Anchor-free Object Detection Algorithm Based on Double Branch Feature Fusion
-
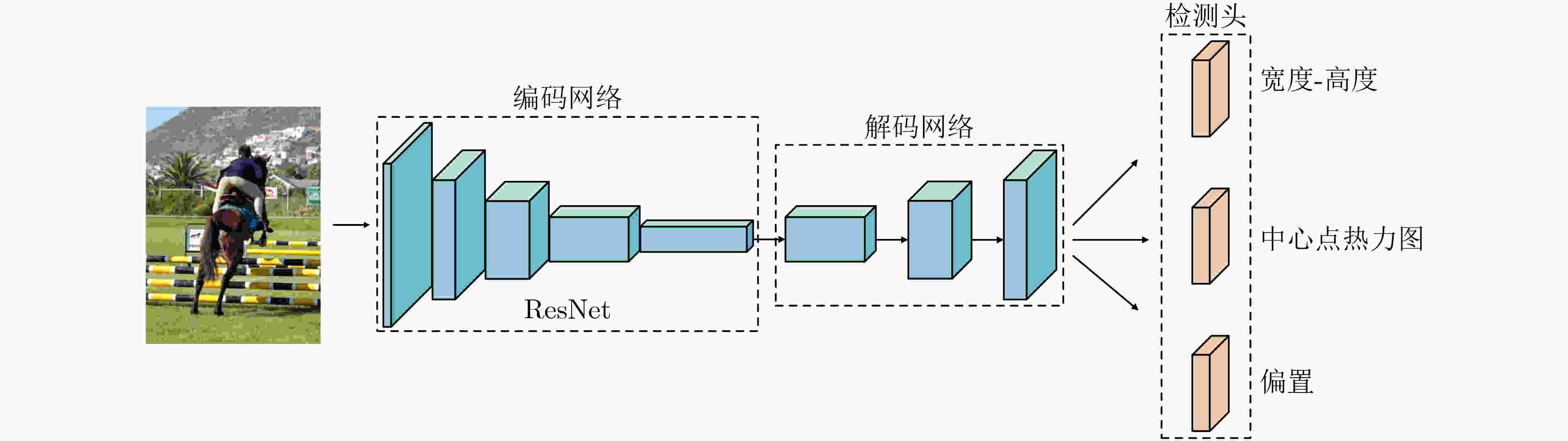
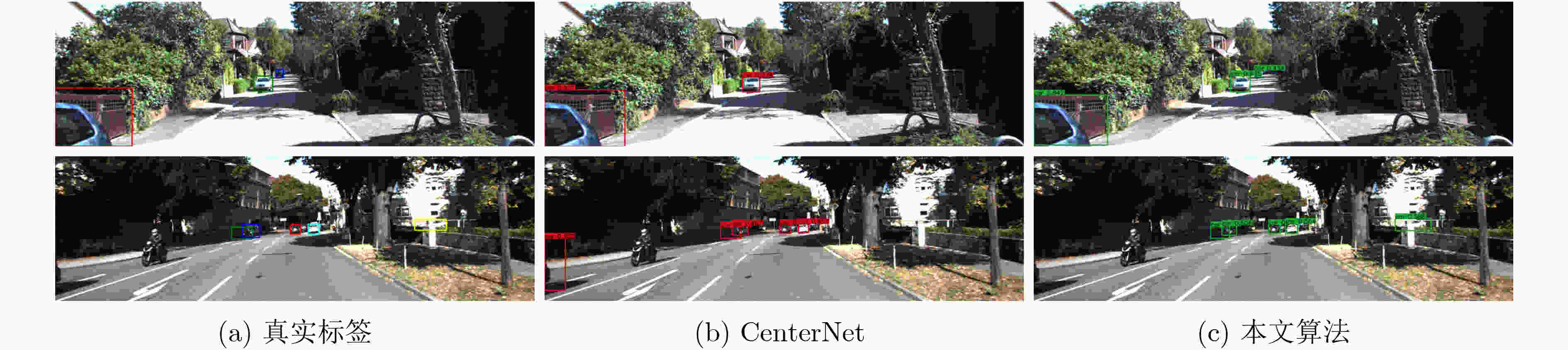
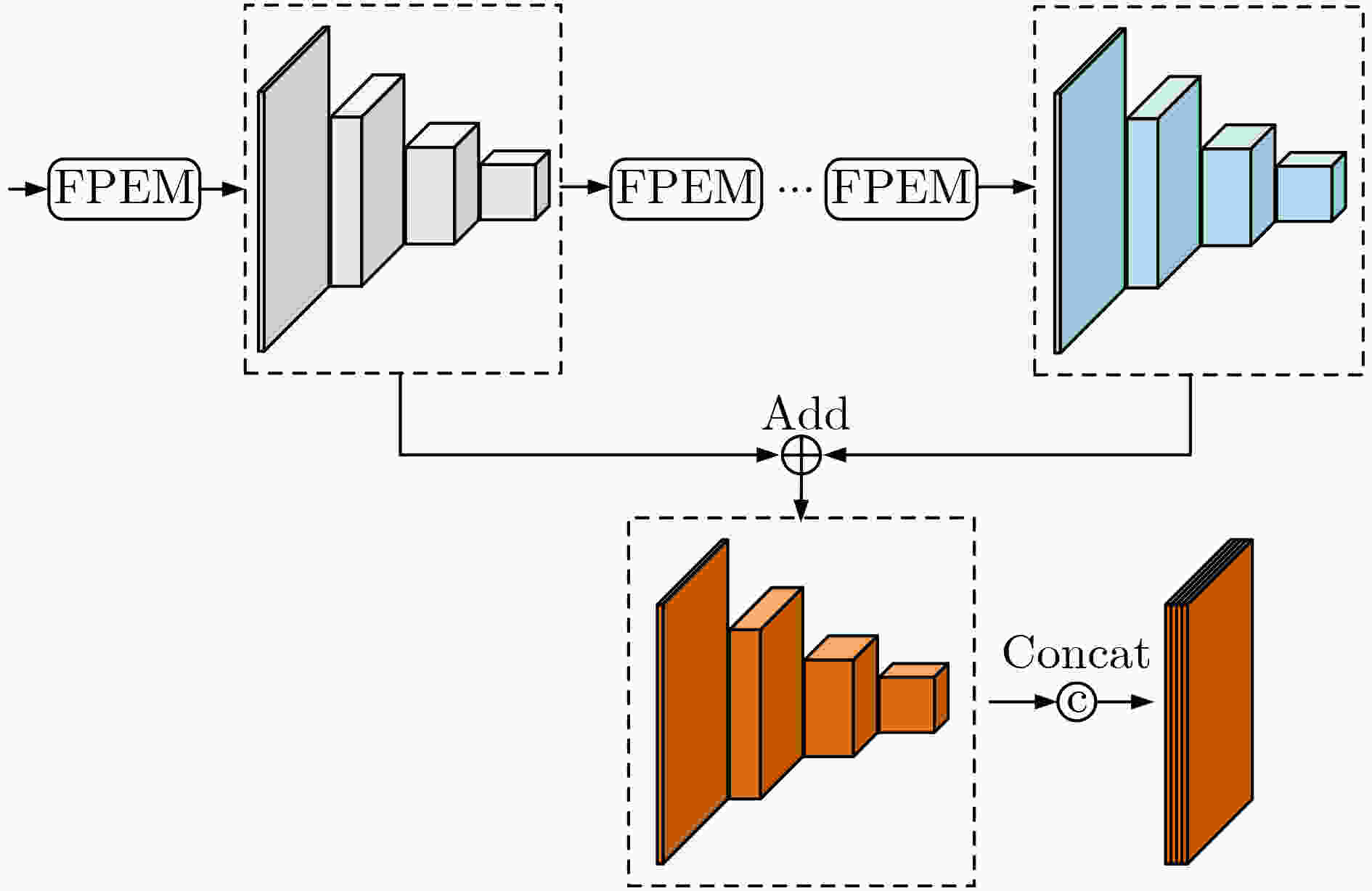
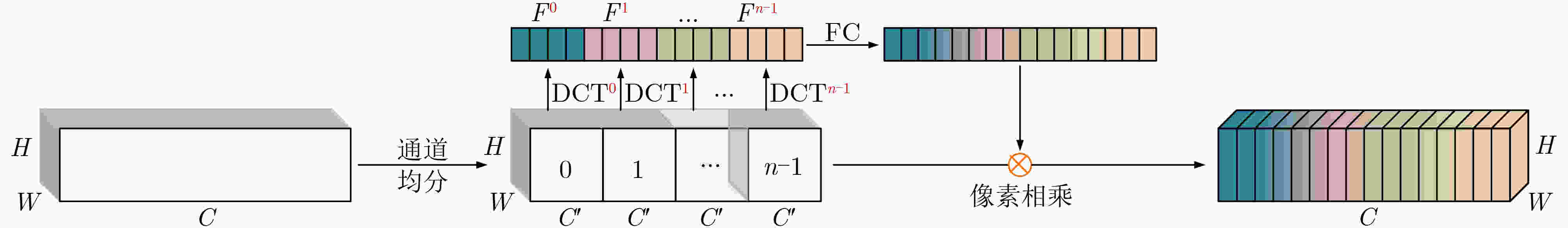
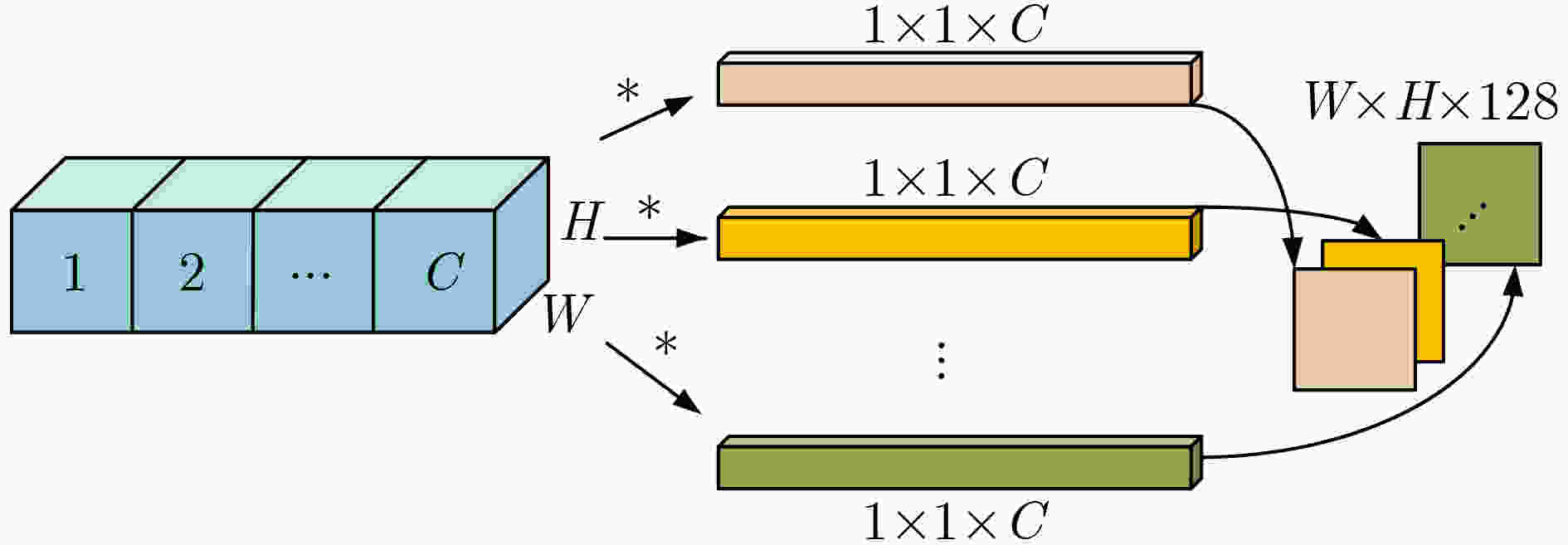
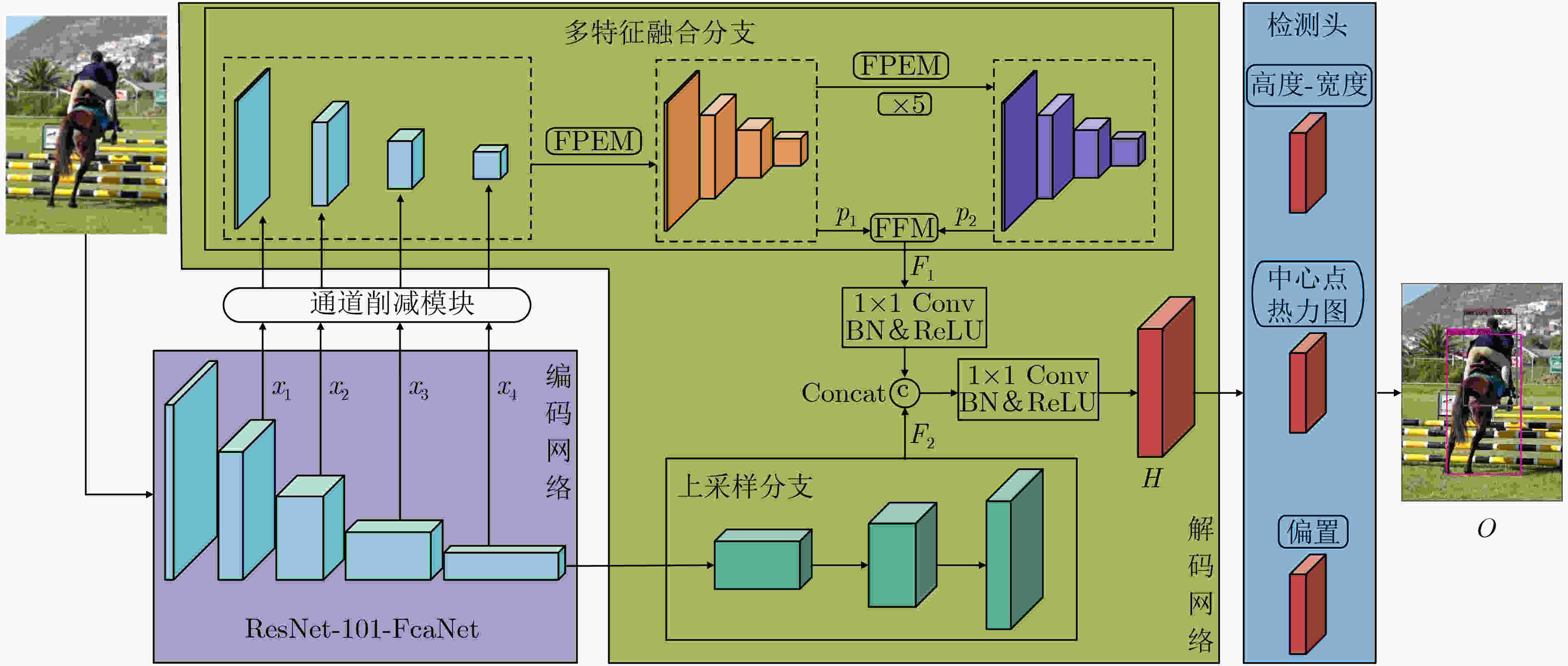
摘要: 针对无锚框目标检测算法CenterNet中,目标特征利用程度不高、检测结果不够准确的问题,该文提出一种双分支特征融合的改进算法。在算法中,一个分支包含了特征金字塔增强模块和特征融合模块,以对主干网络输出的多层特征进行融合处理。同时,为利用更多的高级语义信息,在另一个分支中仅对主干网络的最后一层特征进行上采样。其次,对主干网络添加了基于频率的通道注意力机制,以增强特征提取能力。最后,采用拼接和卷积操作对两个分支的特征进行融合。实验结果表明,在公开数据集PASCAL VOC上的检测精度为82.3%,比CenterNet算法提高了3.6%,在KITTI数据集上精度领先其6%,检测速度均满足实时性要求。该文提出的双分支特征融合方法将不同层的特征进行处理,更好地利用浅层特征中的空间信息和深层特征中的语义信息,提升了算法的检测性能。Abstract: Focusing on the problem of low utilization of object features and inaccurate detection results in CenterNet, an improved algorithm of double branch feature fusion is proposed in the paper. One branch of the algorithm includes feature pyramid enhancement module and feature fusion module to fuse the multi-layer features output from the backbone network. At the same time, in order to use more high-level semantic information, only the last layer of the backbone network is upsampled in the other branch. Secondly, a frequency-based channel attention mechanism is added to the backbone network to enhance feature extraction capability. Finally, the features of the two branches are concatenated and convoluted. The experimental results show that the detection accuracy on PASCAL VOC dataset is 82.3%, which is 3.6% higher than CenterNet, and the detection accuracy on KITTI dataset is 6% higher than CenterNet. The detection speed meets the real-time requirements. The double branch feature fusion method is proposed to process the features of different layers, which makes better use of the spatial information of shallow features and the semantic information of deep features, and improves the detection performance of the algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Object detection /
- Multi-feature fusion /
- Attention mechanism /
- CenterNet
-
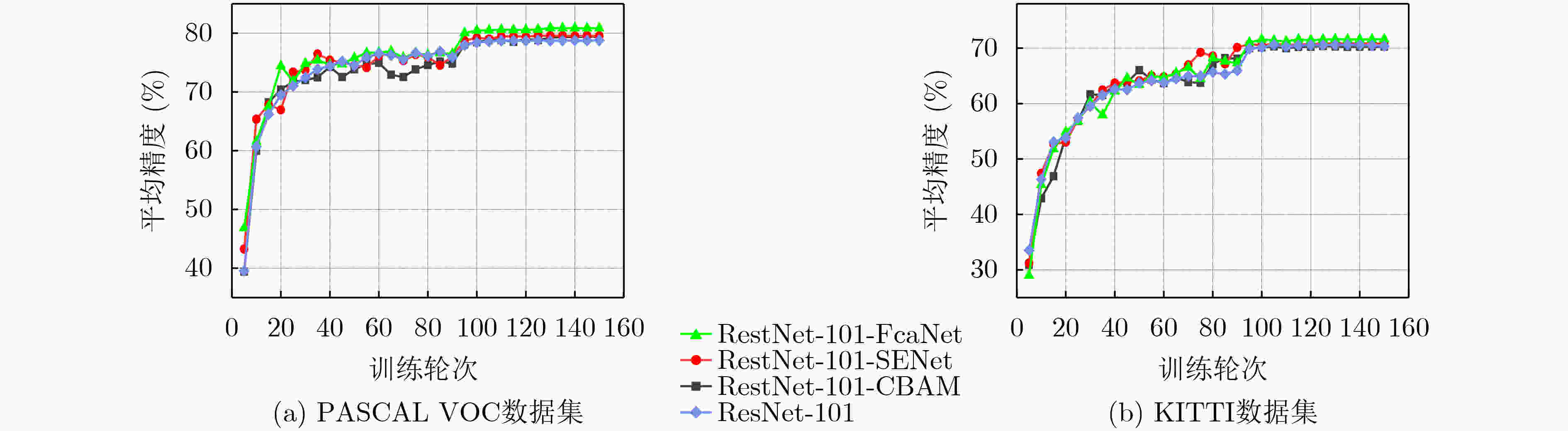
表 1 不同特征增强次数的消融实验结果(%)
增强次数 PASCAL VOC KITTI ResNet-101 Res101-FcaNet ResNet-101 Res101-FcaNet 1 81.57 82.02 73.97 76.52 2 81.63 81.93 73.95 76.48 3 81.66 82.28 74.09 76.45 4 81.59 82.08 74.03 76.45 5 81.87 82.31 74.04 76.53 6 81.66 82.22 74.07 76.49 7 81.67 82.27 74.03 76.51 表 2 PASCAL VOC2007和KITTI数据集的消融实验结果(%)
ResNet-101 上采样
分支多特征融
合分支FcaNet mAP
(VOC)mAP
(KITTI)$ \surd $ $ \surd $ 78.7 70.5 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 80.7 73.7 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 81.8 74.0 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 82.3 76.5 表 3 PASCAL VOC2007数据集测试结果
Algorithm Network Resolution(ppi) mAP(%) fps Faster-RCNN(2015) ResNet-101 600×1000 76.4 5 SSD(2016) VGG-16 512×512 76.8 19 R-FCN(2016) ResNet-101 600×1000 80.5 9 DSSD(2017) ResNet-101 513×513 81.5 5.5 Yolov3(2018) DarkNet-53 544×544 79.3 26 ExtremeNet(2019) Hourglass-104 512×512 79.5 3 FCOS(2019) ResNet-101 800×800 80.2 16 CenterNet(2019) ResNet-18 512×512 75.7 100 CenterNet(2019) ResNet-101 512×512 78.7 30 CenterNet(2019) DLA-34 512×512 80.7 33 CenterNet(2019) Hourglass-104 512×512 80.9 6 CenterNet-DHRNet(2020) DHRNet 512×512 81.9 18 本文 Res101-FcaNet 512×512 82.3 27.6 表 4 本文算法和其他算法在PASCAL VOC2007数据集上各类的检测结果(%)
Class 本文 CenterNet-DLA Faster R-CNN Mask R-CNN R-FCN SSD512 aero 88.7 85.0 76.5 73.7 74.5 70.2 bike 87.8 86.0 79.0 84.4 87.2 84.7 bird 85.0 81.4 70.9 78.5 81.5 78.4 boat 73.8 72.8 65.5 70.8 72.0 73.8 bottle 73.9 68.4 52.1 68.5 69.8 53.2 bus 88.5 86.0 83.1 88.0 86.8 86.2 car 88.4 88.4 84.7 85.9 88.5 87.5 cat 88.5 86.5 86.4 87.8 89.8 86.0 chair 66.7 65.0 52.0 60.3 67.0 57.8 cow 87.1 86.3 81.9 85.2 88.1 83.1 table 75.0 77.6 65.7 73.7 74.5 70.2 dog 88.1 85.2 84.8 87.2 89.8 84.9 horse 89.4 87.0 84.6 86.5 90.6 85.2 mbike 85.7 86.1 77.5 85.0 79.9 83.9 person 83.8 85.0 76.7 76.4 81.2 79.7 plant 58.2 58.1 38.8 48.5 53.7 50.3 sheep 88.3 83.4 73.6 76.3 81.8 77.9 sofa 76.5 79.6 73.9 75.5 81.5 73.9 train 88.0 85.0 83.0 85.0 85.9 82.5 tv 84.8 80.3 72.6 81.0 79.9 75.3 表 5 KITTI数据集上综合的检测结果
Algorithm Network Resolution(ppi) Pedestrian(%) Car(%) Cyclist(%) mAP(%) fps SSD(2016) VGG-16 512×512 48.0 85.1 50.6 61.2 28.9 RFBNet(2018) VGG-16 512×512 61.7 86.4 72.2 73.4 39 SqueezeDet(2017) ResNet-50 1242×375 61.5 86.7 80.0 76.1 22.5 Yolov3(2018) DarkNet-53 544×544 65.8 88.7 73.1 75.8 26 FCOS(2019) ResNet-101 800×800 69.5 89.3 70.1 76.3 19 CenterNet(2019) ResNet-18 512×512 50.6 80.8 59.5 63.6 100 CenterNet(2019) ResNet-101 512×512 60.5 81.3 69.7 70.5 36 CenterNet(2019) DLA-34 512×512 62.3 85.6 73.8 73.9 33 CenterNet(2019) Hourglass-104 512×512 65.5 86.1 73.2 74.9 6 本文 Res101-FcaNet 512×512 62.0 88.9 78.7 76.5 27.6 -
[1] 孙怡峰, 吴疆, 黄严严, 等. 一种视频监控中基于航迹的运动小目标检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2744–2751. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181110SUN Yifeng, WU Jiang, HUANG Yanyan, et al. A small moving object detection algorithm based on track in video surveillance[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2744–2751. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181110 [2] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [3] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [4] LAW H and DENG Jie. CornerNet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 765–781. [5] ZHOU Xingyi, ZHUO Jiacheng, and KRÄHENBÜHL P. Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 850–859. [6] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 9626–9635. [7] ZHOU Xingyi, WANG Dequan, and KRÄHENBÜHL P. Objects as points[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.07850, 2019. [8] WANG Wenhai, XIE Enze, SONG Xiaoge, et al. Efficient and accurate arbitrary-shaped text detection with pixel aggregation network[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 8439–8448. [9] HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, 2021. [10] QIN Zequn, ZHANG Pengyi, WU Fei, et al. FcaNet: Frequency channel attention networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.11879v4, 2020. [11] 王新, 李喆, 张宏立. 一种迭代聚合的高分辨率网络Anchor-free目标检测方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(12): 2533–2541. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0484WANG Xin, LI Zhe, and ZHANG Hongli. High-resolution network Anchor-free object detection method based on iterative aggregation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(12): 2533–2541. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0484 [12] LIU Songtao, HUANG Di, and WANG Yunhong. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 404–419. [13] WU Bichen, WAN A, IANDOLA F, et al. Squeezedet: Unified, small, low power fully convolutional neural networks for real-time object detection for autonomous driving[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 446–454. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
