Bionic SLAM Algorithm Based on Interest Tendency Mechanism
-
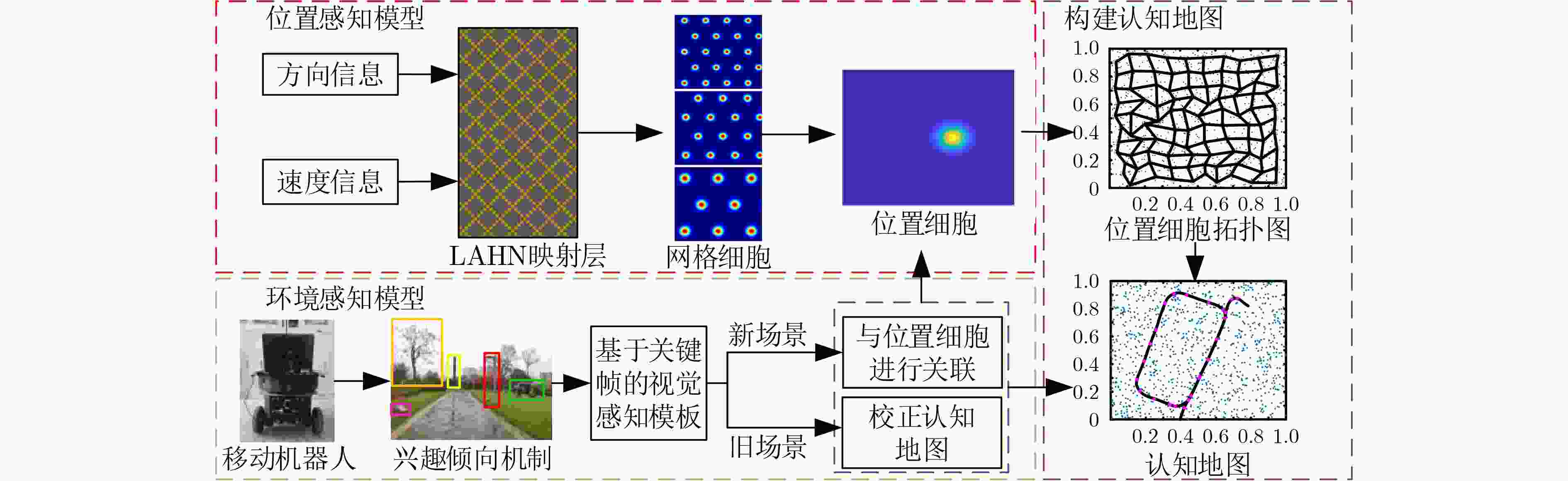
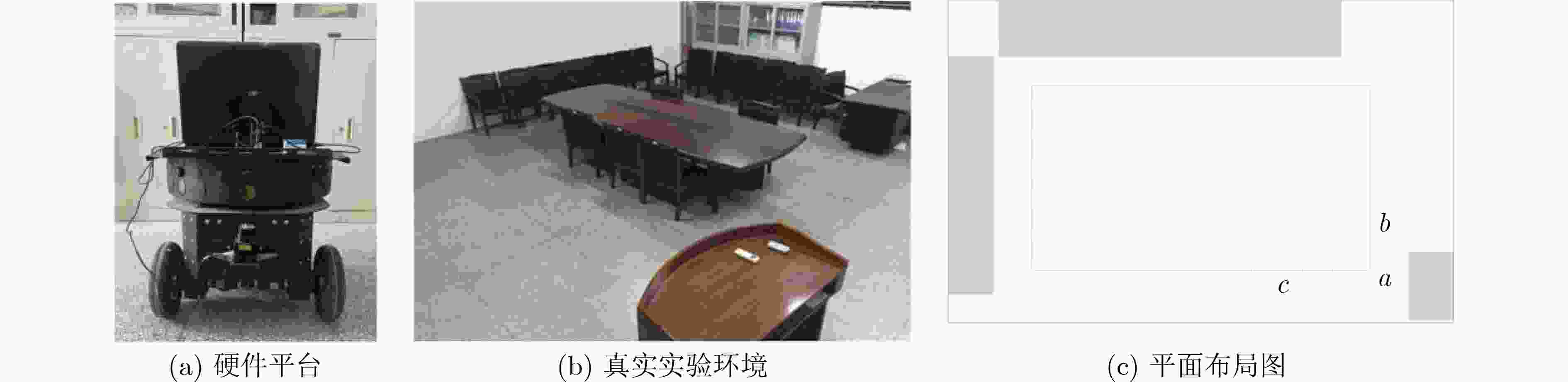
摘要: 该文针对同时定位与地图创建(SLAM)闭环检测算法易受复杂环境因素干扰,导致定位误差较大、闭环检测精度低等问题,受哺乳动物空间认知机理启发,提出一种基于兴趣倾向机制的仿生SLAM算法。采用反Hebbian网络(Lateral Anti-Hebbian Networkm, LAHN)对网格细胞进行建模,通过不规则复杂环境边界信息对网格细胞进行校正来提高算法定位精度。利用兴趣倾向机制对提取的显著性区域进行兴趣赋值,减小冗余显著性区域带来的影响,提高系统闭环准确率。将位置感知模型获取的位置信息与视觉感知模板相关联构建认知地图。在公开数据集及真实环境中进行测试,测试结果表明该文算法在构建认知地图的准确率、实时性以及对环境的适应能力具有优势。Abstract: To address the problem that Simultaneous Location And Mapping (SLAM) closed-loop detection algorithms are easily disturbed by complex environmental factors, resulting in large localization errors and low closed-loop detection accuracy, a bionic SLAM algorithm based on the interest tendency mechanism is proposed, inspired by the spatial cognitive mechanism of mammals. The grid cells are modelled using the Lateral Anti-Hebbian Network (LAHN), which improves the accuracy of the algorithm by correcting the grid cells with irregular and complex environmental boundary information. The tendency of interest mechanism is used to score the extracted areas of significance, reduce the impact of redundant significant areas and improve the accuracy of the system’s closed-loop detection. A cognitive map is constructed by correlating the location information obtained from the location-aware model with a visual perception template. The results of the tests on the public dataset and the real environment show that the proposed algorithm has advantages in terms of accuracy, real time performance and adaptability to the environment.
-
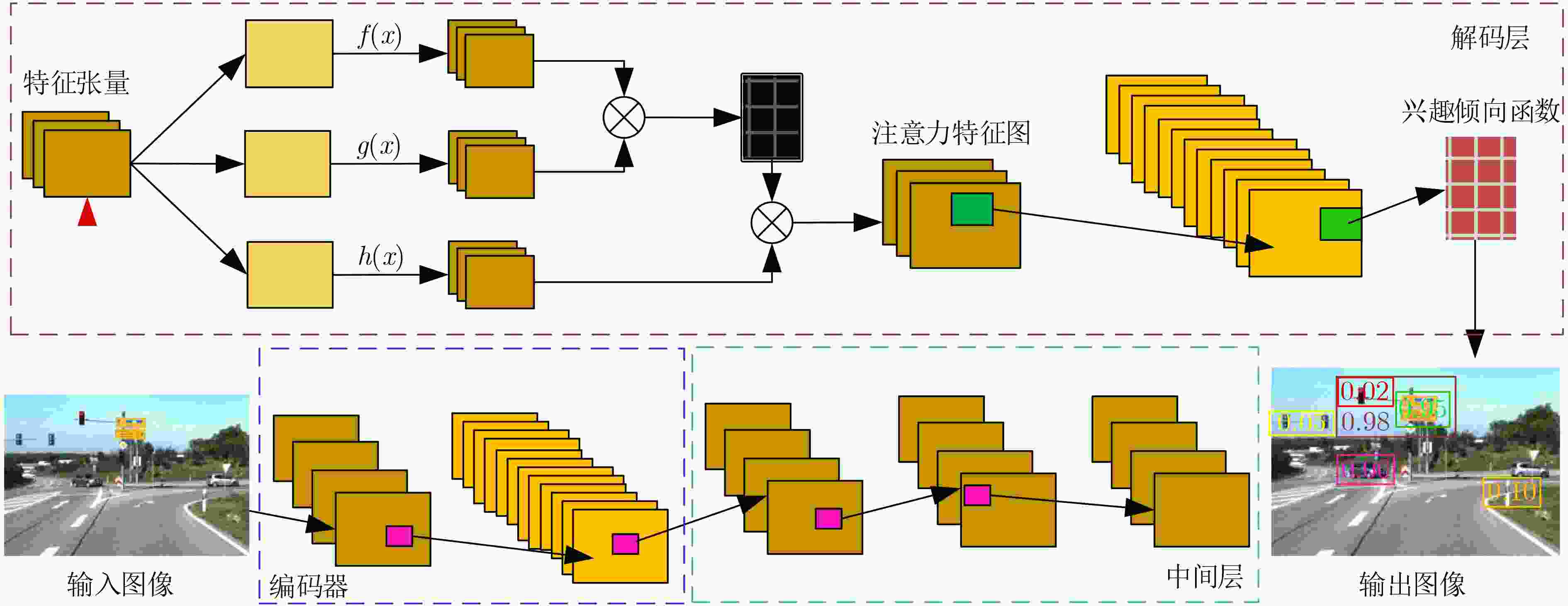
表 1 融合自注意力机制的卷积神经网络参数设置
序号 区域划分 层类型 卷积核 步长 深度 激活函数 0 编码器 Convolution 7×7 1 64 ReLU 1 编码器 Convolution 3×3 2 128 ReLU 2 编码器 Convolution 3×3 2 256 ReLU 3 中间区 Residual Block 3×3 1 256 ReLU 4 中间区 Residual Block 3×3 1 256 ReLU 5 中间区 Residual Block 3×3 1 256 ReLU 6 中间区 Residual Block 3×3 1 256 ReLU 7 中间区 Residual Block 3×3 2 256 ReLU 8 中间区 Residual Block 3×3 2 256 ReLU 9 解码器 Deconvlution 3×3 2 128 ReLU 10 解码器 Self-Attention – – – – 11 解码器 Deconvlution 3×3 1 64 ReLU 12 解码器 Convolution 7×7 1 3 Tanh 13 解码器 Interest Propensity – – – – 表 2 各算法在TUM数据集上的结果对比
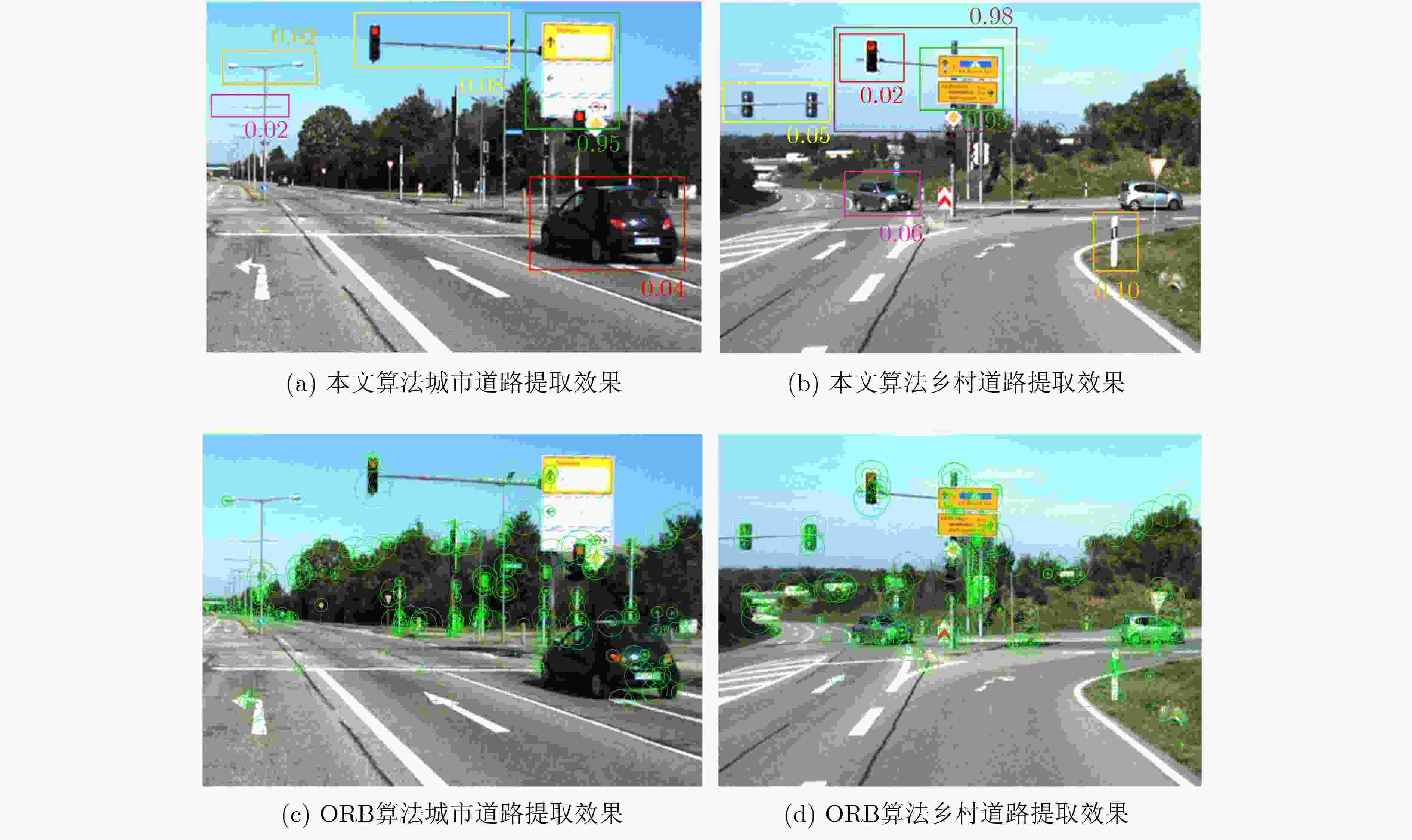
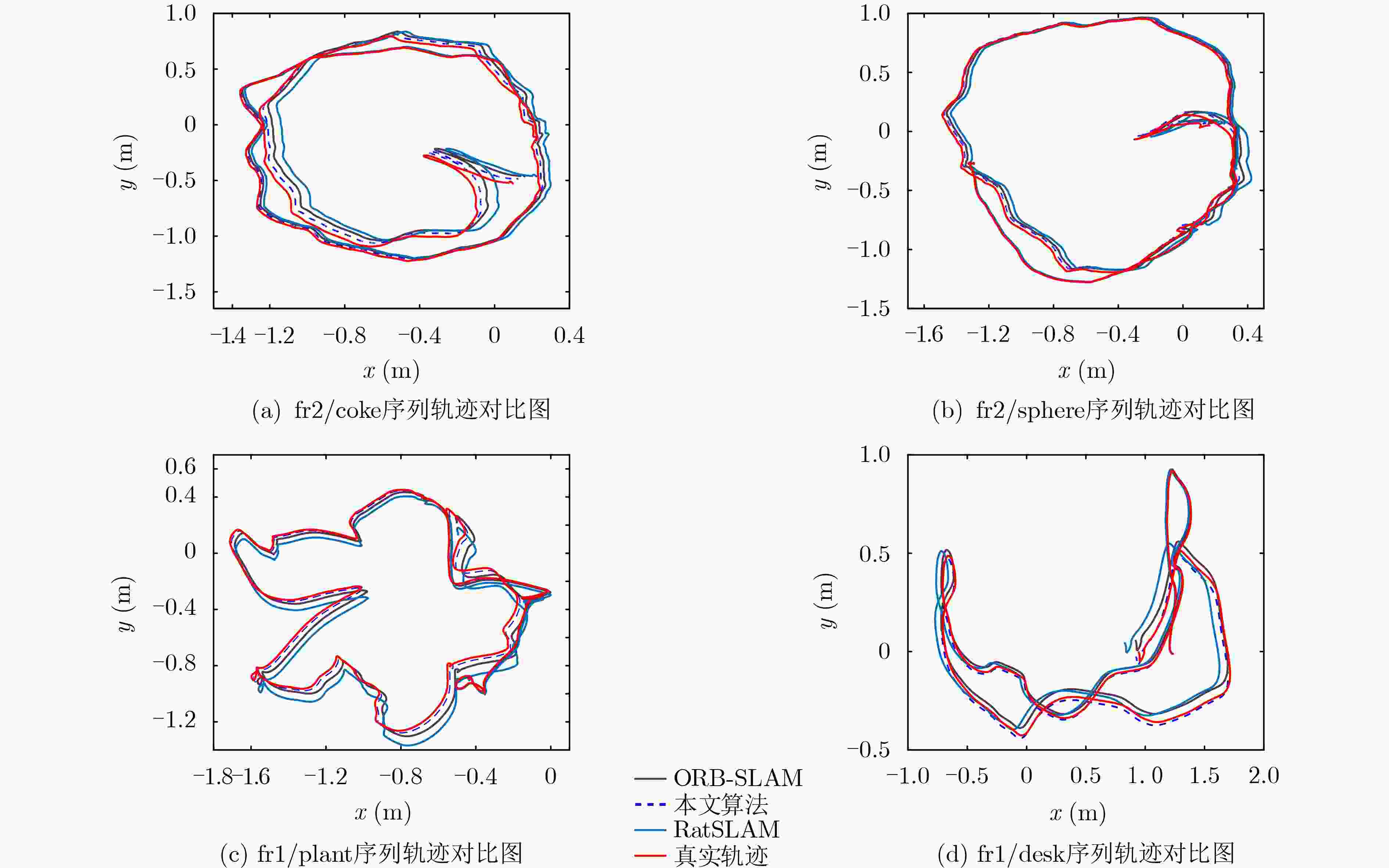
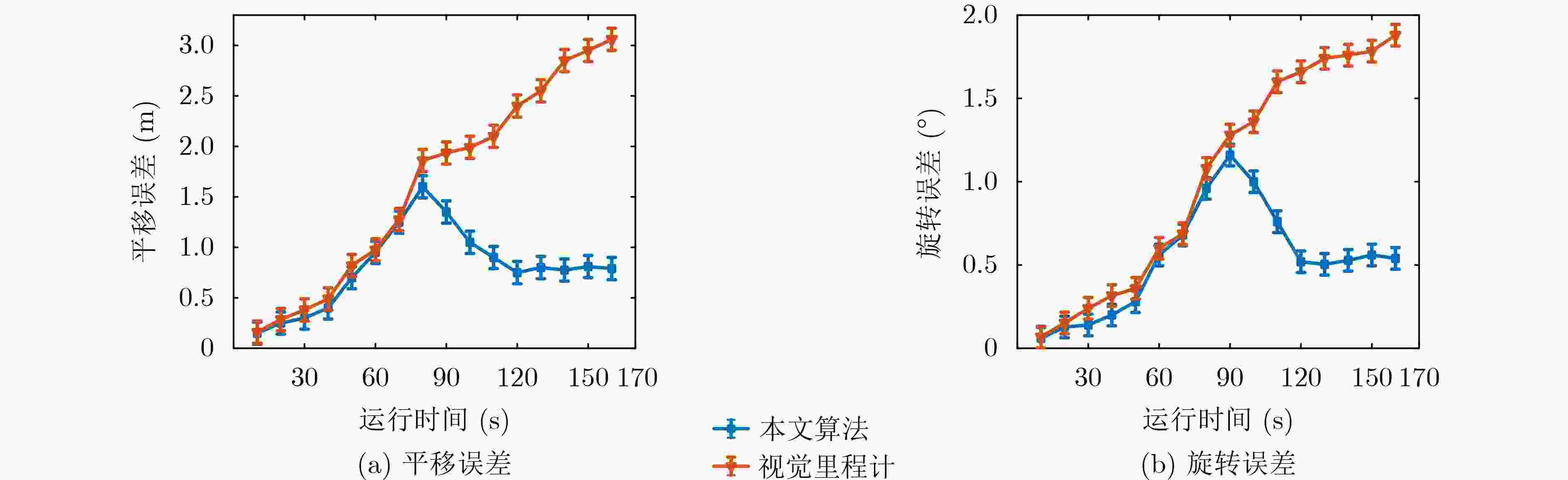
序列 轨迹均方根误差(RMSE/m) 单帧图像处理时间(ms) 闭环准确率(%) ORB-SLAM RatSLAM 本文算法 ORB-SLAM RatSLAM 本文算法 ORB-SLAM RatSLAM 本文算法 fr2/coke 0.056 0.068 0.042 129 211 145 83.4 74.2 88.1 fr2/sphere 0.037 0.043 0.031 135 198 162 82.5 73.4 86.5 fr1/plant 0.052 0.065 0.039 146 230 168 84.2 74.2 89.2 fr1/desk 0.063 0.075 0.051 134 218 153 82.6 72.8 85.1 表 3 各算法在KITTI数据集上的结果对比
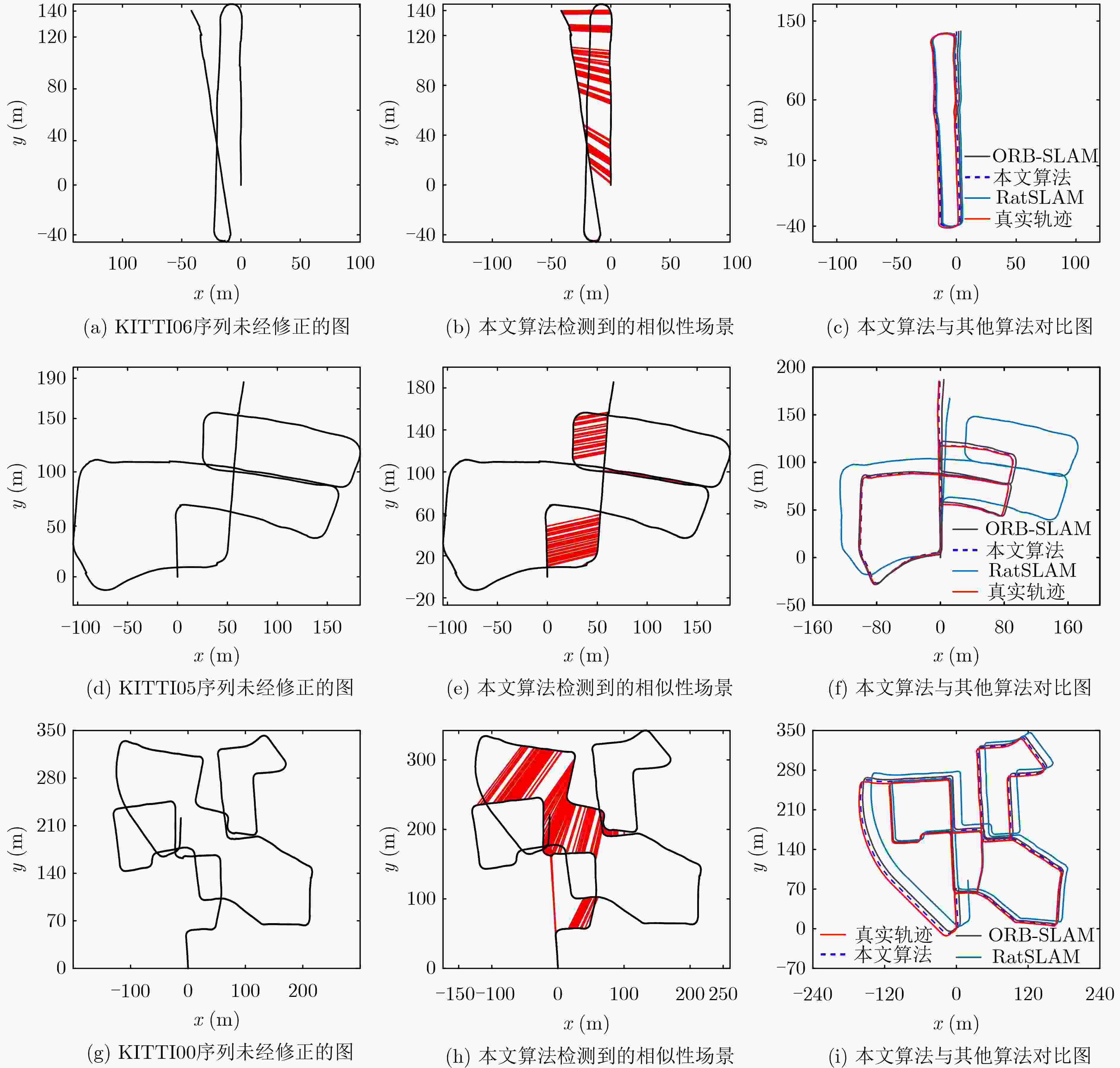
序列 相对平移误差(m) 相对旋转误差(°) 耗时(min) ORB-SLAM RatSLAM 本文算法 ORB-SLAM RatSLAM 本文算法 ORB-SLAM RatSLAM 本文算法 00 8.31 10.59 5.45 3.24 4.34 2.85 9.73 15.96 10.87 01 10.75 12.37 10.42 3.45 3.67 3.02 2.38 3.53 2.97 02 9.59 12.51 7.21 4.82 5.13 3.65 11.44 17.86 13.15 03 12.24 14.12 12.25 5.95 6.58 6.02 1.75 2.91 2.24 04 4.52 5.34 4.25 2.76 3.67 3.71 0.57 0.91 0.71 05 3.82 4.81 2.65 2.02 3.27 1.58 5.48 10.17 7.87 06 3.21 5.72 1.91 1.72 1.94 1.13 2.42 4.42 3.06 表 4 主要参数设置
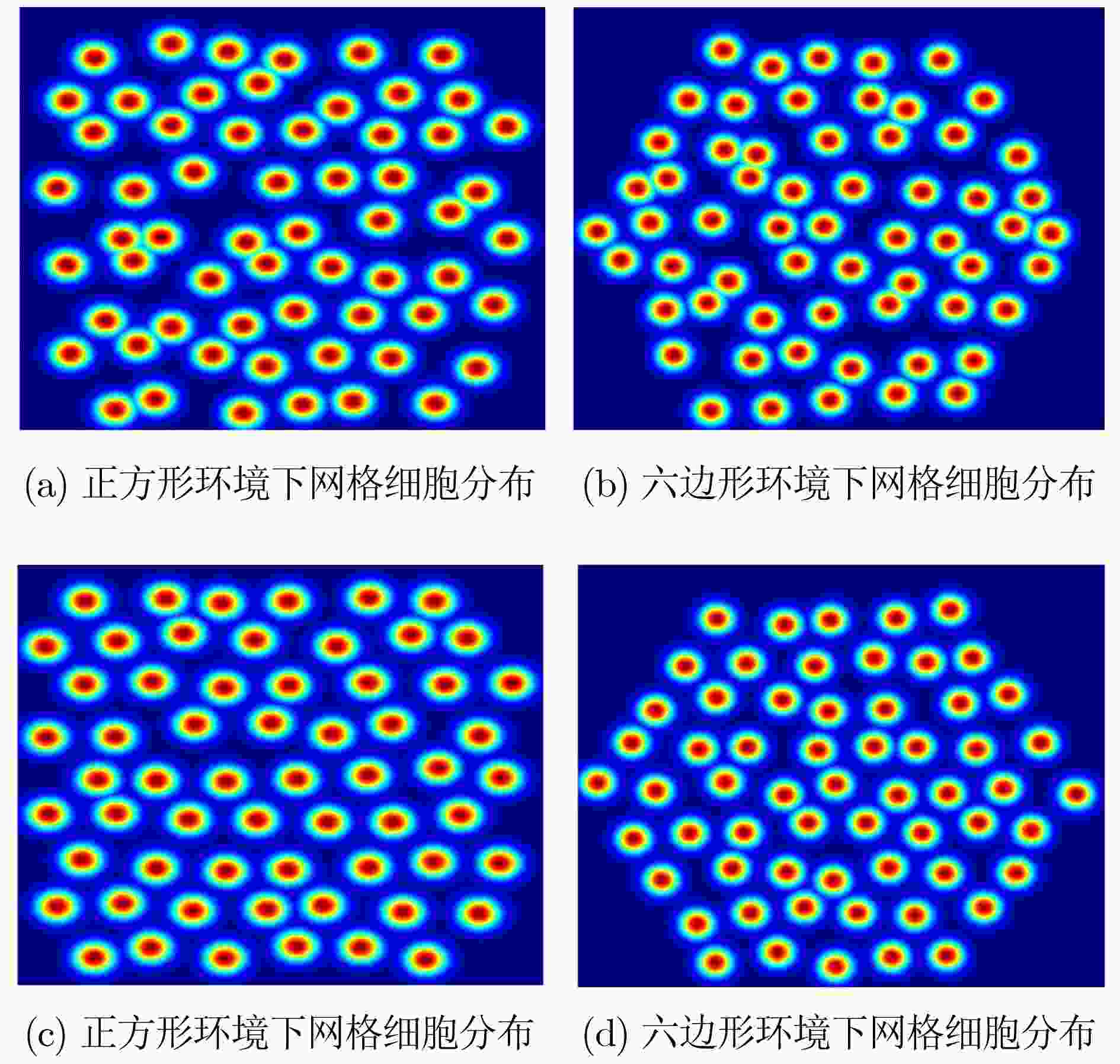
变量名称 参数 数值 运行速度 $ v $ 1 m/s 方向变化范围 $ \mathop \theta \nolimits^{} $ [0, 2π] 位置采样点 $ {n_s} $ 1000 网格细胞总数 $ \mathop N\nolimits_{} $ 260 -
[1] 左燕, 周夏磊, 蒋陶然. 传感器位置误差下外辐射源雷达三维定位代数解算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 555–562. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190292ZUO Yan, ZHOU Xialei, and JIANG Taoran. Algebraic solution for 3D localization of multistatic passive radar in the presence of sensor position errors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 555–562. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190292 [2] 李世宝, 王升志, 刘建航, 等. 基于接收信号强度非齐性分布特征的半监督学习室内定位指纹库构建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2302–2309. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180599LI Shibao, WANG Shengzhi, LIU Jianhang, et al. Semi-supervised indoor fingerprint database construction method based on the nonhomogeneous distribution characteristic of received signal strength[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2302–2309. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180599 [3] 李庆华, 尤越, 沐雅琪, 等. 一种针对大型凹型障碍物的组合导航算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 917–923. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190179LI Qinghua, YOU Yue, MU Yaqi, et al. Integrated navigation algorithm for large concave obstacles[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 917–923. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190179 [4] MOSER E I, KROPFF E, and MOSER M B. Place cells, grid cells, and the brain's spatial representation system[J]. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2008, 31(1): 69–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.061307.090723 [5] MOSER E I, ROUDI Y, WITTER M P, et al. Grid cells and cortical representation[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2014, 15(7): 466–481. doi: 10.1038/nrn3766 [6] YUAN Miaolong, TIAN Bo, SHIM V A, et al. An entorhinal-hippocampal model for simultaneous cognitive map building[C]. Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, USA, 2015: 586–592. [7] HAFTING T, FYHN M, MOLDEN S, et al. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7052): 801–806. doi: 10.1038/nature03721 [8] DOELLER C F, BARRY C, and BURGESS N. Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7281): 657–661. doi: 10.1038/nature08704 [9] O'KEEFE J and DOSTROVSKY J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat[J]. Brain Research, 1971, 34(1): 171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90358-1 [10] SOLSTAD T, BOCCARA C N, KROPFF E, et al. Representation of geometric borders in the entorhinal cortex[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5909): 1865–1868. doi: 10.1126/science.1166466 [11] KRUPIC J, BURGESS N, and O'KEEFE J. Neural representations of location composed of spatially periodic bands[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6096): 853–857. doi: 10.1126/science.1222403 [12] BARRY C, HAYMAN R, BURGESS N, et al. Experience-dependent rescaling of entorhinal grids[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2007, 10(6): 682–684. doi: 10.1038/nn1905 [13] HARDCASTLE K, GANGULI S, and GIOCOMO L M. Environmental boundaries as an error correction mechanism for grid cells[J]. Neuron, 2015, 86(3): 827–839. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.039 [14] JAYAKUMAR S, NARAYANAMURTHY R, RAMESH R, et al. Modeling the effect of environmental geometries on grid cell representations[J]. Frontiers in Neural Circuits, 2019, 12: 120. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2018.00120 [15] REBAI K, AZOUAOUI O, and ACHOUR N. Bio-inspired visual memory for robot cognitive map building and scene recognition[C]. 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 2012: 2985–2990. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2012.6385493. [16] MILFORD M J and WYETH G F. Mapping a suburb with a single camera using a biologically inspired SLAM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(5): 1038–1053. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2004520 [17] GLOVER A J, MADDERN W P, MILFORD M J, et al. FAB-MAP + RatSLAM: Appearance-based SLAM for multiple times of day[C]. 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, USA, 2010: 3507–3512. doi: 10.1109/ROBOT.2010.5509547. [18] HOU Yi, ZHANG Hong, and ZHOU Shilin. Convolutional neural network-based image representation for visual loop closure detection[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 2015: 2238–2245. doi: 10.1109/ICInfA.2015.7279659. [19] 李维鹏, 张国良, 姚二亮, 等. 基于场景显著区域的改进闭环检测算法[J]. 机器人, 2017, 39(1): 23–35. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.2017.0023LI Weipeng, ZHANG Guoliang, YAO Erliang, et al. An improved loop closure detection algorithm based on scene salient regions[J]. Robot, 2017, 39(1): 23–35. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.2017.0023 [20] JUN H, BRAMIAN A, SOMA S, et al. Disrupted place cell remapping and impaired grid cells in a knockin model of alzheimer's disease[J]. Neuron, 2020, 107(6): 1095–1112. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.023 [21] YU Shumei, WU Junyi, XU Haidong, et al. Robustness improvement of visual templates matching based on frequency-tuned model in RatSLAM[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2020, 14: 568091. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2020.568091 [22] 陈孟元, 徐明辉. 基于自组织可增长映射的移动机器人仿生定位算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 1003–1013. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200025CHEN Mengyuan and XU Minghui. Research on mobile robot bionic location algorithm based on growing self-organizing map[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 1003–1013. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200025 [23] 陈孟元, 田德红. 基于多尺度网格细胞到位置细胞的仿生SLAM算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2021, 33(5): 712–723. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2021.18407CHEN Mengyuan and TIAN Dehong. Bionic SLAM algorithm based on multi-scale grid cell to place cell[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2021, 33(5): 712–723. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2021.18407 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
