Research on Optimization Scheme of Task Offloading in Blockchain-enabled Fog Networks
-
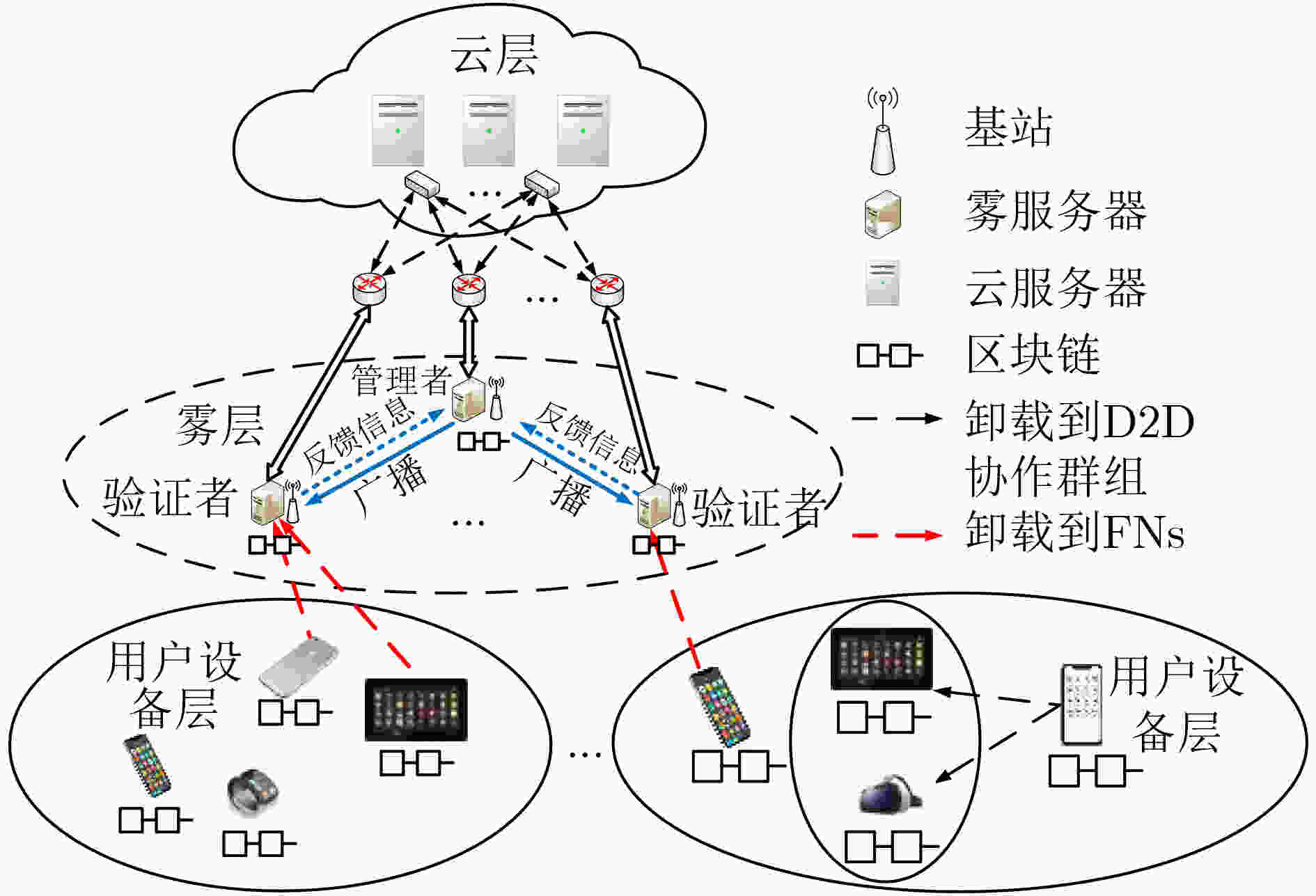
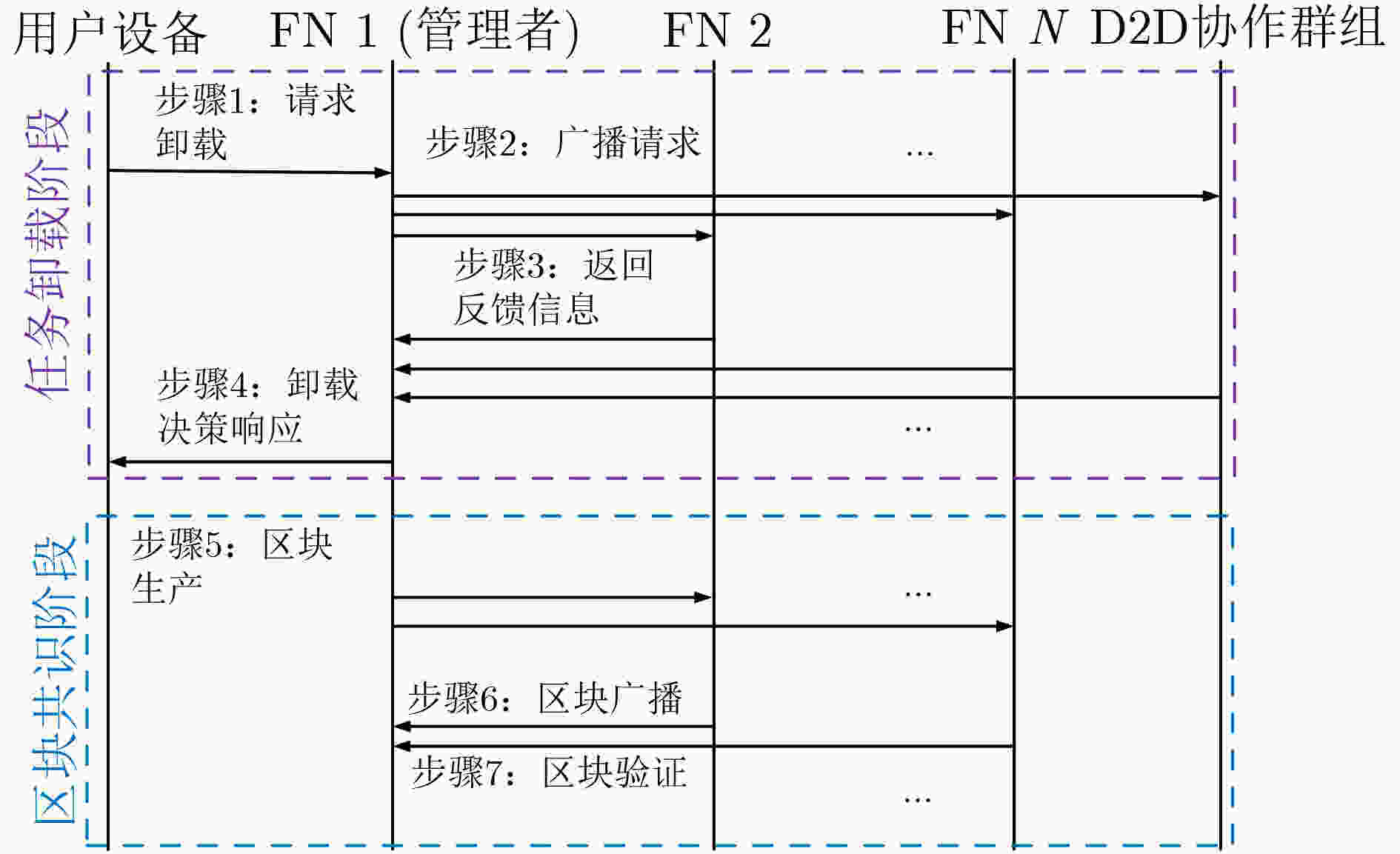
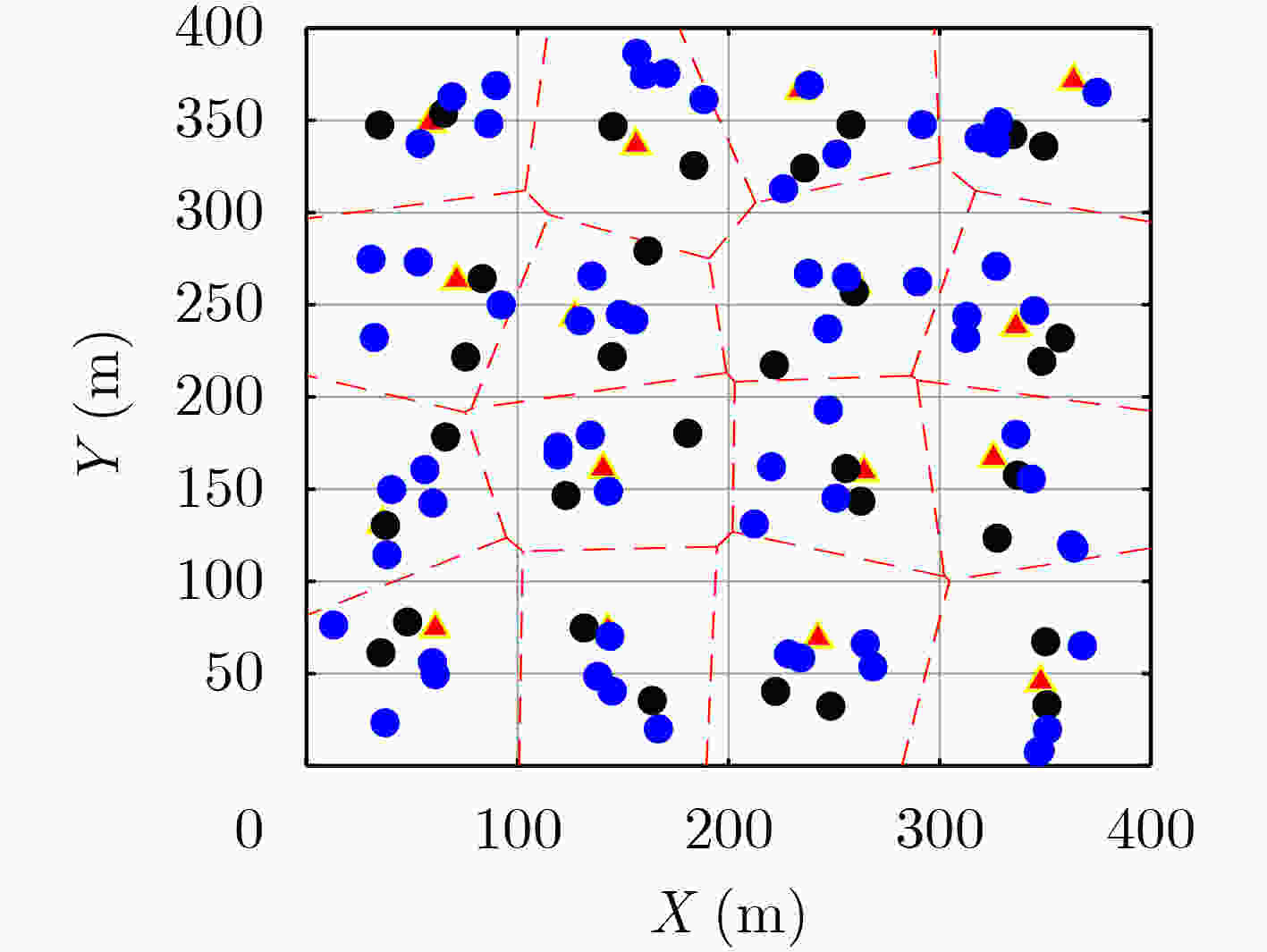
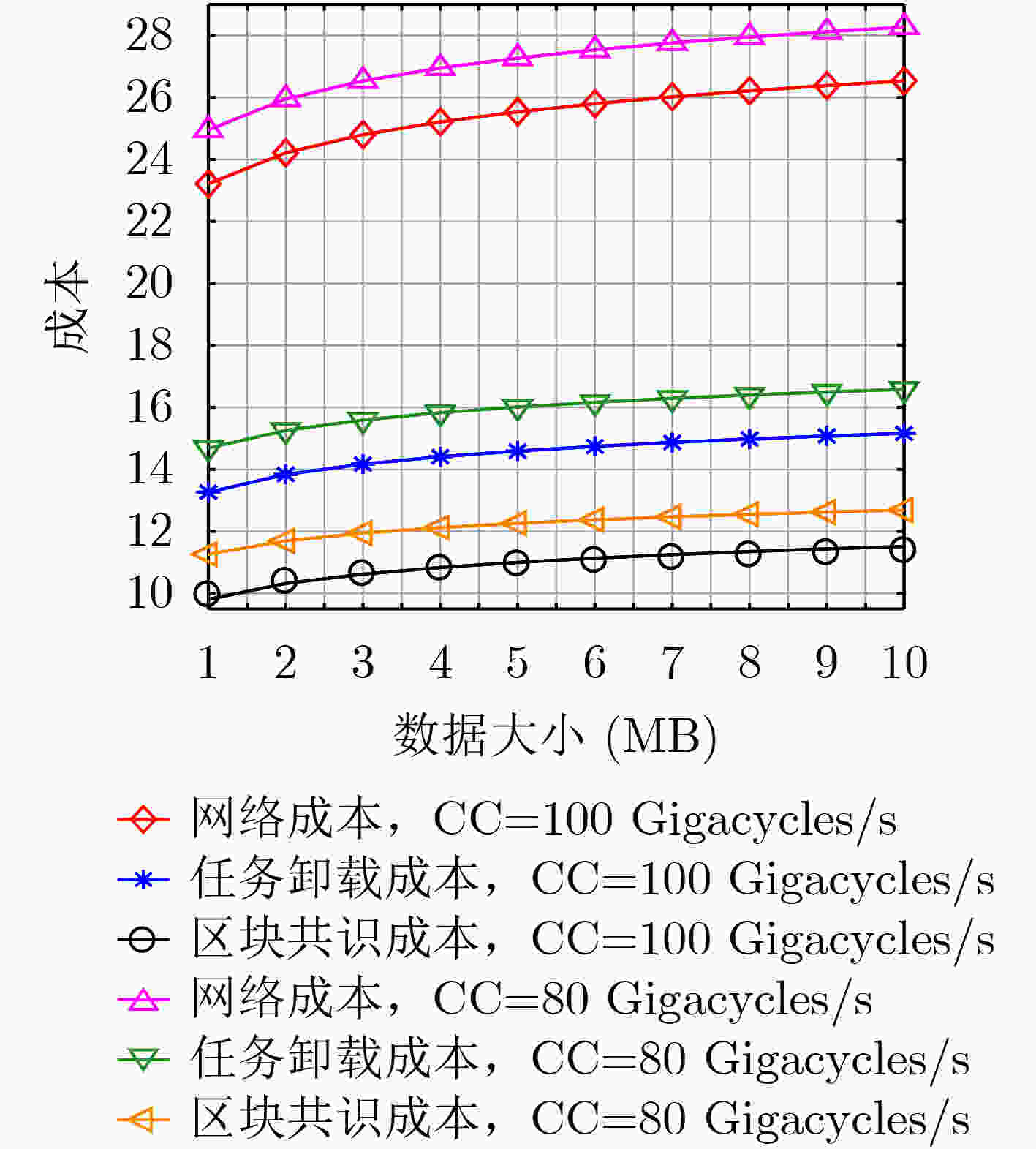
摘要: 当前物联网(IoT)应用的快速增长对用户设备的计算能力是一个巨大的挑战。雾计算(FC)网络可为用户设备提供近距离、快速的计算服务,为资源紧张,计算能力有限的用户设备提供了解决方案。该文提出一个基于区块链的雾网络模型,该模型中用户设备可以将计算密集型任务卸载到计算能力强的节点处理。为最小化任务处理时延和能耗,引入两种任务卸载模型,即设备到设备(D2D)协作群组任务卸载和雾节点(FNs)任务卸载。此外,针对雾计算网络任务卸载过程的数据安全问题,引入区块链技术构建去中心化分布式账本,防止恶意节点修改交易信息,实现数据安全可靠传输。为降低共识机制时延和能耗,提出了改进的基于投票的委托权益证明(DPoS)共识机制,得票数超过阈值的FNs组成验证集,验证集中的FN轮流作为管理者生成新区块。最后,以最小化网络成本为目标,联合优化任务卸载决策、传输速率分配和计算资源分配,提出任务卸载决策和资源分配(TODRA)算法进行求解,并通过仿真实验验证了该算法的有效性。Abstract: The current rapid growth of Internet of Things (IoT) applications is a huge challenge to the computing power of user equipment. The Fog Computing (FC) network can provide short-distance and fast computing services for user equipment, and provides a solution for user equipment with limited resources and limited computing capabilities. A blockchain-enabled fog network model is proposed, in which user equipment can offload computationally intensive tasks to nodes with strong computational capabilities. In order to minimize task processing delay and energy consumption, two task offloading models are introduced, namely Device-to-Device (D2D) collaboration group task offloading and Fog Nodes (FNs) task offloading. In addition, in view of the data security problem of the fog computing network task offloading process, blockchain technology is introduced to build a decentralized distributed ledger to prevent malicious nodes from modifying transaction information and achieve safe and reliable data transmission. In order to reduce the delay and energy consumption of the consensus mechanism, an improved voting-based Delegated-Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism is proposed. FNs with votes exceeding the threshold form a verification set, and the FNs in the verification set take turns as the manager to generate new blocks. Finally, with the goal of minimizing the network cost, the task offloading decision, transmission rate allocation and computing resource allocation are jointly optimized, and the Task Offloading Decision and Resource Allocation (TODRA) algorithm is proposed to solve the problem. The effectiveness of the algorithm is verified by simulation experiments.
-
Key words:
- Task offloading /
- Fog Computing (FC) network /
- Blockchain /
- Resource allocation
-
表 1 任务卸载决策和资源分配算法
算法1 任务卸载决策和资源分配算法(TODRA) (1) 初始化${\boldsymbol{\rho}}$, $ \varphi $, ${t_{\max }}$和最大容忍$\varsigma $,令$t{\text{ = }}0$。 (2) 步骤1当$t \le {t_{\max }}$时,分配传输速率${R_{k,n}}$和卸载决策${\delta _k}$。 (a) 根据式(38)更新对偶变量$ {\boldsymbol{\rho}} $和$ {\boldsymbol{\varphi}} $。 (b) 如果满足条件$||\rho (t + 1) - \rho (t)|| < \varsigma $和
$||\varphi (t + 1) - \varphi (t)|| < \varsigma $,则有
$ R_{k,n}^{\text{*}}{\text{ = }}{R_{k,n}}(t) $, $ \delta _k^{\text{*}}{\text{ = }}{\delta _k}(t) $,并退出循环。(c) 否则,$t{\text{ = }}t + 1$,进入下一次迭代。 (3) 步骤2 令${\phi _{\min }} = \dfrac{{{\delta _k}P_n^{{\text{sta}}}{Q_n}}}{{{E^{\max }} - E_{0,k}^{{\text{tol}}} - {\beta _{k,n}}{P_k}{D_k}}}/\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\frac{1}{{{\phi _n}}}} $,
${\phi _{\max } } = ({F^{\max } }{\text{ - } }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k \in {\varOmega _n} } { {f_{n,k} } } )/\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\frac{1}{ { {\phi _n} } } }$,直到${\phi _{\max }}$与${\phi _{\min }}$的差
值小于等于最大容忍$\varsigma $,返回结果${\phi _{{\text{res}}}}$。(a) 定义变量${\phi _b} = ({\phi _{{\text{min}}}} + {\phi _{{\text{max}}}})/2$。 (b) 如果满足条件${\text{|} }{\phi _{ {\text{max} } } }{{ - } }{\phi _{ {\text{min} } } }| < \varsigma$,则${\phi _{{\text{res}}}}{\text{ = }}{\phi _b}$。 (c) 否则,利用二分法更新拉格朗日乘子$\phi $。 (d) 如果条件$\displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\frac{ { {\phi _b} } }{ { {\phi _n} } } } > {F^{\max } } - {f_{n,w'} }$成立,${\phi _{\max }} = {\phi _b}$,否
则$ {\phi _{\min }} = {\phi _b} $。(e) $ b = b + 1 $,返回(a)。 (f) 把${\phi _{{\text{res}}}}$代入式(42),得到计算资源的最优解。 (4) 算法结束。 -
[1] MILLER D. Blockchain and the internet of things in the industrial sector[J]. IT Professional, 2018, 20(3): 15–18. doi: 10.1109/MITP.2018.032501742 [2] MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHANG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201 [3] BACCARELLI E, SCARPINITI M, NARANJO P G V, et al. Fog of social IoT: When the fog becomes social[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(4): 68–80. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1700031 [4] HUANG Xiaoge, CUI Yifan, CHEN Qianbin, et al. Joint task offloading and QoS-aware resource allocation in fog-enabled internet-of-things networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7194–7206. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2982670 [5] SHARMA P K, CHEN M Y, and PARK J H. A software defined fog node based distributed blockchain cloud architecture for IoT[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 6: 115–124. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2757955 [6] HUANG Xiaoge, FAN Weiwei, CHEN Qianbin, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation in fog computing networks with the candidate mechanism[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(9): 8502–8512. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2991481 [7] FERRAG M A, DERDOUR M, MITHUN MUKHERJEE M, et al. Blockchain technologies for the internet of things: Research issues and challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2188–2204. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2882794 [8] SHARMA P K, SINGH S, JEONG Y S, et al. DistBlockNet: A distributed blockchains-based secure SDN architecture for IoTnetworks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(9): 78–85. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1700041 [9] CHEN M H, DONG Min, and LIANG Ben. Resource sharing of a computing access point for multi-user mobile cloud offloading with delay constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(12): 2868–2881. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2815533 [10] FENG Jie, YU F R, PEI Qingqi, et al. Joint optimization of radio and computational resources allocation in blockchain-enabled mobile edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(6): 4321–4334. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2982627 [11] ZHANG Zhen, HONG Zicong, CHEN Wuhui, et al. Joint computation offloading and coin loaning for blockchain-empowered mobile-edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 9934–9950. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2933445 [12] YUAN Yingying, FENG Guangsheng, LV Hongwu, et al. A near-optimal resource allocation approach to computation offloading under D2D communications[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Internet of Things, Tianjin, China, 2019: 183–188. [13] ZHANG Jing, XIA Weiwei, YAN Feng, et al. Joint computation offloading and resource allocation optimization in heterogeneous networks with mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 19324–19337. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2819690 [14] KUMAR G, L SAHA R, RAI M M, et al. Proof-of-work consensus approach in blockchain technology for cloud and fog computing using maximization-factorization statistics[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6835–6842. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2911969 [15] WANG Siming, YE Dongdong, HUANG Xumin, et al. Consortium blockchain for secure resource sharing in vehicular edge computing: A contract-based approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 1189–1201. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3004475 [16] XU Chenhan, WANG Kun, LI Peng, et al. Making big data open in edges: A resource-efficient blockchain-based approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2019, 30(4): 870–882. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2018.2871449 -





 下载:
下载:
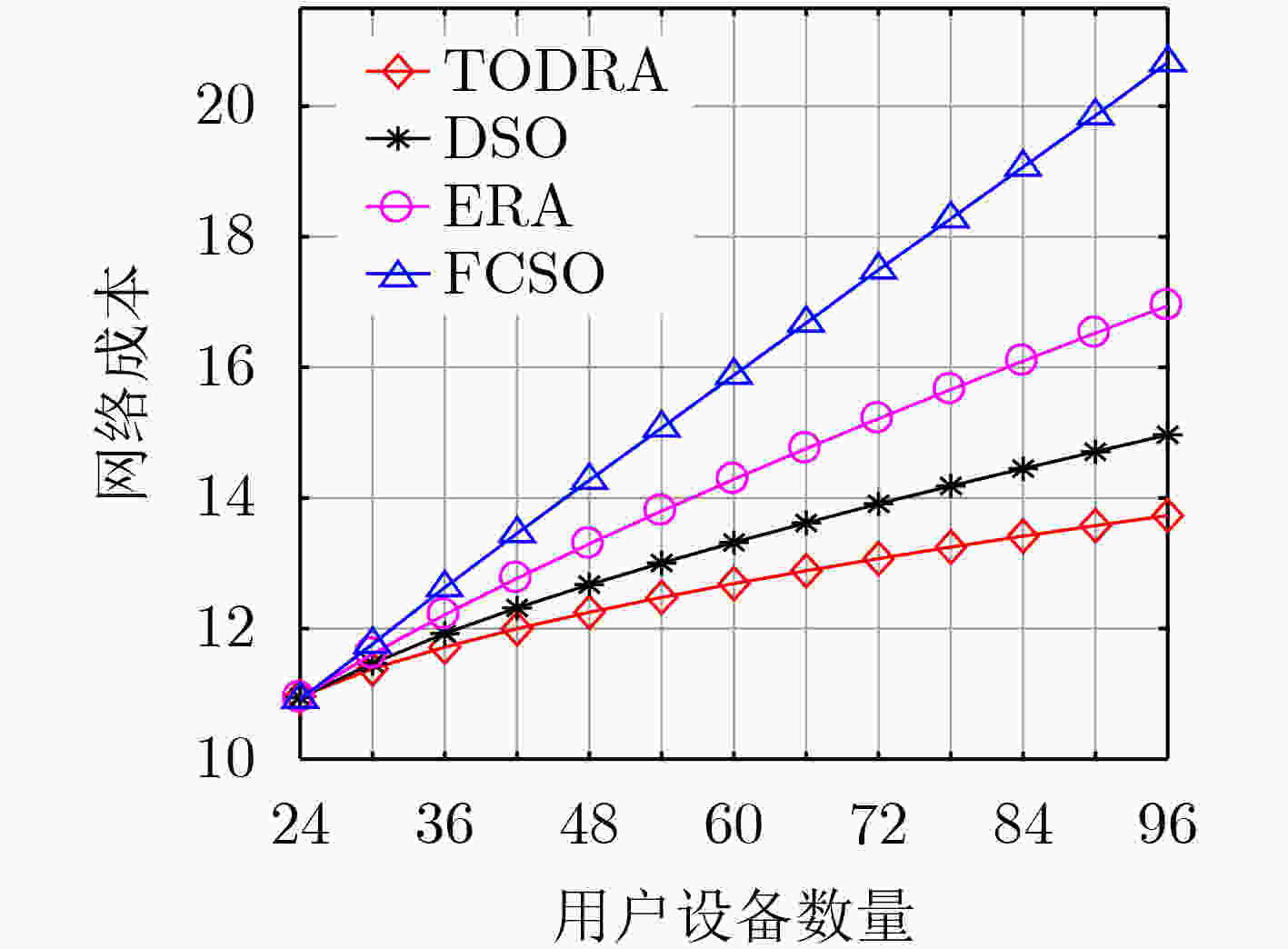
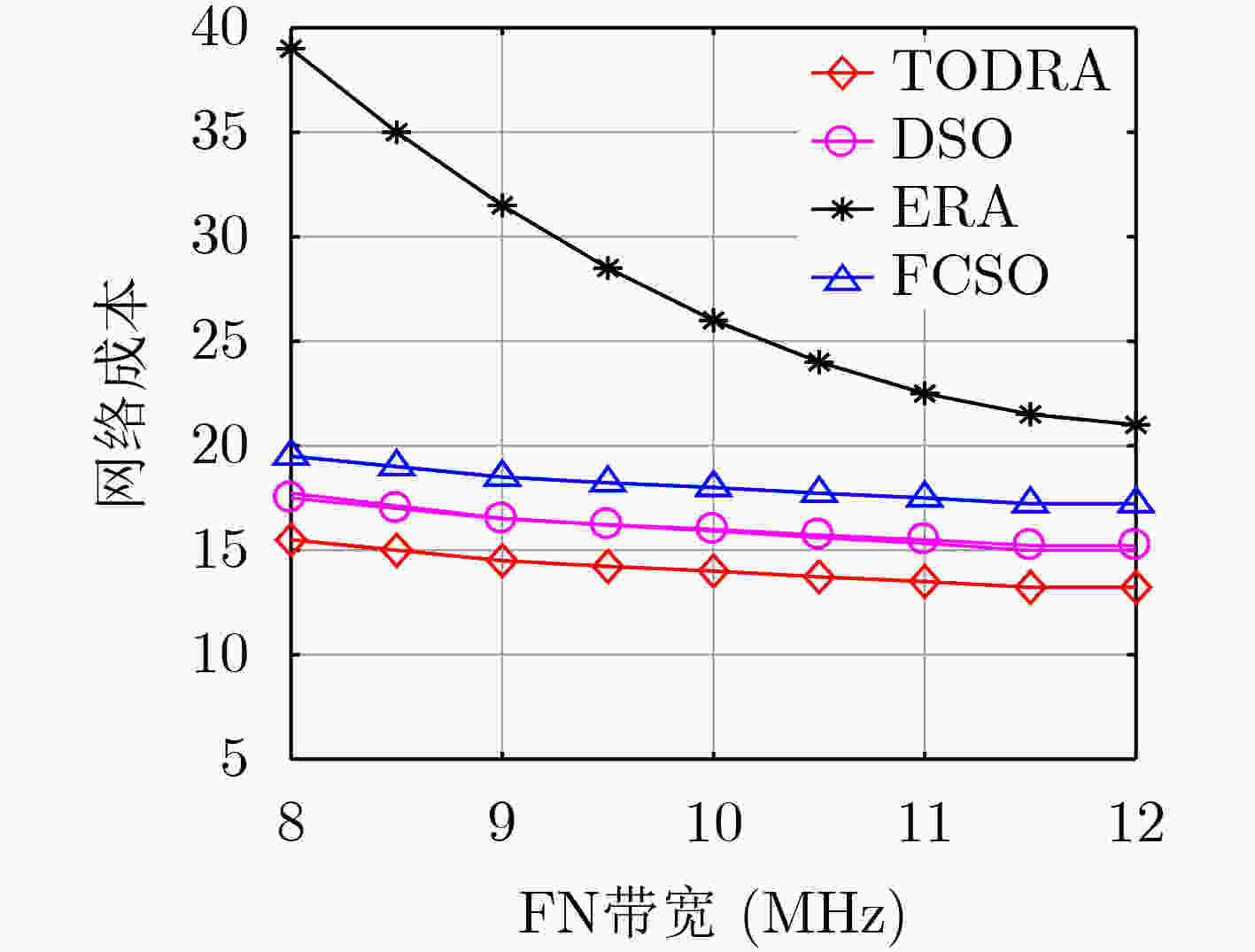

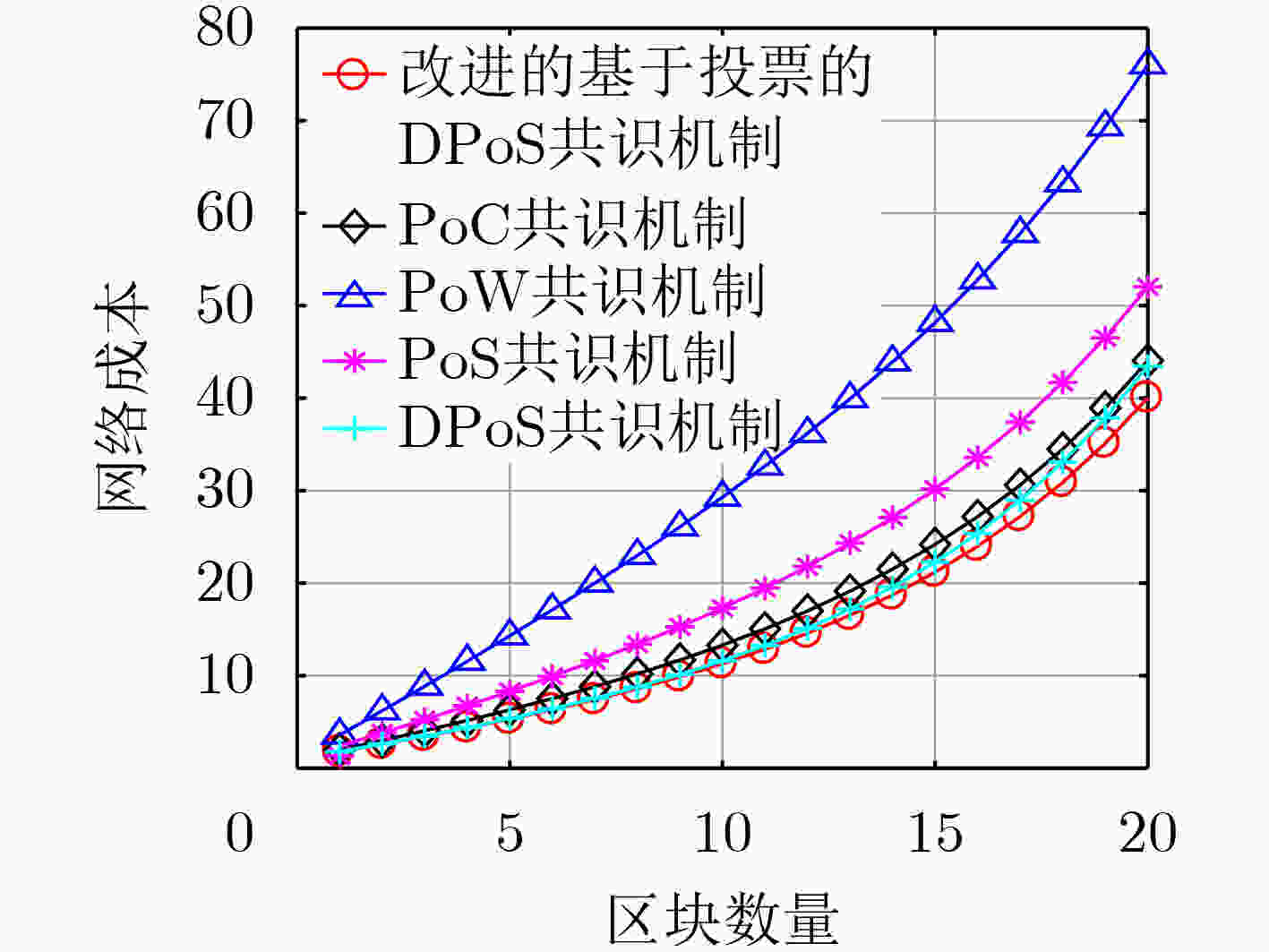


 下载:
下载:
