Certificateless Proxy Signcryption Scheme from Lattice
-
摘要: 无证书代理签密在信息安全领域发挥着越来越重要的作用。现有的大多数无证书代理签密基于传统数学理论,无法抵制量子计算攻击。该文采用格密码技术提出基于无证书的格基代理签密(L-CLPSC)方案。L-CLPSC在带错误学习(LWE)问题和小整数解(SIS)问题的困难假设下满足自适应选择密文攻击下的不可区分性和自适应选择消息攻击下的不可伪造性。相比较而言,L-CLPSC具有更高的计算效率和更低的通信代价。Abstract: Certificateless proxy signcryption plays an increasingly significant role in information security fields. Most of certificateless proxy signcryption schemes are based on traditional mathematic theory and can not resist the quantum computing attacks. In this paper, a new CertificateLess Proxy SignCryption from Lattice (L-CLPSC) is proposed by using lattice-based cryptography technology. L-CLPSC is indistinguishable against adaptive chosen-ciphertext attacks and unforgeable against adaptive chosen-message attacks under Learning With Errors (LWE) and Small Integer Solution (SIS) assumptions. Comparison shows L-CLPSC has higher computation efficiency and lower communication overhead.
-
表 1 实验参数的设置
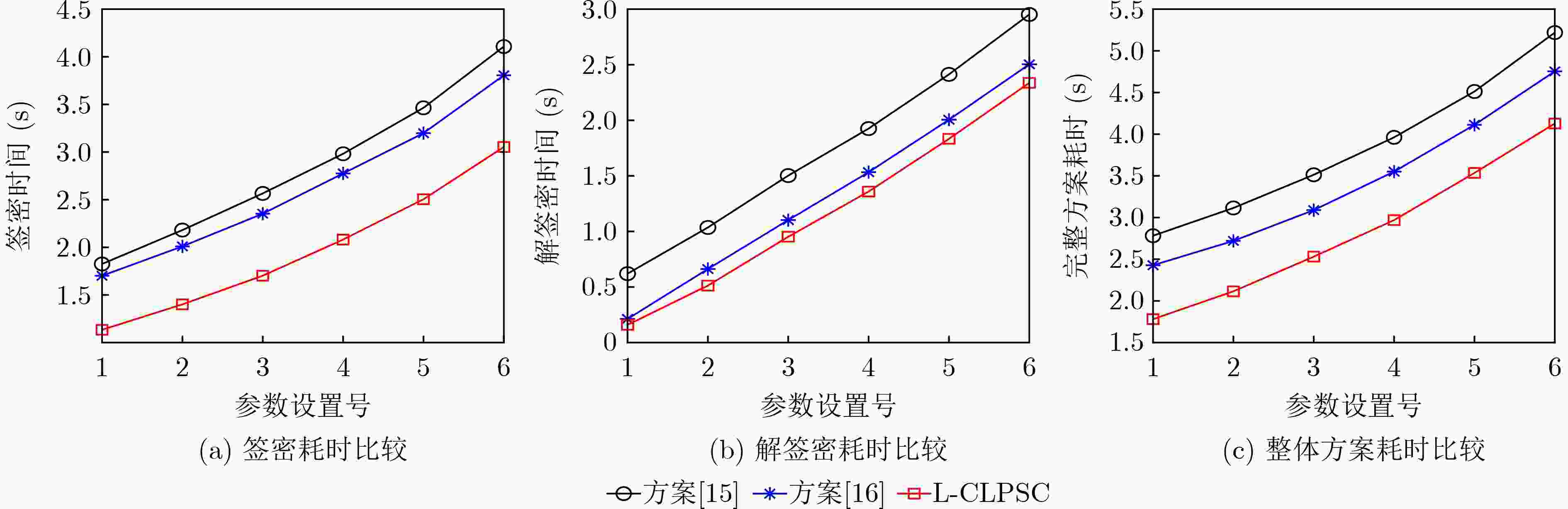
参数设置号 1 2 3 4 5 6 n 128 136 192 214 256 320 m 2816 2992 4608 5992 6144 7680 q 2048 2048 4096 16384 4096 4096 表 2 方案之间在空间维度比较
-
[1] SHAMIR A. Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes[C]. CRYPTO 84 on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 1984: 47–53. [2] AL-RIYAMI S S and PATERSON K G. Certificateless public key cryptography[C]. The 9th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Taipei, China, 2003: 452–473. [3] YU Huifang and WANG Zhicang. Construction of certificateless proxy signcryption scheme from CMGs[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 141910–141919. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943718 [4] SHOR P W. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring[C]. The 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, USA, 1994: 124–134. [5] GENTRY C. Fully homomorphic encryption using ideal lattices[C]. Proceedings of the 41st Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Bethesda, USA, 2009: 169–178. [6] 夏峰, 杨波, 马莎, 等. 基于格的代理签名方案[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 38(6): 84–88.XIA Feng, YANG Bo, MA Sha, et al. Lattice-based proxy signature scheme[J]. Journal of Hunan University:Natural Sciences, 2011, 38(6): 84–88. [7] 江明明, 胡予濮, 王保仓, 等. 格上的高效代理签名[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2014, 37(3): 89–92. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2014.03.018JIANG Mingming, HU Yupu, WANG Baocang, et al. Efficient proxy signature over lattices[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2014, 37(3): 89–92. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2014.03.018 [8] 陈虎, 胡予濮, 连至助, 等. 有效的格上无证书加密方案[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(11): 2884–2897. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004884CHEN Hu, HU Yupu, LIAN Zhizhu, et al. Efficient certificateless encryption schemes from lattices[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(11): 2884–2897. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004884 [9] 路秀华, 温巧燕, 王励成, 等. 无陷门格基签密方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(9): 2287–2293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151044LU Xiuhua, WEN Qiaoyan, WANG Licheng, et al. A lattice-based signcryption scheme without trapdoors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(9): 2287–2293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151044 [10] 欧海文, 范祯, 蔡斌思, 等. 理想格上基于身份的代理签名[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2018, 35(1): 312–317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2018.01.054OU Haiwen, FAN Zhen, CAI Binsi, et al. Identity-based proxy signature scheme over ideal lattices[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2018, 35(1): 312–317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2018.01.054 [11] GENTRY C, PEIKERT C, and VAIKUNTANATHAN V. Trapdoors for hard lattices and new cryptographic constructions[C]. The 40th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Victoria, Canada, 2008: 197–206. [12] MICCIANCIO D and REGEV O. Worst-case to average-case reductions based on Gaussian measures[J]. SIAM Journal on Computing, 2007, 37(1): 267–302. doi: 10.1137/S0097539705447360 [13] LYUBASHEVSKY V. Lattice signatures without trapdoors[C]. The 31st Annual International Conference on Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Cambridge, UK, 2012: 738–755. [14] 俞惠芳, 杨波. 可证安全的无证书混合签密[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(4): 804–813.YU Huifang and YANG Bo. Provably secure certificateless hybrid signcryption[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(4): 804–813. [15] SATO S and SHIKATA J. Lattice-based signcryption without random oracle[C]. The 9th International Conference on Post- Quantum Cryptography, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2018: 331–351. [16] YU Huifang, BAI Lu, HAO Ming, et al. Certificateless signcryption scheme from lattice[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(2): 2687–2695. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3007519 [17] LINDNER R and PEIKERT C. Better key sizes (and attacks) for LWE-based encryption[C]. The Cryptographers' Track at the RSA Conference on Topics in Cryptology, San Francisco, USA, 2011: 319–339. [18] MICCIANCIO D and PEIKERT C. Trapdoors for lattices: Simpler, tighter, faster, smaller[C]. The 31st Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Cambridge, UK, 2012: 700–718. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
