Turbid Water Image Enhancement Algorithm Based on Improved CycleGAN
-
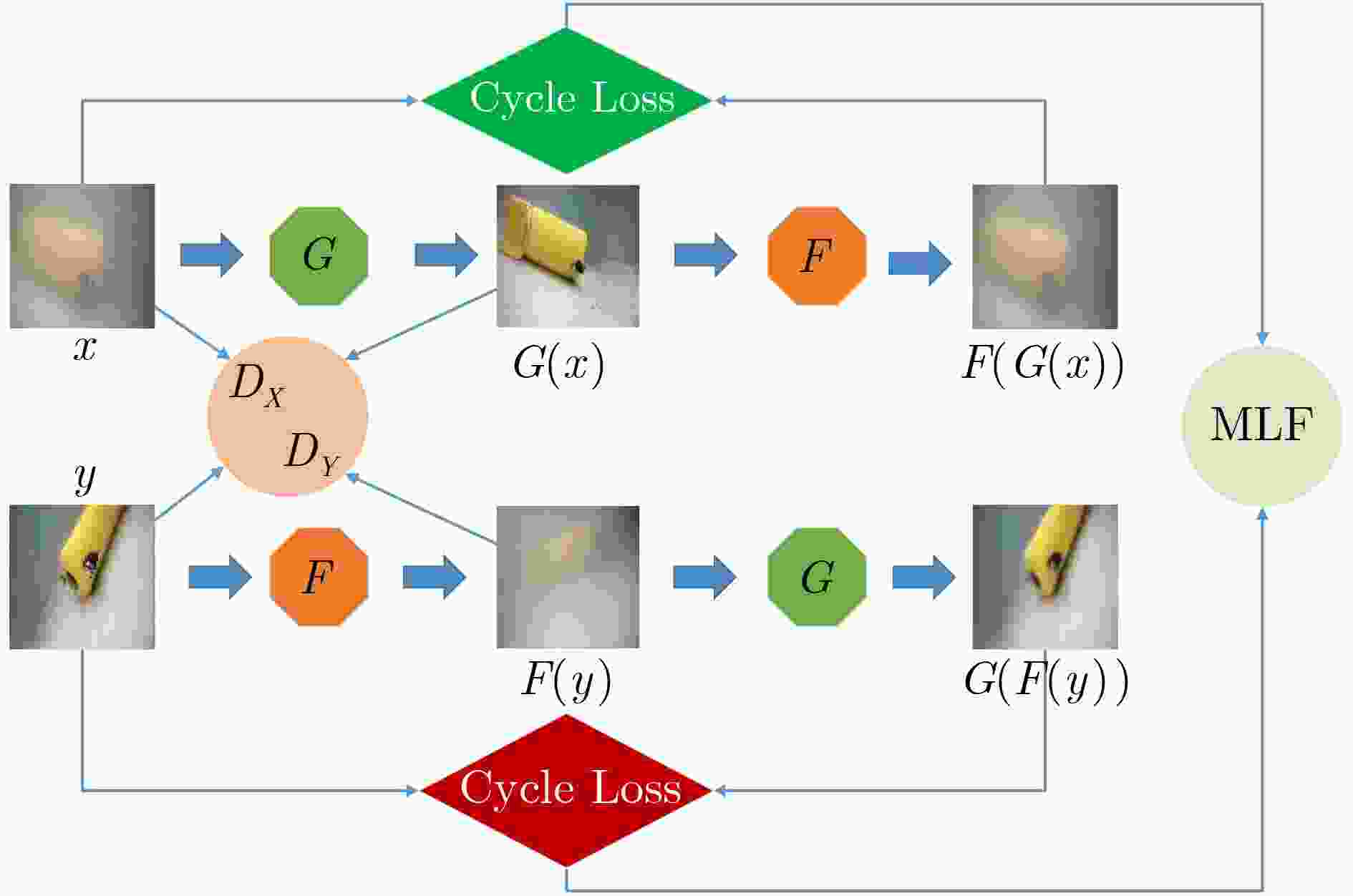
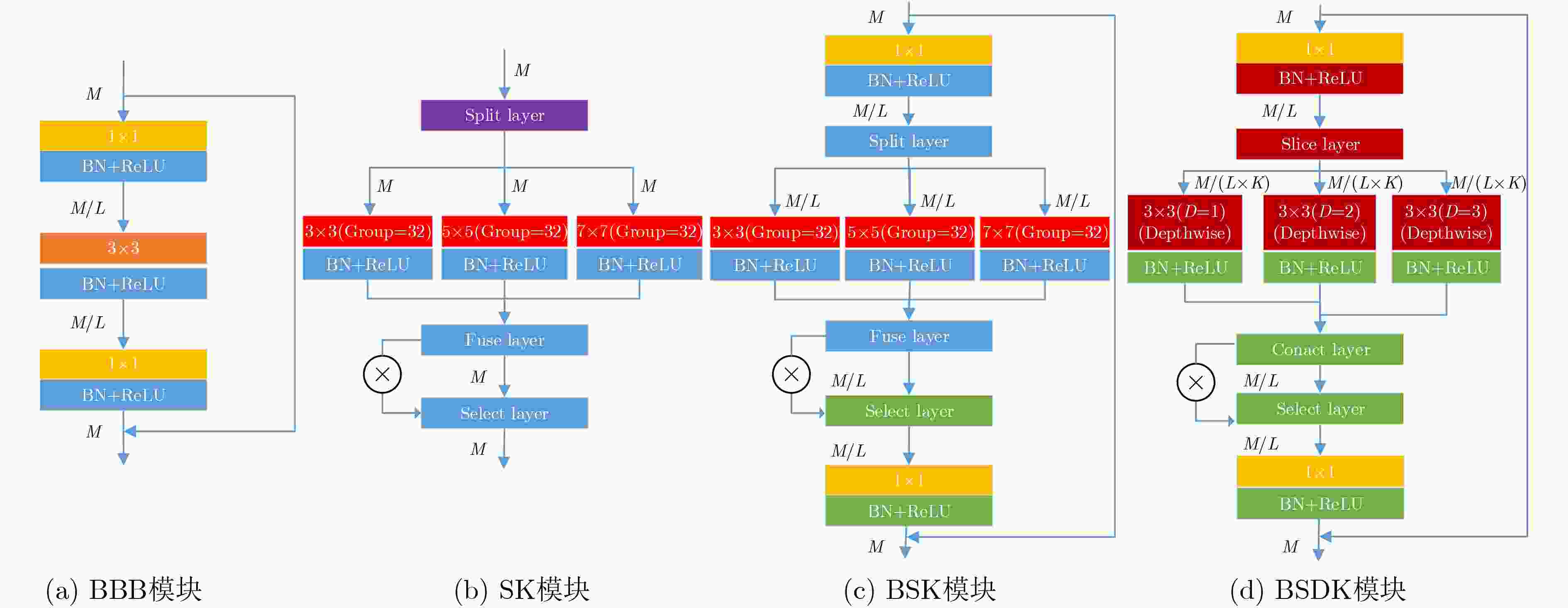
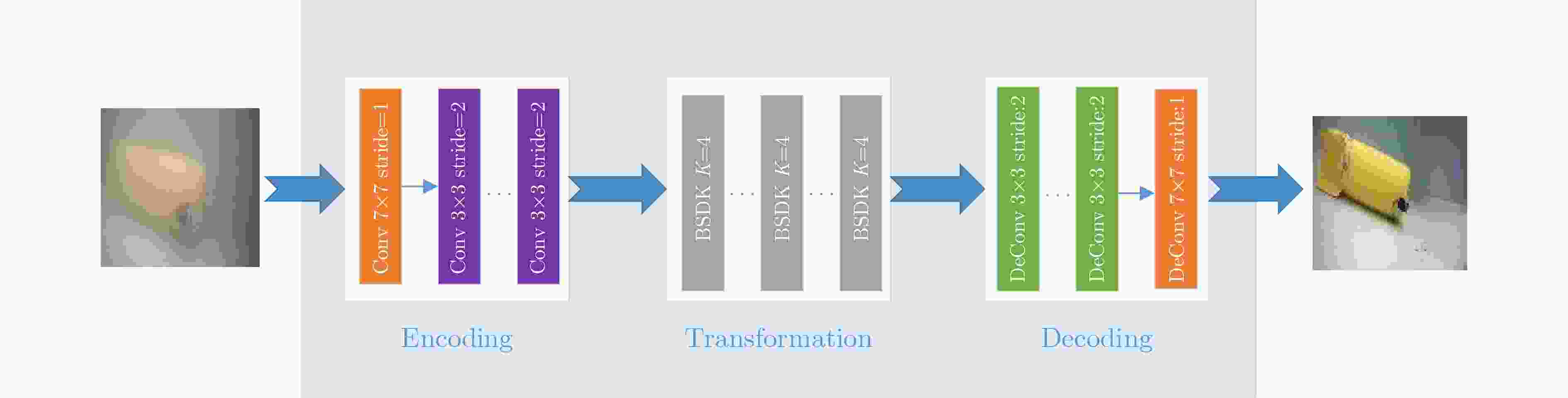
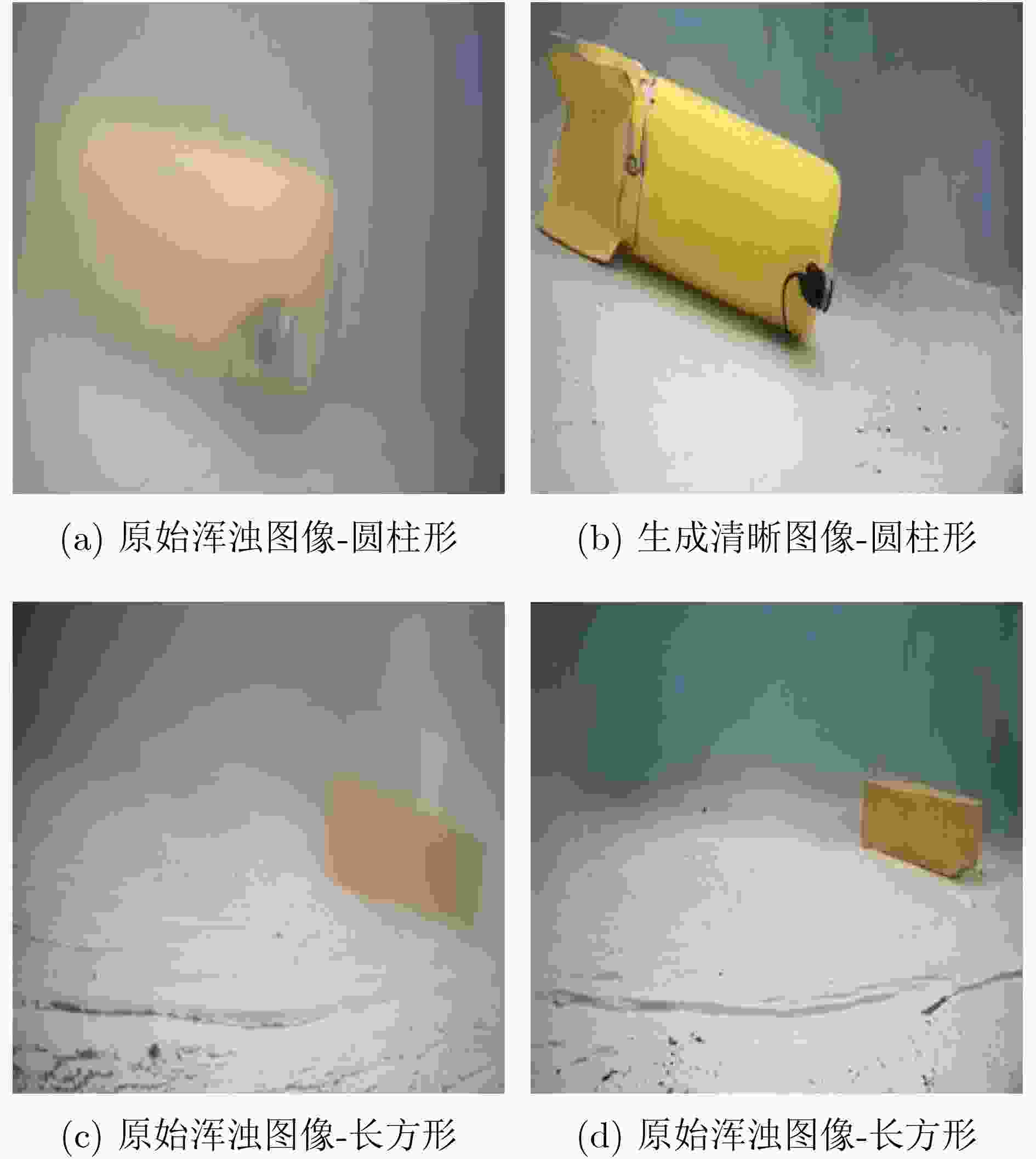
摘要: 针对循环生成对抗网络(Cycle Generative Adversarial Networks, CycleGAN)在浑浊水体图像增强中存在质量差和速度慢的问题,该文提出一种可扩展、可选择和轻量化的特征提取单元BSDK (Bottleneck Selective Dilated Kernel),并利用BSDK设计了一个新的生成器网络BSDKNet。与此同时,提出一种多尺度损失函数MLF(Multi-scale Loss Function)。在自建的浑浊水体图像增强数据集TC(Turbid and Clear)上,该文BM-CycleGAN比原始CycleGAN的精度提升3.27%,生成器网络参数降低4.15MB,运算时间减少0.107s。实验结果表明BM-CycleGAN适合浑浊水体图像增强任务。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of poor quality and slow speed in turbid water image enhancement based on Cycle Generative Adversarial Networks (CycleGAN), a scalable, selective and efficient block Bottleneck Selective Dilated Kernel (BSDK) is proposed, and a new generator network BSDKNet is redesigned by stacking BSDK. At the same time, Multi-scale Loss Function (MLF) is proposed to improve the structural similarity of the clear water image and the generated clear water image. On our turbid water image enhancement dataset Turbid and Clear (TC), the classification accuracy of the proposed BM-CycleGAN is 3.27% higher than that of classical CycleGAN. The generator parameters of BM-CycleGAN is 4.15 MB lower than that of CycleGAN, and the time consuming of BM-CycleGAN is 0.107 s less than that of CycleGAN. The experimental results show that BM-CycleGAN is suitable for turbid water image enhancement.
-
表 1 浑浊水体图像增强算法性能比较
分类准确率(%) 参数大小(MB) 运算时间(s) CycleGAN 95.10 10.97 0.127 SS-CycleGAN 95.92 10.97 0.127 BSK-CycleGAN 96.73 18.21 0.054 BM-CycleGAN 98.37 6.82 0.020 表 2 BSDKNet生成器网络和MLF损失函数对BM-CycleGAN性能的影响
BSDKNet MLF 分类准确率(%) 参数大小(MB) 运算时间(s) CycleGAN 95.10 10.97 0.127 M-CycleGAN
B-CycleGAN
BM-CycleGAN√ 96.09 10.97 0.127 √ 97.27 6.82 0.020 √ √ 98.37 6.82 0.020 表 3 不同权重系数(1–9)MLF对BM-CycleGAN性能的影响
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 分类准确率(%) 95.10 95.51 96.73 97.14 97.55 98.37 97.96 97.14 96.33 表 4 不同多尺度系数(1,2,4,8)条件下的BSDKNet对BM-CycleGAN性能的影响
1 2 4 8 分类准确率(%) 95.10 97.96 98.37 98.78 参数大小(MB) 6.82 6.82 6.82 6.82 运算时间(s) 0.006 0.016 0.021 0.030 -
[1] HMUE P M and PUMRIN S. Image enhancement and quality assessment methods in turbid water: A review article[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Asia (ICCE-Asia), Bangkok, Thailand, 2019: 59–63. [2] HITAM M S, AWALLUDIN E A, YUSSOF W N J H W, et al. Mixture contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization for underwater image enhancement[C]. 2013 International Conference on Computer Applications Technology (ICCAT), Sousse, Tunisia, 2013: 1–5. [3] GHANI A S A and ISA N A M. Enhancement of low quality underwater image through integrated global and local contrast correction[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 37: 332–344. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.08.033 [4] LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, GUO Chunle, et al. A hybrid method for underwater image correction[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2017, 94: 62–67. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.05.023 [5] DENG Xiangyu, WANG Huigang, and LIU Xing. Underwater image enhancement based on removing light source color and Dehazing[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 114297–114309. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936029 [6] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [7] KWOK R. Deep learning powers a motion-tracking revolution[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7776): 137–138. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02942-5 [8] WANG Shiqiang. Efficient deep learning[J]. Nature Computational Science, 2021, 1(3): 181–182. doi: 10.1038/s43588-021-00042-x [9] KUANG Wenhuan, YUAN Congcong, and ZHANG Jie. Real-time determination of earthquake focal mechanism via deep learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1432. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21670-x [10] YANG X S. Data Mining and Deep Learning[M]. YANG X S. Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms (Second Edition). London : Academic Press, 2021: 239–258. [11] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative Adversarial Networks[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [12] RADFORD A, METZ L, and CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[C]. 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016. [13] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, and BOTTOU L. Wasserstein GAN[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1701.07875, 2017. [14] CHEN Xi, DUAN Yan, HOUTHOOFT R, et al. InfoGAN: Interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2016, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 2172−2180. [15] XU Qiantong, HUANG Gao, YUAN Yang, et al. An empirical study on evaluation metrics of generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1806.07755, 2018. [16] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image−to−image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. [17] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. [18] FABBRI C, ISLAM M J, and SATTAR J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 7159–7165. [19] XIE Saining, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5987–5995. [20] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278–4284. [21] LI Xiang, WANG Wenhai, HU Xiaolin, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 510–519. [22] HUANG Xuejun, WEN Liwu, and DING Jinshan. SAR and optical image registration method based on improved CycleGAN[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–6. [23] 李宝奇, 贺昱曜, 强伟, 等. 基于并行附加特征提取网络的SSD地面小目标检测模型[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(1): 84–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.010LI Baoqi, HE Yuyao, QIANG Wei, et al. SSD with parallel additional feature extraction network for ground small target detection[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(1): 84–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.010 [24] HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017. [25] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [26] QIN Yanjun, LUO Haiyong, ZHAO Fang, et al. NDGCN: Network in network, dilate convolution and graph convolutional networks based transportation mode recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(3): 2138–2152. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3060761 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
