Asymmetric Memristor-induced Attractor Asymmetric Evolution and Its Mechanism
-
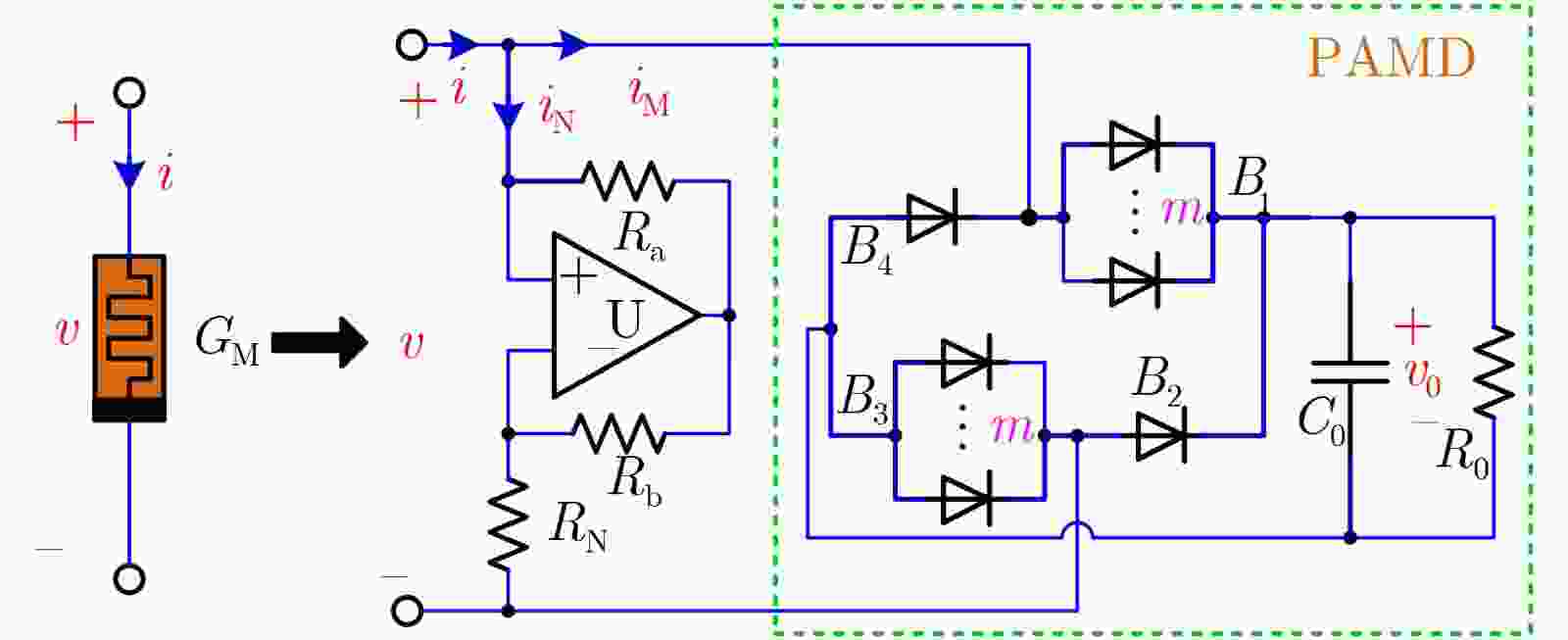
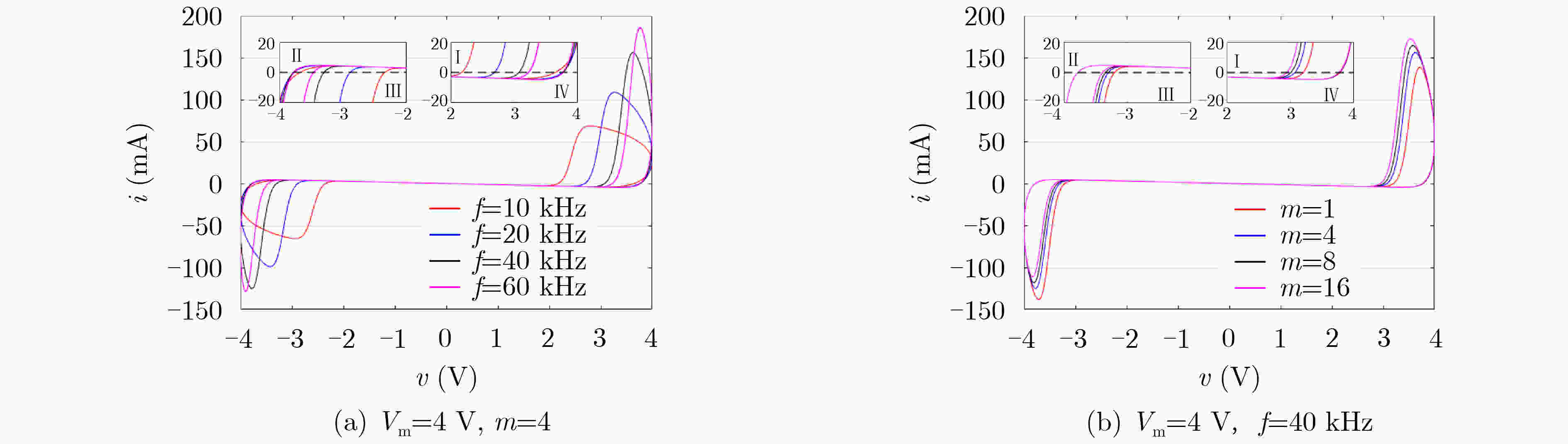
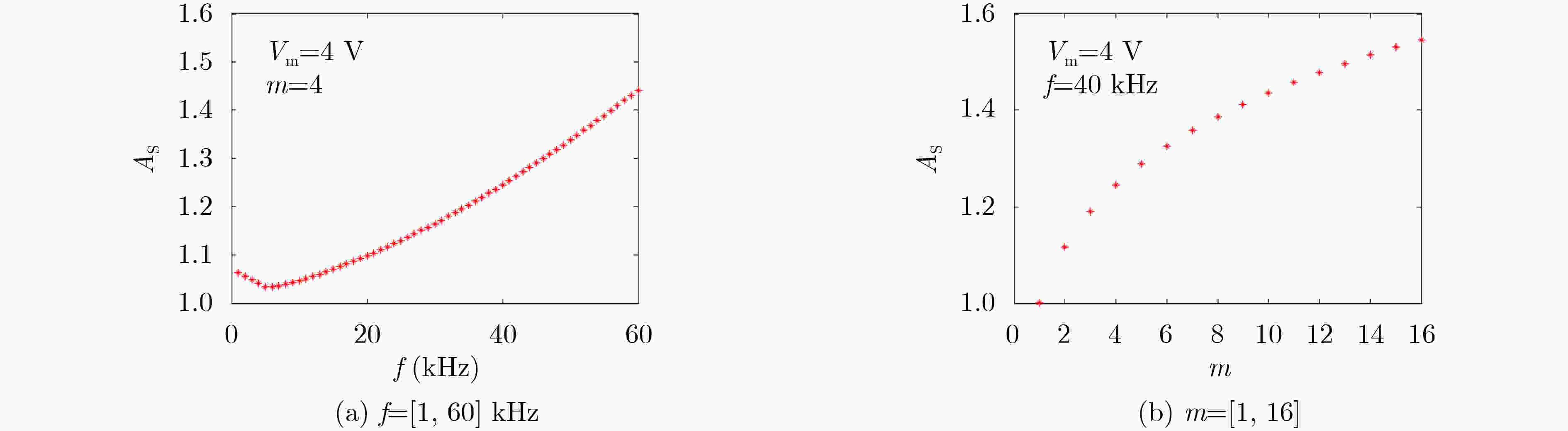
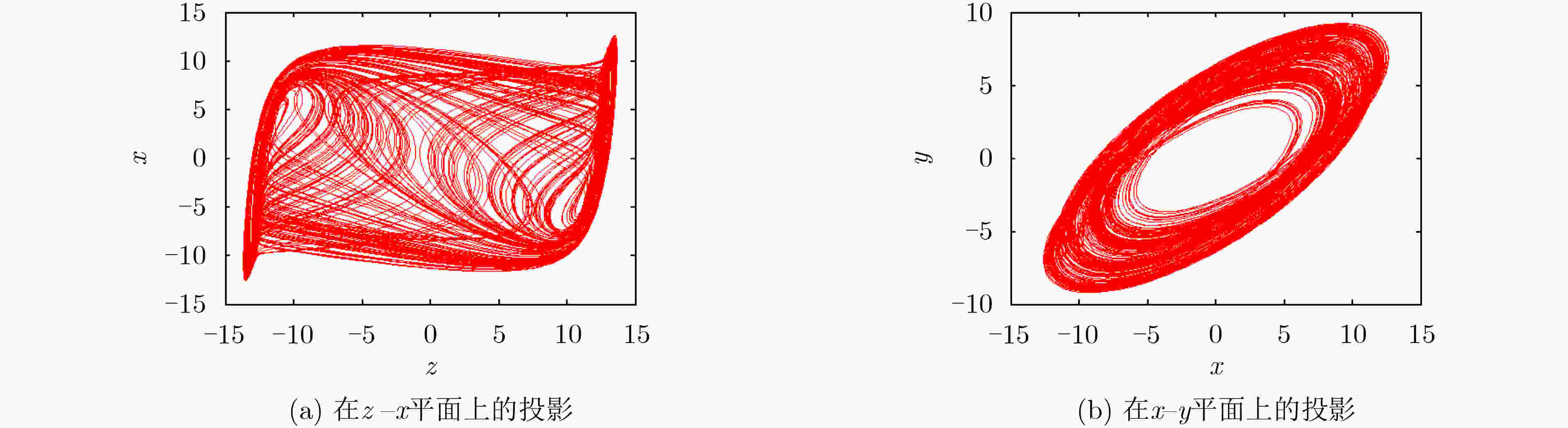
摘要: 紧磁滞回线是评测物理器件或数学模型是否为忆阻的关键依据,其对称特性也是忆阻的重要特征之一。该文提出一种有源非对称忆阻二极管桥模拟器,它通过改变二极管桥中并联二极管的数量可实现紧磁滞回线非对称度的控制。首先,验证了该非对称忆阻模拟器的指纹特征,并着重探讨了激励频率和对称度控制参数对紧磁滞回线非对称度的影响。进一步地,将该非对称忆阻模拟器耦合到Sallen-Key高通滤波器,构建了一种无感忆阻蔡氏电路;建立了相应的无量纲系统,并揭示了系统吸引子的非对称演化现象。结合平衡点稳定性分析、分岔分析和多吸引子状态初值空间分布,阐明了吸引子非对称演化的产生机理。结果表明,受非对称忆阻的影响,无感忆阻蔡氏电路的两个不稳定鞍焦点失去平衡,导致了非对称共存分岔、多稳定模态等行为的产生。最后,由硬件电路实验验证了理论分析与数值仿真的正确性。Abstract: The pinched hysteresis loop is the key basis to judge whether a physical device or a mathematical model is a memristor, and its symmetry property is also one of the important characteristics of a memristor. In this paper, an active asymmetric memristive diode-bridge emulator is proposed, whose asymmetry can be controlled by changing the number of parallel diodes in the diode-bridge. Firstly, the fingerprint of this asymmetric memristor emulator is tested, and the effects of excitation frequency and symmetry control parameter on the asymmetry of the pinched hysteresis loop are discussed. Thereafter, by coupling the asymmetric memristor into a Sallen-Key high-pass filter, an inductor-free memristive Chua’s circuit is constructed. The corresponding dimensionless system is built, upon which the asymmetric evolution feature of system attractor is uncovered. Based on the equilibrium stability analysis, bifurcation analysis and multiple attractors distribution in state initial space, the mechanism of attractor asymmetric evolution is clarified. The results demonstrated that, affected by the asymmetric memristor, two unstable saddle-foci of the inductor-free memristive Chua’s circuit are out of balance, resulting in the generations of asymmetric coexistence bifurcation and multi-stable mode. Finally, the correctness of theoretical analysis and numerical simulation are verified by hardware circuit experiment.
-
Key words:
- Memristor /
- Asymmetric coexisting bifurcation /
- Multi-stable mode /
- Hardware experiment
-
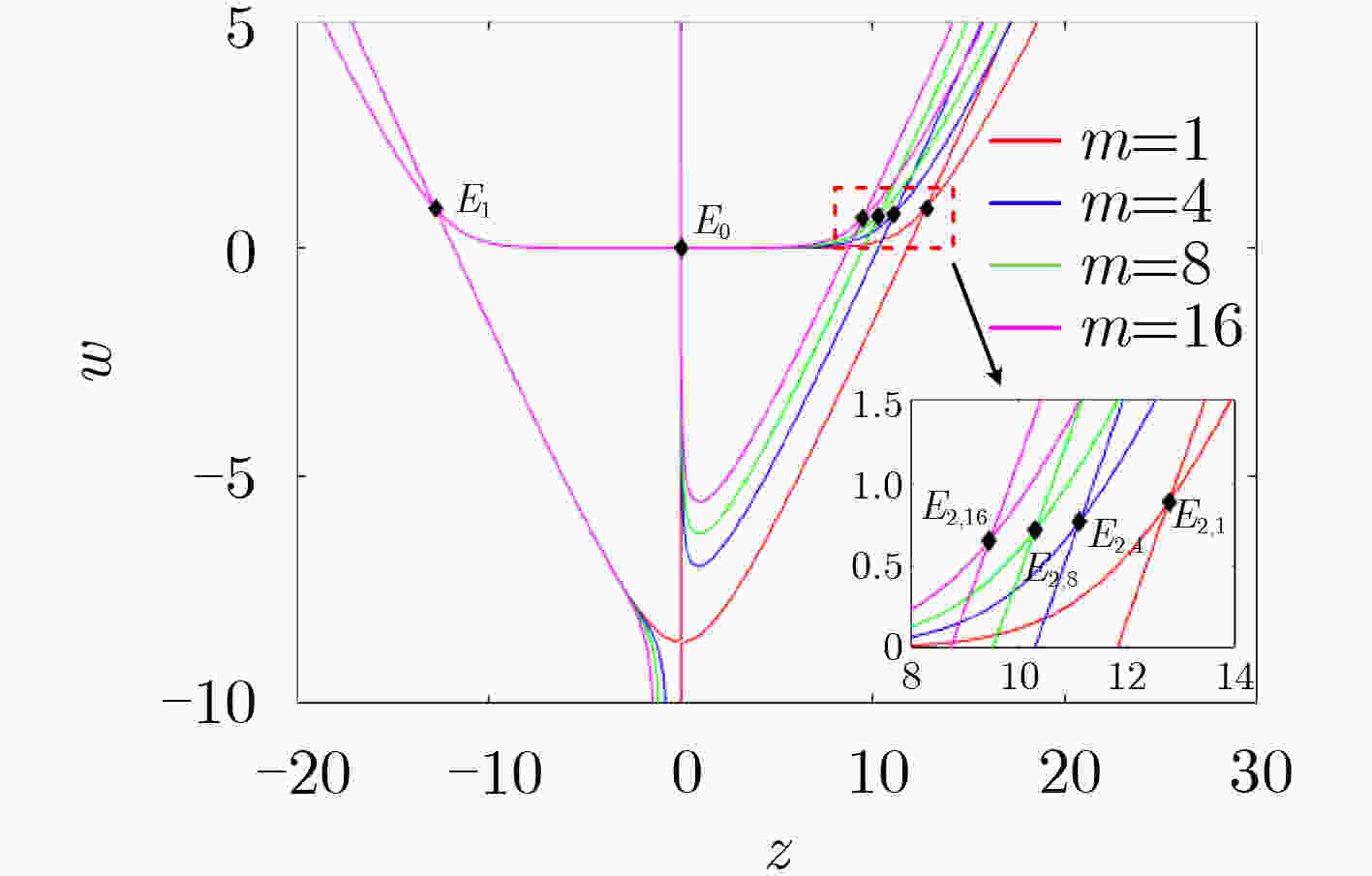
表 1 m取不同值时的系统平衡点稳定性
m 平衡点 特征根 稳定性 1, 4, 8, 16 E0 = (0, 0, 0, 0) 9.329, –1.346±28.225i, –12.000 不稳定指数1鞍焦 1, 4, 8, 16 E1 = (–1.419, –1.419, –12.769, 0.878) –488.920, –10.900, 1.11±27.73i 不稳定指数2鞍焦 1 E2, 1 = (1.419, 1.419, 12.769, 0.878) –488.920, –10.900, 1.11±27.73i, 不稳定指数2鞍焦 4 E2, 4 = (1.237, 1.237, 11.133, 0.766) –421.800, –10.890, 1.13±27.70i 不稳定指数2鞍焦 8 E2, 8 = (1.145, 1.145, 10.306, 0.709) –388.170, –10.870, 1.14±27.68i 不稳定指数2鞍焦 16 E2, 16 = (1.052, 1.052, 9.470, 0.651) –353.930, –10.860, 1.16±27.66i 不稳定指数2鞍焦 -
[1] STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 80–83. doi: 10.1038/nature06932 [2] MINATI L, GAMBUZZA L V, THIO W J, et al. A chaotic circuit based on a physical memristor[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2020, 138: 109990. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109990 [3] XIA Xiaozhu, ZENG Yicheng, and LI Zhijun. Coexisting multiscroll hyperchaotic attractors generated from a novel memristive jerk system[J]. Pramana, 2018, 91(6): 82. doi: 10.1007/s12043-018-1657-3 [4] DONG Yujiao, WANG Guangyi, CHEN Guanrong, et al. A bistable nonvolatile locally-active memristor and its complex dynamics[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2020, 84: 105203. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105203 [5] ASCOLI A, TETZLAFF R, CORINTO F, et al. PSpice switch-based versatile memristor model[C] 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Beijing, China, 2013: 205–208. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2013.6571818. [6] BAO Bocheng, YU Jingjing, HU Fengwei, et al. Generalized memristor consisting of diode bridge with first order parallel RC filter[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2014, 24(11): 1450143. doi: 10.1142/S0218127414501430 [7] DENG Yue and LI Yuxia. A memristive conservative chaotic circuit consisting of a memristor and a capacitor[J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2020, 30(1): 013120. doi: 10.1063/1.5128384 [8] AN Hongyu, LI Jialing, LI Ying, et al. Three dimensional memristor-based neuromorphic computing system and its application to cloud robotics[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2017, 63: 99–113. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.06.023 [9] 王春华, 蔺海荣, 孙晶如, 等. 基于忆阻器的混沌、存储器及神经网络电路研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821WANG Chunhua, LIN Hairong, SUN Jingru, et al. Research progress on chaos, memory and neural network circuits based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821 [10] YAO Peng, WU Huaqiang, GAO Bin, et al. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network[J]. Nature, 2020, 577(7792): 641–646. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1942-4 [11] 董哲康, 杜晨杰, 林辉品, 等. 基于多通道忆阻脉冲耦合神经网络的多帧图像超分辨率重建算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 835–843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190868DONG Zhekang, DU Chenjie, LIN Huipin, et al. Multi-channel memristive pulse coupled neural network based multi-frame images super-resolution reconstruction algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 835–843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190868 [12] 闵富红, 王珠林, 王恩荣, 等. 新型忆阻器混沌电路及其在图像加密中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(10): 2681–2688. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160178MIN Fuhong, WANG Zhulin, WANG Enrong, et al. New memristor chaotic circuit and its application to image encryption[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(10): 2681–2688. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160178 [13] SHI Qingyu, HUANG Xia, YUAN Fang, et al. Design and FPGA implementation of multi-wing chaotic switched systems based on a quadratic transformation[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2021, 30(2): 020507. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/abd74c [14] WANG Guangyi, YUAN Fang, CHEN Guanrong, et al. Coexisting multiple attractors and riddled basins of a memristive system[J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2018, 28(1): 013125. doi: 10.1063/1.5004001 [15] ZHANG Sen, ZHENG Jiahao, WANG Xiaoping, et al. Initial offset boosting coexisting attractors in memristive multi-double-scroll Hopfield neural network[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2020, 102(4): 2821–2841. doi: 10.1007/s11071-020-06072-w [16] BAO Bocheng, WU Pingye, BAO Han, et al. Chaotic bursting in memristive diode bridge-coupled Sallen-Key lowpass filter[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(16): 1104–1105. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.1647 [17] 李芳苑, 陈墨, 武花干. 忆阻高通滤波电路准周期与混沌环面簇发振荡及慢通道效应[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 811–817. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190373LI Fangyuan, CHEN Mo, and WU Huagan. Quasi-periodic, chaotic-torus bursting oscillations and slow passage effect in memristive high-pass filter circuit[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 811–817. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190373 [18] CHANG Hui, LI Yuxia, and CHEN Guanrong. A novel memristor-based dynamical system with multi-wing attractors and symmetric periodic bursting[J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2020, 30(4): 043110. doi: 10.1063/1.5129557 [19] CHEN Mo, REN Xue, WU Huagan, et al. Periodically varied initial offset boosting behaviors in a memristive system with cosine memductance[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2019, 20(12): 1706–1716. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1900360 [20] WU Huagan, YE Yi, CHEN Mo, et al. Periodically switched memristor initial boosting behaviors in memristive hypogenetic jerk system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 145022–145029. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2945754 [21] CHUA L. If it’s pinched it’s a memristor[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2014, 29(10): 104001. doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/29/10/104001 [22] YE Yi, ZHOU Jie, XU Quan, et al. Parallel-type asymmetric memristive diode-bridge emulator and its induced asymmetric attractor[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 156299–156307. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3018728 [23] HU Weipeng, WANG Zhen, ZHAO Yunping, et al. Symmetry breaking of infinite-dimensional dynamic system[J]. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2020, 103: 106207. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2019.106207 [24] KENGNE L K, KENGNE J, PONE J R M, et al. Dynamics, control and symmetry breaking aspects of an infinite-equilibrium chaotic system[J]. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2020, 8(3): 741–758. doi: 10.1007/s40435-020-00613-2 [25] XU Quan, SONG Zhe, QIAN Hui, et al. Numerical analyses and breadboard experiments of twin attractors in two-neuron-based non-autonomous Hopfield neural network[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2018, 227(7): 777–786. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2018-700122-3 [26] RAJAGOPAL K, JAFARI S, PHAM V T, et al. Antimonotonicity, bifurcation and multistability in the vallis model for El Niño[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2019, 29(3): 1950032. doi: 10.1142/S0218127419500329 -





 下载:
下载:

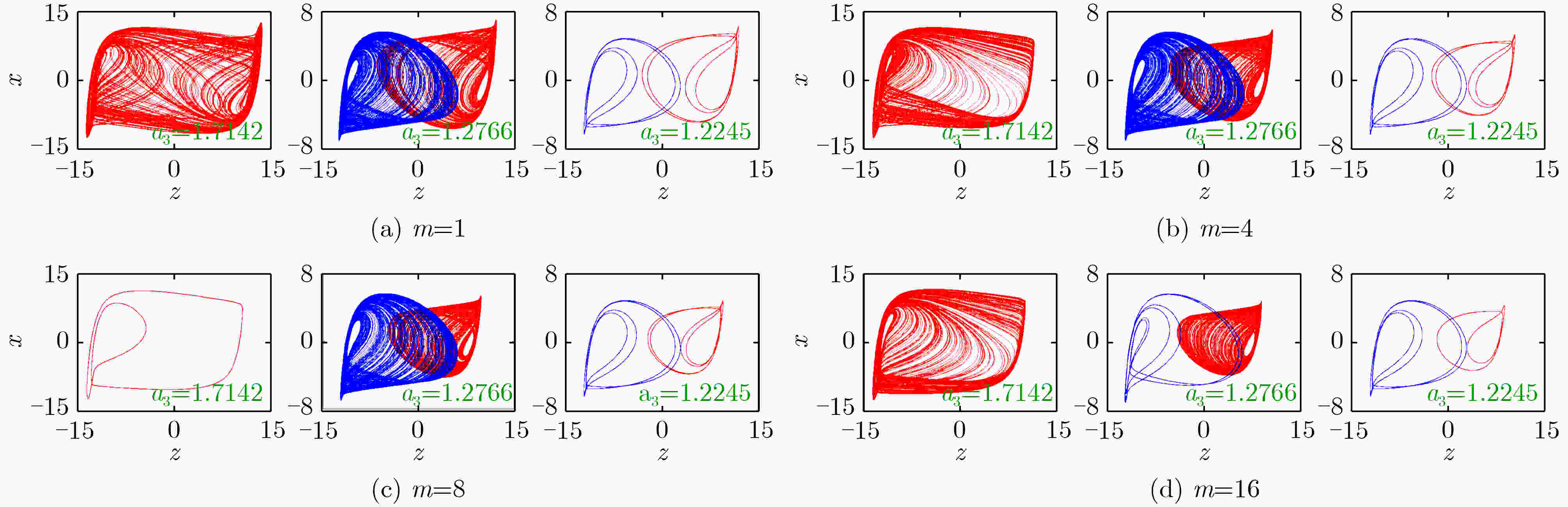
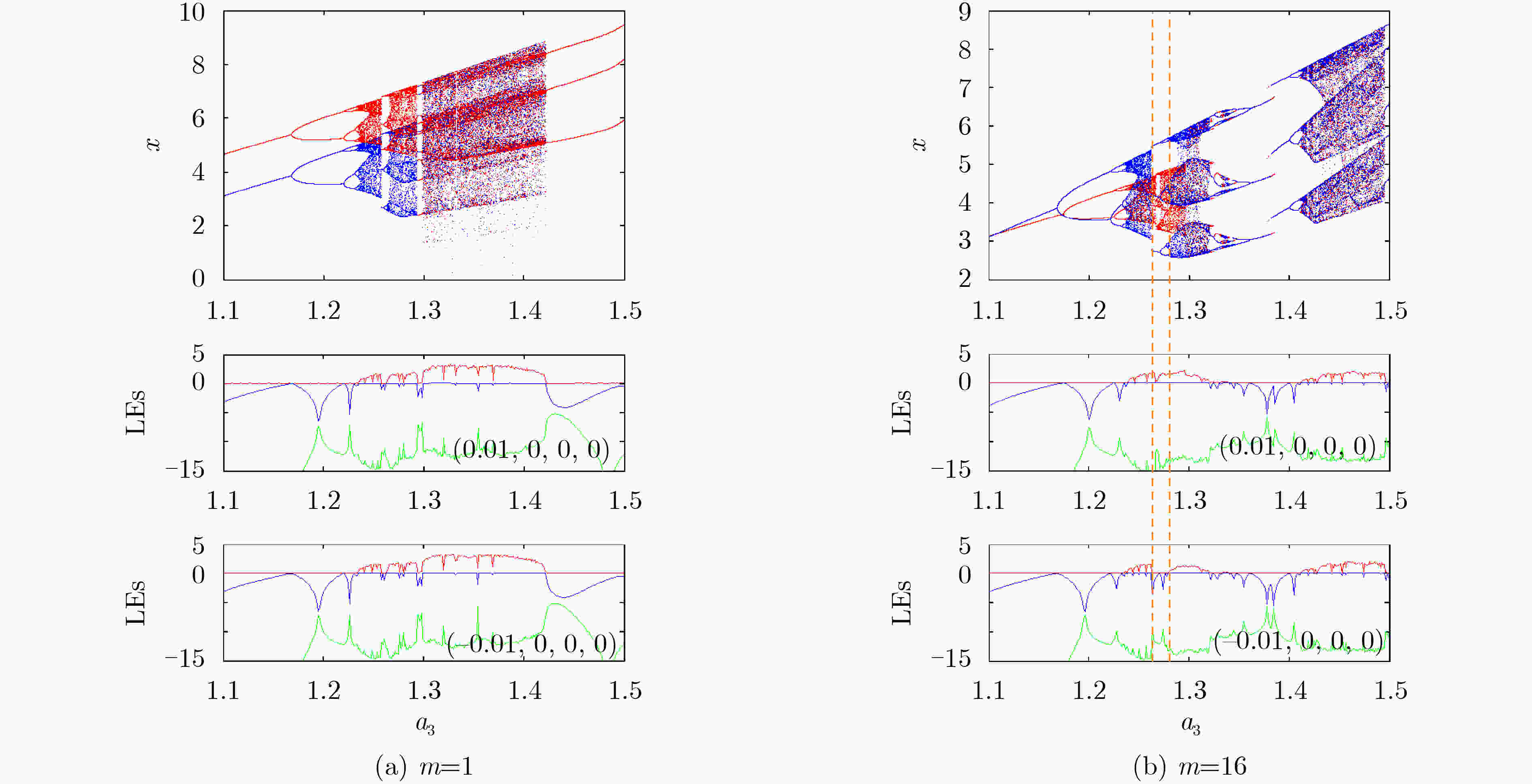
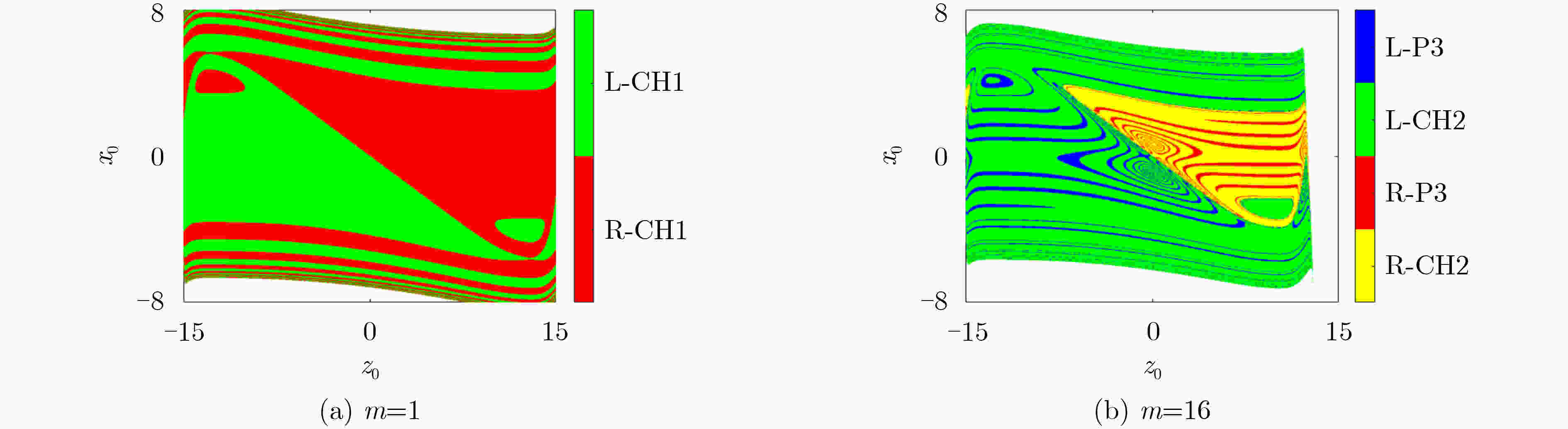
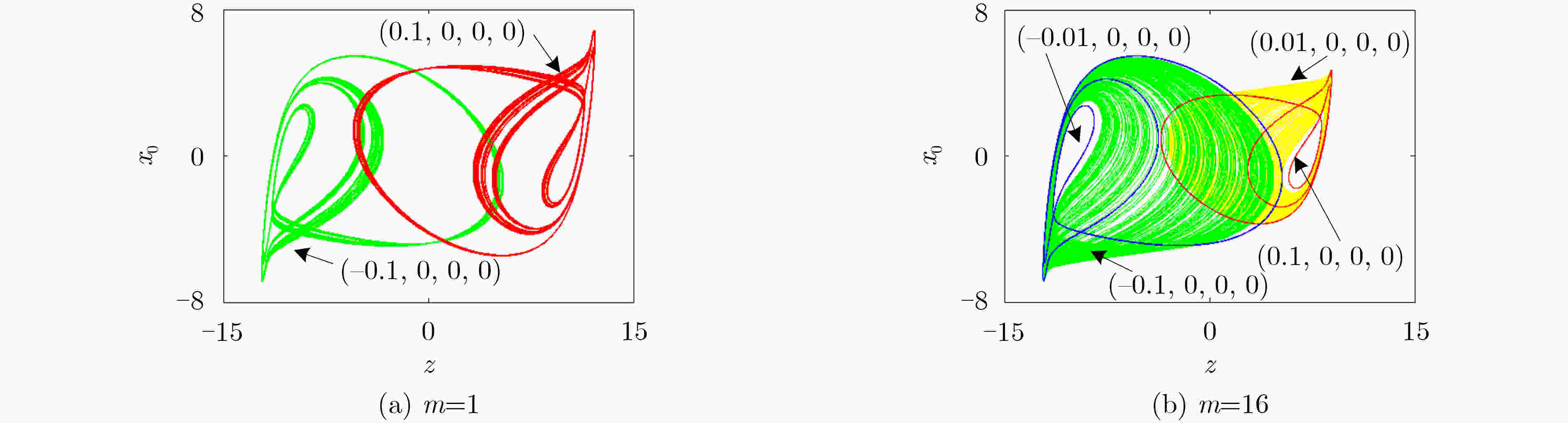
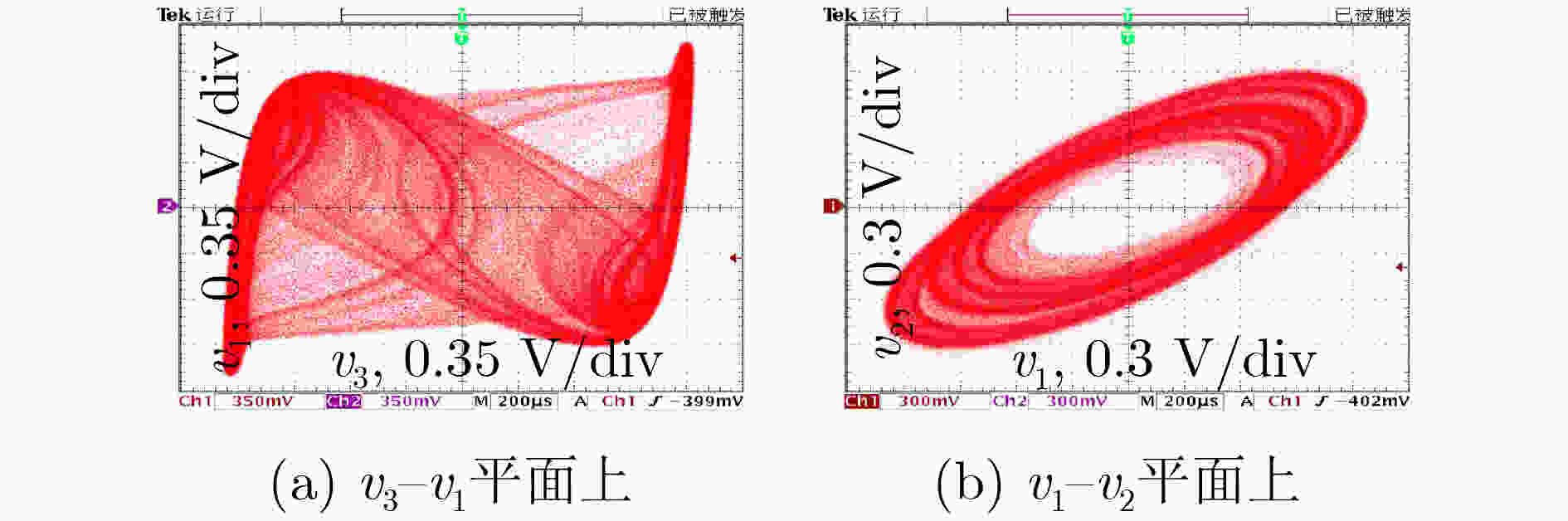
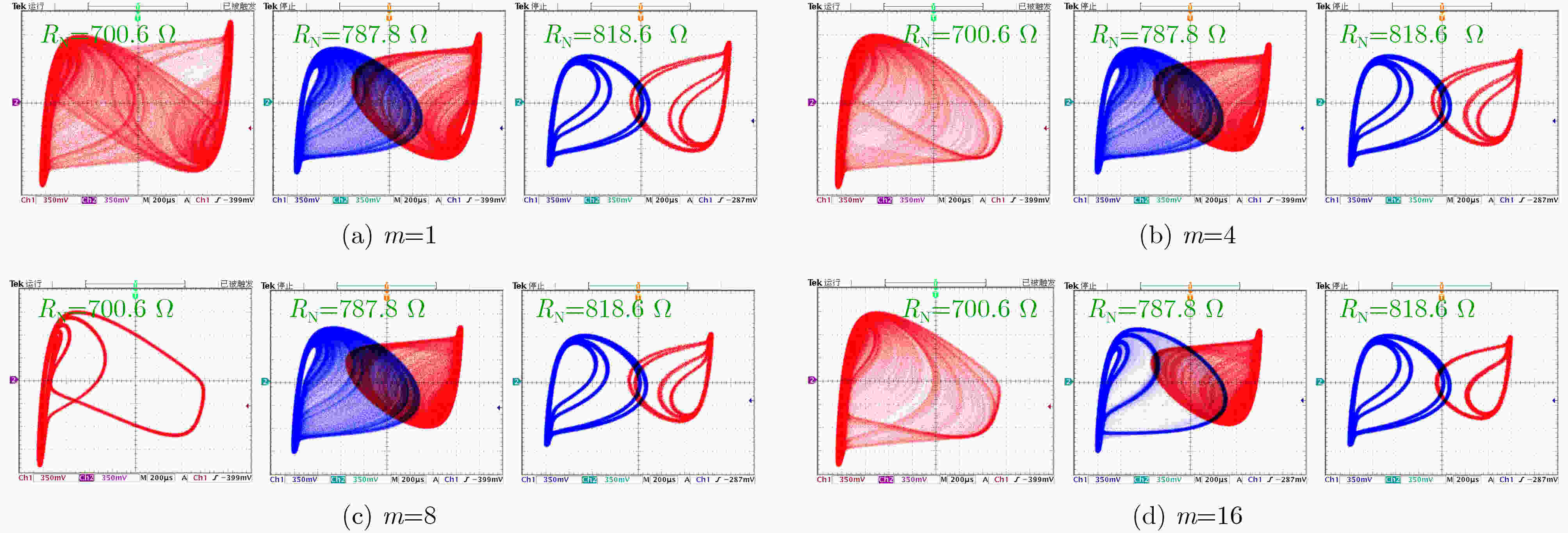


 下载:
下载:
