Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Jamming Resource Scheduling Based on Parallel Genetic Algorithm with Elite Set
-
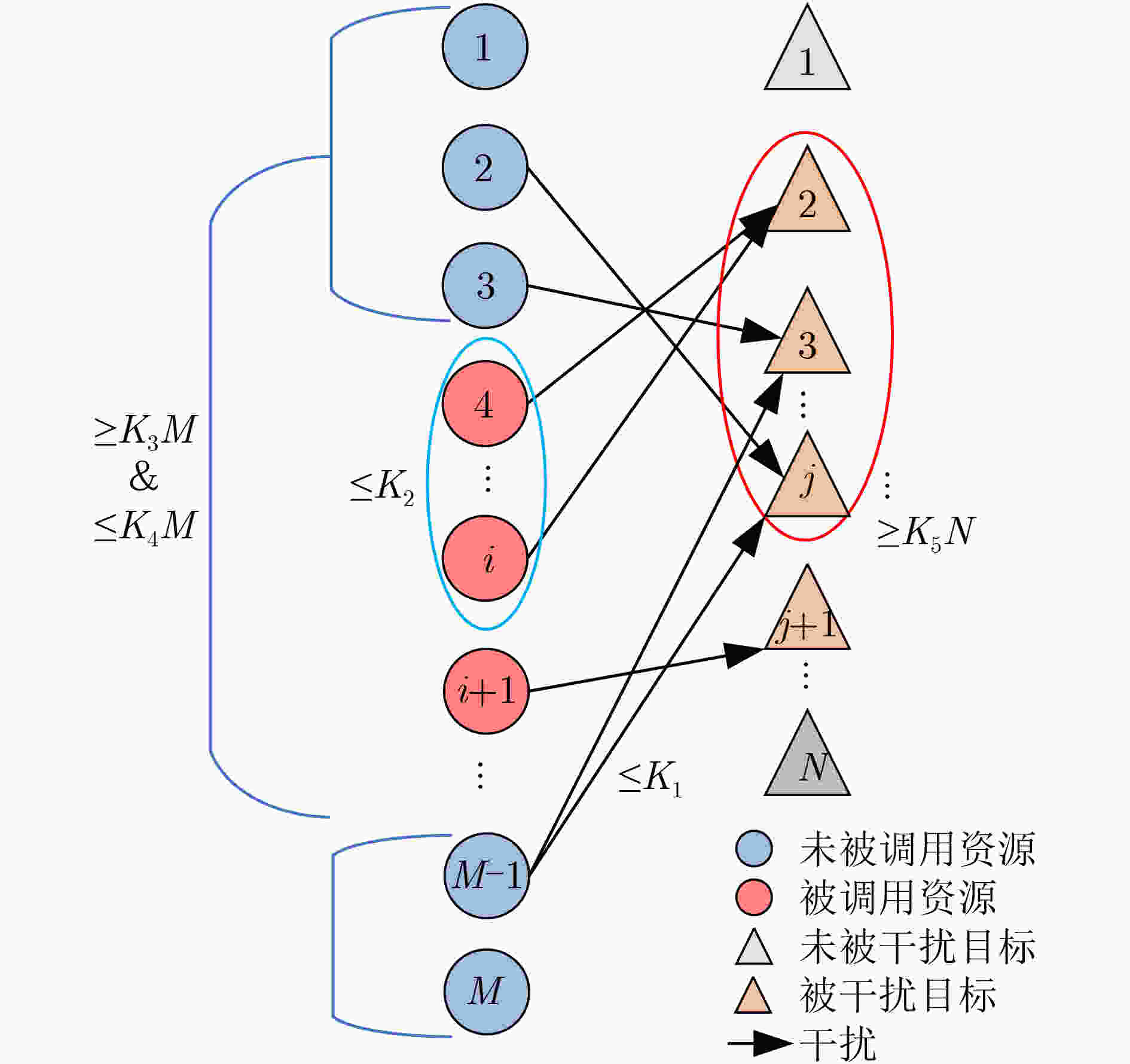
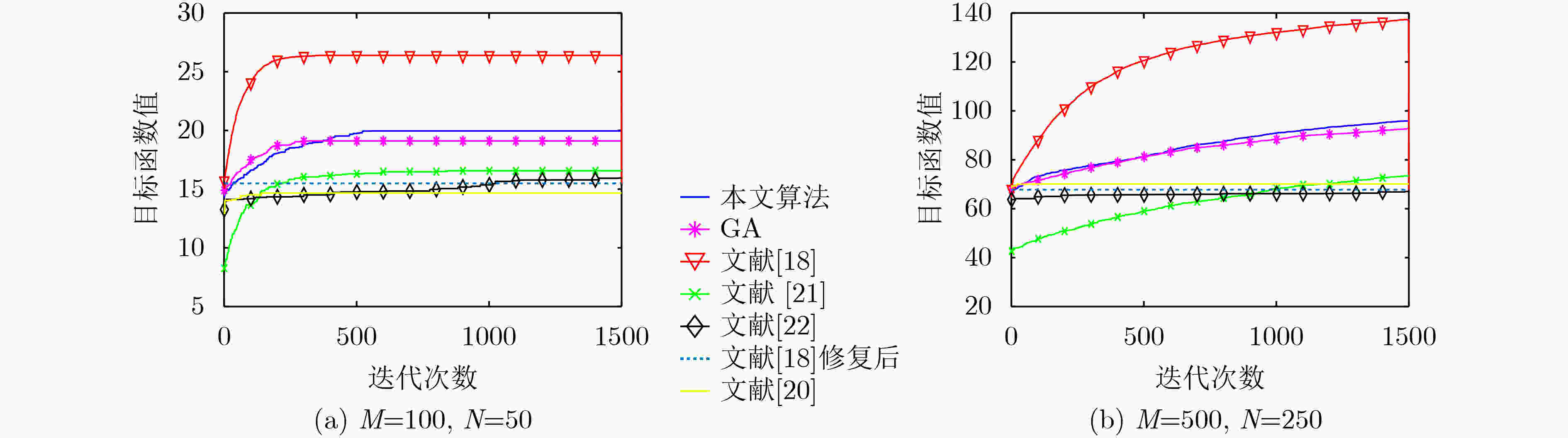
摘要: 在中大规模无人机干扰资源调度中,针对现有模型约束条件简单、调度算法适用规模较小的问题,该文提出了带最少任务数约束的资源调度模型,以最大化干扰效益和最小化成本为目标,用层次分析法对效益与成本指标赋权,并设计了一种用精英集加快收敛的改进并行遗传算法。在中等规模和500:500(干扰资源数:目标数)的更大规模仿真实验中,所提算法与遗传算法、非支配排序遗传算法II、修复遗传算法、基于岛屿模型的并行遗传算法和自适应模拟退火遗传禁忌搜索算法的性能相比,能在更短的时长内达到较优的目标函数值。Abstract: In order to solve the optimization problem of jamming resource scheduling in medium and large-scale Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) jamming scenarios, a jamming resource scheduling model that can meet the minimum number of tasks constraint is proposed to improve the simple constraints and small-scale solution algorithms of the existing models. The interference benefit and cost indicators are weighted by the analytic hierarchy process. Then an improved parallel genetic algorithm is designed, where the elite set is introduced to accelerate the convergence of the algorithm. The simulation results in medium scale and larger scale jamming situations, such as 500:500 (number of jamming resources: number of targets) show that the proposed algorithm converges faster and achieves better objective function value than the existing representative and improved genetic algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Interference countermeasure /
- Resource scheduling /
- Genetic algorithm /
- Parallel algorithm /
- Hybrid mode
-
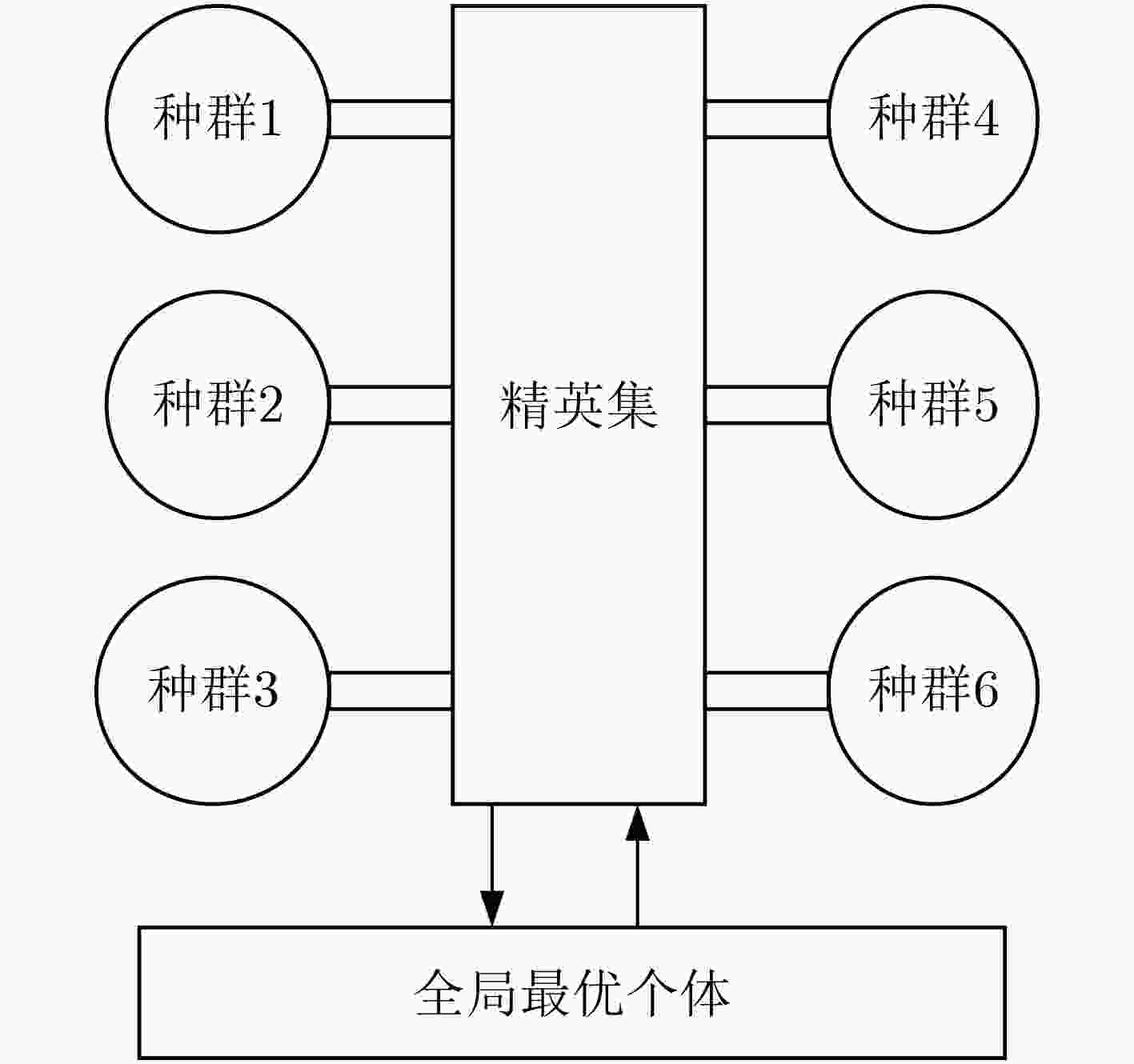
表 1 基于混合模型的并行遗传算法(算法1)
1: t=1// 迭代次数 2:计算总干扰效益矩阵E,规模为M×N 3:初始化S个子种群(pop1,pop2,···,pops),种群规模为P,设置
每个子种群的最差个体g1k,全局最优个体b0;//$S \ge 3$,根据
算法计算最短时间和并行线程而定;4:while(t<tmax) 5:parfors=1:S;//S个子种群并行计算 6:(popk,gk,g1k)=cacaulation(popk);//子种群进行选择,交叉,
变异等遗传操作,并计算操作后的目标函数值,选出最优个
体gk,和最差个体g1k,k=1,2,···,S7:end parfor 8:G=(g1,g2,···,gk);//k=1,2,···,S 9:b1=max(G) 10:if b1>b0 11:b0=b1; 12:end if 13:for k=1:S 14:popk=change(g1k,b0,popk)//所有子种群将最差个体g1k替换
为b015:end for 16:end while 表 2 迭代1500次所用时间/最终目标函数值对比(100次仿真平均值)
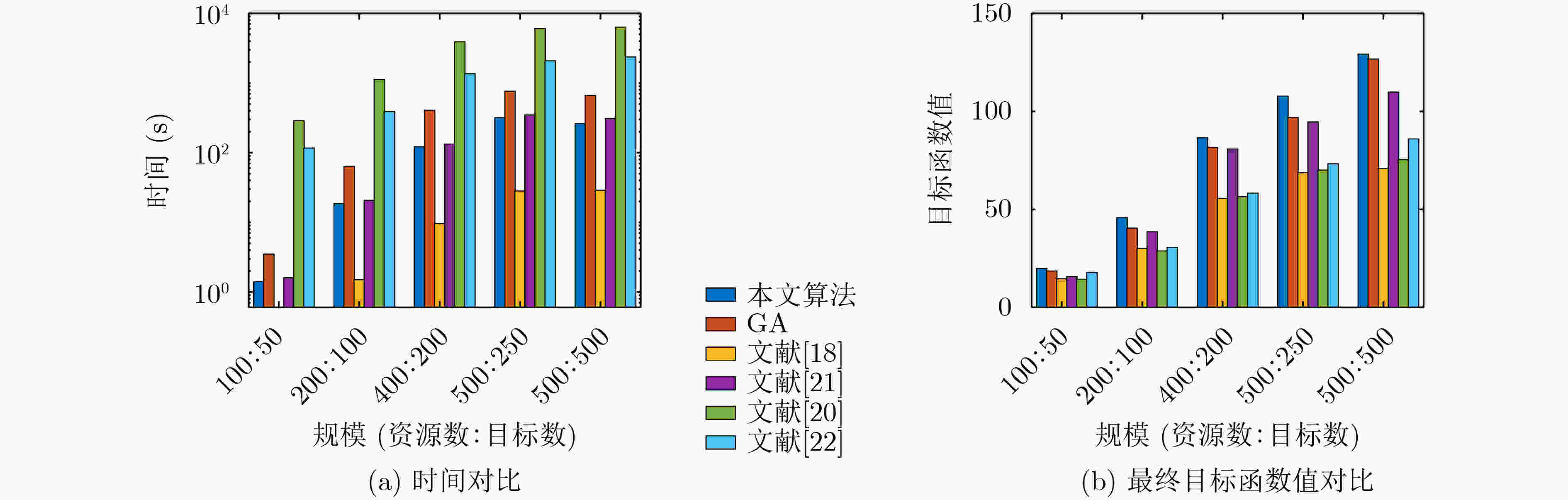
算法 对抗规模 100:50 200:100 400:200 500:250 500:500 耗时(s) 函数值 耗时(s) 函数值 耗时(s) 函数值 耗时(s) 函数值 耗时(s) 函数值 本文算法 3.61 19.87 12.16 42.01 44.66 81.13 69.74 97.27 69.94 120.35 GA 9.84 18.56 37.95 37.85 101.03 76.82 217.29 92.06 212.15 121.03 文献[18] 1.83 14.63 2.42 30.13 3.65 55.34 4.11 67.65 4.20 68.36 文献[21] 5.42 15.72 13.82 36.79 54.42 74.33 78.12 90.80 80.67 98.19 文献[20] 287.60 14.38 1126.33 28.82 3912.38 56.50 6054.23 70.09 6343.78 75.40 文献[22] 13.57 15.71 53.01 28.67 219.72 54.54 300.68 67.34 310.36 68.93 -
[1] AILIYA, YI Wei, and YUAN Ye. Reinforcement learning-based joint adaptive frequency hopping and pulse-width allocation for radar anti-jamming[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. [2] 赵太飞, 宫春杰, 张港, 等. 一种无人机集群安全高效的分区集结控制策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2181–2188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200601ZHAO Taifei, GONG Chunjie, ZHANG Gang, et al. A safe and high efficiency control strategy of unmanned aerial vehicles partition rendezvous[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2181–2188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200601 [3] 石荣, 刘江. 干扰资源分配问题的智能优化应用研究综述[J]. 电光与控制, 2019, 26(10): 54–61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2019.10.012SHI Rong and LIU Jiang. Application of intelligent optimization methods in jamming resource allocation: A review[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2019, 26(10): 54–61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2019.10.012 [4] JIANG Haiqing, ZHANG Yangrui, and XU Hongyi. Optimal allocation of cooperative jamming resource based on hybrid quantum-behaved particle swarm optimisation and genetic algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(1): 185–192. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0119 [5] 张阳, 司光亚, 王艳正. 无人机集群网电攻击行动协同目标分配建模[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 2025–2033. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.15ZHANG Yang, SI Guangya, and WANG Yanzheng. Modeling of cooperative target allocation of the UAV swarm cyberspace attack action[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 2025–2033. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.15 [6] OU Jian, ZHAO Feng, AI Xiaofeng, et al. Quantitative evaluation for self-screening jamming effectiveness based on the changing characteristics of intercepted radar signals[C]. Proceedings of 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. [7] YE Fang, CHE Fei, and GAO Lipeng. Multiobjective cognitive cooperative jamming decision-making method based on Tabu search-artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2018, 2018: 7490895. doi: 10.1155/2018/7490895 [8] 张养瑞, 高梅国, 罗皓月, 等. 基于检测概率的雷达网协同干扰效果评估方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(8): 1778–1786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.08.10ZHANG Yangrui, GAO Meiguo, LUO Haoyue, et al. Evaluation method of cooperative jamming effect on radar net based on detection probability[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(8): 1778–1786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.08.10 [9] ZHAO Ming, ZHAO Lingling, SU Xiaohong, et al. Improved discrete mapping differential evolution for multi-unmanned aerial vehicles cooperative multi-targets assignment under unified model[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2017, 8(3): 765–780. doi: 10.1007/s13042-015-0364-3 [10] 段先华, 孙庆国, 蔡丹. 基于改进遗传算法的协同干扰资源优化分配[J]. 江苏科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 30(5): 466–472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4807.2016.05.011DUAN Xianhua, SUN Qingguo, and CAI Dan. Optimization assignment for cooperative jamming resources based on improved genetic algorithms[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2016, 30(5): 466–472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4807.2016.05.011 [11] GAO Xiangqiang, LIU Rongke, and KAUSHIK A. Hierarchical multi-agent optimization for resource allocation in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32(3): 692–707. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2020.3030920 [12] 韩鹏, 张龙. 雷达干扰资源优化分配博弈模型和算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(2): 78–83,90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.02.018HAN Peng and ZHANG Long. Game model and algorithm of Radar jamming resources optimization allocation[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(2): 78–83,90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.02.018 [13] YIN Changsheng, YANG Ruopeng, ZHU Wei, et al. Research on Radio frequency assignment method based on improved genetic algorithm[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data (ICAIBD), Chengdu, China, 2019: 358–361. [14] YANG Jiao. Research on optimized reconfiguration of distributed distribution network based on ant colony optimization algorithm[C]. Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), Guangzhou, China, 2020: 20–23. [15] YU V F, QIU Meng, PAN He, et al. An improved immunoglobulin-based artificial immune system for the aircraft scheduling problem with alternate aircrafts[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 16532–16545. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3051971 [16] WANG Xiangtuan, HUANG Tianyao, and LIU Yimin. Resource allocation for random selection of distributed jammer towards multistatic Radar system[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 29048–29055. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053762 [17] 许华, 宋佰霖, 蒋磊, 等. 一种通信对抗干扰资源分配智能决策算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(11): 3086–3095. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210115XU Hua, SONG Bailin, JIANG Lei, et al. An intelligent decision-making algorithm for communication countermeasure jamming resource allocation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(11): 3086–3095. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210115 [18] XUE Y, ZHUANG Y, NI Q T, et al. One improved genetic algorithm applied in the problem of dynamic jamming resource scheduling with multi-objective and multi-constraint[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications (BIC-TA), Changsha, China, 2010: 708–712. [19] GONG Yuejiao, CHEN Weineng, ZHAN Zhihui, et al. Distributed evolutionary algorithms and their models: A survey of the state-of-the-art[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 34: 286–300. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.04.061 [20] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182–197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [21] KIZIL A and KARABULUT K. Effects of parameters of an island model parallel genetic algorithm for the quadratic assignment problem[C]. Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on Advanced Applied Informatics (IIAI-AAI), Toyama, Japan, 2019: 444–449. [22] DENG Liyuan, YANG Ping, and LIU Weidong. An improved genetic algorithm[C]. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2019: 47–51. [23] 邓兵, 张韫, 李炳荣. 通信对抗原理及应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017.DENG Bin, ZHANG Yun, and LI Bingrong. Principles and Applications of Communications Countermeasures[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017. [24] 沈阳, 陈永光, 李修和. 基于0-1规划的雷达干扰资源优化分配研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2007, 28(5): 528–532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2007.05.005SHENG Yang, CHENG Yongguang, and LI Xiuhe. Research on optimal distribution of Radar jamming resource based on zero-one programming[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2007, 28(5): 528–532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2007.05.005 [25] LIU Yan, ECKERT C M, and EARL C. A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 161: 113738. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113738 -





 下载:
下载:
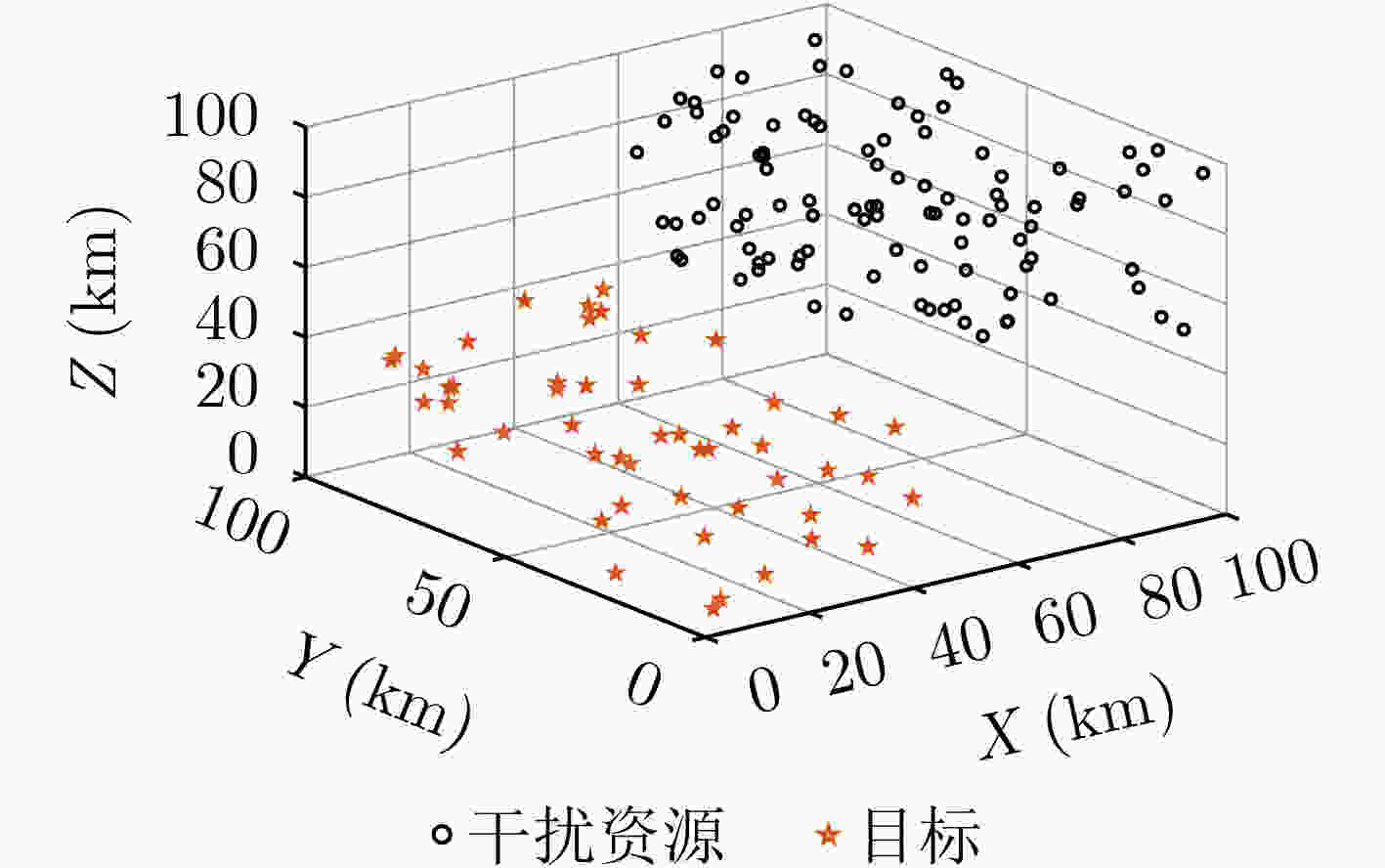
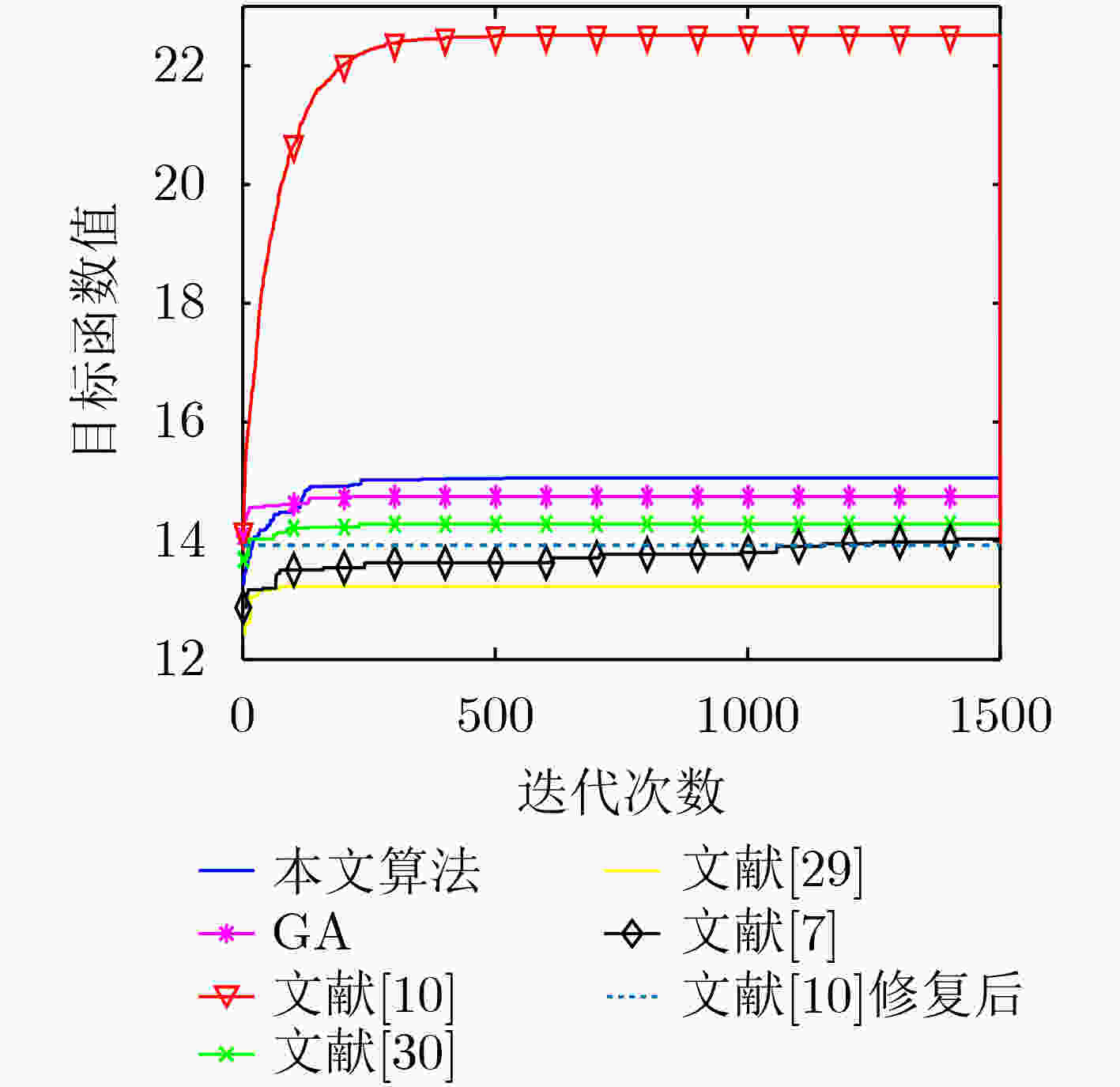


 下载:
下载:
