Feature Fusion Method Based on Label-sensitive Multi-set Orthogonal Correlation
-
摘要: 典型相关分析(CCA)作为一种经典的特征融合方法,广泛用于模式识别领域,其目标是学习相关投影方向使两组变量间的相关性最大,但其没有考虑样本的类标签信息和样本间的信息冗余(MDOCCA),从而影响了融合后特征的监督敏感性和鉴别力。为此,该文提出一种标签敏感的多重集正交相关特征融合方法,该方法在典型相关分析理论基础上,将类标签信息嵌入到特征融合框架,同时加入正交约束确保融合特征最大限度的不相关,减少特征信息冗余,提高鉴别力。在不同图像数据集上的实验结果显示该方法是一种有效的特征融合方法。Abstract: As a classic feature fusion method, Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) is widely used in the field of pattern recognition. Its goal is to learn the relevant projection direction to maximize the correlation between the two sets of variables, but the class label information of the sample and the information between samples redundancy are not considered, which affects the supervisory sensitivity and discriminative power of the fused features. To this end, a label-sensitive Multi-set Discriminant Orthogonal Canonical Correlation Analysis (MDOCCA) feature fusion method is proposed. This method is based on canonical correlation analysis theory. The class label information is embedded into the feature fusion framework, and the orthogonal constraint is added to ensure the maximum fusion of features. Irrelevant, the redundancy of feature information is reduced and the discrimination is improved. Some experiments on multiple image data sets show that this method is an effective feature fusion method.
-
Key words:
- Feature fusion /
- Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) /
- Multi-set /
- Discriminative /
- Orthogonal
-
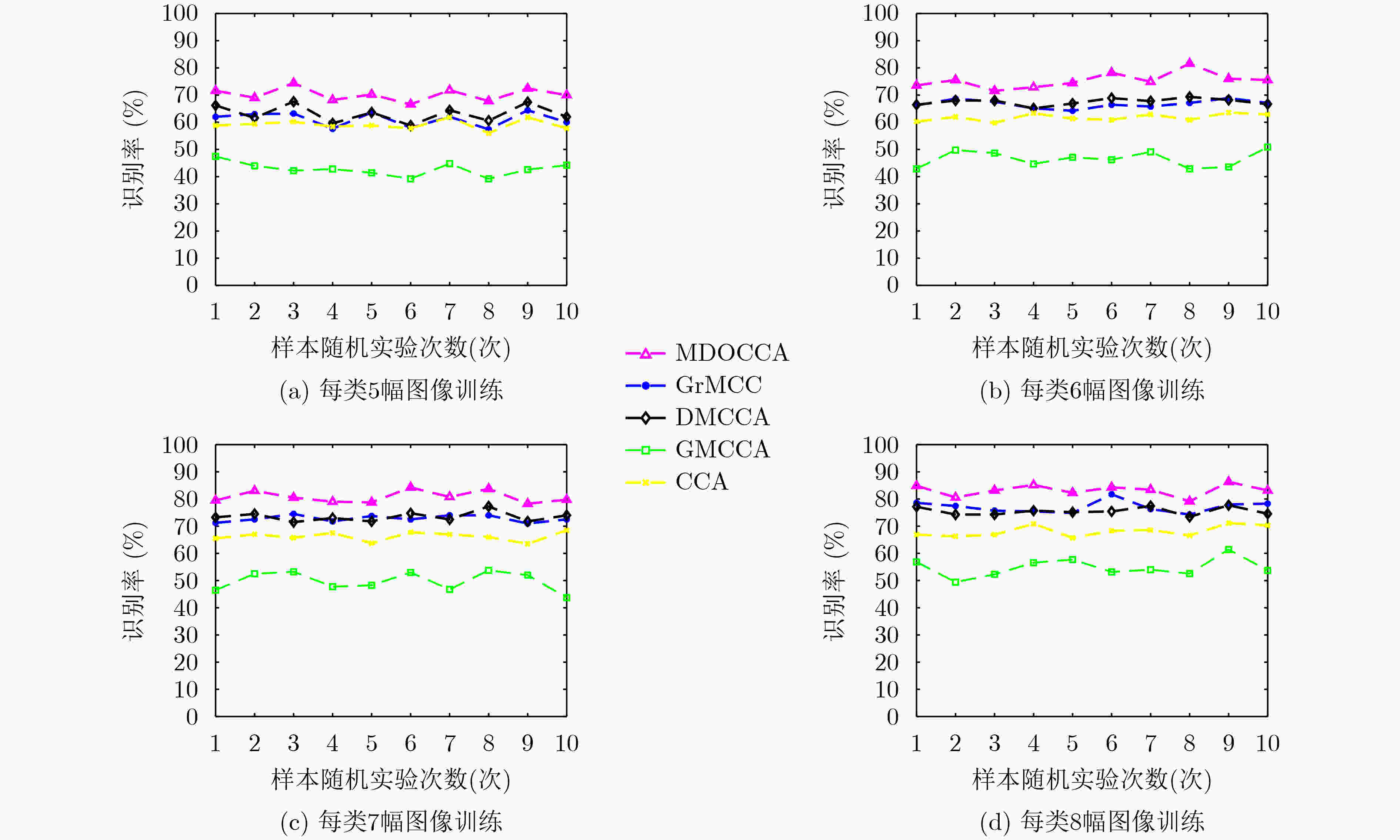
表 1 在GT图像数据集上的识别率变化结果(%)
5训练样本 6训练样本 7训练样本 8训练样本 MDOCCA 70.20±2.39 75.42±2.83 80.75±2.17 83.23±2.15 GrMCC 61.12±2.66 66.71±1.47 72.78±1.23 77.06±2.21 DMCCA 63.18±3.17 67.53±1.26 73.42±1.77 75.51±1.48 GMCCA 48.36±1.95 52.62±1.55 58.30±1.90 62.89±2.69 CCA 59.08±1.81 61.78±1.35 66.22±1.66 68.14±2.01 * A±B:A表示平均识别率,B表示相应的识别率标准差 表 2 在ORL图像数据集上的识别率变化结果(%)
5训练样本 6训练样本 7训练样本 8训练样本 MDOCCA 94.15±1.45 96.50±1.87 97.67±1.61 99.50±0.65 GrMCC 93.40±1.94 95.88±1.15 96.75±1.59 99.38±0.88 DMCCA 93.50±1.73 95.44±1.82 96.92±1.62 99.50±0.65 GMCCA 85.50±1.68 88.75±2.41 91.92±2.78 95.50±2.22 CCA 90.35±1.83 93.19±1.94 93.83±1.68 97.25±1.15 * A±B:A表示平均识别率,B表示相应的识别率标准差 表 3 在AR图像数据集上的识别率变化结果(%)
5训练样本 6训练样本 7训练样本 8训练样本 MDOCCA 98.50±0.45 98.85±0.59 99.19±0.34 99.21±0.28 GrMCC 95.56±0.88 97.38±0.81 98.38±0.36 98.82±0.30 DMCCA 98.27±0.49 98.72±0.58 99.05±0.37 99.18±0.23 GMCCA 93.09±1.18 95.25±0.34 96.60±0.78 97.26±0.42 CCA 97.09±0.70 97.86±0.60 98.46±0.35 98.58±0.20 * A±B:A表示平均识别率,B表示相应的识别率标准差 表 4 在PIE图像数据集上的识别率变化结果(%)
10训练样本 15训练样本 20训练样本 25训练样本 30训练样本 MDOCCA 79.04±0.65 85.41±0.84 87.99±0.65 90.58±0.63 91.12±0.50 GrMCC 64.00±1.03 75.47±1.21 81.39±0.97 85.47±0.70 87.27±0.52 DMCCA 75.71±0.82 82.61±0.82 85.53±0.51 88.31±0.63 89.15±0.42 GMCCA 65.37±0.98 74.33±1.16 79.16±0.86 82.57±1.07 84.46±0.52 CCA 68.99±0.92 77.06±1.29 81.03±0.75 84.12±0.85 85.41±0.44 * A±B:A表示平均识别率,B表示相应的识别率标准差 -
[1] 刘政怡, 段群涛, 石松, 等. 基于多模态特征融合监督的RGB-D图像显著性检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 997–1004. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190297LIU Zhengyi, DUAN Quntao, SHI Song, et al. RGB-D image saliency detection based on multi-modal feature-fused supervision[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 997–1004. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190297 [2] YANG Xinghao, LIU Weifeng, LIU Wei, et al. A survey on canonical correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021, 33(6): 2349–2368. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2019.2958342 [3] WANG Haoting, SMALLWOOD J, MOURAO-MIRANDA J, et al. Finding the needle in a high-dimensional haystack: Canonical correlation analysis for neuroscientists[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 216: 116745. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116745 [4] ZHENG Wenming. Multichannel EEG-based emotion recognition via group sparse canonical correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2017, 9(3): 281–290. doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2016.2587290 [5] JIANG Qingchao, DING S X, WANG Yang, et al. Data-driven distributed local fault detection for large-scale processes based on the GA-regularized canonical correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(10): 8148–8157. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2698422 [6] BHOWMIK B, TRIPURA T, HAZRA B, et al. Real time structural modal identification using recursive canonical correlation analysis and application towards online structural damage detection[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2020, 468: 115101. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.115101 [7] BAO Zhigang, HU Jiang, PAN Guangming, et al. Canonical correlation coefficients of high-dimensional Gaussian vectors: Finite rank case[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 2019, 47(1): 612–640. doi: 10.1214/18-AOS1704 [8] SAMAT A, PERSELLO C, GAMBA P, et al. Supervised and semi-supervised multi-view canonical correlation analysis ensemble for heterogeneous domain adaptation in remote sensing image classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(4): 337. doi: 10.3390/rs9040337 [9] GAO Lei, QI Lin, CHEN Enqing, et al. Discriminative multiple canonical correlation analysis for information fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 1951–1965. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2765820 [10] LAI P L and FYFE C. Kernel and nonlinear canonical correlation analysis[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2000, 10(5): 365–377. doi: 10.1142/S012906570000034X [11] PATEL A M, LI J K J, FINEGAN B, et al. Aortic pressure estimation using blind identification approach on single input multiple output nonlinear Wiener systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(6): 1193–1200. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2688425 [12] SHAO Jie, WANG Leiquan, ZHAO Zhicheng, et al. Deep canonical correlation analysis with progressive and hypergraph learning for cross-modal retrieval[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 214: 618–628. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.06.047 [13] RU Lixiang, WU Chen, DU Bo, et al. Deep canonical correlation analysis network for scene change detection of multi-temporal VHR imagery[C]. The 2019 10th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multitemporal Remote Sensing Images (MultiTemp), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–4. [14] CAI D, HE X, HAN J, et al. Orthogonal Laplacianfaces for face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(11): 3608–3614. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.881945 [15] WANG Li, ZHANG Leihong, BAI Zhaojun, et al. Orthogonal canonical correlation analysis and applications[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 2020, 35(4): 787–807. doi: 10.1080/10556788.2019.1700257 [16] NIELSEN A A. Multiset canonical correlations analysis and multispectral, truly multitemporal remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2002, 11(3): 293–305. doi: 10.1109/83.988962 [17] GAO Lei, ZHANG Rui, QI Lin, et al. The labeled multiple canonical correlation analysis for information fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(2): 375–387. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2859590 [18] CHEN Jia, WANG Gang, and GIANNAKIS G B. Graph multiview canonical correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(11): 2826–2838. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2910475 [19] ZHANG Shichao, LI Xuelong, ZONG Ming, et al. Learning k for kNN classification[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2017, 8(3): 43. doi: 10.1145/2990508 [20] ZHANG Shichao, LI Xuelong, ZONG Ming, et al. Efficient kNN classification with different numbers of nearest neighbors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(5): 1774–1785. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2673241 [21] JIANG Junjun, MA Jiayi, CHEN Chen, et al. SuperPCA: A superpixelwise PCA approach for unsupervised feature extraction of hyperspectral imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4581–4593. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2828029 [22] YUAN Yunhao and SUN Quansen. Graph regularized multiset canonical correlations with applications to joint feature extraction[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(12): 3907–3919. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.06.016 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
