Fast Image Deblurring Based On the Lightweight Progressive Residual Network
-
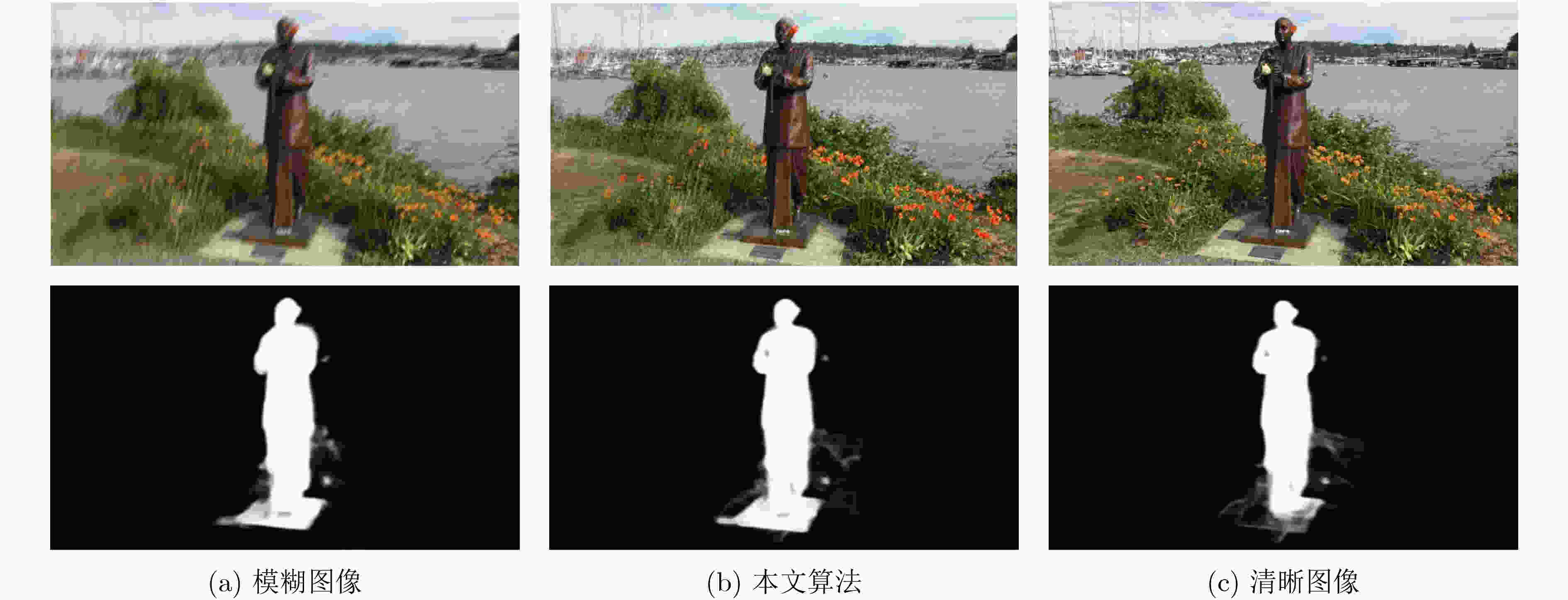
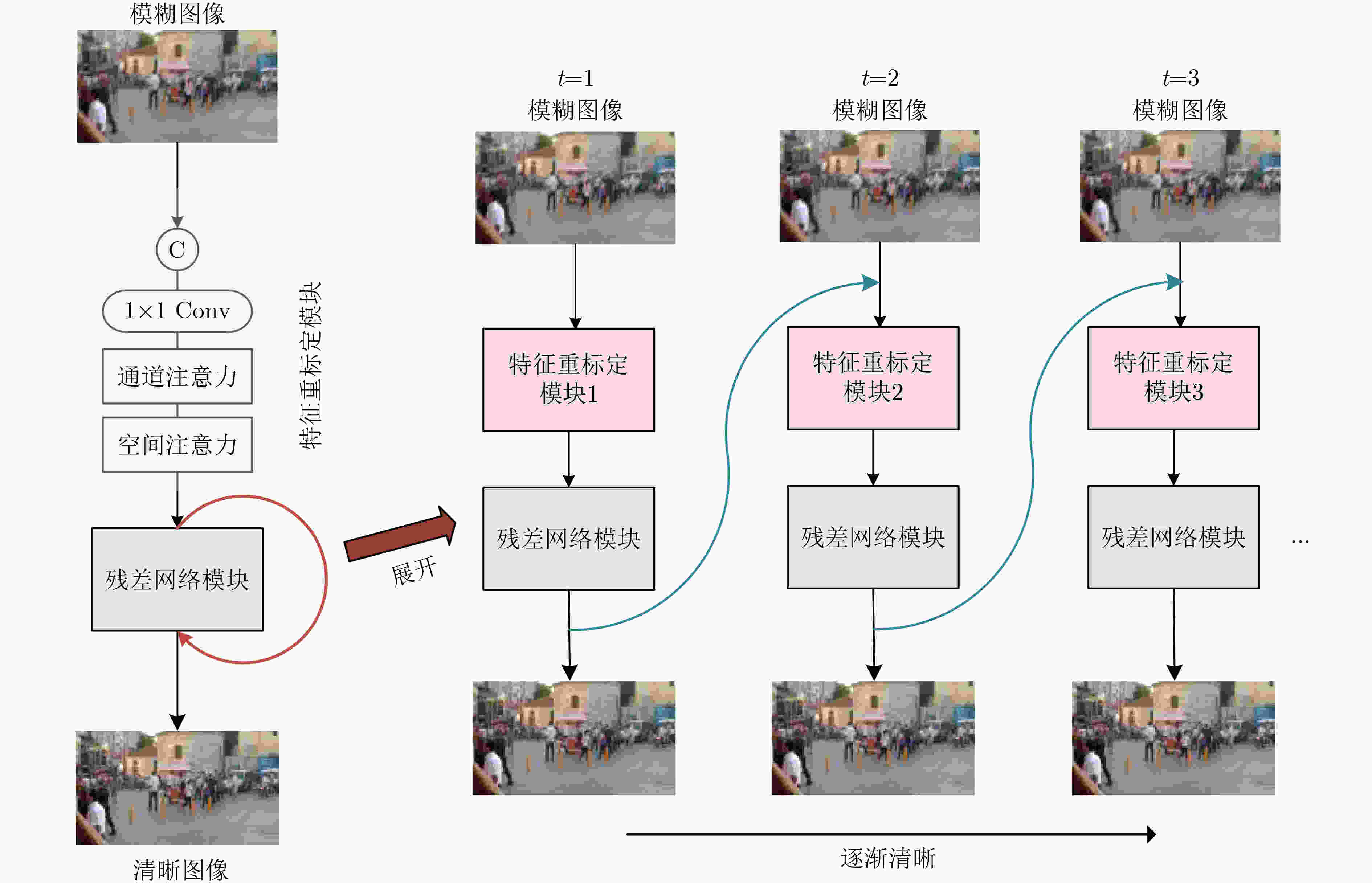
摘要: 基于深度学习的去模糊方法已经取得了较大进展,但是随着网络层数加深,去模糊网络需要更多的计算资源和内存消耗,难以用于实际场景。针对目前的去模糊网络参数量大、运算时间长等问题,该文设计了一种轻量快速的渐进式残差去模糊网络。该网络使用浅层残差网络作为基准模型,可充分利用图像的局部特征信息,加强反向传播时的信息流通。同时,通过多阶段递归调用残差网络并进行参数共享,可大大简化网络模型,减少网络参数。为了进一步提高去模糊网络的特征重建能力,该文引入特征重标定模块进行特征融合,对输入图像与各个残差网络的输出特征图进行通道加权,并对特征图的空间信息进行自适应选择,实现更好的特征重建。实验结果表明,所提算法网络模型参数量小、运行速度快,大幅度领先于现有算法,且对各种空域可变模糊去除均可实现理想复原效果。Abstract: Although deep learning-based methods show their superiority in the field of single image deblurring, it is difficult to be applied to practice for requiring more computing resources and memory consumption as network deepens. In this work, a lightweight and fast progressive residual network for image deburring is proposed. The network takes shallow residual network as basic model to make full use of the local feature information and strengthen the information flow during back propagation. By reusing the residual network recursively in subsequent several stages and sharing parameters, the network model can be greatly simplified and the parameters can be reduced. To improve the reconstruction performance of the network, the feature recalibration module is applied to feature fusion. The channel attention mechanism is applied to integrate input image and output feature map of each residual network, and then the spatial information of feature map is selected adaptively to achieve better feature reconstruction. Experimental results show that the proposed model has fast running speed with a small number of parameters, which is much better than the existing algorithms, and can produce quite promising results for the removal of spatial-invariant blurring.
-
表 1 在合成数据集上PSNR和SSIM结果
表 2 特征重标定模块消融实验
PSNR(dB) 参数量(Mb) 无注意力 30.08 26.316 通道注意力 30.16 26.319 空间注意力 30.14 26.317 通道+空间注意力 30.21 26.321 表 3 残差块递归次数消融实验
递归次数 5 6 7 PSNR(dB) 30.17 30.21 30.21 参数量(Mb) 20.064 26.321 30.712 运行时间(s) 0.02 0.03 0.07 -
[1] LIANG Wang, HANG Yaping, LUO Siwei, et al. Deblurring Gaussian-blur images: A preprocessing for rail head surface defect detection[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations, Logistics and Informatics, Beijing, China, 2011: 451–456. [2] MCCARTHY D M J, CHANDLER J H, and PALMERI A. Monitoring dynamic structural tests using image deblurring techniques[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2013, 569/570: 932–939. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.569-570.932 [3] WANG Ge, SNYDER D L, O’SULLIVAN J A, et al. Iterative deblurring for CT metal artifact reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1996, 15(5): 657–664. doi: 10.1109/42.538943 [4] KUPYN O, BUDZAN V, MYKHAILYCH M, et al. DeblurGAN: Blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8183–8192. [5] PAN Jinshan, SUN Deqing, PFISTER H, et al. Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1628–1636. [6] LI Xu, ZHENG Shicheng, and JIA Jiaya. Unnatural L0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 1107–1114. [7] PAN Jinshan, HU Zhe, SU Zhixun, et al. Deblurring text images via L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 2901–2908. [8] ZHANG Hong, WU Yujie, ZHANG Lei, et al. Image deblurring using tri-segment intensity prior[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 398: 265–279. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.02.082 [9] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3262–3271. [10] VASU S, MALIGIREDDY V R, and RAJAGOPALAN A N. Non-blind deblurring: Handling kernel uncertainty with CNNs[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3272–3281. [11] SUN Jian, CAO Wenfei, XU Zongben, et al. Learning a convolutional neural network for non-uniform motion blur removal[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 769–777. [12] NAH S, KIM T H, and LEE K M. Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 257–265. [13] JAIN V and SEUNG H S. Natural image denoising with convolutional networks[C]. The 21st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2008: 769–776. [14] TAO Xin, GAO Hongyun, SHEN Xiaoyong, et al. Scale-recurrent network for deep image deblurring[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8174–8182. [15] ZHANG Jiawei, PAN Jinshan, REN J, et al. Dynamic scene deblurring using spatially variant recurrent neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2521–2529. [16] GAO Hongyun, TAO Xin, SHEN Xiaoyong, et al. Dynamic scene deblurring with parameter selective sharing and nested skip connections[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3843–3851. [17] KUPYN O, MARTYNIUK T, WU Junru, et al. DeblurGAN-v2: Deblurring (orders-of-magnitude) faster and better[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8877–8886. [18] SUIN M, PUROHIT K, and RAJAGOPALAN A N. Spatially-attentive patch-hierarchical network for adaptive motion deblurring[C]. 2020 Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3603–3612. [19] LIU Qiaohong, SUN Liping, LING Chen, et al. Nonblind image deblurring based on Bi-composition decomposition by local smoothness and nonlocal self-similarity priors[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 63954–63971. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2915314 [20] LIU R W, YIN Wei, XIONG Shengwu, et al. L0-regularized hybrid gradient sparsity priors for robust single-image blind deblurring[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 1348–1352. [21] LI Duo, HU Jie, WANG Changhu, et al. Involution: Inverting the inherence of convolution for visual recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, online, 2021: 12321–12330. [22] BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, HOU Qibin, et al. Salient object detection: A survey[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(2): 117–150. doi: 10.1007/s41095-019-0149-9 [23] PANG Youwei, ZHAO Xiaoqi, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9410–9419. -





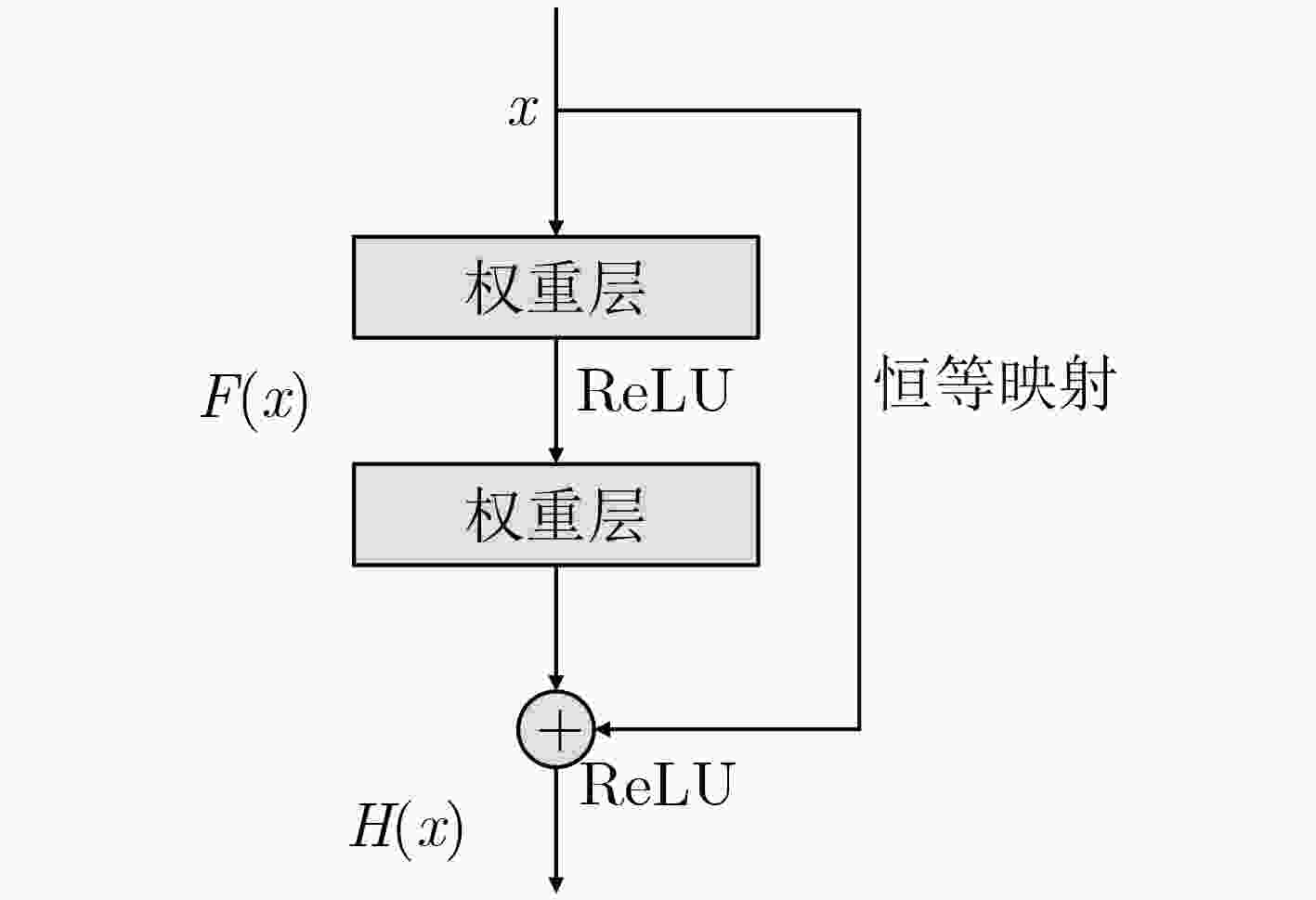
 下载:
下载:
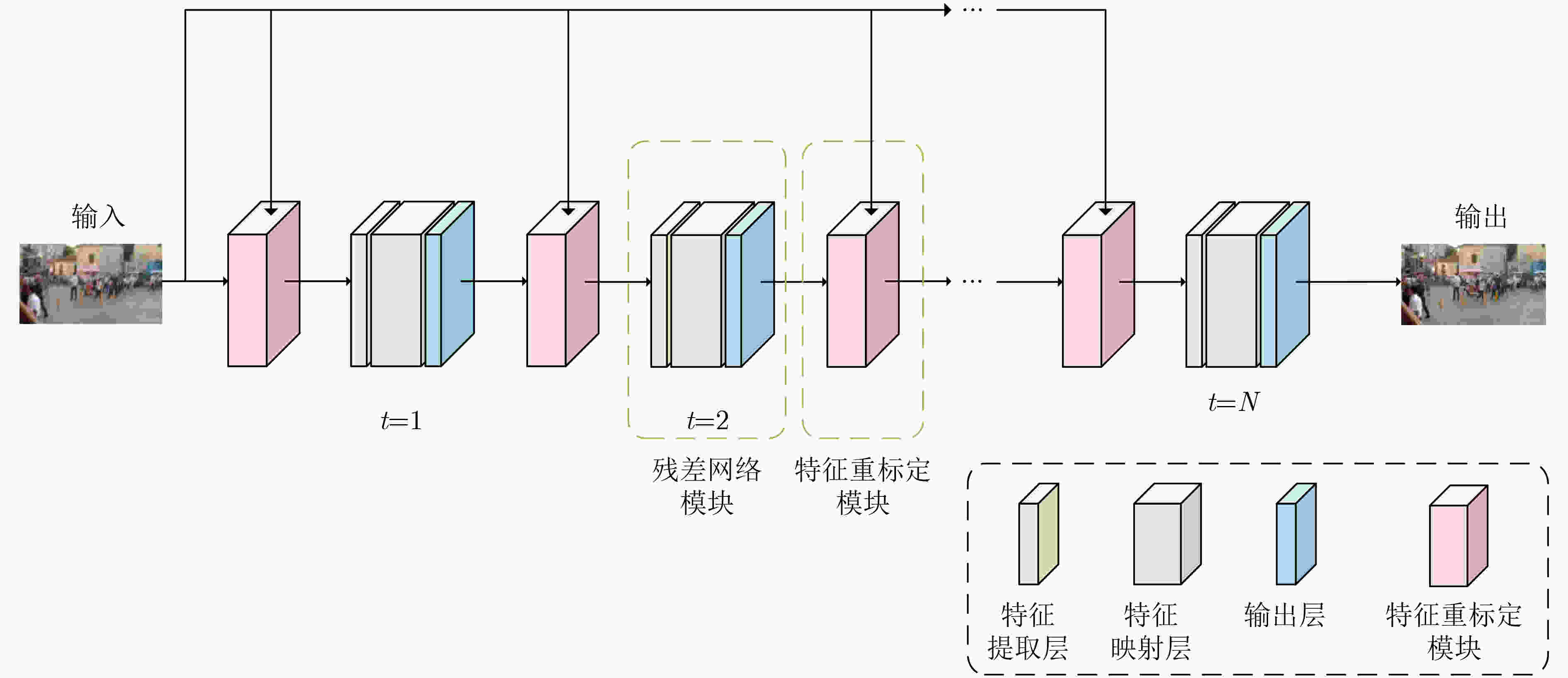
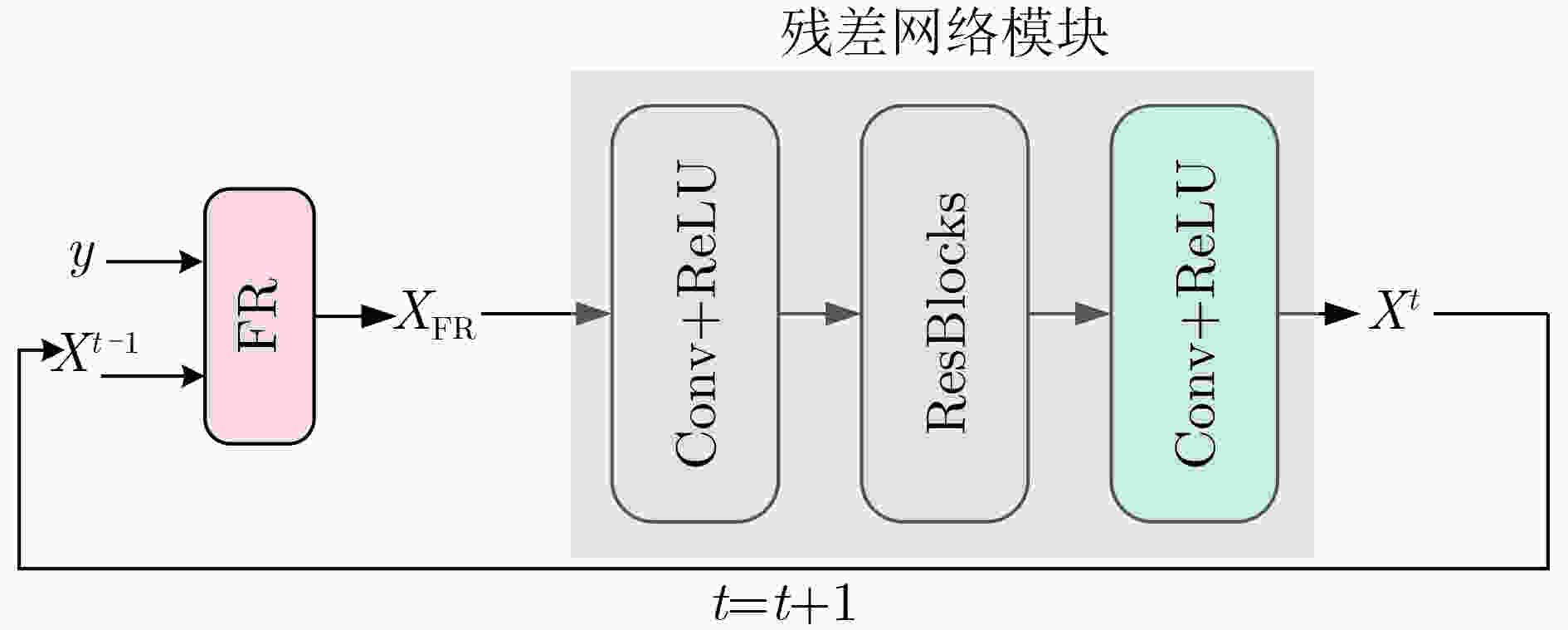
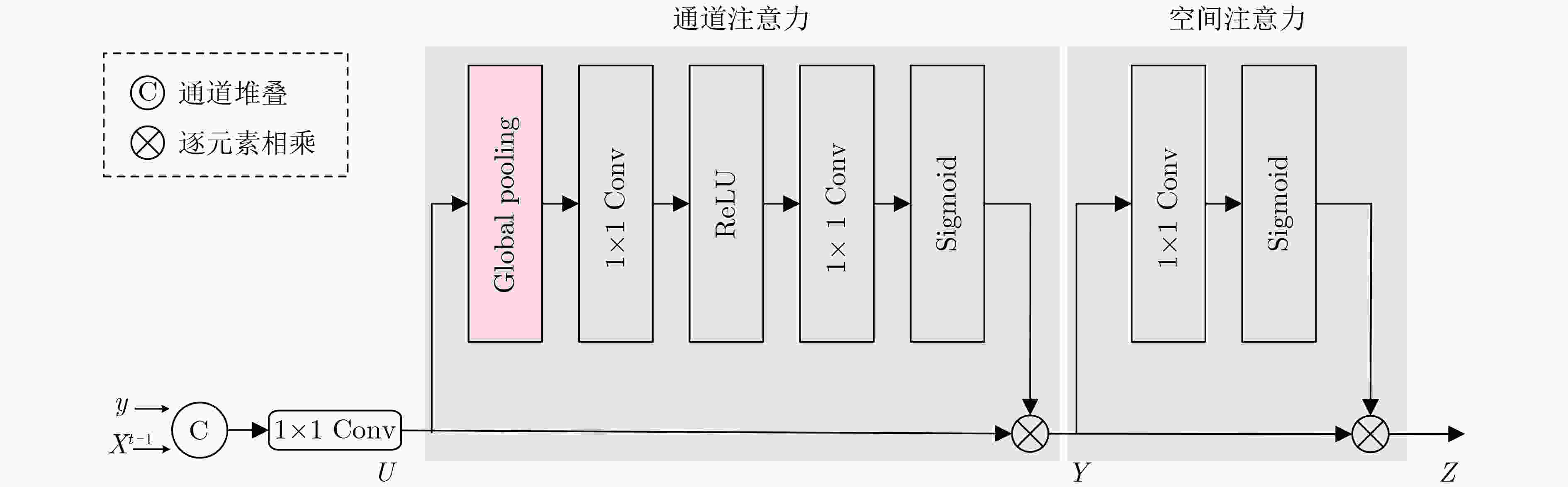






 下载:
下载:
