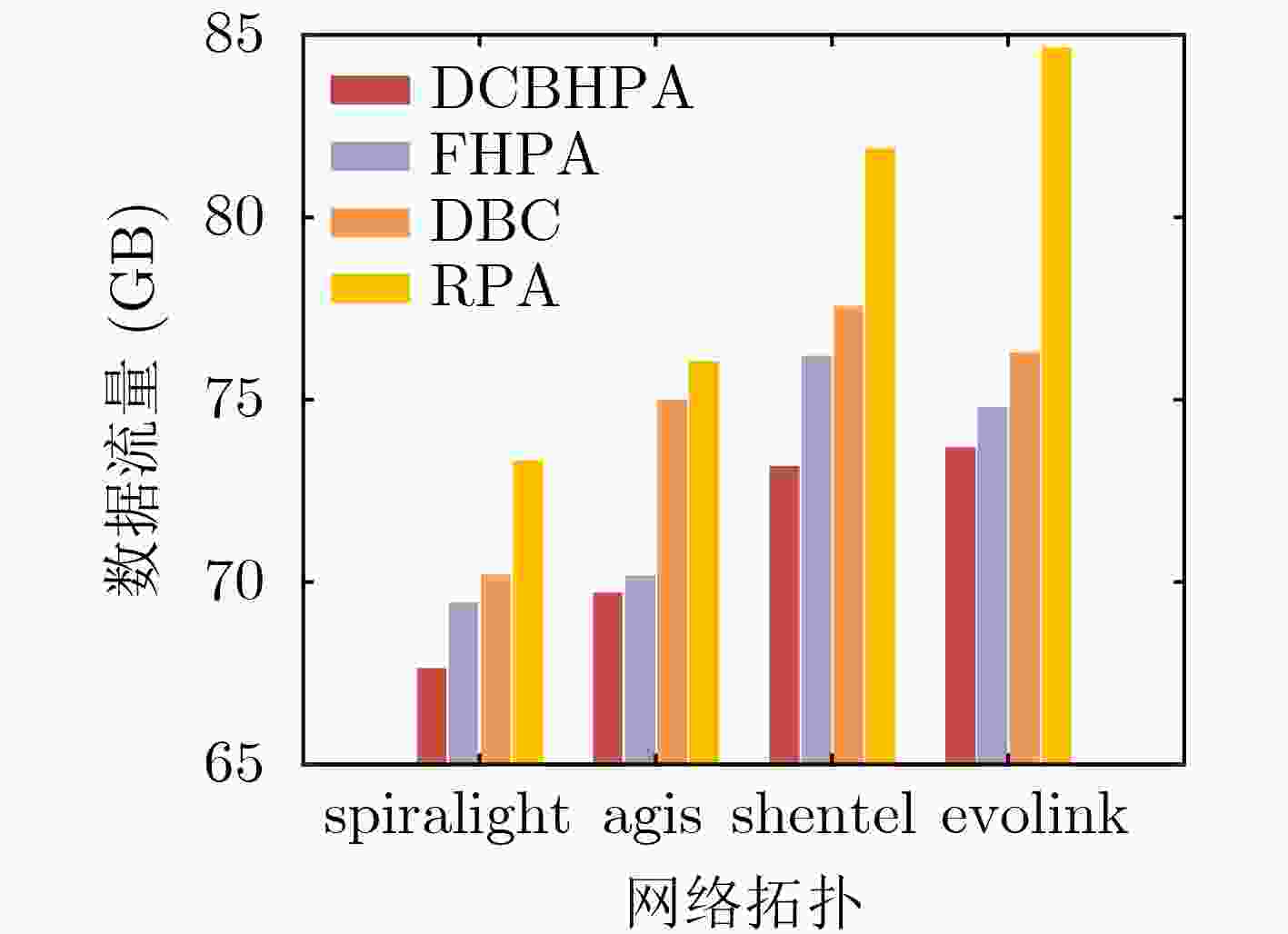
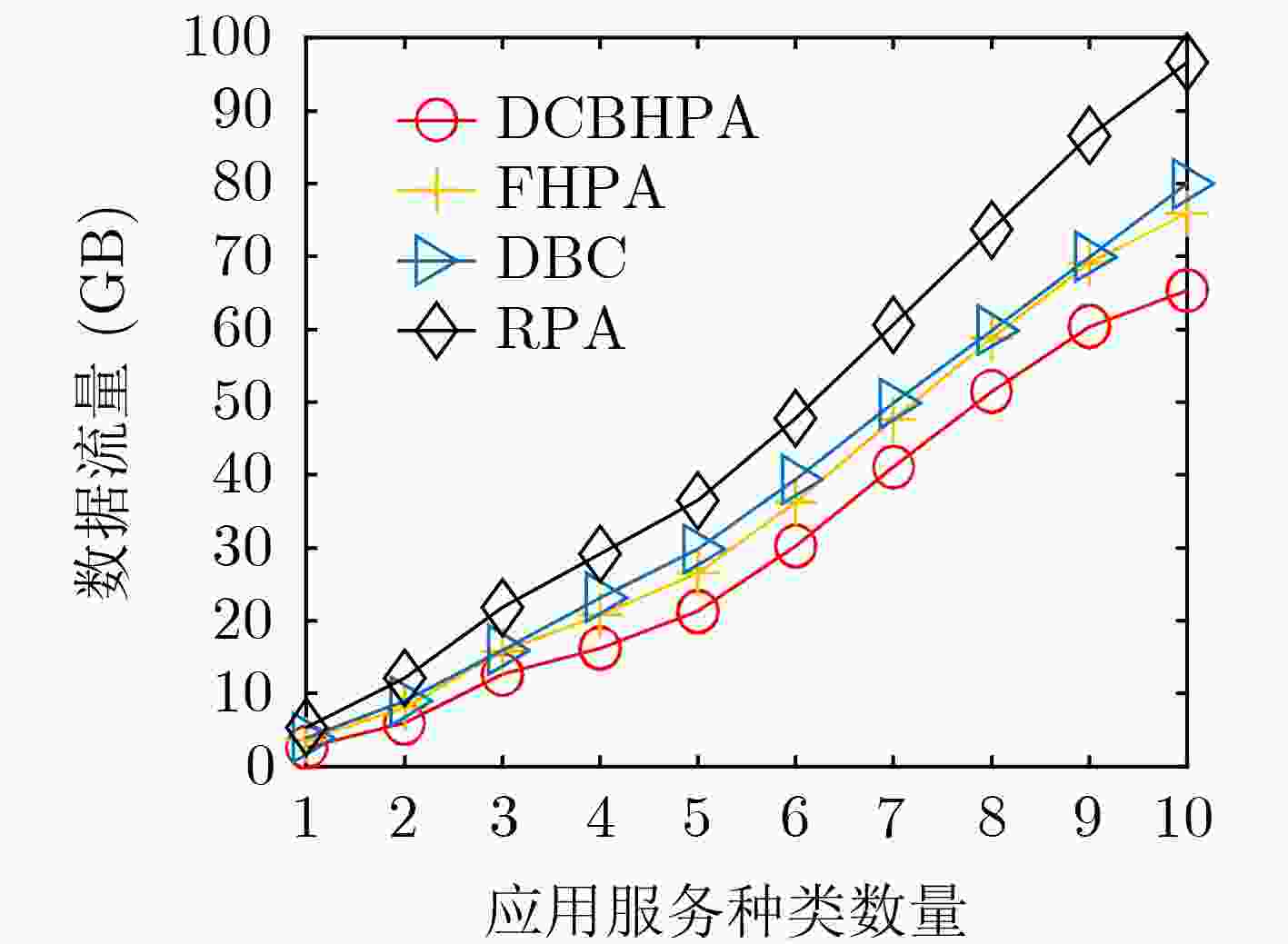
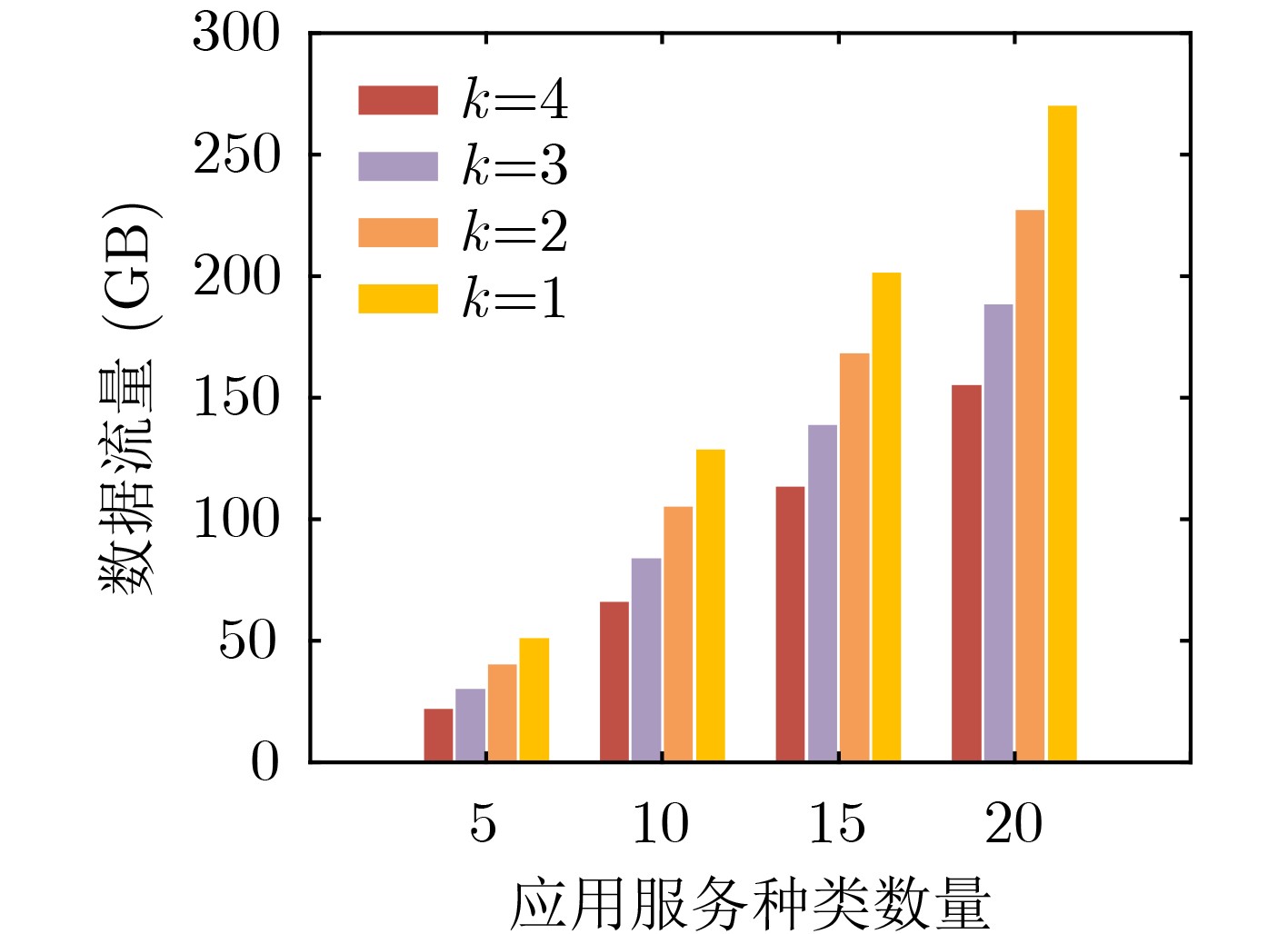
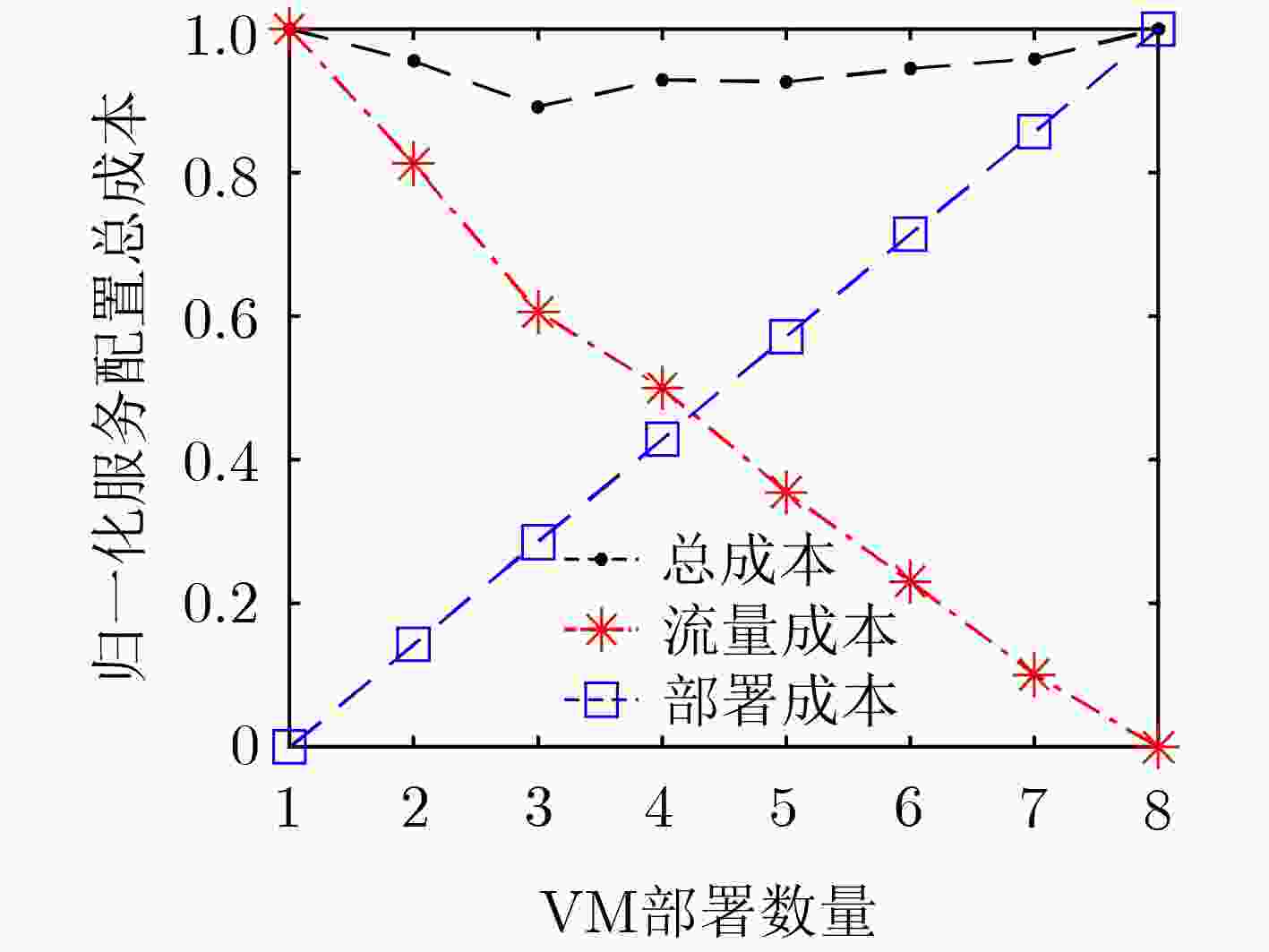
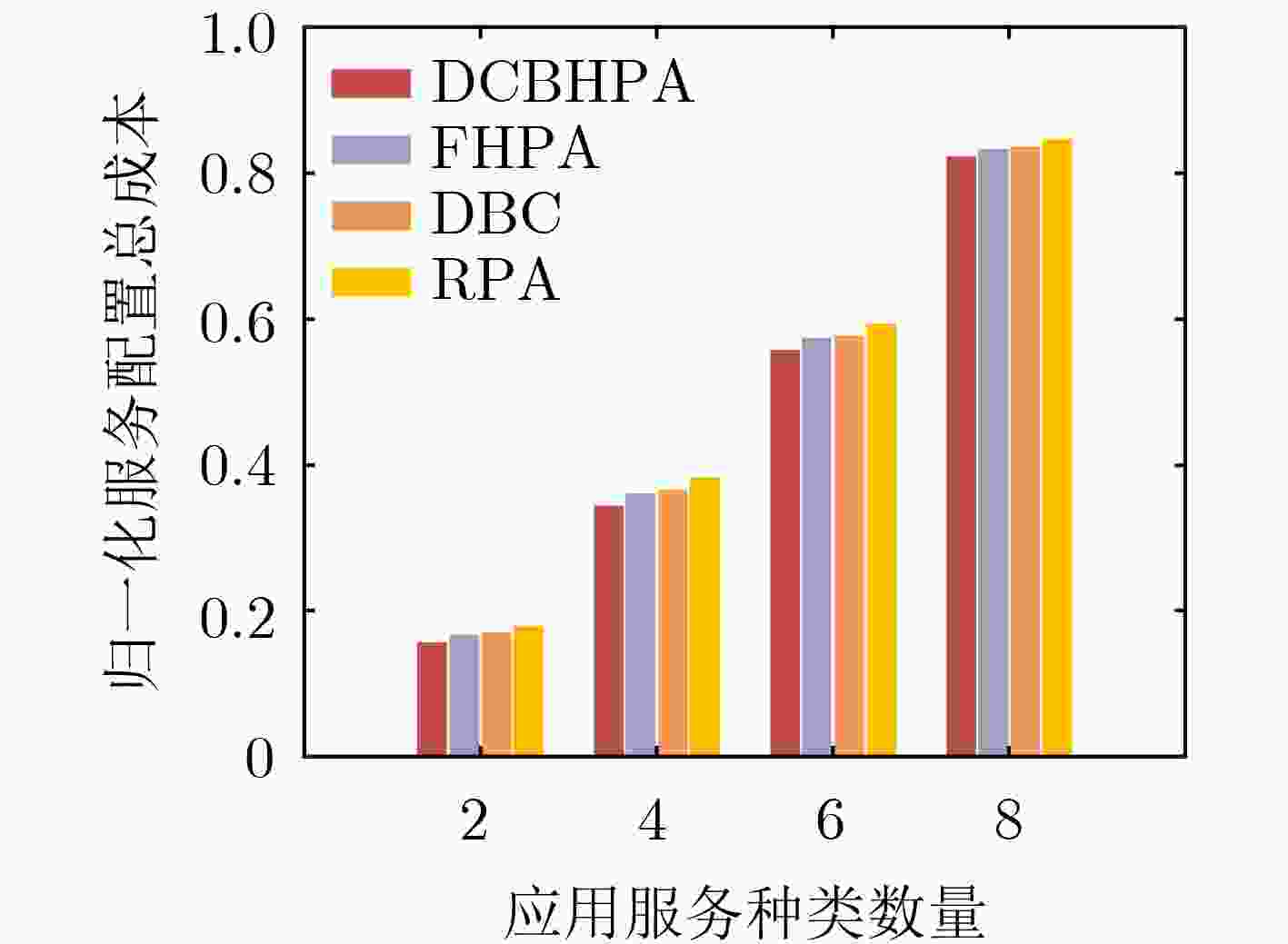


 下载:
下载:
